Comparison of the Rostral Epidural Rete Mirabile and the Patterns of Its Blood Supply in Selected Suiformes and Hippopotamuses
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Methods
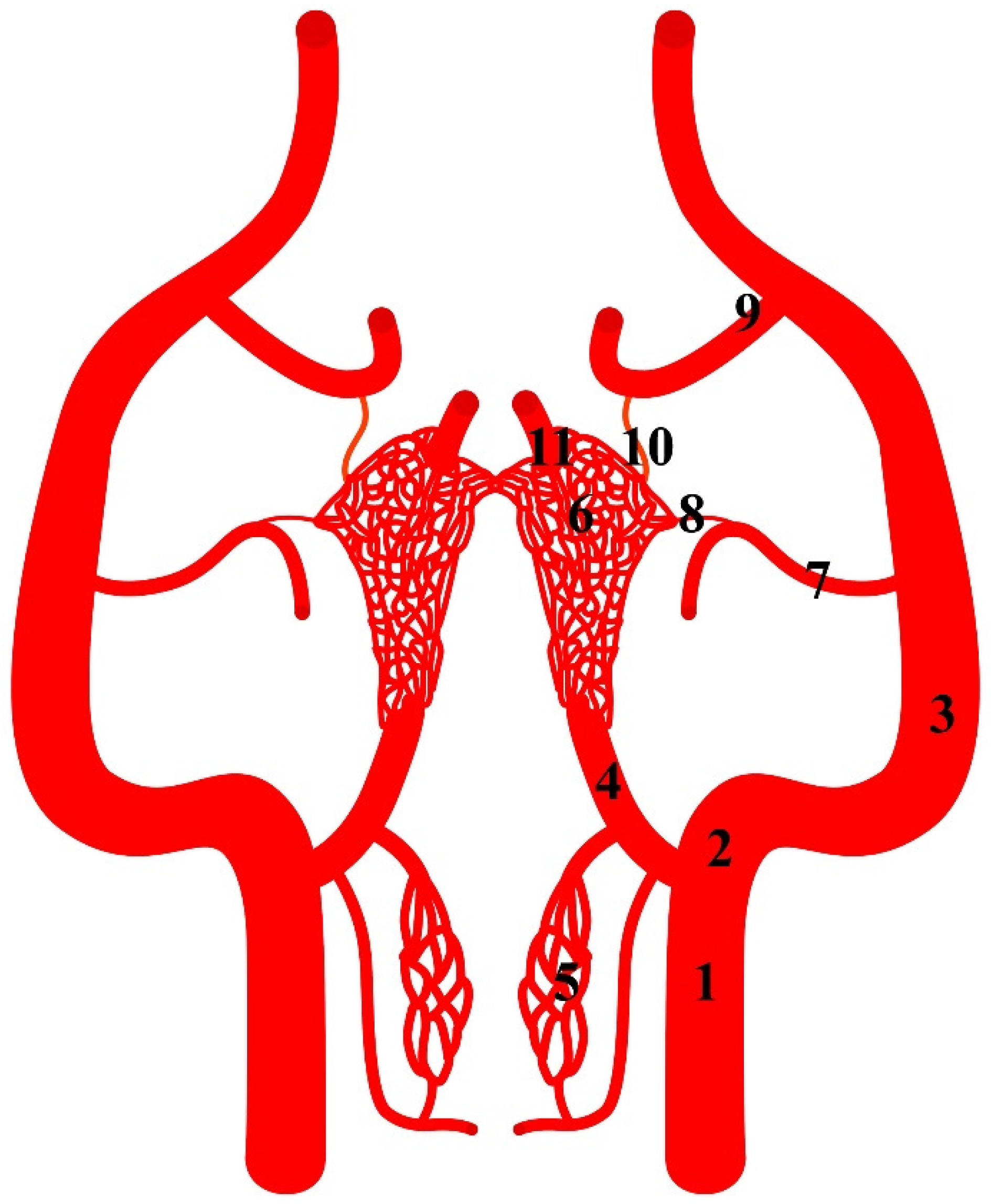
3. Results
3.1. Suidae Family
3.2. Tayassuidae Family
3.3. Hippopotamuses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simoens, P.; Lauwers, H.; De Geest, J.; De Schaepdrijver, L. Functional morphology of the cranial retia mirabilia in the domestic mammals. Schw. Arch. Fur Tierh. 1987, 129, 295–307. [Google Scholar]
- Graczyk, S.; Zdun, M. The structure of the rostral epidural rete mirabile in selected representatives of the Cervidae and Bovidae families. Acta Zool. 2021, 102, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graczyk, S.; Zdun, M. The structure of the rostral epidural rete mirabile and caudal epidural rete mirabile of the domestic pig. Folia Morph. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Jerbi, H.; Khalid, S.; Perez, W. Morphometric study of the rostral epidural rete mirabile in the dromedary (Camelus dromedarius Linnaeus 1758). Int. J. Morph. 2016, 34, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdun, M.; Melnyk, O.O.; Ruszkowski, J.J.; Hetman, M. Arterial circle of the brain in the common wildebeest (Connochaetes taurinus). Anat. Rec. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frąkowiak, H. Magistrale tętnicze głowy u niektórych rzędów ssaków. Rocz. AR Poz. 2003, 336, 5–80. [Google Scholar]
- Castrillo, G. The carotid rete mirabile: Its history and its function. An. Real. Acad. Farm. 2016, 82, 372–407. [Google Scholar]
- Zdun, M.; Grzeczka, A.; Zawadzki, M.; Frąckowiak, H. The rostral epidural rete mirabile of the llama as a place of retrograde transport of various substances–anatomical basics. Med. J. Cell Biol. 2021, 9, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocal, M.; Asian, K. A quantitative study on the retial arteries in the bovine fetus. Ann. Anat. 1994, 176, 151–153. [Google Scholar]
- Khamas, W.A.; Ghoshal, N.G.; Bal, H.S. Histomorphologic structure of the carotid rete cavernous sinus complex and its functional importance in sheep (Ovis aries). Am. J. Vet. Res. 1984, 45, 156–158. [Google Scholar]
- Khamas, W.A.; Ghoshal, N.G. Gross and scanning electron microscopy of the carotid rete-cavernous sinus complex of the sheep (Ovis aries). Anat. Anz. 1985, 159, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Polania-Guzmán, P.V.; Vélez-García, J.F. Gross anatomical adaptations of the craniolateral forearm muscles in Tamandua mexicana (Xenarthra: Myrmecophagidae): Development of accessory muscles and rete mirabile for its arterial supply. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholander, P.F. Evolution of climatic adaptation in homeotherms. Evol 1955, 9, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, W.; Hetem, R.; Mitchell, D.; Maloney, S.; O’Brien, H.; Meyer, L.; Fuller, A. Body water conservation through selective brain cooling by the carotid rete: A physiological feature for surviving climate change? Conserv. Physiol. 2017, 5, cow078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetem, R.S.; Strauss, W.M.; Fick, L.G.; Maloney, S.K.; Meyer, L.C.R.; Fuller, A.; Shobrak, M.; Mitchell, D. Selective brain cooling in Arabian oryx (Oryx leucoryx): A physiological mechanism for coping with aridity? J. Exp. Biol. 2012, 215, 3917–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzymowski, T.; Skipor, J.; Grzegorzewski, W. Cavernous sinus and carotid rete of sheep and sows as a possible place for countercurrent exchange of some neuropeptides and steroid hormones. Anim. Reprod. Sci. 1992, 29, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.; Bell, S. Classification of Mammals Above the Species Level; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, G. The principles of classification and classification of mammals. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 1945, 85, 1–350. [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding, M.; O’Leary, M.A.; Gatesy, J. Relationships of Cetacea (Artiodactyla) among mammals: Increased taxon sampling alters interpretations of key fossils and character evolution. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asher, R.J.; Helgen, K.M. Nomenclature and placental mammal phylogeny. BMC Evol. Biol. 2010, 10, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kid, S.; Doughty, C.; Goldhaber, S. Syncope (fainting). Circul 2016, 133, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seymour, R.; Angove, S.; Snelling, E.; Cassey, P. Scaling of cerebral blood perfusion in primates and marsupials. J. Exper. Biol. 2015, 218, 2631–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature. Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria, 6th ed.; Editorial Committee: Hanover, Germany, 2017; pp. 73–147. [Google Scholar]
- Al Aiyan, A.; Menon, P.; AlDarwich, A.; Almuhairi, F.; Alnuaimi, S.; Bulshawareb, A.; Qablan, M.; Shehab, S. Descriptive analysis of cerebral arterial vascular architecture in dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius). Front. Neuroanat. 2019, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiełtyka-Kurc, A.; Frąckowiak, H.; Nabzdyk, M.; Kowalczyk, K.; Zdun, M.; Tołkacz, M. The arteries on the base of the brain in the camelids. It. J. Zool. 2014, 81, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Ocal, M.; Erden, H.; Ogut, I.; Kara, M. A quantitative study on the retial arteries in one-humped camels. Ann. Anat. 1998, 180, 369–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nickiel, R.; Schwarz, R. Vergleichende Betrachtung der Kopfarterien der Haussaugetiere (Katze, Hund, Schwein, Rind, Schaf, Ziege, Pferd). Comparative analysis of the head arteries of domestic mammals (cat, dog, pig, cattle, sheep, goat, horse). Zent. Für Veterinärmed. Reihe A 1963, 10, 89–120. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąckowiak, H.; Jakubowski, H. Arterial vascularization in the giraffe brain. Ann. Zool. Fenn. 2008, 45, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Frąckowiak, H.; Dębiński, D.; Komosa, M.; Zdun, M. The arterial circle of the brain, its branches and connections in selected representatives of the Antiolopinae. J. Morp. 2015, 276, 766–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąckowiak, H.; Zdun, M.; Kowalczyk, K.; Komosa, M.; Kiełtyka-Kurc, A. Comparison of cerebral base arteries in antelopes of Tragulus, Taurotragus and Boselaphus genera. Zoomorph 2014, 133, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąckowiak, H.; Kulawik, M. Przebieg i zmienność tętnic na podstawie mózgowia u gatunków z podrodziny Caprinae. Rocz. AR. Poz. 2001, 344, 37–48. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Kiełtyka-Kurc, A.; Frąckowiak, H.; Brudnicki, W. The arteries of brain base in species of the Cervid family. Anat. Rec. 2015, 298, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godynicki, S.; Wiland, C. Tętnice podstawy mózgowia u sarny. Rocz. AR. Poz. 1971, 54, 47–54. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Godynicki, S.; Wiland, C. Tętnice podstawy mózgowia u jelenia. Rocz. AR. Poz. 1970, 49, 45–51. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Zdun, M.; Jabłoński, R.; Dębiński, D.; Frąckowiak, H. The Eurasian elk’s (Alces alces) brain base arteries in view of vascular variation. Anat. Rec. 2019, 302, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zdun, M.; Frackowiak, H.; Kiełtyka-Kurc, A.; Kowalczyk, K.; Nabzdyk, M.; Timm, A. The arteries of brain base in species of Bovini tribe. Anat. Rec. 2013, 296, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlton, C.; McKean, T. The carotid and orbital retia of the pronghorn, deer and elk. Anat Rec. 1977, 189, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Shao, B.; Wang, J. The arterial supply to the brain of the yak (Bos grunniens). Ann. Anat. 2007, 189, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuta, K.; Kudo, H.; Sasaki, M.; Kimura, J.; Ismail, D.; Endo, H. Absence of carotid rete mirabile in small tropical ruminants: Implications for the evolution of the arterial system in artiodactyls. J. Anat. 2007, 210, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, H. Cranial arterial pattern of the Sri Lankan spotted chevrotain, Moschiola memmina, and comparative basicranial osteology of the Tragulidae. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniel, P.M.; Dawes, J.D.K.; Prichard, M.M.L. Studies of the Carotid Rete and Its Associated Arteries. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 1953, 237, 173–208. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, P. Observations on the intra-cranial carotid rete and the hypophysis in the mature female pig and sheep. J. Anat. 1977, 124, 689–699. [Google Scholar]
- Graczyk, S.; Zdun, M.; Frąckowiak, H. The internal carotid artery of the domestic pig and Eurasian wild boar in ontogenesis. Aniam. Sci. Gn. 2022, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Kijatkin, E.A. Brain temperature and its role in physiology and pathophysiology: Lessons from 20 years of thermorecording. Temp. (Austin) 2019, 6, 271–333. [Google Scholar]
- Jessen, C. Selective brain cooling in mammals and birds. Jpn. J. Physiol. 2001, 51, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayward, J.; Baker, M. A comparative study of the role of the cerebral blood in the regulation of brain temperature in five mammals. Brain Res. 1969, 16, 417–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, C.R.; Lyman, C.P. Heat storage in running antelopes: Independence of brain and body temperatures. Am. J. Phys. 1972, 222, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caputa, M. Mechanizmy Obrony Mózgu Przed Przegrzaniem u Człowieka i Niektórych Innych Gatunków Ssaków; Roczniki UMK: Toruń, Poland, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Cain, J.; Krausman, P.; Rosenstock, S.; Turner, J. Mechanisms of thermoregulation and water balance in desert ungulates. Wildl. Soc. Bull. 2006, 34, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, A.M.; Hetem, R.S.; Mitchell, D.; Maloney, S.K.; Meyer, L.C.R.; Fuller, A. Selective Brain Cooling Reduces Water Turnover in Dehydrated Sheep. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegorzewski, W.; Skipor, J.; Wasowska, B.; Krzymowski, T. Counter Current Transfer of Oxytocin from the Venous Blood of the Perihypophyseal Cavernous Sinus to the Arterial Blood of Carotid Rete Supplying the Hypophysis and Brain Depends on the Phase of the Estrous Cycle in Pigs. Biol. Reprod. 1995, 52, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegorzewski, W.; Skipor, J.; Wasowska, B.; Krzymowski, T. Counter current transfer of 125I-LHRH in the perihypophyseal cavernous sinus-carotid rete vascular complex, demonstrated on isolated pig heads perfused with autologous blood. Domest Anim. Endocrinol. 1997, 14, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skipor, J.; Wasowska, B.; Grzegorzewski, W.; Zezula-Szpyra, A.; Stefanczyk-Krzymowska, S.; Thiery, J. Transfer of dopamine by counter-current mechanism in the ewes changes with endocrine stage. Biog. Amines. 2001, 16, 431–445. [Google Scholar]
- Skipor, J.; Grzegorzewski, W.; Wasowska, B.; Krzymowski, T. Luteinizing hormone and prolactin are not retrogradetransferred in perihypophyseal vascular complex in ewes. Reprod. Biol. 2004, 4, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Oren, D. Humoral Phototransduction: Blood Is a Messenger. Neuroscientist 1996, 2, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Species | Liquid into the Common Carotid Artery | Liquid into the External Jugular Vein | Liquid into the Common Carotid Artery and External Jugular Vein | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duracryl® Plus (Red) | LBS 3060 Latex (Red) | Duracryl® Plus (Blue) | LBS 3060 Latex (Blue) | Duracryl® Plus (Red + Blue) | LBS 3060 Latex (Red + Blue) | |
| desert warthogs (Phacochoerus aethiopicus) | 3 | 1 | - | - | 1 | - |
| Eurasian wild boars (Sus scrofa) | 6 | 1 | 1 | - | 1 | 1 |
| collared peccaries (Pecari tajacu) | 4 | - | - | - | 1 | 1 |
| pygmy hippopotamuses (Choeropsis liberiensis) | 2 | - | - | - | - | - |
| common hippopotamuses (Hippopotamus amphibius) | 2 | 1 | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdun, M. Comparison of the Rostral Epidural Rete Mirabile and the Patterns of Its Blood Supply in Selected Suiformes and Hippopotamuses. Animals 2023, 13, 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040644
Zdun M. Comparison of the Rostral Epidural Rete Mirabile and the Patterns of Its Blood Supply in Selected Suiformes and Hippopotamuses. Animals. 2023; 13(4):644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040644
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdun, Maciej. 2023. "Comparison of the Rostral Epidural Rete Mirabile and the Patterns of Its Blood Supply in Selected Suiformes and Hippopotamuses" Animals 13, no. 4: 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040644
APA StyleZdun, M. (2023). Comparison of the Rostral Epidural Rete Mirabile and the Patterns of Its Blood Supply in Selected Suiformes and Hippopotamuses. Animals, 13(4), 644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040644






