The Zoonotic Helminth Parasite Fasciola hepatica: Virulence-Associated Cathepsin B and Cathepsin L Cysteine Peptidases Secreted by Infective Newly Excysted Juveniles (NEJ)
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Production, Purification and In Vitro Autocatalytic Processing of Recombinant FhCBs and FhCL3
2.2. Assessment of Enzymatic Activity by Fluorogenic Substrate Assay
2.3. Determination of Inhibitor Specificity against Recombinant FhCBs and FhCL3
2.4. Exo-Carboxypeptidase Activity of Recombinant FhCBs and FhCL3
2.5. Effects of Inhibitors on the Excystment of F. hepatica Metacercariae and Viability of NEJ
3. Results
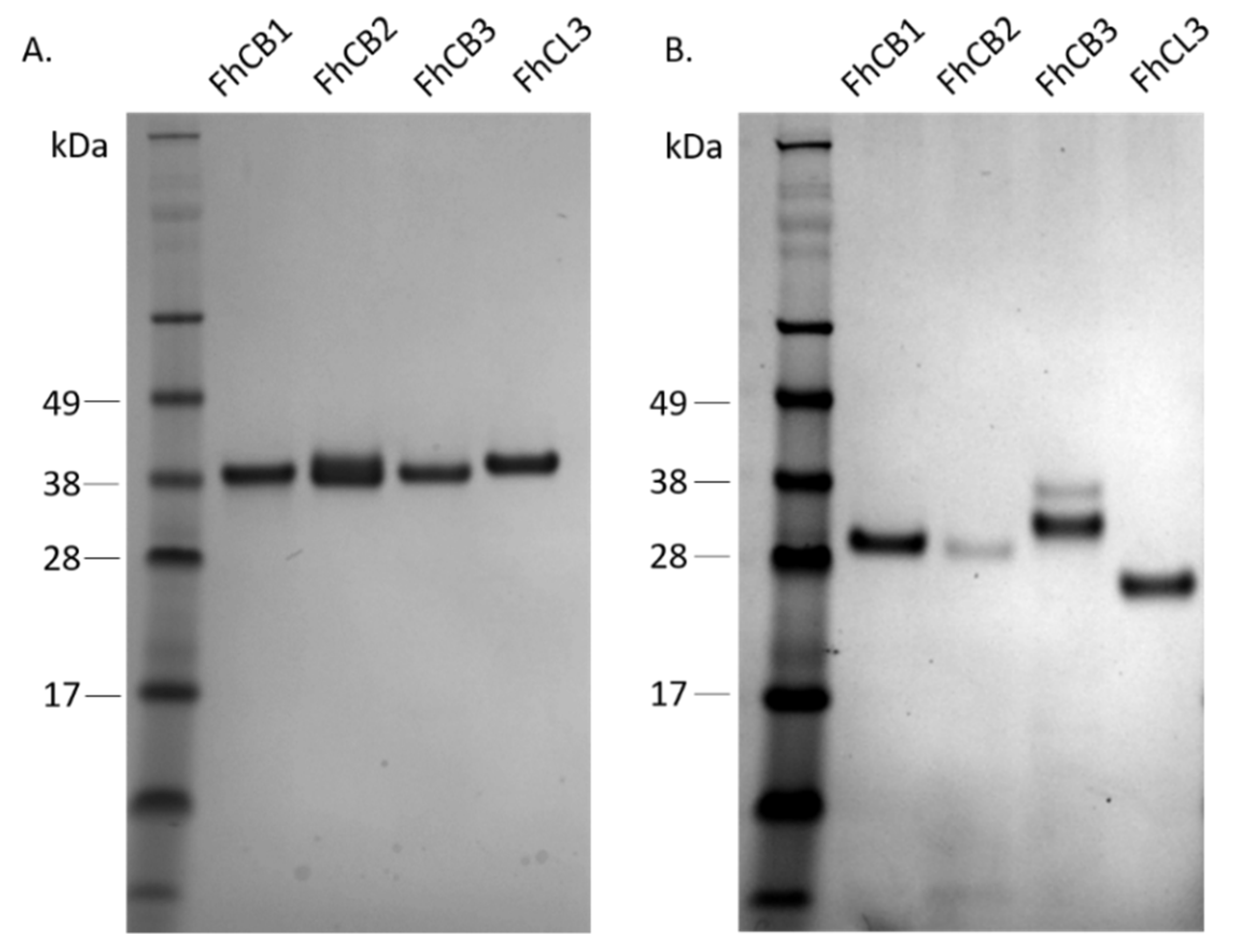
3.1. Production and Isolation of Recombinant F. hepatica FhCB1, FhCB2, FhCB3 and FhCL3
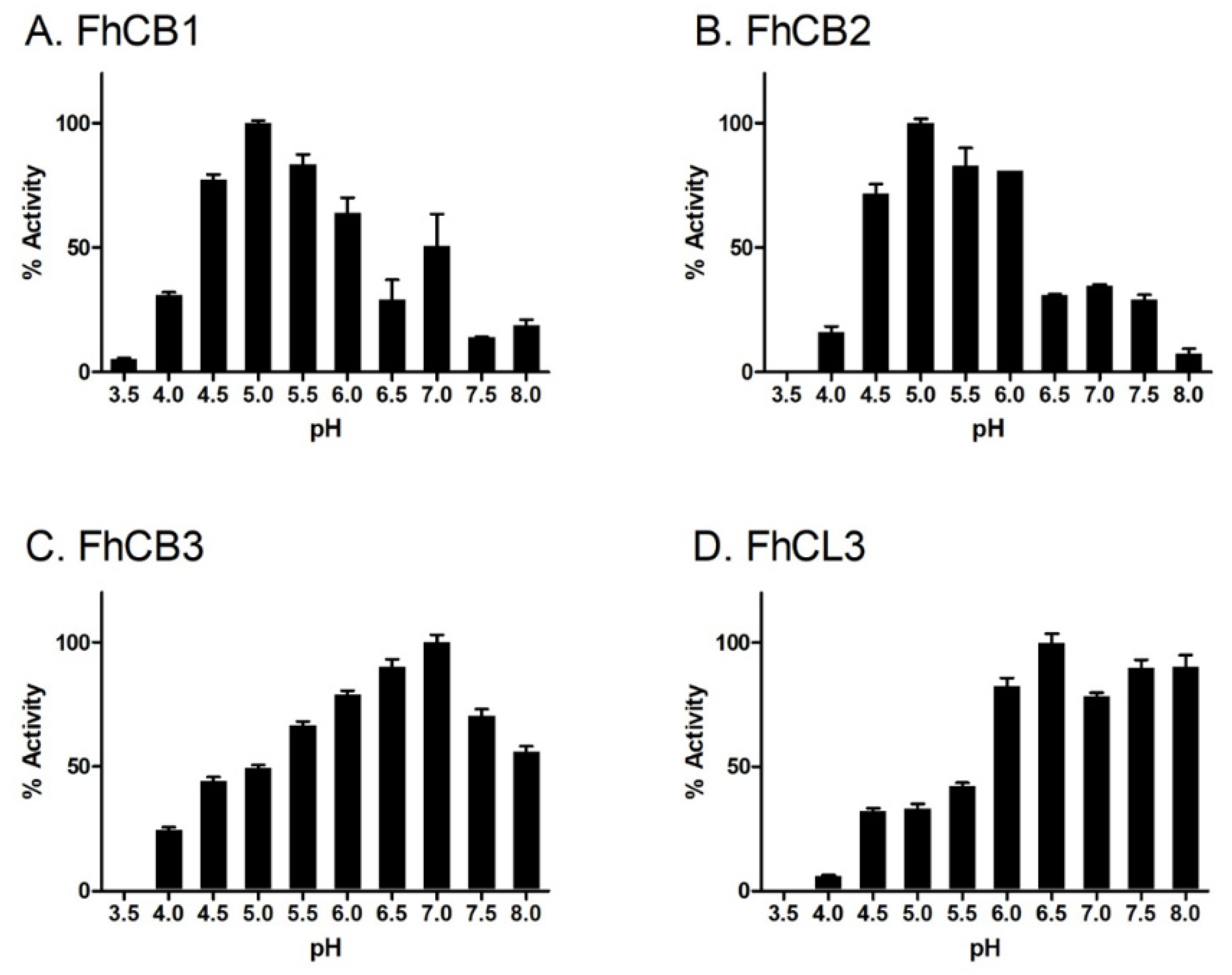
3.2. pH Dependency of Mature F. hepatica FhCB1, FhCB2, FhCB3 and FhCL3
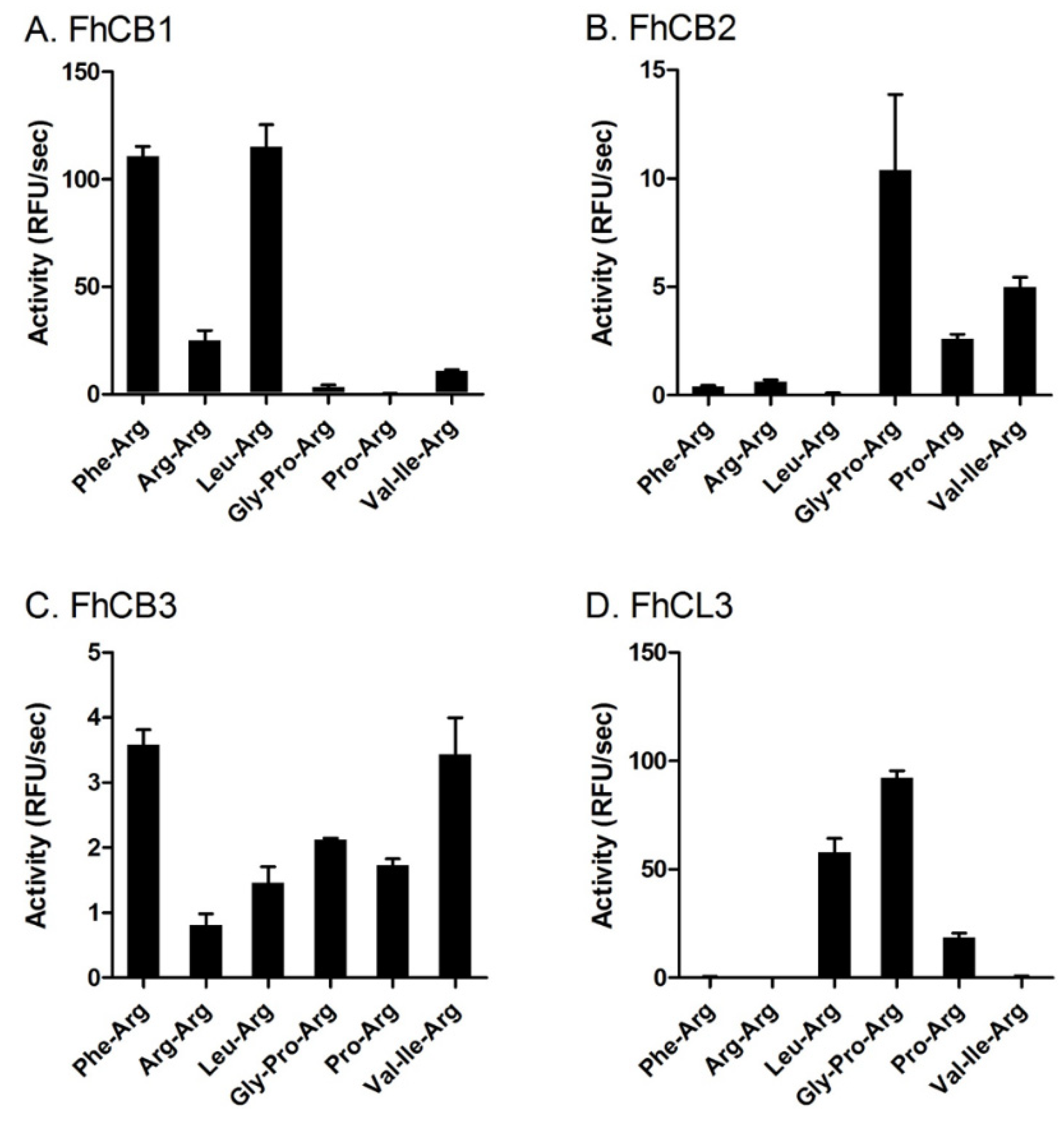
3.3. FhCB1, FhCB2, FhCB3 and FhCL3 Exhibit Distinct Substrate Preference Profiles
3.4. Kinetic Analyses of the Enzymatic Efficiency of FhCB1, FhCB2, FhCB3 and FhCL3
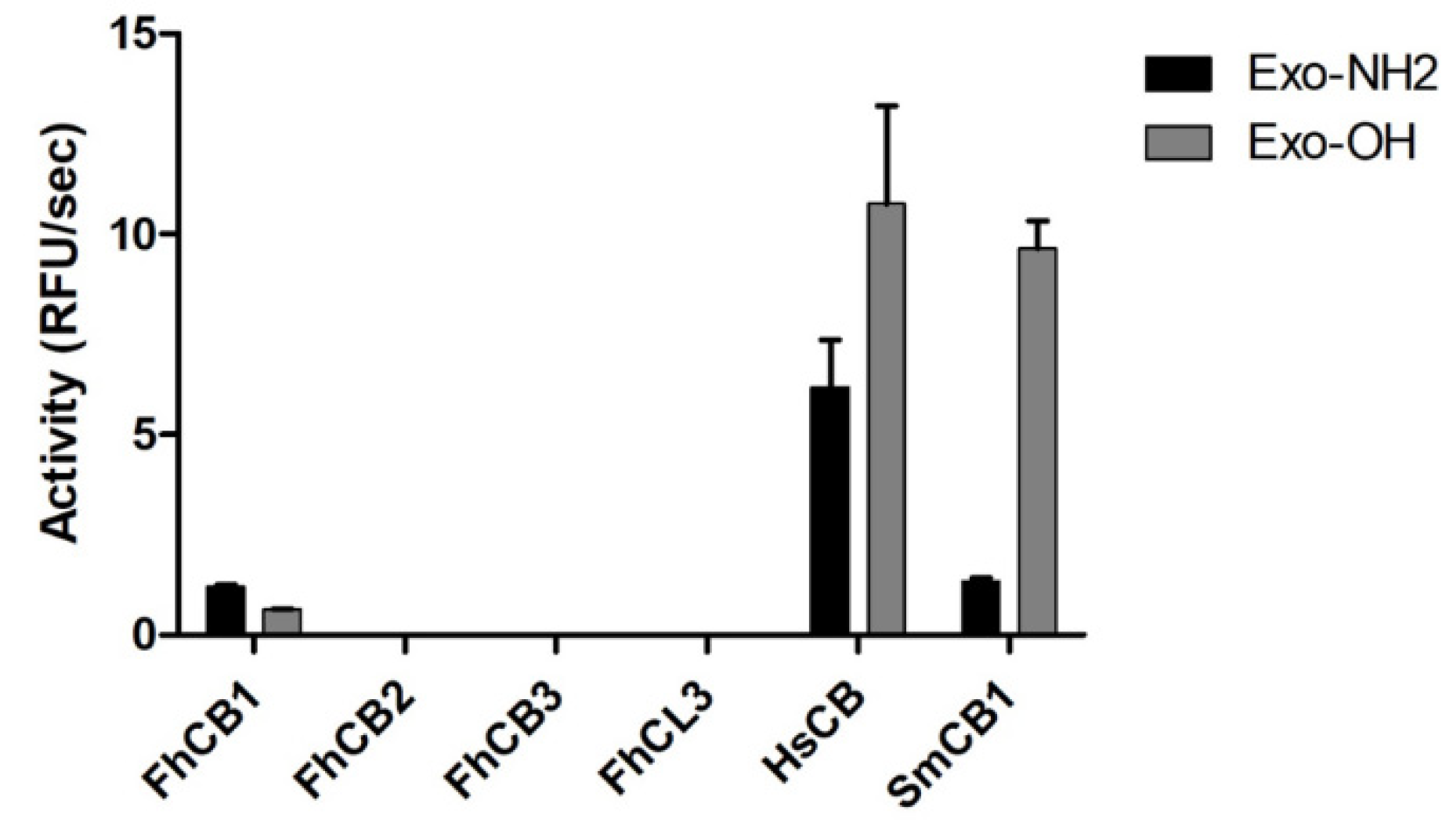
3.5. Exo-Carboxypeptidase Activity
3.6. Inhibitors Screening against FhCB1, FhCB2, FhCB3 and FhCL3
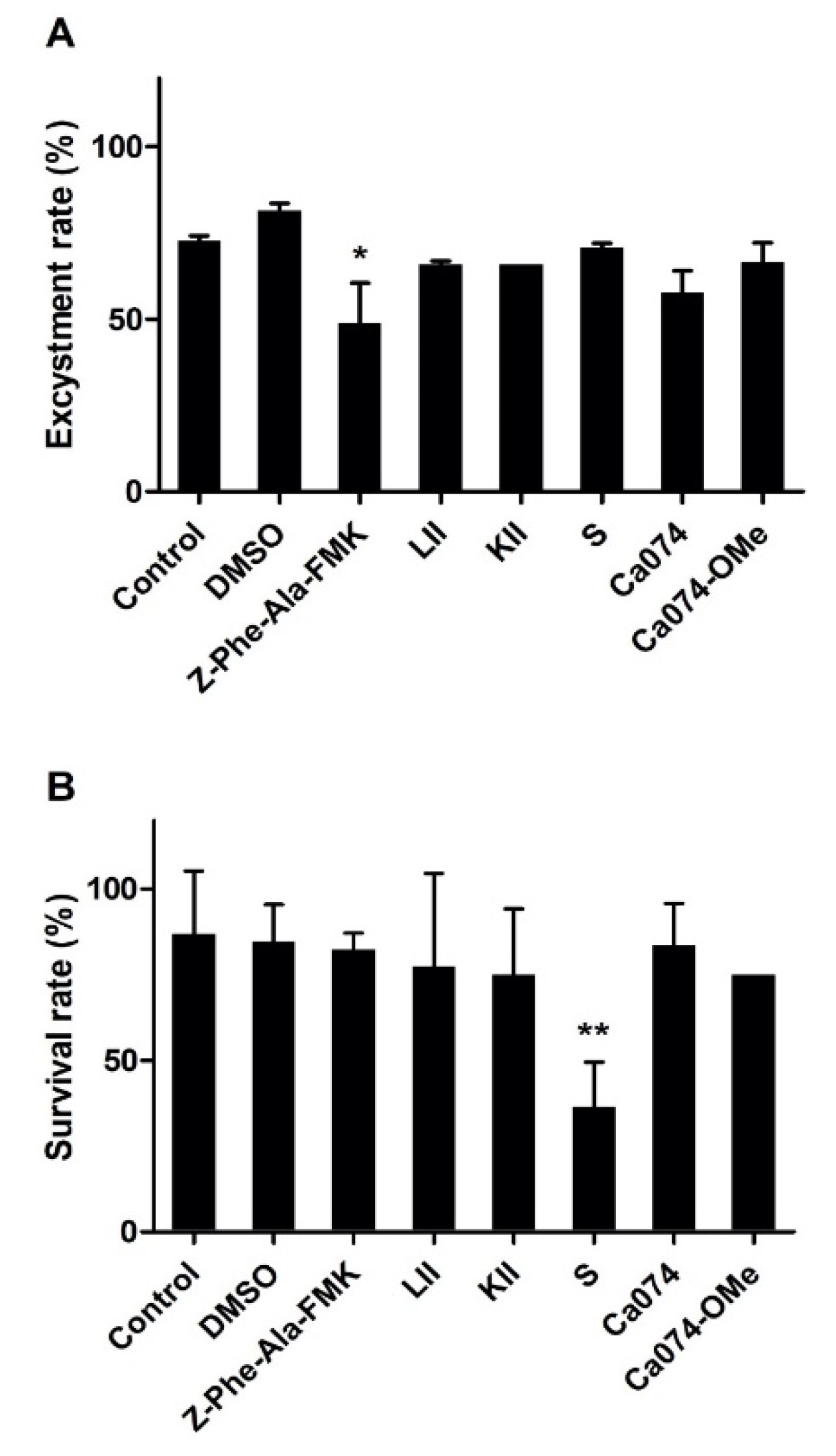
3.7. Effect of Cysteine Peptidases Inhibitors on F. hepatica Metacercarial Excystment In Vitro
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mazeri, S.; Rydevik, G.; Handel, I.; Bronsvoort, B.M.D.; Sargison, N. Estimation of the impact of Fasciola hepatica infection on time taken for UK beef cattle to reach slaughter weight. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripa, B. Global burden of food-borne trematodiasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürst, T.; Keiser, J.; Utzinger, J. Global burden of human food-borne trematodiasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravedo, M.A.; Cabada, M.M. Human fascioliasis: Current epidemiological status and strategies for diagnosis, treatment, and control. Res. Rep. Trop. Med. 2020, 11, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Miguel, J.; Becerro-Recio, D.; Siles-Lucas, M. Insights into Fasciola hepatica juveniles: Crossing the fasciolosis rubicon. Trends Parasitol. 2021, 37, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boray, J.C. Experimental fascioliasis in Australia. Adv. Parasitol. 1969, 7, 95–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Graczyk, T.K.; Fried, B. Development of Fasciola hepatica in the intermediate host. In Fasciolosis; Dalton, J.P., Ed.; CABI Publishing: Wallingford, UK, 1999; pp. 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mas-Coma, S.; Valero, M.A.; Bargues, M.D. Fascioliasis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 766, 77–114. [Google Scholar]
- Cwiklinski, K.; Donnelly, S.; Drysdale, O.; Jewhurst, H.; Smith, D.; De Marco Verissimo, C.; Pritsch, I.C.; O’Neill, S.; Dalton, J.P.; Robinson, M.W. The cathepsin-like cysteine peptidases of trematodes of the genus Fasciola. Adv. Parasitol. 2019, 104, 113–164. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, M.W.; Menon, R.; Donnelly, S.M.; Dalton, J.P.; Ranganathan, S. An integrated transcriptomics and proteomics analysis of the secretome of the helminth pathogen Fasciola hepatica: Proteins associated with invasion and infection of the mammalian host. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 1891–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Maggio, L.S.; Tirloni, L.; Pinto, A.F.M.; Diedrich, J.K.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Carmona, C.; Berasain, P.; da Silva Vaz, I., Jr. A proteomic comparison of excretion/secretion products in Fasciola hepatica newly excysted juveniles (NEJ) derived from Lymnaea viatrix or Pseudosuccinea columella. Exp. Parasitol. 2019, 201, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, L.R.; Good, R.T.; Panaccio, M.; Wijffels, G.L.; Sandeman, R.M.; Spithill, T.W. Fasciola hepatica: Characterization and cloning of the major cathepsin B protease secreted by newly excysted juvenile liver fluke. Exp. Parasitol. 1998, 88, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Law, R.H.; Smooker, P.M.; Irving, J.A.; Piedrafita, D.; Ponting, R.; Kennedy, N.J.; Whisstock, J.C.; Pike, R.N.; Spithill, T.W. Cloning and expression of the major secreted cathepsin B-like protein from juvenile Fasciola hepatica and analysis of immunogenicity following liver fluke infection. Infect. Immun. 2003, 71, 6921–6932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beckham, S.A.; Law, R.H.; Smooker, P.M.; Quinsey, N.S.; Caffrey, C.R.; McKerrow, J.H.; Pike, R.N.; Spithill, T.W. Production and processing of a recombinant Fasciola hepatica cathepsin B-like enzyme (FhcatB1) reveals potential processing mechanisms in the parasite. Biol. Chem. 2006, 387, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckham, S.A.; Piedrafita, D.; Phillips, C.I.; Samarawickrema, N.; Law, R.H.; Smooker, P.M.; Quinsey, N.S.; Irving, J.A.; Greenwood, D.; Verhelst, S.H.; et al. A major cathepsin B protease from the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica has atypical active site features and a potential role in the digestive tract of newly excysted juvenile parasites. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corvo, I.; Cancela, M.; Cappetta, M.; Pi-Denis, N.; Tort, J.F.; Roche, L. The major cathepsin L secreted by the invasive juvenile Fasciola hepatica prefers proline in the S2 subsite and can cleave collagen. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2009, 167, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.W.; Donnelly, S.; Hutchinson, A.T.; To, J.; Taylor, N.L.; Norton, R.S.; Perugini, M.A.; Dalton, J.P. A family of helminth molecules that modulate innate cell responses via molecular mimicry of host antimicrobial peptides. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turk, D.; Guncar, G.; Podobnik, M.; Turk, B. Revised definition of substrate binding sites of papain-like cysteine proteases. Biol. Chem. 1998, 379, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernet, T.; Tessier, D.C.; Chatellier, J.; Plouffe, C.; Lee, T.S.; Thomas, D.Y.; Storer, A.C.; Ménard, R. Structural and functional roles of asparagine 175 in the cysteine protease papain. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 16645–16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujishima, A.; Imai, Y.; Nomura, T.; Fujisawa, Y.; Yamamoto, Y.; Sugawara, T. The crystal structure of human cathepsin L complexed with E-64. FEBS Lett. 1997, 407, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, A.; Hara, T.; Tomoo, K.; Ishida, T.; Fujii, T.; Hata, Y.; Murata, M.; Kitamura, K. Binding mode of CA074, a specific irreversible inhibitor, to bovine cathepsin B as determined by X-ray crystal analysis of the complex. J. Biochem. 1997, 121, 974–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Z.; Hasnain, S.; Hirama, T.; Lee, X.; Mort, J.S.; To, R.; Huber, C.P. Crystal structures of recombinant rat cathepsin B and a cathepsin B-inhibitor complex. Implications for structure-based inhibitor design. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 5527–5533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turk, D.; Podobnik, M.; Kuhelj, R.; Dolinar, M.; Turk, V. Crystal structures of human procathepsin B at 3.2 and 3.3 Angstroms resolution reveal an interaction motif between a papain-like cysteine protease and its propeptide. FEBS Lett. 1996, 384, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jílková, A.; Řezáčová, P.; Lepšík, M.; Horn, M.; Váchová, J.; Fanfrlík, J.; Brynda, J.; McKerrow, J.H.; Caffrey, C.R.; Mareš, M. Structural basis for inhibition of cathepsin B drug target from the human blood fluke, Schistosoma mansoni. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 35770–35781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pritsch, I.C.; Tikhonova, I.G.; Jewhurst, H.L.; Drysdale, O.; Cwiklinski, K.; Molento, M.B.; Dalton, J.P.; Verissimo, C.M. Regulation of the Fasciola hepatica newly excysted juvenile cathepsin L3 (FhCL3) by its propeptide: A proposed ‘clamp-like’ mechanism of binding and inhibition. BMC Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, M.R.; Coulombe, R.; Jenkins, J.; Cygler, M. Structural basis for specificity of papain-like cysteine protease proregions toward their cognate enzymes. Proteins 1998, 32, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, C.M.; Caffrey, C.R.; Donnelly, S.M.; Seshaadri, A.; Lowther, J.; Tort, J.F.; Collins, P.R.; Robinson, M.W.; Xu, W.; McKerrow, J.H.; et al. Structural and functional relationships in the virulence-associated cathepsin L proteases of the parasitic liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 9896–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowther, J.; Robinson, M.W.; Donnelly, S.M.; Xu, W.; Stack, C.M.; Matthews, J.M.; Dalton, J.P. The importance of pH in regulating the function of the Fasciola hepatica cathepsin L1 cysteine protease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collins, P.R.; Stack, C.M.; O’Neill, S.M.; Doyle, S.; Ryan, T.; Brennan, G.P.; Mousley, A.; Stewart, M.; Maule, A.G.; Dalton, J.P.; et al. Cathepsin L1, the major protease involved in liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) virulence: Propetide cleavage sites and autoactivation of the zymogen secreted from gastrodermal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 17038–17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Copeland, R.A. Enzymes: A Practical Introduction to Structure, Mechanism, and Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000; p. 461. [Google Scholar]
- Piedrafita, D.; Parsons, J.C.; Sandeman, R.M.; Wood, P.R.; Estuningsih, S.E.; Partoutomo, S.; Spithill, T.W. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity to newly excysted juvenile Fasciola hepatica in vitro is mediated by reactive nitrogen intermediates. Parasite Immunol. 2001, 23, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrett, A.J.; Kirschke, H. Cathepsin B, cathepsin H, and cathepsin L. Methods Enzymol. 1981, 80 Pt C, 535–561. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, A.J. Fluorimetric assays for cathepsin B and cathepsin H with methylcoumarylamide substrates. Biochem. J. 1980, 187, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koshland, D.E. The Application and Usefulness of the Ratio kcat/KM. Bioorg. Chem. 2002, 30, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupa, J.C.; Hasnain, S.; Nägler, D.K.; Ménard, R.; Mort, J.S. S2′ substrate specificity and the role of His110 and His111 in the exopeptidase activity of human cathepsin B. Biochem. J. 2002, 361 Pt 3, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGonigle, L.; Mousley, A.; Marks, N.J.; Brennan, G.P.; Dalton, J.P.; Spithill, T.W.; Day, T.A.; Maule, A.G. The silencing of cysteine proteases in Fasciola hepatica newly excysted juveniles using RNA interference reduces gut penetration. Int. J. Parasitol. 2008, 38, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cwiklinski, K.; Jewhurst, H.; McVeigh, P.; Barbour, T.; Maule, A.G.; Tort, J.; O’Neill, S.M.; Robinson, M.W.; Donnelly, S.; Dalton, J.P. Infection by the helminth parasite Fasciola hepatica requires rapid regulation of metabolic, virulence, and invasive factors to adjust to its mammalian host. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2018, 17, 792–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Creaney, J.; Wilson, L.; Dosen, M.; Sandeman, R.M.; Spithill, T.W.; Parsons, J.C. Fasciola hepatica: Irradiation-induced alterations in carbohydrate and cathepsin-B protease expression in newly excysted juvenile liver fluke. Exp. Parasitol. 1996, 83, 202–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, C.M.; Donnelly, S.; Lowther, J.; Xu, W.; Collins, P.R.; Brinen, L.S.; Dalton, J.P. The major secreted cathepsin L1 protease of the liver fluke, Fasciola hepatica: A Leu-12 to Pro-12 replacement in the nonconserved C-terminal region of the prosegment prevents complete enzyme autoactivation and allows definition of the molecular events in prosegment removal. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 16532–16543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fallingborg, J. Intraluminal pH of the human gastrointestinal tract. Dan. Med. Bull. 1999, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Morphew, R.M.; Wright, H.A.; Lacourse, E.J.; Porter, J.; Barrett, J.; Woods, D.J.; Brophy, P.M. Towards delineating functions within the fasciola secreted cathepsin l protease family by integrating in vivo based sub-proteomics and phylogenetics. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Maggio, L.S.; Tirloni, L.; Pinto, A.F.; Diedrich, J.K.; Yates Iii, J.R.; Benavides, U.; Carmona, C.; da Silva Vaz, I., Jr.; Berasain, P. Across intra-mammalian stages of the liver fluke Fasciola hepatica: A proteomic study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chantree, P.; Wanichanon, C.; Phatsara, M.; Meemon, K.; Sobhon, P. Characterization and expression of cathepsin B2 in Fasciola gigantica. Exp. Parasitol. 2012, 132, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corvo, I.; O’Donoghue, A.J.; Pastro, L.; Pi-Denis, N.; Eroy-Reveles, A.; Roche, L.; McKerrow, J.H.; Dalton, J.P.; Craik, C.S.; Caffrey, C.R.; et al. Dissecting the active site of the collagenolytic cathepsin L3 protease of the invasive stage of Fasciola hepatica. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasnain, S.; Hirama, T.; Huber, C.P.; Mason, P.; Mort, J.S. Characterization of cathepsin B specificity by site-directed mutagenesis. Importance of Glu245 in the S2-P2 specificity for arginine and its role in transition state stabilization. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, N.N., Jr.; Barrett, A.J. The specificity of cathepsin B. Hydrolysis of glucagon at the C-terminus by a peptidyldipeptidase mechanism. Biochem. J. 1978, 171, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musil, D.; Zucic, D.; Turk, D.; Engh, R.A.; Mayr, I.; Huber, R.; Popovic, T.; Turk, V.; Towatari, T.; Katunuma, N.; et al. The refined 2.15 A X-ray crystal structure of human liver cathepsin B: The structural basis for its specificity. EMBO J. 1991, 10, 2321–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illy, C.; Quraishi, O.; Wang, J.; Purisima, E.; Vernet, T.; Mort, J.S. Role of the occluding loop in cathepsin B activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siricoon, S.; Vichasri Grams, S.; Lertwongvisarn, K.; Abdullohfakeeyah, M.; Smooker, P.M.; Grams, R. Fasciola gigantica cathepsin B5 is an acidic endo- and exopeptidase of the immature and mature parasite. Biochimie 2015, 119, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, B.; Lynas, J.F.; Meighan, M.A.; Brömme, D. Evaluation of dipeptide alpha-keto-beta-aldehydes as new inhibitors of cathepsin S. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, K.; Mercer, E. The fine structure of the cyst wall of the metacercaria of Fasciola hepatica. J. Cell Sci. 1964, 3, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynas, J.F.; Hawthorne, S.J.; Walker, B. Development of peptidyl alpha-keto-beta-aldehydes as new inhibitors of cathepsin L—Comparisons of potency and selectivity profiles with cathepsin B. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2000, 10, 1771–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynas, J.F.; Martin, S.L.; Walker, B. Synthesis and kinetic evaluation of peptide alpha-keto-beta-aldehyde-based inhibitors of trypsin-like serine proteases. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2001, 53, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsell, W.; Bjoerkman, N. Morphological and biochemical studies on absorption and secretion in the alimentary tract of Fasciola hepatica L. J. Parasitol. 1965, 51, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, J.P.; Heffernan, M. Thiol proteases released in vitro by Fasciola hepatica. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1989, 35, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, R.M. Collagenase activity of immature Fasciola hepatica. Nature 1966, 209, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethadavit, M.; Meemon, K.; Jardim, A.; Spithill, T.W.; Sobhon, P. Identification, expression and immunolocalization of cathepsin B3, a stage-specific antigen expressed by juvenile Fasciola gigantica. Acta Trop. 2009, 112, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, C.B.; Mitchell, G.F. Proteolytic cleavage of immunoglobulin by enzymes released by Fasciola hepatica. Vet. Parasitol. 1982, 11, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Peptidase | Z-Phe-Arg-AMC | Z-Gly-Pro-Arg-AMC | Z-Val-Ile-Arg-AMC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FhCB1 | KM | 69 ± 5 * | ||
| Kcat | 1.0 ± 0.2 | - | - | |
| Kcat/KM | 13,596 | |||
| FhCB2 | KM | 52 ± 4 | 71 ± 7 | |
| Kcat | - | 0.4 ± 0.001 | 0.5 ± 0.004 | |
| Kcat/KM | 4933 | 6876 | ||
| FhCB3 | KM | 27 ± 2 | 40 ± 4 | 42 ± 4 |
| Kcat | 0.05 ± 0.007 | 0.02 ± 0.002 | 0.1 ± 0.004 | |
| Kcat/KM | 1708 | 579 | 2266 | |
| FhCL3 | KM | 27 ± 2 | ||
| Kcat | - | 0.5 ± 0.07 | - | |
| Kcat/KM | 17,960 | |||
| Inhibitor | FhCB1 | FhCB2 | FhCB3 | FhCL3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z-Phe-Ala-FMK | 3 ± 0.20 | 904 ± 271 | 246 ± 55.74 | 15 ± 5.95 |
| LII | 7 ± 1.25 | 1840 ± 77 | 211 ± 34.84 | 8 ± 0.60 |
| KII | 466 ± 40.59 | NI * | 227 ± 28.32 | 0.7 ± 0.19 |
| S | 14 ± 2.42 | 345 ± 18.6 | 696 ± 94.80 | 35 ± 2.4 |
| Ca074 | 7317 ± 934 | 5930 ± 567.1 | 540 ± 45.22 | 603 ± 133.3 |
| Ca074ME | 5500 ± 1187 | 3892 ± 299 | 785 ± 130.4 | 249 ± 35.48 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbour, T.; Cwiklinski, K.; Lalor, R.; Dalton, J.P.; De Marco Verissimo, C. The Zoonotic Helminth Parasite Fasciola hepatica: Virulence-Associated Cathepsin B and Cathepsin L Cysteine Peptidases Secreted by Infective Newly Excysted Juveniles (NEJ). Animals 2021, 11, 3495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123495
Barbour T, Cwiklinski K, Lalor R, Dalton JP, De Marco Verissimo C. The Zoonotic Helminth Parasite Fasciola hepatica: Virulence-Associated Cathepsin B and Cathepsin L Cysteine Peptidases Secreted by Infective Newly Excysted Juveniles (NEJ). Animals. 2021; 11(12):3495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123495
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbour, Tara, Krystyna Cwiklinski, Richard Lalor, John Pius Dalton, and Carolina De Marco Verissimo. 2021. "The Zoonotic Helminth Parasite Fasciola hepatica: Virulence-Associated Cathepsin B and Cathepsin L Cysteine Peptidases Secreted by Infective Newly Excysted Juveniles (NEJ)" Animals 11, no. 12: 3495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123495
APA StyleBarbour, T., Cwiklinski, K., Lalor, R., Dalton, J. P., & De Marco Verissimo, C. (2021). The Zoonotic Helminth Parasite Fasciola hepatica: Virulence-Associated Cathepsin B and Cathepsin L Cysteine Peptidases Secreted by Infective Newly Excysted Juveniles (NEJ). Animals, 11(12), 3495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11123495







