The Distribution, Expression Patterns and Functional Analysis of NR1D1 and NR4A2 in the Reproductive Axis Tissues of the Male Tianzhu White Yak
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Collection
2.2. H&E staining
2.3. IHC Staining and IF Assay
2.4. RNA Isolation and cDNA Synthesis
2.5. qPCR
2.6. Western Blot
2.7. Protein and Protein Interaction Network
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Morphologic Observation of Adult Yak HPG Tissues
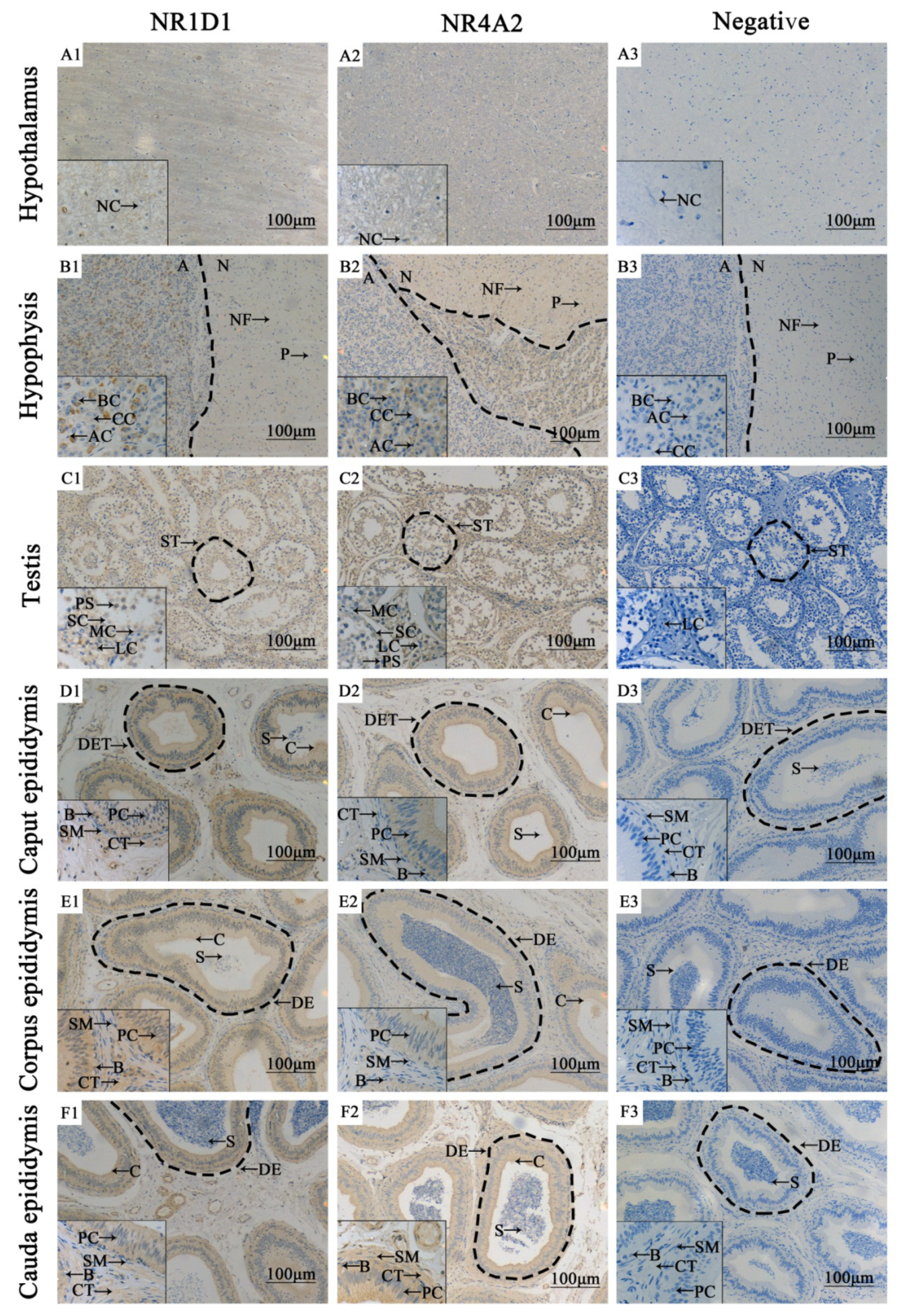
3.2. Subcellular Location Analysis of NR1D1 and NR4A2 in Adult Yak HPG Tissues
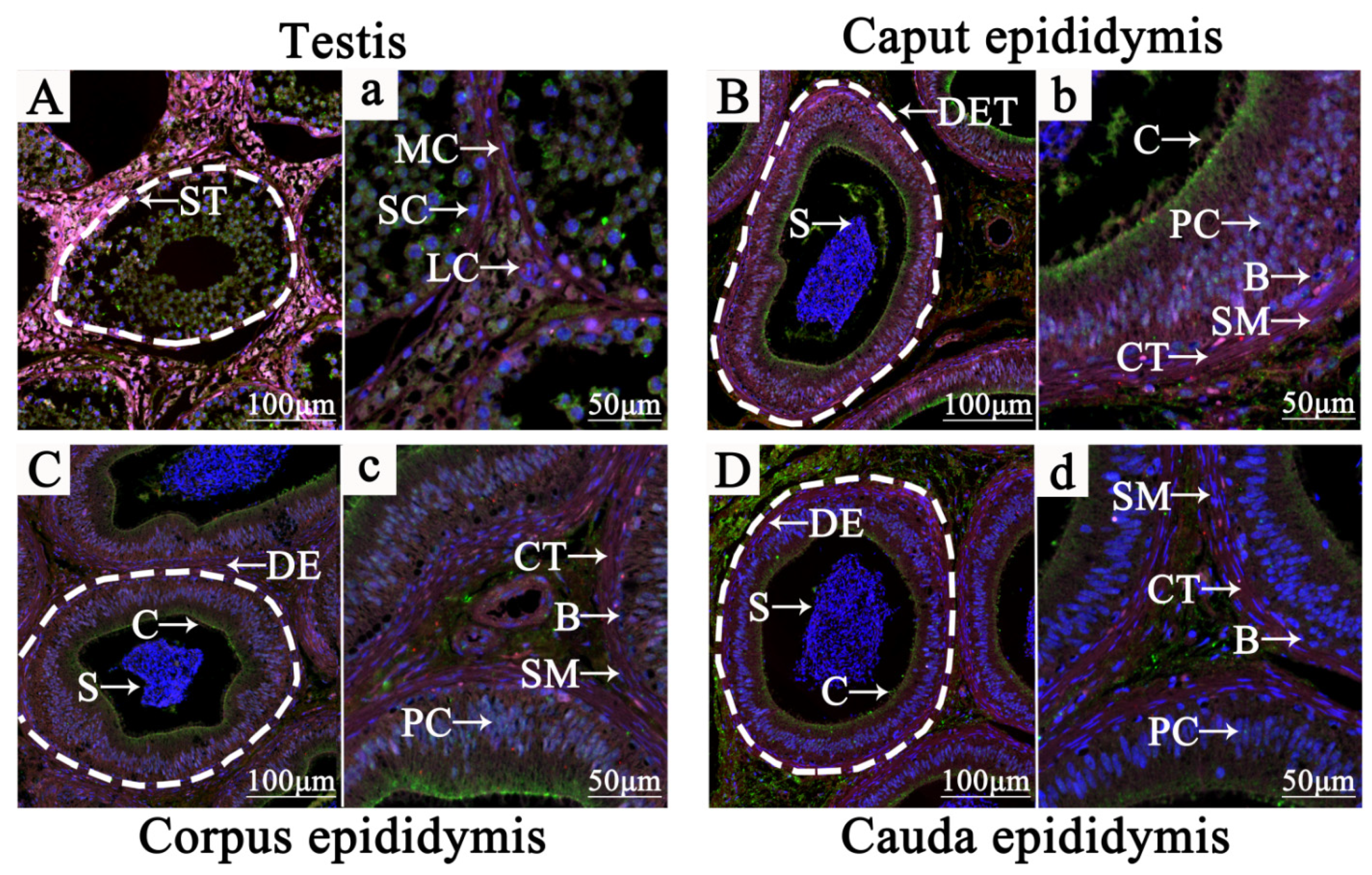
3.3. Localization of NR1D1 and NR4A2 in Adult Yak Testis and Epididymis Tissues
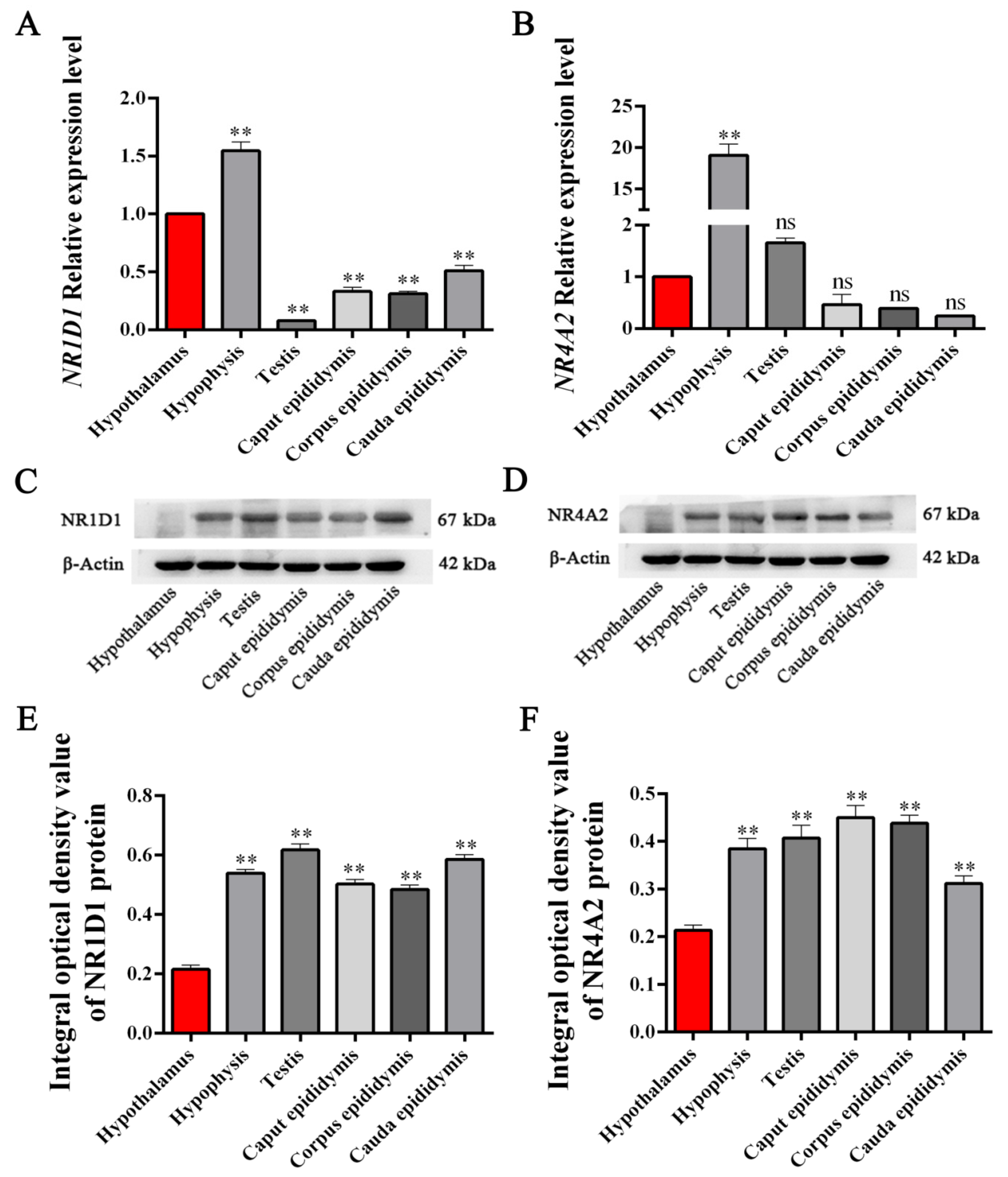
3.4. Expression Levels of NR1D1 and NR4A2 mRNA and Protein in HPG Tissues
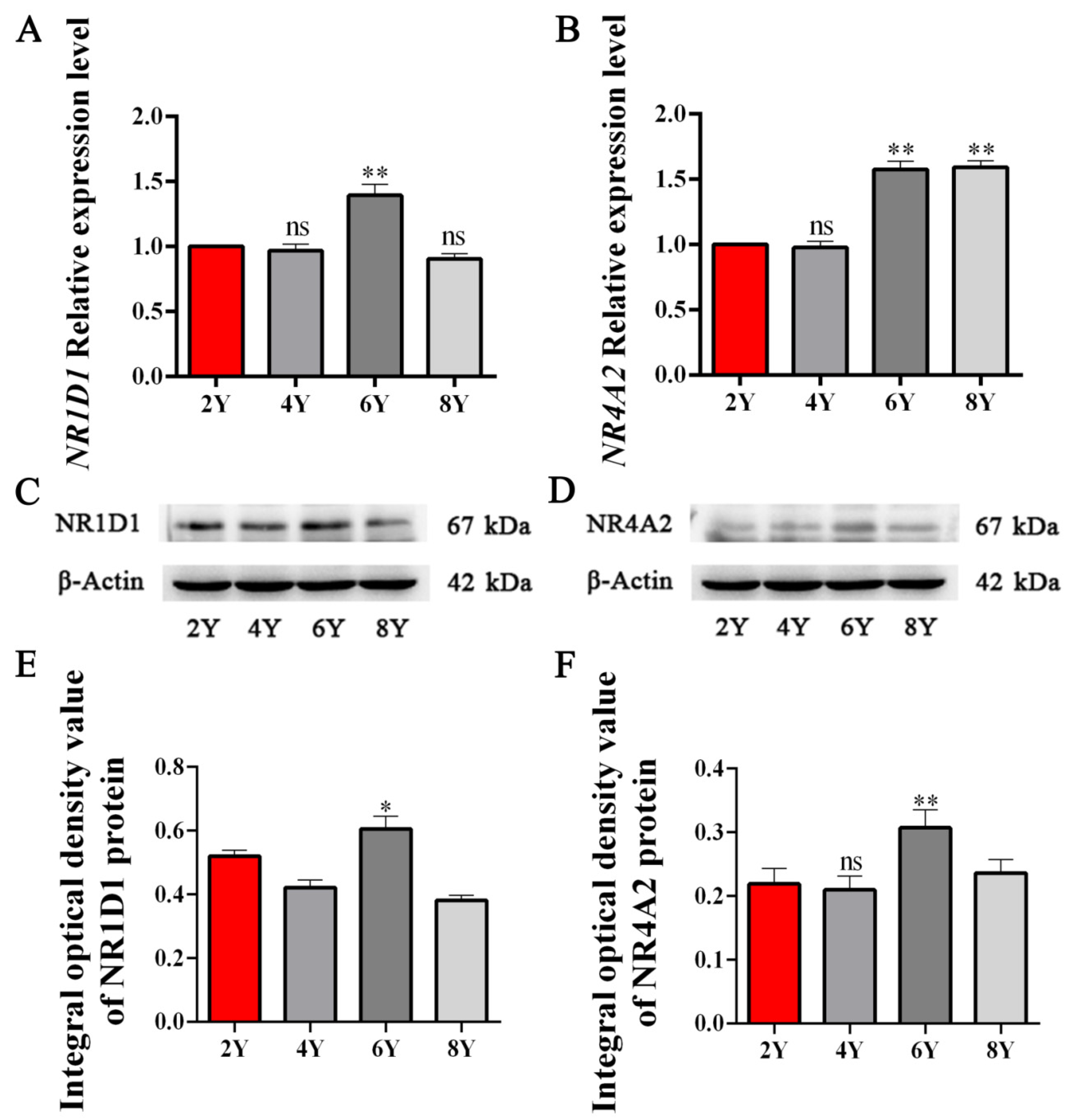
3.5. Expression Patterns of NR1D1 and NR4A2 mRNA and Protein in Yak Testicular Tissues with Different Ages
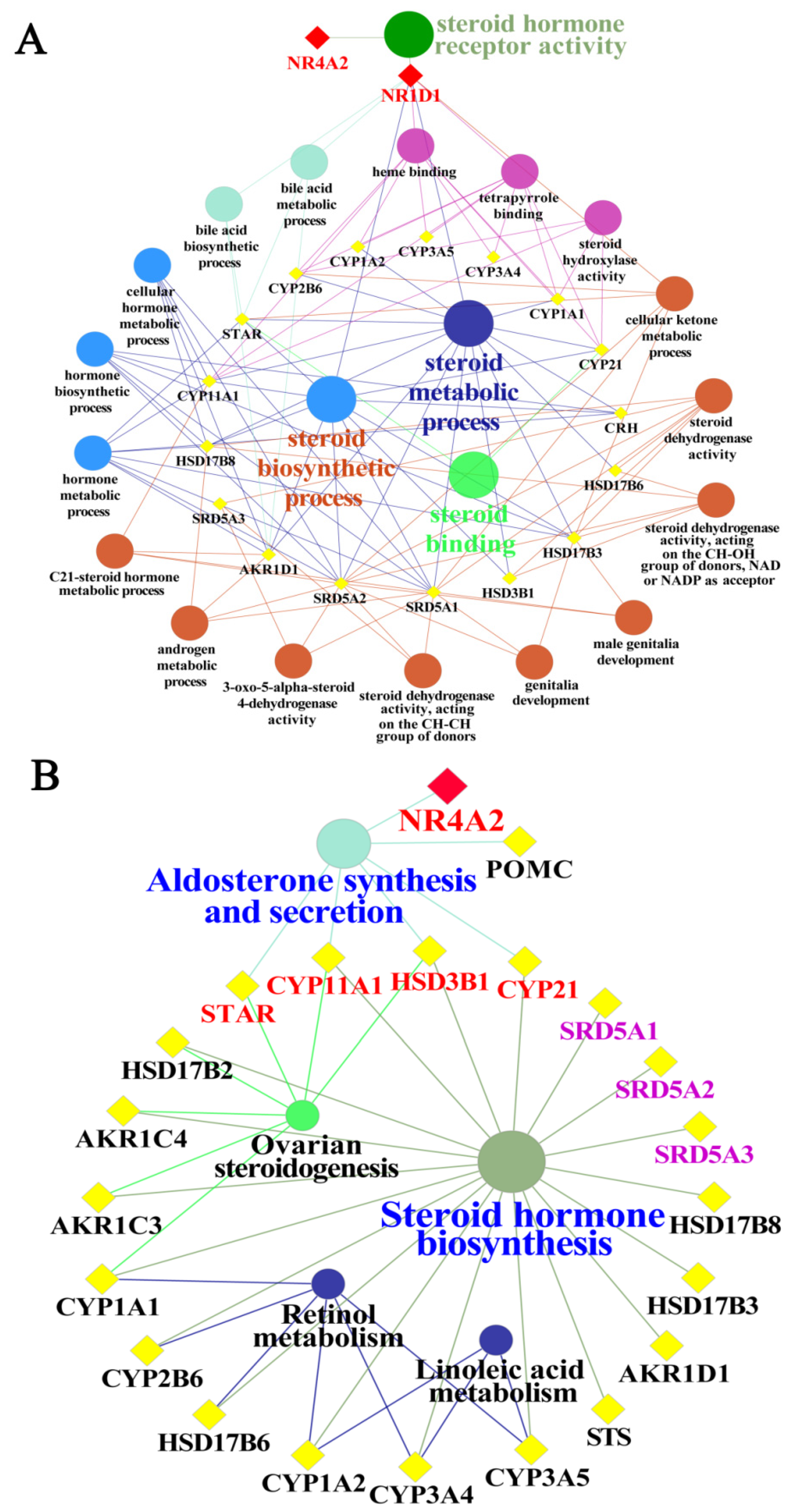
3.6. GO Functional and Pathway Analyses of Yak NR1D1 and NR4A2 in Reproductive Hormone Metabolism
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Hu, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X. Comprehensive analysis of microrna–messenger rna from white yak testis reveals the differentially expressed molecules involved in development and reproduction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Gong, J.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. Yak igf2 promotes fibroblast proliferation via suppression of igf1r and pi3kcg expression. Genes 2018, 9, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Cui, Y.; Yue, J.; He, H.; Yu, C.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Ren, X.; Meng, Y. The histological characteristics, age-related thickness change of skin, and expression of the hsps in the skin during hair cycle in yak (Bos grunniens). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chai, Z.; Hu, D.; Ji, Q.; Xin, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, J. A global analysis of CNVs in diverse yak populations using whole-genome resequencing. BMC Genomics 2019, 20, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.J.; Huang, Y.M.; Chen, B.X. Reproductive patterns of the yak. I. Reproductive phenomena of the female yak. Br. Vet. J. 1993, 149, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, F.H. Mammalian reproductive biology. Mamm. Reprod. Biol. 1989, 71, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revelli, A.; Massobrio, M.; Tesarik, J. Nongenomic actions of steroid hormones in reproductive tissues. Endocr. Rev. 1998, 19, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, E.G.; Yang, L.; Nielsen, M.F.; Kassem, M.; Dhillo, W.S.; Comninos, A.N. The relationship between bone and reproductive hormones beyond estrogens and androgens. Endocr. Rev. 2021, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coen, S.P.; Kate, K.; Byrne, C.J.; Pat, L.; Sean, F.; Crowe, M.A.; Kenny, D.A. Effect of plane of nutrition during the first 12 weeks of life on growth, metabolic and reproductive hormone concentrations, and testicular relative mRNA abundance in preweaned Holstein Friesian bull calves. J. Ani. Sci. 2021, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, A.; Pascual, A. Nuclear hormone receptors and gene expression. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1269–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teboul, M.; Guillaumond, F.; Gréchez-Cassiau, A.; Delaunay, F. The nuclear hormone receptor family round the clock. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2573–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morohashi, K.; Baba, T.; Tanaka, M. Steroid hormones and the development of reproductive organs. Sex. Dev. 2013, 7, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, N. Nuclear hormone receptor nr4a2 is involved in cell transformation and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 8208–8212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Zhang, L.; Ma, T.; Gao, L.; Yang, L.; Wu, M.; Pang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yao, Q.; Xiao, Y.; et al. Bisphenol a attenuates testosterone production in leydig cells via the inhibition of nr1d1 signaling. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Boucher, N.; Brousseau, C.; Tremblay, J.J. The orphan nuclear receptor nur77 regulates hormone-induced star transcription in leydig cells through cooperation with Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase i. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 2021–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, K.P.; Chauvin, T.R. Molecular mechanisms of testosterone action in the testis. Curr. Opin. Endocr. Metab. Res. 2019, 6, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Tremblay, J.J. Nuclear receptors in leydig cell gene expression and function. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 83, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, X. Molecular characteristics of the ho1 gene in yak are potentially adaptive for high altitude habitats. J. Comput. Theor. Nanosci. 2017, 14, 2698–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorska, M.; Gammazza, A.M.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Campanella, C.; Cappello, F.; Wasiewicz, T.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Daca, A.; Sielicka, A.; Popowska, U.; et al. Geldanamycin-induced osteosarcoma cell death is associated with hyperacetylation and loss of mitochondrial pool of heat shock protein 60 (hsp60). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shawki, H.H.; Oishi, H.; Usui, T.; Kitadate, Y.; Basha, W.A.; Abdellatif, A.M.; Hasegawa, K.; Okada, R.; Mochida, K.; El-Shemy, H.A.; et al. Mafb is dispensable for the fetal testis morphogenesis and the maintenance of spermatogenesis in adult mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raucci, F.; D’Aniello, A.; Di Fiore, M.M. Stimulation of androgen production by d-aspartate through the enhancement of star, p450scc and 3β-hsd mrna levels in vivo rat testis and in culture of immature rat leydig cells. Steroids 2014, 84, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Q. Comparative analysis of longissimus dorsi tissue from two sheep groups identifies differentially expressed genes related to growth, development and meat quality-sciencedirect. Genomics 2020, 112, 3322–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The string database in 2021: Customizable protein–protein networks, and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Galon, J.; Mlecnik, B. Cluepedia cytoscape plugin: Pathway insights using integrated experimental and in silico data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinson, J.; Raven, P.; Chew, S. The Endocrine System; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Beato, M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell 1989, 56, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselin-Labat, M.-L.; Vaillant, F.; Sheridan, J.; Pal, B.; Wu, D.; Simpson, E.R.; Yasuda, H.; Smyth, G.; Martin, T.J.; Lindeman, G.; et al. Control of mammary stem cell function by steroid hormone signalling. Nature 2010, 465, 798–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, L.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, C.; Wang, A.; Jin, Y. Circadian clock and steroidogenic-related gene expression profiles in mouse leydig cells following dexamethasone stimulation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebas, P.; Goodall, C.P.; Majewska, M.; Neumann, A.; Giebultowicz, J.M.; Chappell, P.E. Circadian clock and output genes are rhythmically expressed in extratesticular ducts and accessory organs of mice. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwang-Hoon, S.; Jae-Il, P.; Mi-Ock, L.; Jaemog, S.; Keesook, L.; Hueng-Sik, C. LH induces orphan nuclear receptor nur77 gene expression in testicular leydig cells. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, N.M.; Martin, L.J.; Tremblay, J.J. The orphan nuclear receptor nr4a1 regulates insulin-like 3 gene transcription in leydig cells. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 74, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, L.J.; Tremblay, J.J. The human 3beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase/delta5-delta4 isomerase type 2 promoter is a novel target for the immediate early orphan nuclear receptor nur77 in steroidogenic cells. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teerds, K.J.; Huhtaniemi, I.T. Morphological and functional maturation of leydig cells: From rodent models to primates. Hum. Reprod. Update 2015, 4932–4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.Z.; Guo, H.B.; Deng, C.H.; Ou, Y.H.; Peng, A.P. the culture and identification of rat testis leydig cell. Natl. J. Androl. 2006, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Chu, G.; Zhao, L.; Yamauchi, N.; Shigeyoshi, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Hattori, M.A. Rev-erbα regulates circadian rhythms and star expression in rat granulosa cells as identified by the agonist gsk4112. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaire, B. Efferent ducts, epididymis, and vas deferens: Structure, functions, and their regulation. Physiol. Reprod. 1988, 1, 999–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, C.R.; Price, D. Gonad hormone functions, and the reciprocal influence between gonads and hypophysis with its bearing on the problem of sex hormone antagonism. Am. J. Anat. 1932, 50, 13–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierantoni, R.; Fasano, S. Functional morphology and regulation of the hypothalamus-hypophysis-gonadal axis: A comparative overview. In Form and Function in Zoology; Mucchi: Modena, Italy, 1991; pp. 225–243. [Google Scholar]
- Stocco, D.M. Star protein and the regulation of steroid hormone biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2001, 63, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazawa, T.; Inaba, H.; Imamichi, Y.; Sekiguchi, T.; Uwada, J.; Islam, M.S.; Orisaka, M.; Mikami, D.; Ida, T.; Sato, T.; et al. Profiles of 5α-reduced androgens in humans and eels: 5α-dihydrotestosterone and 11-ketodihydrotestosterone are active androgens produced in eel gonads. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, L.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, J.; Bai, X.; An, X.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X. The Distribution, Expression Patterns and Functional Analysis of NR1D1 and NR4A2 in the Reproductive Axis Tissues of the Male Tianzhu White Yak. Animals 2021, 11, 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113117
Dai L, Zhang Q, Shi J, Bai X, An X, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Zhao X. The Distribution, Expression Patterns and Functional Analysis of NR1D1 and NR4A2 in the Reproductive Axis Tissues of the Male Tianzhu White Yak. Animals. 2021; 11(11):3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113117
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Lijun, Quanwei Zhang, Jun Shi, Xu Bai, Xiaoxiao An, Bohao Zhang, Yong Zhang, and Xingxu Zhao. 2021. "The Distribution, Expression Patterns and Functional Analysis of NR1D1 and NR4A2 in the Reproductive Axis Tissues of the Male Tianzhu White Yak" Animals 11, no. 11: 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113117
APA StyleDai, L., Zhang, Q., Shi, J., Bai, X., An, X., Zhang, B., Zhang, Y., & Zhao, X. (2021). The Distribution, Expression Patterns and Functional Analysis of NR1D1 and NR4A2 in the Reproductive Axis Tissues of the Male Tianzhu White Yak. Animals, 11(11), 3117. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11113117






