Development of a Multispecies Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA Using N and RBD Proteins to Detect Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Serum Samples
2.2. Microneutralization Test
2.3. Production of Recombinant Proteins
2.4. Double-Antigen ELISA
2.5. Indirect ELISA
2.6. Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test
2.7. Repeatability and Reproducibility
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Microneutralization Test
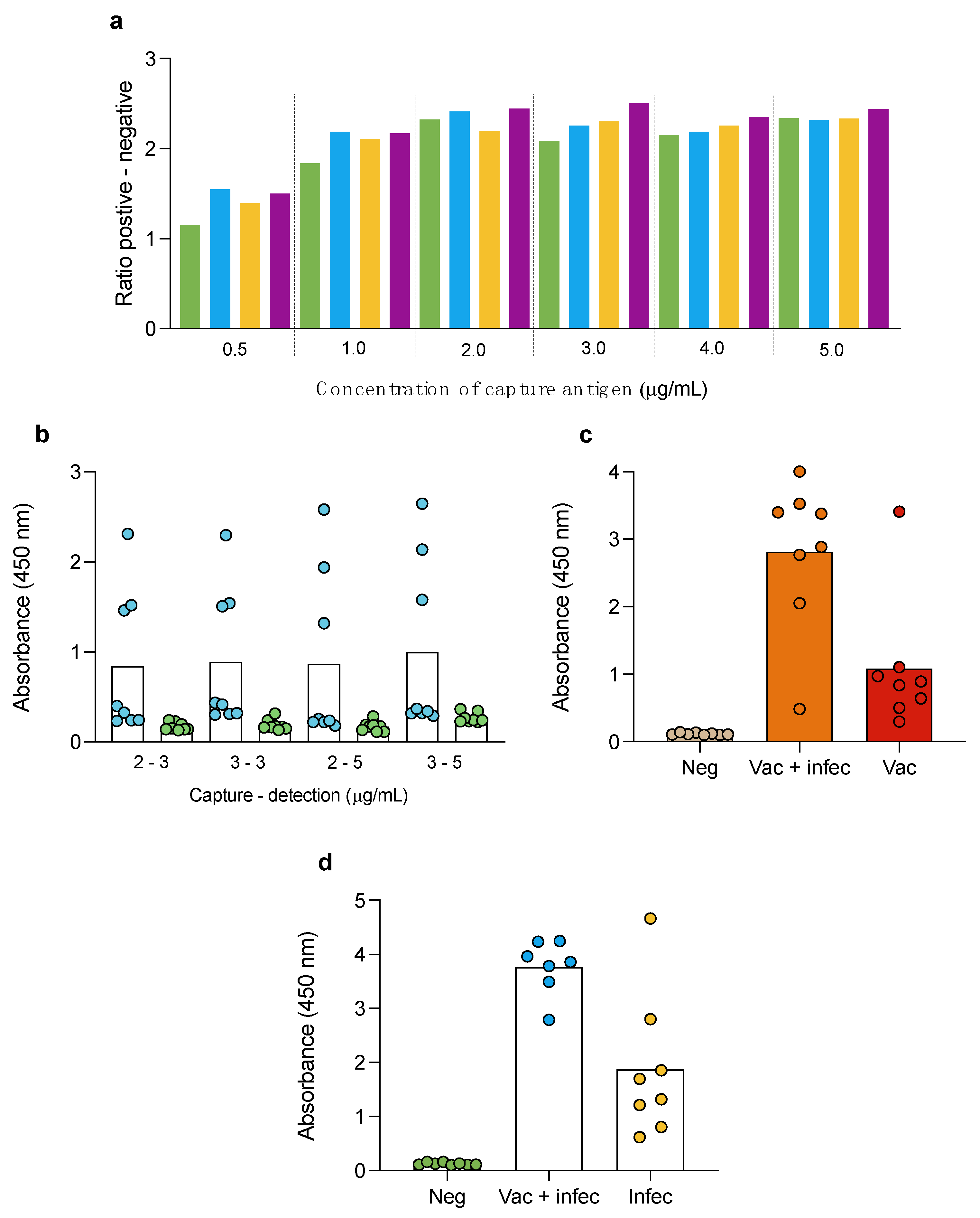
3.2. Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA
3.3. Indirect ELISA
3.4. Surrogate Virus Neutralization Test
3.5. Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA with RBD and N Proteins in Different Animal Species
3.6. Repeatability and Reproducibility of the Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA with RBD and N Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wacharapluesadee, S.; Tan, C.W.; Maneeorn, P.; Duengkae, P.; Zhu, F.; Joyjinda, Y.; Kaewpom, T.; Chia, W.N.; Ampoot, W.; Lim, B.L. Evidence for SARS-CoV-2 related coronaviruses circulating in bats and pangolins in Southeast Asia. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorito, F.; Iovane, V.; Pagnini, U.; Cerracchio, C.; Brandi, S.; Levante, M.; Marati, L.; Ferrara, G.; Tammaro, V.; De Carlo, E.; et al. First Description of Serological Evidence for SARS-CoV-2 in Lactating Cows. Animals 2022, 12, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, G.; Cardillo, L.; Levante, M.; Brandi, S.; Picazio, G.; Napoletano, M.; Martucciello, A.; Fiorito, F.; De Carlo, E.; de Martinis, C. First serological evidence of SARS-CoV-2 natural infection in small ruminants. Vet. Res. Commun. 2023, 47, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garigliany, M.; Van Laere, A.-S.; Clercx, C.; Giet, D.; Escriou, N.; Huon, C.; van der Werf, S.; Eloit, M.; Desmecht, D. Early Release-SARS-CoV-2 Natural Transmission from Human to Cat, Belgium, March 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 3069–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leroy, E.M.; Gouilh, M.A.; Brugère-Picoux, J. The risk of SARS-CoV-2 transmission to pets and other wild and domestic animals strongly mandates a one-health strategy to control the COVID-19 pandemic. One Health 2020, 10, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sit, T.H.C.; Brackman, C.J.; Ip, S.M.; Tam, K.W.S.; Law, P.Y.T.; To, E.M.W.; Yu, V.Y.T.; Sims, L.D.; Tsang, D.N.C.; Chu, D.K.W.; et al. Infection of dogs with SARS-CoV-2. Nature 2020, 586, 776–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grome, H.N.; Meyer, B.; Read, E.; Buchanan, M.; Cushing, A.; Sawatzki, K.; Levinson, K.J.; Thomas, L.S.; Perry, Z.; Uehara, A.J.E.I.D. SARS-CoV-2 outbreak among Malayan tigers and humans, Tennessee, USA, 2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAloose, D.; Laverack, M.; Wang, L.; Killian, M.L.; Caserta, L.C.; Yuan, F.; Mitchell, P.K.; Queen, K.; Mauldin, M.R.; Cronk, B.D.; et al. From People to Panthera: Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Tigers and Lions at the Bronx Zoo. mBio 2020, 11, e02220-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Italiya, J.; Vacek, V.; Matějů, P.; Dering, C.; Celina, S.S.; Ndiaye, A.; Černý, J. First Detection of SARS-CoV-2 in White Rhinoceros during a Small-Scale Coronavirus Surveillance in the Bandia Reserve, Senegal. Animals 2023, 13, 2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lenoch, J.; Kohler, D.; DeLiberto, T.J.; Tang, C.Y.; Li, T.; Tao, Y.J.; Guan, M.; Compton, S.; Zeiss, C.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Exposure in Norway Rats (Rattus norvegicus) from New York City. mBio 2023, 14, e03621-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miot, E.F.; Worthington, B.M.; Ng, K.H.; de Lataillade, L.G.; Pierce, M.P.; Liao, Y.; Ko, R.; Shum, M.H.; Cheung, W.Y.; Holmes, E.C.; et al. Surveillance of Rodent Pests for SARS-CoV-2 and Other Coronaviruses, Hong Kong. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, P.M.; Orbegozo, J.; Watts, D.M.; Morrill, J.C. SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibodies in White-Tailed Deer from Texas. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 22, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, V.L.; Dennis, P.M.; McBride, D.S.; Nolting, J.M.; Madden, C.; Huey, D.; Ehrlich, M.; Grieser, J.; Winston, J.; Lombardi, D.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection in free-ranging white-tailed deer. Nature 2022, 602, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannekens-Jager, M.M.; de Rooij, M.M.; de Groot, Y.; Biesbroeck, E.; de Jong, M.K.; Pijnacker, T.; Smit, L.A.; Schuurman, N.; Broekhuizen-Stins, M.J.; Zhao, S. SARS-CoV-2 infection in dogs and cats is associated with contact to COVID-19 positive household members. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 4034–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Vale, B.; Lopes, A.P.; Fontes, M.d.C.; Silvestre, M.; Cardoso, L.; Coelho, A.C. Bats, pangolins, minks and other animals—Villains or victims of SARS-CoV-2? Vet. Res. Commun. 2021, 45, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.-T.; Han, Y.-J.; Wu, G.-H.; Huang, K.-Y.A.; Huang, P.-N. Overview of Neutralization Assays and International Standard for Detecting SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody. Viruses 2022, 14, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Maghsoudlou, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): The basics. Br. J. Hosp. Med. 2016, 77, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.-J.; Xu, Y.; Huang, J. Developing a double-antigen sandwich ELISA for effective detection of human hepatitis B core antibody. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2008, 31, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watcharatanyatip, K.; Boonmoh, S.; Chaichoun, K.; Songserm, T.; Woratanti, M.; Dharakul, T. Multispecies detection of antibodies to influenza A viruses by a double-antigen sandwich ELISA. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 163, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, S.; Hoque, M.; Adekanmbi, F.; Kelly, P.; Jenkins-Moore, M.; Torchetti, M.K.; Chenoweth, K.; Wood, T.; Wang, C. Antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 in dogs and cats, USA. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, J.M.; Weber, C.; Wernike, K.; Michelitsch, A.; Friedrich, K.; Trimpert, J.; Beer, M.; Kohn, B.; Osterrieder, K.; Müller, E. Prevalence of anti-severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 antibodies in cats in Germany and other European countries in the early phase of the coronavirus disease-19 pandemic. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehesa-Canseco, F.; Pastrana-Unzueta, R.; Carrillo-Guzmán, N.; Liljehult-Fuentes, F.; Pérez-De la Rosa, J.D.; Ramírez-Mendoza, H.; Estrada-Franco, J.G.; Navarro-López, R.; Hernández, J.; Solís-Hernández, M. Neutralizing Antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 Ancestral Strain and Omicron BA.1 Subvariant in Dogs and Cats in Mexico. Pathogens 2023, 12, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melgoza-González, E.; Hinojosa-Trujillo, D.; Resendiz, M.; Mata-Haro, V.; Hernández-Valenzuela, S.; García-Vega, M.; Bravo-Parra, M.; Valenzuela, O.; Velázquez, E.; Soto-Gaxiola, A. Analysis of IgG, IgA, and IgM antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein S1 in convalescent and vaccinated patients with the Pfizer-BioNTech and CanSinoBio vaccines. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 69, e734–e745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, J.; Dehesa-Canseco, F.; Vázquez-López, A.B.; Reséndiz-Sandoval, M.; Caire-Juvera, G.; Solís-Hernández, M.; Valenzuela, O.; Gómez-Gil, B.; Mata-Haro, V. Neutralization of Omicron BA.1, BA.5.1.6, BQ.1.3 and XBB1.1 induced by heterologous vaccination Ad5-nCoV and mRNA-1273. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Vega, M.; Melgoza-González, E.A.; Hernández-Valenzuela, S.; Hinojosa-Trujillo, D.; Reséndiz-Sandoval, M.; Llamas-Covarrubias, M.A.; Loza-López, M.; Valenzuela, O.; Soto-Gaxiola, A.; Hernández-Oñate, M.A.; et al. 19n01, a broadly neutralizing antibody against omicron BA.1, BA.2, BA.4/5, and other SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. iScience 2023, 26, 106562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, R.A.; Ko, R.; Tsang, O.T.; Hui, D.S.; Kwan, M.Y.; Brackman, C.J.; To, E.M.; Yen, H.-l.; Leung, K.; Cheng, S.M. Evaluation of a SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test for detection of antibody in human, canine, cat, and hamster sera. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e02504-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, G.A.; Pereira, S.A.; Ogrzewalska, M.; Pauvolid-Corrêa, A.; Resende, P.C.; Tassinari, W.d.S.; Costa, A.d.P.; Keidel, L.O.; da Rocha, A.S.B.; da Silva, M.F.B. Investigation of SARS-CoV-2 infection in dogs and cats of humans diagnosed with COVID-19 in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco-Lauth, A.M.; Hartwig, A.E.; Porter, S.M.; Gordy, P.W.; Nehring, M.; Byas, A.D.; VandeWoude, S.; Ragan, I.K.; Maison, R.M.; Bowen, R.A. Experimental infection of domestic dogs and cats with SARS-CoV-2: Pathogenesis, transmission, and response to reexposure in cats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 26382–26388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barik, S.; Mohanty, K.; Bisht, D.; Joshi, B.; Jena, S.; Tripathy, S. An overview of enzyme immunoassay: The test generation assay in HIV/AIDS testing. J. AIDS Clin. Res. 2018, 9, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanović, M.; Dietze, K.; Milićević, V.; Radojičić, S.; Valčić, M.; Moritz, T.; Hoffmann, B. Humoral immune response to repeated lumpy skin disease virus vaccination and performance of serological tests. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Xiu, B.; Wang, G.; Chen, K.; Feng, X.; Song, X.; Zhu, C.; Ling, S.; Zhang, H. Double-antigen sandwich ELISA for the detection of anti-hepatitis C virus antibodies. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 171, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardillo, L.; de Martinis, C.; Brandi, S.; Levante, M.; Cozzolino, L.; Spadari, L.; Boccia, F.; Carbone, C.; Pompameo, M.; Fusco, G. SARS-CoV-2 Serological and Biomolecular Analyses among Companion Animals in Campania Region (2020–2021). Microorganisms 2022, 10, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jairak, W.; Charoenkul, K.; Chamsai, E.; Udom, K.; Chaiyawong, S.; Hangsawek, A.; Waenkaew, S.; Mungaomklang, A.; Tangwangvivat, R.; Amonsin, A. Survey of SARS-CoV-2 in dogs and cats in high-risk areas during the second wave of COVID-19 outbreak, Thailand. Zoonoses Public Health 2022, 69, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomorska-Mól, M.; Turlewicz-Podbielska, H.; Gogulski, M.; Ruszkowski, J.J.; Kubiak, M.; Kuriga, A.; Barket, P.; Postrzech, M. A cross-sectional retrospective study of SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence in domestic cats, dogs and rabbits in Poland. BMC Vet. Res. 2021, 17, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dileepan, M.; Di, D.; Huang, Q.; Ahmed, S.; Heinrich, D.; Ly, H.; Liang, Y. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) exposure in pet cats and dogs in Minnesota, USA. Virulence 2021, 12, 1597–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Gao, J.; Huang, K.; Hu, C.; Hui, X.; He, X.; Li, C.; Gong, W.; Lv, C. A serological survey of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in dogs in Wuhan. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, J.; Huang, K.; Yang, Y.; Hui, X.; He, X.; Li, C.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. A serological survey of SARS-CoV-2 in cat in Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bold, D.; Roman-Sosa, G.; Gaudreault, N.N.; Zayat, B.; Pogranichniy, R.M.; Richt, J.A. Development of an Indirect ELISA for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Cats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; et al. Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Porcine Streptococcus suis Based on a Recombinant GMD Protein. Animals 2023, 13, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Zhu, M.; Yuan, Q.; Deng, Z.; Feng, S.; Liu, D.; Yuan, X. Development of an Indirect ELISA to Detect African Swine Fever Virus pp62 Protein-Specific Antibodies. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 798559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, V.; Profaizer, T.; Lozier, B.K.; Elgort, M.G.; Larragoite, E.T.; Williams, E.S.C.P.; Solis-Leal, A.; Lopez, J.B.; Berges, B.K.; Planelles, V.; et al. Evaluation of a Surrogate Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay–Based Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) cPass Neutralization Antibody Detection Assay and Correlation with Immunoglobulin G Commercial Serology Assays. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2021, 145, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WOAH. Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahm/A_summry.htm (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Stevanovic, V.; Vilibic-Cavlek, T.; Tabain, I.; Benvin, I.; Kovac, S.; Hruskar, Z.; Mauric, M.; Milasincic, L.; Antolasic, L.; Skrinjaric, A.; et al. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among pet animals in Croatia and potential public health impact. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 1767–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, C.; Martina, B.; Mirolo, M.; Müller, E.; Klein, R.; Volk, H.; Egberink, H.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, M.; Kaiser, F.; von Köckritz-Blickwede, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibodies in Domestic Cats during First COVID-19 Wave, Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 3115–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Leij, W.J.R.; Broens, E.M.; Hesselink, J.W.; Schuurman, N.; Vernooij, J.C.M.; Egberink, H.F. Serological Screening for Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in Dutch Shelter Cats. Viruses 2021, 13, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neira, V.; Brito, B.; Agüero, B.; Berrios, F.; Valdés, V.; Gutierrez, A.; Ariyama, N.; Espinoza, P.; Retamal, P.; Holmes, E.C. A household case evidences shorter shedding of SARS-CoV-2 in naturally infected cats compared to their human owners. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentealba, N.A.; Moré, G.; Bravi, M.E.; Unzaga, J.M.; De Felice, L.; Salina, M.; Viegas, M.; Jodar, M.S.N.; Valinotto, L.E.; Rivero, F.D. First detection and molecular analysis of SARS-CoV-2 from a naturally infected cat from Argentina. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 260, 109179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallett, S.; Allen, A.J.; Graziadio, S.; Taylor, S.A.; Sakai, N.S.; Green, K.; Suklan, J.; Hyde, C.; Shinkins, B.; Zhelev, Z.; et al. At what times during infection is SARS-CoV-2 detectable and no longer detectable using RT-PCR-based tests? A systematic review of individual participant data. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wen, Z.; Zhong, G.; Yang, H.; Wang, C.; Huang, B.; Liu, R.; He, X.; Shuai, L.; Sun, Z. Susceptibility of ferrets, cats, dogs, and other domesticated animals to SARS–coronavirus 2. Science 2020, 368, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doliff, R.; Martens, P. Cats and SARS-CoV-2: A Scoping Review. Animals 2022, 12, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Bellon, H.; Rodon, J.; Fernández-Bastit, L.; Almagro, V.; Padilla-Solé, P.; Lorca-Oró, C.; Valle, R.; Roca, N.; Grazioli, S.; Trogu, T.; et al. Monitoring Natural SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Lions (Panthera leo) at the Barcelona Zoo: Viral Dynamics and Host Responses. Viruses 2021, 13, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, G.R.; Kaduskar, O.; Deshpande, K.; Bhatt, V.; Yadav, P.; Gurav, Y.; Potdar, V.; Khutwad, K.; Vidhate, S.; Salunke, A.; et al. Longitudinal clinico-serological analysis of anti-nucleocapsid and anti-receptor binding domain of spike protein antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Infect. Dis. IJID Off. Publ. Int. Soc. Infect. Dis. 2021, 112, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, A.; Chozhavel Rajanathan, T.M.; Chandra, H.; Pericherla, H.P.R.; Kumar, S.; Choonia, H.S.; Bajpai, M.; Singh, A.K.; Sinha, A.; Saini, G.; et al. Immunogenic potential of DNA vaccine candidate, ZyCoV-D against SARS-CoV-2 in animal models. Vaccine 2021, 39, 4108–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, S.; Naderi Saffar, K.; Ebrahimi, F.; Khatami, P.; Monazah, A.; Alizadeh, G.-A.; Ettehadi, H.-A.; Rad, I.; Nojehdehi, S.; Kehtari, M.; et al. Development of Inactivated FAKHRAVAC® Vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 Virus: Preclinical Study in Animal Models. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Seiler, P.; Jones, J.C.; Ridout, G.; Camp, K.P.; Fabrizio, T.P.; Jeevan, T.; Miller, L.A.; Throm, R.E.; Ferrara, F. Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Antigens in Humans and Animals. Vaccines 2020, 8, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colitti, B.; Bertolotti, L.; Mannelli, A.; Ferrara, G.; Vercelli, A.; Grassi, A.; Trentin, C.; Paltrinieri, S.; Nogarol, C.; Decaro, N.; et al. Cross-Sectional Serosurvey of Companion Animals Housed with SARS-CoV-2-Infected Owners, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1919–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embregts, C.W.; Verstrepen, B.; Langermans, J.A.; Böszörményi, K.P.; Sikkema, R.S.; de Vries, R.D.; Hoffmann, D.; Wernike, K.; Smit, L.A.; Zhao, S.J.O.H. Evaluation of a multi-species SARS-CoV-2 surrogate virus neutralization test. One Health 2021, 13, 100313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Elslande, J.; Oyaert, M.; Ailliet, S.; Van Ranst, M.; Lorent, N.; Vande Weygaerde, Y.; André, E.; Lagrou, K.; Vandendriessche, S.; Vermeersch, P. Longitudinal follow-up of IgG anti-nucleocapsid antibodies in SARS-CoV-2 infected patients up to eight months after infection. J. Clin. Virol. 2021, 136, 104765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutukina, M.; Kaznadzey, A.; Kireeva, M.; Mazo, I. IgG Antibodies Develop to Spike but Not to the Nucleocapsid Viral Protein in Many Asymptomatic and Light COVID-19 Cases. Viruses 2021, 13, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cutoff | Diagnostic Sensitivity | Diagnostic Specificity | AUC | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Format 1 (RBD protein) | 0.3080 | 80% (CI 95%: 35.5 to 98.9) | 88% (CI 95%: 70.0 to 95.8) | 86.40% (CI 95%: 66.2 to 100) | 0.0113 |
| Format 2 (N protein) | 0.2665 | 60% (CI 95%: 23.0 to 92.9) | 85.19% (CI 95%: 67.5 to 94.1) | 67.41% (CI 95%: 38.7 to 96) | 0.2226 |
| Format 3 (RBD and N protein) | 0.3615 | 80% (CI 95%: 37.5 to 98.9) | 100% (CI 95%: 86.7 to 100) | 88% (CI 95%: 66.3 to 100) | 0.0082 |
| Cutoff | Diagnostic Sensitivity | Diagnostic Specificity | AUC | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| iELISA with RBD protein | 0.7960 | 80% (CI 95%: 37.5 to 98.9) | 89.29% (CI 95%: 72.8 to 96.3) | 85.71% (CI 95%: 64.1 to 100) | 0.0121 |
| iELISA with S1 protein | 1.3333 | 60% (CI 95%: 23.1 to 92.9) | 100% (CI 95%: 87.1 to 100) | 75.38% (CI 95%: 47.1 to 100) | 0.0763 |
| iELISA with N protein | 0.4510 | 60% (CI 95%: 23.1 to 92.9) | 69.23% (CI 95%: 50.0 to 83.5) | 53.46% (CI 95%: 23.6 to 83.3) | 0.8090 |
| Cutoff | Diagnostic Sensitivity | Diagnostic Specificity | AUC | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sVNT | 16.9% | 80.0 (CI 95%: 37.5 to 98.9) | 96.15 (CI 95%: 81.1 to 99.8) | 82.31 (CI 95%: 53.8 to 100) | 0.0241 |
| Cutoff | Diagnostic Sensitivity | Diagnostic Specificity | AUC | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3615 | 83.87 (CI 95%: 67.4 to 92.9) | 100 (CI 95%: 89.8 to 100) | 92.55 (CI 95%: 85.2 to 99.9) | <0.0001 |
| Sample | Absorbance Mean | %CV |
|---|---|---|
| High positive | 4.163 | 10.64 |
| Low positive | 0.6043 | 26.12 |
| High negative | 0.1781 | 12.53 |
| Low negative | 0.1488 | 17.37 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cordero-Ortiz, M.; Reséndiz-Sandoval, M.; Dehesa-Canseco, F.; Solís-Hernández, M.; Pérez-Sánchez, J.; Martínez-Borges, C.; Mata-Haro, V.; Hernández, J. Development of a Multispecies Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA Using N and RBD Proteins to Detect Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Animals 2023, 13, 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13223487
Cordero-Ortiz M, Reséndiz-Sandoval M, Dehesa-Canseco F, Solís-Hernández M, Pérez-Sánchez J, Martínez-Borges C, Mata-Haro V, Hernández J. Development of a Multispecies Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA Using N and RBD Proteins to Detect Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Animals. 2023; 13(22):3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13223487
Chicago/Turabian StyleCordero-Ortiz, Maritza, Mónica Reséndiz-Sandoval, Freddy Dehesa-Canseco, Mario Solís-Hernández, Jahir Pérez-Sánchez, Carlos Martínez-Borges, Verónica Mata-Haro, and Jesús Hernández. 2023. "Development of a Multispecies Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA Using N and RBD Proteins to Detect Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2" Animals 13, no. 22: 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13223487
APA StyleCordero-Ortiz, M., Reséndiz-Sandoval, M., Dehesa-Canseco, F., Solís-Hernández, M., Pérez-Sánchez, J., Martínez-Borges, C., Mata-Haro, V., & Hernández, J. (2023). Development of a Multispecies Double-Antigen Sandwich ELISA Using N and RBD Proteins to Detect Antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Animals, 13(22), 3487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13223487







