Adaptability Challenges for Organic Broiler Chickens: A Commentary
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- -
- Identify solutions to the new challenges that organic poultry chains must face to adapt to future productive scenarios (nutrition, enrichments, etc.);
- -
- Detect consumer viewpoints to provide a future perspective to OPP;
- -
- Summarize and define chicken adaptability to OPP, assessing the main factors of chicken adaptability.
2. Methodology of the Literature Review
2.1. Nutritional Challenges
2.2. Environmental Challenges
2.3. Health Challenges
2.4. Sustainability Issues
- The FCR of the chicken (how much feed is necessary for producing one unit of food);
- The feed ingredients used (i.e., different crops need more or less inputs);
- The cultivation techniques of the crops (i.e., in OPP chemical fertilizers are not allowed, which is also the case for herbicides and other chemical drugs);
- The dietary requirements (energy, protein, amino acid profile, etc.) of the genetic strain.
2.4.1. FCR
2.4.2. Feed Ingredients
2.4.3. Cultivation Techniques
2.4.4. Requirements
2.5. Welfare and Consumer Perceptions
2.6. Broiler Adaptation to OPP
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- OECD-FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2021–2030; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; ISBN 978-92-5-134608-2. [Google Scholar]
- Augère-Granier, M.-L. The EU poultry meat and egg sector. In The EU Poultry Meat and Egg Sector: Main Features, Challenges and Prospects; Publications Office: Brussels, Belgium, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Action Plan for the Development of Organic Production; Eur. Comm. COM/2021/141 Final/2; Document 52021DC0141R(01); European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Escobedo del Bosque, C.I.; Risius, A.; Spiller, A.; Busch, G. Consumers’ Opinions and Expectations of an “Ideal Chicken Farm” and Their Willingness to Purchase a Whole Chicken From This Farm. Front. Anim. Sci. 2021, 2, 682477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, C.; Mugnai, C.; Moscati, L.; Mattioli, S.; Amato, M.G.; Mancinelli, A.C.; Dal Bosco, A. Adaptation to organic rearing system of eight different chicken genotypes: Behaviour, welfare and performance. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 15, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, P.; Opio, C.; Steinfeld, H. Poultry production and the environment—A review. Fao 2007, 153, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Cobanoglu, F.; Kucukyilmaz, K.; Cinar, M.; Bozkurt, M.; Catli, A.; Bintas, E. Comparing the profitability of organic and conventional broiler production. Rev. Bras. Ciência Avícola 2014, 16, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tufarelli, V.; Ragni, M.; Laudadio, V. Feeding forage in poultry: A promising alternative for the future of production systems. Agriculture 2018, 8, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanatico, A.C.; Arsi, K.; Upadhyaya, I.; Morales Ramos, J.; Donoghue, D.; Donoghue, A.M. Sustainable Fish and Invertebrate Meals for Methionine and Protein Feeds in Organic Poultry Production. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2018, 27, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesseraud, S.; Peresson, R.; Lopes, J.; Chagneau, A.M. Dietary lysine deficiency greatly affects muscle and liver protein turnover in growing chickens. Br. J. Nutr. 1996, 75, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prudêncio da Silva, V.; van der Werf, H.M.G.; Spies, A.; Soares, S.R. Variability in environmental impacts of Brazilian soybean according to crop production and transport scenarios. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kernebeek, H.R.J.; Oosting, S.J.; Van Ittersum, M.K.; Bikker, P.; De Boer, I.J.M. Saving land to feed a growing population: Consequences for consumption of crop and livestock products. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2016, 21, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Der Heide, M.E.; Stødkilde, L.; Nørgaard, J.V.; Studnitz, M. The Potential of Locally-Sourced European Protein Sources for Organic Monogastric Production: A Review of Forage Crop Extracts, Seaweed, Starfish, Mussel, and Insects. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burley, H.K.; Patterson, P.H.; Anderson, K.E. Alternative ingredients for providing adequate methionine in organic poultry diets in the United States with limited synthetic amino acid use. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2015, 71, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markets and Markets. Gluten Feed Market by Source (Wheat, Corn, Barley, Rye, Others), by Livestock (Swine, Poultry, Cattle, Aquaculture, Others), & Geography—Trends & Forecasts to 2019. Available online: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/gluten-feed-market-2841408.html (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- Mirzaie, S.; Zirak-Khattab, F.; Hosseini, S.A.; Donyaei-Darian, H. Effects of dietary Spirulina on antioxidant status, lipid profile, immune response and performance characteristics of broiler chickens reared under high ambient temperature. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Bosco, A.; Mugnai, C.; Mattioli, S.; Rosati, A.; Ruggeri, S.; Ranucci, D.; Castellini, C. Transfer of bioactive compounds from pasture to meat in organic free-range chickens. Poult. Sci. 2016, 95, 2464–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, M.; Ganzaroli, A.; Bacenetti, J. Earthworm as an alternative protein source in poultry and fish farming: Current applications and future perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 734, 139460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Xu, E.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Cao, S.; Hu, S.; Wu, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, F.; et al. Dietary Hermetia illucens Larvae Meal Improves Growth Performance and Intestinal Barrier Function of Weaned Pigs Under the Environment of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 812011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuso, A.; Barbi, S.; Macavei, L.I.; Luparelli, A.V.; Maistrello, L.; Montorsi, M.; Sforza, S.; Caligiani, A. Effect of the rearing substrate on total protein and amino acid composition in black soldier fly. Foods 2021, 10, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, T.; Bosch, G. Insects: A protein-rich feed ingredient in pig and poultry diets. Anim. Front. 2015, 5, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 1Colditz, I.G.; Hine, B.C. Resilience in farm animals: Biology, management, breeding and implications for animal welfare. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2016, 56, 1961–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, F.; Cendron, F.; Rovelli, G.; Castellini, C.; Cassandro, M.; Lasagna, E. Emerging Genetic Tools to Investigate Molecular Pathways Related to Heat Stress in Chickens: A Review. Animals 2020, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baracho, M.S.; de Nääs, I.A.; Lima, N.D.S.; Cordeiro, A.F.S.; Moura, D.J. Factors affecting broiler production: A meta-analysis. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Avic. 2019, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, K.A.O.; Nääs, I.A.; Moura, D.J.; Garcia, R.G.; Mendes, A.S. Applying multi-criteria analysis to select the most appropriate broiler rearing environment. Inf. Process. Agric. 2021, 8, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshardt, S.; Sabatier, R.; Dufils, A.; Navarrete, M. Changing perspectives on chicken-pastured orchards for action: A review based on a heuristic model. Agric. Syst. 2022, 196, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothrock, M.J.; Gibson, K.E.; Micciche, A.C.; Ricke, S.C. Pastured Poultry Production in the United States: Strategies to Balance System Sustainability and Environmental Impact. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Bosco, A.; Mugnai, C.; Rosati, A.; Paoletti, A.; Caporali, S.; Castellini, C. Effect of range enrichment on performance, behavior, and forage intake of free-range chickens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2014, 23, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petracci, M.; Berri, C. Poultry Quality Evaluation; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2017; p. 370. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, D.L.M.; Hinch, G.N.; Dyall, T.R.; Warin, L.; Little, B.A.; Lee, C. Outdoor stocking density in free-range laying hens: Radio-frequency identification of impacts on range use. Animal 2017, 11, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bailie, C.L.; Ball, M.E.E.; Connell, N.E.O. Influence of the provision of natural light and straw bales on activity levels and leg health in commercial broiler chickens. Animal 2013, 7, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khazai, N.; Judd, S.E.; Tangpricha, V. Calcium and vitamin D: Skeletal and extraskeletal health. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2008, 10, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kühn, J.; Schutkowski, A.; Kluge, H.; Hirche, F.; Stangl, G.I. Free-range farming: A natural alternative to produce vitamin D-enriched eggs. Nutrition 2014, 30, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwean-Lardner, K.; Fancher, B.I.; Classen, H.L. Impact of daylength on the productivity of two commercial broiler strains. Br. Poult. Sci. 2012, 53, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knap, P.W. Breeding robust pigs. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 2005, 45, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, W.M.; Cheng, H.W.; Croney, C. Methods to address poultry robustness and welfare issues through breeding and associated ethical considerations. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Antunes, P.; Mourão, J.; Campos, J.; Peixe, L. Salmonellosis: The role of poultry meat. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bailey, M.; Taylor, R.; Brar, J.; Corkran, S.; Velásquez, C.; Novoa-Rama, E.; Oliver, H.F.; Singh, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella from antibiotic-free broilers during organic and conventional processing. J. Food Prot. 2020, 83, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesciaroli, M.; Magistrali, C.F.; Filippini, G.; Epifanio, E.M.; Lovito, C.; Marchi, L.; Maresca, C.; Massacci, F.R.; Orsini, S.; Scoccia, E.; et al. Antibiotic-resistant commensal Escherichia coli are less frequently isolated from poultry raised using non-conventional management systems than from conventional broiler. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 314, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alali, W.Q.; Thakur, S.; Berghaus, R.D.; Martin, M.P.; Gebreyes, W.A. Prevalence and distribution of Salmonella in organic and conventional broiler poultry farms. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Overbeke, I.; Duchateau, L.; De Zutter, L.; Albers, G.; Ducatelle, R. A Comparison Survey of Organic and Conventional Broiler Chickens for Infectious Agents Affecting Health and Food Safety. Avian Dis. 2006, 50, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colles, F.M.; Jones, T.A.; McCarthy, N.D.; Sheppard, S.K.; Cody, A.J.; Dingle, K.E.; Dawkins, M.S.; Maiden, M.C.J. Campylobacter infection of broiler chickens in a free-range environment. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 2042–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansson, I.; Ellström, P.; Nilsson, O.; Chaba, M.; Skarin, M.; Fernström, L.; Frosth, S. Differences in Genotype and Antimicrobial Resistance between Campylobacter spp. Isolated from Organic and Conventionally Produced Chickens in Sweden. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, L.K.; Sait, L.C.; Trantham, E.K.; Cogan, T.A.; Humphrey, T.J. Campylobacter Infection Has Different Outcomes in Fast- and Slow-Growing Broiler Chickens. Avian Dis. 2013, 57, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, M.A.; Taylor, R.M.; Brar, J.S.; Corkran, S.C.; Velásquez, C.; Novoa Rama, E.; Oliver, H.F.; Singh, M. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter from antibiotic-free broilers during organic and conventional processing. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, M.; Xiao, X.; Robinson, T.P. Intensifying poultry production systems and the emergence of avian influenza in China: A ‘One Health/Ecohealth’ epitome. Arch. Public Health 2017, 75, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fanatico, A. Parasite Management for Natural and Organic Poultry: Coccidiosis. 2006. Available online: https://attra.ncat.org/product/parasite-management-for-natural-and-organic-poultry-coccidiosis/ (accessed on 5 May 2022).
- Costantini, M.; Ferrante, V.; Guarino, M.; Bacenetti, J. Trends in Food Science & Technology Environmental sustainability assessment of poultry productions through life cycle approaches: A critical review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokkers, E.A.M.; De Boer, I.J.M. British Poultry Science Economic, ecological, and social performance of conventional and organic broiler production in the Netherlands Economic, ecological, and social performance of conventional and organic broiler production in the Netherlands. Br. Poult. Sci. 2009, 50, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinonen, I.; Williams, A.G.; Wiseman, J.; Guy, J.; Kyriazakis, I. Predicting the environmental impacts of chicken systems in the United Kingdom through a life cycle assessment: Broiler production systems. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 8–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, I.; Kyriazakis, I. How can we improve the environmental sustainability of poultry production? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castellini, C.; Boggia, A.; Cortina, C.; Dal Bosco, A.; Paolotti, L.; Novelli, E.; Mugnai, C. A multicriteria approach for measuring the sustainability of different poultry production systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2012, 37, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boggia, A.; Paolotti, L.; Castellini, C. Environmental impact evaluation of conventional, organic and organic-plus poultry production systems using life cycle assessment. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2010, 66, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocchi, L.; Paolotti, L.; Rosati, A.; Boggia, A.; Castellini, C. Assessing the sustainability of different poultry production systems: A multicriteria approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. A farm to fork strategy for a fair, healthy and environmentally-friendly food system. Eur. Comm. 2020, 2507, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Vaarst, M.; Steenfeldt, S.; Horsted, K. Sustainable development perspectives of poultry production. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2015, 71, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rete Rurale Nazionale. L’Italia e la Pac Post 2020 OG 1: Promuovere un Settore Agricolo Intelligente, Resiliente e Diversificato che Garantisca la Sicurezza Alimentare. Le Principali Caratteristiche Delle Aziende Agricole, Agroalimentari e Forestali. 2020. Available online: http://www.pianetapsr.it/flex/downloads/policy_brief/Policy%20Brief_RRN_OG1.pdf (accessed on 30 March 2022).
- Bosco, A.D.; Ruggeri, S.; Mattioli, S.; Mugnai, C.; Sirri, F.; Castellini, C. Effect of Faba Bean Vicia Faba Var. Minor) Inclusion in Starter and Growing Diet on Performance, Carcass and Meat Characteristics of Organic Slow-Growing Chickens. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2013, 12, e76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costantino, A.; Fabrizio, E.; Ghiggini, A.; Bariani, M. Energy & Buildings Climate control in broiler houses: A thermal model for the calculation of the energy use and indoor environmental conditions. Energy Build. 2018, 169, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leinonen, I.; Williams, A.G.; Kyriazakis, I. The effects of welfare-enhancing system changes on the environmental impacts of broiler and egg production. Poult. Sci. 2014, 93, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spain, C.V.; Freund, D.; Mohan-Gibbons, H.; Meadow, R.G.; Beacham, L. Are they buying it? United states consumers’ changing attitudes toward more humanely raised meat, eggs, and dairy. Animals 2018, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hartcher, K.M.; Lum, H.K. Genetic selection of broilers and welfare consequences: A review. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2020, 76, 154–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigors, B. Citizens’ and Farmers’ Framing of “Positive Animal Welfare” and the Implications for Framing Positive Welfare in Communication. Animals 2019, 9, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattioli, S.; Dal Bosco, A.; Ruggeri, S.; Martino, M.; Moscati, L.; Pesca, C.; Castellini, C. Adaptive response to exercise of fast-growing and slow-growing chicken strains: Blood oxidative status and non-enzymatic antioxidant defense. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 4096–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulcini, D.; Zilio, D.M.; Cenci, F.; Castellini, C. Differences in Tibia Shape in Organically Reared Chicken Lines Measured by Means of Geometric Morphometrics. Animals 2021, 11, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahamtani, F.M.; Hinrichsen, L.K.; Riber, A.B. Welfare assessment of conventional and organic broilers in Denmark, with emphasis on leg health. Vet. Rec. 2018, 183, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattioli, S.; Cartoni Mancinelli, A.; Menchetti, L.; Dal Bosco, A.; Madeo, L.; Guarino Amato, M.; Moscati, L.; Cotozzolo, E.; Ciarelli, C.; Angelucci, E.; et al. How the kinetic behavior of organic chickens affects productive performance and blood and meat oxidative status: A study of six poultry genotypes. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalmendal, R.; Bessei, W. The preference for high-fiber feed in laying hens divergently selected on feather pecking. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 1785–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, L. Thinking chickens: A review of cognition, emotion, and behavior in the domestic chicken. Anim. Cogn. 2017, 20, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yeates, J.W. How Good? Ethical Criteria for a ‘Good Life’ for Farm Animals. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2017, 30, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, M.S.; Kang, G.-H.; Joo, S.T. A Review: Influences of Pre-slaughter Stress on Poultry Meat Quality. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 21, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, L.M.; Alali, W.Q.; Gibson, K.E.; Ricke, S.C.; Crandall, P.; Jaroni, D.; Berrang, M. Salmonella and Campylobacter prevalence and concentration on pasture-raised broilers processed on-farm, in a Mobile Processing Unit, and at small USDA-inspected facilities. Food Control 2013, 34, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Bryan, C.A.; Crandall, P.G.; Davis, M.L.; Kostadini, G.; Gibson, K.E.; Alali, W.Q.; Jaroni, D.; Ricke, S.C.; Marcy, J.A. Mobile poultry processing units: A safe and cost-effective poultry processing option for the small-scale farmer in the United States. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2014, 70, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angioloni, S.; Kostandini, G.; Alali, W.Q.; O’Bryan, C.A. Economic feasibility of mobile processing units for small-scale pasture poultry farmers. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2016, 31, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, A.C.; Dal Bosco, A.; Mattioli, S.; Ranucci, D.; Castellini, C. Mobile Poultry Processing Unit as a Resource for Small Poultry Farms: Planning and Economic Efficiency, Animal Welfare, Meat Quality and Sanitary Implications. Animals 2018, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaughan, J.B.; Sejian, V.; Mader, T.L.; Dunshea, F.R. Adaptation strategies: Ruminants. Anim. Front. 2019, 9, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassandro, M.; De Macrhi, M.; Baruchello, M. Environmental adaptability and stability for reproduction traits of local chicken breeds. Acta Agric. Slov. 2004, 1, 201–207. [Google Scholar]
- Faure, J.M.; Mills, A.D. Improving the Adaptability of Animals by Selection, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 9780123945860. [Google Scholar]
- Mulder, H.A. Is GxE a burden or a blessing? Opportunities for genomic selection and big data. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2017, 134, 435–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schutz, K.E.; Jensen, P. Effects of Resource Allocation on Behavioural Strategies: A Comparison of Red Junglefowl (Gallus gallus) and Two Domesticated Breeds of Poultry. Ethology 2001, 107, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okusanya, P.O.; Akinlade, O.O. ADAPTABILITY AND GROWTH PERFORMANCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS OF BROILER CHICKEN TO HIGH TEMPERATURE VARIATIONS IN NORTH CENTRAL NIGERIA. In Proceedings of the 1st National Conference of WITED, Ilaro, Nigeria, 13–16 August 2019; pp. 324–328. [Google Scholar]
- Berghof, T.V.L.; Poppe, M.; Mulder, H.A. Opportunities to Improve Resilience in Animal Breeding Programs. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, J.E.; Kolozsvary, M.B.; Pajerowska-Mukhtar, K.M.; Zhang, B. Toward a Universal Theoretical Framework to Understand Robustness and Resilience: From Cells to Systems. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 8, 579098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, A.C.; Mattioli, S.; Bosco, A.D.; Aliberti, A.; Amato, M.G.; Castellini, C. Performance, behavior, and welfare status of six different organically reared poultry genotypes. Animals 2020, 10, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferreira, V.H.B.; Simoni, A.; Germain, K.; Leterrier, C.; Lansade, L.; Collin, A.; Mignon-Grasteau, S.; Le Bihan-Duval, E.; Guettier, E.; Leruste, H.; et al. Foraging Behavior Shows Individual-Consistency Over Time, and Predicts Range Use in Slow-Growing Free-Range Male Broiler Chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 814054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.H.B.; Simoni, A.; Germain, K.; Leterrier, C.; Lansade, L.; Collin, A.; Mignon-Grasteau, S.; Le Bihan-Duval, E.; Guettier, E.; Leruste, H.; et al. Working for food is related to range use in free-range broiler chickens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, V.H.B.; Barbarat, M.; Lormant, F.; Germain, K.; Brachet, M.; Løvlie, H.; Calandreau, L.; Guesdon, V. Social motivation and the use of distal, but not local, featural cues are related to ranging behavior in free-range chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus). Anim. Cogn. 2020, 23, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, C.; Mattioli, S.; Piottoli, L.; Mancinelli, A.C.; Ranucci, D.; Branciari, R.; Amato, M.G.; Dal Bosco, A. Effect of transport length on in vivo oxidative status and breast meat characteristics in outdoor-reared chicken genotypes. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 15, 191–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fanatico, A.C.; Pillai, P.B.; Hester, P.Y.; Falcone, C.; Mench, J.A.; Owens, C.M.; Emmert, J.L. Performance, livability, and carcass yield of slow- and fast-growing chicken genotypes fed low-nutrient or standard diets and raised indoors or with outdoor access. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 1012–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Failla, S.; Buttazzoni, L.; Zilio, D.M.; Contò, M.; Renzi, G.; Castellini, C.; Amato, M.G. An index to measure the activity attitude of broilers in extensive system. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancinelli, A.C. Chicken Adaptability in Alternative Systems Adaptive Response of Chicken Strains to the Organic and Free Range Rearing Systems. J. Dairy Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 555644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdalena, P.; Barbara, P.; Andrzej, F. The Effect of Different Rearing Conditions on Muscle Characteristics in Broilers of Two Commercial Lines—A Light Microscopic Study. J. Poult. Sci. 2010, 47, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phocas, F.; Belloc, C.; Bidanel, J.; Delaby, L.; Dourmad, J.Y.; Dumont, B.; Ezanno, P.; Fortun-Lamothe, L.; Foucras, G.; Frappat, B.; et al. Review: Towards the agroecological management of ruminants, pigs and poultry through the development of sustainable breeding programmes. II. Breeding strategies. Animal 2016, 10, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cartoni Mancinelli, A.; Mattioli, S.; Menchetti, L.; Dal Bosco, A.; Ciarelli, C.; Amato, M.G.; Castellini, C. The assessment of a multifactorial score for the adaptability evaluation of six poultry genotypes to the organic system. Animals 2021, 11, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustin Evaris, E.; Sarmiento Franco, L.; Sandoval Castro, C. Slow-growing male chickens fit poultry production systems with outdoor access. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2019, 75, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.G.; Li, J.H.; Li, X.; Bao, J. Effects of housing systems on behaviour, performance and welfare of fast-growing broilers. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2014, 27, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ponte, P.I.P.; Alves, S.P.; Bessa, R.J.B.; Ferreira, L.M.A.; Gama, L.T.; Brás, J.L.A.; Fontes, C.M.G.A.; Prates, J.A.M. Influence of pasture intake on the fatty acid composition, and cholesterol, tocopherols, and tocotrienols content in meat from free-range broilers. Poult. Sci. 2008, 87, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo-Ming, A.; Arsi, K.; Moyle, J.R.; Gaunsalis, V.B.; Owens, C.M.; Clark, F.D.; Fanatico, A.; Upadhyay, A.; Donoghue, D.J.; Donoghue, A.M. Meat quality characteristics of fast-growing broilers reared under different types of pasture management: Implications for organic and alternative production systems (Part II). J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2018, 27, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özbek, M.; Petek, M.; Ardlçll, S. Physical quality characteristics of breast and leg meat of slow-and fast-growing broilers raised in different housing systems. Arch. Anim. Breed. 2020, 63, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Bosco, A.; Mugnai, C.; Ruggeri, S.; Mattioli, S.; Castellini, C. Fatty acid composition of meat and estimated indices of lipid metabolism in different poultry genotypes reared under organic system. Poult. Sci. 2012, 91, 2039–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartoni Mancinelli, A.; Di Veroli, A.; Mattioli, S.; Cruciani, G.; Dal Bosco, A.; Castellini, C. Lipid metabolism analysis in liver of different chicken genotypes and impact on nutritionally relevant polyunsaturated fatty acids of meat. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bestman, M.; Verwer, C.; Brenninkmeyer, C.; Willett, A.; Hinrichsen, L.K.; Smajlhodzic, F.; Heerkens, J.L.T.; Gunnarsson, S.; Ferrante, V. Feather-pecking and injurious pecking in organic laying hens in 107 flocks from eight european countries. Anim. Welf. 2017, 26, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, I.C.; Gunnink, H. Effects of a commercial broiler enrichment programme with or without natural light on behaviour and other welfare indicators. Animal 2019, 13, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

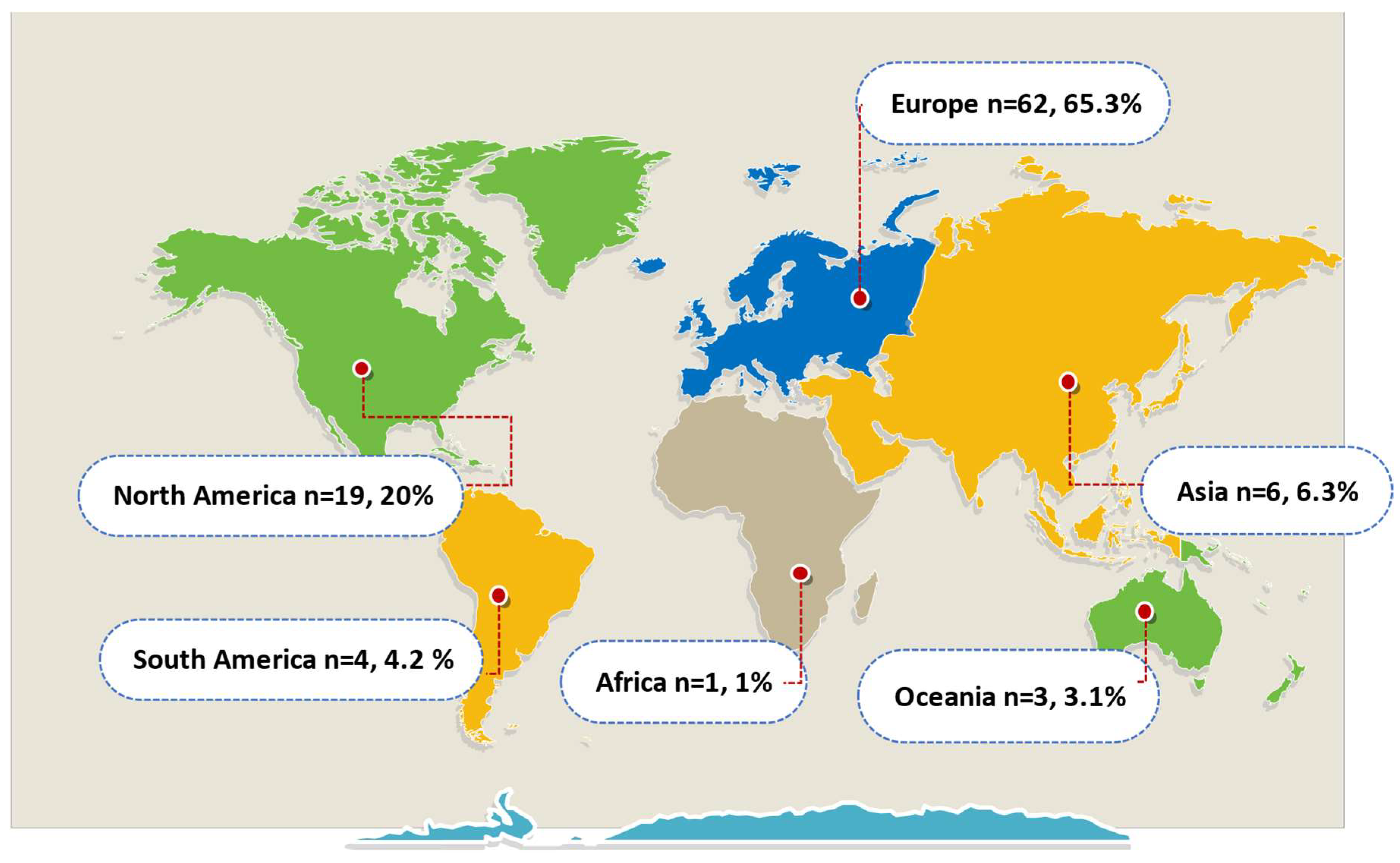
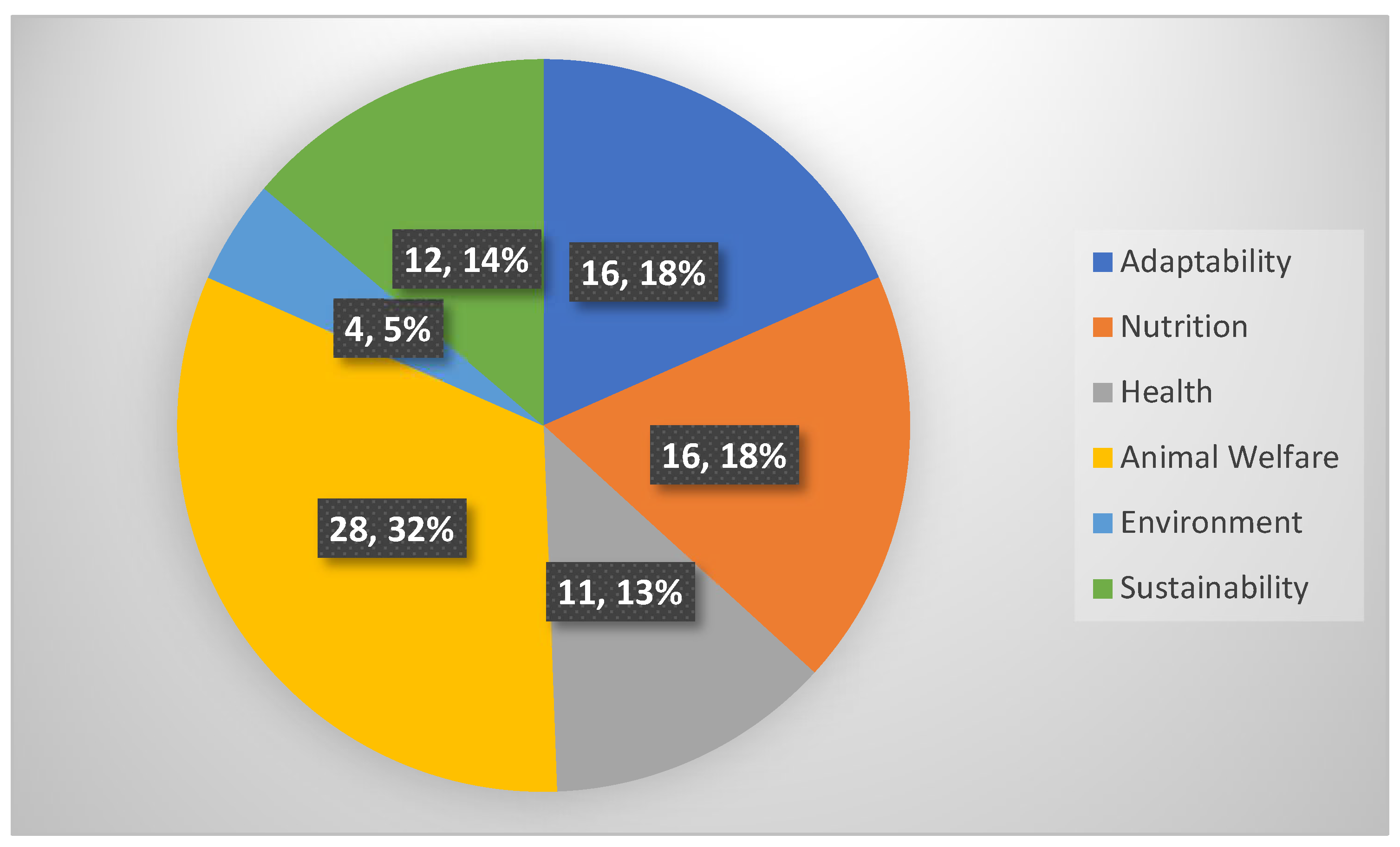
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guarino Amato, M.; Castellini, C. Adaptability Challenges for Organic Broiler Chickens: A Commentary. Animals 2022, 12, 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111354
Guarino Amato M, Castellini C. Adaptability Challenges for Organic Broiler Chickens: A Commentary. Animals. 2022; 12(11):1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111354
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuarino Amato, Monica, and Cesare Castellini. 2022. "Adaptability Challenges for Organic Broiler Chickens: A Commentary" Animals 12, no. 11: 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111354
APA StyleGuarino Amato, M., & Castellini, C. (2022). Adaptability Challenges for Organic Broiler Chickens: A Commentary. Animals, 12(11), 1354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12111354






