Illegal Wildlife Trade and Emerging Infectious Diseases: Pervasive Impacts to Species, Ecosystems and Human Health
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
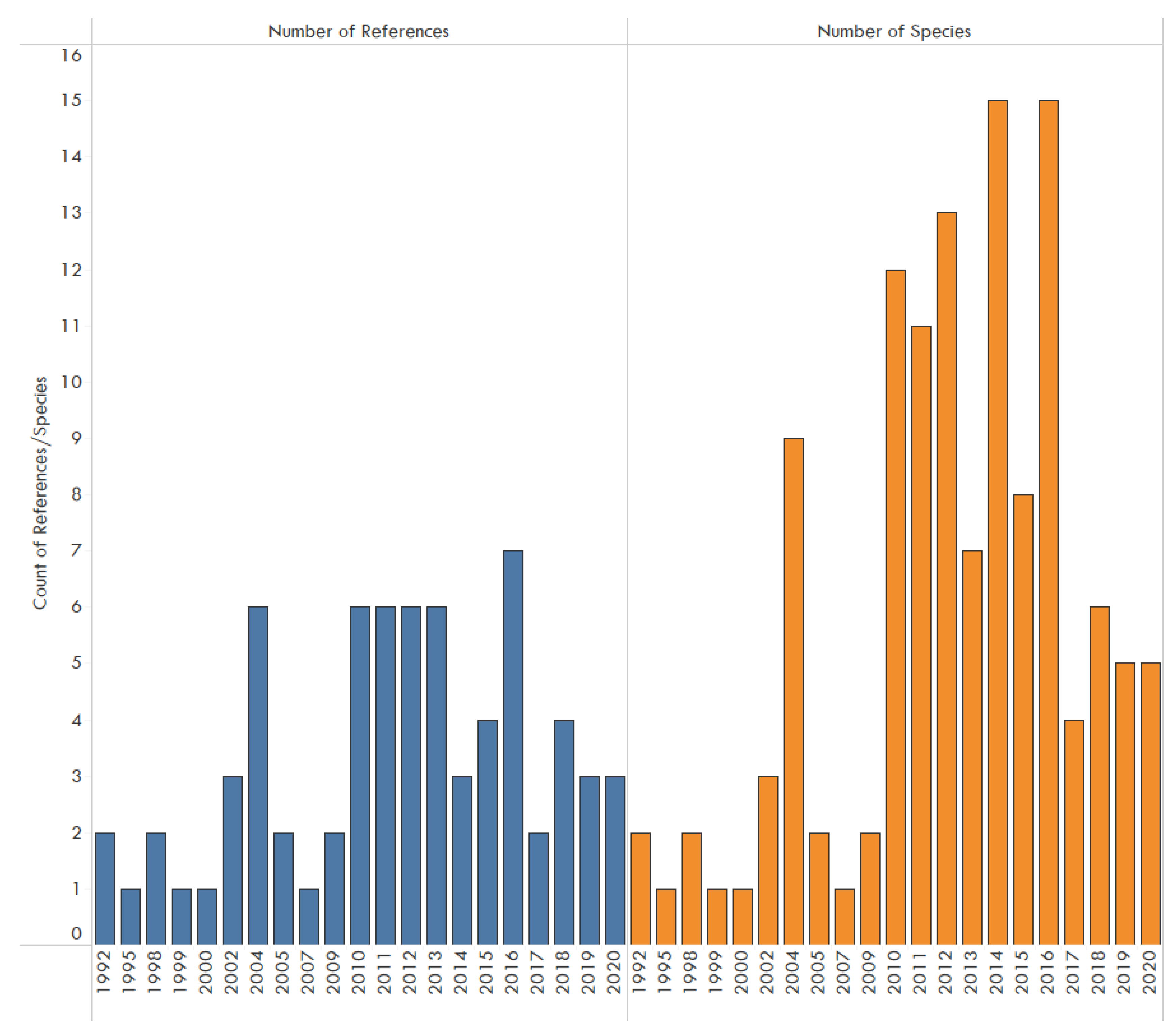
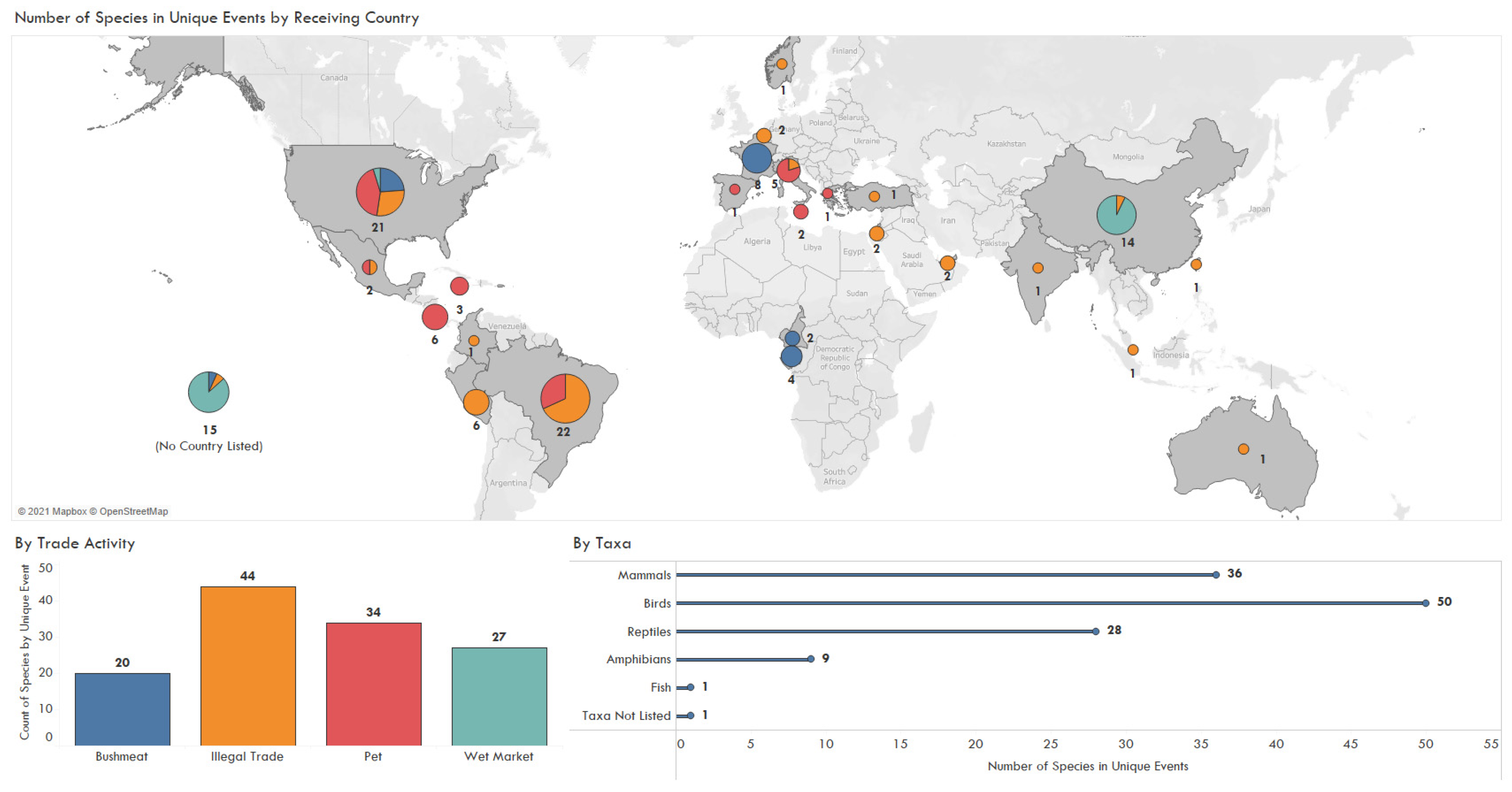
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morse, S.S. Factors in the emergence of infectious diseases. In Plagues and Politics: Infectious Disease and International Policy; Price-Smith, A.T., Ed.; Global Issues Series; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2001; pp. 8–26. ISBN 978-0-230-52424-8. [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham, A.A.; Daszak, P.; Wood, J.L.N. One health, emerging infectious diseases and wildlife: Two decades of progress? Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morens, D.M.; Folkers, G.K.; Fauci, A.S. The challenge of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2004, 430, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguirre, A.A.; Tabor, G.M. Global factors driving emerging infectious diseases. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1149, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, D.; Roberton, S.; Hunter, P.R. Animal origins of SARS coronavirus: Possible links with the international trade in small carnivores. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karesh, W.B.; Cook, R.A.; Bennett, E.L.; Newcomb, J. Wildlife trade and global disease emergence. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 1000–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, A.; Aguirre, A.A. Infectious diseases and the illegal wildlife trade. In Animal Biodiversity and Emerging Diseases: Prediction and Prevention; Sparagano, O.E., Maillard, J.C., Figueroa, J.V., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Malden, MA, USA, 2008; Volume 1149, pp. 16–19. ISBN 978-1-57331-714-6. [Google Scholar]
- Swift, L.; Hunter, P.R.; Lees, A.C.; Bell, D.J. Wildlife trade and the emergence of infectious diseases. EcoHealth 2007, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleaveland, S.; Haydon, D.T.; Taylor, L. Overviews of pathogen emergence: Which pathogens emerge, when and why? In Wildlife and Emerging Zoonotic Diseases: The Biology, Circumstances and Consequences of Cross-Species Transmission; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Childs, J.E., Mackenzie, J.S., Richt, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 85–111. ISBN 978-3-540-70962-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kan, B.; Wang, M.; Jing, H.Q.; Xu, H.F.; Jiang, X.G.; Yan, M.Y.; Liang, W.L.; Zheng, H.; Wan, K.L.; Liu, Q.Y.; et al. Molecular evolution analysis and geographic investigation of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-like virus in palm civets at an animal market and on farms. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 11892–11900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, C.C.; Crameri, G.; Kong, X.G.; Chen, J.D.; Sun, Y.W.; Yu, M.; Xiang, H.; Xia, X.Z.; Liu, S.W.; Ren, T.; et al. Antibodies to SARS coronavirus in civets. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2244–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Bank. People, Pathogens and Our Planet: The Economics of One Health; World Bank Other Operational Studies; The World Bank: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- McKibbin, W.; Lee, J.H.J. Estimating the global economic costs of SARS. In Learning from SARS: Preparing the Next Disease Outbreak Worskshop Summary; Knobler, S., Mahmoud, A., Lemmon, S., Mack, A., Sivits, L., Oberholtzer, K., Eds.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004; pp. 92–109. [Google Scholar]
- Global Financial Stability Report, April 2020: Markets in the Time of COVID-19. Available online: https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/GFSR/Issues/2020/04/14/Global-Financial-Stability-Report-April-2020-49020 (accessed on 11 December 2020).
- Dobson, A.P.; Pimm, S.L.; Hannah, L.; Kaufman, L.; Ahumada, J.A.; Ando, A.W.; Bernstein, A.; Busch, J.; Daszak, P.; Engelmann, J.; et al. Ecology and economics for pandemic prevention. Science 2020, 369, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.F.; Corman, V.M.; Drosten, C. Ecology, evolution and classification of bat coronaviruses in the aftermath of SARS. Antivir. Res. 2014, 101, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.C.P.; Li, X.; Lau, S.K.P.; Woo, P.C.Y. Global epidemiology of bat coronaviruses. Viruses 2019, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, K.G.; Rambaut, A.; Lipkin, W.I.; Holmes, E.C.; Garry, R.F. The proximal origin of SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 450–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilcove, D.S.; Rothstein, D.; Dubow, J.; Phillips, A.; Losos, E. Quantifying threats to imperiled species in the United States. BioScience 1998, 48, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sollund, R. Expressions of speciesism: The effects of keeping companion animals on animal abuse, animal trafficking and species decline. Crime Law Soc. Chang. 2011, 55, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trafficked: 10 Species Threatened by the Wildlife Trade 2020. Available online: https://www.endangered.org/trafficked-national-release/ (accessed on 10 June 2021).
- Aguirre, A.A.; Gore, M.L.; Kammer-Kerwick, M.; Curtin, K.M.; Heyns, A.; Preiser, W.; Shelley, L.I. Opportunities for transdisciplinary science to mitigate biosecurity risks from the intersectionality of illegal wildlife trade with emerging zoonotic pathogens. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, M.; Moran, D.; Kanemoto, K.; Foran, B.; Lobefaro, L.; Geschke, A. International trade drives biodiversity threats in developing nations. Nature 2012, 486, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watsa, M.; Wildlife Disease Surveillance Focus Group. Rigorous wildlife disease surveillance. Science 2020, 369, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Borm, S.; Thomas, I.; Hanquet, G.; Lambrecht, N.; Boschmans, M.; Dupont, G.; Decaestecker, M.; Snacken, R.; van den Berg, T. Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus in smuggled Thai eagles, Belgium. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2005, 11, 702–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, G.E.; Smith, K.F. Summarizing the evidence on the international trade in illegal wildlife. Ecohealth 2010, 7, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.E.; Patel, N.G.; Levy, M.A.; Storeygard, A.; Balk, D.; Gittleman, J.L.; Daszak, P. Global trends in emerging infectious diseases. Nature 2008, 451, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, F.; Fusco, G.; Mari, V.; Occhiogrosso, L.; Miletti, G.; Brunetti, R.; Galiero, G.; Desario, C.; Cirilli, M.; Decaro, N. Circulation of pantropic canine Coronavirus in autochthonous and imported dogs, Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, D.S.; dos Santos, A.C.; da Silva, C.L.R.; Oria, A.P.; Oliveira, A.V.D.; Liborio, F.A.; Athanazio, D.A.; Pinna, M.H. Evidence of leptospiral exposure in neotropical primates rescued from illegal trade and a zoo in Bahia, Brazil. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2016, 36, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachand, N.; Ravel, A.; Onanga, R.; Arsenault, J.; Gonzalez, J.-P. Public health significance of zoonotic bacterial pathogens from bushmeat sold in urban markets of Gabon, Central Africa. J. Wildl. Dis. 2012, 48, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.A.; Silvanose, C.; Manvell, R.; Gough, R.E.; Kinne, J.; Combreau, O.; Launay, F. Medical dilemmas associated with rehabilitating confiscated Houbara bustards (Chlamydotis undulata macqueenii) after avian pox and paramyxovirus type 1 infection. J. Wildl. Dis. 2002, 38, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.; Silvanose, C.; Naldo, J.; Combreau, O.; Launay, F.; Wernery, U.; Kinne, J.; Gough, R.; Manvell, R. Health considerations of the rehabilitation of illegally traded Houbara bustards Chlamydotis undulata macqueenii in the Middle East. Oryx 2000, 34, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brianti, E.; Dantas-Torres, F.; Giannetto, S.; Risitano, A.; Brucato, G.; Gaglio, G.; Otranto, D. Risk for the introduction of exotic ticks and pathogens into Italy through the illegal importation of tortoises, Testudo graeca. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2010, 24, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruningfann, C.; Kaneene, J.; Heamon, J. Investigation of an outbreak of velogenic viscerotropic newcastle-disease in pet birds in Michigan, Indiana, Illinois, and Texas. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1992, 201, 1709–1714. [Google Scholar]
- Burridge, M.J.; Simmons, L.A.; Simbi, B.H.; Peter, T.F.; Mahan, S.M. Evidence of Cowdria ruminantium infection (Heartwater) in Amblyomma sparsum ticks found on tortoises imported into Florida. J. Parasitol. 2000, 86, 1135–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catenazzi, A.; Vredenburg, V.T.; Lehr, E. Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in the live frog trade of Telmatobius (Anura: Ceratophryidae) in the tropical Andes. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2010, 92, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catroxo, M.H.B.; Martins, A.M.C.R.P.F.; Melo, N.A.; Milanelo, L.; Petrella, S.; Fitorra, L.S.; Petri, B.S.S. Ultrastructural identification of circovirus in the liver of Saffron finch (Sicalis flaveola Spp.). Int. J. Morphol. 2011, 29, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catroxo, M.H.B.; Pongiluppi, T.; Melo, N.A.; Milanelo, L.; Petrella, S.; Martins, A.M.C.P.F.; Reboucas, M.M. Identification of poxvirus under transmission electron microscopy during outbreak period in wild birds, in Sao Paulo, Brazil. Int. J. Morphol. 2009, 27, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaber, A.-L.; Cunningham, A. Public health risks from illegally imported african bushmeat and smoked fish: Public health risks from african bushmeat and smoked fish. EcoHealth 2016, 13, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, N.; Bronchain, O.; Panteix, G.; Sylvain, G.; Medeiros, C.; Saunders, R.; Bouts, T.; Luze, A. Propagation method of saving valuable strains from a Mycobacterium liflandii infection in western clawed frogs (Silurana tropicalis). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Zoo Vet. 2012, 43, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.D.; Berto, B.P.; Neves, D.M.; de Oliveiras, V.M.; Flausino, W.; Gomes Lopes, C.W. Oocyst shedding by green-winged-saltator (Saltator similis) in the diagnostic of Coccidiosis and Isospora similisi n. Sp (Apicomplexa: Eimeriidae). Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2013, 22, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corn, J.L.; Coffman, L.M.; Mertins, J.W. Wildlife surveillance for the South African tortoise tick (Amblyomma marmoreum) in Florida. In Proceedings of the Wildlife Disease Association International Conference, Athens, GA, USA, 9–12 August 1999; p. 79. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, R.K.; Oines, O.; Hamnes, I.S.; Schulze, J.E. Illegal wildlife imports more than just animals—Baylisascaris procyonis in raccoons (Procyon lotor) in Norway. J. Wildl. Dis. 2013, 49, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, W.R.; Appel, M.J.; Doster, G.L.; Baker, O.E.; Brown, J.F. Diseases and parasites of red foxes, gray foxes, and coyotes from commercial sources selling to fox-chasing enclosures. J. Wildl. Dis. 1992, 28, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, Y.M.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Oliveira, M.G.X.; Oliveira, M.C.V.; Philadelpho, N.; Romero, D.C.; Milanelo, L.; Guimaraes, M.B.; Ferreira, A.J.P.; Moreno, A.M.; et al. Virulence and antimicrobial resistance of klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from passerine and psittacine birds. Avian Pathol. 2016, 45, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Paula, C.D.; Pacifico-Assis, E.C.; Catao-Dias, J.L. Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in amphibians confiscated from illegal wildlife trade and used in an ex situ breeding program in Brazil. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2012, 98, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schrijver, K. A psittacosis outbreak in customs officers in Antwerp (Belgium). Bull. Inst. Marit. Trop. Med. Gdynia 1998, 49, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- DiGeronimo, P.M.; Hansen, C.; La’Toya, L.; Adamovicz, L.A.; Allender, M.C. Detection of Mycoplasma Sp. in indochinese box turtles (Cuora bourreti). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2019, 50, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolz, G.; Sheleby-Elías, J.; Romero, J.; Vargas, B.; Gutiérrez-Espeleta, G.; Madriz-Ordeñana, K. Prevalence of psittacine beak and feather disease virus and avian polyomavirus in captivity psittacines from Costa Rica. Open J. Vet. Med. 2013, 3, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duncan, A.E.; Woodhouse, S.J.; Shellabarger, W.C. Morbidity and mortality in a large group of amphibians confiscated from the pet trade. In Proceedings of the AAZV Annual Conference, Kansas City, MO, USA, 22–28 October 2011; p. 133. [Google Scholar]
- Galindo-Bustos, M.A.; Hernandez-Jauregui, D.M.B.; Cheng, T.; Vredenburg, V.; Parra-Olea, G. Presence and prevalence of Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in commercial amphibians in Mexico City. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2014, 45, 830–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencay, Y.E.; Yildiz, K.; Gokpinar, S.; Leblebicier, A. A potential infection source for humans: Frozen buffalo meat can harbour tissue cysts of Toxoplasma gondii. Food Control 2013, 30, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghersi, B.M.; Jia, H.; Aiewsakun, P.; Katzourakis, A.; Mendoza, P.; Bausch, D.G.; Kasper, M.R.; Montgomery, J.M.; Switzer, W.M. Wide distribution and ancient evolutionary history of simian foamy viruses in new world primates. Retrovirology 2015, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godoy, S.N.; Matushima, E.R. A Survey of diseases in passeriform birds obtained from illegal wildlife trade in Sao Paulo city, Brazil. J. Avian Med. Surg. 2010, 24, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Astudillo, V.; Pena-Stadlin, J.; Astudillo-Hernandez, M. Anti-leptospiral agglutinins in marmosets (Saguinus oedipus and Saguinus leucopus) from illegal trade. Rev. MVZ Cordoba 2015, 20, 4790–4799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guarner, J.; Johnson, B.J.; Paddock, C.D.; Shieh, W.-J.; Goldsmith, C.S.; Reynolds, M.G.; Damon, I.K.; Regnery, R.L.; Zaki, S.R. Veterinary monkeypox virus working group monkeypox transmission and pathogenesis in prairie dogs. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarares, M.B. Salmonellosis and Aspergillosis prevalence among confiscated birds from illegal wildlife trade from the São Paulo state—Brazil. In Proceedings of the Wildlife Disease Association International Conference, Puerto Iguazú, Argentina, 30 May–4 June 2010; p. 168. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, C. Taiwan Finds 3rd Case of Deadly H5N1 Virus in Birds Smuggled from China. Available online: https://www.medicaldaily.com/taiwan-finds-3rd-case-deadly-h5n1-virus-birds-smuggled-china-241383 (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Hyatt, A.D.; Williamson, M.; Coupar, B.E.H.; Middleton, D.; Hengstberger, S.G.; Gould, A.R.; Selleck, P.; Wise, T.G.; Kattenbelt, J.; Cunningham, A.A.; et al. First identification of a ranavirus from green pythons (Chondropython viridis). J. Wildl. Dis. 2002, 38, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabin, G.; Dewan, Y.; Khatri, H.; Singh, S.K.; Chandra, K.; Thakur, M. Identifying the tick Amblyomma javanense (Acari: Ixodidae) from Chinese pangolin: Generating species barcode, phylogenetic status and its implication in wildlife forensics. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2019, 78, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahrling, P.B.; Geisbert, T.W.; Dalgard, D.W.; Johnson, E.D.; Ksiazek, T.G.; Hall, W.C.; Peters, C.J. Preliminary report: Isolation of Ebola virus from monkeys imported to USA. Lancet 1990, 335, 502–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, R.A.; Wambua, J.; Mwanzia, J.; Rossiter, P.; Wamwayi, H.; Kock, N. Rinderpest Epidemic in the Tsavo National Park Kenya 1994–5; American Association of Zoo Veterinarians, American Association of Wildlife Veterinarians & Wildlide Disease Association: Nairobi, Kenya, 1995; pp. 98–104. [Google Scholar]
- Kolby, J.E.; Smith, K.M.; Berger, L.; Karesh, W.B.; Preston, A.; Pessier, A.P.; Skerratt, L.F. First evidence of amphibian chytrid fungus (Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis) and ranavirus in Hong Kong amphibian trade. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroucau, K.; Ortega, N.; Vorimore, F.; Aaziz, R.; Mitura, A.; Szymanska-Czerwinska, M.; Cicerol, M.; Salinas, J.; Sachse, K.; Caro, M.R. Detection of a novel chlamydia species in captive spur-thighed tortoises (Testudo graeca) in southeastern Spain and proposal of Candidatus chlamydia testudinis. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tan, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.C.; Liu, Y.S.; Yang, L.C. Prevalence and molecular characterization of Spirometra erinaceieuropaei spargana in snakes in Hunan province, China. J. Helminthol. 2020, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souze Lopes, E.; Maciel, W.C.; de Albuquerque, A.H.; Machado, D.N.; de Amorim Bezerra, W.G.; Vasconcelos, R.H.; Lima, B.P.; Marietto Goncalves, G.A.; de Castro Teixeira, R.S. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profile of enterobacteria isolated from psittaciformes of illegal wildlife trade. Acta Sci. Vet. 2015, 43, 1313. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, E.S.; Maciel, W.C.; Medeiros, P.H.Q.S.; Bona, M.D.; Binda, A.H.; Lima, S.V.G.; Gaio, F.C.; Teixeira, R.S.C. Molecular diagnosis of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli isolated from psittaciformes of illegal wildlife Trade. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2018, 38, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loporto, L.S.; Morganti, G.; Moretta, I.; Schembri, P.J. A first record of the tortoise tick, Hyalomma aegyptium (Linnaeus 1758) on Malta. Int. J. Acarol. 2018, 44, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukopoulos, P.; Komnenou, A.; Papadopoulos, E.; Psychas, V. Lethal ozolaimus megatyphlon infection in a green iguana (Iguana iguana rhinolopa). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Zoo Vet. 2007, 38, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lujan-Vega, C.; Mendoza, A.P.; Chavez, A.; Montgomery, J.M.; Brightsmith, D. Gastrointestinal parasites in the live bird markets of Peru. In Proceedings of the Wildlife Disease Association International Conference, Puerto Iguazú, Argentina, 30 May–4 June 2010; p. 194. [Google Scholar]
- Marietto-Gonçalves, G.A.; de Almeida, S.M.; Rodrigues, J. Presence of a human diarrheagenic Escherichia coli clone in captivity kept psittacidaes. Open Microbiol. J. 2011, 5, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marschang, R.E.; Papp, T.; Ferretti, L.; Hochscheid, S.; Bentivegna, F. Detection and partial characterization of herpesviruses from egyptian tortoises (Testudo kleinmanni) imported into Italy from Libya. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2009, 40, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.A.R.; Pereira, I.A.; Rodrigues, D.P.; Siciliano, S. Staphylococcus spp. isolated from wild birds apprehended in the local illegal trade in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and relevance in public health. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, A.P.; Bernal, M.; Cavero, N.; Meza, Y.; Ghersi, B.; Brightsmith, D.J.; Uhart, M. Antibiotic resistant bacterial strains in traded wildlife in Peru. In Proceedings of the 60th Wildlife Disease Association International Conference, Quebec, QC, Canada, 14–19 August 2011; p. 103. [Google Scholar]
- Mendoza, A.P.; Ghersi, B.; Cavero, N.; Villena, M.; Lujan, C.; Ibañez, Y.; Segovia, K.; Razuri, H.; Montgomery, J.; Brightsmith, D. aAvian influenza and newcastle disease viruses in the live bird trade of Peru. In Proceedings of the 59th Wildlife Disease Association International Conference, Puerto Iguazú, Argentina, 30 May–4 June 2010; p. 216. [Google Scholar]
- Pinna, M.H.; Martins, G.; Pinheiro, A.C.O.; Almeida, D.S.; Oriá, A.P.; Lilenbaum, W. Detection of anti-leptospira antibodies in captive nonhuman primates from Salvador, Brazil. Am. J. Primatol. 2011, 74, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mora-Chavarria, E.; Umana-Castro, R.; Abou-Madi, N.; Solano-Gonzalez, S.; Retamosa-Izaguirre, M.; Jimenez-Soto, M.; Blanco-Pena, K. Health assessment of captive psittacine species in prerelease programs at costa rican rescue centers. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2017, 48, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, R.A.; Dronen, N.O.; Blend, C.K. Endohelminths from five rare species of turtles (Bataguridae) from Southeast Asia confiscated by international authorities in Hong Kong, Peoples Republic of China. Zootaxa 2004, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, B.; Szmolka, A.; Mozina, S.S.; Kovac, J.; Strauss, A.; Schlager, S.; Beutlich, J.; Appel, B.; Lusicky, M.; Aprikian, P.; et al. Virulence and antimicrobial resistance determinants of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli (VTEC) and of multidrug-resistant, E. coli from foods of animal origin illegally imported to the EU by flight passengers. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 209, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuschrank-Albano, A.P. Isolation of fungi from orbignys slider (Trachemys dorbigny) failed eggs. In Proceedings of the 59th Wildlife Disease Association International Conference, Puerto Iguazú, Argentina, 30 May–4 June 2010; p. 194. [Google Scholar]
- Niphuis, H.; Bello, R.; Rosemberg, F.; Fagrouch, Z. Reverse zoonotic human herpes virus 1 infection in two young peruvian black spider monkeys at the Taricaya rescue center, Puerto Maldonado, Peru. In Proceedings of the Joint EAZWV and AAZV, Leibniz-IZW Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 6–12 October 2018; pp. 32–33. [Google Scholar]
- Nituch, L.A.; Bowman, J.; Wilson, P.; Schulte-Hostedde, A.I. Molecular epidemiology of aleutian disease virus in free-ranging domestic, hybrid, and wild mink. Evol. Appl. 2012, 5, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ornelas-Eusebio, E.; Sanchez-Godoy, F.D.; Chavez-Maya, F.; De la Garza-Garcia, J.A.; Hernandez-Castro, R.; Garcia-Espinosa, G. First identification of Chlamydia psittaci in the acute illness and death of endemic and endangered psittacine birds in Mexico. Avian Dis. 2016, 60, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, A.A. A psittacosis outbreak in Costa Rica associated with pet birds imported from the United States. In Proceedings of the Joint EAZWV and AAZV Conference, Omaha, NE, USA, 17–22 October 1998; pp. 258–260. [Google Scholar]
- Peeters, M.; Courgnaud, V.; Abela, B.; Auzel, P.; Pourrut, X.; Bibollet-Ruche, F.; Loul, S.; Liegeois, F.; Butel, C.; Koulagna, D.; et al. Risk to human health from a plethora of simian immunodeficiency viruses in primate bushmeat. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percipalle, M.; Giardina, G.; Lipari, L.; Piraino, C.; Macri, D.; Ferrantelli, V. Salmonella infection in illegally imported spur-thighed tortoises (Testudo graeca). Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posthaus, H.; Marschange, R.E.; Gravendyck, M. Study on Herpesvirus Infections in Land Tortoises in Switzerland; American Association of Zoo Veterinarians: Houston, TX, USA, 1997; pp. 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Raso, T.D.; Godoy, S.N.; Milanelo, L.; de Souza, C.A.I.; Matuschima, E.R.; Araujo, J.P.; Pinto, A.A. An outbreak of chlamydiosis in captive blue-fronted amazon parrots (Amazona aestiva) in Brazil. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2004, 35, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raso, T.F.; Friciello Teixeira, R.H.; Torres Carrasco, A.O.; Araujo Junior, J.P.; Pinto, A.A. Chlamydophila psittaci infections in hyacinth macaws (Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus) confiscated in Brazil. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2013, 44, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, C.A.R.; Pereira, I.A.; Araújo, M.D.S.D.; Santos, A.F.M.; Lopes, R.P.; Christakis, S.; Rodrigues, D.D.P.; Siciliano, S. Characteristics of Salmonella spp. isolated from wild birds confiscated in illegal trade markets, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 3416864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saidenberg, A.B.; Teixeira, R.H.F.; Guedes, N.M.R.; Allgayer, M.D.C.; Melville, P.A.; Benites, N.R. Molecular detection of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in asymptomatic captive psittacines. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2012, 32, 922–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Salmonellosis associated with pet turtles—Wisconsin and Wyoming, 2004. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2005, 54, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Schloegel, L.M.; Toledo, L.F.; Longcore, J.E.; Greenspan, S.E.; Vieira, C.A.; Lee, M.; Zhao, S.; Wangen, C.; Ferreira, C.M.; Hipolito, M.; et al. Novel, panzootic and hybrid genotypes of amphibian chytridiomycosis associated with the bullfrog trade. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 5162–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seal, B.S.; King, D.J.; Locke, D.P.; Senne, D.A.; Jackwood, M.W. Phylogenetic relationships among highly virulent newcastle disease virus isolates obtained from exotic birds and poultry from 1989 to 1996. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, K.M.; Anthony, S.J.; Switzer, W.M.; Epstein, J.H.; Seimon, T.; Jia, H.; Sanchez, M.D.; Huynh, T.T.; Galland, G.G.; Shapiro, S.E.; et al. Zoonotic viruses associated with illegally imported wildlife products. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sockett, D. Mycobacterium bovis infection in U.S. Deer and Elk Farms. In Proceedings of the AAZV Conference, St. Louis, MO, USA, 9–14 October 1993; pp. 224–227. [Google Scholar]
- Suepaul, R.B.; Seetahal, J.F.R.; Oura, C.; Gyan, L.; Ramoutar, V.V.; Ramkissoon, V.; Sahadeo, N.; Carrington, C.V.F. Novel poxviral infection in three finch species illegally imported into Trinidad, West Indies, with implications for native birds. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2019, 50, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauer, A.M.; Karesh, W.; Reed, T. Yaws: An Emerging Zoonosis of Gorillas? In Proceedings of the AAZV and AAWV Joint Conference, South Padre Island, TX, USA, 23–29 October 2010; pp. 3–4. [Google Scholar]
- Temmam, S.; Davoust, B.; Chaber, A.-L.; Lignereux, Y.; Michelle, C.; Monteil-Bouchard, S.; Raoult, D.; Desnues, C. Screening for viral pathogens in African simian bushmeat seized at A French airport. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singapore Jails Two Vietnamese Rare Bird Smugglers—VnExpress International. Available online: https://e.vnexpress.net/news/news/singapore-jails-two-vietnamese-rare-bird-smugglers-3521472.html (accessed on 16 February 2021).
- Vosloo, W.; Bastos, A.D.S.; Michel, A.; Thomson, G.R. Tracing movement of African buffalo in Southern Africa. Rev. Sci. Tech.Off. Int. Epizoot. 2001, 20, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidasi, H.W.; Neto, J.H.; Moraes, D.M.C.; Linhares, G.F.C.; Jayme, V.D.S.; Andrade, M.A. Enterobacterial detection and Escherichia coli antimicrobial resistance in parrots seized from the illegal wildlife trade. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Zoo Vet. 2013, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Li, W.; Hua, L.; Gong, S.; Xiao, J.; Hou, F.; Ge, Y.; Yang, G. Spirometra (Pseudophyllidea, Diphyllobothriidae) severely infecting wild-caught snakes from food markets in Guangzhou and Shenzhen, Guangdong, China: Implications for public health. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wolf, K.N.; Lewbart, G.A.; Mashima, T.Y. Spring viremia of carp virus: Animal health policy considerations. In Proceedings of the AAZV Conference, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 4–10 October 2003; pp. 207–208. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe, N.D.; Switzer, W.M.; Carr, J.K.; Bhullar, V.B.; Shanmugam, V.; Tamoufe, U.; Prosser, A.T.; Torimiro, J.N.; Wright, A.; Mpoudi-Ngole, E.; et al. Naturally acquired simian retrovirus infections in central African hunters. Lancet 2004, 363, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, K.B.; Campos, P.F.; Gilbert, M.T.P.; Kolokotronis, S.-O.; Hynes, W.H.; DeSalle, R.; Daszak, P.; MacPhee, R.D.E.; Greenwood, A.D. Historical mammal extinction on Christmas Island (Indian Ocean) correlates with introduced infectious disease. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yossepowitch, O.; Gotesman, T.; Assous, M.; Marva, E.; Zimlichman, R.; Dan, M. Opisthorchiasis from imported raw fish. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 2122–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zevallos, S.; Elias, R.K.; Berenguel, R.A.; Weaver, T.J.; Reading, R.P. Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis in confiscated Telmatobius in Lima, Peru. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Outbreak of Salmonella Infections Linked to Pet Turtles, October 2019, Salmonella, CDC. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/salmonella/oranienburg-10-19/index.html (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- Allen, T.; Murray, K.A.; Zambrana-Torrelio, C.; Morse, S.S.; Rondini, C.; Di Marco, M.; Breit, N.; Olival, K.J.; Daszak, P. Global hotspots and correlates of emerging zoonotic diseases. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, T.R.; Jones, K.E.; Dobson, A.P.; Clennon, J.A.; Pascual, M. COVID-clarity demands unification of health and environmental policy. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2021, 27, 1319–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguirre, A.A.; Catherina, R.; Frye, H.; Shelley, L. Illicit wildlife trade, wet markets, and COVID-19: Preventing future pandemics. World Med. Health Policy 2020, 12, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Wildlife Report. Available online: //www.unodc.org/unodc/en/data-and-analysis/wildlife.html (accessed on 10 May 2021).
- University of California-Davis. PREDICT. Available online: https://ohi.vetmed.ucdavis.edu/programs-projects/predict-project (accessed on 2 June 2021).
- Aguirre, A.A.; Basu, N.; Kahn, L.H.; Morin, X.K.; Echaubard, P.; Wilcox, B.A.; Beasley, V.R. Transdisciplinary and social-ecological health frameworks—Novel approaches to emerging parasitic and vector-borne diseases. Parasite Epidemiol. Control 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.A.; Aguirre, A.A.; De Paula, N.; Siriaroonrat, B.; Echaubard, P. Operationalizing one health employing social-ecological systems theory: Lessons from the greater mekong sub-region. Front. Public Health 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Category | Pathogen Category | Affected Category | Species Affected | Trade Activity Category | Zoonotic Potential | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral | Canine coronavirus-II | Mammals | Canis lupus | Pet | N | [28] |
| Bacterial | Leptospira spp. | Mammals | Cebus sp. | Pet | Y | [29] |
| Bacterial | Campylobacter spp., Salmonella spp., Shigella spp. | Mammals | N/A | Bushmeat | Y | [30] |
| Viral | Avian poxvirus, paramyxovirus-1 | Birds | Chlamydotis undulata, C. macqueenii | Illegal Trade | N | [31] |
| Bacterial | Chlamydophila psittaci, Clostridium perfringens, Pasteurella multocida, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella spp. | Birds | Chlamydotis undulata | Illegal Trade | Y/N | [32] |
| Endoparasite | Unindentified endoparasites | |||||
| Fungal | Aspergillus fumigatus | |||||
| Protozoan | Giardia spp., Haemoproteus spp., Leucocytozoon spp., Trichomonas spp. | |||||
| Viral | Adenovirus, avian pneumovirus, avian poxvirus, avian reovirus, paramyxovirus-1, paramyxovirus-2 | |||||
| Ectoparasite | Hyalomma aegyptium | Reptiles | Testudo graeca | Illegal Trade | N | [33] |
| Viral | Newcastle disease virus | Birds | Amazona oratrix | Pet | Y | [34] |
| Bacterial | Ehrlichia ruminantium | Invertebrates | Amblyomma sparsum | Legal Trade | N | [35] |
| Fungal | Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis | Amphibians | Telmatobius marmoratus | Legal Trade | N | [36] |
| Viral | Avian circovirus | Birds | Sicalis flaveola | Illegal Trade | N | [37] |
| Viral | Avian poxvirus | Birds | Passeriformes | Pet | N | [38] |
| Bacterial | Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter spp., Klebsiella oxytoca, Listeria spp., Staphylococcus spp. | Mammals, Reptiles | N/A | Bushmeat | Y | [39] |
| Bacterial | Mycobacterium liflandii | Amphibians | Silurana tropicalis | Legal Trade | N | [40] |
| Protozoan | Coccidiasina | Birds | Saltator similis | Illegal Trade | N | [41] |
| Ectoparasite | Amblyomma marmoreum | Reptiles | N/A | Pet | N | [42] |
| Endoparasite | Baylisascaris procyonis, Toxascaris leonina, Toxocara canis | Mammals | Procyon lotor | Illegal Trade | Y/N | [43] |
| Ectoparasite | Cediopsylla simplex, Otodectes cynotis, Pulex simulans | Mammals | Vulpes vulpes, Urocyon cinereoargenteus, Canis latrans | Illegal Trade | Y/N | [44] |
| Endoparasite | Echinococcus multilocularis, unindentified endoparasites | |||||
| Protozoan | Cystoisospora spp., Sarcocystis spp. | |||||
| Viral | rabies | |||||
| Bacterial | Klebsiella pneumoniae | Birds | Passeriformes, Psittaciformes | Illegal Trade | Y | [45] |
| Fungal | Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis | Amphibians | Dendrobates tinctorius | Illegal Trade | N | [46] |
| Bacterial | Chlamydophila psittaci | Birds | budgerigars | Illegal Trade | Y | [47] |
| Bacterial | Mycoplasma spp. | Reptiles | Cuora bourreti | Pet | Y | [48] |
| Viral | Psittacine beak and feather disease virus | Birds | Ara ambigua, Ara macao | Pet | N | [49] |
| Fungal | Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis | Amphibians | 53 different species | Pet | N | [50] |
| Viral | ranavirus | |||||
| Fungal | Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis | Amphibians | Hyla eximia | Pet | N | [51] |
| Protozoan | Toxoplasma gondii | Mammals | Bubalus bubalis | Illegal Trade | Y | [52] |
| Viral | Simian foamy virus | Mammals | Multiple species | Illegal Trade | Y | [53] |
| Bacterial | Citrobacter freundii, Enterobacter spp., Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp., Salmonella spp. | Birds | Passeriformes | Pet | Y/N | [54] |
| Endoparasite | Tapeworms, Trichomonas spp. | |||||
| Fungal | Aspergillus fumigatus | |||||
| Viral | Avian poxvirus | |||||
| Bacterial | Leptospira spp. | Mammals | Saguinus oedipus | Illegal Trade | Y | [55] |
| Viral | Monkeypox virus | Mammals | Cricetomys sp., Funiscuirus sp., Graphiurus sp. | Pet | Y | [56] |
| Fungal | Aspergillus fumigatus | Birds | N/A | Illegal Trade | Y | [57] |
| Viral | H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza | Birds | N/A | Illegal Trade | Y | [58] |
| Viral | Ranavirus | Reptiles | Chondropython viridis | Illegal Trade | N | [59] |
| Ectoparasite | Amblyomma javanense | Mammals | Manis pentadactyla | Illegal Trade | N | [60] |
| Viral | Simian foamy virus | Mammals | Macaca fascicularis | Legal Trade | Y | [61] |
| Viral | Morbillivirus | Mammals | Tragelaphus imberbis, Syncerus caffer, Aepyceros melampus, Taurotragus oryx | Not Trade Related | N | [62] |
| Fungal | Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis | Amphibians | Multiple species | Illegal Trade | N | [63] |
| Viral | Ranavirus | |||||
| Bacterial | Chlamydophila spp., Escherichia coli | Reptiles | Testudo graeca | Pet | Y | [64] |
| Endoparasite | Spirometra spp. | Reptiles | Elaphe carinata, E. taeniura, Zaocys dhumnades | Wet Market | Y | [65] |
| Bacterial | Enterobacter spp. | Birds | Psittaciformes | Illegal Trade | Y | [66] |
| Bacterial | Escherichia coli | Birds | Psittaciformes | Illegal Trade | Y | [67] |
| Ectoparasite | Hyalomma aegyptium | Reptiles | Testudo graeca, T. kleinmanni | Pet | N | [68] |
| Endoparasite | Ozolaimus megatyphlon | Reptiles | Iguana iguana | Pet | N | [69] |
| Endoparasite | Acuariidae. Ascaridoidea, Capillarinae, Cestoda, Coccidia | Birds | N/A | Wet Market | Y/N | [70] |
| Bacterial | Escherichia coli | Birds | Aratinga leucophthalmus, Amazonia aestiva | Pet | Y | [71] |
| Viral | Herpesvirus | Reptiles | Testudo kleinmanni | Pet | N | [72] |
| Bacterial | Staphylococcus spp. | Birds | Emberizidae sp, Thraupidae sp | Illegal Trade | Y | [73] |
| Bacterial | Aeromonas caviae, Campylobacter jejuni, Salmonella spp. | Birds | Multiple species | Wet Market | Y | [74] |
| Viral | Newcastle disease virus | Birds | N/A | Wet Market | Y | [75] |
| Bacterial | Leptospira spp. | Mammals | Multiple species | Illegal Trade | Y | [76] |
| Viral | Avian circovirus, avian polyomavirus | Birds | Amazona auropalliata, Amazona autumnalis, Ara macao | Pet | N | [77] |
| Endoparasite | Unindentified endoparasites | Reptiles | Multiple species | Illegal Trade | UNK | [78] |
| Bacterial | Escherichia coli | N/A | N/A | Bushmeat | Y | [79] |
| Fungal | Fusarium solani | Reptiles | Trachemys dorbigny | Illegal Trade | Y | [80] |
| Viral | Human herpesvirus 1 | Mammals | Ateles chamek | Illegal Trade | Y | [81] |
| Viral | Aleutian disease virus | Mammals | Mephitis mephitis, Neovison vison | Legal Trade | Y | [82] |
| Bacterial | Chlamydophila psittaci | Birds | Psittaciformes | Illegal Trade | Y | [83] |
| Bacterial | Chlamydophila psittaci | Birds | Ara macao, Ara ambigua | Pet | Y | [84] |
| Viral | Simian immunodeficiency virus | Mammals | N/A | Bushmeat | Y | [85] |
| Bacterial | Salmonella spp. | Reptiles | Testudo graeca, Testudo hermanni | Pet | Y | [86] |
| Viral | Herpesvirus | Reptiles | Multiple species | Legal Trade | N | [87] |
| Bacterial | Chlamydia psittaci, Escherichia coli, Shigella spp. | Birds | Psittaciformes | Pet | Y | [88] |
| Bacterial | Chlamydophila psittaci | Birds | Anodorhynchus hyacinthinus | Pet | Y | [89] |
| Bacterial | Salmonella panama, Salmonella typhimurium | Birds | Chrysomus ruficapillus, Sporophila falcirostris | Illegal Trade | Y | [90] |
| Bacterial | Escherichia coli | Birds | Multiple species | Illegal Trade | Y | [91] |
| Bacterial | Salmonella spp. | Reptiles | N/A | Pet | Y | [92] |
| Fungal | Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis | Amphibians | Lithobates catesbeianus | Wet Market | N | [93] |
| Viral | Newcastle disease virus | Birds | N/A | Pet | Y | [94] |
| Viral | Cytomegalovirus, lymphocryptovirus, simian foamy virus | Mammals | Multiple species | Bushmeat | Y | [95] |
| Bacterial | Mycobacterium bovis | Mammals | N/A | Legal Trade | Y | [96] |
| Viral | Avian poxvirus, canarypoxvirus | Birds | Oryzoborus angolensis, O. crassirostris, Sporophila intermedia | Pet | N | [97] |
| Bacterial | Trepona pallidum | Mammals | Gorilla gorilla | Legal Trade | Y | [98] |
| Viral | Alphavirus, arenavirus, coronavirus, filovirus, flavivirus, hantavirus, herpesvirus, nairovirus, orthobunyavirus, paramyxovirus, phlebovirus, poxvirus | Mammals | Cercopithecidae | Bushmeat | Y | [99] |
| Viral | H5N1 highly pathogenic avian influenza | Birds | Spizaetus nipalensis | Illegal Trade | Y | [25] |
| Viral | H3N8 avian influenza | Birds | Garrulax canorus | Illegal Trade | N | [100] |
| Viral | Coxsackievirus | Mammals | Syncerus caffer | Not Trade Related | Y | [101] |
| Bacterial | Citrobacter spp., Enterobacter spp., Escherichia coli, Hafnia aivei, Klebsiella spp., Proteus spp., Providencia alcalifaciens, Salmonella typhimurium, Serratia spp. | Birds | Multiple species | Illegal Trade | Y | [102] |
| Endoparasite | Spirometra spp. | Reptiles | Multiple species | Wet Market | Y | [103] |
| Viral | Spring viremia of carp virus | Fish | Cyprinus rubrofuscus | Legal Trade | N | [104] |
| Viral | Simian foamy virus | Mammals | N/A | Bushmeat | Y | [105] |
| Viral | Trypanosoma lewisi | Mammals | Rattus macleari, R. nativitatis | Not Trade Related | N | [106] |
| Endoparasite | Opisthorchis spp. | Fish, Mammals | N/A | Illegal Trade | Y | [107] |
| Fungal | Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis | Amphibians | Telmatobius spp. | Illegal Trade | N | [108] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rush, E.R.; Dale, E.; Aguirre, A.A. Illegal Wildlife Trade and Emerging Infectious Diseases: Pervasive Impacts to Species, Ecosystems and Human Health. Animals 2021, 11, 1821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061821
Rush ER, Dale E, Aguirre AA. Illegal Wildlife Trade and Emerging Infectious Diseases: Pervasive Impacts to Species, Ecosystems and Human Health. Animals. 2021; 11(6):1821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061821
Chicago/Turabian StyleRush, Elizabeth R., Erin Dale, and A. Alonso Aguirre. 2021. "Illegal Wildlife Trade and Emerging Infectious Diseases: Pervasive Impacts to Species, Ecosystems and Human Health" Animals 11, no. 6: 1821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061821
APA StyleRush, E. R., Dale, E., & Aguirre, A. A. (2021). Illegal Wildlife Trade and Emerging Infectious Diseases: Pervasive Impacts to Species, Ecosystems and Human Health. Animals, 11(6), 1821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11061821





