A Detailed Analysis of the Effect of Different Environmental Factors on Fish Phototactic Behavior: Directional Fish Guiding and Expelling Technique
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
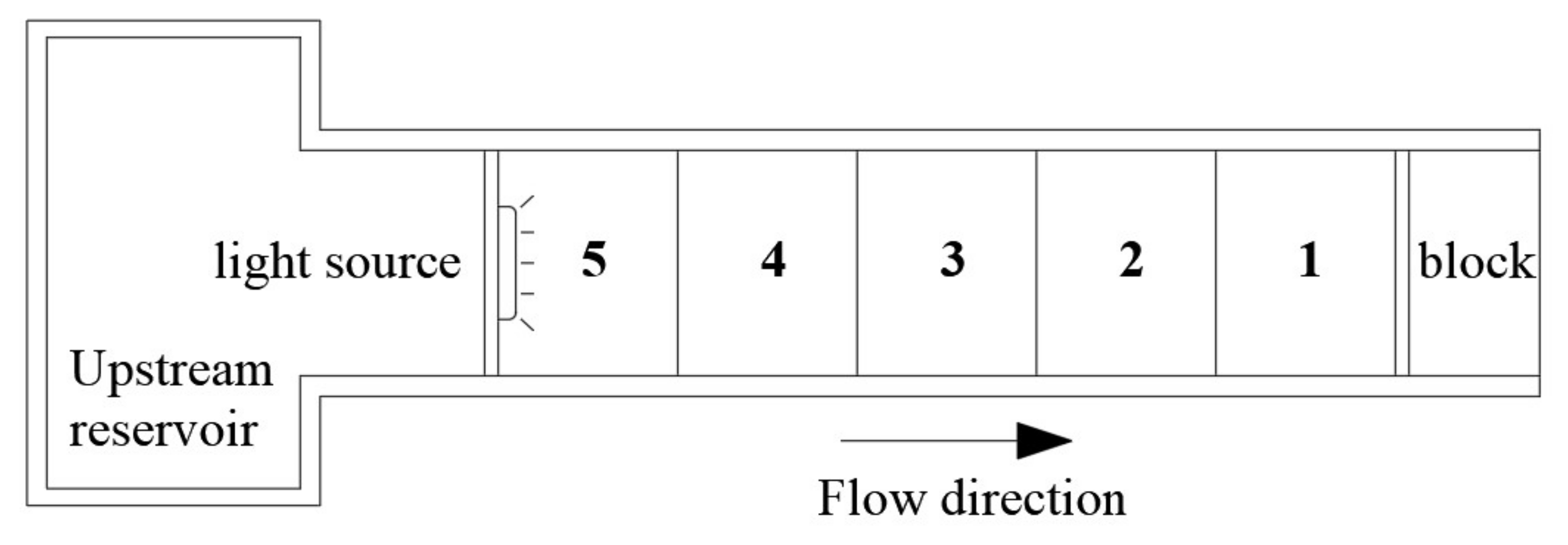
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Experimental Method
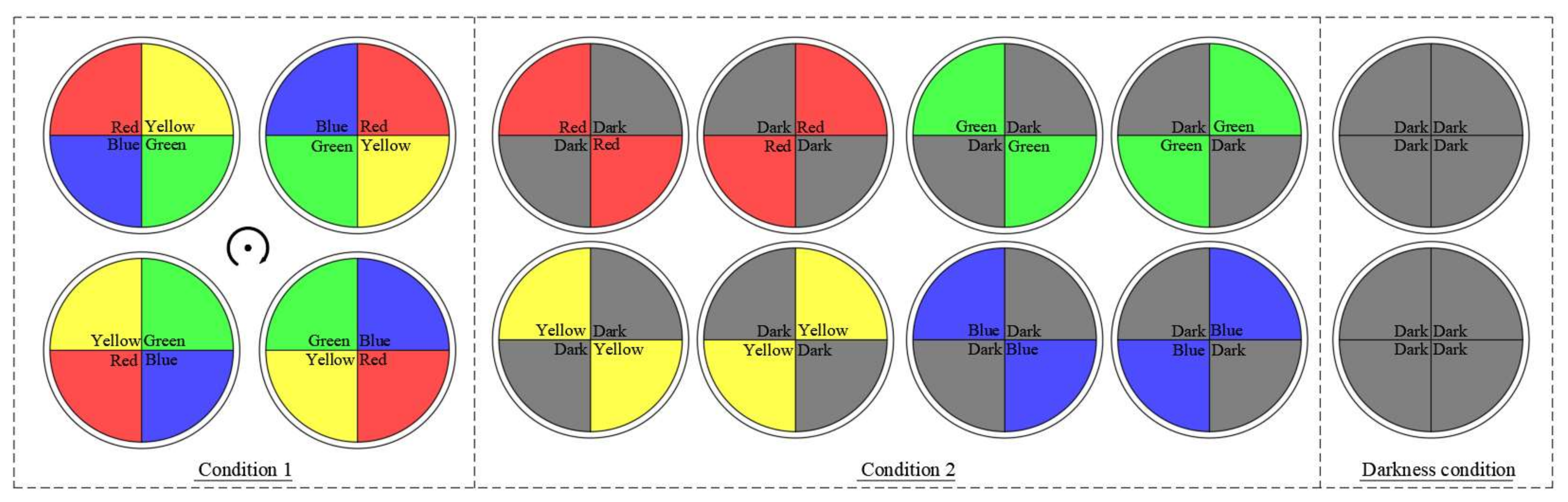
2.3.1. Selection of the Color of Light
- (1)
- The lights were arranged in the four areas of the circular sink in the order of red, yellow, green, and blue, and the phototactic behavior of the fish in each region was observed. After each trial, the original light color sequence was rotated clockwise to proceed to the next experiment.
- (2)
- Four light colors were paired with darkness (which mimicked night-time conditions) and arranged in four regions; the light of the same color was arranged diagonally. The color was rotated clockwise at the end of each experiment, keeping the order unchanged to ensure that there is no interference with the location of the tank on fish selection during the experiment. An experimental treatment in the absence of light (dark treatment) was set up to compare and observe the preference and avoidance of the fish.
2.3.2. Phototaxis Experiment
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Sensitivity of S. waltoni to the Light of Different Colors
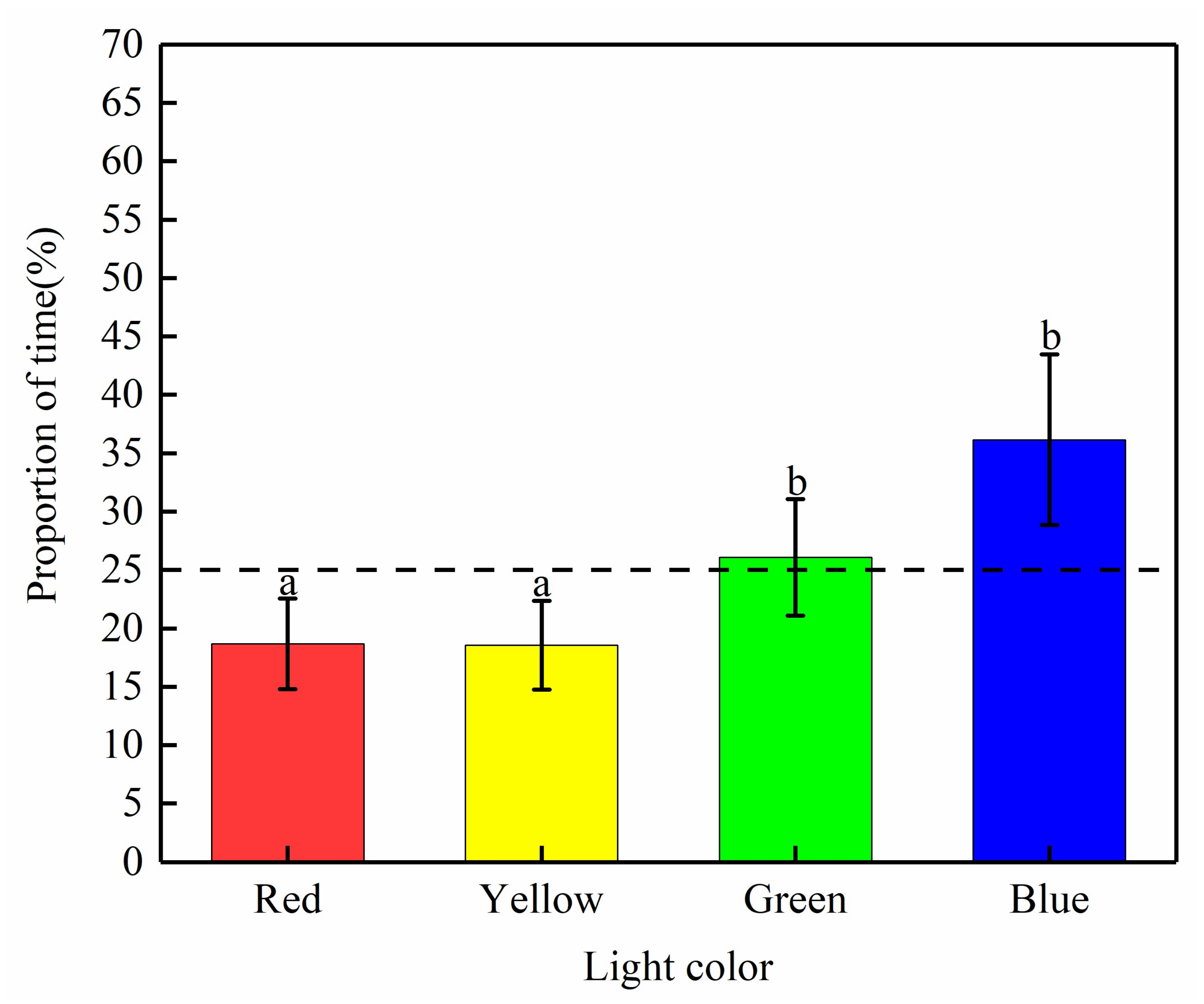
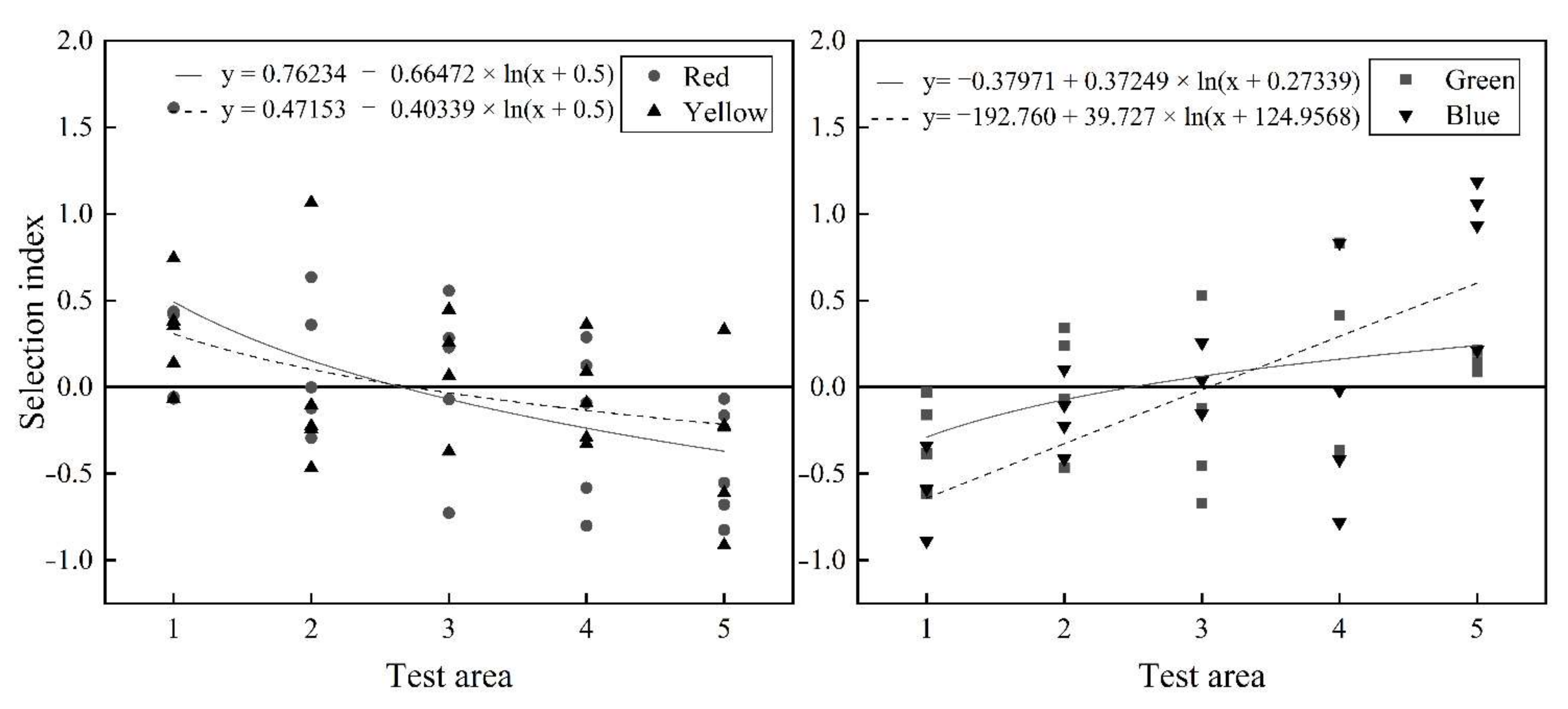
3.1.1. Preference of the Light of Different Colors by S. waltoni
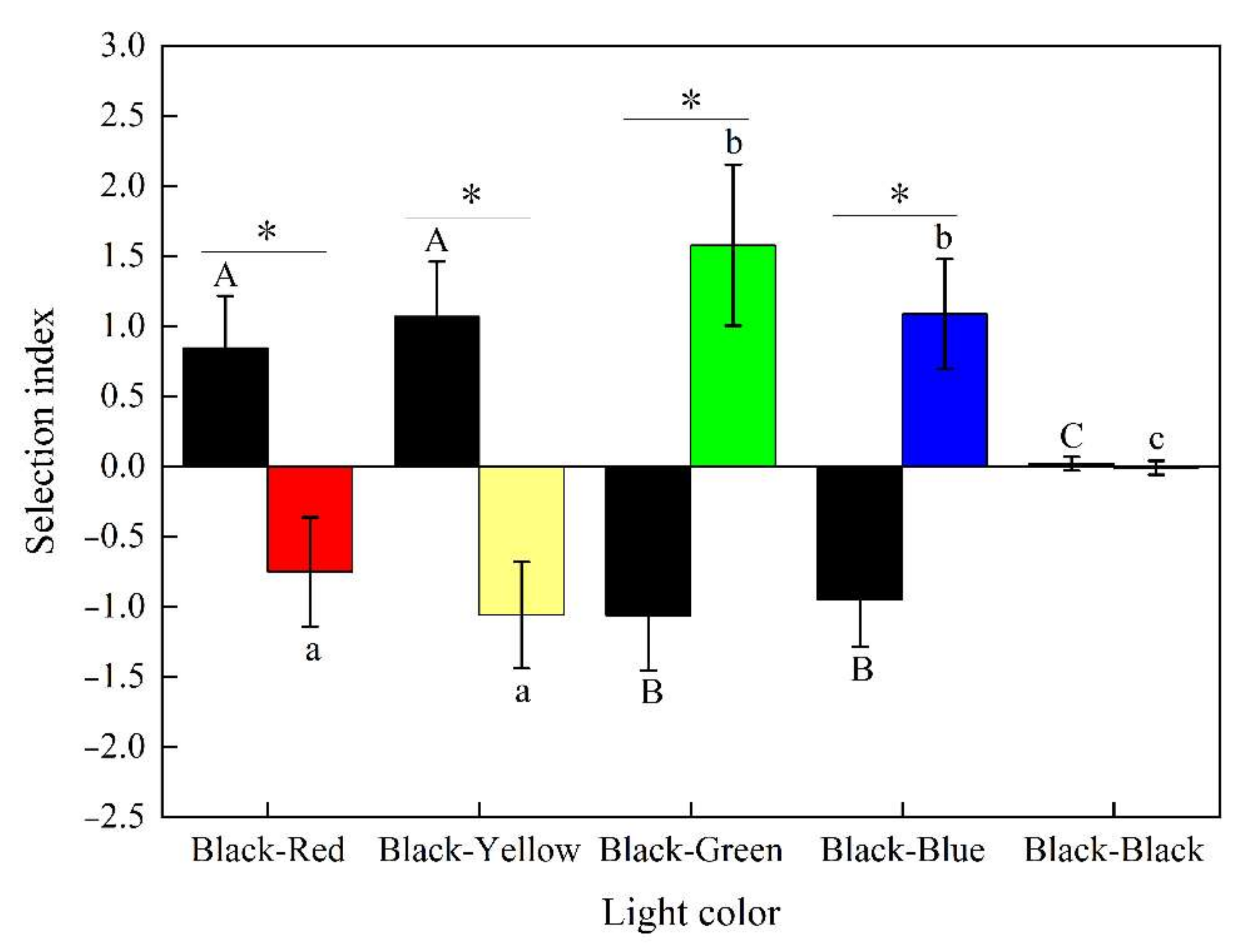
3.1.2. Determining the Phototaxis Behavior of S. waltoni in the Simulated Night-Time Environment
3.2. Behavioral Analysis of Water Flow Affecting the Light-Sensing Environment of Fish
3.3. Coupling Analysis of Rheotaxis and Phototaxis of S. waltoni at Different Water Temperatures
3.4. Phototaxis Threshold of Fish in Different Light Environments
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of the Color of Light by S. waltoni
4.2. Preference of Light Intensity in S. waltoni
4.3. Influence of Water Temperature on Phototaxis and Fluidity of Fish
4.4. Interaction between Phototaxis and Fluidity
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Newbold, L.R.; Shi, X.T.; Hou, Y.Q.; Han, D.J.; Kemp, P.S. Swimming performance and behaviour of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis): Application to fish passage and exclusion criteria. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 95, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Pinheiro, A.N.; Bochechas, J.H. Effects of small hydropower plants on fish assemblages in medium-sized streams in central and northern Portugal. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2006, 16, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Jorde, K.; Habit, E.; Caamaño, D.; Parra, O. Downstream environmental effects of dam operations: Changes in habitat quality for native fish species. River Res. Appl. 2015, 7, 312–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, I.G.; Berghuis, A.P. Upstream passage of fish through a vertical-slot fishway in an Australian subtropical river. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2002, 9, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roscoe, D.W.; Hinch, S.G. Effectiveness monitoring of fish passage facilities: Historical trends, geographic patterns and future directions. Fish Fish. 2010, 11, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.J.; Jackson, P.R.; Engel, F.L.; LeRoy, J.Z.; Neeley, R.N.; Finney, S.T. Entrainment, retention, and transport of freely swimming fish in junction gaps between commercial barges operating on the Illinois Waterway. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.; Montie, E.W.; Mann, K.A.; Mann, D.A. Ultrasound detection in the Gulf menhaden requires gas-filled bullae and an intact lateral line. J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 212, 3422–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arimoto, T.; Akiyama, S.; Kikuya, K.; Kobayashi, H. Fish-herding effect of an air bubble curtain and its application to setnet fisheries. Fish Behav. Relat. Fish. Oper. 1991, 196, 155–160. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, S.; Brüning, A.; Hölker, F.; Kloas, W. Study of biological action of light on fish. J. Light Vis. Environ. 2013, 37, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mesquita, F.D.O.; Godinho, H.P.; Azevedo, P.G.D.; Young, R.J. A preliminary study into the effectiveness of stroboscopic light as an aversive stimulus for fish. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2008, 111, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, B.J.; Murchy, K.A.; Cupp, A.R.; Amberg, J.J.; Gaikowski, M.P.; Mensinger, A.F. Acoustic deterrence of bighead carp (Hypophthalmichthys nobilis) to a broadband sound stimulus. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 43, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castrosantos, T. Optimal swim speeds for traversing velocity barriers: An analysis of volitional high-speed swimming behavior of migratory fishes. J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 208, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rick, I.P.; Bakker, T.C.M. Males do not see only red: UV wavelengths and male territorial aggression in the three-spined stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus). Naturwissenschaften 2008, 95, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenneth, J.R. Illumination, Vision, and Schooling of Astyanax mexicanus (Fillipi). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 1964, 21, 1453–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayarri, M.J.; Madrid, J.A.; Sánchez-Vázquez, F.J. Influence of light intensity, spectrum and orientation on sea bass plasma and ocular melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2002, 32, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vera, L.M.; Davie, A.; Taylor, J.F.; Migaud, H. Differential light intensity and spectral sensitivities of Atlantic salmon, European sea bass and Atlantic cod pineal glands ex vivo. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 65, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamizar, N.; Blanco-Vives, B.; Migaud, H.; Davie, A.; Carboni, S.; Sanchez-Vazques, F.J. Effects of light during early larval development of some aquacultured teleosts: A review. Aquaculture 2011, 315, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanome, T.; Mizusawa, K.; Hasegawa, E.; Takahashi, A. Green light stimulates somatic growth in the barfin flounder, Verasper moseri. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Genet. Physiol. 2009, 311, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downing, G.; Litvak, M.K. The effect of light intensity and spectrum on the incidence of first feeding by larval haddock. J. Fish Biol. 2001, 59, 1566–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duray, M.; Kohno, H. Effects of continuous lighting on growth and survival of first-feeding larval rabbitfish. Siganus Guttatus Aquac. 1988, 72, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appelbaum, S.; Mcgeer, J.C. Effect of diet and light regime on growth and survival of African catfish (Clarias gariepinus) larvae and early juveniles. Aquac. Nutr. 1998, 4, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baras, E.; Tissier, F.; Westerloppe, L.; Mélard, C.; Philippart, J.C. Feeding in darkness alleviates density-dependent growth of juvenile vundu catfish Heterobranchus longifilis (Clariidae). Aquat. Living Resour. 1998, 11, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Dai, H.C.; Shi, X.T.; Deng ZQ, D.; Mao, J.Q.; Luo, J.; Huang, W.Q.; Xu, J.W.; Zhang, N.; Sun, S.K. Investigating feasible light configurations for fish restoration: An ethological insight. Fish. Res. 2020, 234, 105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeuf, G.; Bail, P.Y.L. Does light have an influence on fish growth? Aquaculture 1999, 177, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchin, A.B. Effect of illumination on fish and amphibian: Development, growth, physiological and biochemical processes. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 13, 567–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, T.M.; Lindmark, E.M.; Lundström, T.S.; Gustavsson, L.H. Flow characterization of an attraction channel as entrance to fishways. River Res. Appl. 2011, 27, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vowles, A.S.; Kemp, P.S. Effects of light on the behaviour of brown trout (Salmo trutta) encountering accelerating flow: Application to downstream fish passage. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 47, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, N.J.; Hinch, S.G.; Bett, N.N.; Braun, D.C.; Casselman, M.T.; Cooke, S.J.; Gelchu, A.; Lingard, S.; Middleton, C.T.; Minke-Martin, V.; et al. Reducing Carryover Effects on the Migration and Spawning Success of Sockeye Salmon through a Management Experiment of Dam Flows. River Res. Appl. 2017, 33, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juell, J.E.; Oppedal, F.; Boxaspen, K.; Taranger, G.L. Submerged light increases swimming depth and reduces fish density of Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. in production cages. Aquac. Res. 2003, 34, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stien, L.H.; Fosseidengen, J.E.; Malm, M.E.; Sveier, H.; Torgersen, H.; Wright, D.W.; Oppedal, F. Low intensity light of different colours modifies Atlantic salmon depth use. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 62, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juell, J.E.; Fosseidengen, J.E. Use of artificial light to control swimming depth and fish density of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) in production cages. Aquaculture 2004, 233, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, J.C.; Baker, C.F.; Carton, A.G. The lateral line can mediate rheotaxis in fish. Nature 1997, 389, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laine, A.; Jokivirta, T.; Katopodis, C. Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar L. and sea trout, Salmo trutta L. passage in a regulated northern river—Fishway efficiency, fish entrance and environmental factors. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2002, 9, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.J.; Baumgartner, L.J.; Zampatti, B.P.; Beyer, K. Low light inhibits native fish movement through a vertical-slot fishway: Implications for engineering design. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2017, 24, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, N.W.; Munday, P.L. Effects of climate change on fish reproduction and early life history stages. Mar. Freshw. Res. 2011, 62, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Samaras, A.; Papandroulakis, N.; Lika, K.; Pavlidis, M. Water temperature modifies the acute stress response of European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax L.(1758). J. Therm. Biol. 2018, 78, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, N.R.; Fish, J.D.; Wootton, R.J. Feeding and growth of juvenile sea bass: The effect of ration and temperature on growth rate and efficiency. J. Fish Biol. 1996, 49, 206–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Yu, Z.Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, X.L.; Shang, C.X. Spatial-temporal variation of lake surface water temperature and its driving factors in Yunnan-Guizhou Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 4688–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugg, A.; Copeland, C. Review of cold water pollution in the murray–darling basin and the impacts on fish communities. Ecol. Manag. Restor. 2014, 15, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Marin, L.A.; Rokaya, P.; Sanyal, P.R.; Sereda, J.; Lindenschmidt, K.E. Changes in streamflow and water temperature affect fish habitat in the Athabasca River basin in the context of climate change. Ecol. Model. 2019, 407, 108718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.Z.; Zhang, G.R.; Wei, K.J.; Ji, W.; Yan, R.J.; Wei, Q.W. Gardner JPA Phylogeography of the threatened tetraploid fish, Schizothorax waltoni, in the Yarlung Tsangpo River on the southern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Implications for conservation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Wardle, C.S. Optomotor response and erratic response: Quantitative analysis of fish reaction to towed fishing gears. Fish. Res. 2003, 60, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.F.; North, B.P.; Porter, M.J.R.; Bromage, N.R.; Migaud, H. Photoperiod can be used to enhance growth and improve feeding efficiency in farmed rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.W.; Liu, Q.; Cui, X.; Shen, X.F.; Hu, P.F.; Liu, W.L.; Ge, Y.W.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.L.; Song, C.B.; et al. Growth, development and survival of European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae cultured under different light spectra and intensities. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 2066–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spence, R.; Smith, C. Innate and learned colour preference in the zebrafish. Danio Rerio. Ethol. 2008, 114, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, J.F.P.; Gallagher, T.; Hart, N.S.; Barnes, A.C.; Smullen, R.P.; Collin, S.P.; Temple, S.E. Tank colour increases growth, and alters colour preference and spectral sensitivity, in barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Aquaculture 2011, 322, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Nai, H.T.; Lim, L.S. Why is cannibalism less frequent when larvae of sutchi catfish Pangasianodon hypophthalmus are reared under dim light. Aquaculture 2015, 46, 1958–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcón, J.; Migaud, H.; Muñoz-Cueto, J.A.; Carrillo, M. Current knowledge on the melatonin system in teleost fish. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2010, 165, 69–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navarro, F.K.S.P.; Navarro, R.D.; Murgas, L.D.S.; Felizardo, V.O. Effect of photoperiod stress assessment and locomotor activity of female lambari (Astyanax bimaculatus). CiÊNcia E Agrotecnologia 2014, 38, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kitagawa, A.T.; Costa, L.S.; Paulino, R.R.; Luz, R.K.; Rosa, P.V.; Guerra-Santos, B.; Fortes-Silva, R. Feeding behavior and the effect of photoperiod on the performance and hematological parameters of the pacamã catfish (Lophiosilurus alexandri). Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2015, 171, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.B.; Ha, J.C.; Gonçalves-de-Freitas, E. Light intensity can trigger different agonistic responses in juveniles of three cichlid species. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2012, 45, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarmento, C.G.; Almeida, E.S.; Marcon, J.L.; Carvalho, T.B. Body color pattern and agressiveness related to behavioral context and light intensity in an Amazonian cichlid, Laetacara fulvipinnis Staeck & Schindler, 2007. Mar. Freshw. Behav. Physiol. 2017, 50, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmon, M.; Witherington, B.E. Artificial Lighting and Seafinding by Loggerhead Hatchlings: Evidence for Lunar Modulation. In Copeia; American Society of Ichthyologists and Herpetologists (ASIH): Lawrence, KS, USA, 1995; p. 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Gonçalves, D. Hormones and social behavior of teleost fish. In Fish Behavior; Magnhagen, C., Braithwaite, V.A., Forsgren, E., Kapoor, E.B.G., Eds.; Science Publishers: Enfield, NH, USA, 2008; pp. 61–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahel, F.J.; McLaughlin, R.L. Selective fragmentation and the management of fish movement across anthropogenic barriers. Ecol. Appl. 2018, 28, 2066–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Partridge, J.C.; Cummings, M.E. Adaptation of visual pigments to the aquatic environment. In Adaptive Mechanisms in the Ecology of Vision; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1999; pp. 251–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanailides, C.; Paschos, I.; Tsoumani, M.; Perdikaris, C.; Kapareliotis, A. Capacity for thermal acclimation and winter mortality of sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax in freshwater earthen ponds. Ital. J. Zool. 2010, 77, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLean, M.F.; Hanson, K.C.; Cooke, S.J.; Hinch, S.G.; Patterson, D.A.; Nettles, T.L.; Litvak, M.K.; Crossin, G.T. Physiological stress response, reflex impairment and delayed mortality of white sturgeon Acipenser transmontanus exposed to simulated fisheries stressors. Conserv. Physiol. 2016, 4, cow031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, X.P.; Zhen, W.Y.; Li, X.; Cao, P.; Gong, L.; Xu, F. A Study of the Impact of Different Flow Velocities and Light Colors at the Entrance of a Fish Collection System on the Upstream Swimming Behavior of Juvenile Grass Carp. Water 2019, 11, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bunt, C.M. Fishway entrance modifications enhance fish attraction. Fish. Manag. Ecol. 2001, 8, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, R.P.; Simmons, M.A. Characterization of gatewell orifice lighting at the bonneville dam second powerhouse and compendium of research on light guidance with juvenile salmonids. Tech. Rep. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


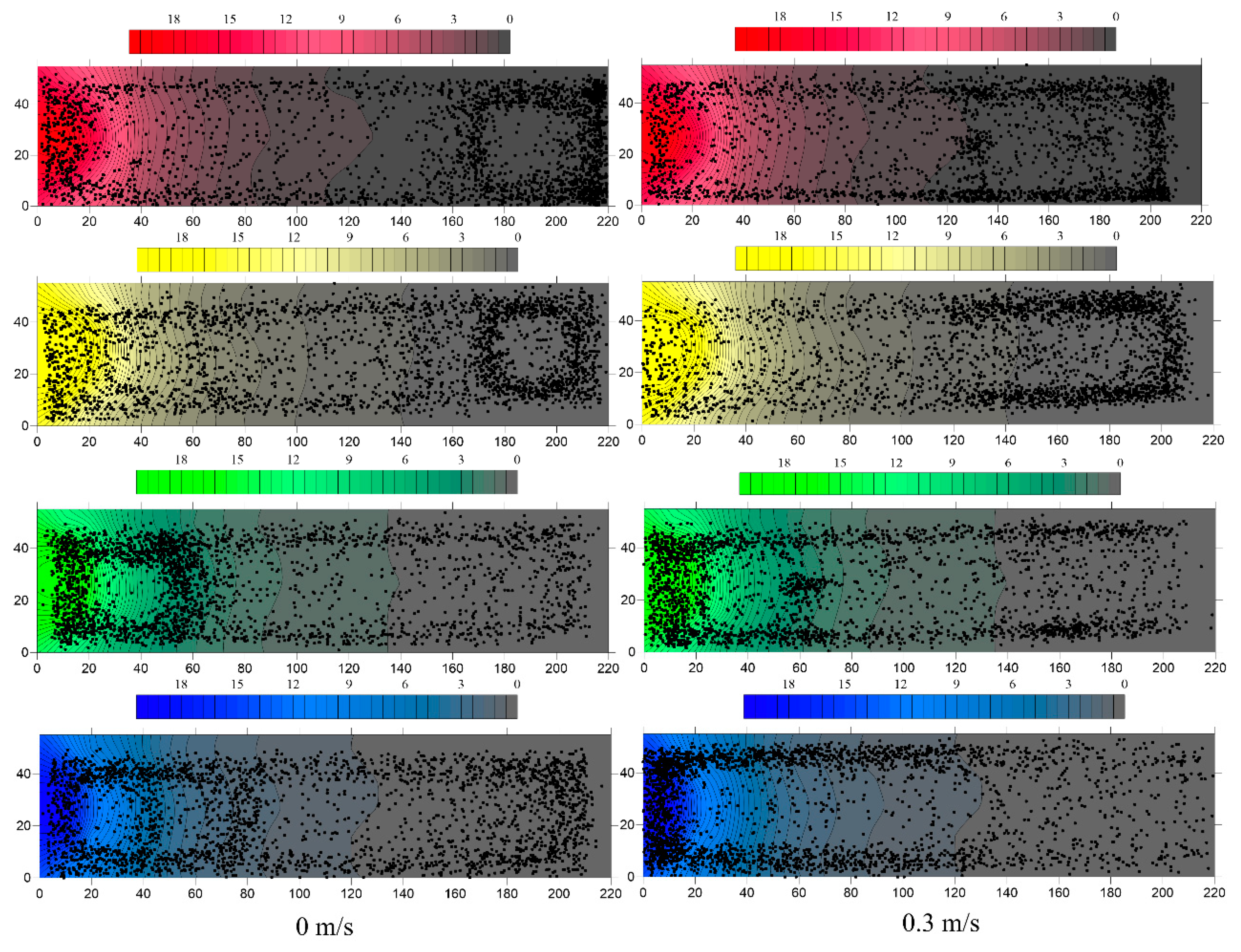


| Temperature/Velocity | 0 m/s | 0.3 m/s |
|---|---|---|
| 15 °C | Red | Red |
| Yellow | Yellow | |
| Green | Green | |
| Blue | Blue | |
| 18 °C | Red | Red |
| Yellow | Yellow | |
| Green | Green | |
| Blue | Blue |
| Circular flume | Area 1 | Area 2 | Area 3 | Area 4 | |
| 24.32% | 17.33% | 25.62% | 32.73% | ||
| Rectangular flume | Area 1 | Area 2 | Area 3 | Area 4 | Area 5 |
| 37.26% | 18.55% | 6.61% | 11.64% | 25.94% | |
| Red | Yellow | Green | Blue | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 m/s | 0.45 a ± 0.35 | 0.61 a ± 0.41 | 1.46 a ± 0. 32 | 2.87 a ± 0.84 |
| 0.3 m/s | 0.15 b ± 0.11 | 0.15 b ± 0.03 | 2.03 a ± 0.59 | 4.10 b ± 0.10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Sang, W.; Dai, H.; Lin, C.; Ke, S.; Mao, J.; Wang, G.; Shi, X. A Detailed Analysis of the Effect of Different Environmental Factors on Fish Phototactic Behavior: Directional Fish Guiding and Expelling Technique. Animals 2022, 12, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030240
Xu J, Sang W, Dai H, Lin C, Ke S, Mao J, Wang G, Shi X. A Detailed Analysis of the Effect of Different Environmental Factors on Fish Phototactic Behavior: Directional Fish Guiding and Expelling Technique. Animals. 2022; 12(3):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030240
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiawei, Wenlu Sang, Huichao Dai, Chenyu Lin, Senfan Ke, Jingqiao Mao, Gang Wang, and Xiaotao Shi. 2022. "A Detailed Analysis of the Effect of Different Environmental Factors on Fish Phototactic Behavior: Directional Fish Guiding and Expelling Technique" Animals 12, no. 3: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030240
APA StyleXu, J., Sang, W., Dai, H., Lin, C., Ke, S., Mao, J., Wang, G., & Shi, X. (2022). A Detailed Analysis of the Effect of Different Environmental Factors on Fish Phototactic Behavior: Directional Fish Guiding and Expelling Technique. Animals, 12(3), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12030240






