Combination of Freezing, Low Sodium Brine, and Cold Smoking on the Quality and Shelf-Life of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Fillets as a Strategy to Innovate the Market of Aquaculture Products
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
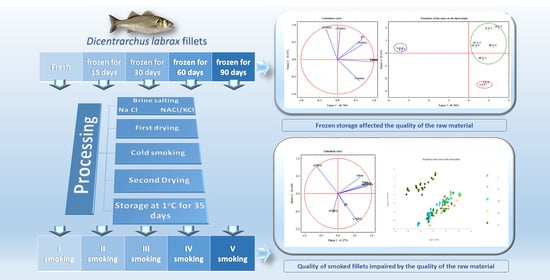
2.1. Fish Sampling and Processing
2.2. Salting, Smoking, Storage, and Sampling
2.3. Physical-Chemical Parameters
2.3.1. Color
2.3.2. Texture Profile Analysis
2.3.3. Water Holding Capacity
2.3.4. Muscular pH
2.3.5. Determination of the NA, K, and Salt Content
2.3.6. Water Activity Determination
2.4. Biochemical Parameters Related to the Shelf-Life
2.5. Sensory Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Color
3.2. Texture
3.3. Water Holding Capacity (WHC)
3.4. Muscular pH
3.5. NA, K, and Salt Content
3.6. Biochemical Parameters Related to the Shelf-Life
3.7. Sensory Analysis
3.8. Correlation among Quality Parameters of Raw and Smoked Fillets by Principal Component Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Grigorakis, K. Compositional and organoleptic quality of farmed and wild gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata) and sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) and factors affecting it: A review. Aquaculture 2007, 272, 55–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trocino, A.; Xiccato, G.; Majolini, D.; Tazzoli, M.; Tulli, F.; Tibaldi, E.; Messina, C.M.; Santulli, A. Levels of dioxin-like polychlorinated biphenyls (DL-PCBs) and metals in European sea bass from fish farms in Italy. Food Chem. 2012, 134, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, G.; Terova, G.; Gasco, L.; Piccolo, G.; Roncarati, A.; Moretti, V.M.; Centoducati, G.; Gatta, P.P.; Pais, A. Current status and future perspectives of Italian finfish aquaculture. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2014, 24, 15–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitoyannis, I.S.; Kotsanopoulos, K.V. Smoking of fish and seafood: History, methods and effects on physical, nutritional and microbiological properties. Food Bioproc. Tech. 2012, 5, 831–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Guillen, M.C.; Gomez-Estaca, J.; Gimenez, B.; Montero, P. Alternative fish species for cold-smoking process. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1525–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leroi, F.; Joffraud, J.J.; Chevalier, F. Effect of salt and smoke on the microbiological quality of cold-smoked salmon during storage at 5 degrees C as estimated by the factorial design method. J. Food Prot. 2000, 63, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab-Tehrany, E.; Jacquot, M.; Gaiani, C.; Imran, M.; Desobry, S.; Linder, M. Beneficial effects and oxidative stability of omega-3 long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 25, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Bono, G.; Arena, R.; Randazzo, M.; Morghese, M.; Manuguerra, S.; La Barbera, L.; Ozogul, F.; Sadok, S.; Santulli, A. The combined impact of cold smoking and natural antioxidants on quality and shelf life of dolphinfish (Coryphaena hippurus) fillets. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Bono, G.; Arena, R.; Randazzo, M.; Manuguerra, S.; Santulli, A. Polyphenols from halophytes and modified atmosphere packaging improve sensorial and biochemical markers of quality of common dolphinfish (Coryphaena hippurus) fillets. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 4, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Messina, C.M.; Bono, G.; Renda, G.; La Barbera, L.; Santulli, A. Effect of natural antioxidants and modified atmosphere packaging in preventing lipid oxidation and increasing the shelf-life of common dolphinfish (Coryphaena hippurus) fillets. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkeland, S.; Bencze Rørå, A.M.; Skåra, T.; Bjerkeng, B. Effects of cold smoking procedures and raw material characteristics on product yield and quality parameters of cold smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) fillets. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurgisladottir, S.; Ingvarsdottir, H.; Torrissen, O.J.; Cardinal, M.; Hafsteinsson, H. Effects of freezing/thawing on the microstructure and the texture of smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rora, A.M.B.; Einen, O. Effects of freezing on quality of cold-smoked salmon based on the measurements of physiochemical characteristics. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkeland, S.; Bjerkeng, B. The quality of cold-smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) as affected by salting method, time and temperature. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 963–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, P.; Gómez-Guillén, M.; Borderias, A. Influence of salmon provenance and smoking process on muscle functional characteristics. J. Food Sci. 2003, 68, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Giménez, B.; Gómez-Guillén, C.; Montero, P. Influence of frozen storage on aptitude of sardine and dolphinfish for cold-smoking process. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, M.; Cornet, J.; Serot, T.; Baron, R. Effects of the smoking process on odour characteristics of smoked herring (Clupea harengus) and relationships with phenolic compound content. Food Chem. 2006, 96, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, O.; Salmeron, J.; Guillen, M.D.; Casas, C. Effect of freezing on the physicochemical, textural and sensorial characteristics of salmon (Salmo salar) smoked with a liquid smoke flavouring. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinal, M.; Knockaert, C.; Torrissen, O.; Sigurgisladottir, S.; Mørkøre, T.; Thomassen, M.; Vallet, J.L. Relation of smoking parameters to the yield, colour and sensory quality of smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuentes, A.; Fernández-Segovia, I.; Barat, J.M.; Serra, J.A. Influence of sodium replacement and packaging on quality and shelf life of smoked sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.). LWT-Food Sci.Technol. 2011, 44, 917–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guideline: Sodium Intake for Adults and Children; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 1–466. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Assembly Sixty-Sixth World Health Assembly Follow-Up to the Political Declaration of the High-Level Meeting of the General Assembly on the Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Aburto, N.J.; Ziolkovska, A.; Hooper, L.; Elliott, P.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Meerpohl, J.J. Effect of lower sodium intake on health: Systematic review and meta-analyses. BMJ 2013, 346, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barat, J.-M.; Perez-Esteve, E.; Aristoy, M.-C.; Toldra, F. Partial replacement of sodium in meat and fish products by using magnesium salts. A review. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, A.; Fernández-Segovia, I.; Serra, J.A.; Barat, J.M. Development of a smoked sea bass product with partial sodium replacement. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, A.; Fernandez-Segovia, I.; Serra, J.A.; Barat, J.M. Effect of partial sodium replacement on physicochemical parameters of smoked sea bass during storage. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2012, 18, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giese, E.; Meyer, C.; Ostermeyer, U.; Lehmann, I.; Fritsche, J. Sodium reduction in selected fish products by means of salt substitutes. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2019, 245, 1651–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osheba, A.S. Technological attempts for production of low sodium smoked herring fish (Renga). Adv. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 5, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Gómez-Guillén, M.; Montero, P.; Sopelana, P.; Guillén, M. Oxidative stability, volatile components and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons of cold-smoked sardine (Sardina pilchardus) and dolphinfish (Coryphaena hippurus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.R.; Lozano, R.D.; Alman, D.H.; Orchard, S.E.; Keitch, J.A.; Connely, R.; Graham, L.A.; Acree, W.L.; John, R.S.; Hoban, R.F. CIE Recommendations on uniform color spaces, color-difference equations, and metric color terms. Color Res. Appl 1977, 2, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbán, E.; Sinesio, F.; Paoletti, F. The functional properties of the proteins, texture and the sensory characteristics of frozen sea bream fillets (Sparus aurata) from different farming systems. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 1997, 30, 214–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, B.; Fidalgo, F.; Mendes, R.; Costa, G.; Cordeiro, C.; Marques, A.; Saraiva, J.A.; Nunes, M.L. Effect of high pressure processing in the quality of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets: Pressurization rate, pressure level and holding time. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 22, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; AOAC: Rockville, MD, USA, 1990; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Greiff, K.; Fuentes, A.; Aursand, I.G.; Erikson, U.; Masot, R.; Alcaniz, M.; Barat, J.M. Innovative nondestructive measurements of water activity and the contentof salts in low-salt hake minces. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1953, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepage, G.; Roy, C.C. Improved recovery of fatty acid through direct transesterification without prior extraction or purification. J. Lipid Res. 1984, 25, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.M.; Renda, G.; La Barbera, L.; Santulli, A. By-products of farmed European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) as a potential source of n-3 PUFA. Biologia 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Botsoglou, N.A.; Fletouris, D.J.; Papageorgiou, G.E.; Vassilopoulos, V.N.; Mantis, A.J.; Trakatellis, A.G. Rapid, sensitive, and specific thiobarbituric acid method for measuring lipid peroxidation in animal tissue, food, and feedstuff samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 1931–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Communities Commission (ECC). Commission Decision of 8 March 1995 fixing the total volatile basic nitrogen (TVB-N) limit values for certain categories of fishery products and specifying the analysis methods to be used. OJEC 1995, 97, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- European Communities Commission (ECC). Laying down common marketing standards for certain fishery products. OJEC 1996, 334, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, B.M.; Messini, A.; Parisi, G.; Scappini, F.; Vigiani, V.; Giorgi, G.; Vincenzini, M. Sensory, physical, chemical and microbiological changes in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets packed under modified atmosphere/air or prepared from whole fish stored in ice. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underwood, A.J. Experiments in Ecology: Their Logical Design and Interpretation Using Analysis of Variance; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; ISBN 0521556961. [Google Scholar]
- Regost, C.; Jakobsen, J.V.; Rørå, A.M.B. Flesh quality of raw and smoked fillets of Atlantic salmon as influenced by dietary oil sources and frozen storage. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagiz, Y.; Kristinsson, H.G.; Balaban, M.O.; Marshall, M.R. Effect of high pressure treatment on the quality of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and mahi mahi (Coryphaena hippurus). J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, C509–C515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, M.P.; Hultin, H.O. Effect of pH on lipid oxidation using trout hemolysate as a catalyst: A possible role for deoxyhemoglobin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3141–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.; Montero, P.; Hurtado, O.; Borderías, A.J. Biological characteristics affect the quality of farmed Atlantic salmon and smoked muscle. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigurgisladottir, S.; Sigurdardottir, M.S.; Torrissen, O.; Vallet, J.L.; Hafsteinsson, H. Effects of different salting and smoking processes on the microstructure, the texture and yield of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fillets. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Fan, W.; Zhong, S.Y.; Ma, C.W.; Li, P.L.; Zhou, K.; Peng, Z.H.; Zhu, M.J. Quality evaluation of tray-packed tilapia fillets stored at 0 degrees C based on sensory, microbiological, biochemical and physical attributes. Afr. J. Biotechnol 2010, 9, 692–701. [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Valdez, H.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Márquez-Ríos, E.; Torres-Arreola, W. Effect of previous chilling storage on quality loss in frozen (–20 °C) sierra (Scomberomorus sierra) muscle packed with a low-density polyethylene film containing butylated hydroxytoluene. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 35, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, S.; Kerry, J.P.; Sheehan, D.; Buckley, D.J.; Morrissey, P.A. Antioxidative effect of added tea catechins on susceptibility of cooked red meat, poultry and fish patties to lipid oxidation. Food Res. Int. 2001, 34, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweet, C.W. Activity of antioxidants in fresh fish. J. Food Sci. 1973, 38, 1260–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, N.P.; Goicoechea, E.; Manzanos, M.J.; Guillén, M.D. Effect of smoking using smoke flavorings on several characteristics of farmed sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) fillets and on their evolution during vacuum-packed storage at refrigeration temperature. J. Food Process Preserv. 2017, 41, e12800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizo, A.; Fuentes, A.; Fernández-Segovia, I.; Barat, J.M. Feasibility of processing temperatures on the quality and shelf-life of smoke-flavoured cod. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampels, S. The effects of processing technologies and preparation on the final quality of fish products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Object of Assessment | Criteria | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Freshness Category | ||||
| Extra Score 3 | A Score 2 | B Score 1 | Not Admitted Score 0 | |
| External evaluation | ||||
| Texture of fillet with skin | Very firm, rigid, elastic | Fairly rigid, firm, slightly less elastic | Slightly soft, less elastic | Soft (flaccid) |
| Skin odor | Fresh seaweed | Neutral | Slightly sour | Sour |
| Flesh | ||||
| Flesh color | Translucent, smooth, bluish Color around the spinal column: absent | Slightly modified and waxy Color around the spinal column: slightly pink | Slightly opaque and waxy Color around the spinal column: pink | Opaque, yellow Color around the spinal column: red |
| Smoked Fillets | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh Fillets | NaCl | NaCl/KCl | |
| Lipids | 6.16 ± 2.34 AB | 5.93 ± 0.31 A | 6.58 ± 0.86 B |
| Moisture | 74.13 ± 1.78 A | 72.79 ± 0.3 B | 71.3 ± 0.55 B |
| Ash | 1.42 ± 0.21 A | 4.14 ± 0.19 B | 4.86 ± 0.19 B |
| Protein | 18.29 ± 4.33 A | 17.14 ± 1.52 B | 17.26 ± 1.6 B |
| aw | 0.987 ± 0.001 A | 0.942 ± 0.004 B | 0.95 ± 0.004 B |
| Smoked Fillets | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T35 | ||||
| Fresh Fillets | NaCl | NaCl/KCl | NaCl | NaCl/KCl | |
| SFA | 21.29 ± 0.32 A | 21.14 ± 0.48 A | 20.82 ± 1.59 A | 19.96 ± 1.94 A | 19.73 ± 1.39 A |
| MUFA | 45.79 ± 2.67 A | 45.33 ± 0.43 A | 46.11 ± 0.35 A | 46.68 ± 2.09 A | 46.40 ± 0.96 A |
| PUFA | 32.91 ± 2.99 A | 33.54 ± 0.91 A | 33.07 ± 1.24 A | 33.36 ± 0.15 A | 33.87 ± 2.35 A |
| Tot n-3 | 15.26 ± 2.74 A | 15.75 ± 0.52 A | 15.88 ± 0.54 A | 15.70 ± 0.86 A | 16.05 ± 2.87 A |
| Tot n-6 | 16.96 ± 0.23 A | 17.04 ± 0.45 A | 16.47 ± 0.65 A | 16.91 ± 0.65 A | 17.08 ± 0.56 A |
| Raw Fillet (Smoking) | Texture | Odor | Color | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fresh (I) | 3.00 ± 0.00 a | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 1.67 ± 0.47 | 2.22 ± 0.69 |
| Thawed (II) | 2.00 ± 0.00 b | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 0.00 |
| Thawed (III) | 1.50 ± 0.71 c | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 1.50 ± 0.71 | 1.67 ± 0.29 |
| Thawed (IV) | 1.00 ± 0.00 d | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 1.67 ± 0.58 |
| Thawed (V) | 1.00 ± 0.00 d | 2.00 ± 0.00 | 1.25 ± 0.35 | 1.42 ± 0.52 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Messina, C.M.; Arena, R.; Ficano, G.; La Barbera, L.; Morghese, M.; Santulli, A. Combination of Freezing, Low Sodium Brine, and Cold Smoking on the Quality and Shelf-Life of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Fillets as a Strategy to Innovate the Market of Aquaculture Products. Animals 2021, 11, 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010185
Messina CM, Arena R, Ficano G, La Barbera L, Morghese M, Santulli A. Combination of Freezing, Low Sodium Brine, and Cold Smoking on the Quality and Shelf-Life of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Fillets as a Strategy to Innovate the Market of Aquaculture Products. Animals. 2021; 11(1):185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010185
Chicago/Turabian StyleMessina, Concetta Maria, Rosaria Arena, Giovanna Ficano, Laura La Barbera, Maria Morghese, and Andrea Santulli. 2021. "Combination of Freezing, Low Sodium Brine, and Cold Smoking on the Quality and Shelf-Life of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Fillets as a Strategy to Innovate the Market of Aquaculture Products" Animals 11, no. 1: 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010185
APA StyleMessina, C. M., Arena, R., Ficano, G., La Barbera, L., Morghese, M., & Santulli, A. (2021). Combination of Freezing, Low Sodium Brine, and Cold Smoking on the Quality and Shelf-Life of Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) Fillets as a Strategy to Innovate the Market of Aquaculture Products. Animals, 11(1), 185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11010185