Testing Two Somatic Cell Count Cutoff Values for Bovine Subclinical Mastitis Detection Based on Milk Microbiota and Peripheral Blood Leukocyte Transcriptome Profile
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. S rRNA Gene Sequencing Procedure and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. RNA-Seq and Transcriptomic Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Taxonomic Profiling Analysis and Core Microbiota Identification
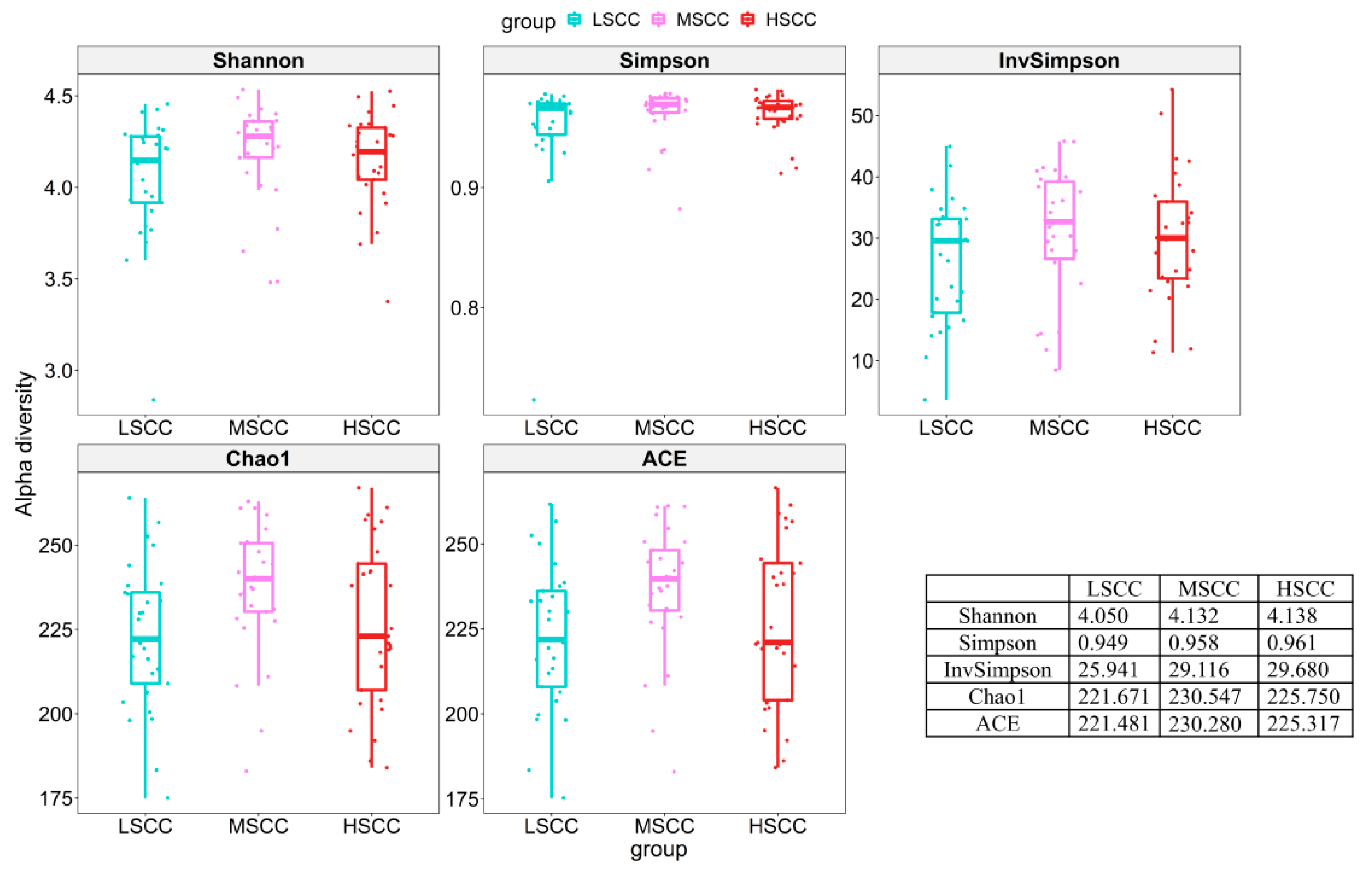
3.2. Pairwise Comparison of Microbial Community Diversity of Groups with Different SCC Levels
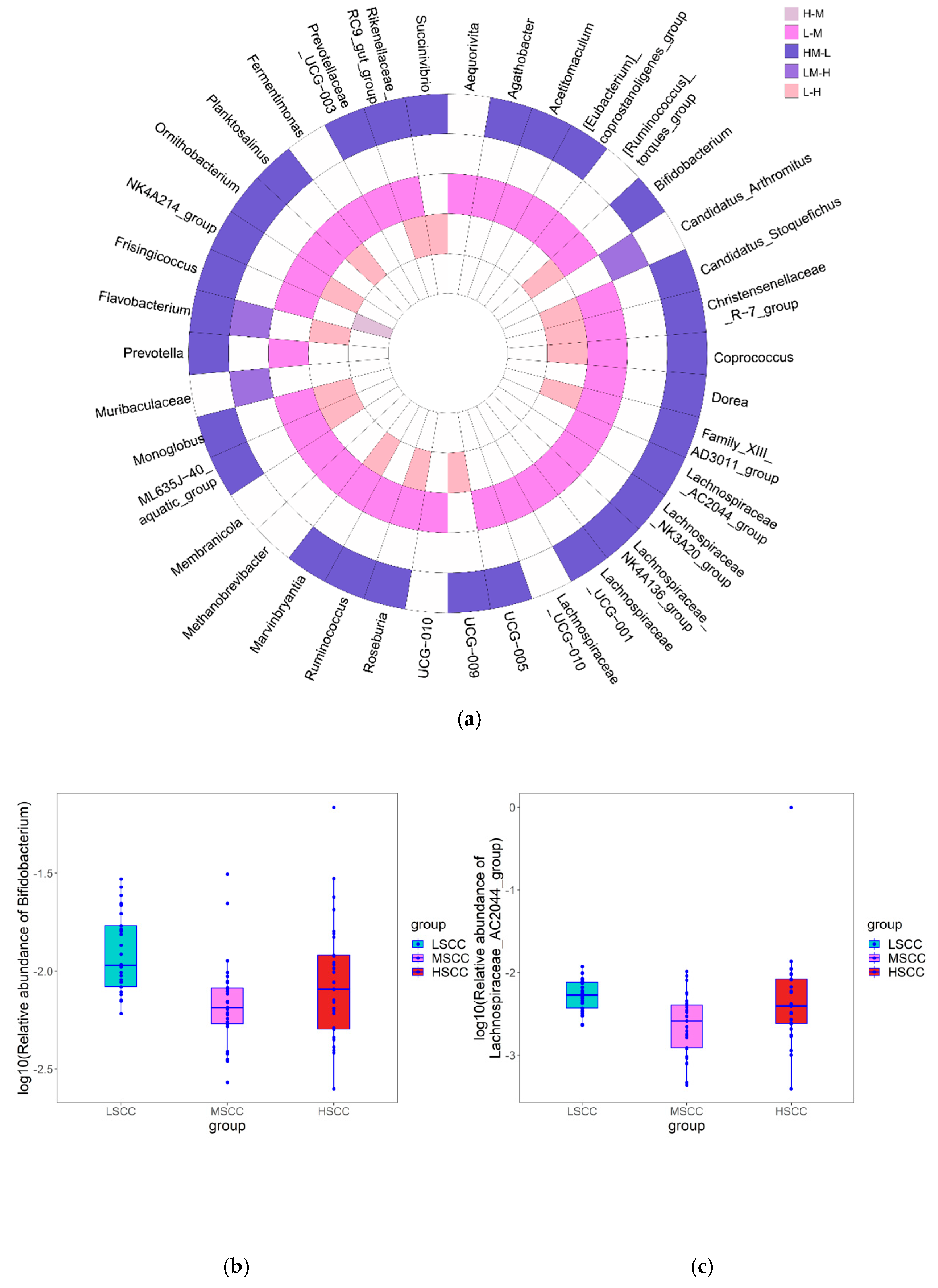
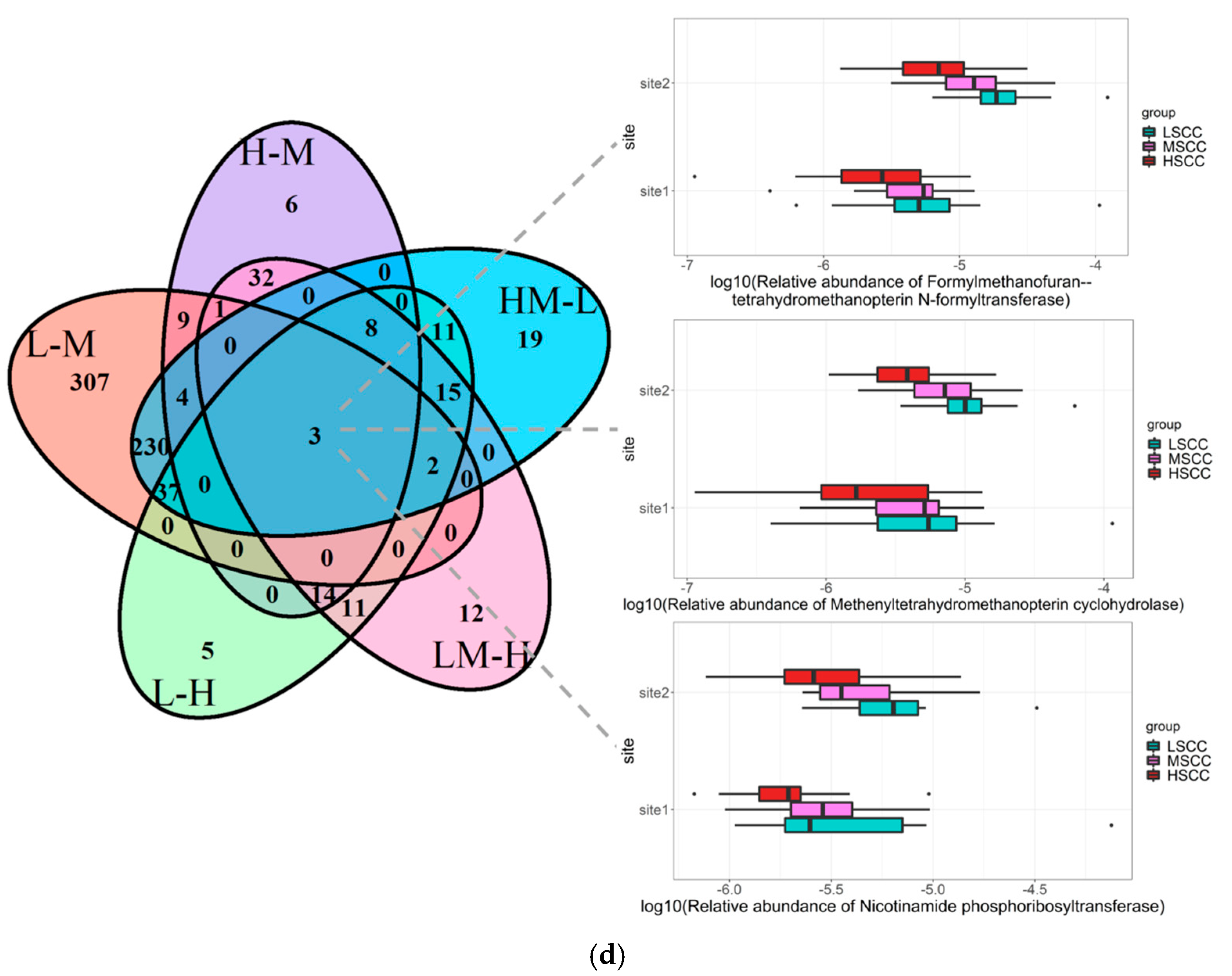
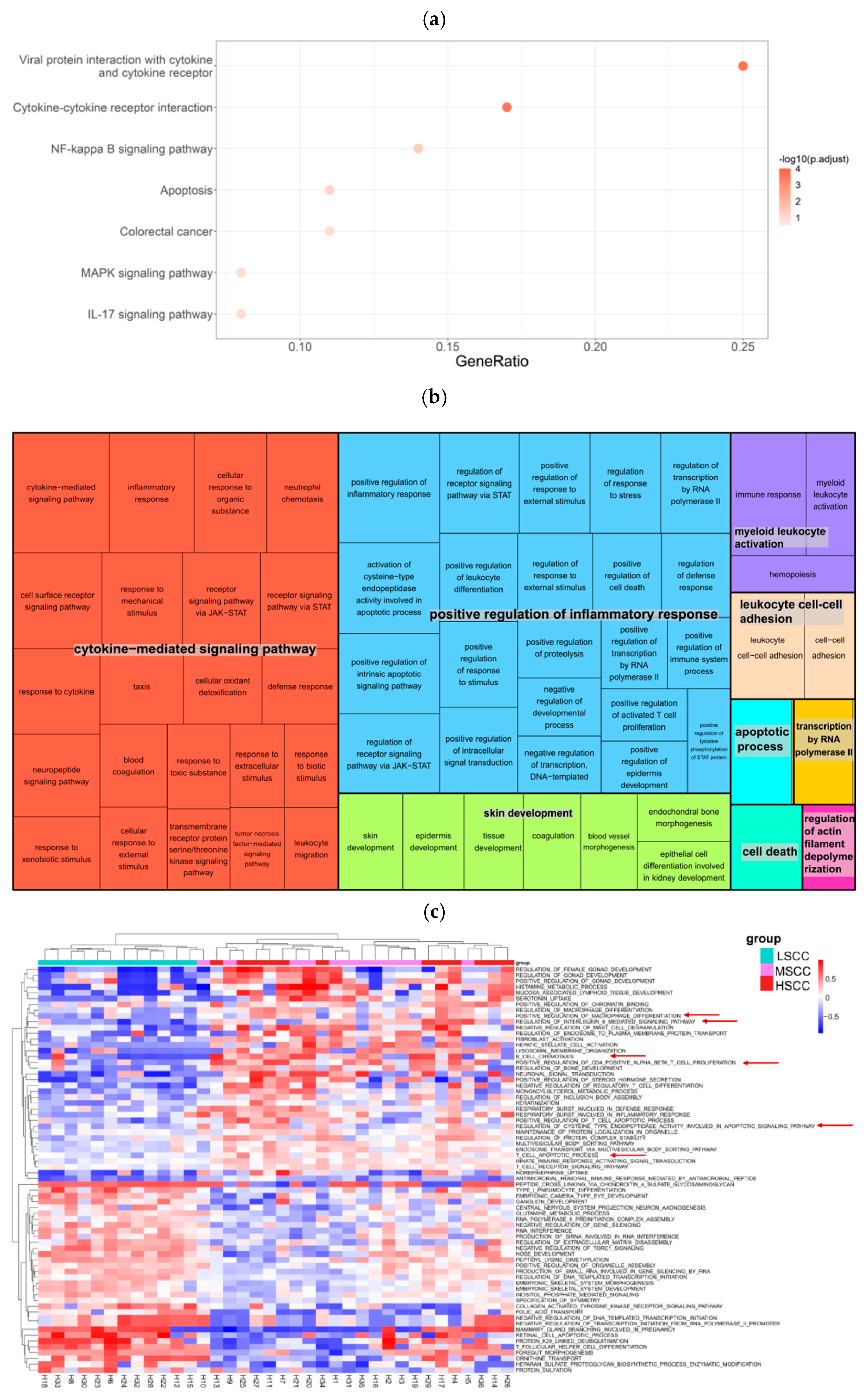
3.3. Identification of Differentially Abundant Genera and Metabolic Pathways in Groups with Different SCC Levels
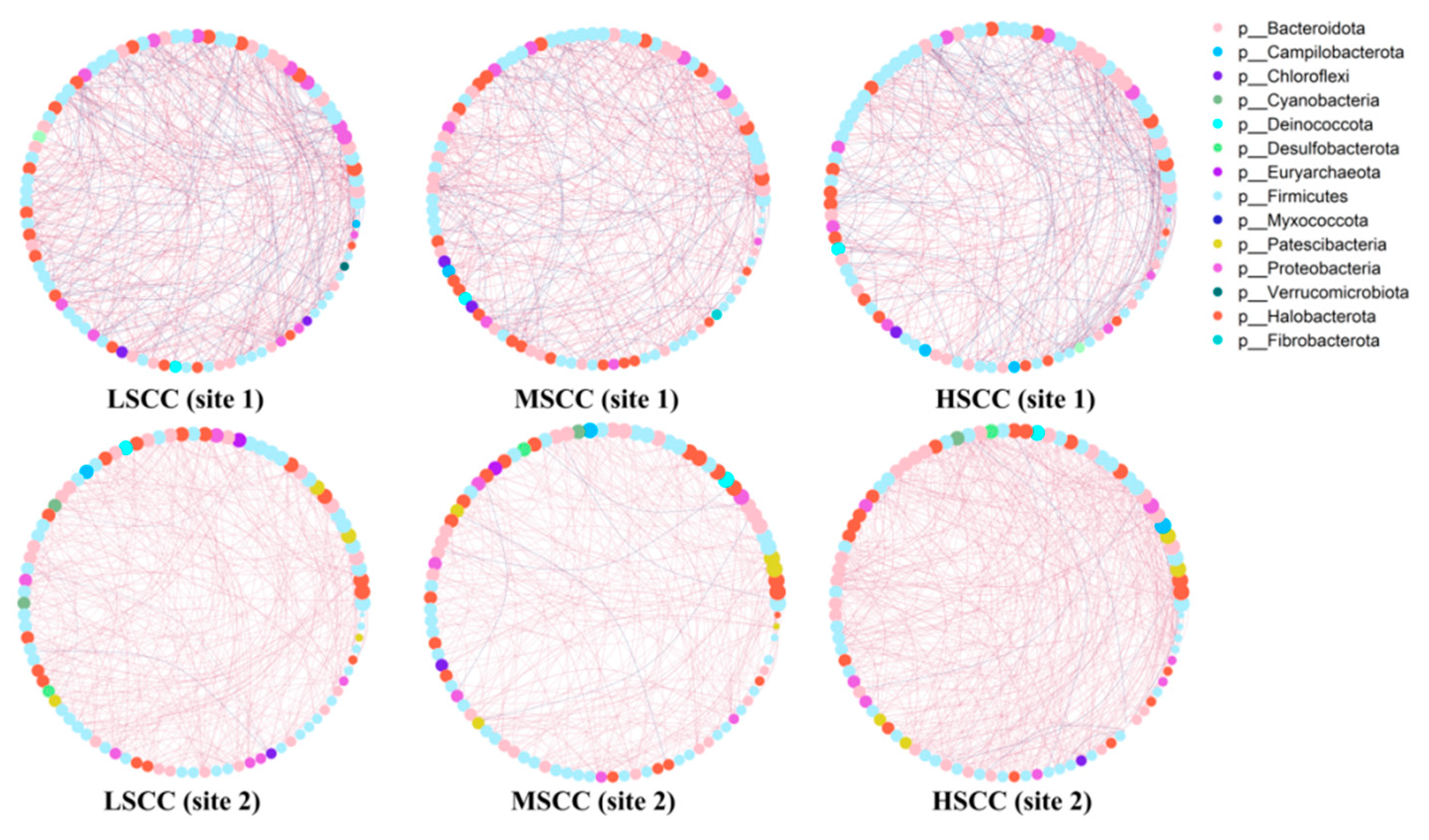
3.4. Comparative Analysis of Microbial Interaction Network
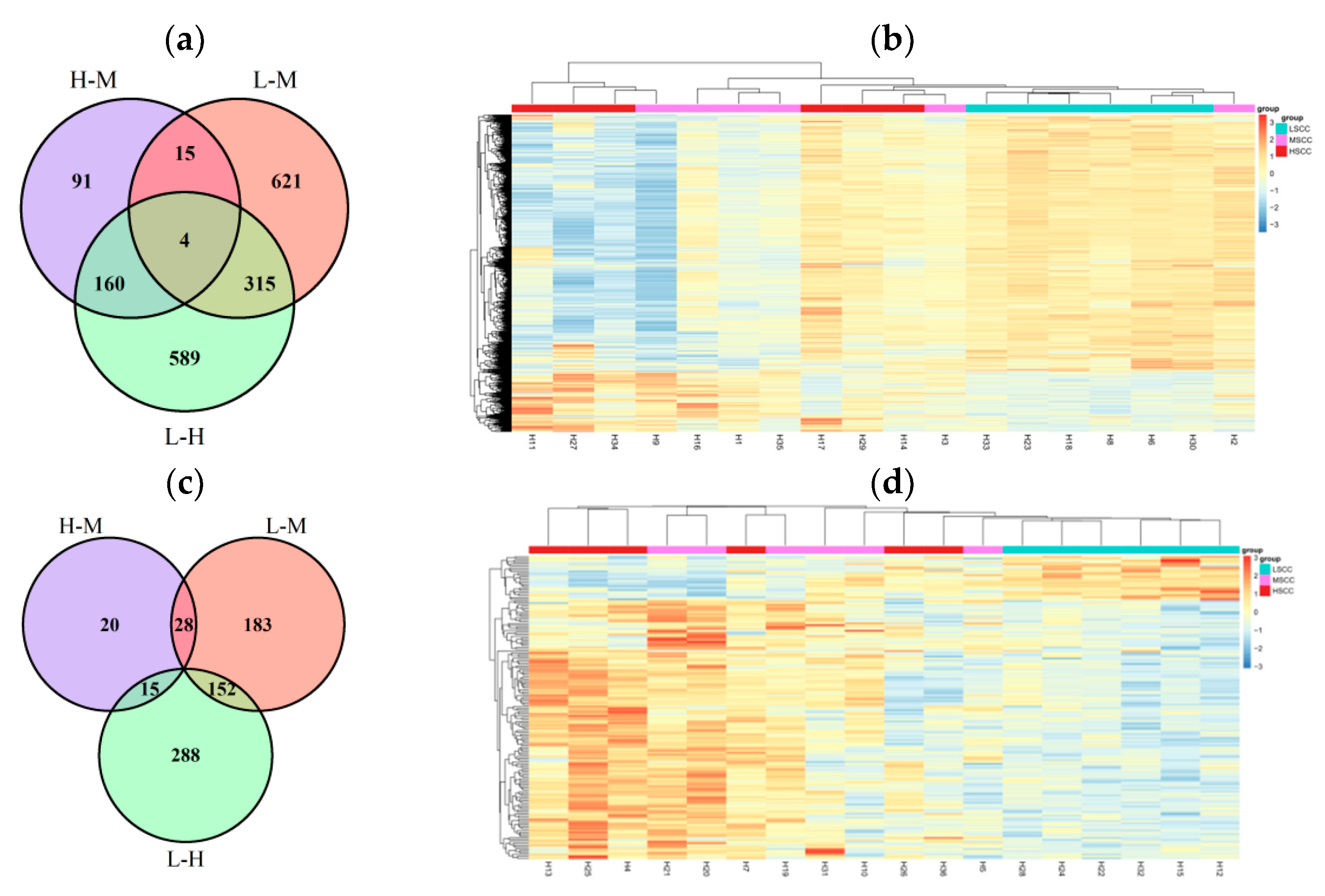
3.5. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes between Groups
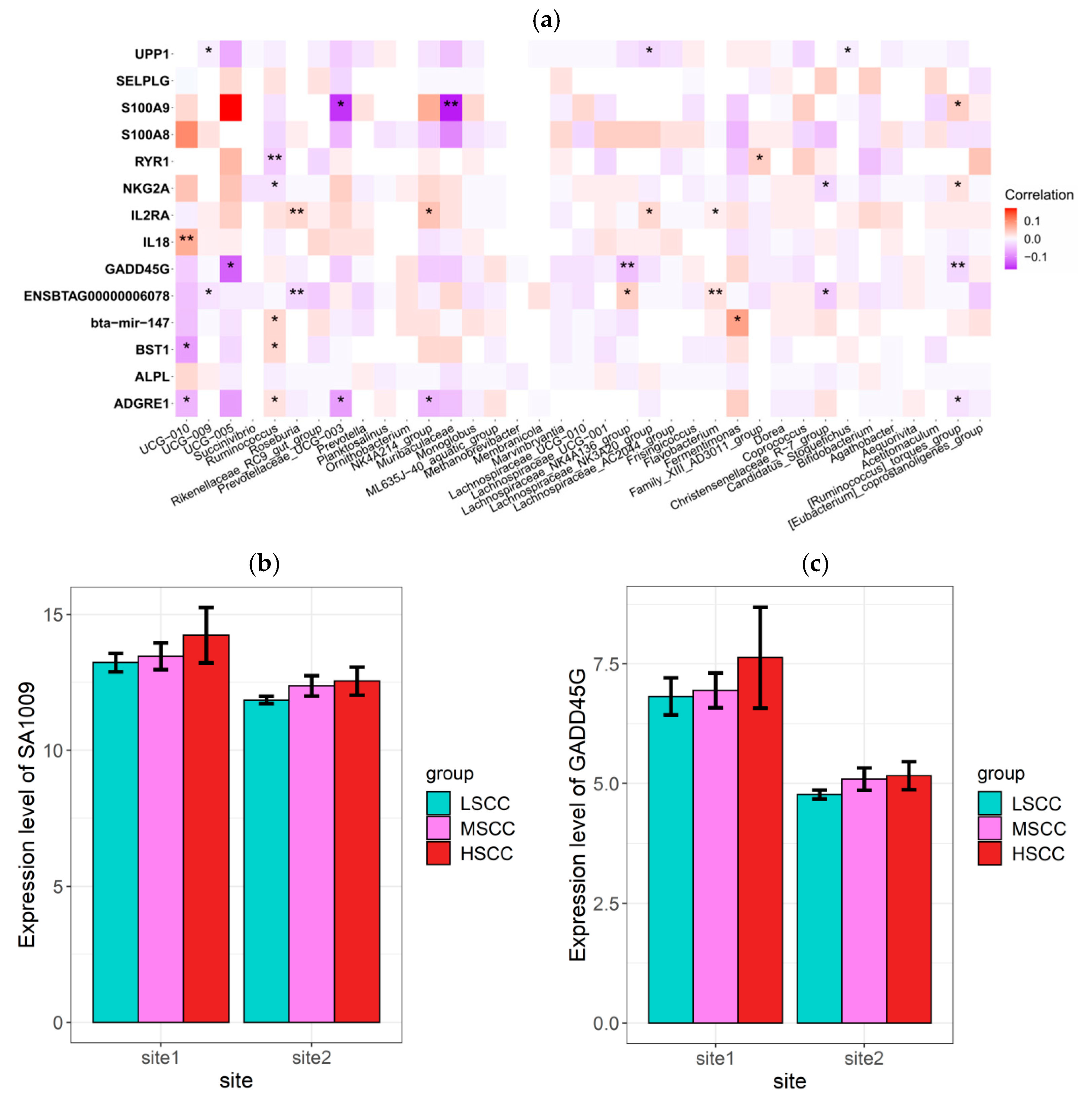
3.6. Correlation Analysis between Microbiota and Gene Profiles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Nan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, M.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, F.; Xue, F.; Hua, D.; Li, K.; et al. Coupling 16S rDNA Sequencing and Untargeted Mass Spectrometry for Milk Microbial Composition and Metabolites from Dairy Cows with Clinical and Subclinical Mastitis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 8496–8508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, P.V.; Das, D.N.; Suresh, K.P.; Shome, B.R. Threshold somatic cell count for delineation of subclinical mastitis cases. Vet. World 2018, 11, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, D.; Diesterbeck, U.S.; Failing, K.; Konig, S.; Brugemann, K.; Zschock, M.; Wolter, W.; Czerny, C.P. Somatic cell counts and bacteriological status in quarter foremilk samples of cows in Hesse, Germany—A longitudinal study. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 5716–5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, P.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y. The Distribution of SCC and Its Correlation with Milk Production Traits in Chinese Holsteins. Acta Vet. Zootech. Sin. 2010, 12, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafizur Rahaman Sumon, S.M.; Parvin, M.S.; Ehsan, M.A.; Islam, M.T. Relationship between somatic cell counts and subclinical mastitis in lactating dairy cows. Vet. World 2020, 13, 1709–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsback, L.; Lindmark-Mansson, H.; Andren, A.; Svennersten-Sjaunja, K. Evaluation of quality changes in udder quarter milk from cows with low-to-moderate somatic cell counts. Animal 2010, 4, 617–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hand, K.J.; Godkin, A.; Kelton, D.F. Milk production and somatic cell counts: A cow-level analysis. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 1358–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, S.; Virchow, F.; Torgerson, P.R.; Bischoff, M.; Biner, B.; Hartnack, S.; Ruegg, S.R. Test characteristics of milk amyloid A ELISA, somatic cell count, and bacteriological culture for detection of intramammary pathogens that cause subclinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7419–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petzer, I.M.; Karzis, J.; Donkin, E.F.; Webb, E.C.; Etter, E.M.C. Somatic cell count thresholds in composite and quarter milk samples as indicator of bovine intramammary infection status. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2017, 84, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, M.D.; Xie, X.; Bao, H.D.; Sun, L.C.; He, T.; Zhao, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, H.; Wei, R.C.; et al. Insights Into the Bovine Milk Microbiota in Dairy Farms With Different Incidence Rates of Subclinical Mastitis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gryaznova, M.V.; Syromyatnikov, M.Y.; Dvoretskaya, Y.D.; Solodskikh, S.A.; Klimov, N.T.; Mikhalev, V.I.; Zimnikov, V.I.; Mikhaylov, E.V.; Popov, V.N. Microbiota of Cow’s Milk with Udder Pathologies. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, K.; Gunther, J.; Talbot, R.; Petzl, W.; Zerbe, H.; Schuberth, H.J.; Seyfert, H.M.; Glass, E.J. Escherichia coli- and Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis differentially modulate transcriptional responses in neighbouring uninfected bovine mammary gland quarters. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, Z.; Buggiotti, L.; Salavati, M.; Marchitelli, C.; Palma-Vera, S.; Wylie, A.; Takeda, H.; Tang, L.; Crowe, M.A.; Wathes, D.C.; et al. Global transcriptomic profiles of circulating leucocytes in early lactation cows with clinical or subclinical mastitis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 4611–4623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derakhshani, H.; Fehr, K.B.; Sepehri, S.; Francoz, D.; De Buck, J.; Barkema, H.W.; Plaizier, J.C.; Khafipour, E. Invited review: Microbiota of the bovine udder: Contributing factors and potential implications for udder health and mastitis susceptibility. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 10605–10625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, D.; Kleinhans, S.; Reimann, G.; Stuckler, P.; Reith, F.; Ilves, K.; Pedastsaar, K.; Yan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Lorenzana, R.; et al. Associations between different udder health groups defined based on a combination of total and differential somatic cell count and the future udder health status of dairy cows. Prev. Vet. Med. 2021, 192, 105374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Zheng, Z.Q.; Liu, B.; Ji, X.Y.; Bai, Y.S.; Zhang, W.G. Whole blood transcriptional profiling comparison between different milk yield of Chinese Holstein cows using RNA-seq data. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, W.T.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.L.; Ning, C.; Ding, X.D.; Wang, W.W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, L. Integrative analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation and gene expression profiles reveals important epigenetic genes related to milk production traits in dairy cattle. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2021, 138, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falentin, H.; Rault, L.; Nicolas, A.; Bouchard, D.S.; Lassalas, J.; Lamberton, P.; Aubry, J.M.; Marnet, P.G.; Le Loir, Y.; Even, S. Bovine Teat Microbiome Analysis Revealed Reduced Alpha Diversity and Significant Changes in Taxonomic Profiles in Quarters with a History of Mastitis. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagahata, H.; Mukai, T.; Natsume, Y.; Okuda, M.; Ando, T.; Hisaeda, K.; Gondaira, S.; Higuchi, H. Effects of intramammary infusion of Bifidobacterium breve on mastitis pathogens and somatic cell response in quarters from dairy cows with chronic subclinical mastitis. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 91, e13406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, G.; Bicalho, M.L.; Meira, E.; Rossi, R.E.; Foditsch, C.; Machado, V.S.; Teixeira, A.G.V.; Santisteban, C.; Schukken, Y.H.; Bicalho, R.C. Microbiota of Cow’s Milk; Distinguishing Healthy, Sub-Clinically and Clinically Diseased Quarters. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ai, D.M.; Pan, H.F.; Li, X.X.; Wu, M.; Xia, L. Association network analysis identifies enzymatic components of gut microbiota that significantly differ between colorectal cancer patients and healthy controls. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsanelli, A.C.; Athayde, F.R.F.; Agostinho, S.D.; Riggio, M.P.; Dutra, I.S. Dental biofilm and its ecological interrelationships in ovine periodontitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2021, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mac Aogain, M.; Narayana, J.K.; Tiew, P.Y.; Ali, N.A.B.M.; Yong, V.F.L.; Jaggi, T.K.; Lim, A.Y.H.; Keir, H.R.; Dicker, A.J.; Thng, K.X.; et al. Integrative microbiomics in bronchiectasis exacerbations. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbons, S.M.; Duvallet, C.; Alm, E.J. Correcting for batch effects in case-control microbiome studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2018, 14, e1006102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nearing, J.T.; Douglas, G.M.; Hayes, M.G.; MacDonald, J.; Desai, D.K.; Allward, N.; Jones, C.M.A.; Wright, R.J.; Dhanani, A.S.; Comeau, A.M.; et al. Microbiome differential abundance methods produce different results across 38 datasets. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, S.; Pakdel, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Reecy, J.M.; Farsani, S.F.; Ebrahimie, E. Integration of machine learning and meta-analysis identifies the transcriptomic bio-signature of mastitis disease in cattle. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brand, K.S.; Filor, V.; Baumer, W. Early inflammatory events of mastitis—A pilot study with the isolated perfused bovine udder. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nan, X.M.; Zhao, Y.G.; Jiang, L.S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Hua, D.K.; Liu, J.; Yao, J.H.; Yang, L.; et al. Consumption of Supplementary Inulin Modulates Milk Microbiota and Metabolites in Dairy Cows with Subclinical Mastitis. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2022, 88, e02059-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nan, X.M.; Zhao, Y.G.; Jiang, L.S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Hua, D.K.; Liu, J.; Yao, J.H.; Yang, L.; et al. Dietary Supplementation of Inulin Ameliorates Subclinical Mastitis via Regulation of Rumen Microbial Community and Metabolites in Dairy Cows. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e00105-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, T.; Guo, R.; Cui, W.; Yu, W.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; et al. Variation of Serum Uric Acid Is Associated With Gut Microbiota in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 761757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Sarwar, K.; Dedrick, S.; Momeni, B.; Kelly, R.; Zeiger, R.; O’Connor, G.; Sandel, M.; Bacharier, L.; Beigelman, A.; Laranjo, N.; et al. Association of the Gut Microbiome and Metabolome with Wheeze Frequency in Childhood Asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immun. 2021, 147, Ab53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norstebo, H.; Dalen, G.; Rachah, A.; Heringstad, B.; Whist, A.C.; Nodtvedt, A.; Reksen, O. Factors associated with milking-to-milking variability in somatic cell counts from healthy cows in an automatic milking system. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 172, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

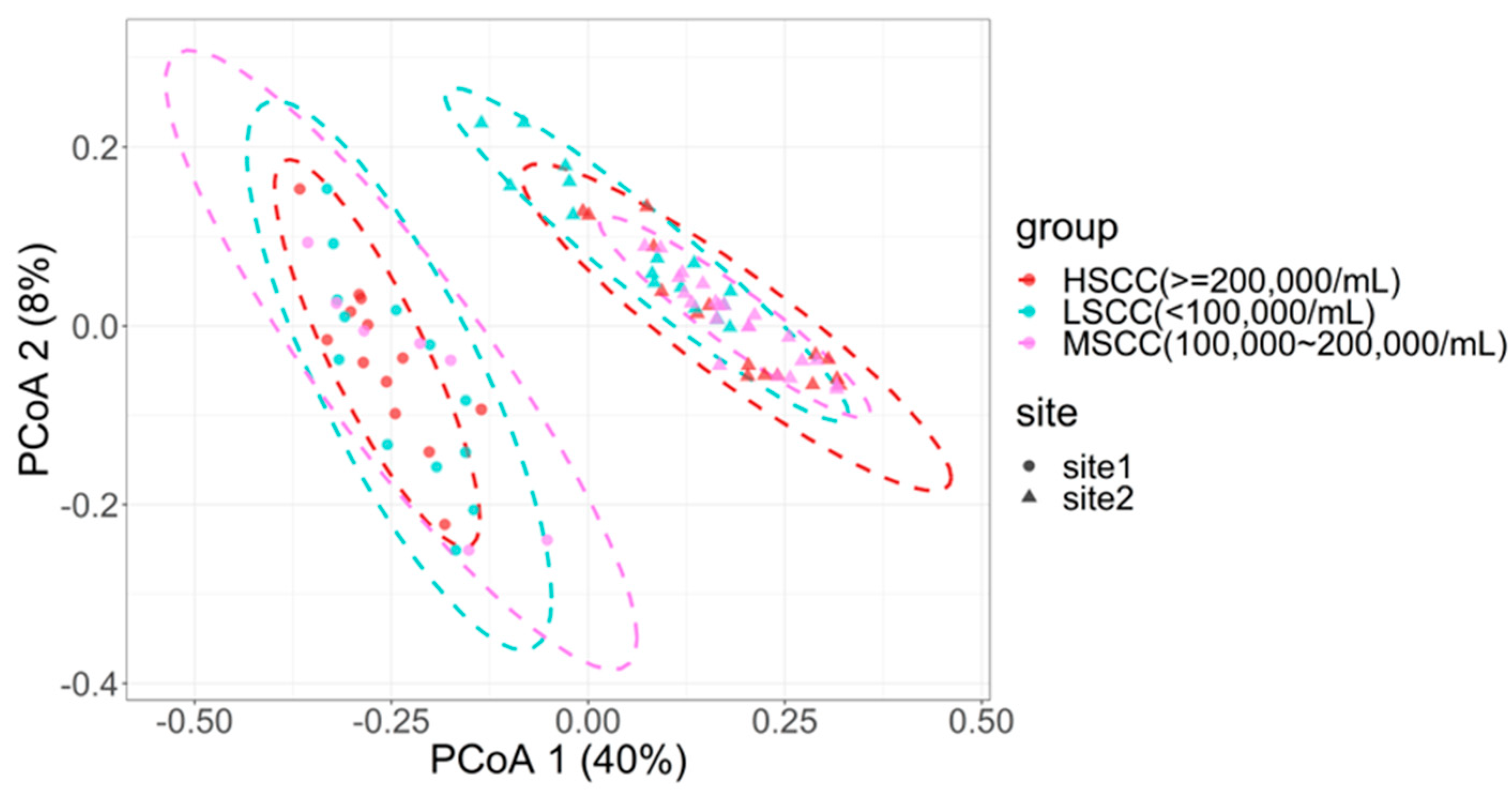
| Factors | Groups Incorporated in the Model (F Statistic/p Value) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-M (n = 58) | H-M (n = 58) | L-H (n = 58) | LM-H (n = 87) | HM-L (v = 87) | |
| site | 18.86/10−4 | 22.53/10−4 | 18.78/10−4 | 22.98/10−4 | 23.6/10−4 |
| group | 2.41/0.01 | 0.75/0.67 | 1.95/0.04 | 0.97/0.41 | 2.03/0.02 |
| lactation stage | 1.19/0.23 | 1.39/0.15 | 1.17/0.24 | 1.24/0.18 | 1.29/0.15 |
| parity | 1.19/0.22 | 1.10/0.28 | 1.22/0.21 | 1.23/0.18 | 1.17/0.21 |
| Comparison | Degree | Betweenness Centrality | Closeness Centrality | Transitivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSCC vs. HSCC | 0.20 a */0.19 b | 0.08 a/0.19 b | 0.90 a **/0.99 b ** | 0.19 a/0.25 b ** |
| LSCC vs. MSCC | 0.13 a/0.17 b | 0.15 a/0.08 b | 0.98 a **/0.79 b ** | 0.08 a/0.32 b ** |
| MSCC vs. HSCC | 0.14 a/0.36 b ** | 0.10 a/0.18 b | 0.98 a **/0.99 b ** | 0.19 a/0.42 b ** |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Yu, Y. Testing Two Somatic Cell Count Cutoff Values for Bovine Subclinical Mastitis Detection Based on Milk Microbiota and Peripheral Blood Leukocyte Transcriptome Profile. Animals 2022, 12, 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131694
Zhang J, Li W, Tang Y, Liu X, Zhang H, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Xiao W, Yu Y. Testing Two Somatic Cell Count Cutoff Values for Bovine Subclinical Mastitis Detection Based on Milk Microbiota and Peripheral Blood Leukocyte Transcriptome Profile. Animals. 2022; 12(13):1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131694
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jinning, Wenlong Li, Yongjie Tang, Xueqin Liu, Hailiang Zhang, Yueling Zhou, Yachun Wang, Wei Xiao, and Ying Yu. 2022. "Testing Two Somatic Cell Count Cutoff Values for Bovine Subclinical Mastitis Detection Based on Milk Microbiota and Peripheral Blood Leukocyte Transcriptome Profile" Animals 12, no. 13: 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131694
APA StyleZhang, J., Li, W., Tang, Y., Liu, X., Zhang, H., Zhou, Y., Wang, Y., Xiao, W., & Yu, Y. (2022). Testing Two Somatic Cell Count Cutoff Values for Bovine Subclinical Mastitis Detection Based on Milk Microbiota and Peripheral Blood Leukocyte Transcriptome Profile. Animals, 12(13), 1694. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12131694








