Life Cycle of Edible Jellyfish Acromitus hardenbergi Stiasny, 1934 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) Inhabiting a Brackish-Water Environment
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
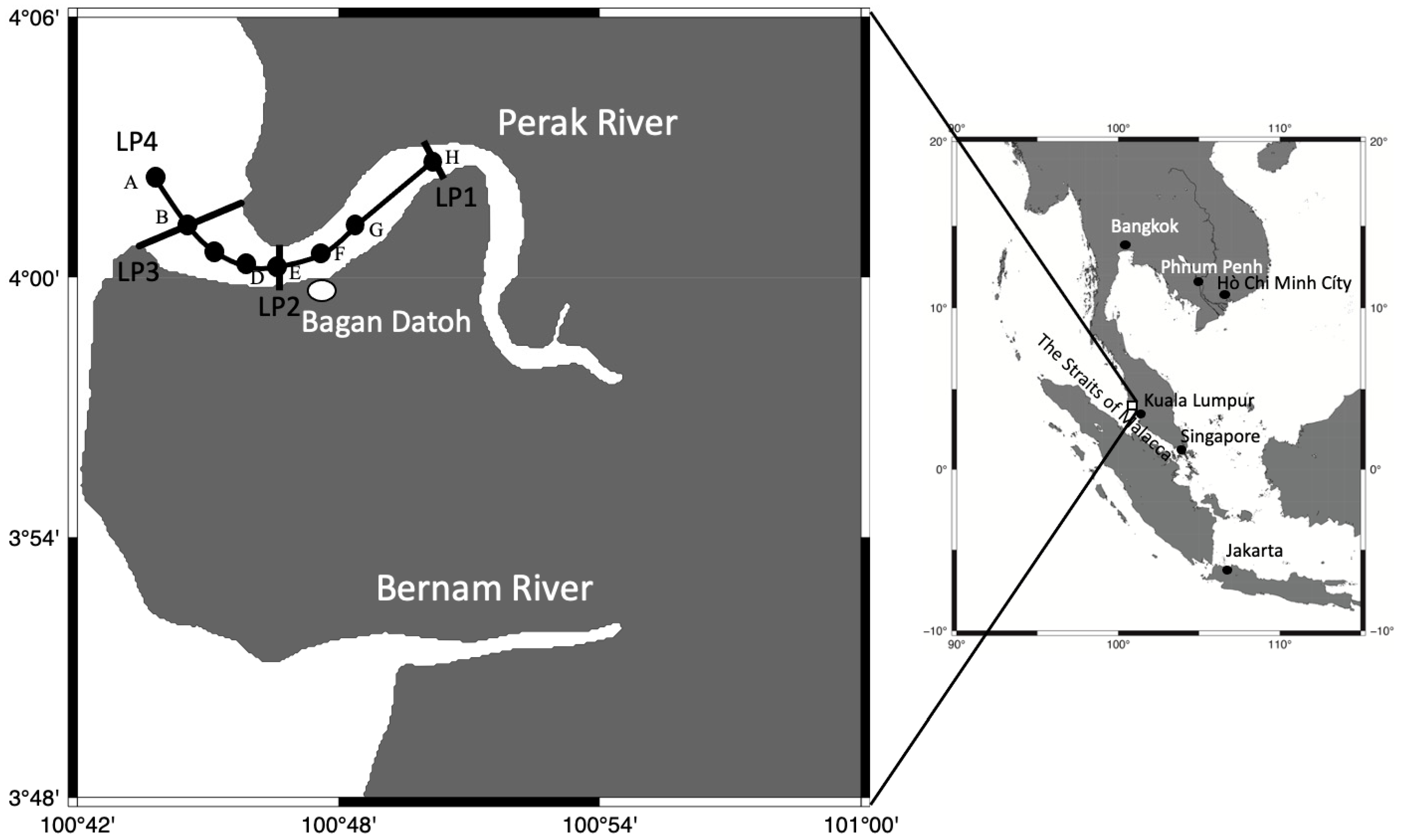
2.1. Environmental Data Collection
2.2. Jellyfish Collection
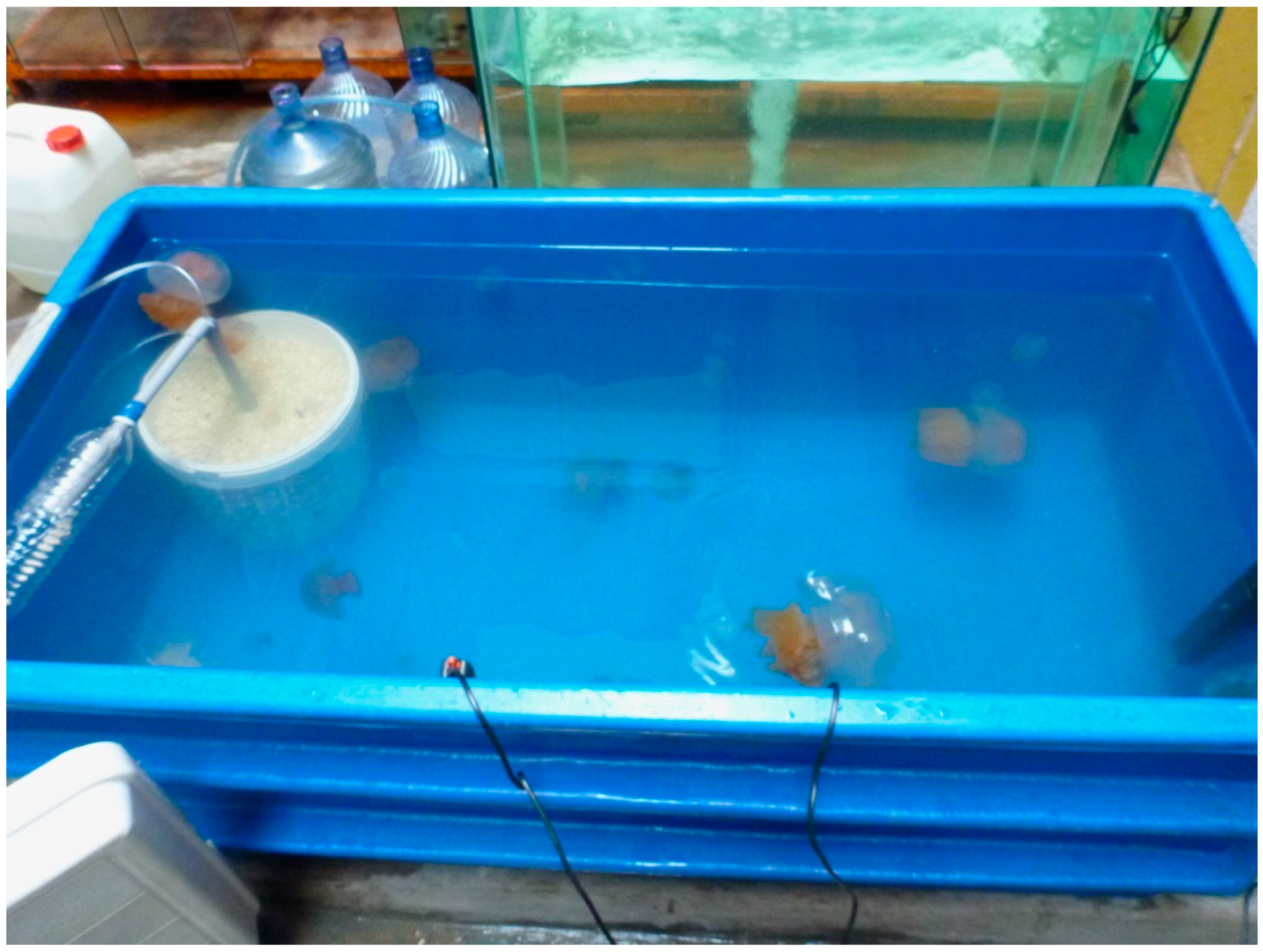
2.3. Animal Maintenance
2.4. Examination of Suitable Salinity for Planula Settlement
2.5. Observation of Life Cycle
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
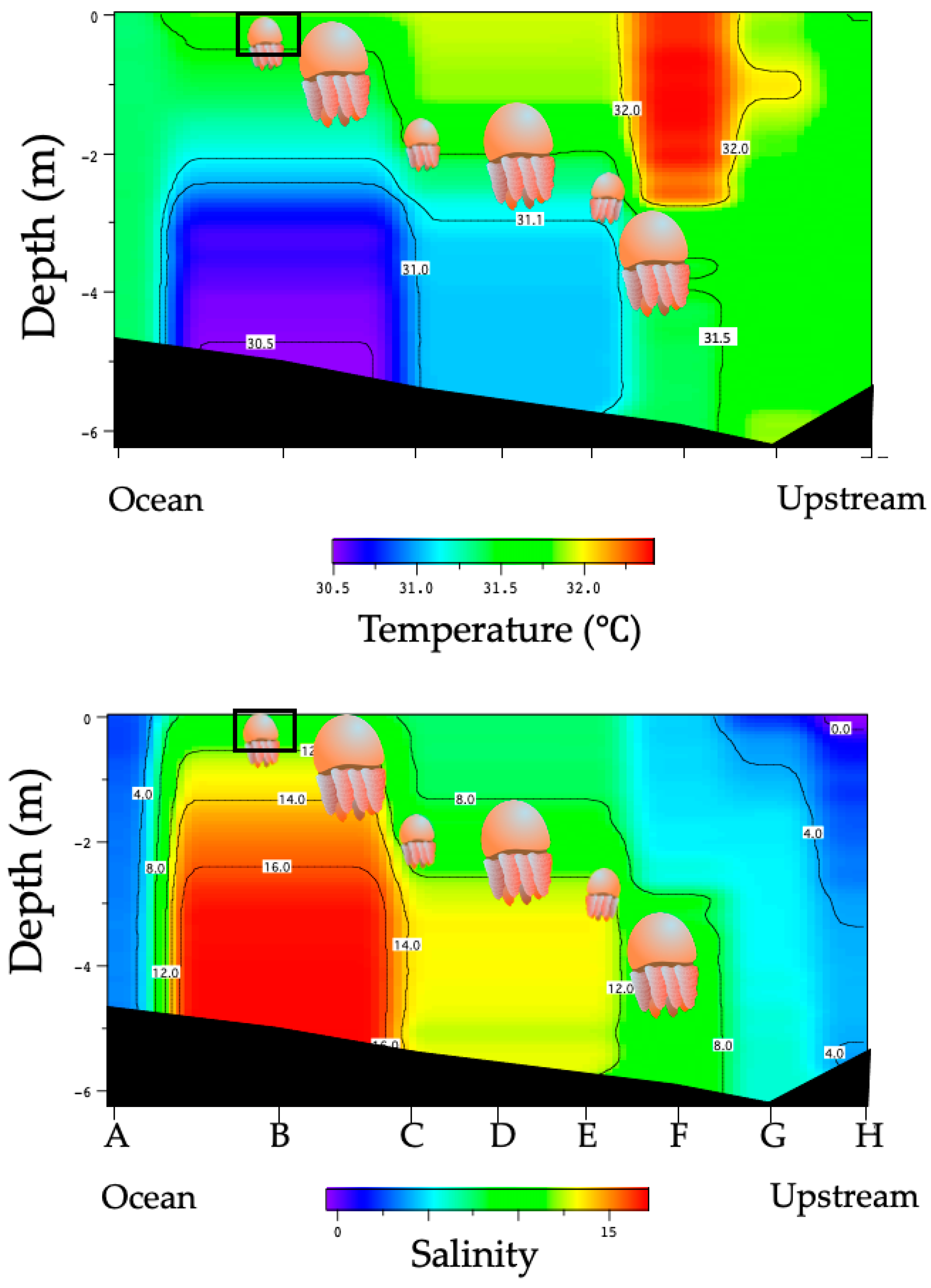
3.1. Environmental Conditions in the Perak River
3.2. Distribution of Acromitus hardenbergi in the Perak River
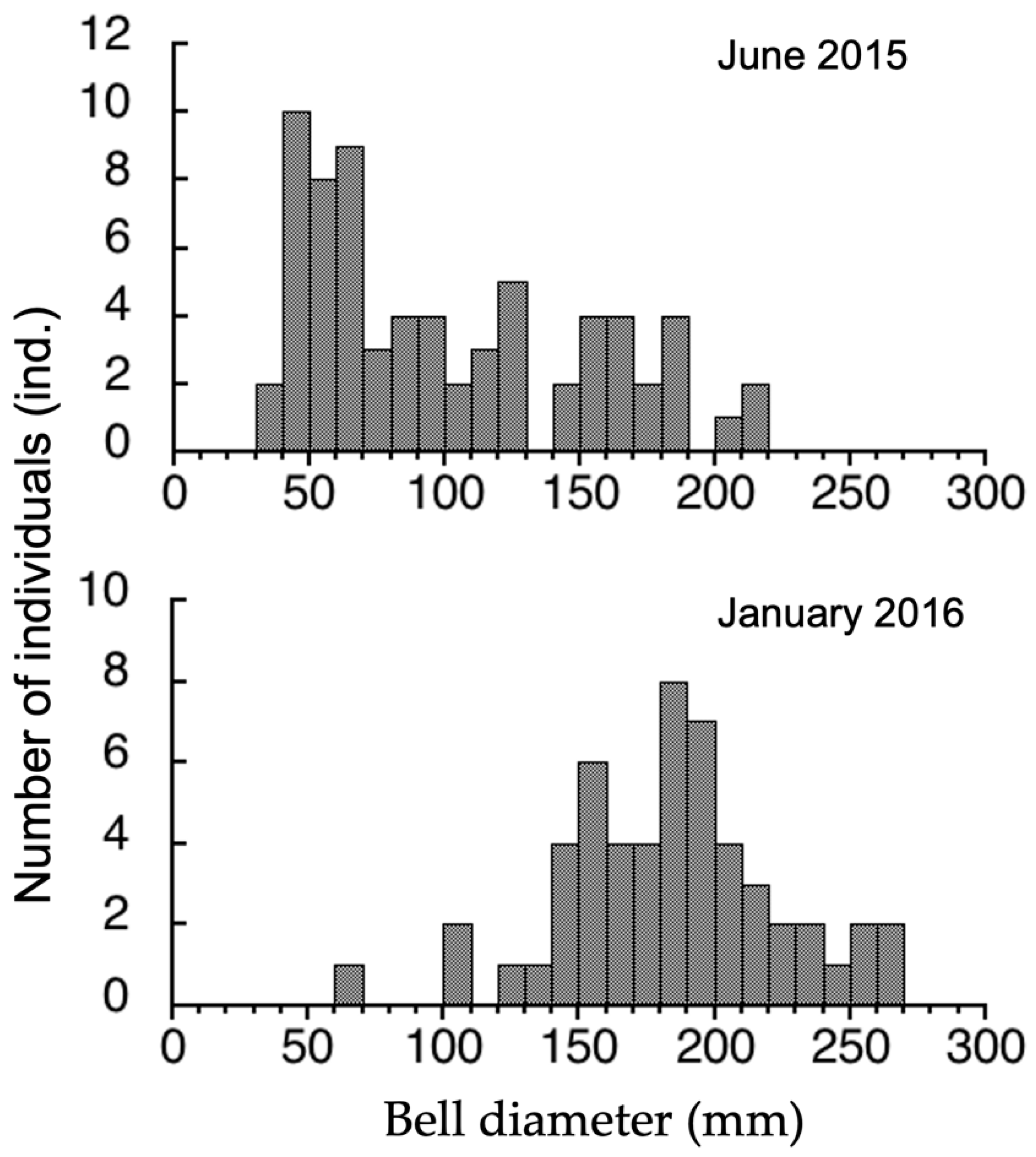
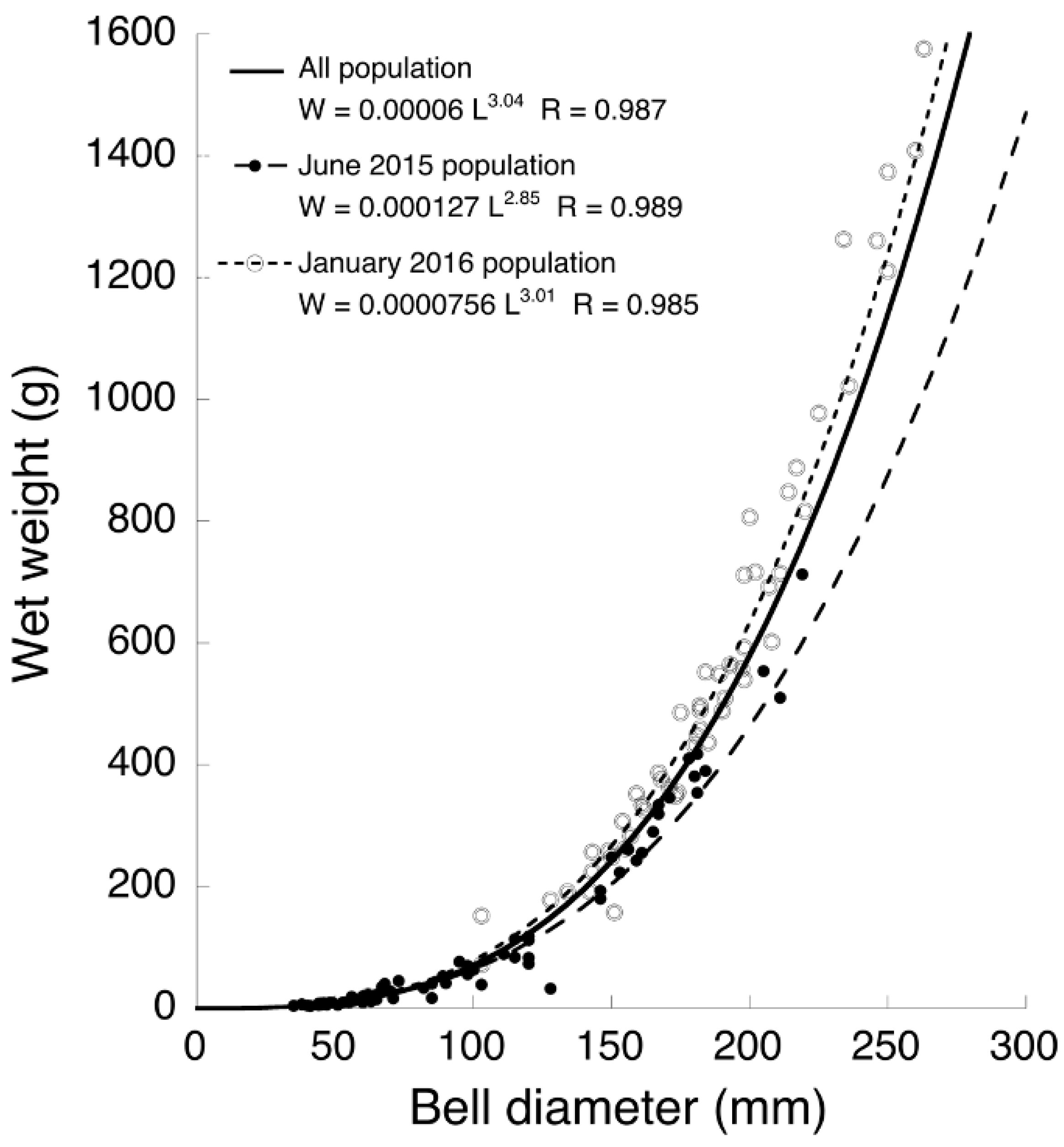
3.3. Seasonal Difference in Size Distribution of A. hardenbergi Medusae in Perak River
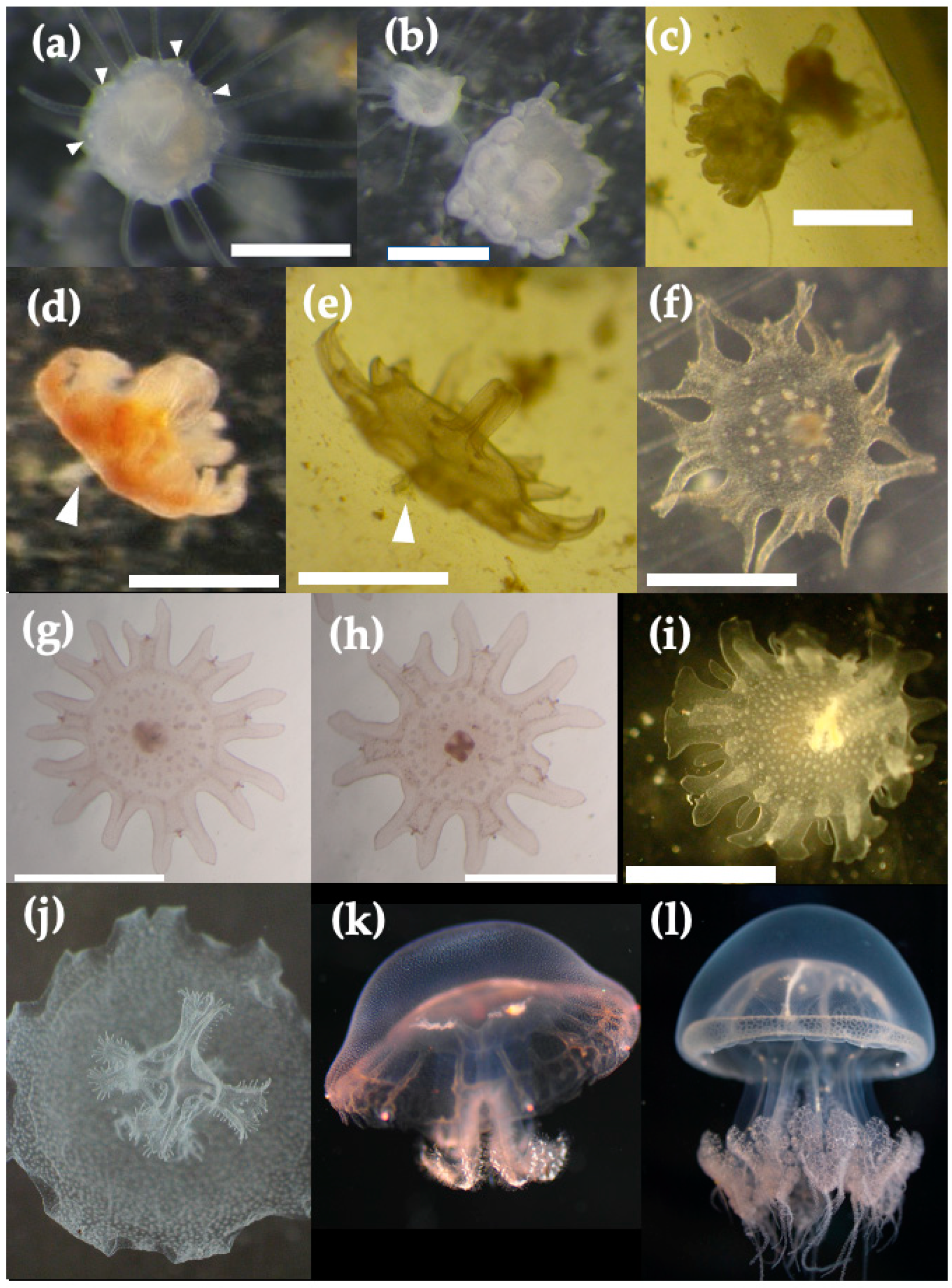
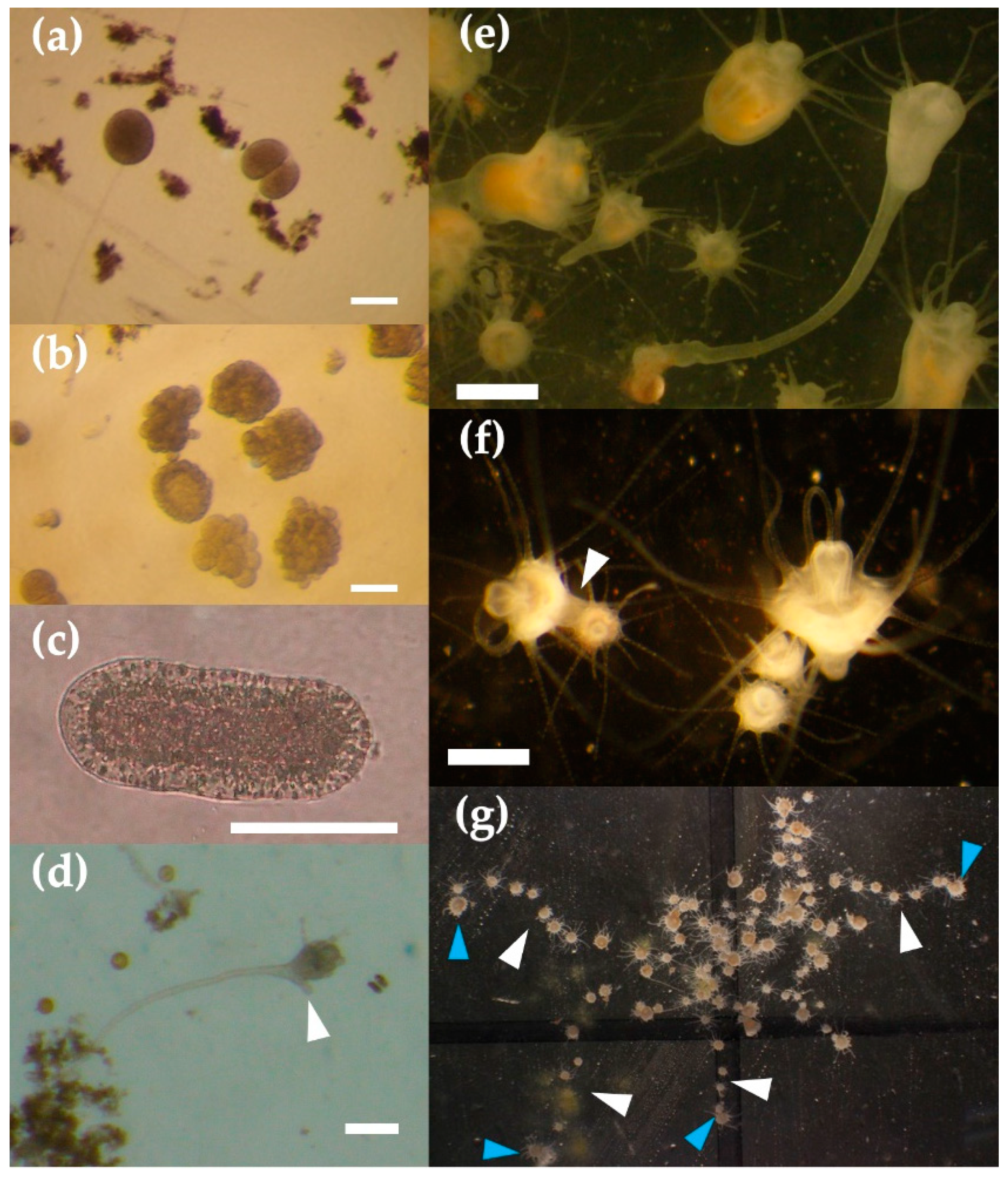
3.4. Life Cycle of Acromitus hardenbergi
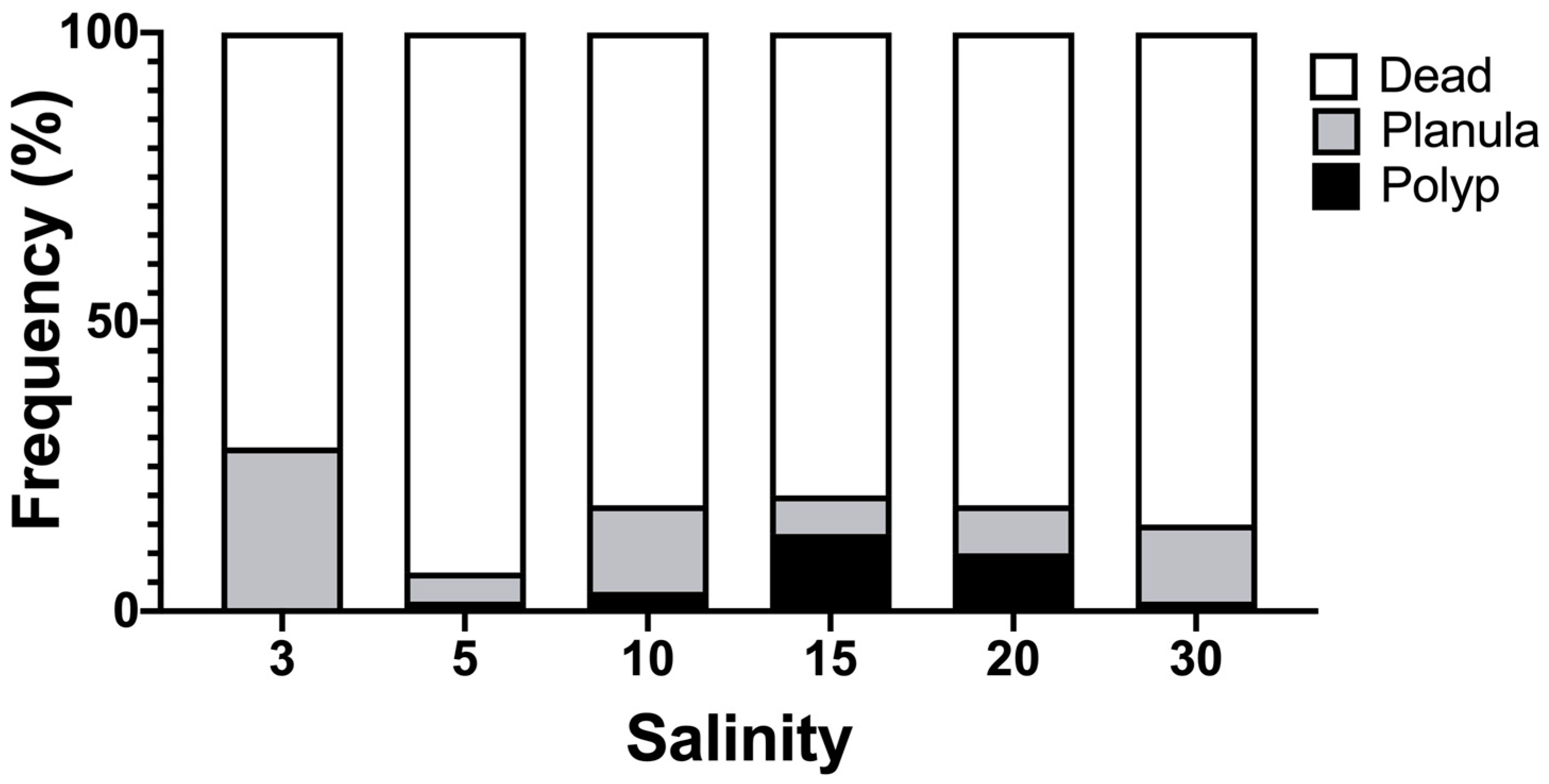
3.5. Suitable Salinity for Planula Settlement
4. Discussion
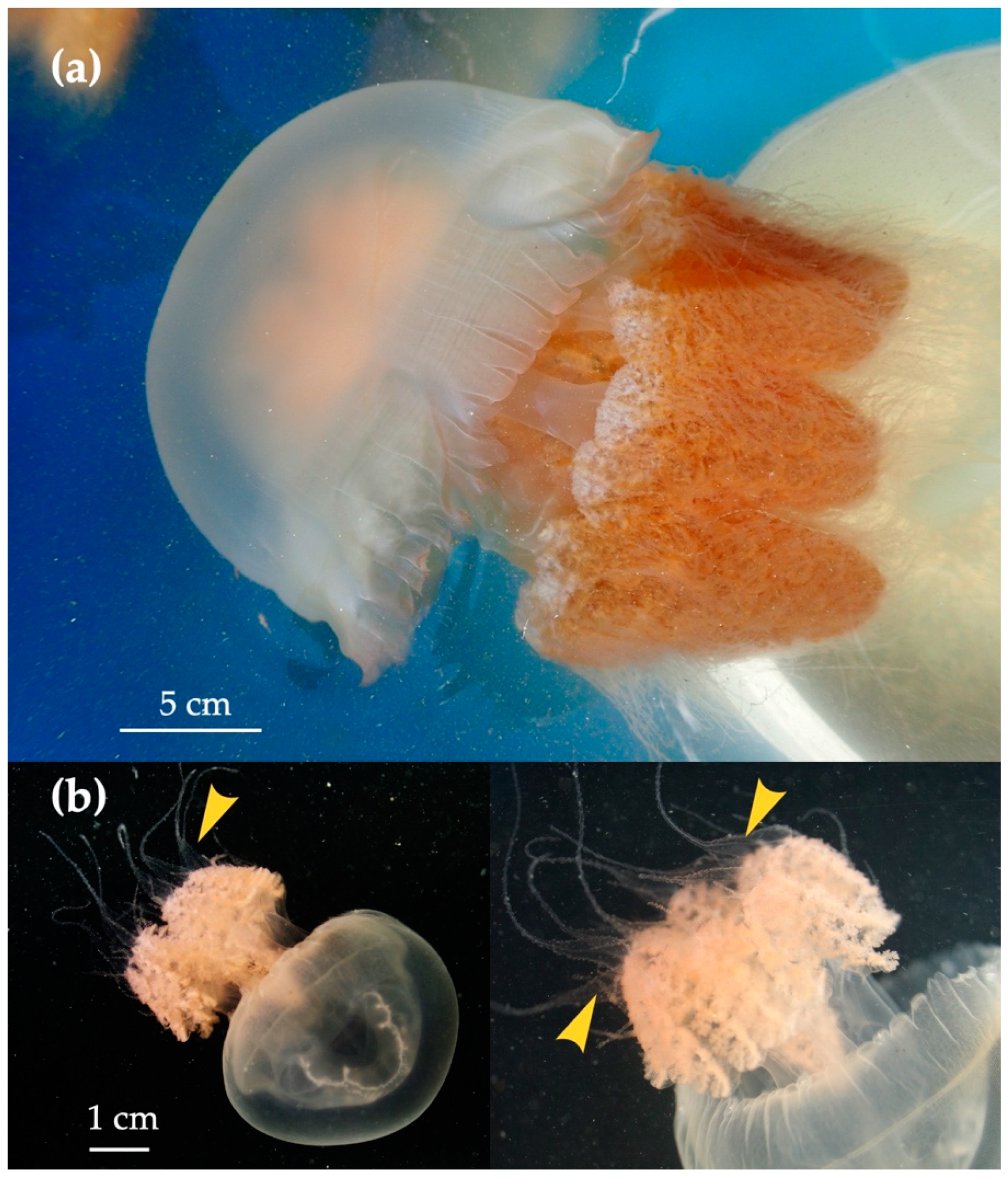
4.1. Medusa Stage
4.2. Planula Stage
4.3. Polyp Stage
4.4. Strobilation Stage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kingsford, M.J.; Pitt, K.A.; Gillanders, B.M. Management of jellyfish fisheries, with special reference to the order Rhizostomeae. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2000, 38, 85–156. [Google Scholar]
- Brotz, L. Jellyfish fisheries—A global assessment. In So Long, and Thanks for All the Fish: The Sea Around Us, 1999–2014—A Fifteen-Year Retrospective. A Sea Around Us Report to the Pew Charitable Trusts; Pauly, D., Zeller, D., Eds.; Sea Around Us, Fisheries Centre, The University of British Columbia: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2014; pp. 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Brotz, L.; Pauly, D. Studying Jellyfish Fisheries: Toward Accurate National Catch Reports and Appropriate Methods for Stock Assessments. Jellyfish: Ecology, Distribution Patterns and Human Interactions; Mariottini, G.L., Ed.; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 313–329. [Google Scholar]
- Brotz, L.; Schiariti, A.; Lopez-Martinez, J.; Alvarez-Tello, J.; Hsieh, Y.H.P.; Jones, R.P.; Quinones, J.; Dong, Z.J.; Morandini, A.C.; Preciado, M.; et al. Jellyfish fisheries in the Americas: Origin, state of the art, and perspectives on new fishing grounds. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2017, 27, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.; Hobson, V.; Tang, K.W. Balancing fishery and conservation: A case study of the barrel jellyfish Rhizostoma octopus in South Wales. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 74, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, M.; Omori, M. Synopsis of edible jellyfishes collected from Southeast Asia, with notes on jellyfish fisheries. Plankton Benthos Res. 2010, 5, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishikawa, J.; Ohtsuka, S.; Mulyadi; Mujiono, N.; Lindsay, D.J.; Miyamoto, H.; Nishida, S. A new species of the commercially harvested jellyfish Crambionella (Scyphozoa) from central Java, Indonesia with remarks on the fisheries. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2014, 95, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, J.; Thu, N.T.; Ha, T.M. Jellyfish fisheries in northern Vietnam. Plankton Benthos Res. 2008, 3, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Omori, M.; Nakano, E. Jellyfish fisheries in southeast Asia. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, J.; Thu, N.T.; Yusoff, F.; Lindsay, D.; Mulyadi, M.N.; Ohtsuka, S.; Nishida, S. Jellyfish fisheries in Southeast Asia with special reference to those in Vietnam, Indonesia and Malaysia. Kaiyo Mon. 2009, 41, 401–411. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa, J.; Srinui, K.; Otsuka, S.; Kondo, Y.; Miyake, H.; Lindsay, D.; Iida, A. Jellyfish fisheries in Thailand. Aquabiology 2019, 41, 13–18. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Khong, N.M.H.; Yusoff, F.M.; Jamilah, B.; Basri, M.; Maznah, I.; Chan, K.W.; Nishikawa, J. Nutritional composition and total collagen content of three commercially important edible jellyfish. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khong, N.M.H.; Yusoff, F.M.; Jamilah, B.; Basri, M.; Maznah, I.; Chan, K.W.; Armania, N.; Nishikawa, J. Improved collagen extraction from jellyfish (Acromitus hardenbergi) with increased physical-induced solubilization processes. Food Chem. 2018, 251, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, M.M.; Nishikawa, J.; Kuppan, P. Commercial jellyfish—A little known industry in Malaysia. Fishmail 2010, 18, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zulikha, N.Z.; Yusoff, F.M.; Nishikawa, J.; Arshad, A.; Matias-Peralta, H.M. Mesozooplankton composition and abundance in a tropical estuary during monsoon season. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 8, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nursuhayat, A.S.; Yusoff, F.M.; Shariff, M. Spatial and temporal distribution of phytoplankton in Perak estuary, Malaysia, during monsoon season. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 8, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wessel, P.; Luis, J.F.; Uieda, L.; Scharroo, R.; Wobbe, F.; Smith, W.H.F.; Tian, D. The generic mapping tools version 6. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2019, 20, 5556–5564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitt, K.A. Life history and settlement preferences of the edible jellyfish Catostylus mosaicus (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). Mar. Biol. 2000, 136, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Adachi, A.; Ikeda, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Ohtsuka, S.; Srinui, K.; Muthuwan, V.; Taleb, S.; Yusoff, F.M.; Metillo, E.; et al. New exhibitions of beautiful Southeast Asian jellyfish at aquaria: Collection and life cycle. In Proceedings of the 10th International Aquarium Congress, Fukushima, Japan, 7–10 November 2018; pp. 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Straehler-Pohl, I.; Widmer, C.L.; Morandini, A.C. Characterizations of juvenile stages of some semaeostome Scyphozoa (Cnidaria), with recognition of a new family (Phacellophoridae). Zootaxa 2011, 2741, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, L.; Jarms, G. New insights into reproductive traits of scyphozoans: Special methods of propagation in Sanderia malayensis Goette, 1886 (Pelagiidae, Semaeostomeae) enable establishing a new classification of asexual reproduction in the class Scyphozoa. Mar. Biol. 2009, 156, 1411–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiariti, A.; Morandini, A.C.; Jarms, G.; Paes, R.V.; Franke, S.; Mianzan, H. Asexual reproduction strategies and blooming potential in Scyphozoa. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 510, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamner, W.H.; Janssen, R.M. Growth, degrowth, and irreversible cell differentiation in Aurelia aurita. Am. Zool. 1974, 14, 833–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Z.L.; Shibata, M.; Makabe, R.; Ikeda, H.; Uye, S.I. Body size reduction under starvation, and the point of no return, in ephyrae of the moon jellyfish Aurelia aurita. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2014, 510, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldstein, J.; Riisgard, H.U. Population dynamics and factors controlling somatic degrowth of the common jellyfish, Aurelia aurita, in a temperate semi-enclosed cove (Kertinge Nor, Denmark). Mar. Biol. 2016, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, K.; Kawahara, M.; Ikeda, H.; Uye, S. Experimental induction of gonadal maturation and spawning in the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). Mar. Biol. 2007, 152, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.S.; Zhuang, Z.M.; Chen, S.Q.; Yan, J.P.; Liu, C.L.; Sun, J.M. A large-scale breeding experiment and observations on development of Cyanea nozakii (Scyphozoa, Cyaneidae) from fertilized eggs to larval medusae. Hydrobiologia 2015, 754, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N.; Nakajima, Y.; Koizumi, O.; Fujisawa, T.; Takahashi, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Deguchi, R. Neuropeptides trigger oocyte maturation and subsequent spawning in the hydrozoan jellyfish Cytaeis uchidae. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2013, 80, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, K.S.; Yasuda, A.; Murata, Y.; Kumakura, E.; Yamada, S.; Endo, N.; Nogata, Y. Quantitative effects of pycnocline and dissolved oxygen on vertical distribution of moon jellyfish Aurelia aurita s.l.: A case study of Mikawa Bay, Japan. Hydrobiologia 2016, 766, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Kakinuma, Y. Adaptive ability of two scyphomedusae to their salinity environment. Kaiyo Mon. 2009, 41, 393–400. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Graham, W.M.; Pages, F.; Hamner, W.M. A physical context for gelatinous zooplankton aggregations: A review. Hydrobiologia 2001, 451, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, C.L. How to Keep Jellyfish in Aquariums: An Introductory Guide for Maintaining Healthy Jellies; Wheatmark: Tucson, AZ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara, M.; Uye, S.; Ohtsu, K.; Iizumi, H. Unusual population explosion of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) in East Asian waters. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2006, 307, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, K.; Ma, C.H.; Gao, H.W.; Li, F.Q.; Zhang, M.Z.; Qiu, Y.T.; Wang, B. Research on the jellyfish (Rhopilema esculentum Kishinouye) and associated aquaculture techniques in China: Current status. Aquac. Int. 2007, 15, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, D.R. Life-history of the cannonball jellyfish, Stomolophus meleagris L Agassiz, 1860 (Scyphozoa, Rhizostomida). Biol. Bull. 1982, 162, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kienberger, K.; Riera-Buch, M.; Schönemann, A.M.; Bartsch, V.; Halbauer, R.; Prieto, L. First description of the life cycle of the jellyfish Rhizostoma luteum (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiariti, A.; Kawahara, M.; Uye, S.; Mianzan, H.W. Life cycle of the jellyfish Lychnorhiza lucerna (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae). Mar. Biol. 2008, 156, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, M.; Uye, S. Effects of low salinity on the physiological ecology of planulae and polyps of scyphozoans in the East Asian Marginal Seas: Potential impacts of monsoon rainfall on medusa population size. Hydrobiologia 2018, 815, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikinger, R. Cotylorhiza tuberculata (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa)—Life history of a stationary population. Mar. Ecol. 1992, 13, 333–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, D.K.; Fitt, W.K.; Fleck, J. Checkpoints in the life-cycle of Cassiopea spp.: Control of metagenesis and metamorphosis in a tropical jellyfish. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 1996, 40, 331–338. [Google Scholar]
- Toshino, S.; Miyake, H.; Ohtsuka, S.; Okuizumi, K.; Adachi, A.; Hamatsu, Y.; Urata, M.; Nakaguchi, K.; Yamaguchi, S. Development and polyp formation of the giant box jellyfish Morbakka virulenta (Kishinouye, 1910) (Cnidaria: Cubozoa) collected from the Seto Inland Sea, western Japan. Plankton Benthos Res. 2013, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Underwood, A.H.; Straehler-Pohl, I.; Carrette, T.J.; Sleeman, J.; Seymour, J.E. Early life history and metamorphosis in Malo maxima Gershwin, 2005 (Carukiidae, Cubozoa, Cnidaria). Plankton Benthos Res. 2018, 13, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyake, H.; Hashimoto, J.; Chikuchishin, M.; Miura, T. Scyphopolyps of Sanderia malayensis and Aurelia aurita attached to the tubes of vestimentiferan tube worm, Lamellibrachia satsuma, at submarine fumaroles in Kagoshima Bay. Mar. Biotechnol. 2004, 6, S174–S178. [Google Scholar]
- Thein, H.; Ikeda, H.; Uye, S. The potential role of podocysts in perpetuation of the common jellyfish Aurelia aurita s.l. (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) in anthropogenically perturbed coastal waters. Hydrobiologia 2012, 690, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, H.; Ohtsu, K.; Uye, S.I. Fine structure, histochemistry, and morphogenesis during excystment of the podocysts of the giant jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai (Scyphozoa, Rhizostomeae). Biol. Bull. 2011, 221, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.S.; Suzuki, K.W.; Kumakura, E.; Sato, K.; Oe, Y.; Sato, T.; Sawada, H.; Masuda, R.; Nogata, Y. Seasonal alternation of the ontogenetic development of the moon jellyfish Aurelia coerulea in Maizuru Bay, Japan. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Ikeguchi, S.-i.; Takayama, K.; Yoshikawa, M.; Arima, S.; Suzuki, N. On the moon jelly which develops to ephyra directly from planula. Aquabiology 2019, 41, 54–59. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda, T. Ecological studies on the jelly-fish, Aurelia aurita (L.), in Urazoko Bay, Fukui prefecture—XI. An observation on ephyra formation. Publ. Seto Mar. Lab. 1975, 22, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takauchi, S.; Miyake, H.; Hirata, N.; Nagai, M.; Suzuki, N.; Ogiso, S.; Ikeguchi, S. Morphological characteristics of ephyrae of Aurelia coerulea derived from planula strobilation. Fish. Sci. under review.


| Transect Line | Temperature (°C) | Salinity | Distance from LP3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| LP1 | 29.1–29.3 | 0.1–0.5 | 10 km |
| LP2 | 29.0–29.3 | 0.5–3.5 | 3.5 km |
| LP3 | 28.7–29.2 | 2.0–10.0 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miyake, H.; Honda, S.; Nishikawa, J.; Yusoff, F.M. Life Cycle of Edible Jellyfish Acromitus hardenbergi Stiasny, 1934 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) Inhabiting a Brackish-Water Environment. Animals 2021, 11, 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072138
Miyake H, Honda S, Nishikawa J, Yusoff FM. Life Cycle of Edible Jellyfish Acromitus hardenbergi Stiasny, 1934 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) Inhabiting a Brackish-Water Environment. Animals. 2021; 11(7):2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072138
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiyake, Hiroshi, Shiho Honda, Jun Nishikawa, and Fatimah Md. Yusoff. 2021. "Life Cycle of Edible Jellyfish Acromitus hardenbergi Stiasny, 1934 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) Inhabiting a Brackish-Water Environment" Animals 11, no. 7: 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072138
APA StyleMiyake, H., Honda, S., Nishikawa, J., & Yusoff, F. M. (2021). Life Cycle of Edible Jellyfish Acromitus hardenbergi Stiasny, 1934 (Scyphozoa: Rhizostomeae) Inhabiting a Brackish-Water Environment. Animals, 11(7), 2138. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11072138






