Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiota between Wild and Captive Golden Snub-Nosed Monkeys
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. 16S rRNA Genes Amplicon Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
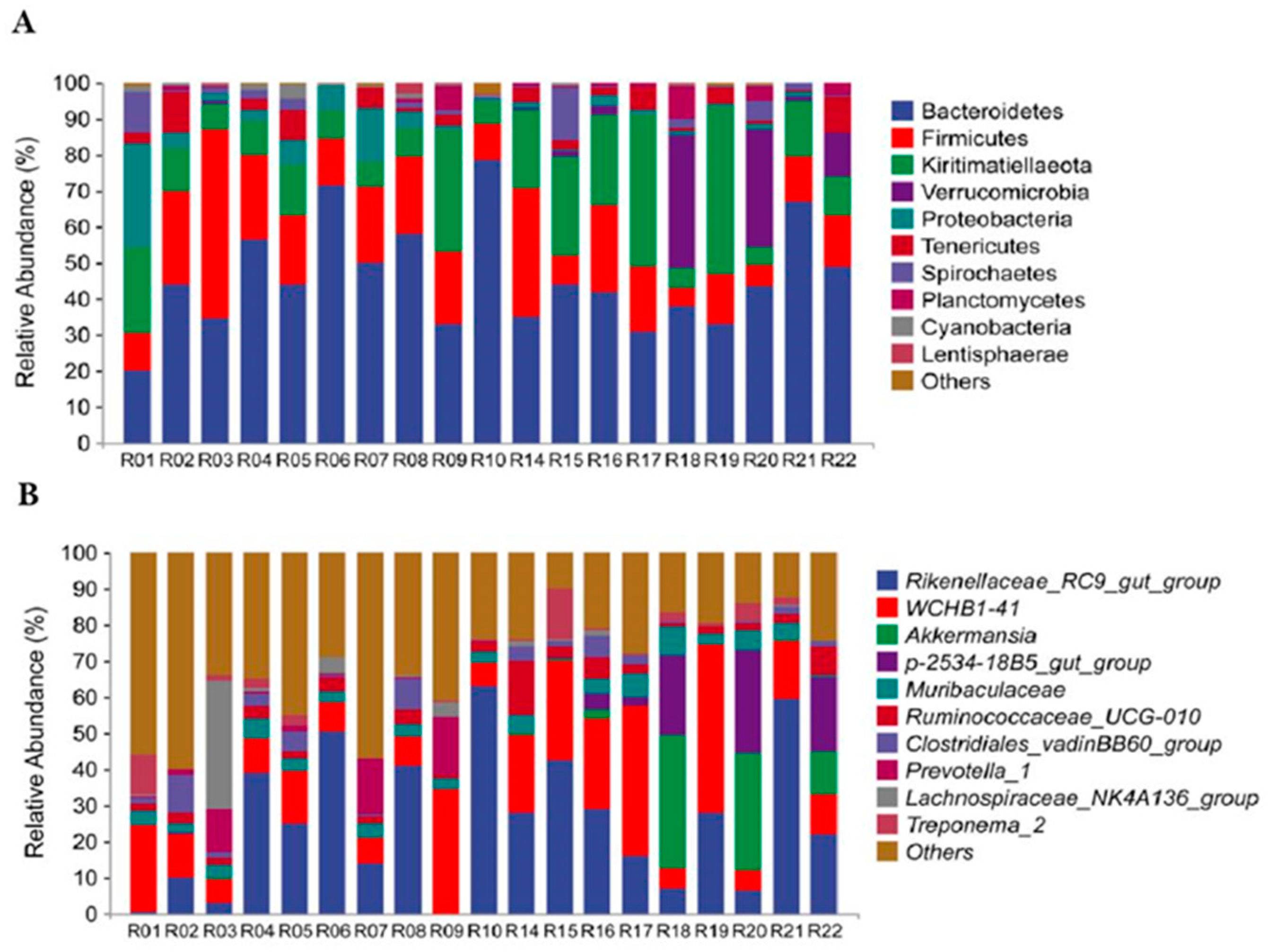
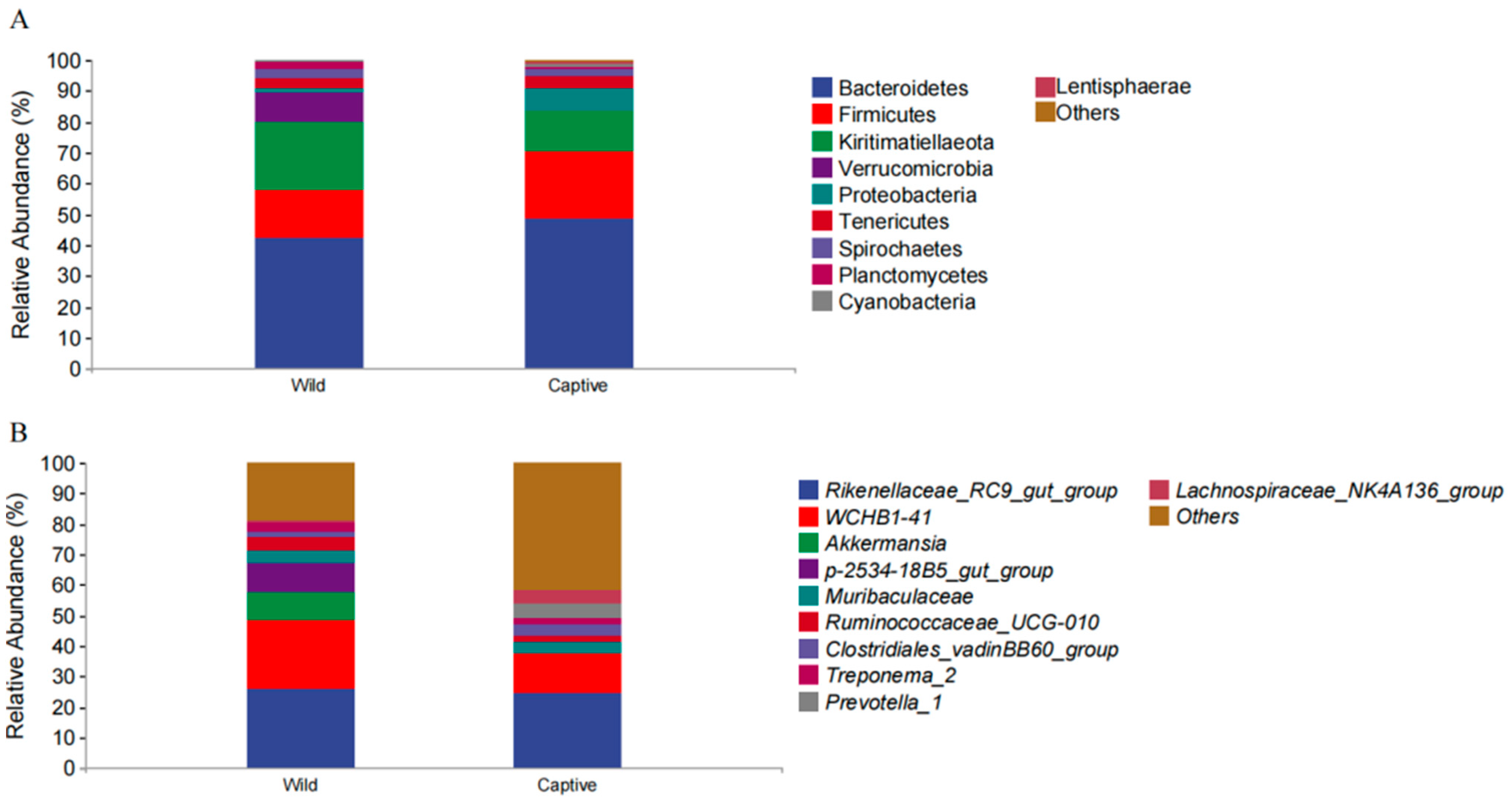
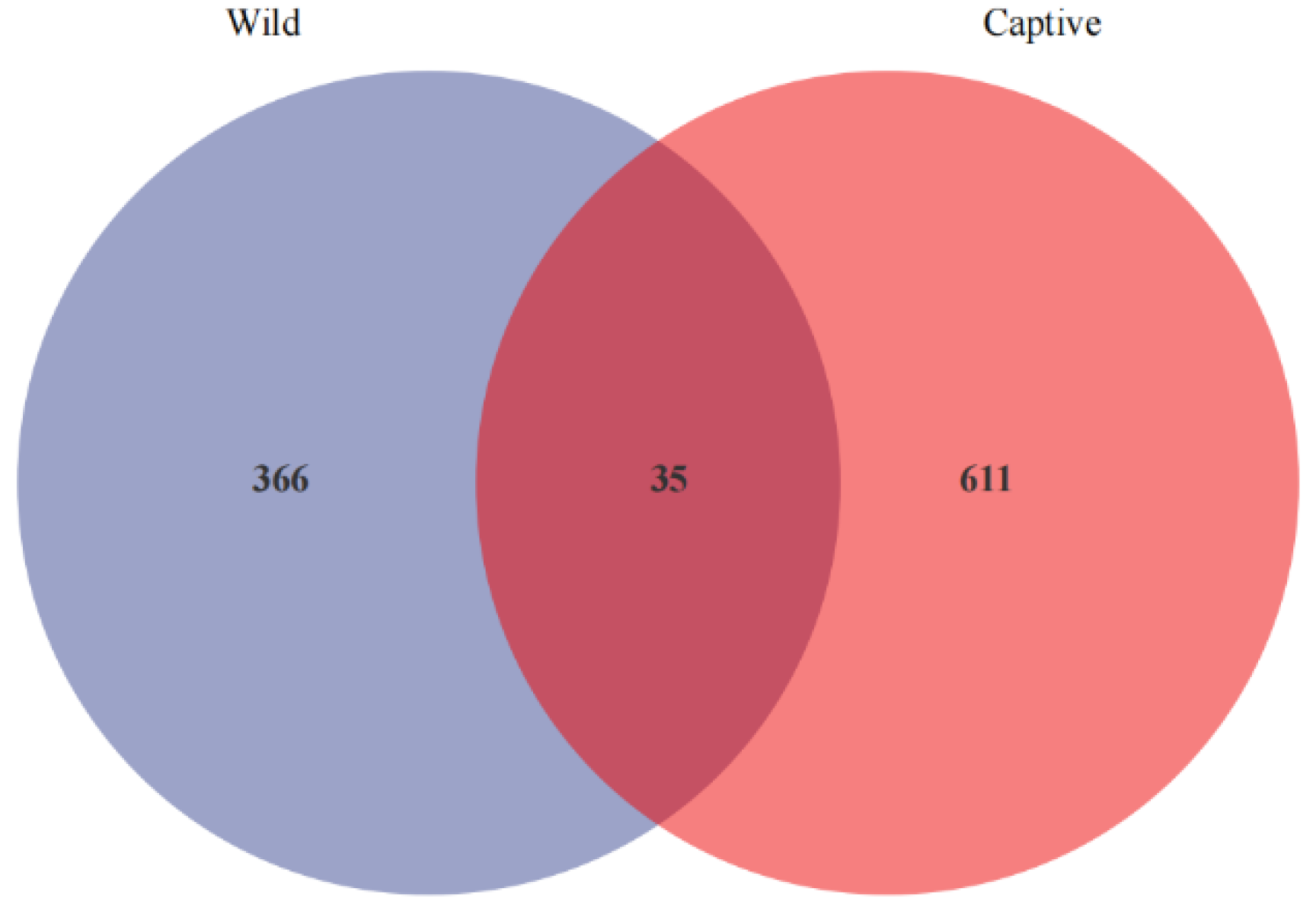
3.1. Microbial Community Profiles
3.2. Diversity Analysis of Microbiota in Captive and Wild Golden Snub-Nosed Monkey
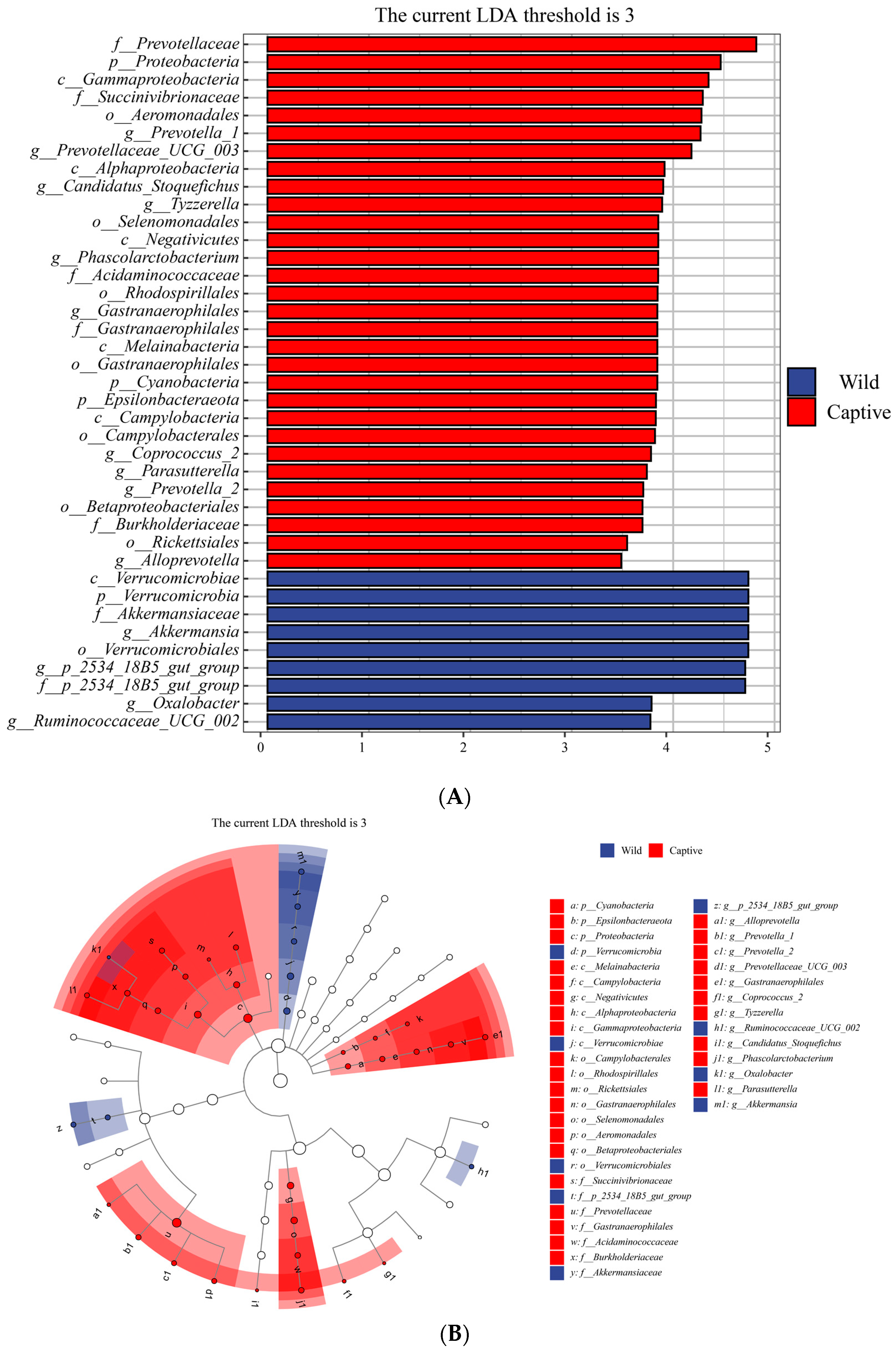
3.3. Microbial Taxa Differences in the Gut Microbiota between Wild and Captive Golden Snub-Nosed Monkeys
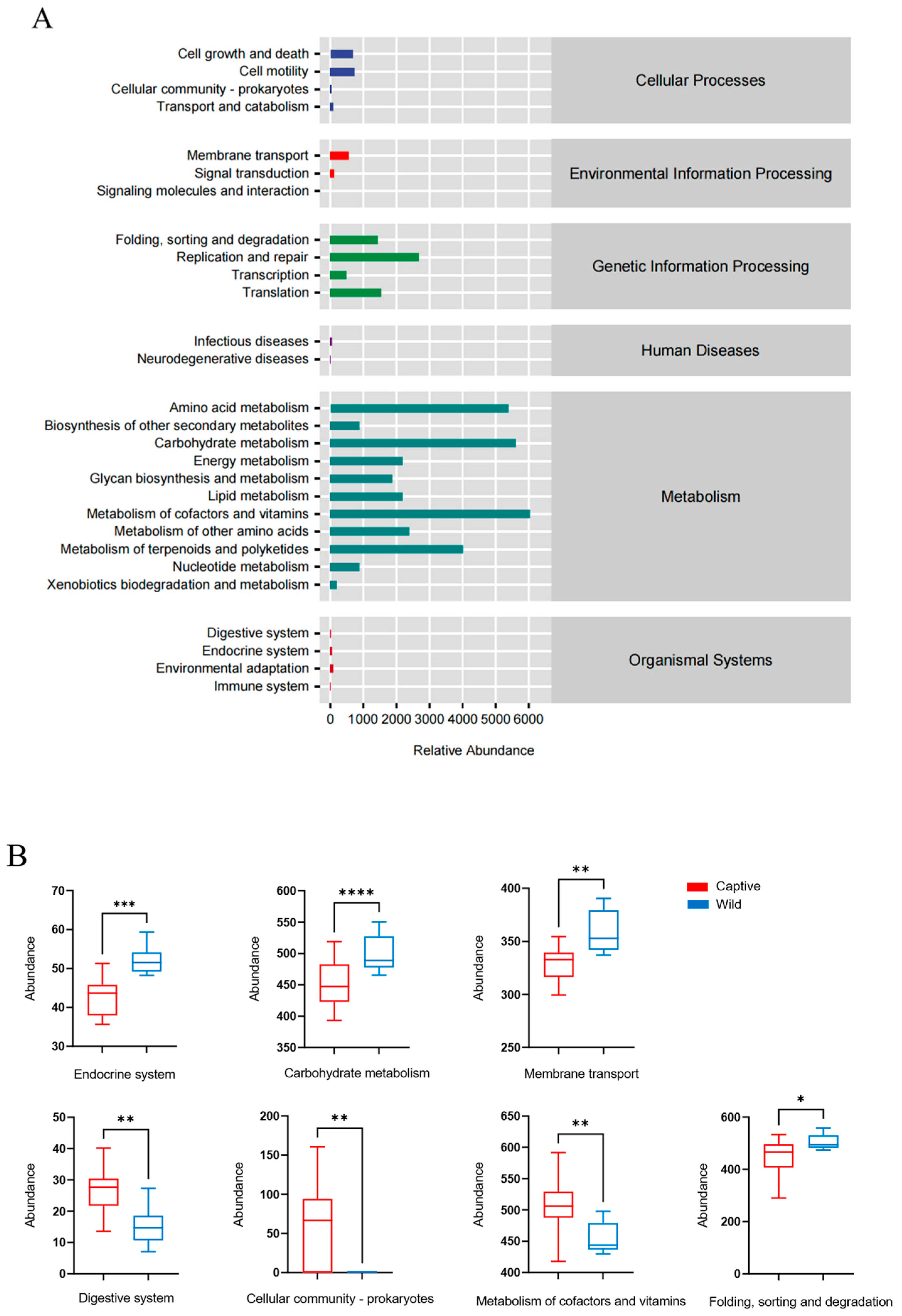
3.4. Functional Differences in Predicted Metagenomic between the Gut Microbiota of Wild and Captive Golden Snub-Nosed Monkeys
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, W.; Yan, X. China Species Red List; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, B.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, J.; Kumar, S.; Sun, X.; Liu, Z.; Pan, H.; Lin, Y.; Liu, G.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing of the snub-nosed monkey provides insights into folivory and evolutionary history. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.-G.; Garber, P.A.; Ji, W.; Huang, Z.-P.; Huang, K.; Zhang, P.; Guo, S.-T.; Wang, X.-W.; He, G.; Zhang, P.; et al. Satellite telemetry and social modeling offer new insights into the origin of primate multilevel societies. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Xiang, J.-T.; Wang, C.-H.; Ren, D.; David, J.; Xu, T. Lichen as a biomonitor for vehicular emission of metals: A risk assessment of lichen consumption by the Sichuan snub-nosed monkey (Rhinopithecus roxellana). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 180, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crees, J.J.; Collins, A.C.; Stephenson, P.; Meredith, H.M.; Young, R.P.; Howe, C.; Price, M.R.S.; Turvey, S.T. A comparative approach to assess drivers of success in mammalian conservation recovery programs. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 30, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yan, L.; Wang, C.; Li, D.; Jin, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, F. Large-scale genetic survey provides insights into the captive management and reintroduction of giant pandas. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2014, 31, 2663–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevelline, B.K.; Fontaine, S.S.; Hartup, B.K.; Kohl, K.D. Conservation biology needs a microbial renaissance: A call for the consideration of host-associated microbiota in wildlife management practices. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2019, 286, 20182448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Wu, Q.; Hu, Y.; Huang, G.; Nie, Y.; Yan, L. Conservation metagenomics: A new branch of conservation biology. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenzie, V.J.; Song, S.J.; Delsuc, F.; Prest, T.L.; Oliverio, A.M.; Korpita, T.M.; Alexiev, A.; Amato, K.R.; Metcalf, J.L.; Kowalewski, M.; et al. The effects of captivity on the mammalian gut microbiome. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrodia, T.; Das, S.; Bakshi, S.; Das, B. Structure, functions, and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Hum. Microbiome Health Dis. Part A 2022, 191, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Clayton, J.B.; Gomez, A.; Amato, K.; Knights, D.; Travis, D.A.; Blekhman, R.; Knight, R.; Leigh, S.; Stumpf, R.; Wolf, T.; et al. The gut microbiome of nonhuman primates: Lessons in ecology and evolution. Am. J. Primatol. 2018, 80, e22867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Hamady, M.; Lozupone, C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ramey, R.R.; Bircher, J.S.; Schlegel, M.L.; Tucker, T.A.; Schrenzel, M.D.; Knight, R.; et al. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science 2008, 320, 1647–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, J.B.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Long, H.T.; Tuan, B.V.; Cabana, F.; Huang, H.; Vangay, P.; Ward, T.; Minh, V.V.; Tam, N.A.; et al. Associations between nutrition, gut microbiome, and health in a novel nonhuman primate model. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.; Pamp, S.J.; Hill, J.A.; Surana, N.K.; Edelman, S.M.; Troy, E.B.; Reading, N.C.; Villablanca, E.J.; Wang, S.; Mora, J.R.; et al. Gut immune maturation depends on colonization with a host-specific microbiota. Cell 2012, 149, 1578–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, I.; Blaser, M.J. The human microbiome: At the interface of health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, K.R.; Metcalf, J.L.; Song, S.J.; Hale, V.L.; Clayton, J.; Ackermann, G.; Humphrey, G.; Niu, K.; Cui, D.; Zhao, H.; et al. Using the gut microbiota as a novel tool for examining colobine primate GI health. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2016, 7, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, C.; Stojanović, O.; Colin, D.J.; Suarez-Zamorano, N.; Tarallo, V.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Rigo, D.; Fabbiano, S.; Stevanović, A.; Hagemann, S.; et al. Gut microbiota orchestrates energy homeostasis during cold. Cell 2015, 163, 1360–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardiolo, G.; Romeo, O.; Zumbo, A.; Di Marsico, M.; Sutera, A.M.; Cigliano, R.A.; Paytuví, A.; D’Alessandro, E. Characterization of the Nero Siciliano Pig Fecal Microbiota after a Liquid Whey-Supplemented Diet. Animals 2023, 13, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-C.; Zhang, J.-L.; Pan, H.-J.; Chen, Y.-X.; Mao, S.-X.; Qi, J.-W.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Xiang, Z.-F.; Li, M. Unique characteristics of gut microbiota in black snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus strykeri) reveal an enzymatic mechanism of adaptation to dietary vegetation. Zool. Res. 2023, 44, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Mao, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Pan, H. Metatranscriptomic Analyses Reveal Important Roles of the Gut Microbiome in Primate Dietary Adaptation. Genes 2023, 14, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, J.W.; Warne, R.W. Captivity and animal microbiomes: Potential roles of microbiota for influencing animal conservation. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 85, 820–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eigeland, K.A.; Lanyon, J.M.; Trott, D.J.; Ouwerkerk, D.; Blanshard, W.; Milinovich, G.J.; Gulino, L.-M.; Martinez, E.; Merson, S.; Klieve, A.V. Bacterial community structure in the hindgut of wild and captive dugongs (Dugong dugon). Aquat. Mamm. 2012, 38, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, S.; Feng, L.; Wang, T.; Ge, J. Comparison of the gut microbiota composition between wild and captive sika deer (Cervus nippon hortulorum) from feces by high-throughput sequencing. AMB Express 2017, 7, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, J.B.; Vangay, P.; Huang, H.; Ward, T.; Hillmann, B.M.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Travis, D.A.; Long, H.T.; Tuan, B.V.; Minh, V.V.; et al. Captivity humanizes the primate microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10376–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malukiewicz, J.; Cartwright, R.A.; Dergam, J.A.; Igayara, C.S.; Kessler, S.E.; Moreira, S.B.; Nash, L.T.; Nicola, P.A.; Pereira, L.C.; Pissinatti, A.; et al. The gut microbiome of exudivorous marmosets in the wild and captivity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, V.L.; Tan, C.L.; Niu, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Knight, R.; Amato, K.R. Gut microbiota in wild and captive Guizhou snub-nosed monkeys, Rhinopithecus brelichi. Am. J. Primatol. 2019, 81, e22989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, T.; Chang, W.-S.; Marcelino, V.R.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; You, Y.; Holmes, E.C.; Shi, M.; Zhang, C. Characterization of the gut microbiome and resistomes of wild and zoo-captive macaques. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, N.; Seo, S.-U.; Chen, G.Y.; Núñez, G. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2013, 13, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.T.; Davis-Richardson, A.G.; Giongo, A.; Gano, K.A.; Crabb, D.B.; Mukherjee, N.; Casella, G.; Drew, J.C.; Ilonen, J.; Knip, M.; et al. Gut microbiome metagenomics analysis suggests a functional model for the development of autoimmunity for type 1 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerner, B.P.; Sarvetnick, N.E. Type 1 diabetes: Role of intestinal microbiome in humans and mice. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1243, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Mishra, S.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Ning, R.; Kong, F.; Zeng, B.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y. Comparative study of gut microbiota in wild and captive giant pandas (Ailuropoda melanoleuca). Genes 2019, 10, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, S.M.; Marchesi, J.R.; Scully, P.; Codling, C.; Ceolho, A.-M.; Quigley, E.M.; Cryan, J.F.; Dinan, T.G. Early life stress alters behavior, immunity, and microbiota in rats: Implications for irritable bowel syndrome and psychiatric illnesses. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stecher, B.; Robbiani, R.; Walker, A.W.; Westendorf, A.M.; Barthel, M.; Kremer, M.; Chaffron, S.; Macpherson, A.J.; Buer, J.; Parkhill, J.; et al. Salmonella enterica serovar typhimurium exploits inflammation to compete with the intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stecher, B.; Hardt, W.-D. The role of microbiota in infectious disease. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Li, R.; Raes, J.; Arumugam, M.; Burgdorf, K.S.; Manichanh, C.; Nielsen, T.; Pons, N.; Levenez, F.; Yamada, T.; et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010, 464, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursell, L.K.; Haiser, H.J.; Van Treuren, W.; Garg, N.; Reddivari, L.; Vanamala, J.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Knight, R. The intestinal metabolome: An intersection between microbiota and host. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.T.; Luo, X.; Hou, R.; Raubenheimer, D.; Ji, W.; Jin, X.; Jiang, Z.; Yu, X.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; et al. Nutrient balancing by captive golden snub-nosed monkeys (Rhinopithecus roxellana). Int. J. Primatol. 2018, 39, 1124–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.T.; Hou, R.; Garber, P.A.; Raubenheimer, D.; Righini, N.; Ji, W.H.; Jay, O.; He, S.J.; Wu, F.; Li, F.F.; et al. Nutrient-specific compensation for seasonal cold stress in a free-ranging temperate colobine monkey. Funct. Ecol. 2018, 32, 2170–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; Wong, J.; Heiner, C.; Oh, S.; Theriot, C.M.; Gulati, A.S.; McGill, S.K.; Dougherty, M.K. High-throughput amplicon sequencing of the full-length 16S rRNA gene with single-nucleotide resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Gregory Caporaso, J. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2′s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.H. Measurement of diversity. Nature 1949, 163, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pielou, E.C. The measurement of diversity in different types of biological collections. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, I.J. The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 1953, 40, 237–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Hamady, M.; Kelley, S.T.; Knight, R. Quantitative and qualitative β diversity measures lead to different insights into factors that structure microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1576–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.; Knight, R. UniFrac: A new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 8228–8235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 326–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J.; Walsh, D.C. PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, and the Mantel test in the face of heterogeneous dispersions: What null hypothesis are you testing? Ecol. Monogr. 2013, 83, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenney, E.A.; Rodrigo, A.; Yoder, A.D. Patterns of gut bacterial colonization in three primate species. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, V.L.; Tan, C.L.; Knight, R.; Amato, K.R. Effect of preservation method on spider monkey (Ateles geoffroyi) fecal microbiota over 8 weeks. J. Microbiol. Methods 2015, 113, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Prince, A.L.; Bader, D.; Hu, M.; Ganu, R.; Baquero, K.; Blundell, P.; Alan Harris, R.; Frias, A.E.; Grove, K.L.; et al. High-fat maternal diet during pregnancy persistently alters the offspring microbiome in a primate model. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Dai, L.; Xiong, C.; Tang, X.; Yang, Y.; Mu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ding, J.; et al. Metagenomic analysis of the Rhinopithecus bieti fecal microbiome reveals a broad diversity of bacterial and glycoside hydrolase profiles related to lignocellulose degradation. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barelli, C.; Albanese, D.; Donati, C.; Pindo, M.; Dallago, C.; Rovero, F.; Cavalieri, D.; Tuohy, K.M.; Hauffe, H.C.; De Filippo, C. Habitat fragmentation is associated to gut microbiota diversity of an endangered primate: Implications for conservation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, H.M.; Judge, D.S. Kloss gibbon (Hylobates klossii) behavior facilitates the avoidance of human predation in the Peleonan forest, Siberut Island, Indonesia. Am. J. Primatol. 2015, 77, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, N.; Behie, A.M.; Rothman, J.M.; Ryan, K.G. Nutritional composition of the diet of the northern yellow-cheeked crested gibbon (Nomascus annamensis) in northeastern Cambodia. Primates 2018, 59, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ding, H.; Wang, T.; Hooper, L.V.; Koh, G.Y.; Nagy, A.; Semenkovich, C.F.; Gordon, J.I. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15718–15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, C.; Huasai, S.; Chen, A. Effects of dietary forage to concentrate ratio on nutrient digestibility, ruminal fermentation and rumen bacterial composition in Angus cows. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Li, B.; Watanabe, K. Diet and activity budget of Rhinopithecus roxellana in the Qinling Mountains, China. Primates 2007, 48, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; He, S.; Wu, F.; Chapman, C.A.; Pan, R.; Garber, P.A.; Guo, S.; Li, B. Seasonal variation in diet and nutrition of the northern-most population of Rhinopithecus roxellana. Am. J. Primatol. 2018, 80, e22755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Filippo, C.; Cavalieri, D.; Di Paola, M.; Ramazzotti, M.; Poullet, J.B.; Massart, S.; Collini, S.; Pieraccini, G.; Lionetti, P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14691–14696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Forano, E. Microbial degradation of complex carbohydrates in the gut. Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 289–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Nilsson, A.; Akrami, R.; Lee, Y.S.; De Vadder, F.; Arora, T.; Hallen, A.; Martens, E.; Björck, I.; Bäckhed, F. Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of Prevotella. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeth, R.A.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Buffa, J.A.; Org, E.; Sheehy, B.T.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; et al. Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seksik, P.; Rigottier-Gois, L.; Gramet, G.; Sutren, M.; Pochart, P.; Marteau, P.; Jian, R.; Dore, J. Alterations of the dominant faecal bacterial groups in patients with Crohn’s disease of the colon. Gut 2003, 52, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cai, G.; Qiu, Y.; Fei, N.; Zhang, M.; Pang, X.; Jia, W.; Cai, S.; Zhao, L. Structural segregation of gut microbiota between colorectal cancer patients and healthy volunteers. ISME J. 2012, 6, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizrahi, I.; Wallace, R.J.; Moraïs, S. The rumen microbiome: Balancing food security and environmental impacts. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 19, 553–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monira, S.; Nakamura, S.; Gotoh, K.; Izutsu, K.; Watanabe, H.; Alam, N.H.; Endtz, H.P.; Cravioto, A.; Ali, S.I.; Nakaya, T.J.; et al. Gut microbiota of healthy and malnourished children in Bangladesh. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, W.S.; Lord, G.M.; Punit, S.; Lugo-Villarino, G.; Mazmanian, S.K.; Ito, S.; Glickman, J.N.; Glimcher, L.H. Communicable ulcerative colitis induced by T-bet deficiency in the innate immune system. Cell 2007, 131, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devkota, S.; Wang, Y.; Musch, M.W.; Leone, V.; Fehlner-Peach, H.; Nadimpalli, A.; Antonopoulos, D.A.; Jabri, B.; Chang, E.B. Dietary-fat-induced taurocholic acid promotes pathobiont expansion and colitis in Il10−/− mice. Nature 2012, 487, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevers, D.; Kugathasan, S.; Denson, L.A.; Vázquez-Baeza, Y.; Van Treuren, W.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.; Knights, D.; Song, S.J.; Yassour, M.; et al. The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset Crohn’s disease. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 382–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satokari, R. High intake of sugar and the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory gut bacteria. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca-Saavedra, P.; Mendez-Vilabrille, V.; Miranda, J.M.; Nebot, C.; Cardelle-Cobas, A.; Franco, C.M.; Cepeda, A. Food additives, contaminants and other minor components: Effects on human gut microbiota—A review. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 74, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frugé, A.D.; Van der Pol, W.; Rogers, L.Q.; Morrow, C.D.; Tsuruta, Y.; Demark-Wahnefried, W. Fecal Akkermansia muciniphila is associated with body composition and microbiota diversity in overweight and obese women with breast cancer participating in a presurgical weight loss trial. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, M.; Belzer, C.; de Vos, W.M. Akkermansia muciniphila and its role in regulating host functions. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 106, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, T.P.; Sun, X.; Patel, V.H.; Sanz, C.; Morgan, D.; Dantas, G. The microbiome and resistome of chimpanzees, gorillas, and humans across host lifestyle and geography. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1584–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassotti, T.T.; de Angelis Zvoboda, D.; da Fontoura Xavier Costa, L.; De Araujo, A.J.G.; Pereira, R.I.; Soares, R.O.; Wagner, P.G.C.; Frazzon, J.; Frazzon, A.P.G. Antimicrobial Resistance Profiles in Enterococcus spp. Isolates from Fecal Samples of Wild and Captive Black Capuchin Monkeys (Sapajus nigritus) in South Brazil. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muegge, B.D.; Kuczynski, J.; Knights, D.; Clemente, J.C.; González, A.; Fontana, L.; Henrissat, B.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. Diet drives convergence in gut microbiome functions across mammalian phylogeny and within humans. Science 2011, 332, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, M.; Pan, H. Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiota between Wild and Captive Golden Snub-Nosed Monkeys. Animals 2023, 13, 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101625
Wang Y, Yang X, Zhang M, Pan H. Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiota between Wild and Captive Golden Snub-Nosed Monkeys. Animals. 2023; 13(10):1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101625
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yunting, Xuanyi Yang, Mingyi Zhang, and Huijuan Pan. 2023. "Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiota between Wild and Captive Golden Snub-Nosed Monkeys" Animals 13, no. 10: 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101625
APA StyleWang, Y., Yang, X., Zhang, M., & Pan, H. (2023). Comparative Analysis of Gut Microbiota between Wild and Captive Golden Snub-Nosed Monkeys. Animals, 13(10), 1625. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13101625



