Peptidomics Analysis of Virulent Peptides Involved in Streptococcus suis Pathogenesis
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. Preparation of Peptidome
2.3. LC-MS/MS
2.4. Peptidomic Data Analysis
3. Results
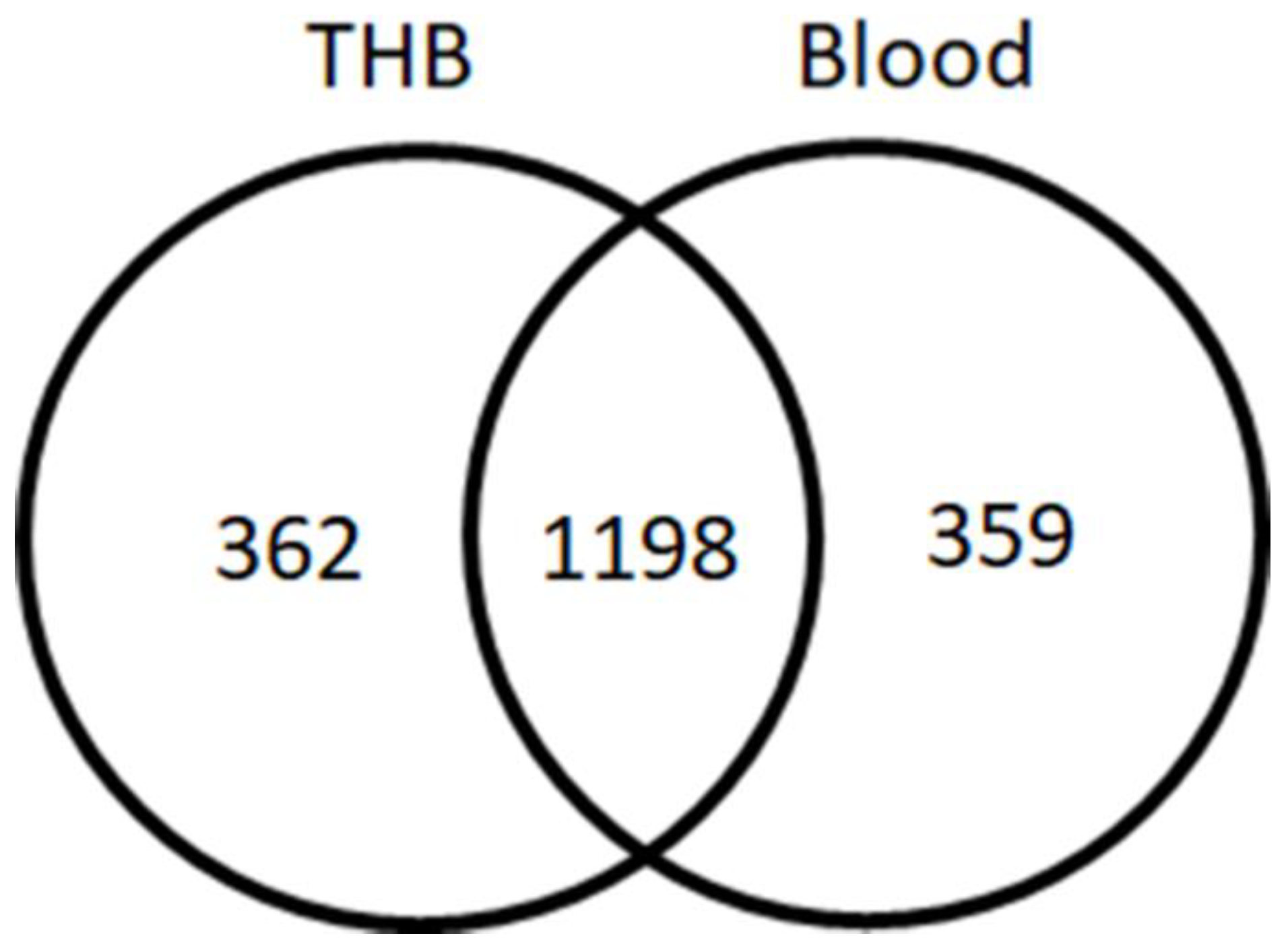
Peptidomic Analysis by LC-MS/MS
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Staats, J.J.; Feder, I.; Okwumabua, O.; Chengappa, M.M. Streptococcus suis: Past and present. Vet. Res. Commun. 1997, 21, 381–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdacs, M.; Nemeth, A.; Knausz, M.; Barrak, I.; Stajer, A.; Mestyan, G.; Melegh, S.; Nyul, A.; Toth, A.; Agoston, Z.; et al. Streptococcus suis: An Underestimated Emerging Pathogen in Hungary? Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baums, C.G.; Valentin-Weigand, P. Surface-associated and secreted factors of Streptococcus suis in epidemiology, pathogenesis and vaccine development. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2009, 10, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, A.A.; Loeffen, P.L.; van den Berg, A.J.; Storm, P.K. Identification, purification, and characterization of a thiol-activated hemolysin (suilysin) of Streptococcus suis. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 1742–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, H.E.; Damman, M.; van der Velde, J.; Wagenaar, F.; Wisselink, H.J.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Smits, M.A. Identification and characterization of the cps locus of Streptococcus suis serotype 2: The capsule protects against phagocytosis and is an important virulence factor. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Llarena, F.J.; Bou, G. Proteomics as a Tool for Studying Bacterial Virulence and Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.J.; Wang, A.H.J.; Jennings, M.P. Discovery of virulence factors of pathogenic bacteria. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2008, 12, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatellier, S.; Harel, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gottschalk, M.; Higgins, R.; Devriese, L.A.; Brousseau, R. Phylogenetic diversity of Streptococcus suis strains of various serotypes as revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequence comparison. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1998, 48 Pt 2, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.; Cloos, J. Cell sensitivity assays: The MTT assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 731, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiden, C.; Jaresitthikunchai, J.; Kerdsin, A.; Meekhanon, N.; Roytrakul, S.; Nuanualsuwan, S. Streptococcus suis serotyping by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardou, P.; Mariette, J.; Escudie, F.; Djemiel, C.; Klopp, C. jvenn: An interactive Venn diagram viewer. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Santos, A.; von Mering, C.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P.; Kuhn, M. STITCH 5: Augmenting protein-chemical interaction networks with tissue and affinity data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D380–D384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Segura, M.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basavanna, S.; Khandavilli, S.; Yuste, J.; Cohen, J.M.; Hosie, A.H.; Webb, A.J.; Thomas, G.H.; Brown, J.S. Screening of Streptococcus pneumoniae ABC transporter mutants demonstrates that LivJHMGF, a branched-chain amino acid ABC transporter, is necessary for disease pathogenesis. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 3412–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sato, Y.; Okamoto-Shibayama, K.; Azuma, T. The malQ gene is essential for starch metabolism in Streptococcus mutans. J. Oral Microbiol. 2013, 5, 21285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Khemlani, A.; Lorenz, N.; Loh, J.M.; Langley, R.J.; Proft, T. Streptococcal 5′-Nucleotidase A (S5nA), a Novel Streptococcus pyogenes Virulence Factor That Facilitates Immune Evasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 31126–31137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, P.; Pian, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Xie, W.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, Y. Streptococcus suis adenosine synthase functions as an effector in evasion of PMN-mediated innate immunit. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thammavongsa, V.; Kern, J.W.; Missiakas, D.M.; Schneewind, O. Staphylococcus aureus synthesizes adenosine to escape host immune responses. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 2417–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chuang-Smith, O.N.; Frank, K.L.; Guenther, B.D.; Kern, M.; Schlievert, P.M.; Herzberg, M.C. Ecto-5′-nucleotidase: A candidate virulence factor in Streptococcus sanguinis experimental endocarditis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Du, N.; Ma, S.; Hu, Q.; Lu, G.; Chen, W.; Zeng, C. In vitro transcriptome analysis of two Chinese isolates of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2014, 12, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrando, M.L.; van Baarlen, P.; Orru, G.; Piga, R.; Bongers, R.S.; Wels, M.; De Greeff, A.; Smith, H.E.; Wells, J.M. Carbohydrate availability regulates virulence gene expression in Streptococcus suis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rameshwaram, N.R.; Singh, P.; Ghosh, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S. Lipid metabolism and intracellular bacterial virulence: Key to next-generation therapeutics. Future Microbiol. 2018, 13, 1301–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazaei, C. Mycobacterium tuberculosis and lipids: Insights into molecular mechanisms from persistence to virulence. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2018, 23, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yuan, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhou, D.; Yang, K.; Duan, Z.; Guo, R.; Liang, W.; Hu, Q.; et al. MnmE, a Central tRNA-Modifying GTPase, Is Essential for the Growth, Pathogenicity, and Arginine Metabolism of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yuan, F.; Liu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhou, D.; Yang, K.; Guo, R.; Liang, W.; Zou, G.; Zhou, R.; et al. Proteomic and Metabolomic Analyses Provide Insights into the Mechanism on Arginine Metabolism Regulated by tRNA Modification Enzymes GidA and MnmE of Streptococcus suis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 597408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Shang, K.; Huang, J.; Ran, W.; Kashif, J.; Wang, L. Overexpression of an ABC transporter and mutations of GyrA, GyrB, and ParC in contributing to high-level ciprofloxacin resistance in Streptococcus suis type 2. Biosci. Trends 2014, 8, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Garch, F.; Lismond, A.; Piddock, L.J.; Courvalin, P.; Tulkens, P.M.; Van Bambeke, F. Fluoroquinolones induce the expression of patA and patB, which encode ABC efflux pumps in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob Chemother 2010, 65, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.B.; Chen, J.Q.; Zhao, Y.L.; Bai, J.W.; Ding, W.Y.; Zhou, Y.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.H. Sub-MICs of Azithromycin Decrease Biofilm Formation of Streptococcus suis and Increase Capsular Polysaccharide Content of S. suis. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grauslund, M.; Didion, T.; Kielland-Brandt, M.C.; Andersen, H.A. BAP2, a gene encoding a permease for branched-chain amino acids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1269, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, K.; Myers, A.R.; Pisithkul, T.; Claas, K.R.; Satyshur, K.A.; Amador-Noguez, D.; Keck, J.L.; Wang, J.D. Molecular mechanism and evolution of guanylate kinase regulation by (p)ppGpp. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 735–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ye, C.; Bai, X.; Zhang, J.; Jing, H.; Zheng, H.; Du, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, S.; Jin, D.; Xu, Y.; et al. Spread of Streptococcus suis sequence type 7, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurung, M.; Tamang, M.D.; Moon, D.C.; Kim, S.R.; Jeong, J.H.; Jang, G.C.; Jung, S.C.; Park, Y.H.; Lim, S.K. Molecular Basis of Resistance to Selected Antimicrobial Agents in the Emerging Zoonotic Pathogen Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2332–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, T.L.; Waack, U.; Anderson, T.K.; Bayles, D.O.; Zaia, S.R.; Goertz, I.; Eppinger, M.; Hau, S.J.; Brockmeier, S.L.; Shore, S.M. Comparative Virulence and Genomic Analysis of Streptococcus suis Isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 620843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.M.; Coker, A.R.; Fossati, G.; Mascagni, P.; Coates, A.R.; Wood, S.P. Mycobacterium tuberculosis chaperonin 10 heptamers self-associate through their biologically active loops. J. Bacteriol. 2003, 185, 4172–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, D.; Liu, M.; Yang, X.; Zong, B.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Bei, W.; Tan, C. Effect of the glycosyltransferases on the capsular polysaccharide synthesis of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 185, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecht, U.; Wisselink, H.J.; Jellema, M.L.; Smith, H.E. Identification of two proteins associated with virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 3156–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prados de la Torre, E.; Rodriguez-Franco, A.; Rodriguez-Ortega, M.J. Proteomic and Bioinformatic Analysis of Streptococcus suis Human Isolates: Combined Prediction of Potential Vaccine Candidates. Vaccines 2020, 8, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pian, Y.; Wang, P.; Liu, P.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, B.; Yuan, Y.; Jiang, Y. Proteomics identification of novel fibrinogen-binding proteins of Streptococcus suis contributing to antiphagocytosis. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, T.; Tan, M.; Liu, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, L.; Zhu, J.; Li, L.; Zhou, R. GidA, a tRNA Modification Enzyme, Contributes to the Growth, and Virulence of Streptococcus suis Serotype 2. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Locus | Annotated Protein Function (Amino-Acid Length) | Function or Subcellular Location |
|---|---|---|
| SSU05_2116 | 5′-nucleotidase/2′,3′-cyclic phosphodiesterase and related esterases (448) | nucleotide catabolic activity |
| SSU05_2039 | transcriptional regulator (149) | DNA-binding transcription factor activity |
| N/A | α-1,4 glucan phosphorylase (755) | carbohydrate metabolism |
| SSU05_1489 | K01223 6-phospho-beta-glucosidase [EC-3.2.1.86] (474) | carbohydrate metabolism |
| SSU05_0392 | 4-α-glucanotransferase (364) | carbohydrate metabolism |
| SSU05_1803 | 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (244) | fatty acid biosynthesis |
| SSU05_2063 | PTS system ascorbate-specific transporter subunit IIC (482) | cell membrane/membrane |
| SSU05_1254 | ABC transporter permease (197) | transmembrane transporter |
| SSU05_1106 | ABC-type phosphate transport system (83) | periplasmic component |
| SSU05_0780 | branched-chain amino acid permease (188) | cell membrane/membrane |
| gmk | guanylate kinase (216) | GMP recycling |
| tetM | TetM (639) | response to antibiotic |
| groS | 10 kDa chaperonin (102) | ATPase activity |
| SSU05_0642 | putative low-temperature requirement A (371) | transmembrane protein |
| cps2J | Cps2J (332) | capsular biosynthesis |
| mrp | truncated MRP (1261) | secreted protein |
| rpsB | 30S ribosomal protein S2 (258) | ribosomal protein |
| SSU05_1457 | hypothetical protein (91) | |
| SSU05_0461 | hypothetical protein (567) | |
| SSU05_1869 | hypothetical protein (178) | |
| SSU05_0141 | hypothetical protein (318) | |
| SSU05_1991 | hypothetical protein (412) |
| Identified Protein | S. suis Serotype | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virulent | Non-Virulent | |||||
| 2 | 14 | 7 | 9 | 25 | 27 | |
| 5′-nucleotidase/2′,3′-cyclic phosphodiesterase and related esterases | + | + | + | |||
| transcriptional regulator | + | + | ||||
| α-1,4 glucan phosphorylase | + | + | ||||
| K01223 6-phospho-beta-glucosidase [EC-3.2.1.86] | + | + | + | |||
| 4-α-glucanotransferase | + | |||||
| 3-oxoacyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase | + | + | + | + | ||
| PTS system ascorbate-specific transporter subunit IIC | + | + | ||||
| ABC transporter permease | + | + | ||||
| ABC-type phosphate transport system | + | + | ||||
| branched-chain amino acid permease | + | |||||
| guanylate kinase | + | + | + | + | + | |
| TetM | + | + | + | |||
| 10 kDa chaperonin | + | |||||
| putative low-temperature requirement A | + | |||||
| Cps2J | + | |||||
| truncated MRP | + | |||||
| 30S ribosomal protein S2 | + | + | ||||
| SSU05_1457 hypothetical protein | + | |||||
| SSU05_0461 hypothetical protein | + | |||||
| SSU05_1869 hypothetical protein | + | + | ||||
| SSU05_0141 hypothetical protein | + | |||||
| SSU05_1991 hypothetical protein | + | + | + | + | ||
| Sum | 7 | 9 | 9 | 5 | 9 | 6 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaiden, C.; Jaresitthikunchai, J.; Phaonakrop, N.; Roytrakul, S.; Kerdsin, A.; Nuanualsuwan, S. Peptidomics Analysis of Virulent Peptides Involved in Streptococcus suis Pathogenesis. Animals 2021, 11, 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092480
Chaiden C, Jaresitthikunchai J, Phaonakrop N, Roytrakul S, Kerdsin A, Nuanualsuwan S. Peptidomics Analysis of Virulent Peptides Involved in Streptococcus suis Pathogenesis. Animals. 2021; 11(9):2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092480
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaiden, Chadaporn, Janthima Jaresitthikunchai, Narumon Phaonakrop, Sittiruk Roytrakul, Anusak Kerdsin, and Suphachai Nuanualsuwan. 2021. "Peptidomics Analysis of Virulent Peptides Involved in Streptococcus suis Pathogenesis" Animals 11, no. 9: 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092480
APA StyleChaiden, C., Jaresitthikunchai, J., Phaonakrop, N., Roytrakul, S., Kerdsin, A., & Nuanualsuwan, S. (2021). Peptidomics Analysis of Virulent Peptides Involved in Streptococcus suis Pathogenesis. Animals, 11(9), 2480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani11092480






