Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Extraintestinal E. coli Populations Pre- and Post-Antimicrobial Therapy on Broilers Affected by Colisepticemia
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Escherichia coli Isolation
2.3. Serotyping
2.4. Pulse-Field Gel Electrophoresis
2.5. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.6. Whole-Genome Sequencing and De Novo Assembly
2.7. In Silico Analyses
2.8. SNP Calling
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. E. coli Isolation
3.2. Serotyping
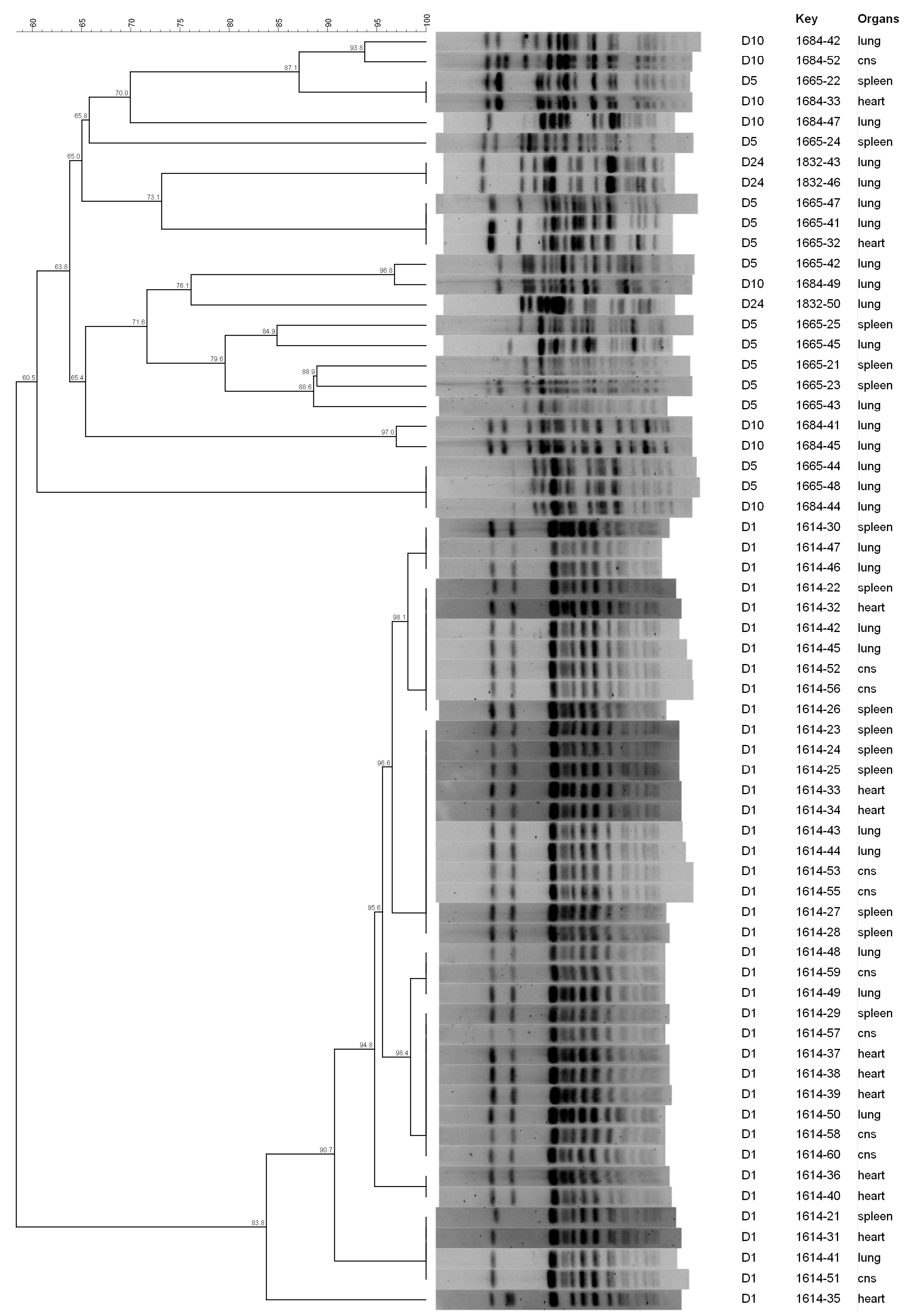
3.3. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis
3.4. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
3.5. Whole-Genome Sequencing
3.5.1. SNP Calling
3.5.2. Characterization of Genetic Determinants of Enrofloxacin Resistance
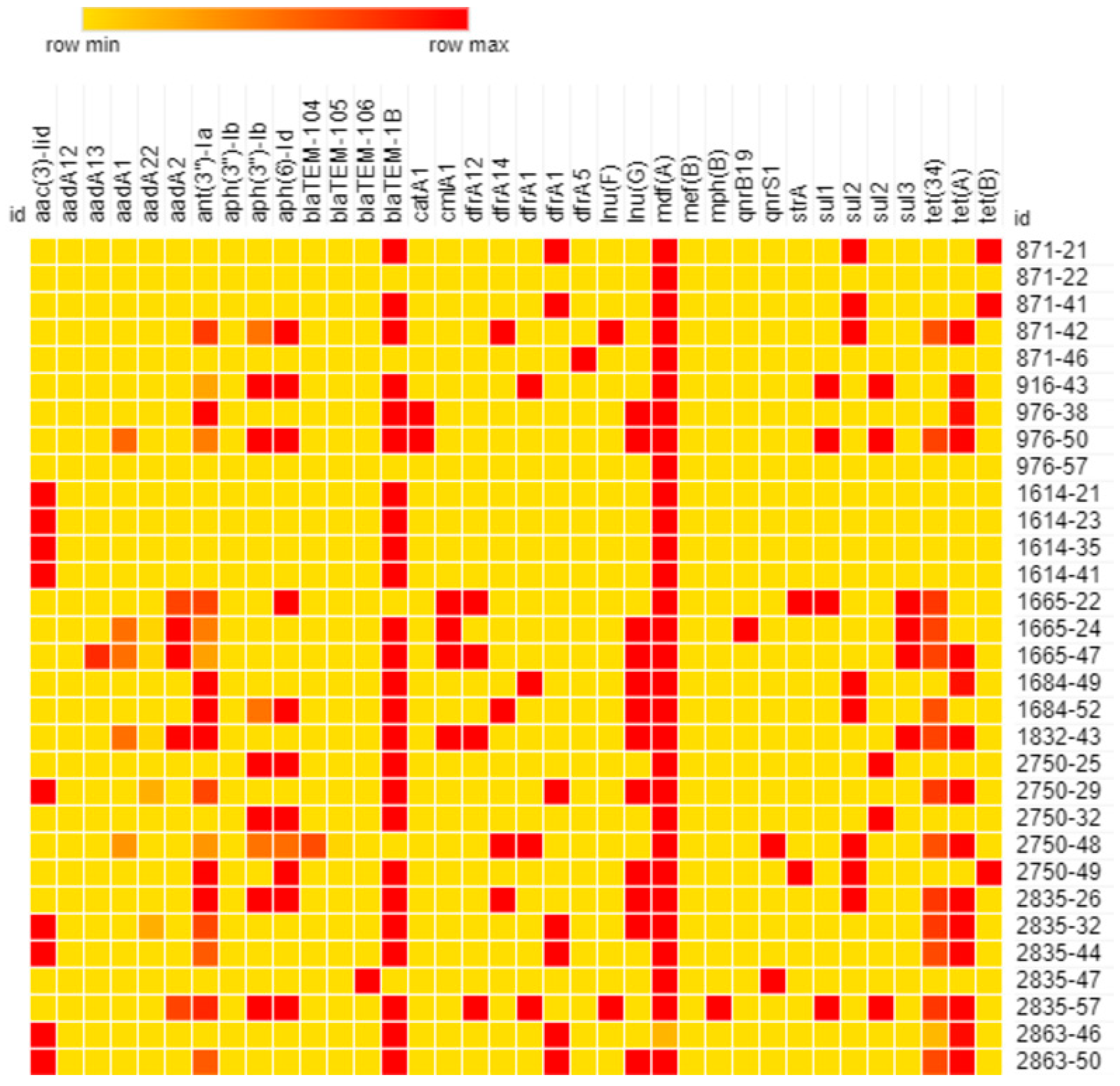
3.5.3. In Silico Resistome Characterization
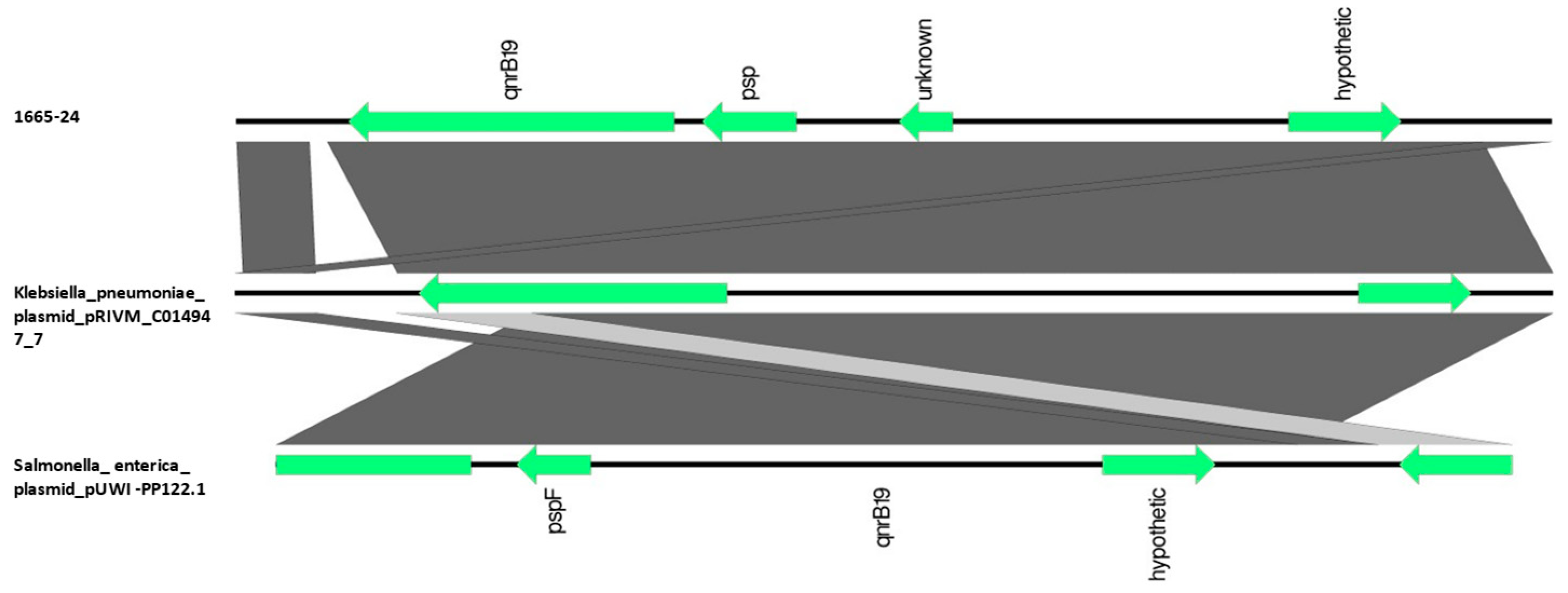
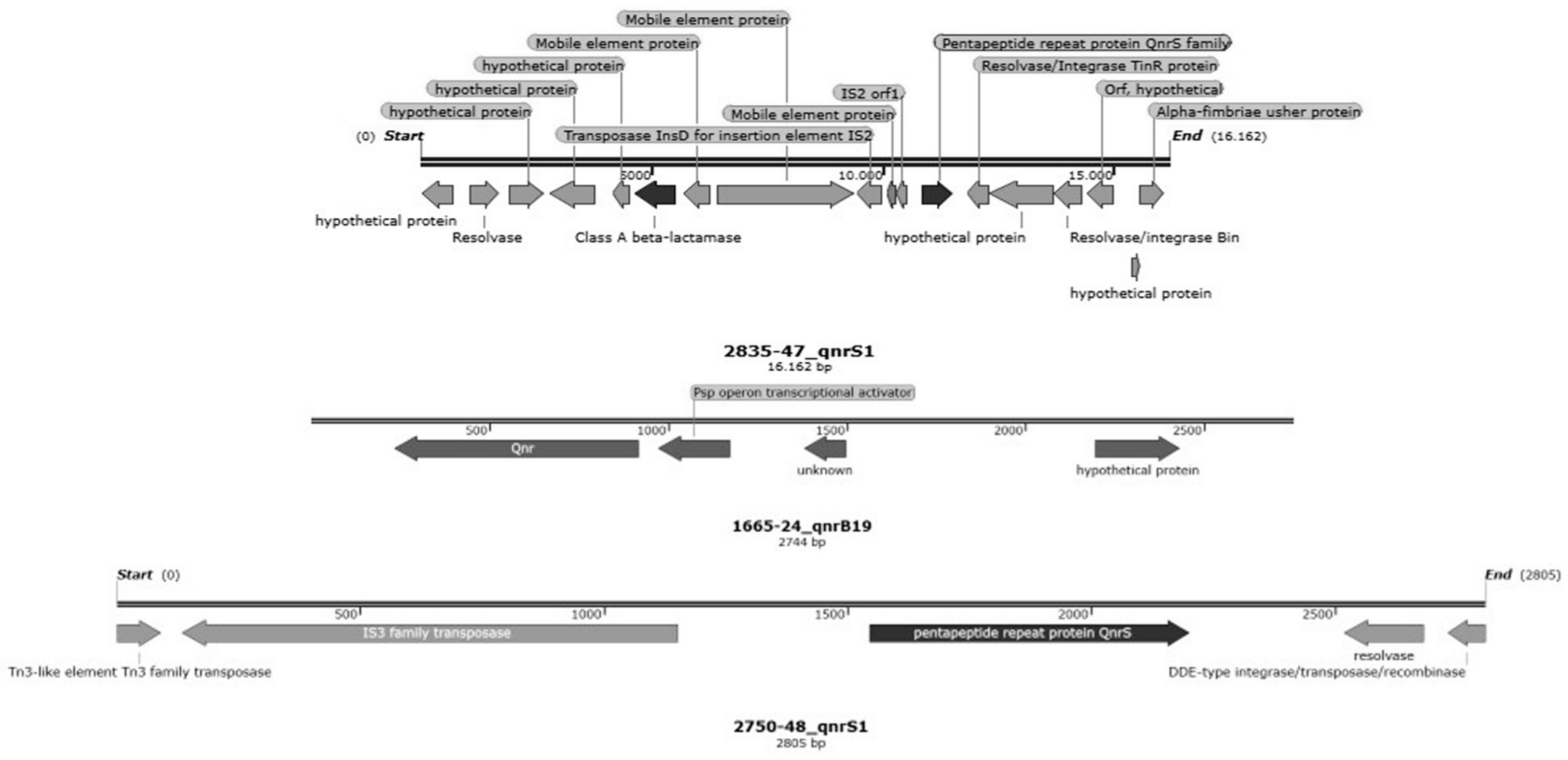
3.5.4. Localization of Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guabiraba, R.; Schouler, C. Avian colibacillosis: Still many black holes. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2015, 362, fnv118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landman, W.J.M.; van Eck, J.H.H. The incidence and economic impact of the Escherichia coli peritonitis syndrome in Dutch poultry farming. Avian Pathol. 2015, 44, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Daud, N.H.b.; Htin, N.N.; Abba, Y.; Paan, F.H.; Kyaw, T.; Khaing, A.T.; Abdullah, F.F.J.; Mohammed, K.; Adamu, L.; Tijjani, A. An outbreak of colibacillosis in a broiler farm. J. Vet. Adv. 2014, 4, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, J.F.; Matter, L.B.; Trindade, M.M.; Camillo, G.; Lovato, M.; de Ávila Botton, S.; Castagna de Vargas, A. Virulence factors and antimicrobial sus-ceptibility profile of extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolated from an avian colisepticemia outbreak. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 103, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.H.; Xue, C.; Islam, M.R.; Islam, M.; Cao, Y. A longitudinal study on the incidence of mortality of infectious diseases of commercial layer birds in Bangladesh. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 109, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokholm, N.M.; Permin, A.; Bisgaard, M.; Christensen, J.P. Causes of mortality in commercial organic layers in Denmark. Avian Dis. 2010, 54, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandekerchove, D.; De Herdt, P.; Laevens, H.; Pasmans, F. Colibacillosis in caged layer hens: Characteristics of the disease and the aetiological agent. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanella, A.; Alborali, G.L.; Bardotti, M.; Candotti, P.; Guadagnini, P.F.; Martino, P.A.; Stonfer, M. Severe Escherichia coli O111 septi-caemia and polyserositis in hens at the start of lay. Avian Pathol. 2000, 29, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, T.J.; Nolan, L.K. Pathogenomics of the virulence plasmids of Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 750–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- LeStrange, K.; Markland, S.M.; Hoover, D.G.; Sharma, M.; Kniel, K.E. An evaluation of the virulence and adherence properties of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli. One Health 2017, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stromberg, Z.R.; Johnson, J.R.; Fairbrother, J.M.; Kilbourne, J.; Van Goor, A.; Curtiss, R., 3rd; Mellata, M. Evaluation of Escherichia coli isolates from healthy chickens to determine their potential risk to poultry and human health. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dissanayake, D.; Octavia, S.; Lan, R. Population structure and virulence content of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from outbreaks in Sri Lanka. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 168, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquali, F.; Lucchi, A.; Braggio, S.; Giovanardi, D.; Franchini, A.; Stonfer, M.; Manfreda, G. Genetic diversity of Escherichia coli isolates of animal and environmental origins from an integrated poultry production chain. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fratamico, P.M.; DebRoy, C.; Liu, Y.; Needleman, D.S.; Baranzoni, G.M.; Feng, P. Advances in molecular serotyping and subtyping of Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landman, W.J.M.; Buter, G.J.; Dijkman, R.; Van Eck, J.H.H. Molecular typing of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli colonies origi-nating from outbreaks of E. coli peritonitis syndrome in chicken flocks. Avian Pathol. 2014, 43, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huja, S.; Oren, Y.; Trost, E.; Brzuszkiewicz, E.; Biran, D.; Blom, J.; Goesmann, A.; Gottschalk, G.; Hacker, J.; Ron, E.Z.; et al. Genomic avenue to avian colisepticemia. MBio 2015, 6, e01681-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cordoni, G.; Woodward, M.J.; Wu, H.; Alanazi, M.; Wallis, T.; La Ragione, R.M. Comparative genomics of European avian pathogenic E. coli (APEC). BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosario, C.C.; López, C.C.; Téllez, I.G.; Navarro, O.A.; Anderson, R.C.; Eslava, C.C. Serotyping and virulence genes detection in Escherichia coli isolated from fertile and infertile eggs, dead-in-shell embryos, and chickens with yolk sac infection. Avian Dis. 2004, 48, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, C.; Huan, H.; Zhang, L.; Mu, X.; Gao, Q.; Dong, X.; Gao, S.; Liu, X. Isolation, identification, and pathogenicity of O142 avian pathogenic Escherichia coli causing black proventriculus and septicemia in broiler breeders. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 32, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.H.; Maurer, J.J.; Hubert, S.; De Villena, J.F.; McDermott, P.F.; Meng, J.; Ayers, S.; English, L.; White, D.G. Antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular characterization of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 107, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, M.L.; Reid, C.J.; Roy Chowdhury, P.; Bushell, R.N.; Esbert, N.; Tivendale, K.A.; Noormohammadi, A.H.; Islam, S.; Marenda, M.S.; Browning, G.F.; et al. Whole genome sequence analysis of Australian avian pathogenic Escherichia coli that carry the class 1 integrase gene. Microb. Genom. 2019, 5, e000250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, T.; Stegger, M.; Olsen, R.H.; Sekse, C.; Nordstoga, A.B.; Pohjanvirta, T.; Lilje, B.; Lyhs, U.; Andersen, P.S.; Pedersen, K. Spread of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli ST117 O78: H4 in Nordic broiler production. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roth, N.; Käsbohrer, A.; Mayrhofer, S.; Zitz, U.; Hofacre, C.; Domig, K.J. The application of antibiotics in broiler production and the resulting antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli: A global overview. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 1791–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavicchio, L.; Dotto, G.; Giacomelli, M.; Giovanardi, D.; Grilli, G.; Franciosini, M.P.; Trocino, A.; Piccirillo, A. Class 1 and class 2 integrons in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli from poultry in Italy. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovanardi, D.; Lupini, C.; Pesente, P.; Rossi, G.; Ortali, G.; Catelli, E. Characterization and antimicrobial resistance analysis of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from Italian turkey flocks. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2661–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhung, N.T.; Chansiripornchai, N.; Carrique-Mas, J.J. Antimicrobial resistance in bacterial poultry pathogens: A review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dheilly, A.; Le Devendec, L.; Mourand, G.; Jouy, E.; Kempf, I. Antimicrobial resistance selection in avian pathogenic E. coli during treatment. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 166, 655–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ørskov, F.; Ørskov, I. Serotyping of Escherichia coli. Methods Microbiol. 1984, 14, 43–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribot, E.M.; Fair, M.A.; Gautom, R.; Cameron, D.N.; Hunter, S.B.; Swaminathan, B.; Barrett, T.J. Standardization of pulsed-field gel electro-phoresis protocols for the subtyping of Escherichia coli O157: H7, Salmonella, and Shigella for PulseNet. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2006, 3, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, J.R.; Sutherland, K.; Owen, R.J. Inhibition of DNAse activity in PFGE analysis of DNA from Campylobacter jejuni. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1994, 19, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated From Animals; Approved Standard, 3rd ed.; CLSI document M31-A3; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2008; ISBN 1-56238-659-X. [Google Scholar]
- INNUca. Available online: https://github.com/B-UMMI/INNUca (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- ABRicate. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/abricate (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Zankari, E.; Allesøe, R.; Joensen, K.; Cavaco, L.M.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M. PointFinder: A novel web tool for WGS-based detection of antimicrobial resistance associated with chromosomal point mutations in bacterial pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roer, L.; Tchesnokova, V.; Allesoe, R.; Muradova, M.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Ahrenfeldt, J.; Thomsen, M.C.F.; Lund, O.; Hansen, F.; Hammerum, A.M.; et al. Development of a web tool for Escherichia coli subtyping based on fimh alleles. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Whole Genome Sequencing Data Web Tools: Centre for Genomic Epidemiology. Available online: https://cge.cbs.dtu.dk/services/FimTyper/ (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Robertson, J.; Nash, J.H.E. MOB-suite: Software tools for clustering, reconstruction and typing of plasmids from draft assem-blies. Microb. Genom. 2018, 4, e000206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snippy. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/snippy (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pairwise SNP Distance Matrix. Available online: https://github.com/tseemann/snp-dists (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Jiang, L.; Yang, W.; Jiang, X.; Yao, T.; Wang, L.; Yang, B. Virulence-related O islands in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1992237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojesen, A.M.; Ahmed, U.; Skaarup, H.; Espinosa-Gongora, C. Recurring outbreaks by the same Escherichia coli ST10 clone in a broiler unit during 18 months. Vet. Res. 2022, 53, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Samudio, V.; Pecchio, M.; Pimentel-Peralta, G.; Quintero, Y.; Herrera, M.; Landires, I. Molecular Epidemiology of Escherichia coli Clinical Isolates from Central Panama. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacoby, G.A.; Strahilevitz, J.; Hooper, D.C. Plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hopkins, K.L.; Davies, R.H.; Threlfall, E.J. Mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli and Salmonella: Recent de-velopments. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2005, 25, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schink, A.K.; Kadlec, K.; Schwarz, S. Detection of qnr genes among Escherichia coli isolates of animal origin and complete se-quence of the conjugative qnrB19-carrying plasmid pQNR2078. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiegen, U.; Klein, G.; de Jong, A.; Kehrenberg, C. Detection of a Novel qnrB19-Carrying Plasmid Variant Mediating Decreased Fluoroquinolone Susceptibility in Salmonella enterica Serovar Hadar. Microb. Drug Resist. 2017, 23, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S.N.; Frasson, I.; Bergo, C.; Manganelli, R.; Cavallaro, A.; Palù, G. Characterisation of qnr plasmid-mediated quinolone re-sistance in Enterobacteriaceae from Italy: Association of the qnrB19 allele with the integron element ISCR1 in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 35, 578–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martín-Gutiérrez, G.; Rodríguez-Martínez, J.M.; Pascual, Á.; Rodríguez-Beltrán, J.; Blázquez, J. Plasmidic qnr Genes Confer Clinical Resistance to Ciprofloxacin under Urinary Tract Physiological Conditions. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02615–e02616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carroll, A.C.; Wong, A. Plasmid persistence: Costs, benefits, and the plasmid paradox. Can. J. Microbiol. 2018, 64, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cottell, J.L.; Webber, M.A.; Piddock, L.J.V. Persistence of transferable extended-spectrum-β-lactamase resistance in the absence of antibiotic pressure. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4703–4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, E.A.J.; Dierikx, C.M.; van Essen-Zandbergen, A.; van Roermund, H.J.W.; Mevius, D.J.; Stegeman, A.; Klinkenberg, D. The IncI1 plasmid carrying the blaCTX-M-1 gene persists in in vitro culture of an Escherichia coli strain from broilers. BMC Microbiol. 2014, 14, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Porse, A.; Schønning, K.; Munck, C.; Sommer, M.O.A. Survival and evolution of a large multidrug resistance plasmid in new clinical bacterial hosts. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 2860–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Day of Sampling | N° of E. coli Isolates | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lungs | Spleen | Heart | Cns | Total | |
| D1 | 26 | 24 | 24 | 17 | 91 |
| D5 | 23 | 8 | 8 | 2 | 41 |
| D10 | 24 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 40 |
| D24 * | 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| Total | 78 | 35 | 38 | 28 | 179 |
| Day of Sampling | Serogroups | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2 | O20 | O78 | O86 | O128 | O153 | O157 | Not Typable | Total | |
| D1 | 1 | 36 | 5 | 49 | 91 | ||||
| D5 | 1 | 3 | 37 | 41 | |||||
| D10 | 1 | 39 | 40 | ||||||
| D24 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | |||||
| Total | 1 | 1 | 40 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 127 | 179 |
| Day | MIC (mg/L) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.016 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.12 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | |
| D1 | 16 * | 43 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 9 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 5 ** |
| D5 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 12 | 12 | 7 | |||||
| D10 | 1 * | 1 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 10 | 6 | 13 | |||
| D24 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | ||||||||
| Farm | E. coli Genome ID | Day of Sampling | Phenotypes * | Genotypes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genes | Mutations | ||||
| A | 871-21 | 1 | R | - | gyrA S83L; parC D475E |
| 871-22 | 1 | S | - | ||
| 871-41 | 1 | R | - | gyrA S83L | |
| 871-42 | 1 | R | - | gyrA S83L; parC S80R | |
| 871-46 | 1 | S | - | gyrA D87G | |
| 916-43 | 5 | R | - | parC S80I; gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N | |
| 976-38 | 10 | R | - | parC S80I; gyrA S83L | |
| 976-50 | 10 | R | - | gyrA S83L | |
| 976-57 | 10 | S | - | ||
| B | 1614-21 | 1 | S | - | |
| 1614-23 | 1 | S | - | ||
| 1614-35 | 1 | S | - | ||
| 1614-41 | 1 | S | - | ||
| 1665-22 | 5 | R | - | parC S80R; gyrA S83L | |
| 1665-24 | 5 | R | qnrB19 | parC S80R; gyrA S83L | |
| 1665-47 | 5 | R | - | parE S458A; parC S80I; gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N | |
| 1684-49 | 10 | R | - | gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N; parC S80I | |
| 1684-52 | 10 | I | - | gyrA S83L; parC E84G | |
| 1832-43 | 20 | R | - | parE S458A; parC S80I; gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N | |
| C | 2750-29 | 1 | R | - | gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N; parC S80I |
| 2750-25 | 1 | S | - | ||
| 2750-32 | 1 | S | - | ||
| 2750-48 | 1 | R | qnrS1 | gyrA S83L | |
| 2750-49 | 1 | S | - | gyrA S83L | |
| 2835-26 | 5 | R | - | parC S80I; gyrA S83L; gyrA D87Y | |
| 2835-32 | 5 | R | - | gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N; parC S80I | |
| 2835-44 | 5 | R | - | parC S80I; gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N | |
| 2835-47 | 5 | I | qnrS1 | ||
| 2835-57 | 5 | R | - | gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N; parC S80I | |
| 2863-46 | 10 | R | - | gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N; parC S80I | |
| 2863-50 | 10 | R | - | gyrA S83L; gyrA D87N; parC S80I | |
| Farm | Isolate | Day of Sampling | Plasmid | Chromosome—AMR Genes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Cluster ID | Predicted Mobility | AMR Genes | ||||
| A | 871-21 | 1 | AF098 | Non-mobilizable | tet(B); blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); sul2; dfrA1 |
| 871-22 | 1 | - | - | - | mdf(A) | |
| 871-41 | 1 | AA178 | Conjugative | blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); sul2; tet(B); dfrA1 | |
| 871-42 | 1 | AB595 | Mobilizable | aph(6)-Id; dfrA14; aph(3”)-Ib; sul2 | mdf(A); Inu(F); ant(3”)-Ia | |
| 871-42 | 1 | AG600 | Non-mobilizable | tet(A) | - | |
| 871-46 | 1 | AB233 | Conjugative | blaTEM-1B | mdf(A) | |
| 871-46 | 1 | AA176 | Conjugative | dfrA5 | - | |
| 916-43 | 5 | AA176 | Conjugative | sul3; aph(3”)-Ib; aph(6)-Id; dfrA1; sul1 | mdf(A); tet(A); blaTEM-1B | |
| 976-38 | 10 | AB233 | Non-mobilizable | catA1; tet(A); blaTEM-1B | mdf(A) | |
| AD069 | Non-mobilizable | ant(3”)-Ia; lnu(G) | ||||
| 976-50 | 10 | AA619 | Conjugative | lnu(G); blaTEM-1B | aadA1 | |
| AA374 | Mobilizable | tet(A); sul2; aph(3”)-Ib; aph(6)-Id; catA1 | ||||
| 976-57 | 10 | - | - | - | mdf(A) | |
| B | 1614-21 | 1 | AA474 | Conjugative | aac(3)-IId; blaTEM-1B | mdf(A) |
| 1614-23 | 1 | AA175 | Conjugative | aac(3)-IId; blaTEM-1B | mdf(A) | |
| 1614-35 | 1 | AA175 | Conjugative | aac(3)-IId; blaTEM-1B | mdf(A) | |
| 1614-41 | 1 | AA474 | Conjugative | aac(3)-IId; blaTEM-1B | mdf(A) | |
| 1665-22 | 5 | AA738 | Conjugative | strA; aph(6)-Id; sul3; sul1; cmlA1 | mdf(A); ant(3”)-Ia; aadA2 | |
| 1665-22 | novel | Non-mobilizable | cmlA1; dfrA12 | - | ||
| 1665-24 | 5 | AG685 | Non-mobilizable | sul3; aadA2; cmlA1 | mdf(A); blaTEM-1B; lnu(G); aadA1 | |
| AB042 | Mobilizable | qnrB19 | ||||
| 1665-47 | 5 | AG685 | Non-mobilizable | sul3; dfrA12; aadA2; cmlA1 | mdf(A); aadA13; tet(A); Inu(G); blaTEM-1B; aasA1 | |
| 1684-49 | 10 | AA474 | Conjugative | sul2; tet(A); blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); lnu(G); ant(3”)-Ia; dfrA1 | |
| 1684-52 | 10 | AA619 | Conjugative | blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); tet(34) | |
| AB595 | Mobilizable | aph(6)-Id; dfrA14; aph(3”)-Ib; sul2 | ||||
| AD068 | Non-mobilizable | ant(3”)-Ia_1; lnu(G)_1 | ||||
| 1832-43 | 24 | AG658 | Non-mobilizable | sul3; cmlA1; aadA2; dfrA12 | mdf(A); tet(34); ant(3”)-Ia; tet(A); lnu(G); aadA1 | |
| AD448 | Non-mobilizable | blaTEM-1B | ||||
| C | 2750-25 | 1 | AC120 | Non-mobilizable | aph(6)-Id; aph(3”)-Ib; sul2; tet(A); blaTEM-1B | mdf(A) |
| 2750-29 | 1 | AA474 | Conjugative | tet(A); dfrA1; aac(3)-IId; blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); ant(3”)-Ia | |
| novel | Conjugative | Inu(G) | ||||
| 2750-32 | 1 | AA176 | Conjugative | aph(6)-Id; aph(3”)-Ib; sul2; blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); tet(A) | |
| 2750-48 | 1 | AB711 | Conjugative | blaTEM-1B; qnrS1 | mdf(A); tet(A) | |
| AB595 | Mobilizable | aph(6)-Id; dfrA14; aph(3”)-Ib; sul2 | ||||
| 2750-49 | 1 | AA281 | Conjugative | blaTEM-1B | dfrA1_10; mdf(A)_1; sul2_2 | |
| AB193 | Non-mobilizable | aph(6)-Id; strA; ant(3”)-Ia; tet(B); lnu(G) | ||||
| 2835-26 | 5 | AA179 | Conjugative | sul2; tet(A); blaTEM-1B | aph(6)-Id; aph(3”)-Ib; lnu(G); ant(3”)-Ia; dfrA14 | |
| 2835-32 | 5 | AA474 | Conjugative | aac(3)-IId; tet(A); blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); dfrA1; ant(3”)-Ia | |
| AA304 | Conjugative | lnu(G) | ||||
| 2835-44 | 5 | AA474 | Conjugative | tet(A); dfrA1; aac(3)-IId; blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); dfrA1; ant(3”)-Ia | |
| 2835-47 | 5 | AB233 | Conjugative | blaTEM-106; qnrS1 | mdf(A) | |
| 2835-57 | 5 | AA738 | Conjugative | tet(A); mph(B); sul2; aph(3”)-Ib; aph(6)-Id; sul1; ant(3”)-Ia; dfrA1; dfrA12; nu(F); blaTEM-1B | mdf(A); aadA2 | |
| 2863-46 | 10 | AA474 | Conjugative | tet(A); aac(3)-IId; blaTEM-1B | dfrA1; mdf(A); ant(3”)-Ia | |
| 2863-50 | 10 | AA474 | Conjugative | aac(3)-IId; tet(A); blaTEM-1B; lnu(G) | mdf(A); dfrA1; ant(3”)-Ia | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pasquali, F.; Crippa, C.; Parisi, A.; Lucchi, A.; Gambi, L.; Merlotti, A.; Remondini, D.; Stonfer, M.; Manfreda, G. Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Extraintestinal E. coli Populations Pre- and Post-Antimicrobial Therapy on Broilers Affected by Colisepticemia. Animals 2023, 13, 2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162590
Pasquali F, Crippa C, Parisi A, Lucchi A, Gambi L, Merlotti A, Remondini D, Stonfer M, Manfreda G. Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Extraintestinal E. coli Populations Pre- and Post-Antimicrobial Therapy on Broilers Affected by Colisepticemia. Animals. 2023; 13(16):2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162590
Chicago/Turabian StylePasquali, Frédérique, Cecilia Crippa, Antonio Parisi, Alex Lucchi, Lucia Gambi, Alessandra Merlotti, Daniel Remondini, Maurizio Stonfer, and Gerardo Manfreda. 2023. "Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Extraintestinal E. coli Populations Pre- and Post-Antimicrobial Therapy on Broilers Affected by Colisepticemia" Animals 13, no. 16: 2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162590
APA StylePasquali, F., Crippa, C., Parisi, A., Lucchi, A., Gambi, L., Merlotti, A., Remondini, D., Stonfer, M., & Manfreda, G. (2023). Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Extraintestinal E. coli Populations Pre- and Post-Antimicrobial Therapy on Broilers Affected by Colisepticemia. Animals, 13(16), 2590. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13162590







