Perosomus Elumbis in Piglets: Pathological, Radiological and Cytogenetic Findings
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Case History
2.3. Epidemiological Investigation at the Farm
2.4. Radiological Exams
2.5. Gross Examination
2.6. Cytogenetic Examination
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological Investigation at the Farm
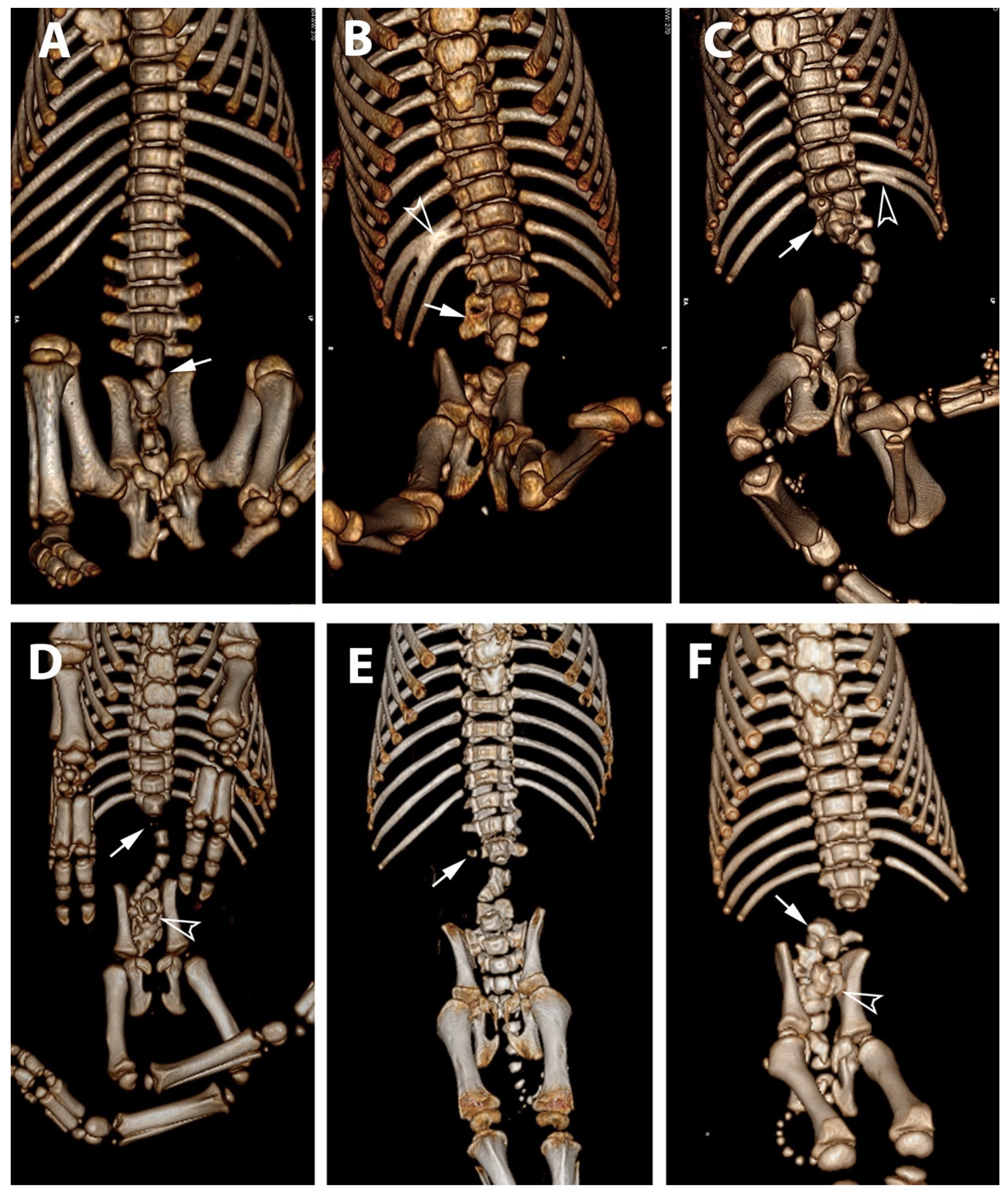
3.2. Radiological Exams
3.3. Gross Examination
3.4. Cytogenetic Examination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Agerholm, J.S.; Holm, W.; Schmidt, M.; Hyttel, P.; Fredholm, M.; McEvoy, F.J. Perosomus elumbis in Danish Holstein cattle. BMC Vet. Rec. 2014, 10, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dennis, S.M. Perosomus elumbis in sheep. Aust. Vet. J. 1975, 51, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlović, M.; Ilijas, B. Perosomus elumbis in a piglet. Dtsch. Tierarztl Wochenschr. 1977, 84, 350–351. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Avedillo, L.J.; Camón, J. Perosomus elumbis in a pig. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, C.B.; Romão, M.A.; Ferreira, A.M. Perosomus elumbis in a puppy. J. Comp. Pathol. 2012, 147, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhauser, I.; Geburek, F.; Wohlsein, P. Perosomus elumbis, cerebral aplasia, and spina bifida in an aborted thoroughbred foal. Res. Vet. Sci. 2012, 92, 266–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, E.; Alpay, G.; Yilmazbas-Mecitoglu, G.; Alasonyalilar-Demirer, A.; Akgül, B.; Inan-Ozturkoglu, S.; Ozyigit, M.O.; Seyrek-Intas, D.; Seyrek-Intas, K.; Yesilbag, K.; et al. Perosomus elumbis in a Holstein calf infected with bovine viral diarrhea virus. Tierarztl Prax. Ausg. G Grosstiere Nutztiere 2013, 41, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooksbank, N.H. Congenital deformity of the tail in pigs. Br. Vet. J. 1958, 114, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurtl, E.F. Lehrbuch der Patologischen Anatomie der Haussäugethiere, 2nd ed.; Reimer, G., Ed.; Nabu Press: Berlin, Germany, 1832; pp. 88–91. [Google Scholar]
- Albarella, S.; Ciotola, F.; D’Anza, E.; Coletta, A.; Zicarelli, L.; Peretti, V. Congenital Malformations in River Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Animals 2017, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Albarella, S.; D’Anza, E.; Galdiero, G.; Esposito, L.; De Biase, D.; Paciello, O.; Ciotola, F.; Peretti, V. Cytogenetic Analyses in Ewes with Congenital Abnormalities of the Genital Apparatus. Animals 2019, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romagnoli, S.; Schlafer, D.H. Disorders of sexual differentiation in puppies and kittens: A diagnostic and clinical approach. Vet. Clin. North. Am. Small. Anim. Pract. 2006, 36, 573–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albarella, S.; De Lorenzi, L.; Catone, G.; Magi, G.E.; Petrucci, L.; Vullo, C.; D’Anza, E.; Parma, P.; Raudsepp, T.; Ciotola, F.; et al. Diagnosis of XX/XY blood cell chimerism at low percentage in horse. J. Equine Vet. Sc. 2018, 69, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciotola, F.; Albarella, S.; Pasolini, M.P.; Auletta, L.; Esposito, L.; Iannuzzi, L.; Peretti, V. Molecular and Cytogenetic Studies in a Case of XX SRY-Negative Sex Reversal in an Arabian Horse. Sex. Dev. 2012, 6, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ovidio, D.; Melidone, R.; Rossi, G.; Albarella, S.; Noviello, E.; Fioretti, A.; Meomartino, L. Multiple congenital malformations in a ferret (Mustela Putorius Furo). J. Exot. Pet. Med. 2015, 24, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducos, A.; Pinton, A.; Berland, H.M.; Séguéla, A.; Brun-Baronnat, C.; Bonnet, N.; Darré, R.; Milan, D. Cleft palate associated with an unbalanced karyotype in piglets sired by a heterozygous carrier boar with a balanced constitutional reciprocal translocation. Vet. Rec. 2004, 154, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrì, F.; Ciotola, F.; Rapisarda, G.; Lanteri, G.; Albarella, S.; Aiudi, G.; Liotta, L.; Marino, F. A rare case of simple syndactyly in a puppy. J. Small. Anim. Pract. 2014, 55, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannuzzi, A.; Genualdo, V.; Perucatti, A.; Pauciullo, A.; Varricchio, G.; Incarnato, D.; Matassino, D.; Iannuzzi, L. Fatal Outcome in a Newborn Calf Associated with Partial Trisomy 25q and Partial Monosomy 11q, 60, XX, der(11)t(11;25)(q11;q14∼21). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2015, 146, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peretti, V.; Ciotola, F.; Albarella, S.; Restucci, B.; Meomartino, L.; Ferretti, L.; Barbieri, V.; Iannuzzi, L. Increased SCE levels in Mediterranean Italian buffaloes affected by limb malformation (transversal hemimelia). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 120, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducos, A.; Revay, T.; Kovacs, A.; Hidas, A.; Pinton, A.; Bonnet-Garnier, A.; Bonnet-Garnier, A.; Molteni, L.; Slota, E.; Switonski, M.; et al. Cytogenetic screening of livestock populations in Europe: An overview. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 120, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahofer, A.; Letko, A.; Häfliger, I.M.; Jagannathan, V.; Ducos, A.; Richard, O.; Peter, V.; Nathues, H.; Drögemüller, C. Chromosomal imbalance in pigs showing a syndromic form of cleft palate. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Letko, A.; Schauer, A.M.; Derks, M.F.L.; Grau-Roma, L.; Drögemüller, C.; Grahofer, A. Phenotypic and Genomic Analysis of Cystic Hygroma in Pigs. Genes 2021, 12, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peretti, V.; Ciotola, F.; Iannuzzi, L. Characterization, conservation and sustainability of endangered animal breeds in Campania (Southern Italy). Nat. Sci. 2013, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peretti, V.; Ciotola, F.; Dario, C.; Albarella, S.; Di Meo, G.P.; Perucatti, A.; Barbieri, V.; Iannuzzi, L. Sister chromatid exchange (SCE) for the first time in Casertana pig breed. Hereditas 2006, 143, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piegari, G.; Iovane, V.; Carletti, V.; Fico, R.; Costagliola, A.; De Biase, D.; Prisco, F.; Paciello, O. Assessment of Google Glass for Photographic Documentation in Veterinary Forensic Pathology: Usability Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2018, 21, e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piegari, G.; Prisco, F.; De Biase, D.; Meomartino, L.; Fico, R.; Paciello, O. Cardiac laceration following non-penetrating chest trauma in dog and cat. Forensic. Sci. Int. 2018, 290, e5–e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciotola, F.; Albarella, S.; Scopino, G.; Carpino, S.; Monaco, F.; Peretti, V. Crossbreeding effect on genome stability in pig (Sus scrofa scrofa). Folia Biol. 2014, 62, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, I. Standard karyotype of the domestic pig. Committee for the Standardized Karyotype of the Domestic Pig. Hereditas 1988, 109, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulley, R.C.; Edwards, M.J. Prevalence of congenital abnormalities in pigs. Aust. Vet. J. 1984, 61, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Randen, P.M.; Olson, K.M.; Null, D.J.; Hutchison, J.L. Harmful recessive effects on fertility detected by absence of homozygous haplotpyes. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 6153–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Charlier, C.; Agerholm, J.S.; Coppieters, W.; Karlskov-Mortensen, P.; Li, W.; de Jong, G.; Fasquelle, C.; Karim, L.; Cirera, S.; Cambisano, N.; et al. A deletion in the bovine FANCI gene compromises fertility by causing fetal death and brachyspina. PLoS ONE. 2012, 7, e43085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluge, J.P.; Maré, C.J. Swine pseudorabies: Abortion, clinical disease, and lesions in pregnant gilts infected with pseudorabies virus (Aujeszky’s disease). Am. J. Vet. Res. 1974, 35, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rohrer, G.A.; Nonneman, D.J.; Wiedmann, R.T.; Schneider, J.F. A study of vertebra number in pigs confirms the association of vertnin and reveals additional QTL. BMC Genet. 2015, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Animal | Observed Malformations | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thoracic Vertebrae | Lumbar Vertebrae | Sacral Vertebrae | Coccygeal Vertebrae and Other Abnormalities | |
| 1 * | None | partial aplasia of L4, quite complete aplasia of the vertebral canal of L5, partial aplasia with absence of the vertebral canal of L6; scoliotic deviation toward the right. | partial aplasia of S1 with absence of the vertebral canal. | Coccygeal vertebrae: no visible abnormalities other abnormalities: duplication of the first tract of the ureters; caudal dislocation of the left kidney with a dorso-medial bended shape and some cortical small cists |
| 2 * | None | the lumbar tract showed a lordotic and scoliotic curvature; L2-L3-L4 were irregularly fused and L3-L4 without a vertebral canal; L5 and L6 were present only as a bud of the body with the agenesia of the vertebral arch. | S1 and S2 missed the vertebral canal and were irregularly articulated | Coccygeal vertebrae: only the first five metameric were visible |
| 3 * | None | the lumbo-sacral junction showed a slight lordotic curvature; L6 missed the vertebral canal. | S1 was present only as a bud of the body with the agenesia of the vertebral arch | Coccygeal vertebrae: Only four coccygeal vertebrae were present. |
| 4 ** | T14 was partially fused with L1. | L1 was partially fused with T14 and its body was wedge shaped (hemi vertebra) L2 had a dysplastic vertebral canal and was partially fused with L3; the residual lumbar vertebrae were present only as a bud, without a vertebral canal and with a scoliotic curvature toward the left | S1 was present as a small bud, the remnant were partially fused and with a kyphotic curvature. | Coccygeal vertebrae: Visible until the Co15 with some hemi vertebrae. Other abnormalities: Partial fusion of the left 13th and 14th ribs; the pelvis was tilted toward the left; severe hyper extension of the left knee with inversion of the normal angle. |
| 5 ** | Visible T16 with a complete aplasia of the vertebral canal. | vertebrae L1 had only a slight mineralization of the body and the remnant (L2-L6) were present only as a bud of the body with a complex lordotic-scoliotic curvature toward the right. | the body of S1 was partially fragmented and without the vertebral canal; S2 was visible only as a small bud; no other sacral vertebrae were visible. | Coccygeal vertebrae: The coccygeal vertebrae were absent. Other abnormalities: both the knees had an inverted angle. |
| 6 ** | Visible T15 | partial aplasia of L2 with an incomplete vertebral canal; L3 without the vertebral canal and a right fragmented lateral process; the remnant lumbar vertebrae (L4-L6) were present only as a bud of the bodies and with a lordotic curvature. | partial dysplasia of the body of S1 with a not fused cranio-ventral portion of the body and without the vertebral canal. | Coccygeal vertebrae no visible abnormalities. |
| 7 ** | None | partial aplasia of L4 without the vertebral canal; L5 and L6 were present only as a small bud of the bodies. | no visible abnormalities | Coccygeal vertebrae no visible abnormalities Other abnormalities Severe hyper extension of both the knees and the tarsi. |
| 8 ** | None | L1 was dysplastic with bifid dorsal process and the vertebral canal communicating with the dorsal soft tissues of the lumbar tract; absence of the vertebrae from L2 to L4; L5 and L6 partially fused and with aplasia of the vertebral canal. | Sacral vertebrae S1 and S2 were partially fused and irregularly fragmented without the vertebral canal. | Coccygeal vertebrae no visible abnormalities. |
| Animal | Sex | Visceral Congenital Anomalies | Acquired Pathologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 * | M | Renal anomalies characterized by a distinct transverse ridge on the lateral surface of the left kidney running backwards. The left kidney is dislocated in caudal abdomen Agenesis of the left adrenal gland | Outer necropsy: there are multifocal areas of ulceration over the hind limb region; these areas show an ovoid morphology, distinct edges and a diameter range from 2 × 2 cm to 5 × 3 cm; There is atrophy of the hind limb muscles and hypertrophy of the forelimbs Inner Necropsy: there is a severe and bi-lateral bronco-pneumonia associated with pulmonary oedema; the mediastinal lymph nodes are slightly enlarged; mild congestion is observed on both natural and cut surface |
| 2 * | M | Renal anomalies characterized by hypoplasy of left kidney associated with dislocation of the left kidney in the caudal abdomen | Outer necropsy There is a focal sub-cutis oedema over the intermandibular region; this area shows an ovoid morphology with indistinct edges Inner Necropsy: there is a moderate bronco-pneumonia associated with severe pulmonary oedema; the mediastinic lymph nodes are slightly enlarged; moderate congestion is observed on both natural and cut surface |
| 3 * | F | Renal anomalies characterized by hypoplasia of left kidney | Inner necropsy: There is a moderate haemorrhagic gastro-enteritis and sero-hemorrhagic effusion in the pericardial sac. Both liver and spleen are congested with slightly enlarged and rounded edges |
| 4 ** | F | Pulmonary atelectasis Renal anomalies characterized by hypoplasia of left kidney associated with dislocation of the left kidney in the caudal abdomen | no macroscopic alteration |
| 5 ** | M | no macroscopic alteration | Inner necropsy: moderate pulmonary oedema |
| 6 ** | M | no macroscopic alteration | Inner necropsy: subcutaneous haemorrhages |
| 7 ** | F | Pulmonary atelectasis Renal anomalies characterized by hypoplasia of left kidney | no macroscopic alteration |
| 8 ** | M | no macroscopic alteration | Inner necropsy: there is a mild sero-hemorrhagic abdominal effusion and moderate pulmonary oedema |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Piegari, G.; D’Anza, E.; Costanza, D.; Prisco, F.; Meomartino, L.; d’Aquino, I.; Albarella, S.; Paciello, O.; Ciotola, F. Perosomus Elumbis in Piglets: Pathological, Radiological and Cytogenetic Findings. Animals 2021, 11, 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041132
Piegari G, D’Anza E, Costanza D, Prisco F, Meomartino L, d’Aquino I, Albarella S, Paciello O, Ciotola F. Perosomus Elumbis in Piglets: Pathological, Radiological and Cytogenetic Findings. Animals. 2021; 11(4):1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041132
Chicago/Turabian StylePiegari, Giuseppe, Emanuele D’Anza, Dario Costanza, Francesco Prisco, Leonardo Meomartino, Ilaria d’Aquino, Sara Albarella, Orlando Paciello, and Francesca Ciotola. 2021. "Perosomus Elumbis in Piglets: Pathological, Radiological and Cytogenetic Findings" Animals 11, no. 4: 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041132
APA StylePiegari, G., D’Anza, E., Costanza, D., Prisco, F., Meomartino, L., d’Aquino, I., Albarella, S., Paciello, O., & Ciotola, F. (2021). Perosomus Elumbis in Piglets: Pathological, Radiological and Cytogenetic Findings. Animals, 11(4), 1132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041132









