Phylogeography and Ecological Niche Modeling of the Alashan Pit Viper (Gloydius cognatus; Reptilia, Viperidae) in Northwest China and Adjacent Areas
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.3. Phylogenetic Analyses
2.4. Population Genetic Analyses
2.5. Testing Correlations between Genetic, Environmental, and Geographic Distances
2.6. Divergence Dating
2.7. Inference of Demographic Histories
2.8. Ecological Niche Modeling
3. Results
3.1. Phylogenetic Relationships
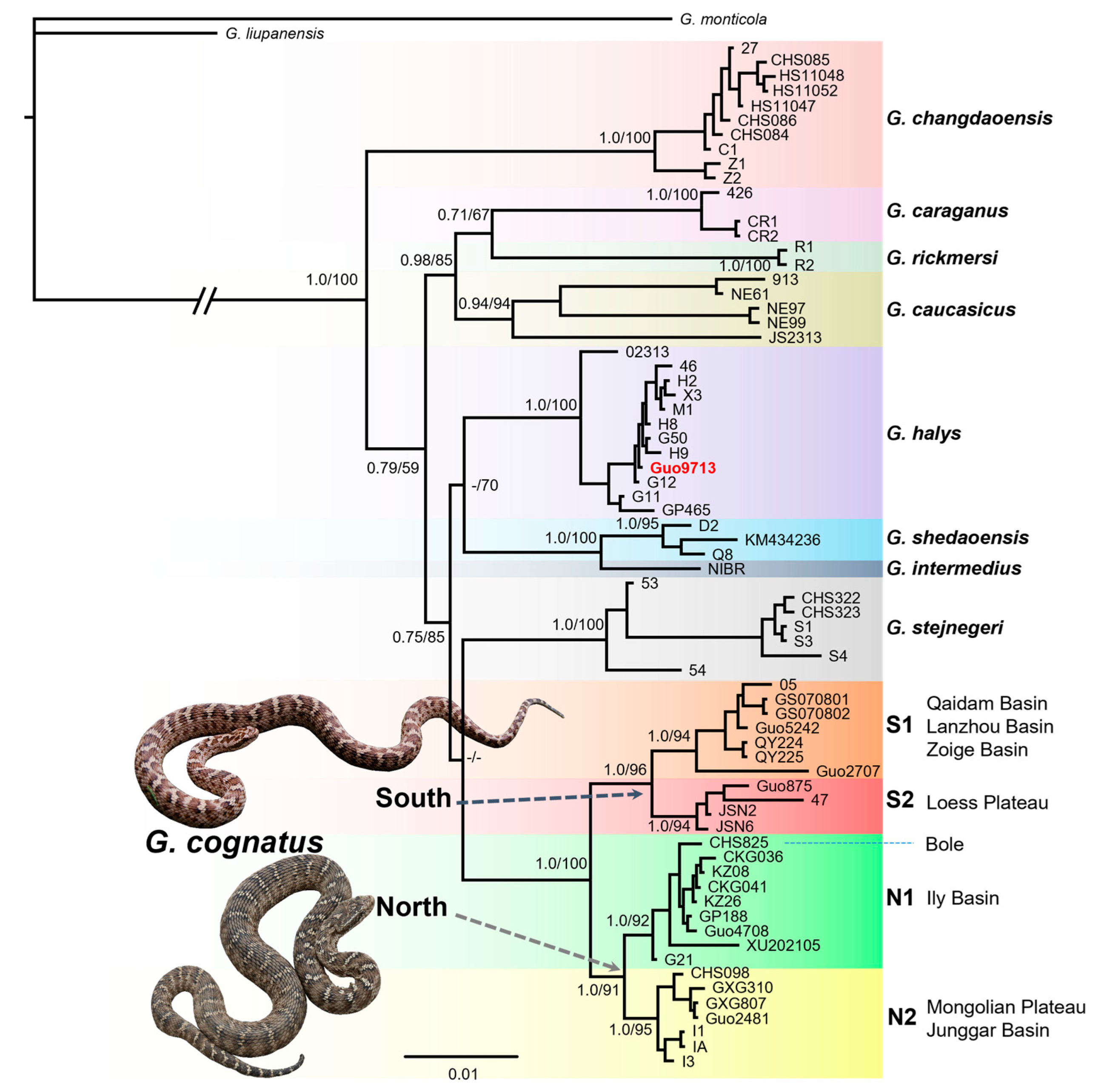
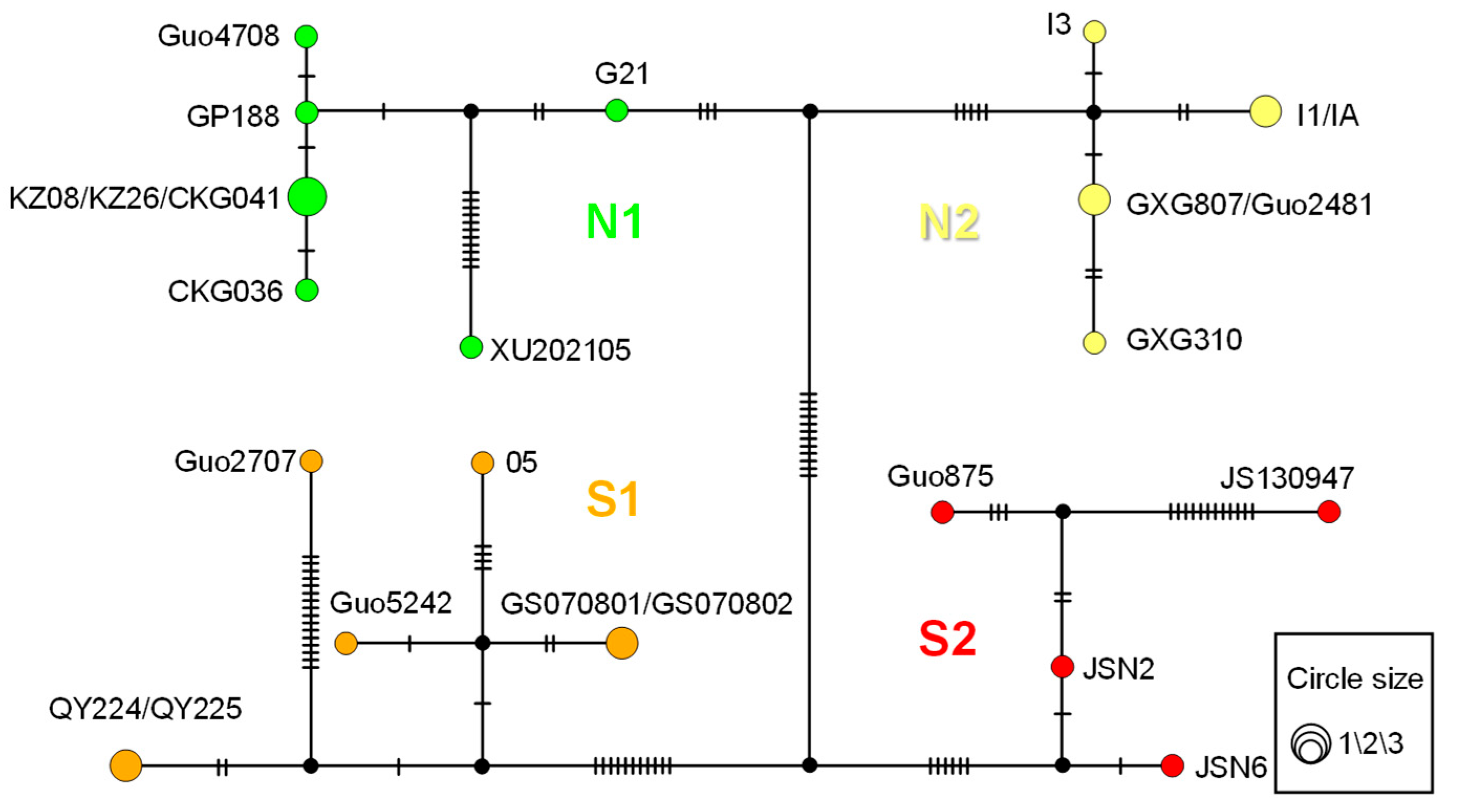
3.2. Genetic Diversity and Genetic Structure
3.3. Geography and Environment Impact on Genetic Structure
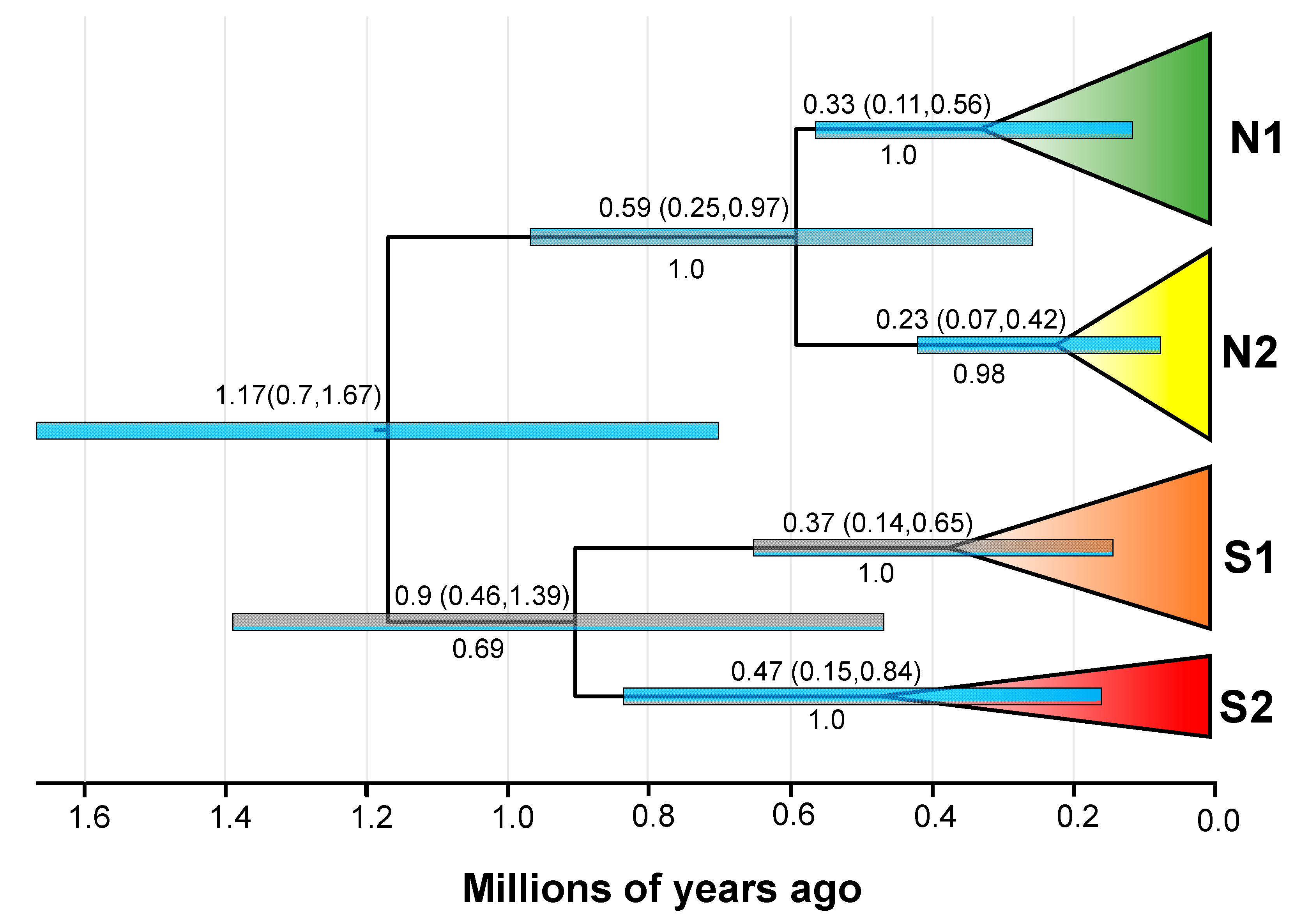
3.4. Divergence Time and Historical Demographic Change
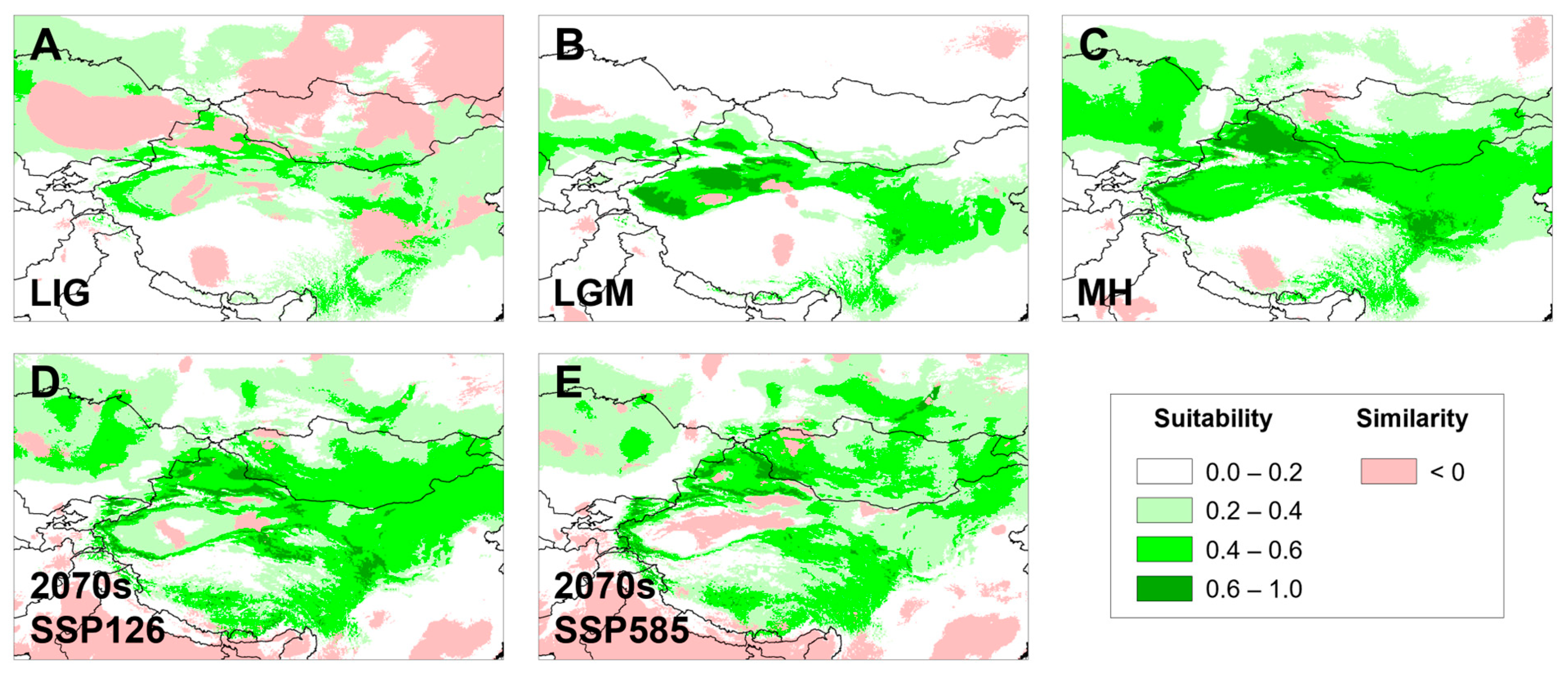
3.5. Temporal Changes in Suitable Distributional Areas
4. Discussion
4.1. Allopatric Divergence in the Ice Age
4.2. Genetic Structure and Diversity
4.3. Historical Population Demography
4.4. Conservation Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hewitt, G.M. Genetic consequences of climatic oscillations in the Quaternary. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursenbacher, S.; Schweiger, S.; Tomovic, L.; Crnobrnja-Isailovic, J.; Fumagalli, L.; Mayer, W. Molecular phylogeography of the nose-horned viper (Vipera ammodytes, Linnaeus (1758)): Evidence for high genetic diversity and multiple refugia in the Balkan peninsula. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 46, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickerson, M.J.; Carstens, B.C.; Cavender-Bares, J.; Crandall, K.A.; Graham, C.H.; Johnson, J.B.; Rissler, L.; Victoriano, P.F.; Yoder, A.D. Phylogeography’s past, present, and future: 10 years after Avise, 2000. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2010, 54, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazzi, N.A.; Moreno, J.S.; Ortiz-Movliav, C.; Palacio, R.D. Biogeographic regions and events of isolation and diversification of the endemic biota of the tropical Andes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7985–7990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janzen, F.J.; Krenz, J.G.; Haselkorn, T.S.; Brodie, E.D.; Brodie, E.D. Molecular phylogeography of common garter snakes (Thamnophis sirtalis) in western North America: Implications for regional historical forces. Mol. Ecol. 2002, 11, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbrink, F.T.; Castoe, T.A. Molecular phylogeography of snakes. In Snakes: Ecology and Conservation; Mullin, S.J., Seigel, R.A., Eds.; Cornell University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 38–77. [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Iraola, I.; Freitas, I.; Jiménez-Ruíz, Y.; Geniez, P.; García-París, M.; Martínez-Freiría, F. Phylogeographic and paleoclimatic modelling tools improve our understanding of the biogeographic history of Hierophis viridiflavus (Colubridae). Animals 2023, 13, 2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; He, S.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, E. Molecular phylogeography of endangered sharp-snouted pitviper (Deinagkistrodon acutus; Reptilia, Viperidae) in Mainland China. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2007, 44, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Gan, X.N.; He, S.P.; Zhao, E.M. A phylogeographic, demographic and historical analysis of the short-tailed pitviper (Gloydius brevicaudus): Evidence for early divergence and late expansion during the Pleistocene. Mol. Ecol. 2011, 20, 1905–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reading, C.J.; Luiselli, L.M.; Akani, G.C.; Bonnet, X.; Amori, G.; Ballouard, J.M.; Filippi, E.; Naulleau, G.; Pearson, D.; Rugiero, L. Are snake populations in widespread decline? Biol. Lett. 2010, 6, 777–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.H.; Gao, X.Y.; Huang, J.F.; Zhang, M.L. Plant phylogeography in arid Northwest China: Retrospectives and perspectives. J. Syst. Evol. 2015, 53, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Yu, Q.S.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, X.K.; Hu, J.; Fan, B.L. Regional-scale differentiation and phylogeography of a desert plant Allium mongolicum (Liliaceae) inferred from chloroplast DNA sequence variation. Plant Syst. Evol. 2017, 303, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.F.; Zhang, H.X.; Pan, B.R.; Zhang, M.L. Intraspecific divergences and phylogeography of Panzerina lanata (Lamiaceae) in northwest China. PeerJ 2019, 7, e6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ma, S.; Zhang, D.; Wei, B.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, B. Diversification and historical demography of Haloxylon ammodendron in relation to Pleistocene climatic oscillations in northwestern China. PeerJ 2022, 10, e14476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, M.L. Phylogeography of the arid shrub Atraphaxis frutescens (Polygonaceae) in northwestern China: Evidence from cpDNA sequences. J. Hered. 2015, 106, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhang, X.Z.; Tang, N.; Liu, J.J.; Xu, L.R.; Wang, K. Phylogeography of Libanotis buchtormensis (Umbelliferae) in disjunct populations along the deserts in Northwest China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.C. The Chinese Quaternary Vegetation and Environment; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1998. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.H.; Zhang, M.L. Phylogeography of Lagochilus ilicifolius (Lamiaceae) in relation to Quaternary climatic oscillation and aridification in northern China. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2011, 39, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.J.; Zhang, M.L. Phylogeographical structure inferred from cpDNA sequence variation of Zygophyllum xanthoxylon across north-west China. J. Plant Res. 2015, 128, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, F.; Ma, S.; Wang, C.; Wei, B.; Zhang, Y. Phylogeography of Amygdalus mongolica in relation to Quaternary climatic aridification and oscillations in northwestern China. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, D.; Chen, F.; Bloemendal, J.; Guo, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Formation and evolution of the Badain Jaran Desert, North China, as revealed by a drill core from the desert centre and by geological survey. Palaeogeogr. Palaeocl. Palaeoecol. 2015, 426, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.F.; Zhang, J.G.; Abuduhamiti, B.; Wang, W.T.; Jia, Z.Q. Phylogeographic patterns of the desert poplar in Northwest China shaped by both geology and climatic oscillations. BMC Evol. Biol. 2018, 18, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.H.; Yang, Z.P.; Zhang, Z.C.; Comes, H.P.; Qi, Z.C.; Li, P.; Fu, C.X. Plio-Pleistocene climatic change drives allopatric speciation and population divergence within the Scrophularia incisa complex (Scrophulariaceae) of desert and steppe subshrubs in Northwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 985372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, D.R.; Liu, T.L.; Wang, L.Y.; Zhou, D.W.; Liu, J.Q. Evolutionary history of an alpine shrub Hippophae tibetana (Elaeagnaceae): Allopatric divergence and regional expansion. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2011, 102, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Z.H.; Chen, J.; Zhao, G.F.; Guo, Y.P.; Kou, Y.X.; Ma, Y.Z. Response of a desert shrub to past geological and climatic change: A phylogeographic study of Reaumuria soongarica (Tamaricaceae) in western China. J. Syst. Evol. 2012, 50, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.H.; Yan, M.C. The uplift of the Qinghai-Xizang (Tibetan) plateau and its effect on the formation and evolution of China desert. Arid Zone Res. 1996, 13, 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Sun, Y.; Qiang, X. Mid-Pleistocene formation of modern-like desert landscape in North China. Catena 2022, 216, 106399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.P.; Zhang, R.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhou, D.W.; Liu, J.Q. Allopatric divergence and regional range expansion of Juniperus sabina in China. J. Sys. Evol. 2010, 48, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.H.; Zhang, M.L. Diversification of plant species in arid Northwest China: Species-level phylogeographical history of Lagochilus Bunge ex Bentham (Lamiaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2013, 68, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Zeng, L.Q.; Gong, X. High genetic diversity and population differentiation in the critically endangered plant species Trailliaedoxa gracilis (Rubiaceae). Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2016, 34, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, Z.; Zhai, J.; Chen, X.; Jiao, P.; Zhang, S.; Sun, J.; Qin, R.; Liu, H.; Wu, Z.; Li, Z. Phylogeography reveals geographic and environmental factors driving genetic differentiation of Populus sect. Turanga in Northwest China. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 705083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Wen, L. Impacts of Quaternary glaciation, geological history and geography on animal species history in continental East Asia: A phylogeographic review. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 4497–4514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Montgelard, C.; Nazarizadeh, M.; Moghaddasi, A.; Fatemizadeh, F.; Simonov, E.; Kami, H.G.; Kaboli, M. Evolutionary history and postglacial colonization of an Asian pit viper (Gloydius halys caucasicus) into Transcaucasia revealed by phylogenetic and phylogeographic analyses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetz, P.; Freed, P.; Aguilar, R.; Reyes, F.; Hošek, J. The Reptile Database. Available online: https://www.reptile-database.org (accessed on 16 October 2023).
- Sindaco, R.; Venchi, A.; Grieco, C. The Reptiles of the Western Palearctic Volume 2: Annotated Checklist and Distributional Atlas of the Snakes of Europe, North Africa, the Middle East and Central Asia, with an Update to the Volume 1; Societas Herpetologica Italica: Latina, Italy, 2013; pp. 188–189, 298. [Google Scholar]
- Orlov, N.L.; Sundukov, Y.; Kropachev, I. Distribution of pitvipers of “Gloydius blomhoffii” complex in Russia with the first records of Gloydius blomhoffii blomhoffii at Kunashir Island (Kuril Archipelago, Russian Far East). Russ. J. Herpetol. 2014, 21, 169–178. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, P.; Tiutenko, A.; Mazepa, G.; Borkin, L.J.; Simonov, E. Alai! Alai!—A new species of the Gloydius halys (Pallas, 1776) complex (Viperidae, Crotalinae), including a brief review of the complex. Amphib. Reptil. 2016, 37, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloyd, H.K.; Conant, R. Snakes of the Agkistrodon Complex: A Monographic Review; Society for the Study of Amphibians and Reptiles (SSAR): Oxford, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Orlov, N.L.; Barabanov, A.V. Analysis of nomenclature, classification, and distribution of the Agkistrodon halys-Agkistrodon intermedius complexes: A critical review. Russ. J. Herpetol. 1999, 6, 167–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonov, E. Differences in habitat use, daily activity patterns and preferred ambient temperatures of adult and neonate Gloydius halys halys from an isolated population in southwest Siberia: Preliminary data. Herpetol. Notes 2009, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Simonov, E.; Wink, M. Population genetics of the Halys pit viper (Gloydius halys) at the northern distribution limit in Siberia. Amphib. Reptil. 2012, 33, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.S.; Yang, D.W.; Zhang, W.Y.; Qi, S.; Li, P.P.; Ding, L. Distribution and intraspecies taxonomy of Gloydius halys-Gloydius intermedius complex in China (Serpentes: Crotalinae). Chin. J. Zool. 2016, 51, 777–798, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, G.; Fang, Y.; Ding, L.; Huang, S.; Hou, M.; Liu, J.; Li, P. A new moth-preying alpine pit viper species from Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau (Viperidae, Crotalinae). Amphib. Reptil. 2017, 38, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakoori, S.; Todehdehghan, F.; Shiravi, A.; Hojati, V. The assessment of captive breeding in the Caucasian viper (Gloydius halys caucasicus) in Iran. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2015, 3, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Fatemizadeh, F.; Mohammadi, A.; Kaboli, M. Captive breeding and ex-situ conservation of the Caucasian pit viper Gloydius caucasicus. Herpetol. Bull. 2023, 165, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, P.; Vogel, G. An updated list of Asian pitvipers and a selection of recent publications. In Asian Pitvipers. Breeding Experience and Wildlife; Visser, D., Ed.; Edition Chimaira: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2015; pp. 545–565. [Google Scholar]
- Hoge, A.R.; Romano-Hoge, S.A. Poisonous snakes of the world. Part I. Check list of the pit vipers; Viperoidea, Viperidae, Crotalinae. Mem. Inst. Butantan. 1981, 42/43, 179–310. [Google Scholar]
- Gumprecht, A.; Tillack, F.; Orlov, N.L.; Captain, A.; Ryabow, S. Asian Pitvipers; Geitje Books: Berlin, Germany, 2004; 368p. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.M.; Adler, K.K. Herpetology of China. Contributions to Herpetology; No. 10; Society for Study of Amphibians and Reptiles: Oxoford, OH, USA, 1993; p. 273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, E.M. Snakes of China; Anhui Sciences and Technology Publishing House: Hefei, China, 2006; pp. 123–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, A.T.; Sobeŕon, J.; Pearson, R.G.; Anderson, R.P.; Martínez-Meyer, E.; Nakamura, M.; Araújo, M.B. Ecological Niches and Geographic Distributions; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kozak, K.H.; Graham, C.H.; Wiens, J.J. Integrating GIS-based environmental data into evolutionary biology. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 23, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guisan, A.; Thuiller, W. Predicting species distribution: Offering more than simple habitat models. Ecol. Lett. 2005, 8, 993–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Serrano, D.F.; Knowles, L.L. Ecological niche models in phylogeographic studies: Applications, advances and precautions. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 233–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Myers, E.A.; Wang, L.; Huang, S.; He, Y.; Peng, P.; Guo, P. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Gloydius (Serpentes: Crotalinae). Asian Herpetol. Res. 2012, 3, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.N.; Liang, D.; Wang, Y.Y.; Guo, P.; Huang, S.; Zhang, P. A large-scale systematic framework of Chinese snakes based on a unified multilocus marker system. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 148, 106807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arèvalo, E.; Davis, S.K.; Sites, J.W. Mitochondrial DNA sequence divergence and phylogenetic relationships among eight chromosome races of the Sceloporus grammicus complex (Phrynosomatidae) in central Mexico. Syst. Biol. 1994, 43, 387–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbrink, F.T.; Lawson, R.; Slowinski, J.B. Mitochondrial DNA phylogeography of the polytypic North American rat snake (Elaphe obsoleta): A critique of the subspecies concept. Evolution 2000, 54, 2107–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouy, M.; Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. SeaView version 4: A multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanfear, R.; Frandsen, P.B.; Wright, A.M.; Senfeld, T.; Calcott, B. PartitionFinder 2: New methods for selecting partitioned models of evolution for molecular and morphological phylogenetic analyses. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 772–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; van der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Hohna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambaut, A.; Drummond, A.J.; Xie, D.; Baele, G.; Suchard, M.A. Posterior summarization in Bayesian phylogenetics using Tracer 1.7. Syst. Biol. 2018, 67, 901–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.T.; Schmidt, H.A.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minh, B.Q.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Von Haeseler, A. Ultrafast approximation for phylogenetic bootstrap. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FigTree. Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 23 September 2023).
- Leigh, J.; Bryant, D. PopART: Full-feature software for haplotype network construction. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2015, 6, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada, D.; Crandall, K.A. Intraspecific gene genealogies: Trees grafting into networks. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2001, 16, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Excoffier, L.; Laval, G.; Schneider, S. Arlequin ver. 3.0: An integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2005, 1, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Isolation by distance. Genetics 1943, 28, 114–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.J.; Bradburd, G.S. Isolation by environment. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 5649–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersts, P. Geographic Distance Matrix Generator (Version 1.23). Available online: http://biodiversityinformatics.amnh.org/open_source/gdmg (accessed on 24 February 2023).
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P. Vegan, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, E.; Van de Peer, Y. zt: A software tool for simple and partial mantel tests. J. Stat. Softw. 2002, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A. BEAST: Bayesian evolutionary analysis by sampling trees. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Guo, X.G.; Chen, D.L.; Li, J.; Yue, B.S.; Zeng, X.M. Diversification and historical demography of the rapid racerunner (Eremias velox) in relation to geological history and Pleistocene climatic oscillations in arid Central Asia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2019, 130, 244–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajima, F. Statistical method for testing the neutral mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 1989, 123, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.X. Statistical tests of neutrality of mutations against population growth, hitchhiking and background selection. Genetics 1997, 147, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Onsins, S.E.; Rozas, J. Statistical properties of new neutrality tests against population growth. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002, 19, 2092–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, A.J.; Rambaut, A.; Shapiro, B.; Pybus, O.G. Bayesian coalescent inference of past population dynamics from molecular sequences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlic, I.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2020, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Modell. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Bae, M.; Jin, D. On a robust MaxEnt process regression model with sample-selection. Entropy 2018, 20, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boria, R.A.; Olson, L.E.; Goodman, S.M.; Anderson, R.P. Spatial filtering to reduce sampling bias can improve the performance of ecological niche models. Ecol. Model. 2014, 275, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.L.; Bennett, J.R.; French, C.M. SDMtoolbox 2.0: The next generation Python-based GIS toolkit for landscape genetic, biogeographic and species distribution model analyses. PeerJ 2017, 5, e4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.P.; Raza, A. The effect of the extent of the study region on GIS models of species geographic distributions and estimates of niche evolution: Preliminary tests with montane rodents (genus Nephelomys) in Venezuela. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 37, 1378–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barve, N.; Barve, V.; Jiménez-Valverde, A.; Lira-Noriega, A.; Maher, S.P.; Peterson, A.T.; Soberón, J.; Villalobos, F. The crucial role of the accessible area in ecological niche modeling and species distribution modeling. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1810–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscarella, R.; Galante, P.J.; Soley-Guardia, M.; Boria, R.A.; Kass, J.M.; Uriarte, M.; Anderson, R.P. ENMeval: An R package for conducting spatially independent evaluations and estimating optimal model complexity for Maxent ecological niche models. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 1198–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Kearney, M.; Phillips, S. The art of modelling range-shifting species. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 330–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Z.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, S.Q.; Zhao, J.D.; Cui, J.X. Quaternary glaciations in China. In Quaternary Glaciations—Extent and Chronology Part III; Ehlers, J., Gibbard, P.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; pp. 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.X.; Xu, Q.Q.; Shen, Y.P. The relationship between climate change and Quaternary glacial cycles on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau: Review and speculation. Quat. Int. 2002, 97–98, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Z.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, J.; Xu, L. 2006. A preliminary study on timing of the oldest Pleistocene glaciation in Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Quat. Int. 2006, 154–155, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Sun, D.; Chen, F.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, X.; Li, B. Chronology and paleoenvironmental records of a drill core in the central Tengger Desert of China. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2014, 85, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sun, D.; Xu, W.; Wang, F.; Liang, B.; Ma, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, F. Paleomagnetic chronology and paleoenvironmental records from drill cores from the Hetao Basin and their implications for the formation of the Hobq Desert and the Yellow River. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2017, 156, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Fu, A.; Ma, X.; Gui, D.; Chen, Y. Distribution pattern of plant species diversity in the mountainous region of Ili River Valley, Xinjiang. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 177, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyarkov, N.A.; Orlova, V.F.; Chirikova, M.A. The mitochondrial phylogeography and intraspecific taxonomy of the Steppe Racerunner, Eremias arguta (Pallas) (Lacertidae: Sauria, Reptilia), reflects biogeographic patterns in Middle Asia. Zootaxa 2014, 3895, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dujsebayeva, T.N.; Malakhov, D.V.; Berezovikov, N.N.; Guo, X.G.; Liu, J.L.; Cherednichenko, A.V. Comparative analysis of the distribution and habitats of two Eremias species (Reptilia, Lacertidae) using niche-based GIS modeling. Russ. J. Herpetol. 2019, 26, 281–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, T.; Song, Q.; Guo, X. Taxonomical status of Eremias arguta from Bole City and Ili River Valley, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region, China. Sichuan J. Zool. 2018, 37, 387–399, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Evolution and the Genetics of Populations; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, J.; Stevens, T.; Rittner, M.; Stockli, D.; Garzanti, E.; Limonta, M.; Bird, A.; Andò, S.; Vermeesch, P.; Saylor, J.; et al. Loess Plateau storage of Northeastern Tibetan Plateau-derived Yellow River sediment. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Liu, S.; Peng, T.; Ma, Z.; Feng, Z.; Li, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Song, C.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Late Pliocene establishment of exorheic drainage in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau as evidenced by the Wuquan formation in the Lanzhou Basin. Geomorphology 2018, 303, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z. The formation of river terraces and evolution of drainage system in the middle Yellow River. Acta Geograph. Sinica 1989, 44, 429–440, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avise, J.C. Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.-F.; Cui, Z.-J.; Su, Z. The Quaternary Glaciations and Environmental Variations in China; Hebei Science and Technology Press: Shijiazhuang, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, N.; Wang, S.; Dujsebayeva, T.N.; Chen, D.L.; Ali, A.; Guo, X.G. Geography and past climate changes have shaped the evolution of a widespread lizard in arid Central Asia. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2023, 184, 107781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moritz, C.C. Defining “evolutionary significant units” for conservation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1994, 9, 373–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.J.; Bernatchez, L. Adaptive evolutionary conservation: Towards a unified concept for defining conservation units. Mol. Ecol. 2001, 12, 2741–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palsbøll, P.J.; Bérubé, M.; Allendorf, F.W. Identification of management units using population genetic data. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.K.; Xu, K. Studies on Neurotoxins in the venom of Agkistrodon species in China. In From Water onto Land—A Volume Issued to Commemorate the 90th Birthday of the Late Professor Liu Cheng-Zhao; Zhao, E.M., Ed.; China Forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 304–311, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.S.; Do, M.S.; Jeon, H.S.; Lee, S.C.; An, J. Complete mitochondrial genome of Gloydius saxatilis (viperidae: Crotalinae) from Korea. Mitochondrial DNA B 2021, 6, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhu, F.; Wang, X.; Xiao, R.; Fang, M.; Sun, L.; Li, P.; Guo, P. The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Gloydius shedaoensis (Squamata: Viperidae). Mitochondrial DNA A 2016, 27, 4679–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.S.; Liu, J.C.; Giri, R.; Owens, J.B.; Santra, V.; Kuttalam, S.; Selvan, M.; Guo, K.J.; Malhotra, A. Molecular phylogenetic analysis of the genus Gloydius (Squamata, Viperidae, Crotalinae), with description of two new alpine species from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. ZooKeys 2021, 1061, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Thorpe, R.S. A phylogeny of four mitochondrial gene regions suggests a revised taxonomy for Asian pitvipers (Trimeresurus and Ovophis). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2004, 32, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenwick, A.M.; Greene, H.W.; Parkinson, C.L. The serpent and the egg: Unidirectional evolution of reproductive mode in vipers? J. Zoolog. Syst. Evol. Res. 2012, 50, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, C.L.; Campbell, J.A.; Chippindale, P.T.; Schuett, G. Multigene phylogenetic analysis of pitvipers, with comments on their biogeography. In Biology of the Vipers; Schuett, G.W., Höggren, M., Douglas, M.E., Greene, H.W., Eds.; Eagle Mountain Publishing: Eagle Mountain, UT, USA, 2002; pp. 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Kraus, F.; Mink, D.G.; Brown, W.M. Crotaline intergeneric relationships based on mitochondrial DNA sequence data. Copeia 1996, 1996, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüster, W.; Ferguson, J.E.; Quijada-Mascareñas, J.A.; Pook, C.E.; Salomão, M.D.G.; Thorpe, R.S. Tracing an invasion: Landbridges, refugia, and the phylogeography of the Neotropical rattlesnake (Serpentes: Viperidae: Crotalus durissus). Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüster, W.; Peppin, L.; Pook, C.E.; Walker, D.E. A nesting of vipers: Phylogeny and historical biogeography of the Viperidae (Squamata: Serpentes). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2008, 49, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, C.L.; Zamudio, K.R.; Greene, H.W. Phylogeography of the pitviper clade Agkistrodon: Historical ecology, species status, and conservation of cantils. Mol. Ecol. 2000, 9, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüster, W.; Salomão, M.D.G.; Quijada-Mascareñas, J.A.; Thorpe, R.S.; Duckett, G.J.; Puorto, M.G.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Thorpe, R.S.; Warrell, D.A. Origins and evolution of the South American pitviper fauna: Evidence from mitochondrial DNA sequence analysis. In Biology of the Vipers; Schuett, G.W., Höggren, M., Douglas, M.E., Greene, H.W., Eds.; Eagle Mountain Publishing: Eagle Mountain, UT, USA, 2002; pp. 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ursenbacher, S.; Carlsson, M.; Helfer, V.; Tegelström, H.; Fumagalli, L. Phylogeography and Pleistocene refugia of the adder (Vipera berus) as inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequence data. Mol. Ecol. 2006, 15, 3425–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinenko, O.; Stümpel, N.; Mazanaeva, L.; Bakiev, A.; Shiryaev, K.; Pavlov, A.; Kotenko, T.; Kukushkin, O.; Chikin, Y.; Duisebayeva, T.; et al. Mitochondrial phylogeny shows multiple independent ecological transitions and northern dispersion despite of Pleistocene glaciations in meadow and steppe vipers (Vipera ursinii and Vipera renardi). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2015, 84, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenk, P.; Kalyabina, S.; Wink, M.; Joger, U. Evolutionary relationships among the true vipers (Reptilia: Viperidae) inferred from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2001, 19, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stümpel, N.; Rajabizadeh, M.; Avcı, A.; Wüster, W.; Joger, U. Phylogeny and diversification of mountain vipers (Montivipera, Nilson et al., 2001) triggered by multiple Plio-Pleistocene refugia and high-mountain topography in the Near and Middle East. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 101, 336–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
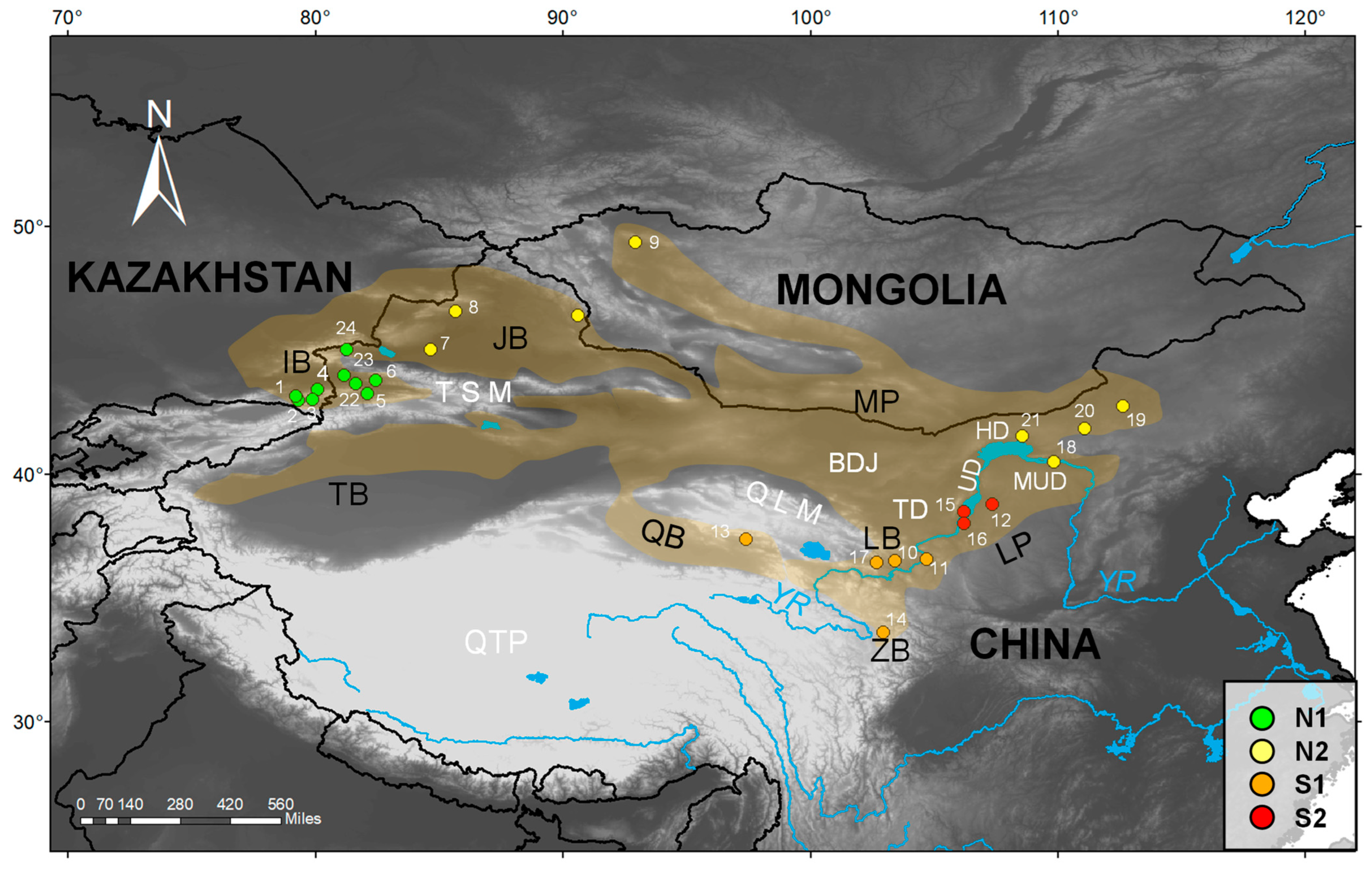



| Species | Site Number | Voucher Number | Geographic Origin | Locality | Latitude | Longitude | Altitude (m) | GenBank Accession Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ND4 | Cytb | ||||||||
| G. cognatus | 1 | KZ26 | IB | Raiymbek District, Almaty Region, Kazakhstan | 43.16 | 79.21 | 1774 | OR513115 | OR513141 |
| G. cognatus | 2 | KZ08 | IB | Raiymbek District, Almaty Region, Kazakhstan | 42.97 | 79.31 | 1847 | OR513116 | OR513140 |
| G. cognatus | 3 | CKG041 | IB | Raiymbek District, Almaty Region, Kazakhstan | 43.02 | 79.89 | 2065 | OR513126 | OR513130 |
| G. cognatus | 4 | CKG036 | IB | Uygur District, Almaty Region, Kazakhstan | 43.43 | 80.07 | 1361 | OR513127 | OR513129 |
| G. cognatus | 5 | XU202105 | IB | Gongliu County, Xinjiang, China | 43.26 | 82.09 | 1263 | OR513128 | OR513142 |
| G. cognatus | 6 | Guo4708 | IB | Nilka County, Xinjiang | 43.80 | 82.43 | 1084 | OR513121 | OR513134 |
| G. cognatus | 7 | Guo2481 | JB | Wusu City, Xinjiang, China | 45.05 | 84.66 | 965 | OR513123 | OR513132 |
| G. cognatus | 8 | GXG310 | JB | Hoboksar, Xinjiang, China | 46.58 | 85.65 | 1120 | OR513118 | OR513138 |
| G. cognatus | 9 | GXG807 | MP | Tsalgar, Uvs, Mongolia | 49.37 | 92.93 | 1140 | OR513117 | OR513139 |
| G. cognatus | 10 | Guo5242 | LB | Yongdeng County, Gansu, China | 36.49 | 103.4 | 1880 | OR513120 | OR513135 |
| G. cognatus | 11 | Guo2707 | LB | Jingyuan County, Gansu, China | 36.55 | 104.68 | 1538 | OR513122 | OR513133 |
| G. cognatus | 12 | Guo875 | LP | Otog Banner, Inner Mongolia, China | 38.79 | 107.34 | 1337 | OR513124 | OR513136 |
| G. cognatus | 13 | GS070802 | QB | Delingha City, Qinghai, China | 37.38 | 97.40 | 3000 | OR513125 | OR513131 |
| G. halys | – | Guo9713 | MP | Orgil, Khovsgol, Mongolia | 48.60 | 99.32 | 1610 | OR513119 | OR513137 |
| Lineage | n | H | S | Hd | π |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 8 | 6 | 17 | 0.8929 ± 0.111 | 0.00306 ± 0.00132 |
| N2 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 0.8667 ± 0.129 | 0.00172 ± 0.00034 |
| S1 | 7 | 5 | 30 | 0.9048 ± 0.103 | 0.00614 ± 0.00222 |
| S2 | 4 | 4 | 20 | 1.0000 ± 0.177 | 0.00638 ± 0.00213 |
| Total | 25 | 19 | 84 | 0.9767 ± 0.018 | 0.01427 ± 0.00103 |
| Lineage | N1 | N2 | S1 | S2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1 | 0.002 | 0.721 ** | 0.798 *** | 0.779 *** |
| N2 | 0.009 | 0.003 | 0.809 *** | 0.797 *** |
| S1 | 0.021 | 0.022 | 0.006 | 0.616 *** |
| S2 | 0.017 | 0.019 | 0.016 | 0.006 |
| Clade | Tajima’s D | Fu’s FS | R2 | SSD | Rg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (p-Value) | (p-Value) | (p-Value) | (p-Value) | (p-Value) | |
| South | −0.3224 (0.31) | 0.4234 (0.544) | 0.1609 *** | 0.0515 (0.11) | 0.1117 * |
| North | 0.0266 (0.547) | −0.6367 (0.366) | 0.1470 *** | 0.0448 (0.11) | 0.0477 (0.37) |
| All | −0.0128 (0.571) | −1.0839 (0.320) | 0.1218 *** | 0.0148 (0.35) | 0.0168 (0.26) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, R.; Dujsebayeva, T.N.; Chen, D.; Mijidsuren, B.; Xu, F.; Guo, X. Phylogeography and Ecological Niche Modeling of the Alashan Pit Viper (Gloydius cognatus; Reptilia, Viperidae) in Northwest China and Adjacent Areas. Animals 2023, 13, 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233726
Xu R, Dujsebayeva TN, Chen D, Mijidsuren B, Xu F, Guo X. Phylogeography and Ecological Niche Modeling of the Alashan Pit Viper (Gloydius cognatus; Reptilia, Viperidae) in Northwest China and Adjacent Areas. Animals. 2023; 13(23):3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233726
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Rui, Tatjana N. Dujsebayeva, Dali Chen, Byambasuren Mijidsuren, Feng Xu, and Xianguang Guo. 2023. "Phylogeography and Ecological Niche Modeling of the Alashan Pit Viper (Gloydius cognatus; Reptilia, Viperidae) in Northwest China and Adjacent Areas" Animals 13, no. 23: 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233726
APA StyleXu, R., Dujsebayeva, T. N., Chen, D., Mijidsuren, B., Xu, F., & Guo, X. (2023). Phylogeography and Ecological Niche Modeling of the Alashan Pit Viper (Gloydius cognatus; Reptilia, Viperidae) in Northwest China and Adjacent Areas. Animals, 13(23), 3726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13233726







