Genomic Dissection through Whole-Genome Resequencing of Five Local Pig Breeds from Shanghai, China
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
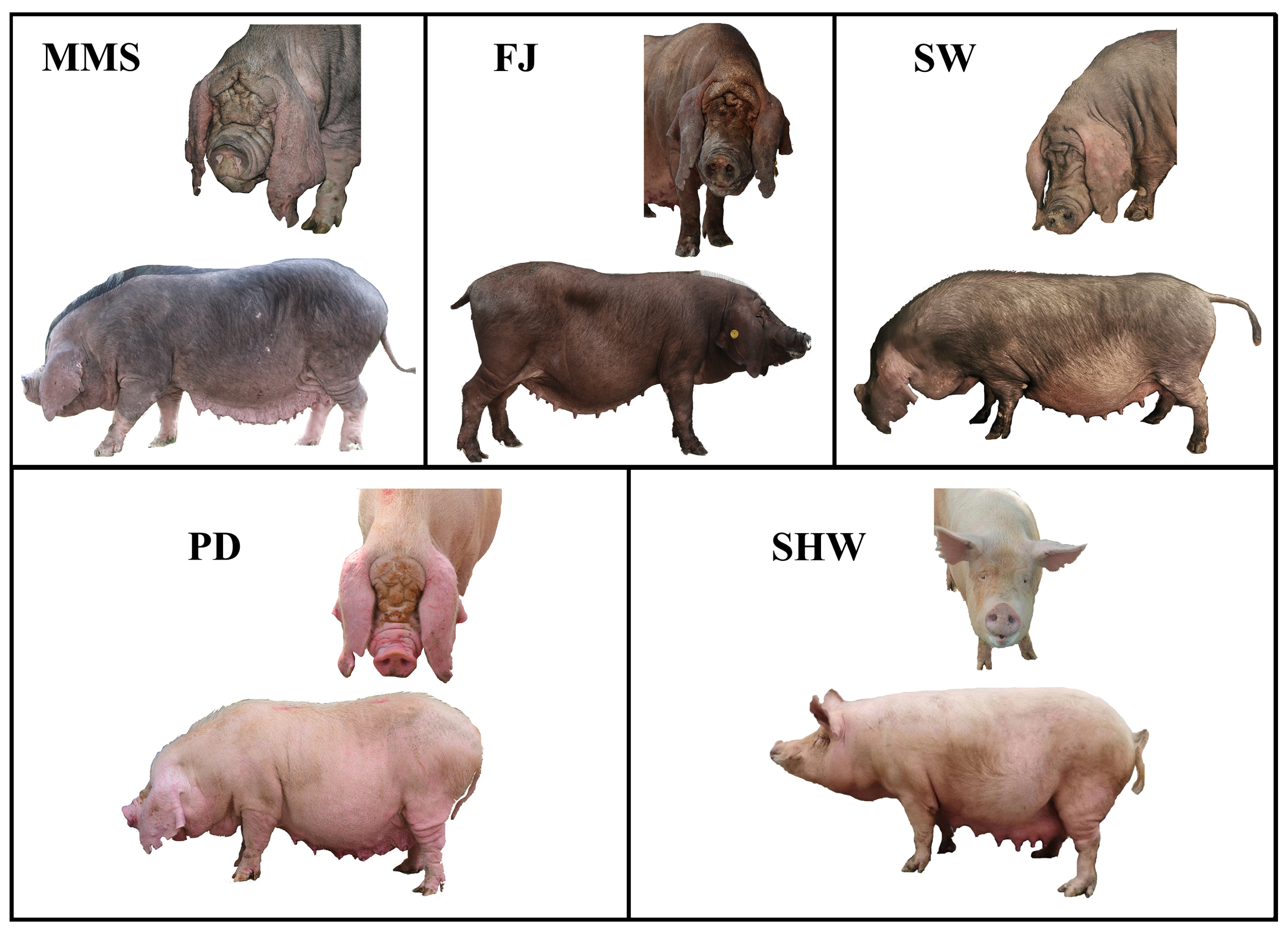
2.1. Sample Collection and Sequencing
2.2. Variant Calling and Annotation
2.3. Genetic Analysis of the Population
2.4. Genome-Wide Selective Sweeps Detection
2.5. Enrichment Analysis and PPI Network Construction
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Variant Identification in Shanghai Local Breeds
3.2. Population Genetic Structure
3.3. Selection Signature Detection of Indigenous Shanghai Pig Population
3.4. Functional Analysis of Genes in Selected Regions
3.5. Protein–Protein Interaction (PPI) Subnetwork
3.6. Polymorphisms of MSRB3 within Indigenous Shanghai Population
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cesar, A.; Silveira, A.; Freitas, P.; Guimaraes, E.; Batista, D.; Torido, L.; Meirelles, F.V.; Antunes, R. Influence of Chinese breeds on pork quality of commercial pig lines. Genet. Mol. Res. 2010, 9, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.; Li, S.T.; Yao, W.Y.; Xie, C.D.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, Z.J.; Wang, D.; Xu, K.; Shen, Z.J.; Mu, Y. The Meishan pig genome reveals structural variation-mediated gene expression and phenotypic divergence underlying Asian pig domestication. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 2077–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, M.; Lympany, C.; Haley, C.; Brown, I.; Warkup, C. The eating quality of pork from Meishan and Large White pigs and their reciprocal crosses. Anim. Sci. J. 1995, 60, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, L.; Milan, D.; Ecolan, P.; Le Callennec, C. Myosin heavy chain composition of different skeletal muscles in Large White and Meishan pigs. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 82, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haley, C.; Lee, G. Genetic basis of prolificacy in Meishan pigs. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1993, 48, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rothammer, S.; Seichter, D.; Förster, M.; Medugorac, I. A genome-wide scan for signatures of differential artificial selection in ten cattle breeds. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Wu, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Gao, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Gao, H. Genome-wide detection of selective signatures in Simmental cattle. J. Appl. Genet. 2014, 55, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabeti, P.C.; Varilly, P.; Fry, B.; Lohmueller, J.; Hostetter, E.; Cotsapas, C.; Xie, X.; Byrne, E.H.; McCarroll, S.A.; Gaudet, R. Genome-wide detection and characterization of positive selection in human populations. Nature 2007, 449, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voight, B.F.; Kudaravalli, S.; Wen, X.; Pritchard, J.K. A map of recent positive selection in the human genome. PLoS Biol. 2006, 4, e72. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, R.; Williamson, S.; Kim, Y.; Hubisz, M.J.; Clark, A.G.; Bustamante, C. Genomic scans for selective sweeps using SNP data. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. The genetical structure of populations. Ann. Eugen. 1949, 15, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weir, B.S.; Cockerham, C.C. Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 1984, 1358–1370. [Google Scholar]
- Nei, M.; Li, W.-H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1979, 76, 5269–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watterson, G. On the number of segregating sites in genetical models without recombination. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1975, 7, 256–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tian, S.; Jin, L.; Zhou, G.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.; Yeung, C.K.; Chen, L.; Ma, J. Genomic analyses identify distinct patterns of selection in domesticated pigs and Tibetan wild boars. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, M.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, G.; Yin, Z.; Wang, C. Identification of signatures of selection by whole-genome resequencing of a Chinese native pig. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 566255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Du, H.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Jing, X.; Yang, H. Population Genetic Structure and Selection Signature Analysis of Beijing Black Pig. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 860669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, D.W.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2001; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, M.; Hakonarson, H. ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, D.H.; Novembre, J.; Lange, K. Fast model-based estimation of ancestry in unrelated individuals. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1655–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felsenstein, J. PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package), Version 3.5 c; Joseph Felsenstein: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: An online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H. A statistical framework for SNP calling, mutation discovery, association mapping and population genetical parameter estimation from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, J.; Jaehnig, E.J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, B. WebGestalt 2019: Gene set analysis toolkit with revamped UIs and APIs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W199–W205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P. STRING v11: Protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, J.; Tang, B.; Wang, A.; Dong, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, C.; Sun, Y. The genome sequence archive family: Toward explosive data growth and diverse data types. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2021, 19, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partners, C.-N.M.a. Database resources of the national genomics data center, china national center for bioinformation in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D27–D38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, W.H.O.; Quirino, C.R.; Bartholazzi-Junior, A.; Rua, M.A.S.; Serapião, R.V.; Oliveira, C.S. Variants in the CYP19A1 gene can affect in vitro embryo production traits in cattle. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 2233–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.E.; Pfeiffer, C.A.; Brooks, K.E.; Spate, L.D.; Benne, J.A.; Cecil, R.; Samuel, M.S.; Murphy, C.N.; Behura, S.; McLean, M.K. New perspective on conceptus estrogens in maternal recognition and pregnancy establishment in the pig. Biol. Reprod. 2019, 101, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, C.; Rubin, C.-J.; Sharifi, A.R.; Ha, N.-T.; Weigend, S.; Waldmann, K.-H.; Distl, O.; Pant, S.D.; Fredholm, M.; Schlather, M. Analysis of porcine body size variation using re-sequencing data of miniature and large pigs. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsunomiya, Y.T.; Do Carmo, A.S.; Carvalheiro, R.; Neves, H.H.; Matos, M.C.; Zavarez, L.B.; Pérez O’Brien, A.M.; Sölkner, J.; McEwan, J.C.; Cole, J.B. Genome-wide association study for birth weight in Nellore cattle points to previously described orthologous genes affecting human and bovine height. BMC Genet. 2013, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Wang, Z.; Pan, C.; Chen, H.; Lan, X. Detection of 15-bp deletion mutation within PLAG1 gene and its effects on growth traits in goats. Animals 2021, 11, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyko, A.R.; Quignon, P.; Li, L.; Schoenebeck, J.J.; Degenhardt, J.D.; Lohmueller, K.E.; Zhao, K.; Brisbin, A.; Parker, H.G.; Vonholdt, B.M. A simple genetic architecture underlies morphological variation in dogs. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, X.; Yan, H.; Zhao, K.; Shi, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, N. Porcine methionine sulfoxide reductase B3: Molecular cloning, tissue-specific expression profiles, and polymorphisms associated with ear size in Sus scrofa. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liu, C.; Xiong, X.; Fang, S.; Yang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, J.; Guo, Y.; Huang, L. Copy number variation in the MSRB3 gene enlarges porcine ear size through a mechanism involving miR-584-5p. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2018, 50, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Breed (Individuals) | Average_Clean_Reads | Average_Align_Rate | Average_Depth (×) | Coverage (%) | Coverage_5× (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duroc (31) | 335,518,499 | 99.51 | 12.00 | 97.51 | 87.68 |
| Landrace (21) | 382,512,941 | 99.58 | 15.25 | 97.09 | 88.65 |
| Yorkshire (24) | 347,694,640 | 99.49 | 12.29 | 97.32 | 87.33 |
| FJ (30) | 214,356,978 | 99.80 | 12.33 | 97.27 | 90.78 |
| SW (31) | 227,504,591 | 99.79 | 13.11 | 97.40 | 91.72 |
| MMS (29) | 234,489,784 | 99.43 | 13.35 | 97.28 | 90.65 |
| PD (30) | 217,872,738 | 98.65 | 12.30 | 97.18 | 90.24 |
| SHW (30) | 224,392,603 | 99.66 | 12.85 | 97.45 | 90.87 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, J.; Sun, L.; Pan, H.; Zhang, S.; Xu, J.; He, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, D.; Wu, C.; et al. Genomic Dissection through Whole-Genome Resequencing of Five Local Pig Breeds from Shanghai, China. Animals 2023, 13, 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233727
Gao J, Sun L, Pan H, Zhang S, Xu J, He M, Zhang K, Zhou J, Zhang D, Wu C, et al. Genomic Dissection through Whole-Genome Resequencing of Five Local Pig Breeds from Shanghai, China. Animals. 2023; 13(23):3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233727
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Jun, Lingwei Sun, Hongmei Pan, Shushan Zhang, Jiehuan Xu, Mengqian He, Keqing Zhang, Jinyong Zhou, Defu Zhang, Caifeng Wu, and et al. 2023. "Genomic Dissection through Whole-Genome Resequencing of Five Local Pig Breeds from Shanghai, China" Animals 13, no. 23: 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233727
APA StyleGao, J., Sun, L., Pan, H., Zhang, S., Xu, J., He, M., Zhang, K., Zhou, J., Zhang, D., Wu, C., & Dai, J. (2023). Genomic Dissection through Whole-Genome Resequencing of Five Local Pig Breeds from Shanghai, China. Animals, 13(23), 3727. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233727





