The Time Course of Inflammatory Biomarkers Following a One-Hour Exercise Bout in Canines: A Pilot Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Plasma Analysis
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
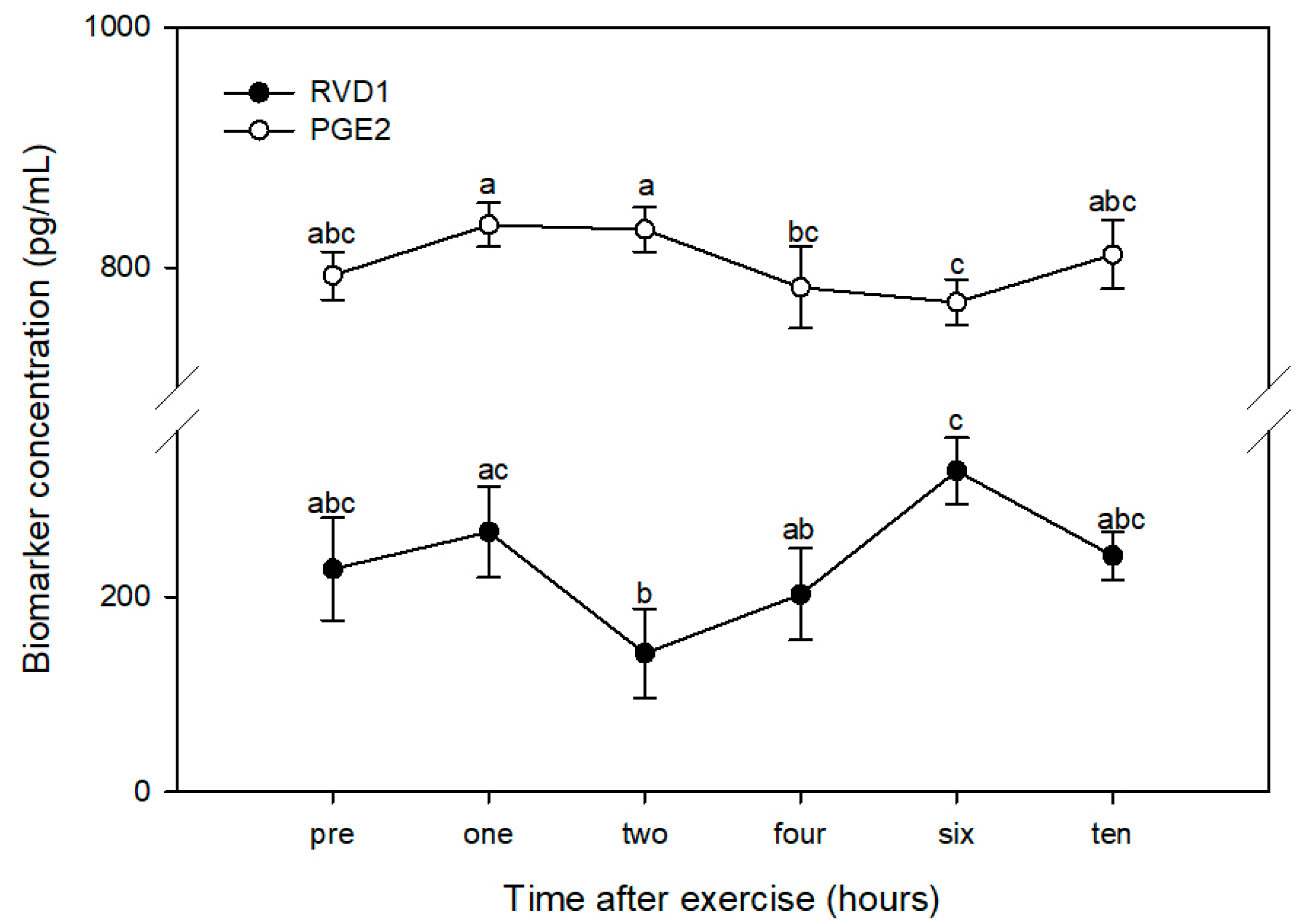
3.1. PGE2
3.2. RvD1
3.3. IL-1β, TNFα, and NO
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paolucci, E.M.; Loukov, D.; Bowdish, D.M.E.; Heisz, J.J. Exercise reduces depression and inflammation but intensity matters. Biol. Psychol. 2018, 133, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, A.L.; Oliveira, V.N.; Agostini, G.G.; Oliveira, R.J.; Oliveira, A.C.; White, G.E.; Wells, G.D.; Teixeira, D.N.; Espindola, F.S. Exercise intensity and recovery: Biomarkers of injury, inflammation, and oxidative stress. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2016, 30, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Chaki, B.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. High-intensity exercise induced oxidative stress and skeletal muscle damage in postpubertal boys and girls: A comparative study. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 1045–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacNicol, J.L.; Lindinger, M.I.; Pearson, W. A time-course evaluation of inflammatory and oxidative markers following high-intensity exercise in horses: A pilot study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 124, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindinger, M.I.; MacNicol, J.M.; Karrow, N.A.; Pearson, W. Effects of a novel dietary supplement on indices of muscle injury and articular GAG release in horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2017, 48, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, V.; Barrera, R.; Duque, F.J.; Ruiz, P.; Zaragoza, C. Effect of exercise on serum markers of muscle inflammation in Spanish Greyhounds. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2015, 76, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilkiw, J.E.; Davis, P.E.; Church, D.B. Hematologic, biochemical, blood-gas, and acid-base values in greyhounds before and after exercise. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1989, 50, 583–586. [Google Scholar]
- Lassen, E.D.; Craig, A.M.; Blythe, L.L. Effects of racing on hematologic and serum biochemical values in greyhounds. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1986, 188, 1299–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, P.G.; Stevenson, E.; Davison, G.W.; Howatson, G. The effects of montmorency tart cherry concentrate supplementation on recovery following prolonged, intermittent exercise. Nutrients 2016, 8, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas-Ortega, M.; Cruz, R.; Vega-López, M.A.; Cabrera-González, M.; Hernández-Hernández, J.M.; Lavalle-Montalvo, C.; Kouri, J.B. Exercise modulates the expression of IL-1β and IL-10 in the articular cartilage of normal and osteoarthritis-induced rats. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2015, 211, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, D.C.; Jackson, C.A.; Colahan, P.T.; Norton, N.; Hurley, D.J. Exercise-induced alterations in pro-inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandin F2α in horses. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 118, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capó, X.; Martorell, M.; Sureda, A.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A. Effects of dietary docosahexaenoic, training and acute exercise on lipid mediators. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2016, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baccarin, R.Y.; Rasera, L.; Machado, T.S.; Michelacci, Y.M. Relevance of synovial fluid chondroitin sulphate as a biomarker to monitor polo pony joints. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 78, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verheggen, R.J.H.M.; Eijsvogels, T.M.H.; Catoire, M.; Terink, R.; Ramakers, R.; Bongers, C.C.W.G.; Mensink, M.; Hermus, A.R.M.M.; Thijssen, D.H.J.; Hopman, M.T.E. Cytokine responses to repeated, prolonged walking in lean versus overweight/obese individuals. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheele, C.; Nielsen, S.; Pedersen, B.K. ROS and myokines promote muscle adaptation to exercise. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.E. Is immunosenescence influenced by our lifetime “dose” of exercise? Biogerontology 2016, 17, 581–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pillon Barcelos, R.; Freire Royes, L.F.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Bresciani, G. Oxidative stress and inflammation: Liver responses and adaptations to acute and regular exercise. Free Radic. Res. 2017, 51, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markworth, J.F.; Maddipati, K.R.; Cameron-Smith, D. Emerging roles of pro-resolving lipid mediators in immunological and adaptive responses to exercise-induced muscle injury. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 22, 110–134. [Google Scholar]
- Markworth, J.F.; Vella, L.; Lingard, B.S.; Tull, D.L.; Rupasinghe, T.W.; Sinclair, A.J.; Maddipati, K.R.; Cameron-Smith, D. Human inflammatory and resolving lipid mediator responses to resistance exercise and ibuprofen treatment. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R1281–R1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.J.; Pena Calderin, E.; Hill, B.G.; Bhatnagar, A.; Hellmann, J. Exercise promotes resolution of acute inflammation by catecholamine-mediated stimulation of resolvin D1 biosynthesis. J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 3013–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padodara, R.J.; Jacob, N. Olfactory sense in different animals. Indian J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Polgar, Z.; Kinnunen, M.; Ujvary, D.; Mislosi, A.; Gacsi, M. A test of canine olfactory capacity: Comparing various dog breeds and wolves in a natural detections task. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sugawara, J.; Murakami, H.; Maeda, S.; Kuno, S.; Matsuda, M. Change in post-exercise vagal reactivation with exercise training and detraining in young men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 85, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downey, A.E.; Chenoweth, L.M.; Townsend, D.K.; Ranum, J.D.; Ferguson, C.S.; Harms, C.A. Effects of inspiratory muscle training on exercise responses in normoxia and hypoxia. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2007, 156, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capó, X.; Martorell, M.; Sureda, A.; Riera, J.; Drobnic, F.; Tur, J.A.; Pons, A. Effects of Almond- and Olive Oil-Based Docosahexaenoic- and Vitamin E-Enriched Beverage Dietary Supplementation on Inflammation Associated to Exercise and Age. Nutrients 2016, 8, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umamaheswaran, S.; Dasari, S.K.; Yang, P.; Lutgendorf, S.K.; Sood, A.K. Stress, inflammation, and eicosanoids: An emerging perspective. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2018, 37, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garami, A.; Steiner, A.A.; Romanovsky, A.A. Fever and hypothermia in systemic inflammation. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2018, 157, 565–597. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, C.D.; Cotter, J.D.; Thorburn, M.S.; Walker, R.J.; Gerrard, D.F. Exercise can be pyrogenic in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 292, R143–R149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolli, R.; Shinmura, K.; Tang, X.L.; Kodani, E.; Xuan, Y.T.; Guo, Y.; Dawn, B. Discovery of a new function of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2: COX-2 is a cardioprotective protein that alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury and mediates the late phase of preconditioning. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 55, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caru, M.; Levesque, A.; Lalonde, F.; Curnier, D. An overview of ischemic preconditioning in exercise performance: A systematic review. J. Sport. Health. Sci. 2019, 8, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incognito, A.V.; Burr, J.F.; Millar, P.J. The Effects of Ischemic Preconditioning on Human Exercise Performance. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trappe, T.A.; Liu, S.Z. Effects of prostaglandins and COX-inhibiting drugs on skeletal muscle adaptations to exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 115, 909–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, A.T.V.; Palla, A.R.; Blake, M.R.; Yucel, N.D.; Wang, Y.X.; Magnusson, K.E.G.; Holbrook, C.A.; Kraft, P.E.; Delp, S.L.; Blau, H.M. Prostaglandin E2 is essential for efficacious skeletal muscle stem-cell function, augmenting regeneration and strength. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6675–6684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trappe, T.A.; Fluckey, J.D.; White, F.; Lambert, C.P.; Evans, W.J. Skeletal muscle PGF(2) (alpha) and PGE(2) in response to eccentric resistance exercise: Influence of ibuprofen acetaminophen. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5067–5070. [Google Scholar]
- Souza, A.V.; Giolo, J.S.; Teixeira, R.R.; Vilela, D.D.; Peixoto, L.G.; Justino, A.B.; Caixeta, D.C.; Puga, G.M.; Espindola, F.S. Salivary and plasmatic antioxidant profile following continuous, resistance, and high-intensity interval exercise: Preliminary study. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5425021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalliokoski, K.K.; Langberg, H.; Ryberg, A.K.; Scheede-Bergdahl, C.; Doessing, S.; Kjaer, A.; Kjaer, M.; Boushel, R. Nitric oxide and prostaglandins influence local skeletal muscle blood flow during exercise in humans: Coupling between local substrate uptake and blood flow. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 291, R803–R809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heinonen, I.; Saltin, B.; Hellsten, Y.; Kalliokoski, K.K. The effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition with and without inhibition of prostaglandins on blood flow in different human skeletal muscles. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 117, 1175–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, S.; Ciccarone, F.; Limongi, D.; Checconi, P.; Palamara, A.T.; Ciriolo, M.R. Glutathione and Nitric Oxide: Key Team Players in Use and Disuse of Skeletal Muscle. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehrenbach, E.; Schneider, M.E. Trauma-induced systemic inflammatory response versus exercise-induced immunomodulatory effects. Sports Med. 2006, 36, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazwinski, M.; Milizio, J.G.; Wakshlag, J.J. Assessment of serum myokines and markers of inflammation associated with exercise in endurance racing sled dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Pfeil, D.J.; Cummings, B.P.; Loftus, J.P.; Levine, C.B.; Mann, S.; Downey, R.L.; Griffitts, C.; Wakshlag, J.J. Evaluation of plasma inflammatory cytokine concentrations in racing sled dogs. Can. Vet. J. 2015, 56, 1252–1256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, R.F.; Fernandes, W.R. Post-ride inflammatory markers in endurance horses. Cienc. Rural 2016, 46, 1256–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Time | PGE2 (pg/mL) | RvD1 (pg/mL) | IL-1β (pg/mL) | TNFα (pg/mL) | NO (µg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRE | 793.5 ± 20.1 | 228.5 ± 52.5 | 89.3 ± 6.9 | 319.7 ± 305.3 | 7.2 ± 0.8 |
| 1 | 835.6 ± 18.3 | 266.5 ± 46.6 | 90.1 ± 3.8 | 321.4 ± 306.9 | 7.1 ± 2.3 |
| 2 | 831.8 ± 18.3 | 141.9 ± 45.8 | 99.0 ± 5.7 | 15.1 ± 0.3 | 5.9 ± 0.2 |
| 4 | 783.6 ± 34.2 | 202.4 ± 47.2 | 93.9 ± 7.8 | 316.5 ± 301.8 | 5.8 ± 0.9 |
| 6 | 771.3 ± 19.2 | 329.2 ± 34.2 | 89.3 ± 6.7 | 14.4 ± 0.6 | 7.4 ± 3.5 |
| 10 | 810.8 ± 28.6 | 242.0 ± 24.4 | 97.4 ± 6.9 | 320.7 ± 305.7 | 7.9 ± 4.3 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pearson, W.; Guazzelli Pezzali, J.; Antunes Donadelli, R.; Wagner, A.; Buff, P. The Time Course of Inflammatory Biomarkers Following a One-Hour Exercise Bout in Canines: A Pilot Study. Animals 2020, 10, 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030486
Pearson W, Guazzelli Pezzali J, Antunes Donadelli R, Wagner A, Buff P. The Time Course of Inflammatory Biomarkers Following a One-Hour Exercise Bout in Canines: A Pilot Study. Animals. 2020; 10(3):486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030486
Chicago/Turabian StylePearson, Wendy, Julia Guazzelli Pezzali, Renan Antunes Donadelli, Ashley Wagner, and Preston Buff. 2020. "The Time Course of Inflammatory Biomarkers Following a One-Hour Exercise Bout in Canines: A Pilot Study" Animals 10, no. 3: 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030486
APA StylePearson, W., Guazzelli Pezzali, J., Antunes Donadelli, R., Wagner, A., & Buff, P. (2020). The Time Course of Inflammatory Biomarkers Following a One-Hour Exercise Bout in Canines: A Pilot Study. Animals, 10(3), 486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10030486





