Investigation of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3) Disease Periods and Factors Influencing CyHV-3 Transmission in A Low Stocking Density Infection Trial
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish and Virus
2.2. Trial 1: Disease Periods Trial
2.3. Trial 2: Direct and Indirect Contact Trial
2.4. Nucleic Acid Purification and Detection of CyHV-3 by qPCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Trial 1: Disease Periods Trial
3.2. Trial 2: Direct and Indirect Contact Trial
3.2.1. Transmission
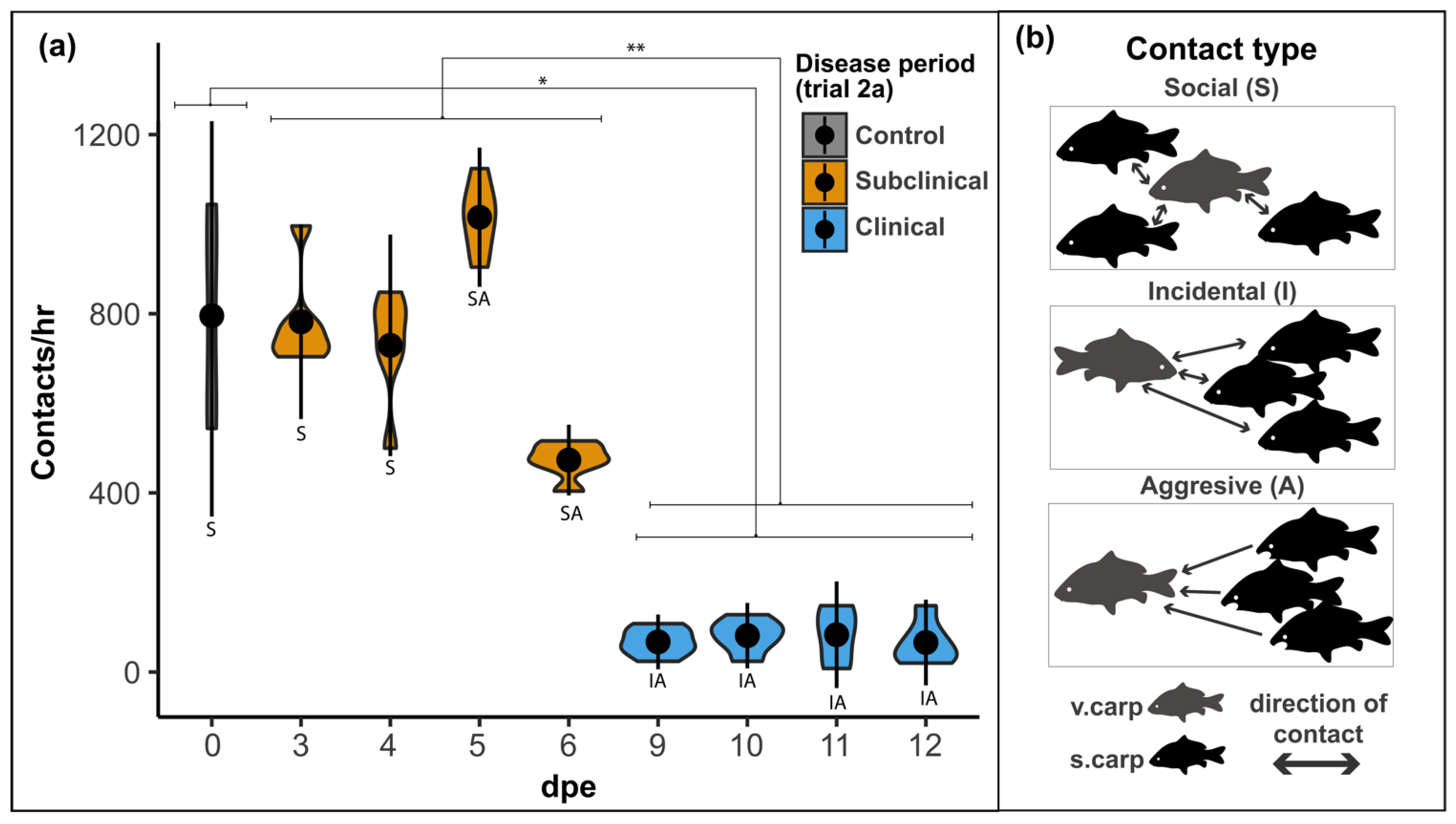
3.2.2. Contact Rate
3.2.3. Viral Load
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hedrick, R.P.; Gilad, O.; Yun, S.; Spangenberg, J.V.; Marty, G.D.; Nordhausen, R.W.; Kebus, M.J.; Bercovier, H.; Eldar, A. A Herpesvirus Associated with Mass Mortality of Juvenile and Adult Koi, a Strain of Common Carp. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2000, 12, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretzinger, A.C.; Fischer-Scherl, T.; Oumouna, M.; Hoffmann, R.; Truyen, U. Mass Mortalities in Koi. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 1999, 9, 182–185. [Google Scholar]
- Haenen, O.L.M.; Way, K.; Bergmann, S.M.; Ariel, E. The emergence of koi herpesvirus and its significance to European aquaculture. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2004, 24, 293–307. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.; Weng, M.-C.; Shiau, J.-R.; Lin, S.-Y. Detection of Koi Herpesvirus in Koi Cyprinus carpio in Taiwan. Fish Pathol. 2004, 39, 109–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, K.; Sano, M.; Kurita, J.; Ito, T.; Iida, T. Improvement of a PCR Method with the Sph I-5 Primer Set for the Detection of Koi Herpesvirus (KHV). Fish Pathol. 2005, 40, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.; Ito, T.; Kurita, J.; Miwa, S.; Iida, T. Diagnosis of koi herpesvirus (KHV) disease in Japan. Bull. Fish. Res. Agen Suppl. No 2005, 2, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- World Organization for Animal Health (OIE). Manual of Diagnostic Tests for Aquatic Animals, 7th ed.; 2018; Chapter 2.3.7. Infection with koi Herpesvirus. Available online: http://www.oie.int/standard-setting/aquatic-manual/acccess-online (accessed on 5 August 2019).
- Ababneh, M.; Hananeh, W.; Alzghoul, M. Mass Mortality Associated with Koi Herpesvirus in Common Carp in Iraq. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunarto, A.; Rukyani, A.; Itami, T. Indonesian experience on the outbreak of koi herpesvirus in koi and carp (Cyprinus carpio). Bull. Fish. Res. Agency 2005, 2, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- McColl, K.A.; Sunarto, A. Biocontrol of the Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio) in Australia: A Review and Future Directions. Fishes 2020, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thresher, R.E.; Allman, J.; Stremick-Thompson, L. Impacts of an Invasive Virus (CyHV-3) on Established Invasive Populations of Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio) in North America. Biol. Invasions 2018, 20, 1703–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhi, S.K.; Tolo, I.; McEachran, M.; Primus, A.; Mor, S.K.; Phelps, N.B.D. Koi Herpesvirus and Carp Oedema Virus: Infections and Coinfections during Mortality Events of Wild Common Carp in the United States. J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolo, I.E.; Padhi, S.K.; Williams, K.; Singh, V.; Halvorson, S.; Mor, S.K.; Phelps, N.B.D. Susceptibility of Pimephales promelas and Carassius auratus to a Strain of Koi Herpesvirus Isolated from Wild Cyprinus Carpio in North America. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waltzek, T.; Kelley, G.; Alfaro, M.; Kurobe, T.; Davison, A.; Hedrick, R. Phylogenetic Relationships in the Family Alloherpesviridae. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2009, 84, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, C.; Palmeiro, B. Selected Emerging Infectious Diseases of Ornamental Fish. Vet. Clin. North Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2013, 16, 261–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.L.; Mullis, L.; LaPatra, S.E.; Groff, J.M.; Goodwin, A. Detection of Koi Herpesvirus DNA in Tissues of Infected Fish. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.-J.; Jung, S.-J.; Choi, T.-J.; Kim, H.-R.; Rajendran, K.V.; Kim, Y.-J.; Park, M.-A.; Chun, S.-K. A Viral Disease Occurring in Cultured Carp Cyprinus Carpio in Korea. Fish Pathol. 2001, 36, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gilad, O.; Yun, S.; Zagmutt-Vergara, F.; Leutenegger, C.; Bercovier, H.; Hedrick, R. Concentrations of a Koi Herpesvirus (KHV) in Tissues of Experimentally-Infected Cyprinus Carpio Koi as Assessed by Real-Time TaqMan PCR. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2004, 60, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, S.; Kiryu, I.; Yuasa, K.; Ito, T.; Kaneko, T. Pathogenesis of Acute and Chronic Diseases Caused by Cyprinid Herpesvirus-3. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 695–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilad, O.; Yun, S.; Adkison, M.A.; Way, K.; Willits, N.H.; Bercovier, H.; Hedrick, R.P. Molecular Comparison of Isolates of an Emerging Fish Pathogen, Koi Herpesvirus, and the Effect of Water Temperature on Mortality of Experimentally Infected Koi. J. Gen. Virol. 2003, 84, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, K.; Ito, T.; Sano, M. Effect of Water Temperature on Mortality and Virus Shedding in Carp Experimentally Infected with Koi Herpesvirus. Fish Pathol. 2008, 43, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakus, K.; Ouyang, P.; Boutier, M.; Ronsmans, M.; Reschner, A.; Vancsok, C.; Jazowiecka-Rakus, J.; Vanderplasschen, A. Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3: An Interesting Virus for Applied and Fundamental Research. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cano, I.; Mulhearn, B.; Akter, S.; Paley, R. Seroconversion and Skin Mucosal Parameters during Koi Herpesvirus Shedding in Common Carp, Cyprinus Carpio. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St-Hilaire, S.; Beevers, N.; Way, K.; Le Deuff, R.; Martin, P.; Joiner, C. Reactivation of Koi Herpesvirus Infections in Common Carp Cyprinus Carpio. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2005, 67, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Chen, S.; Russell, D.S.; Löhr, C.V.; Milston-Clements, R.; Song, T.; Miller-Morgan, T.; Jin, L. Analysis of Stress Factors Associated with KHV Reactivation and Pathological Effects from KHV Reactivation. Virus Res. 2017, 240, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.-R.; Bently, J.; Beck, L.; Reed, A.; Miller-Morgan, T.; Heidel, J.R.; Kent, M.L.; Rockey, D.D.; Jin, L. Analysis of Koi Herpesvirus Latency in Wild Common Carp and Ornamental Koi in Oregon, USA. J. Virol. Methods 2013, 187, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandín, I.; Dopazo, C.P. Host Range, Host Specificity and Hypothesized Host Shift Events among Viruses of Lower Vertebrates. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boutier, M.; Donohoe, O.; Kopf, R.K.; Humphries, P.; Becker, J.A.; Marshall, J.; Vanderplasschen, A. Biocontrol of Carp: The Australian Plan Does Not Stand Up to a Rational Analysis of Safety and Efficacy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.M.; Sadowski, J.; Kiełpiński, M.; Bartłomiejczyk, M.; Fichtner, D.; Riebe, R.; Lenk, M.; Kempter, J. Susceptibility of Koi × Crucian Carp and Koi × Goldfish Hybrids to Koi Herpesvirus (KHV) and the Development of KHV Disease (KHVD). J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Matbouli, M.; Soliman, H. Transmission of Cyprinid Herpesvirus-3 (CyHV-3) from Goldfish to Naïve Common Carp by Cohabitation. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 536–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempter, J.; Kielpinski, M.; Panicz, R.; Sadowski, J.; Myslowski, B.; Bergmann, S.M. Horizontal transmission of koi herpes virus (KHV) from potential vector species to common carp. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2012, 32, 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Fabian, M.; Baumer, A.; Steinhagen, D. Do Wild Fish Species Contribute to the Transmission of Koi Herpesvirus to Carp in Hatchery Ponds? J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, K.; Sano, M.; Oseko, N. Goldfish Is Not a Susceptible Host of Koi Herpesvirus (KHV) Disease. Fish Pathol. 2013, 48, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- McColl, K.A.; Sunarto, A.; Slater, J.; Bell, K.; Asmus, M.; Fulton, W.; Hall, K.; Brown, P.; Gilligan, D.; Hoad, J.; et al. Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 as a Potential Biological Control Agent for Carp (Cyprinus Carpio) in Australia: Susceptibility of Non-Target Species. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 1141–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kwon, S.R.; Olesen, N.J.; Yuasa, K. The Susceptibility of Silver Crucian Carp (Carassius Auratus Langsdorfii) to Infection with Koi Herpesvirus (KHV). J. Fish Dis. 2019, 42, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, S.M.; Kempter, J. Detection of koi herpesvirus (KHV) after re-activation in persistently infected common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) using non-lethal sampling methods. Bull. Eur. Assoc. Fish Pathol. 2011, 31, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Uchii, K.; Minamoto, T.; Honjo, M.N.; Kawabata, Z. Seasonal Reactivation Enables Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 to Persist in a Wild Host Population. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 87, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, O.; Yun, S.; Andree, K.; Adkison, M.; Zlotkin, A.; Bercovier, H.; Eldar, A.; Hedrick, R. Initial Characteristics of Koi Herpesvirus and Development of a Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay to Detect the Virus in Koi, Cyprinus Carpio Koi. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2002, 48, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, N.G.H.; Norman, R.A.; Way, K.; Peeler, E.J. Modelling the Koi Herpesvirus (KHV) Epidemic Highlights the Importance of Active Surveillance within a National Control Policy: Modelling KHV Control Options. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 48, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Meza, O.A.; Loza-Rubio, E.; Martínez-Maya, J.J.; García-Espinosa, G. The First Detection of Koi Herpesvirus (Cy HV 3) in Migratory Wild Ducks in North America. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2020, 32, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, N.G.H.; Way, K.; Jeffery, K.R.; Peeler, E.J. The Role of Live Fish Movements in Spreading Koi Herpesvirus throughout England and Wales: The Spread of KHV by Fish Movements. J. Fish Dis. 2010, 33, 1005–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutier, M.; Ronsmans, M.; Rakus, K.; Jazowiecka-Rakus, J.; Vancsok, C.; Morvan, L.; Peñaranda, M.M.D.; Stone, D.M.; Way, K.; van Beurden, S.J.; et al. Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3. In Advances in Virus Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 93, pp. 161–256. [Google Scholar]
- Pikarsky, E.; Ronen, A.; Abramowitz, J.; Levavi-Sivan, B.; Hutoran, M.; Shapira, Y.; Steinitz, M.; Perelberg, A.; Soffer, D.; Kotler, M. Pathogenesis of Acute Viral Disease Induced in Fish by Carp Interstitial Nephritis and Gill Necrosis Virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 9544–9551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costes, B.; Raj, V.S.; Michel, B.; Fournier, G.; Thirion, M.; Gillet, L.; Mast, J.; Lieffrig, F.; Bremont, M.; Vanderplasschen, A. The Major Portal of Entry of Koi Herpesvirus in Cyprinus Carpio Is the Skin. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 2819–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamek, M.; Syakuri, H.; Harris, S.; Rakus, K.Ł.; Brogden, G.; Matras, M.; Irnazarow, I.; Steinhagen, D. Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 Infection Disrupts the Skin Barrier of Common Carp (Cyprinus Carpio, L.). Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutier, M.; Ronsmans, M.; Ouyang, P.; Fournier, G.; Reschner, A.; Rakus, K.; Wilkie, G.S.; Farnir, F.; Bayrou, C.; Lieffrig, F.; et al. Rational Development of an Attenuated Recombinant Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 Vaccine Using Prokaryotic Mutagenesis and In Vivo Bioluminescent Imaging. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1004690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dishon, A.; Davidovich, M.; Ilouze, M.; Kotler, M. Persistence of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 in Infected Cultured Carp Cells. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4828–4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, T.; Kuzuya, Y.; Yasumoto, S.; Yasuda, M.; Kobayashi, T. Histopathological and Ultrastructural Features of Koi Herpesvirus (KHV)-Infected Carp Cyprinus Carpio, and the Morphology and Morphogenesis of KHV. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2008, 80, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilouze, M.; Dishon, A.; Kotler, M. Coordinated and Sequential Transcription of the Cyprinid Herpesvirus-3 Annotated Genes. Virus Res. 2012, 169, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, G.; Boutier, M.; Stalin Raj, V.; Mast, J.; Parmentier, E.; Vandewalle, P.; Peeters, D.; Lieffrig, F.; Farnir, F.; Gillet, L.; et al. Feeding Cyprinus Carpio with Infectious Materials Mediates Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 Entry through Infection of Pharyngeal Periodontal Mucosa. Vet. Res. 2012, 43, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaghan, S.J.; Thompson, K.D.; Adams, A.; Bergmann, S.M. Sensitivity of Seven PCRs for Early Detection of Koi Herpesvirus in Experimentally Infected Carp, Cyprinus Carpio L., by Lethal and Non-Lethal Sampling Methods. J. Fish Dis. 2015, 38, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, V.; Fournier, G.; Rakus, K.; Ronsmans, M.; Ouyang, P.; Michel, B.; Delforges, C.; Costes, B.; Farnir, F.; Leroy, B.; et al. Skin Mucus of Cyprinus Carpio Inhibits Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 Binding to Epidermal Cells. Vet. Res. 2011, 42, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swee, U.B.; McCrimmon, H.R. Reproductive Biology of the Carp, Cyprinus Carpio L., in Lake St. Lawrence, Ontario. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 1966, 95, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchii, K.; Telschow, A.; Minamoto, T.; Yamanaka, H.; Honjo, M.N.; Matsui, K.; Kawabata, Z. Transmission Dynamics of an Emerging Infectious Disease in Wildlife through Host Reproductive Cycles. ISME J. 2011, 5, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelberg, A.; Smirnov, M.; Hutoran, M.; Diamant, A.; Bejerano, Y.; Kotler, M. Epidemilogical description of a new viral disease afflicting cultured Cyprinus carpio in Israel. Isr. J. Aquac. 2003, 55, 5–12. [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu, T.; Yoshida, N.; Kasai, H.; Yoshimizu, M. Survival of Koi Herpesvirus (KHV) in Environmental Water. Fish Pathol. 2006, 41, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haramoto, E.; Kitajima, M.; Katayama, H.; Ito, T.; Ohgaki, S. Development of virus concentration methods for detection of koi herpesvirus in water. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honjo, M.N.; Minamoto, T.; Matsui, K.; Uchii, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Suzuki, A.A.; Kohmatsu, Y.; Iida, T.; Kawabata, Z. Quantification of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 in Environmental Water by Using an External Standard Virus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamoto, T.; Honjo, M.N.; Uchii, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Suzuki, A.A.; Kohmatsu, Y.; Iida, T.; Kawabata, Z. Detection of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 DNA in River Water during and after an Outbreak. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, T.; Honjo, M.N.; Yamanaka, H.; Tanaka, N.; Itayama, T.; Kawabata, Z. Detection of Cyprinid Herpesvirus-3 DNA in Lake Plankton. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 530–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reno, P.W. Factors involved in the dissemination of disease in fish populations. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1998, 10, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bebak-Williams, J.; McAllister, P.E.; Smith, G.; Boston, R. Effect of Fish Density and Number of Infectious Fish on the Survival of Rainbow Trout Fry, Oncorhynchus Mykiss (Walbaum), during Epidemics of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis. J. Fish Dis. 2002, 25, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.G. Using Simple Models to Review the Application and Implications of Different Approaches Used to Simulate Transmission of Pathogens among Aquatic Animals. Prev. Vet. Med. 2009, 88, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behringer, D.C.; Karvonen, A.; Bojko, J. Parasite Avoidance Behaviours in Aquatic Environments. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omori, R.; Adams, B. Disrupting Seasonality to Control Disease Outbreaks: The Case of Koi Herpes Virus. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 271, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; Emerson, M.; et al. Reporting Animal Research: Explanation and Elaboration for the ARRIVE Guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, J.C. Epidemiologic Methods for the Study of Infectious Diseases; Weber, D.J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mueller, N.H.; Gilden, D.H.; Cohrs, R.J.; Mahalingam, R.; Nagel, M.A. Varicella Zoster Virus Infection: Clinical Features, Molecular Pathogenesis of Disease, and Latency. Neurol. Clin. 2008, 26, 675–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eide, K.E.; Miller-Morgan, T.; Heidel, J.R.; Kent, M.L.; Bildfell, R.J.; LaPatra, S.; Watson, G.; Jin, L. Investigation of Koi Herpesvirus Latency in Koi. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 4954–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zida, S.; Kolia-Diafouka, P.; Kania, D.; Sotto, A.; Foulongne, V.; Bolloré, K.; Ouangraoua, S.; Méda, N.; Carrère-Kremer, S.; Van de Perre, P.; et al. Combined Testing for Herpes Simplex Virus and Mycobacterium Tuberculosis DNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients with Aseptic Meningitis in Burkina Faso, West Africa. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomas, J. Aragon Epitools: Epidemiology Tools. R Package Version 0.5–10.1. Available online: https://CRAN.R-Project.Org/Package=epit (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Taiyun, W.; Viliam, S. R Package “Corrplot”: Visualization of a Correlation Matrix (Version 0.84); 2017. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/corrplot/index.html (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Sunarto, A.; McColl, K.A.; St. Crane, M.J.; Schat, K.A.; Slobedman, B.; Barnes, A.C.; Walker, P.J. Characteristics of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 in Different Phases of Infection: Implications for Disease Transmission and Control. Virus Res. 2014, 188, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, J.K.; Sarkar, D.; Chakraborty, P.; Bhakta, J.N.; Jana, B.B. Density Dependent Ambient Ammonium as the Key Factor for Optimization of Stocking Density of Common Carp in Small Holding Tanks. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 952–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Sorensen, P.W. Using Boat Electrofishing to Estimate the Abundance of Invasive Common Carp in Small Midwestern Lakes. North Am. J. Fish. Manag. 2012, 32, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, M.W.; Ling, N.; Hicks, B.J.; Tempero, G.W. Movement, Social Cohesion and Site Fidelity in Adult Koi Carp, Cyprinus Carpio. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2009, 16, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penne, C.R.; Pierce, C.L. Seasonal Distribution, Aggregation, and Habitat Selection of Common Carp in Clear Lake, Iowa. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2008, 137, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajer, P.G.; Chizinski, C.J.; Sorensen, P.W. Using the Judas Technique to Locate and Remove Wintertime Aggregations of Invasive Common Carp. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2011, 18, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosal, R.; Eichmiller, J.J.; Witthuhn, B.A.; Sorensen, P.W. Attracting Common Carp to a Bait Site with Food Reveals Strong Positive Relationships between Fish Density, Feeding Activity, Environmental DNA, and Sex Pheromone Release That Could Be Used in Invasive Fish Management. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 6714–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, S.M.; Jin, Y.; Franzke, K.; Grunow, B.; Wang, Q.; Klafack, S. Koi Herpesvirus (KHV) and KHV Disease (KHVD)—A Recently Updated Overview. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Sano, M.; Kurita, J.; Yuasa, K.; Iida, T. Carp Larvae Are Not Susceptible to Koi Herpesvirus. Fish Pathol. 2007, 42, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bergmann, S.M.; Monro, E.S.; Kempter, J. Can Water Disinfection Prevent the Transmission of Infectious Koi Herpesvirus to Naïve Carp?—A Case Report. J. Fish Dis. 2017, 40, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hershberger, P.K.; Gregg, J.L.; Grady, C.A.; Hart, L.M.; Roon, S.R.; Winton, J.R. Factors Controlling the Early Stages of Viral Haemorrhagic Septicaemia Epizootics: Low Exposure Levels, Virus Amplification and Fish-to-Fish Transmission: VHSV Infectivity and Transmission. J. Fish Dis. 2011, 34, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garver, K.A.; Mahony, A.A.M.; Stucchi, D.; Richard, J.; Van Woensel, C.; Foreman, M. Estimation of Parameters Influencing Waterborne Transmission of Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus (IHNV) in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffer, J.T.; Mayer, B.T.; Fong, Y.; Swan, D.A.; Wald, A. Herpes Simplex Virus-2 Transmission Probability Estimates Based on Quantity of Viral Shedding. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2014, 11, 20140160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edenborough, K.M.; Gilbertson, B.P.; Brown, L.E. A Mouse Model for the Study of Contact-Dependent Transmission of Influenza A Virus and the Factors That Govern Transmissibility. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 12544–12551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinmeyer, S.H.; Wilke, C.O.; Pepin, K.M. Methods of Modelling Viral Disease Dynamics across the within- and between-Host Scales: The Impact of Virus Dose on Host Population Immunity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, E.W.; Dominik, J.W.; Rowberg, A.H.; Higbee, G.A. Influenza Virus Population Dynamics in the Respiratory Tract of Experimentally Infected Mice. Infect. Immun. 1976, 13, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, M.; Murphy, C.M.; Zhang, Z.; Durand, S.; Esteves, I.; Doel, C.; Alexandersen, S. Influence of Exposure Intensity on the Efficiency and Speed of Transmission of Foot-and-Mouth Disease. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 140, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, C.; Hollingsworth, T.D.; Chapman, R.; de Wolf, F.; Hanage, W.P. Variation in HIV-1 Set-Point Viral Load: Epidemiological Analysis and an Evolutionary Hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 17441–17446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanquart, F.; Grabowski, M.K.; Herbeck, J.; Nalugoda, F.; Serwadda, D.; Eller, M.A.; Robb, M.L.; Gray, R.; Kigozi, G.; Laeyendecker, O.; et al. A Transmission-Virulence Evolutionary Trade-off Explains Attenuation of HIV-1 in Uganda. eLife 2016, 5, e20492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, I.; Hoare, D.; Krause, J. Effects of Parasites on Fish Behaviour; a Review and Evolutionary Perspective. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2000, 10, 131–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.B.; Lafferty, K.D.; van Oosterhout, C.; Cable, J. Parasite Transmission in Social Interacting Hosts: Monogenean Epidemics in Guppies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Poulin, R.; FitzGerald, G.J. Shoaling as an Anti-Ectoparasite Mechanism in Juvenile Sticklebacks (Gasterosteus Spp.). Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1989, 24, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, O.; Valtonen, E.T.; Benesh, D.P. Host Manipulation by Parasites in the World of Dead-End Predators: Adaptation to Enhance Transmission? Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008, 275, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Freeman, J.L. Zebrafish as a Model for Investigating Developmental Lead (Pb) Neurotoxicity as a Risk Factor in Adult Neurodegenerative Disease: A Mini-Review. NeuroToxicology 2014, 43, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanagihara, D.; Watanabe, S.; Mitarai, G. Neuroanatomical Substrate for the Dorsal Light Response. Neurosci. Res. 1993, 16, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelton, G. 8 The Regulation of Breathing. In Fish Physiology; Hoar, W.S., Randall, D.J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1970; Volume 4, pp. 293–359. [Google Scholar]
- Rakus, K.; Ronsmans, M.; Forlenza, M.; Boutier, M.; Piazzon, M.C.; Jazowiecka-Rakus, J.; Gatherer, D.; Athanasiadis, A.; Farnir, F.; Davison, A.J.; et al. Conserved Fever Pathways across Vertebrates: A Herpesvirus Expressed Decoy TNF-α Receptor Delays Behavioral Fever in Fish. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondračková, M.; Dávidová, M.; Gelnar, M.; Jurajda, P. Susceptibility of Prussian Carp Infected by Metacercariae of Posthodiplostomum Cuticola (v. Nordmann, 1832) to Fish Predation. Ecol. Res. 2006, 21, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Oosterhout, C.; Mohammed, R.S.; Hansen, H.; Archard, G.A.; McMullan, M.; Weese, D.J.; Cable, J. Selection by Parasites in Spate Conditions in Wild Trinidadian Guppies (Poecilia Reticulata). Int. J. Parasitol. 2007, 37, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoagland, R.J. The Incubation Period of Infectious Mononucleosis. Am. J. Public Health Nations Health 1964, 54, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, P.; Read, R.C.; Amlôt, R.; Chadborn, T.; Rice, C.; Bostock, J.; Yardley, L. Reducing Risks from Coronavirus Transmission in the Home—The Role of Viral Load. BMJ 2020, 369, m1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, T.; Lee, E.; Lee, C.; Kim, H.; Rhee, H.; Park, S.Y.; Son, H.-J.; Yu, S.; Park, J.W.; et al. Clinical Course and Molecular Viral Shedding Among Asymptomatic and Symptomatic Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection in a Community Treatment Center in the Republic of Korea. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, N.E.; Halloran, M.E.; Yang, Y.; Longini, I.M. Transmissibility and Pathogenicity of Ebola Virus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Household Secondary Attack Rate and Asymptomatic Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loehle, C. Social Barriers to Pathogen Transmission in Wild Animal Populations. Ecology 1995, 76, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milinski, M.; Bakker, T.C.M. Female Sticklebacks Use Male Coloration in Mate Choice and Hence Avoid Parasitized Males. Nature 1990, 344, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, A.J.W.; Duff, A.J.; Krause, J.; Barber, I. Shoaling Behaviour of Sticklebacks Infected with the Microsporidian Parasite, Glugea Anomala. Env. Biol. Fish 2005, 72, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugatkin, L.A.; FitzGerald, G.J.; Lavoie, J. Juvenile Three-Spined Sticklebacks Avoid Parasitized Conspecifics. Env. Biol. Fish 1994, 39, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesecker, J.M.; Skelly, D.K.; Beard, K.H.; Preisser, E. Behavioral Reduction of Infection Risk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9165–9168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulin, R.; Marcogliese, D.J.; McLaughlin, J.D. Skin-Penetrating Parasites and the Release of Alarm Substances in Juvenile Rainbow Trout. J. Fish Biol. 1999, 55, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| CyHV-3 Disease Period. | Definition | Experimental Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-infectious | Time period between when a host is exposed to a pathogen and when the host becomes infectious to other hosts. | Determined by measuring the time between inoculation of carp with CyHV-3 and viral detection in gill swabs. |
| Incubation period | Time period from pathogen exposure to onset of clinical disease signs. | Determined by measuring the time between inoculation of carp with CyHV-3 and observation of clinical signs. |
| Prodromal period | Time period between when a host becomes infectious and prior to the development of clinical signs. | Determined by subtracting the pre-infectious period from the incubation period. |
| Clinical period | Time period during which clinical signs are observed. | Determined by measuring the time between first observation of clinical signs of KHVD and experimental endpoints. |
| Infectious period | Time period in which the host can infect another host or vector. | Determined by measuring the time between first detection of CyHV-3 in gill swabs and experimental endpoints. |
| Variable Name. | Variable Type | Variable Description * |
|---|---|---|
| Days post exposure (dpe) | Continuous | Indicates either days post inoculation via skin swabbing or days post cohabitation with infected v.carp. |
| Viral load | Continuous | Log copy number or average log copy number of CyHV-3 genome copies per 50 μL of tissue supernatant measured by specific qPCR. |
| Transmission | Continuous | Proportion of s.carp determined to be positive for CyHV-3 after 4 dpe. |
| Contact rate | Continuous | Average (avg) number of brief contacts between v.carp and s.carp expressed as contacts/h (avg 15 min count × 4). |
| Vector disease score | Continuous | A score based on 4 categories of pathological signs scored on 1:4 point scale, yielding a 1:16 points indicating the level of gross pathology observed in v.carp. |
| Transmissibility (t) | Continuous | Likelihood of CyHV-3 transmission given physical contacts in Trial 2a, calculated for each trial replicate of Trial 2a/b as: t = transmission(Trial 2a)/avg contacts (Trial 2a) |
| ||
| ||
| Contact type | Categorical | Categorization of contacts between v.carp and s.carp (Trial 2a) as social, incidental, or aggressive. |
| Dependent Variable | Predictor(s) | Interaction | Coefficients | Adjusted r^2 | p-Value | AIC | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Estimate | SE | p-Value | ||||||
| Transmission | Viral load (gill), contact rate | Yes | Intercept | −56.09 | 33.64 | 1.71 × 10−1 | 0.80 | 2.50 × 10−2 | 36.12 |
| Log viral load (gill) | 8.16 | 5.42 | 2.07 × 10−1 | ||||||
| Log contacts/h | 4.91 | 5.36 | 4.11 × 10−1 | ||||||
| Interaction | −0.26 | 0.97 | 8.02 × 10−1 | ||||||
| Transmission | Viral load (kidney), contact rate | Yes | Intercept | −9.57 | 32.51 | 7.83 × 10−1 | 0.81 | 2.10 × 10−2 | 35.55 |
| Log viral load (kidney) | −0.14 | 7.17 | 9.85 × 10−1 | ||||||
| Log contacts/h | −1.09 | 6.32 | 8.72 × 10−1 | ||||||
| Interaction | 0.82 | 1.43 | 5.96 × 10−1 | ||||||
| Transmission | Viral load (gill), contact rate | No | Intercept | −48.45 | 16.19 | 3.00 × 10−2 | 0.83 | 5.00 × 10−3 | 34.26 |
| log viral load (gill) | 6.79 | 1.65 | 9.00 × 10−3 | ||||||
| log contacts/h | 3.53 | 1.34 | 4.70 × 10−2 | ||||||
| Transmission | Viral load (kidney), contact rate | No | Intercept | −27.54 | 8.37 | 2.20 × 10−2 | 0.83 | 5.00 × 10−3 | 34.19 |
| log viral load (kidney) | 3.96 | 0.69 | 2.00 × 10−3 | ||||||
| log contacts/h | 2.5 | 0.94 | 4.60 × 10−2 | ||||||
| Transmissibility | Viral load (gill) | Na | Intercept | −0.30 | 0.11 | 3.11 × 10−2 | 0.74 | 3.90 × 10−3 | 14.98 |
| Log viral load (gill) | 0.09 | 0.02 | 3.90 × 10−3 | ||||||
| Transmissibility | Viral load (kidney) | Na | Intercept | −0.69 | 0.10 | 4.77 × 10−4 | 0.91 | 1.34 × 10−4 | 23.79 |
| Log viral load (kidney) | 0.16 | 0.02 | 1.34 × 10−4 | ||||||
| Vector disease score | Viral load (gill) | Na | Intercept | −12.99 | 3.38 | 8.50 × 10−3 | 0.85 | 6.97 × 10−4 | 40.40 |
| Log viral load (gill) | 3.80 | 0.60 | 6.97 × 10−4 | ||||||
| Vector disease score | Viral load (kidney) | Na | Intercept | −20.78 | 10.28 | 8.98 × 10−2 | 0.50 | 3.04 × 10−2 | 50.07 |
| Log viral load (kidney) | 5.16 | 1.83 | 3.04 × 10−2 | ||||||
| Trial 2a/b Serial Experiments (dpe) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 3–6 dpe avg (SD) | 9–12 dpe avg (SD) |
| Transmission (Trial 2a) | 10 | 9 | 13 | 12 | 8 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 11.00 (1.83) | 5.00 (2.16) |
| Transmission (Trial 2b) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0.00 (0.00) | 1.25 (0.96) |
| Avg contacts (15 min count period) | 195.50 | 182.33 | 253.83 | 118.33 | 16.83 | 20.33 | 20.83 | 16.50 | 187.50 (55.60) | 18.63 (2.27) |
| Min contact for transmission | 31.28 | 32.41 | 31.24 | 15.78 | 4.49 | 32.53 | 8.33 | 6.60 | 27.67 (7.95) | 6.87 (3.07) |
| Transmissibility (t) | 5.12 × 10−2 | 4.94 × 10−2 | 5.12 × 10−2 | 1.01 × 10−1 | 4.75 × 10−1 | 1.48 × 10−1 | 2.40 × 10−1 | 2.42 × 10−1 | 6.33 × 10−2 (0.03) | 2.76 × 10−1 (0.14) |
| t attributable to direct contact (direct transmission) | 5.12 × 10−2 | 4.94 × 10−2 | 5.12 × 10−2 | 1.01 × 10−1 | 3.56 × 10−1 | 4.92 × 10−2 | 1.92 × 10−1 | 2.42 × 10−1 | 6.33 × 10−2 (0.03) | 2.10 × 10−1 (0.13) |
| t not attributable to direct contact (indirect transmission) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 1.19 × 10−1 | 9.84 × 10−2 | 4.80 × 10−2 | 0.00 | 0.00 (0.00) | 6.63 × 10−2 (0.05) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tolo, I.E.; Bajer, P.G.; Wolf, T.M.; Mor, S.K.; Phelps, N.B.D. Investigation of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3) Disease Periods and Factors Influencing CyHV-3 Transmission in A Low Stocking Density Infection Trial. Animals 2022, 12, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010002
Tolo IE, Bajer PG, Wolf TM, Mor SK, Phelps NBD. Investigation of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3) Disease Periods and Factors Influencing CyHV-3 Transmission in A Low Stocking Density Infection Trial. Animals. 2022; 12(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleTolo, Isaiah E., Przemyslaw G. Bajer, Tiffany M. Wolf, Sunil K. Mor, and Nicholas B. D. Phelps. 2022. "Investigation of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3) Disease Periods and Factors Influencing CyHV-3 Transmission in A Low Stocking Density Infection Trial" Animals 12, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010002
APA StyleTolo, I. E., Bajer, P. G., Wolf, T. M., Mor, S. K., & Phelps, N. B. D. (2022). Investigation of Cyprinid Herpesvirus 3 (CyHV-3) Disease Periods and Factors Influencing CyHV-3 Transmission in A Low Stocking Density Infection Trial. Animals, 12(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12010002







