Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Porcine Streptococcus suis Based on a Recombinant GMD Protein
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Serum Samples and Materials
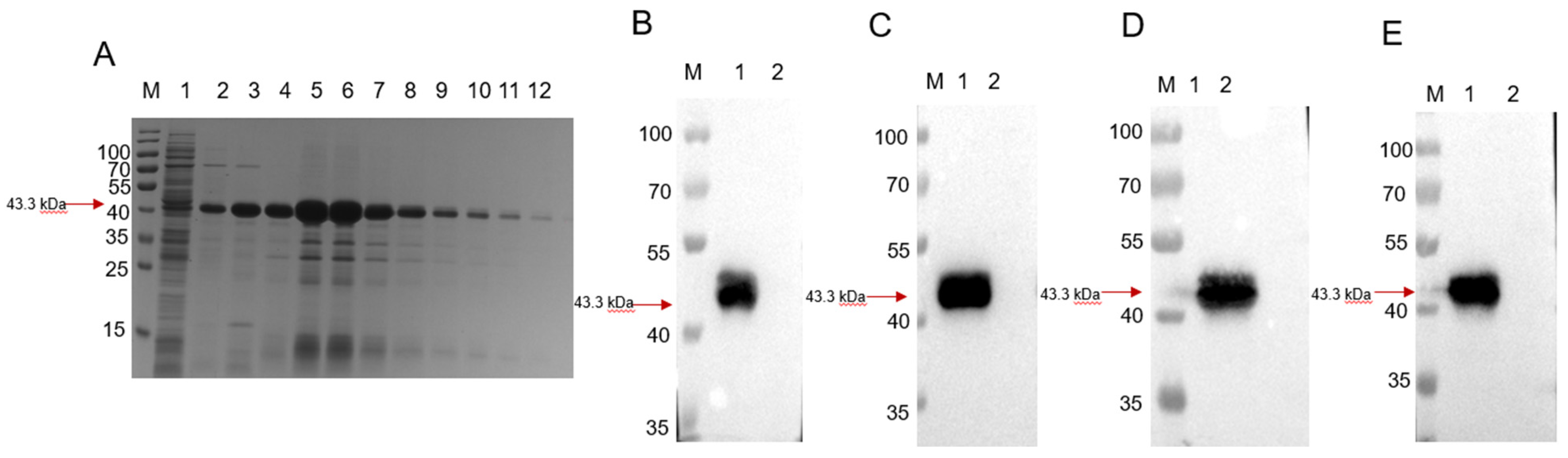
2.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant GMD Protein
2.3. Optimizing ELISA Indirect Conditions
2.4. Determining the Critical Value
2.5. Specificity Analysis
2.6. Sensitivity Analysis
2.7. Reproducibility Assay for Indirect ELISA
2.8. Conformance Rate Experiment
2.9. Elimination of GMD Antibodies after S. suis Type 2 Challenge in Clinically Healthy Pigs
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Expression and Purification of the Recombinant GMD Protein
3.2. ELISA Optimization Using Recombinant GMD Protein
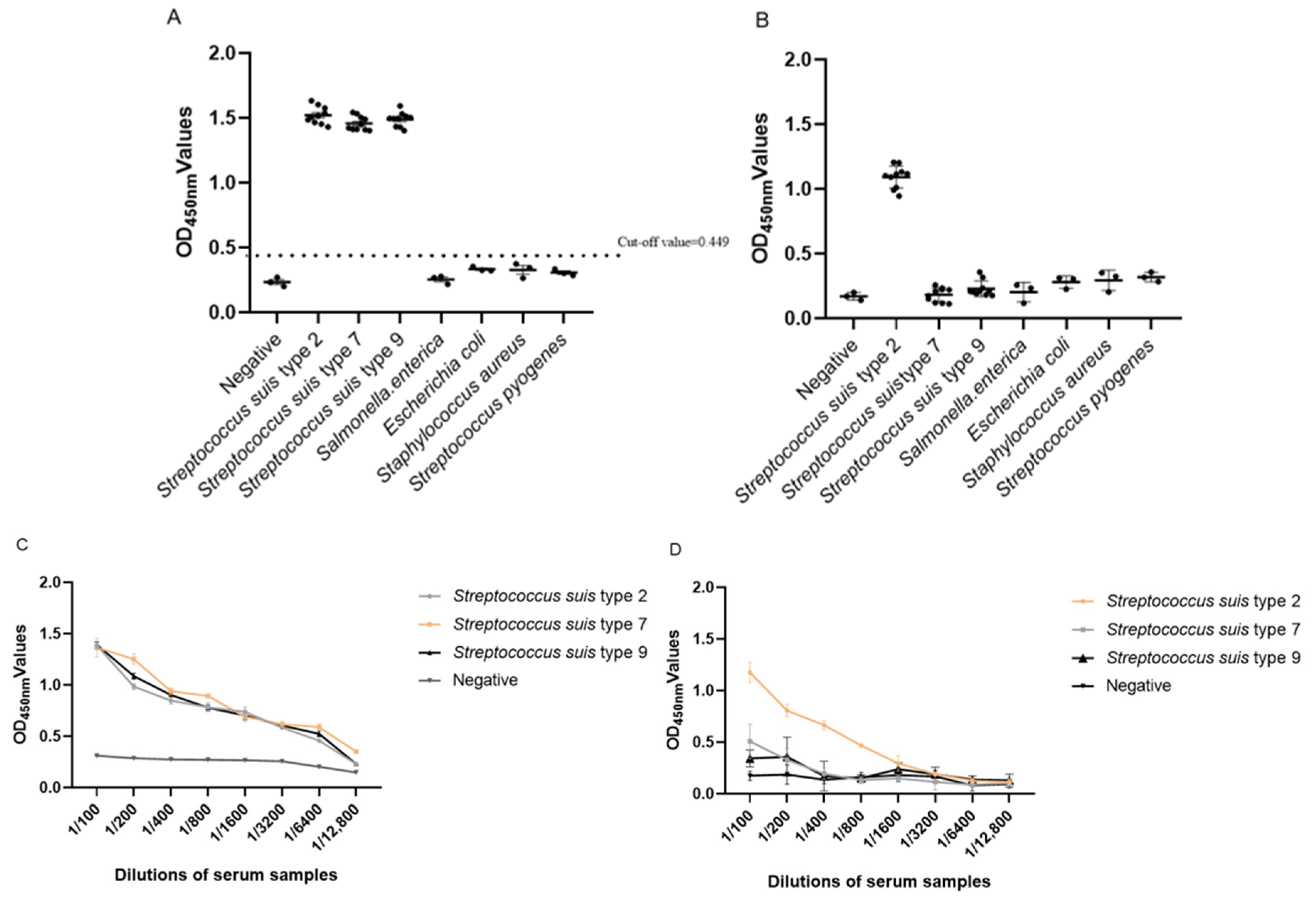
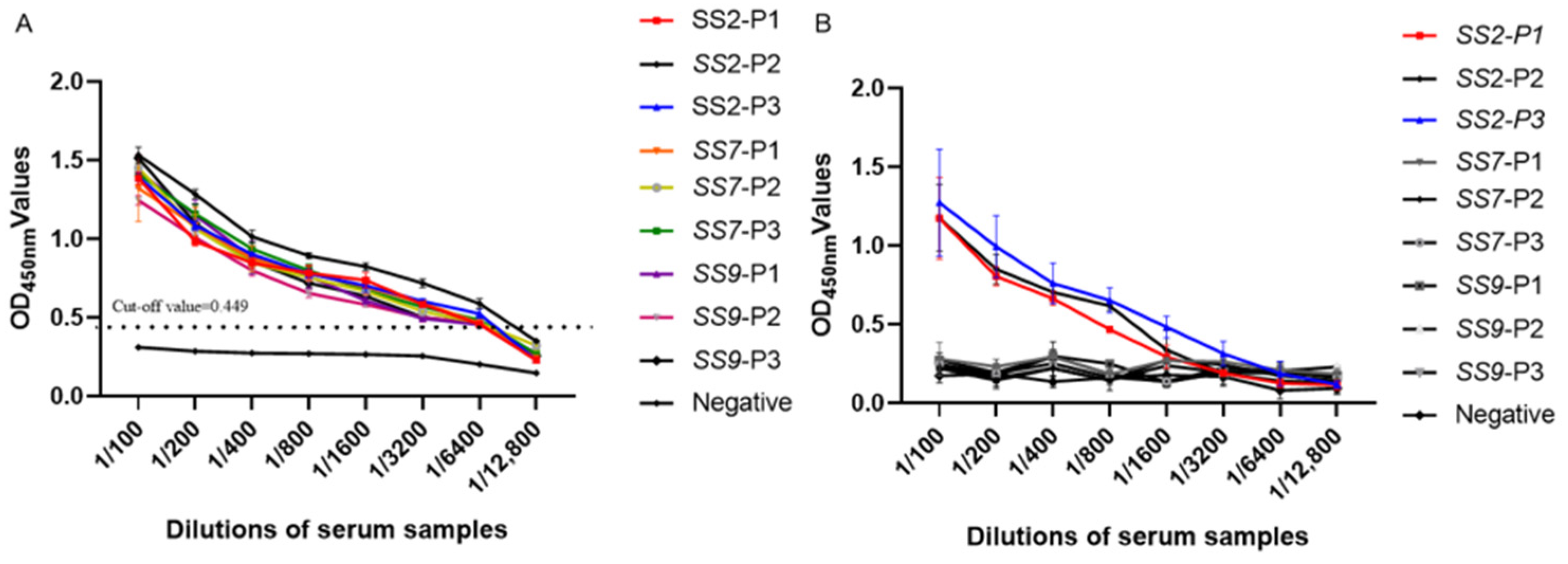
3.3. Specificity Analysis of Indirect ELISA
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis Test of Indirect ELISA
3.5. Reproducibility Assay for Indirect ELISA
3.6. Results of the Conformance Rate Experiments
3.7. Eliminating GMD Antibody in Clinical Healthy Pigs Infected with S. suis Type 2
3.8. Seroprevalence of S. suis in East China
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M.; Xu, J. Streptococcus suis infections in humans: The Chinese experience and the situation in North America. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2007, 8, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyette-Desjardins, G.; Auger, J.P.; Xu, J.; Segura, M.; Gottschalk, M. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent-an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatrongjit, R.; Kerdsin, A.; Gottschalk, M.; Takeuchi, D.; Hamada, S.; Oishi, K.; Akeda, Y. First human case report of sepsis due to infection with Streptococcus suis serotype 31 in Thailand. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton-Hadley, F.A. Streptococcus suis type 2 infections. Br. Vet. J. 1983, 139, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staats, J.J.; Feder, I.; Okwumabua, O.; Chengappa, M.M. Streptococcus suis: Past and present. Vet. Res. Commun. 1997, 21, 381–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, B.; Gissot, V.; Ploy, M.C.; Vignon, P. Recurrent septic shock due to Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1998, 36, 2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, M.; Segura, M. The pathogenesis of the meningitis caused by Streptococcus suis: The unresolved questions. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 76, 259–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.J.; Liu, X.C.; Wang, S.W.; Liu, L.G.; Zu, R.Q.; Zhong, W.J.; Zhu, X.P.; Xiang, N.J.; Yuan, H.; Meng, L.; et al. Matched case–control study for risk factors of human Streptococcus suis infection in Sichuan Province, China. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi 2005, 26, 636–639. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, J.; Wang, C.; Feng, Y.; Yang, W.; Song, H.; Chen, Z.; Yu, H.; Pan, X.; Zhou, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome caused by Streptococcus suis serotype 2. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e151. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Jing, H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, L.; Zu, R.; Luo, L.; et al. Human Streptococcus suis outbreak, Sichuan, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 914–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, I.D.; Blackmore, D.K. Occupational exposure to Streptococcus suis type 2. Epidemiol. Infect. 1989, 103, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.; Hao, H.J.; Xiong, G.H.; Geng, H.R.; Zheng, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Cai, X.H.; Jiang, Y.Q. Development of colloidal gold-based immunochromatographic assay for rapid detection of Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 133, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Campo Sepúlveda, E.M.; Altman, E.; Kobisch, M.; D’allaire, S.; Gottschalk, M. Detection of antibodies against Streptococcus suis capsular type 2 using a purified capsular polysaccharide antigen-based indirect ELISA. Vet. Microbiol. 1996, 52, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.J.; Wang, L.; Shen, Z.Q.; Qin, W.; Hu, J.; Jiang, S.J.; Li, S.G. Development of an Indirect Dot-PPA-ELISA using glutamate dehydrogenase as a diagnostic antigen for the rapid and specific detection of Streptococcus suis and its application to clinical specimens. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupas, D.; Vignon, M.; Géraut, C. Streptococcus suis meningitis. A severe noncompensated occupational disease. J. Occup. Med. 1992, 34, 1102–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecht, U.; Wisselink, H.J.; Van Dijk, J.E.; Smith, H.E. Virulence of Streptococcus suis type 2 strains in newborn germfree pigs depends on phenotype. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Expósito Raya, N.; Mestre Luaces, M.; Silva Rodriguez, R.; Nazábal Gálvez, C.; Peña Rivero, M.; Martínez De La Puente, N.; Font Batista, M.; Guillén Nieto, G. Preformulation study of the vaccine candidate P64k against Neisseria meningitidis. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 1999, 29, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Guo, M.; Kong, L.; Gao, Y.; Ma, J.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Sun, J. TLR4 Agonist Combined with Trivalent Protein JointS of Streptococcus suis Provides Immunological Protection in Animals. Vaccines 2021, 9, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Ma, J.; Dong, W.; Song, W.; Wang, K.; Lu, C.; Yao, H. Novel variant serotype of streptococcus suis isolated from piglets with meningitis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 976–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lun, Z.R.; Wang, Q.P.; Chen, X.G.; Li, A.X.; Zhu, X.Q. Streptococcus suis: An emerging zoonotic pathogen. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Fittipaldi, N.; Calzas, C.; Gottschalk, M. Critical Streptococcus suis Virulence Factors: Are They All Really Critical? Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susilawathi, N.M.; Tarini, N.M.A.; Fatmawati, N.N.D.; Mayura, P.I.B.; Suryapraba, A.A.A.; Subrata, M.; Sudewi, A.A.R.; Mahardika, G.N. Streptococcus suis-Associated Meningitis, Bali, Indonesia, 2014–2017. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werinder, A.; Aspán, A.; Backhans, A.; Sjölund, M.; Guss, B.; Jacobson, M. Streptococcus suis in Swedish grower pigs: Occurrence, serotypes, and antimicrobial susceptibility. Acta Vet. Scand. 2020, 62, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, J.G.; Zimmerer, E.J.; Maddux, R.L. Conjugation of antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus suis. Vet. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromwell, G.L. Why and how antibiotics are used in swine production. Anim. Biotechnol. 2002, 13, 7–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.A.; Wertz, J.E. Bacteriocins: Evolution, ecology, and application. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2002, 56, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonifait, L.; Grignon, L.; Grenier, D. Fibrinogen induces biofilm formation by Streptococcus suis and enhances its antibiotic resistance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 4969–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Li, R.; Zhang, A.; He, H.; Hua, Y.; Xia, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, H.; Jin, M. Characterization of Streptococcus suis isolates from the diseased pigs in China between 2003 and 2007. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 137, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, J.; Ren, J.; Zhou, D.; Luo, Y.B.; Hu, M.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Rapid Detection of mrp, epf, and sly Genes by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification in Streptococcus suis. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brassard, J.; Gottschalk, M.; Quessy, S. Cloning and purification of the Streptococcus suis serotype 2 glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and its involvement as an adhesin. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 102, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, M.; Higgins, R.; Jacques, M.; Mittal, K.R.; Henrichsen, J. Description of 14 new capsular types of Streptococcus suis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 2633–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ye, C.; Fu, H.; Yue, M.; Li, X.; Fang, W. Stk and Stp1 participate in Streptococcus suis serotype 2 pathogenesis by regulating capsule thickness and translocation of certain virulence factors. Microb. Pathog. 2021, 152, 104607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, S.; Tien Le, H.T.; Osawa, R.; Tohya, M.; Nomoto, R.; Kawamura, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Kikuchi, N.; Kikuchi, K.; Sekizaki, T. Development of an appropriate PCR system for the reclassification of Streptococcus suis. J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 107, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiden, C.; Jaresitthikunchai, J.; Kerdsin, A.; Meekhanon, N.; Roytrakul, S.; Nuanualsuwan, S. Streptococcus suis serotyping by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kataoka, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Sunaga, S.; Imada, Y.; Ishikawa, H.; Kishima, M.; Nakazawa, M. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of antibody against Streptococcus suis type 2 in infected pigs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1996, 58, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Zhang, A.; Chen, H.; Zhou, R. Recent Proceedings on Prevalence and Pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2019, 32, 473–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thongkamkoon, P.; Kiatyingangsulee, T.; Gottschalk, M. Serotypes of Streptococcus suis isolated from healthy pigs in Phayao Province, Thailand. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, N.T.; Hoa, N.T.; Nga, T.V.; Linh Le, D.; Chau, T.T.; Sinh, D.X.; Phu, N.H.; Chuong, L.V.; Diep, T.S.; Campbell, J.; et al. Streptococcus suis meningitis in adults in Vietnam. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 659–667. [Google Scholar]
- Neila-Ibáñez, C.; Casal, J.; Hennig-Pauka, I.; Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N.; Gottschalk, M.; Migura-García, L.; Pailler-García, L.; Napp, S. Stochastic Assessment of the Economic Impact of Streptococcus suis-Associated Disease in German, Dutch and Spanish Swine Farms. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 676002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez De Los Ríos, J.; Reynaga, E.; García-Gonzàlez, M.; Càmara, J.; Ardanuy, C.; Cuquet, J.; Quesada, M.D.; Navarro, M.; Vilamala, A.; Párraga-Niño, N.; et al. Clinical and Epidemiological Characteristics of Streptococcus suis Infections in Catalonia, Spain. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 792233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Number | Inter-Assay CV (%) | Intra-Assay CV (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X ± SD | CV (%) | X ± SD | CV (%) | |
| 1 | 1.150 ± 0.040 | 3.48% | 1.154 ± 0.052 | 4.51% |
| 2 | 1.302 ± 0.042 | 3.23% | 1.364 ± 0.033 | 2.42% |
| 3 | 1.336 ± 0.037 | 2.77% | 1.359 ± 0.045 | 3.31% |
| 4 | 0.285 ± 0.016 | 5.61% | 0.297 ± 0.020 | 6.73% |
| 5 | 0.348 ± 0.023 | 6.61% | 0.382 ± 0.027 | 7.07% |
| 6 | 0.415 ± 0.028 | 6.75% | 0.432 ± 0.026 | 6.02% |
| Commercial Streptococcus suis Type 2 ELISA Kit | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | ||
| GMD-ELISA | Positive | 29 | 5 | 34 |
| Negative | 0 | 66 | 66 | |
| Total | 29 | 71 | 100 | |
| Positive coincidence rate | 93% | |||
| Negative coincidence rate | 100% | |||
| The total coincidence rate | 95% | |||
| Sample Type | No. Samples | No. Positive | Positive Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total number of samples | 167 | 56 | 33.5% |
| Vaccinated pigs | 42 | 35 | 83.3% |
| Unvaccinated pigs | 31 | 6 | 19.4% |
| Unknow | 94 | 15 | 16% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, N.; Wang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; et al. Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Porcine Streptococcus suis Based on a Recombinant GMD Protein. Animals 2023, 13, 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040719
Dong N, Wang Z, Sun Q, Chen X, Zhang H, Zheng J, Zhang X, Qiu Y, Li Z, Li B, et al. Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Porcine Streptococcus suis Based on a Recombinant GMD Protein. Animals. 2023; 13(4):719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040719
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Nihua, Zhaofei Wang, Qing Sun, Xiaojun Chen, Hailong Zhang, Jiayang Zheng, Xinya Zhang, Yafeng Qiu, Zongjie Li, Beibei Li, and et al. 2023. "Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Porcine Streptococcus suis Based on a Recombinant GMD Protein" Animals 13, no. 4: 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040719
APA StyleDong, N., Wang, Z., Sun, Q., Chen, X., Zhang, H., Zheng, J., Zhang, X., Qiu, Y., Li, Z., Li, B., Liu, K., Shao, D., Wei, J., Sun, J., & Ma, Z. (2023). Establishment and Application of an Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Porcine Streptococcus suis Based on a Recombinant GMD Protein. Animals, 13(4), 719. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13040719







