The Effect of Different Preoperative Depilation Ways on the Healing of Wounded Skin in Mice
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Ethics Statement
2.2. Anesthesia
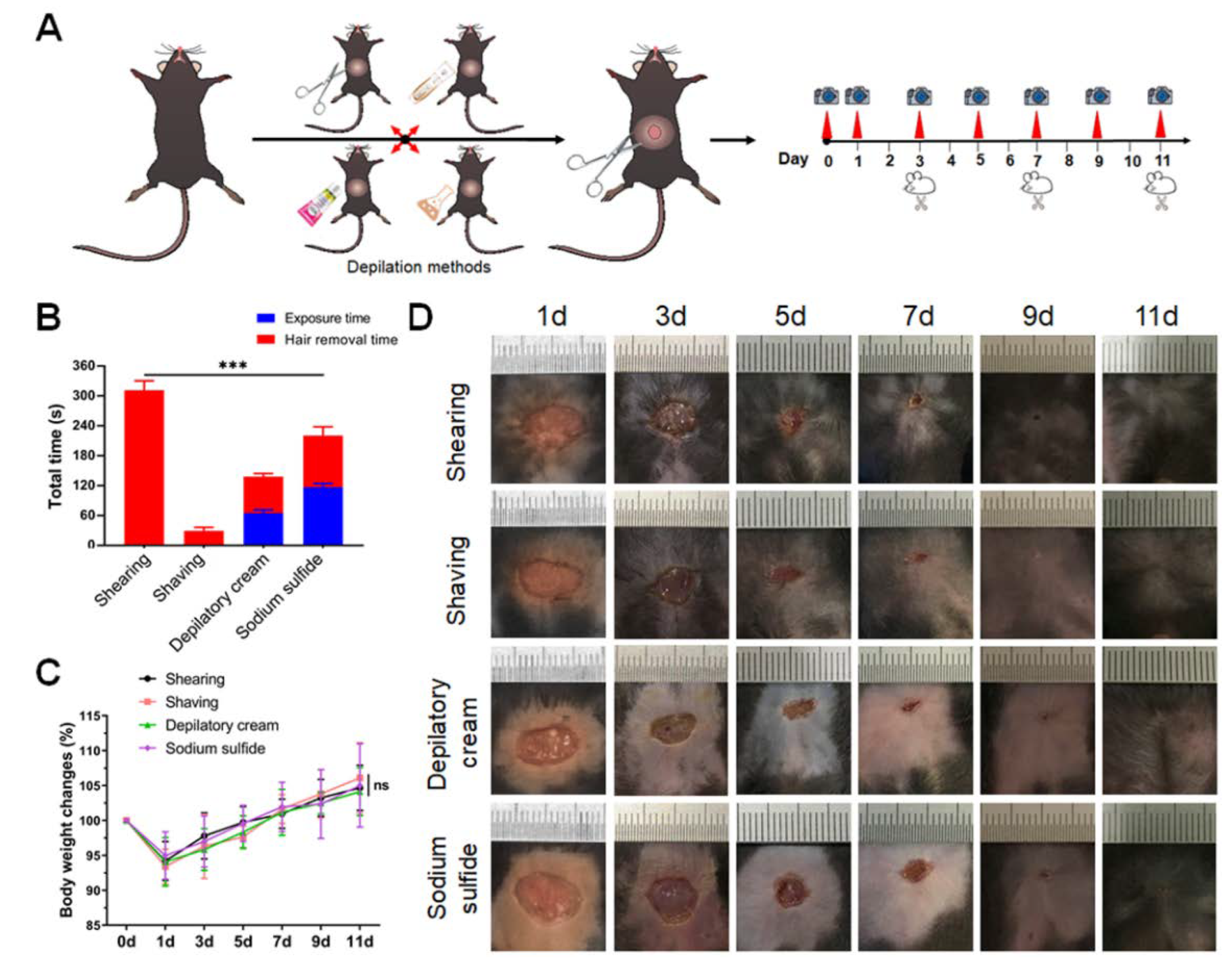
2.3. Depilation and Trauma Model
2.4. Calculation of Wound Contraction Rate and Wound Healing Time
2.5. Histopathology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sodium Sulfide Tends to Cause the Symptoms of Inflammation around the Wounded Area
3.2. Sodium Sulfide Aqueous Solution Depilation Prolongs the Healing Time
3.3. Chemical Depilation Enhances the Inflammatory Response of Wounded Area
3.4. Chemical Depilation Decreases the Content and Delays Regeneration of Collagen Fibers
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaniotakis, I.; Antoniou, E.; Kostomitsopoulos, N.; Karapsias, S.; Mirilas, P.; Salakos, C. Stress response to ovariohysterectomy in rabbits: Role of anaesthesia and surgery. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 38, 697–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baum, B. Not Just Uterine Adenocarcinoma-Neoplastic and Non-Neoplastic Masses in Domestic Pet Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus): A Review. Vet. Pathol. 2021, 58, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsueh, C.; Giuffrida, M.; Mayhew, P.D.; Case, J.B.; Singh, A.; Monnet, E.; Holt, D.E.; Cray, M.; Curcillo, C.; Runge, J.J. Evaluation of pet owner preferences for operative sterilization techniques in female dogs within the veterinary community. Vet. Surg. 2018, 47, O15–O25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okoli, C.C.; Anyanwu, S.N.; Emegoakor, C.D.; Chianakwana, G.U.; Ihekwoaba, E.; Ughasoro, M.D.; Egwuonwu, O.A.; Nzeako, H. Does preoperative chemical depilation make any difference in postoperative wound infection? Niger J. Clin. Pract. 2020, 23, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karegoudar, J.S.; Prabhakar, P.J.; Vijayanath, V.; Anitha, M.R.; Surpur, R.R.; Patil, V.M. Shaving Versus Depilation Cream for Pre-operative Skin Preparation. Indian J. Surg. 2012, 74, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kjønniksen, I.; Andersen, B.M.; Søndenaa, V.G.; Segadal, L. Preoperative hair removal–a systematic literature review. Aorn J. 2002, 75, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.L.; Achten, J.; Knight, R.; Png, M.E.; Bruce, J.; Dutton, S.; Madan, J.; Vadher, K.; Dritsaki, M.; Masters, J.; et al. Negative-pressure wound therapy compared with standard dressings following surgical treatment of major trauma to the lower limb: The WHiST RCT. Randomized Control. Trial 2020, 24, 1–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huss, M.K.; Casey, K.M.; Hu, J.; Moorhead, R.C.; Chum, H.H. Evaluation of 3 Alcohol-based Agents for Presurgical Skin Preparation in Mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci 2020, 59, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kick, B.L.; Gumber, S.; Wang, H.; Moore, R.H.; Taylor, D.K. Evaluation of 4 Presurgical Skin Preparation Methods in Mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2019, 58, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duverger, O.; Morasso, M.I. To grow or not to grow: Hair morphogenesis and human genetic hair disorders. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 25-26, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, C.N.; Shah, M.; Lynde, C.; Fleming, P. Hair Removal Practices: A Literature Review. Skin Therapy Lett. 2021, 26, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Pany, A.; Klang, V.; Brunner, M.; Ruthofer, J.; Schwarz, E.; Valenta, C. Effect of Physical and Chemical Hair Removal Methods on Skin Barrier Function in vitro: Consequences for a Hydrophilic Model Permeant. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2019, 32, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, J.; Melen, K. Preoperative hair removal to reduce surgical site infection. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 26, CD004122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adisa, A.O.; Lawal, O.O.; Adejuyigbe, O. Evaluation of two methods of preoperative hair removal and their relationship to postoperative wound infection. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries 2011, 5, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexander, J.W.; Fischer, J.E.; Boyajian, M.; Palmquist, J.; Morris, M.J. The influence of hair-removal methods on wound infections. Arch. Surg. 1983, 118, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, N.L.; Ramos-Rivera, E.; Raiciulescu, S.; Lee, S.H.; Christy, A.C. Comparison of Two Hair Removal Methods in Sprague-Dawley Rats (Rattus norvegicus). J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2021, 60, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, F.; Tavakkoli Yaraki, M.; Farrokhnia, A.; Bamdad, M. Keratin nanoparticles obtained from human hair for removal of crystal violet from aqueous solution: Optimized by Taguchi method. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 143, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Panicker, A.G.; Indrakumar, S.; Chatterjee, K. Comparative study of keratin extraction from human hair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, M.F.; Jorysz, M.; Schieren, G.; Knight, K.R.; O’Brien, B.M. Hair removal by a depilatory does not affect survival in rodent experimental flaps. Ann. Plast Surg. 1992, 29, 297–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, G.; Li, X.; Sun, W.; Liang, Y.; Gan, D.; Liu, G.; Song, W.; Wang, Z. Study on the chemical constituents of nut oil from Prunus mira Koehne and the mechanism of promoting hair growth. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 258, 112831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Valle, J.M.; Fisk, E.A.; Noland, E.L.; Pak, D.; Zhang, J.; Crim, M.J.; Lawrence, F.R.; Hankenson, F.C. Comparison of Aqueous and Alcohol-based Agents for Presurgical Skin Preparation Methods in Mice. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2018, 57, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilkenny, C.; Browne, W.; Cuthill, I.C.; Emerson, M.; Altman, D.G. Animal research: Reporting in vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1577–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.F.; Lu, J.J.; Tang, J.F.; Zheng, X.; Liang, Y.Q.; Wang, X.F.; Wang, Y.J.; Mao, L.G.; Chen, J.Q. Action of a Novel PDE4 inhibitor ZL-n-91 on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furumoto, K.; Ogita, K.; Kamisaka, T.; Kawasumi, A.; Takata, K.; Maeta, N.; Itoi, T.; Nohara, M.; Saeki, K.; Kanda, T. Effects of Multimodal Analgesic Protocol, with Buprenorphine and Meloxicam, on Mice Well-Being: A Dose Finding Study. Animals 2021, 11, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, B.; Gervasoni, D. Improving Stereotaxic Neurosurgery Techniques and Procedures Greatly Reduces the Number of Rats Used per Experimental Group-A Practice Report. Animals 2021, 11, 2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil, J.; Quiros, M.; Nusrat, A.; Parkos, C. Innate immune cell-epithelial crosstalk during wound repair. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2983–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.; Yi, X.; Liang, T.; Jiang, S.; He, R.; Hu, Y.; Bai, L.; Wang, C.; Wang, K.; Zhu, L. Autograft microskin combined with adipose-derived stem cell enhances wound healing in a full-thickness skin defect mouse model. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, T.; Bai, X.; Jing, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Xie, S.; et al. Notch signal deficiency alleviates hypertrophic scar formation after wound healing through the inhibition of inflammation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020, 682, 108286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, T.; Mansur, F.; Palek, R.; Manzoor, S.; Liska, V. A Double Edged Sword Role of Interleukin-22 in Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Bian, L.; Iriyama, S.; Jian, Z.; Fan, B.; Luo, J.; Wang, D.D.; Young, C.D.; Han, G.; Wang, X.J. Smad7 Ameliorates TGF-β-Mediated Skin Inflammation and Associated Wound Healing Defects but Not Susceptibility to Experimental Skin Carcinogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, Z.; Song, W.; He, Y.; Li, H. Multilayer Injectable Hydrogel System Sequentially Delivers Bioactive Substances for Each Wound Healing Stage. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 29787–29806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashram, S.; El-Samad, L.M.; Basha, A.A.; El Wakil, A. Naturally derived targeted therapy for wound healing: Beyond classical strategies. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, A.; Schaller, M.; Joshi, A.; Davis, F.M.; denDekker, A.; Boniakowski, A.; Bermick, J.; Obi, A.; Moore, B.; Henke, P.K.; et al. Ly6C(Hi) Blood Monocyte/Macrophage Drive Chronic Inflammation and Impair Wound Healing in Diabetes Mellitus. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1102–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pemmari, T.; Laakso, J.; Patrikainen, M.S.; Parkkila, S.; Järvinen, T.A.H. Car6Carbonic Anhydrase VI in Skin Wound Healing Study on Knockout Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, R.; Tanaka, K.; Shimokawa, I. Identification and functional analysis of inflammation-related miRNAs in skin wound repair. Dev. Growth Differ. 2018, 60, 306–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diegelmann, R.F.; Evans, M.C. Wound healing: An overview of acute, fibrotic and delayed healing. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Hao, J.; Jin, R.; Yi, Y.; Bodduluri, S.R.; Hua, Y.; Anand, A.; Deng, Y.; Haribabu, B.; Egilmez, N.K.; et al. Epidermal Fatty Acid Binding Protein Mediates Depilatory-Induced Acute Skin Inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, S0022-202X(21)02623-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chu, C.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Jin, S.; Yang, R.; Rung, S.; Li, J.; Qu, Y.; Man, Y. Dissecting the microenvironment around biosynthetic scaffolds in murine skin wound healing. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.F.; Chou, F.P.; Yu, T.S.; Lee, H.J.; Chiu, C.T. Depilatory creams increase the number of hair follicles, and dermal fibroblasts expressing interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, and tumor necrosis factor-β in mouse skin. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2021, 25, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, S.; Dong, L.; An, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Tu, Y.; Tao, J. Skin healing and collagen changes of rats after fractional erbium:yttrium aluminum garnet laser: Observation by reflectance confocal microscopy with confirmed histological evidence. Lasers Med. Sci. 2016, 31, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhashim, M.; Lombardo, J. Effect of Topical Garlic on Wound Healing and Scarring: A Clinical Trial. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Jia, L.; Zhang, X. The Effect of Different Preoperative Depilation Ways on the Healing of Wounded Skin in Mice. Animals 2022, 12, 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050581
He X, Jia L, Zhang X. The Effect of Different Preoperative Depilation Ways on the Healing of Wounded Skin in Mice. Animals. 2022; 12(5):581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050581
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xinyi, Lintao Jia, and Xiao Zhang. 2022. "The Effect of Different Preoperative Depilation Ways on the Healing of Wounded Skin in Mice" Animals 12, no. 5: 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050581
APA StyleHe, X., Jia, L., & Zhang, X. (2022). The Effect of Different Preoperative Depilation Ways on the Healing of Wounded Skin in Mice. Animals, 12(5), 581. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani12050581






