Diversification of Morphological Features of the Dark European Honey Bee of the ‘Augustow M’ Line
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Lead apiary (locality: Plaska);
- Associate apiaries (localities: Jasionowo, Bryzgiel, Lipsk, Danowskie);
- Conservation area apiaries (localities: Plaska Municipality, Rubcowo, Sucha Rzeczka, Muly).
2.1. Morphological Analyzes
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Bees of the Augustow M line have the features of the Dark European honey bee.
- The values of the cubital index, glossa length and tergite 4 width of the Augustow M line are consistent with the morphological feature references valid for the Apis m. mellifera.
- The program for the conservation of genetic resources of Dark European honey bees of the Augustow M line can be pursued based on the lead, associate and conservation area apiaries. The diversification of morphological features did not shrink during the study period.
- Dwarfing trends were noted for the Dark European honey bee based on results of the authors’ research and on literature of the 1960s concerning Apis m. mellifera sizes in Poland measured by the width of abdominal tergite 4.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alpatov, W.W. Biometrical studies on variation and races of the honey bee (Apis mellifera L.). Q. Rev. Biol. 1929, 4, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpatov, W.W. Porody miedonosnoj pczeły i ich ispolzowanije w sielskom chozjajstwie. Sredi Prirodi 1948, 4, 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Alpatov, W.W. Some data on the comparative biologie of different bee races. Bee World 1932, 13, 138–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpatov, W.W. Über der Verkleinerung der Rüsellänge der Honigbiene von Süden nach Norden hin. Zool. Anz. 1925, 65, 103–111. [Google Scholar]
- Goetze, G. Die beste Biene: Züchtungs- und Rassen-Kunde der Honigbiene nach dem heutigen Stand von Wissenschaft und Praxis; Leipzig, Goetze (red.): Hamburg, Germany, 1940; pp. 64–198. [Google Scholar]
- Goetze, G. Die Honigbiene in Natürlicher und Künstlicher Zuchtauslese; P. Parey, Goetze (red.): Hamburg, Germany, 1964; pp. 265–273. [Google Scholar]
- Cornuet, J.M.; Fresnaye, J.; Tassencourt, L. Discrimination et classification de populations d’abeilles a partir de caractéres biométriques. Apidologie 1975, 6, 145–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruttner, F. Biometrical-statistical analysis of the geographic variability of Apis mellifera L. I. Material and Methods. Apidologie 1978, 9, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresnaye, J. Biométrie de L’abeille, 2nd ed.; Echauffour (Orne); Office pour l’lnformation et la Documentation en Apiculture, 1981; 56p. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttner, F. Geographical variability and classification (Chapter 2) W: Rinderer, T.E. In Bee Genetics and Breeding; Academic Press Inc.: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 23–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bornus, L.; Demianowicz, A.; Gromisz, M. Morfometryczne badania krajowej pszczoły miodnej. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1966, 10, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.J.F.; Paxton, R.J. The conservation of bees: A global perspective. Apidologie 2009, 40, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zayed, A. Bee genetics and conservation. Apidologie 2009, 40, 237–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruttner, F. Biogeography and Taxonomy of Honeybees; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1988; pp. 3–278. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttner, F. Graded geographical variability in honeybees and environment. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1985, 24, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ruttner, F.; Milner, E.; Dews, J.E. The Dark European Honeybee Apis Mellifera Mellifera LINNAEUS 1758; British Isles Bee Breeders Association: Derby, UK, 1990; pp. 5–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gromisz, M. Zasoby pszczoły rodzimej i ich ochrona. W: Cierzniak T. (red.) Postępy apidologii w Polsce. Wyższa Szkoła Pedagog. Bydg. 1997, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Troszkiewicz, J. Informator o Hodowli Pszczół; KCHZ: Warsaw, Poland, 2006; pp. 3–34. [Google Scholar]
- Jaszczyńska, M. Ochrona zasobów genetycznych pszczół. Wiad. Zootech. 2006, 44, 56–60. [Google Scholar]
- Jaszczyńska, M.; Troszkiewicz, J.; Kwiatkowski, T. The Black bee genetic resource conservation programme in Poland. In Proceedings of the 45 Naukowa Konferencja Pszczelarska, Puławy, Poland, 11–12 September 2008; p. 62. [Google Scholar]
- Paleolog, J. Ochrona Zasobów Genetycznych Zwierząt Gospodarskich i Dziko Żyjących; PWRiL, Litwińczuk Z. (red.): Warsaw, Poland, 2011; pp. 195–211. [Google Scholar]
- Skonieczna, Ł. Conservation of Apis mellifera mellifera in Poland. In Proceedings of the BIBBA-SICAMM BIBBA 50th Anniversary Conference 2014 Combined with SICAMM Biennial Conference, Llangollen, UK, 26–28 September 2014; pp. 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Skonieczna, Ł.; Naruszewicz, W. Protection of natural populations of Apis m. mellifera in isolated areas of Augustów Old Virgin Forest and The Kampinos National Park and conservation breeding program of Północna (North) line. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference Black Bee Apis mellifera mellifera, Wierzba, Poland, 2–6 September 2002; pp. 69–84. [Google Scholar]
- Büchler, R.; Costa, C.; Hatjina, F.; Andonov, S.; Meixner, M.D.; Le Conte, Y.; Uzunov, A.; Berg, S.; Bienkowska, M.; Bouga, M.; et al. The influence of genetic origin and its interaction with environmental effects on the survival of Apis mellifera L. colonies in Europe. J. Apicult. Res. 2014, 53, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hatjina, F.; Costa, C.; Büchler, R.; Uzunov, A.; Drazic, M.; Filipi, J.; Charistos, L.; Ruottinen, L.; Andonov, S.; Meixner, M.D.; et al. Population dynamics of European honey bee genotypes under different environmental conditions. J. Apicult. Res. 2014, 53, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meixner, M.; Buchler, R.; Costa, C.; Andonov, S.; Bienkowska, M.; Bouga, M.; Filipi, J.; Hatjina, F.; Ivanova, E.; Kezic, N.; et al. Looking for the Best Bee—An experiment about interaction between origins and environment of honey bee strains in Europe. Am. Bee J. 2015, 155, 663–669. [Google Scholar]
- Uzunov, A.; Costa, C.; Panasiuk, B.; Meixner, M.; Kryger, P.; Hatjina, F.; Bouga, M.; Andonov, S.; Bienkowska, M.; Le Conte, Y.; et al. Swarming, defensive and hygienic behaviour in honey bee colonies of different genetic origin in a pan-European experiment. J. Apicult. Res. 2014, 53, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gromisz, M. Przydatność niektórych cech morfologicznych w systematyce wewnątrz gatunku Apis mellifica L. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1967, 11, 37–50. [Google Scholar]
- Tofilski, A. Automatic measurement of honeybee wings. In Automated Object Identification in Systematics: Theory, Approaches and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Guler, A. A morphometric model for determining the effect of commercial queen bee Osage on the native honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) population in a Turkish province. Apidologie 2010, 41, 622–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, H.V.; Hoelmer, K.; Norman, P.; Allen, T. Computer-assisted measurement and identification of honey bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1982, 75, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauhausen, D.; Keller, R. Methods of classification of honeybee races using wing characters—A review. J. Apicult. Sci. 2003, 47, 103–107. [Google Scholar]
- Kauhausen-Keller, D.; Keller, R. Morphometric control of breeding in the honeybee. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1996, 40, 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Čermak, K.; Kašpar, F.A. Metod of classifying honey bee races by their body characters. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 2000, 44, 81–86. [Google Scholar]
- Samborski, J.; Prabucki, J.; Chuda-Mickiewicz, B.; Perużyński, G. Operation rate and sensitivity of devices used for determining cubital index value. J. Apicult. Sci. 2002, 46, 35–47. [Google Scholar]
- Rostecki, P. Zróżnicowanie Morfologiczne Linii Hodowlanych Pszczoły Środkowoeuropejskiej w Rejonach Zamkniętych, Pasiekach Zachowawczych i Współpracujących. Ph.D. Thesis, West Pomeranian University of Technology in Szczecin, Szczecin, Poland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rostecki, P.; Samborski, J.; Prabucki, J.; Chuda-Mickiewicz, B. A comparison of various hardware for the measurement of the cubital index. J. Apicult. Sci. 2007, 51, 49–53. [Google Scholar]
- Gerula, D.; Tofilski, A.; Węgrzynowicz, P.; Skowronek, W. Computer-assisted discrimination of honeybee subspecies used for breeding in Poland. J. Apicult. Sci. 2009, 53, 105–114. [Google Scholar]
- Szymula, J.; Skowronek, W.; Bieńkowska, M. Use of various morphological traits measured by microscope or by computer methods in the honeybee taxonomy. J. Apicult. Sci. 2010, 54, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Tofilski, A. Using geometric morphometrics and standard morphometry to discriminate three honeybee subspecies. Apidologie 2008, 39, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandemir, I.; Özkan, A.; Fuchs, S. Reevaluation of honeybee (Apis mellifera) microtaxonomy: A geometric morphometric approach. Apidologie 2011, 42, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bustamante, T.; Baiser, B.; Ellis, J.D. Comparing classical and geometric morphometric methods to discriminate between the South African honey bee subspecies Apis mellifera scutellata and Apis mellifera capensis (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Apidologie 2020, 51, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleksa, A.; Burczyk, J. Markery DNA w hodowli zachowawczej rodzimych linii pszczoły miodnej. Wiad. Zootech. 2010, 48, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Oleksa, A.; Tofilski, A. Wing geometric morphometrics and microsatellite analysis provide similar discrimination of honey bee subspecies. Apidologie 2015, 46, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Madras-Majewska, B.; Skonieczna, Ł. Variability of morphological characteristics of middle-European bees of the ‘Northern M’ line. Med. Weter. 2018, 74, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demianowicz, A.; Gromisz, M. Morfologia pszczoły. Pszczelnictwo. In Wyd. Promoc. Albatros; Prabucki J. (red.): Szczecin, Poland, 1998; pp. 111–141. [Google Scholar]
- Zee, R.; Gray, A.; Holzmann, C.; Pisa, L.; Brodschneider, R.; Chlebo, R.; Coffey, M.F.; Kence, A.; Kristiansen, P.; Mutinelli, F.; et al. Standard survey methods for estimating colony losses and explanatory risk factors in Apis mellifera. J. Apicult. Res. 2013, 52, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Misis, A.P. External morphplogical characteristics of the honeybees in SSR Lithuania. In Proceedings of the 21st International Apicultural Congress, City of College Park, WA, USA, 14–17 August 1967; pp. 164–167. [Google Scholar]
- Lefévre-Lafargue, C.; Louveaux, J.; Mesquida, J. Étude d’une population locale d’abeilles dans le basin rennais en 1970–1971. Apidologie 1973, 4, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornuet, J.-M.; Fresnaye, J.; Lavie, J.; Hanout, J.B.S.; Mary-Lafrague, C. Étude biométrique de deux populations d’abéilles Cévenoles. Apidologie 1978, 9, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gromisz, M. Ocena morfologiczna pszczół z pasiek zarodowych. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1972, 16, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Prabucki, J.; Chuda-Mickiewicz, B. Przydatność użytkowa pszczoły środkowoeuropejskiej (Apis mellifera mellifera L.) w warunkach poużytkowych Pomorza Zachodniego. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1995, 39, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Bornus, L. Pomiary wielkości pszczoły i niektórych jej części ciała. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1960, 4, 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Gromisz, M.; Bornus, L. Morfologiczno-matematyczne modele populacji pszczoły krajowej. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1971, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gromisz, M. Morfologiczna ocena populacji rojów w pasiekach zarodowych. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1981, 25, 51–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gromisz, M.; Płatek, M. Model matematyczno-morfologiczny pszczoły kampinoskiej. Pszczel. Zesz. Nauk. 1999, 43, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
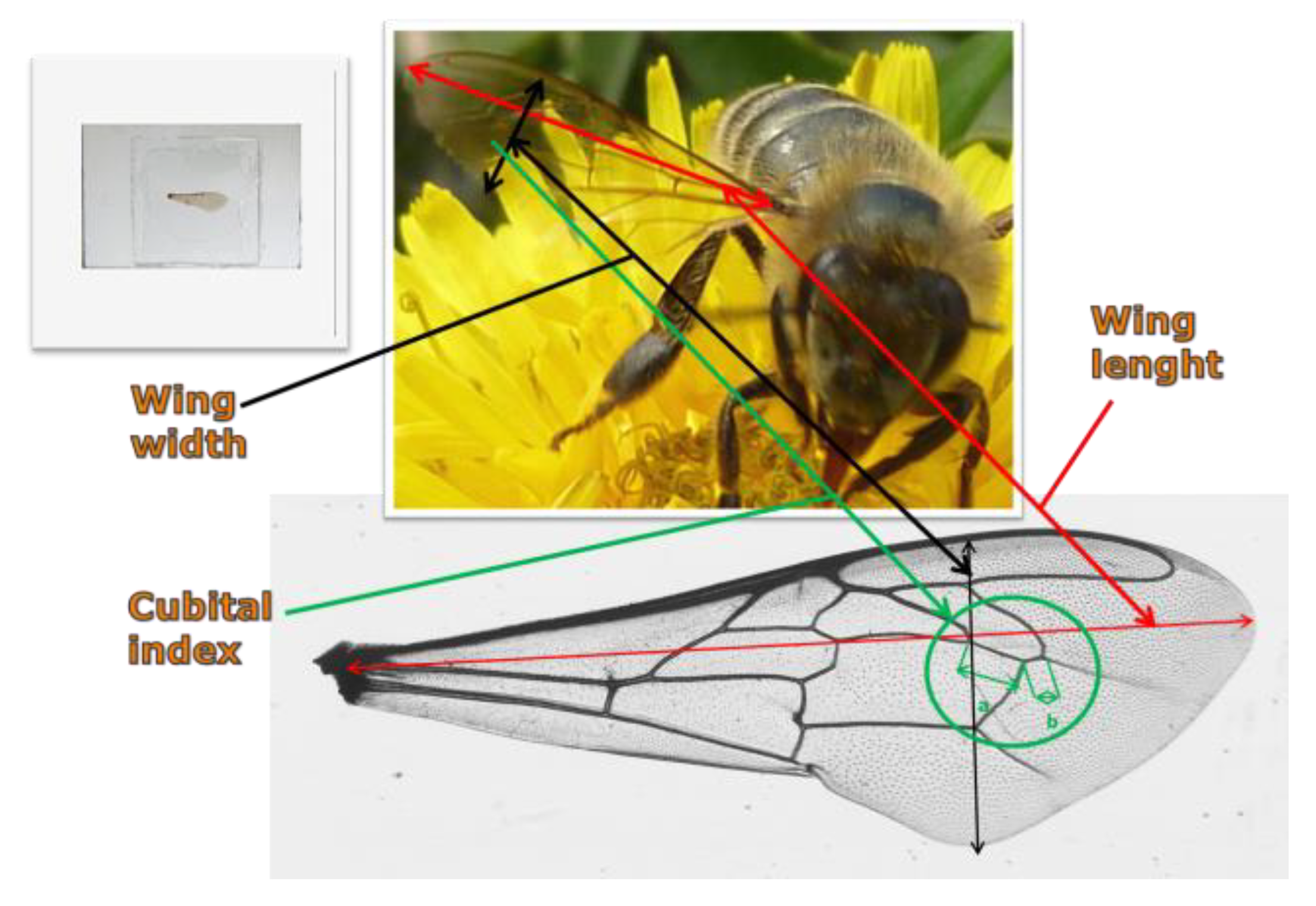
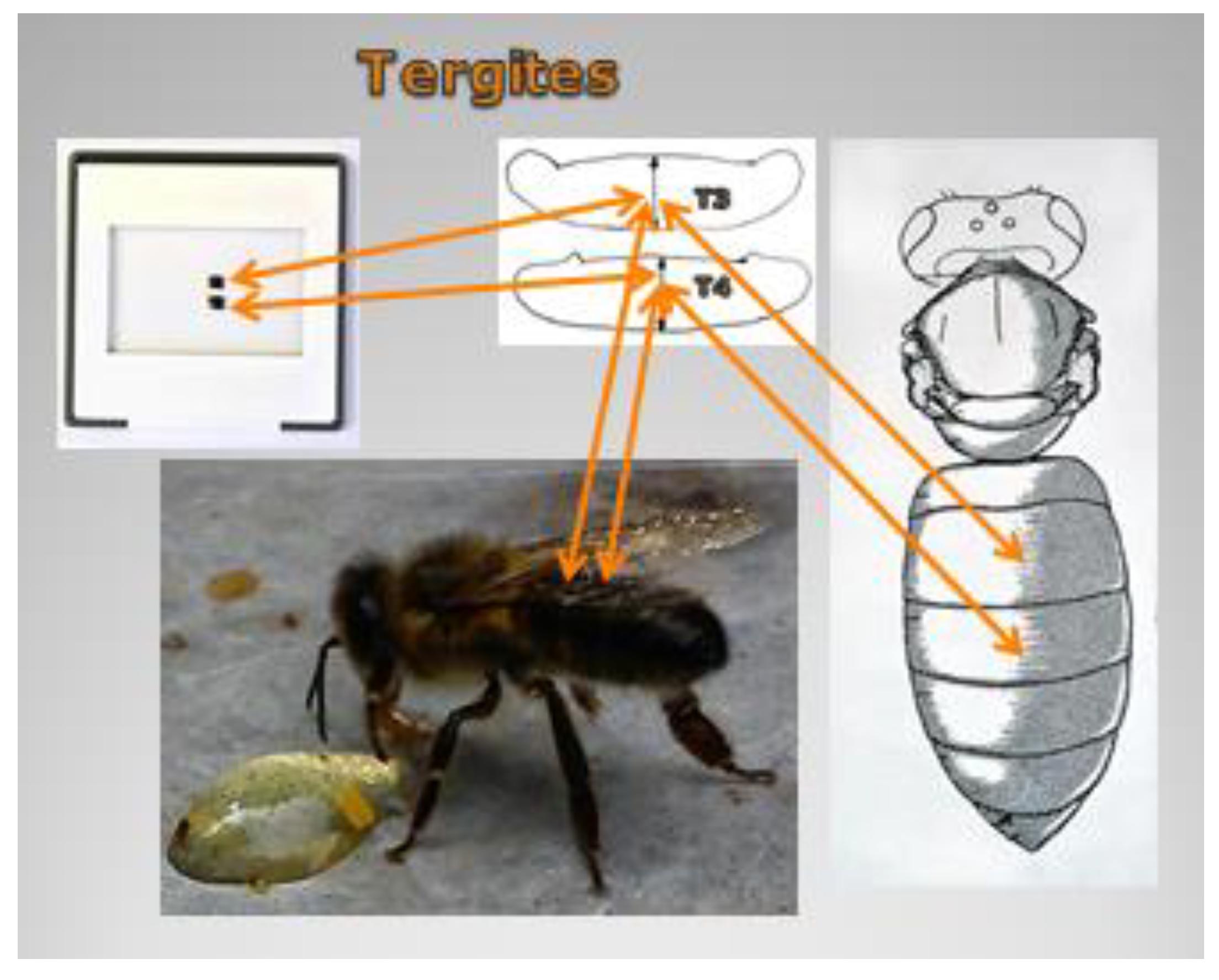


| Line | Feature | Number [n] | Range | Mean ± SE | ±SD | Variation Coefficient [V] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Augustow | Wing length (mm) | 6927 | 8.741–10.121 | 9.390 ± 0.002 | 0.172 | 1.83 |
| Wing width (mm) | 6927 | 2.812–3.581 | 3.195 ± 0.001 | 0.103 | 3.24 | |
| Wing form factor | 6927 | 2.610–3.320 | 2.941 ± 0.001 | 0.083 | 2.8 | |
| Cubital index (Goetze) | 6927 | 1.029–2.678 | 1.664 ± 0.003 | 0.254 | 15.23 | |
| Tergite 4 width (mm) | 6927 | 1.885–2.821 | 2.284 ± 0.001 | 0.086 | 3.75 | |
| Tergites 3 + 4 width (mm) | 6927 | 4.012–5.365 | 4.764 ± 0.002 | 0.157 | 3.29 | |
| Glossa length (mm) | 6927 | 5.521–6.618 | 6.104 ± 0.002 | 0.157 | 2.57 | |
| Reference of morphological features * | ||||||
| Cubital index (Goetze) | 1.25–2.00 | 1.63 | ||||
| Tergite 4 width (mm) | 2.04–2.60 | 2.32 | ||||
| Glossa length (mm) | 5.75–6.50 | 5.90 | ||||
| Apiaries | Feature | Number [n] | Range | Mean ± SE | ±SD | Variation Coefficient [V] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead | Wing length (mm) | 4174 | 8.741–10.121 | 9.374 ± 0.003 | 0.165 | 1.76 |
| Wing width (mm) | 2.812–3.528 | 3.171 ± 0.002 | 0.107 | 3.38 | ||
| Cubital index (Goetze) | 1.029–2.678 | 1.665 ± 0.004 | 0.258 | 15.51 | ||
| Tergite 4 width (mm) | 1.885–2.597 | 2.268 ± 0.001 | 0.092 | 4.05 | ||
| Tergites 3 + 4 width (mm) | 4.012–5.263 | 4.741 ± 0.003 | 0.167 | 3.52 | ||
| Glossa length (mm) | 5.521–6.618 | 6.082 ± 0.002 | 0.157 | 2.58 | ||
| Associate | Wing length (mm) | 1576 | 8.93–9.924 | 9.434 ± 0.004 | 0.162 | 1.72 |
| Wing width | 2.962–3.581 | 3.244 ± 0.002 | 0.079 | 2.43 | ||
| Cubital index (Goetze) | 1.062–2.659 | 1.695 ± 0.006 | 0.252 | 14.87 | ||
| Tergite 4 width (mm) | 2.110–2.531 | 2.31 ± 0.002 | 0.06 | 2.59 | ||
| Tergites 3 + 4 width (mm) | 4.258–5.197 | 4.808 ± 0.003 | 0.118 | 2.45 | ||
| Glossa length (mm) | 5.673–6.588 | 6.137 ± 0.004 | 0.141 | 2.29 | ||
| Conservation area | Wing length (mm) | 1177 | 8.776–9.961 | 9.382 ± 0.006 | 0.199 | 2.13 |
| Wing width | 2.959–3.474 | 3.214 ± 0.003 | 0.091 | 2.83 | ||
| Cubital index (Goetze) | 1.098–2.604 | 1.620 ± 0.007 | 0.232 | 14.82 | ||
| Tergite 4 width (mm) | 2.021–2.821 | 2.302 ± 0.002 | 0.079 | 3.45 | ||
| Tergites 3 + 4 width (mm) | 4.299–5.365 | 4.786 ± 0.004 | 0.148 | 3.09 | ||
| Glossa length (mm) | 5.609–6.611 | 6.138 ± 0.005 | 0.164 | 2.68 | ||
| Reference of morphological features * | ||||||
| Cubital index (Goetze) | 1.25–2.00 | 1.63 | ||||
| Tergite 4 width (mm) | 2.04–2.60 | 2.32 | ||||
| Glossa length (mm) | 5.75–6.50 | 5.90 | ||||
| Apiaries | Number [n] | Wing Length [mm] | Wing Width [mm] | Cubital Index (Goetze) | Tergite 4 Width [mm] | Tergites 3 + 4 Width [mm] | Glossa Length [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | ||
| Lead | 4174 | 9.376 b | 3.178 b | 1.663 a | 2.280 a | 4.7651 a | 6.100 a |
| Associate | 1576 | 9.405 a | 3.198 a | 1.641 a | 2.285 a | 4.774 a | 6.101 a |
| Apiaries | Number [n] | Wing Length [mm] | Wing Width [mm] | Cubital Index (Goetze) | Tergite 4 Width [mm] | Tergites 3 + 4 Width [mm] | Glossa Length [mm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | ||
| Lead and associate | 5750 | 9.382 b | 3.186 a | 1.657 a | 2.282 b | 4.768 a | 6.105 a |
| Conservation area | 1177 | 9.412 a | 3.174 a | 1.680 a | 2.295 a | 4.781 a | 6.097 a |
| Wing Length | Wing Width | Wing Form Factor | Cubital Index | Tergite 4 Width | Tergites 3 + 4 Width | Glossa Length | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wing length | 1 | ||||||
| Wing width | 0.509 | 1 | |||||
| <0.0001 | |||||||
| Wing form factor | 0.026 | −0.846 | 1 | ||||
| 0.0447 | <0.0001 | ||||||
| Cubital index | −0.006 | −0.096 | 0.106 | 1 | |||
| 0.6398 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | |||||
| Tergite 4 width | 0.276 | 0.373 | −0.266 | −0.030 | 1 | ||
| <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0219 | ||||
| Tergites 3 + 4 width | 0.310 | 0.396 | −0.270 | −0.023 | 0.865 | 1 | |
| <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0802 | <0.0001 | |||
| Glossa length | 0.267 | 0.359 | −0.251 | −0.058 | 0.191 | 0.202 | 1 |
| <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Author | Cubital Index | |
|---|---|---|
| Acc. to Goetze | Acc. to Alpatov [%] | |
| Gromisz & Bornus 1971 [54] | 1.658 * | 60.30 |
| Gromisz 1972 [51] | 1.626 * | 61.50 |
| Gromisz 1981 [55] | 1.628 * | 61.40 |
| Gromisz & Platek 1999 [56] | 1.600 * | 62.50 |
| Rostecki 2009 [36]—Augustow M line | 1.850 | 54.80 |
| The authors’ research—Augustow M line | 1.664 | 60.10 ** |
| Feature | Species | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Middle-European | Crainian | Caucasian | |
| Tergite 4 width | z = 24.2718x − 57.1845 | z = 24.2718x − 55.8252 | z = 24.2718x − 54.4175 |
| Glossa length | z = 10.2042x − 62.3980 | z = 10.2042x − 65.9184 | z = 10.2042x − 71.3878 |
| Cubital index | z = 0.311x − 19.082 | z = 0.311x − 15.925 | z = 0.311x − 16.983 |
| Line | Area | Feature | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tergite 4 Width [z] | Glossa Length [z] | Cubital Index [z] | |||
| Augustow M | Lead apiary | −2.1361 | −0.3531 | 0.0345 | 0.8412 |
| Associate apiaries | −1.1166 | 0.1978 | −0.3343 | 0.5496 | |
| Conservation area apiaries | −1.3108 | 0.2182 | 0.5014 | 0.6768 | |
| Area | Feature/Consistency with the Reference | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cubital Index | Tergite 4 | Glossa Length | ||||||||||
| Range | +/− | Mean | +/− | Range | +/− | Mean | +/− | Range | +/− | Mean | +/− | |
| Lead apiary | 1.03–2.68 | − | 1.665 | + | 1.89–2.60 | − | 2.268 | + | 5.52–6.62 | − | 6.082 | + |
| Associate apiaries | 1.06–2.66 | − | 1.695 | + | 2.11–2.53 | + | 2.310 | + | 5.67–6.59 | − | 6.137 | + |
| Conservation area apiaries | 1.10–2.60 | − | 1.620 | + | 2.02–2.82 | − | 2.302 | + | 5.61–6.61 | − | 6.138 | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madras-Majewska, B.; Skonieczna, L. Diversification of Morphological Features of the Dark European Honey Bee of the ‘Augustow M’ Line. Animals 2021, 11, 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041156
Madras-Majewska B, Skonieczna L. Diversification of Morphological Features of the Dark European Honey Bee of the ‘Augustow M’ Line. Animals. 2021; 11(4):1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041156
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadras-Majewska, Beata, and Lucja Skonieczna. 2021. "Diversification of Morphological Features of the Dark European Honey Bee of the ‘Augustow M’ Line" Animals 11, no. 4: 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041156
APA StyleMadras-Majewska, B., & Skonieczna, L. (2021). Diversification of Morphological Features of the Dark European Honey Bee of the ‘Augustow M’ Line. Animals, 11(4), 1156. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11041156





