The Intestinal Microbiome in Dogs with Chronic Enteropathies and Cobalamin Deficiency or Normocobalaminemia—A Comparative Study
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Inclusion
2.2. Study Design, Baseline Data, and Diagnostic Investigations
2.3. Serum Cobalamin and Methylmalonic Acid Concentrations
2.4. Microbiome Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Data and Clinical Diagnosis
3.2. Serum Cobalamin and Methylmalonic Acid Concentrations
3.3. Cobalamin Supplementation, Concurrent Medication, and Diet
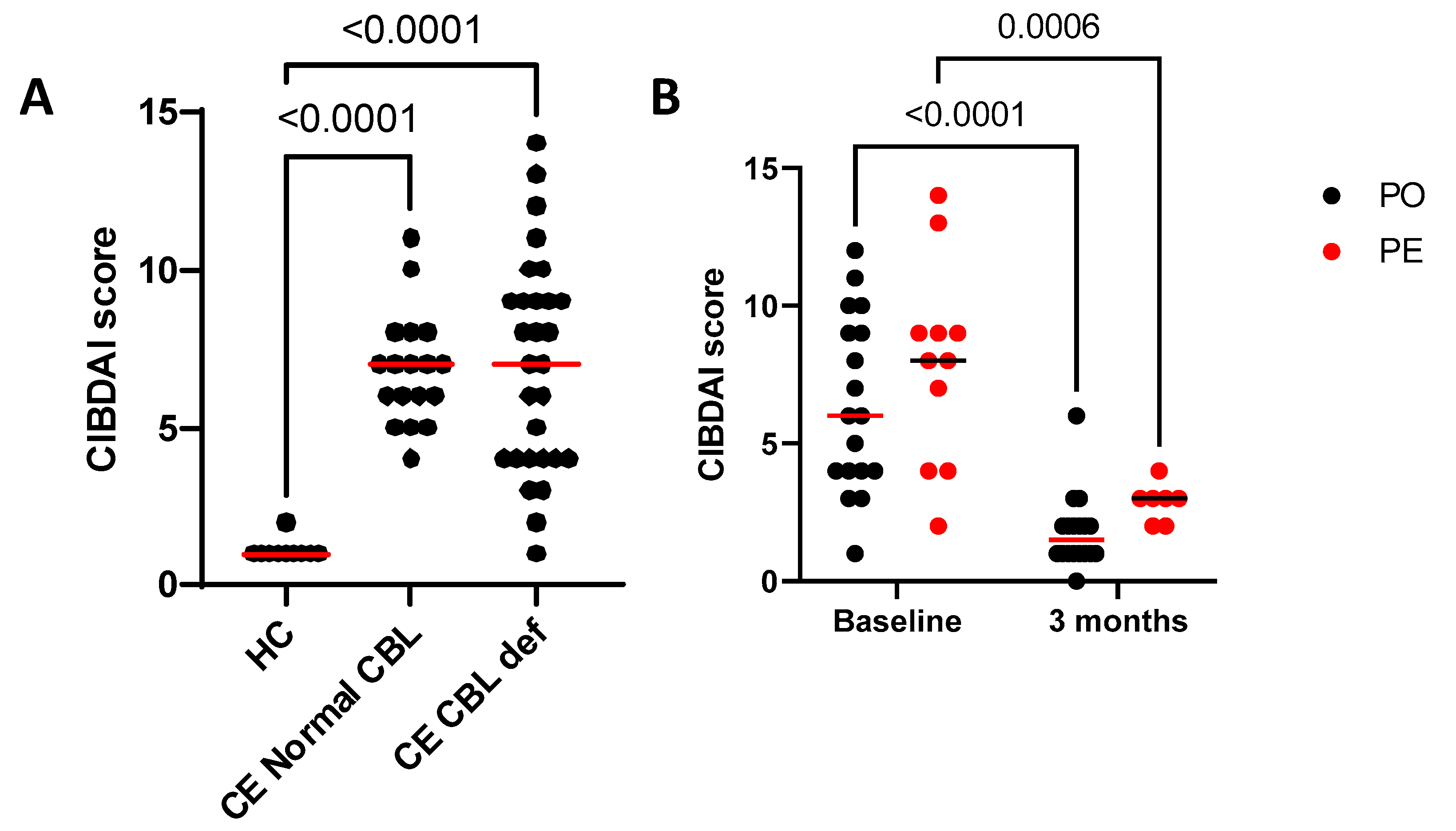
3.4. Canine Inflammatory Bowel Disease Activity Index
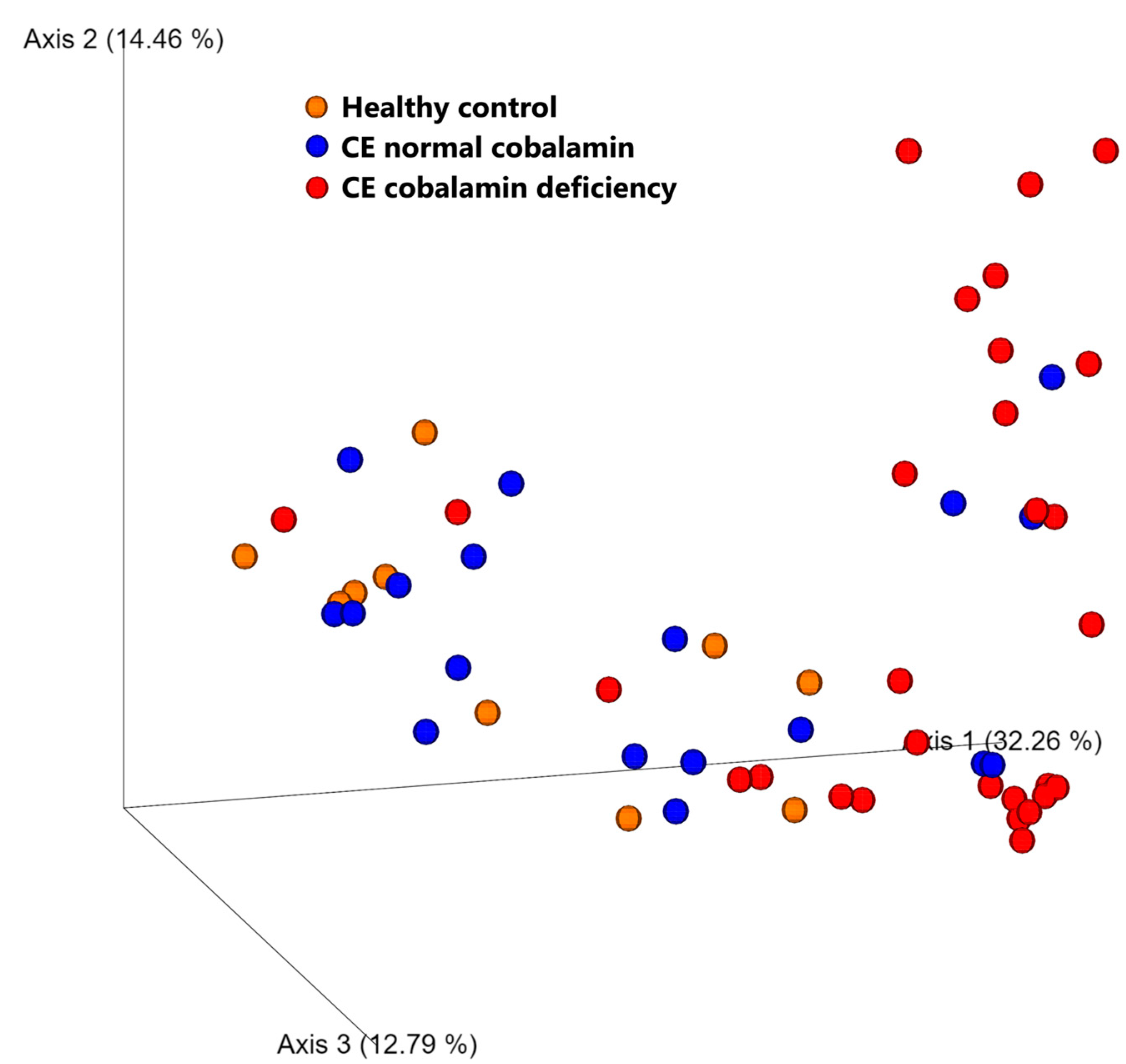
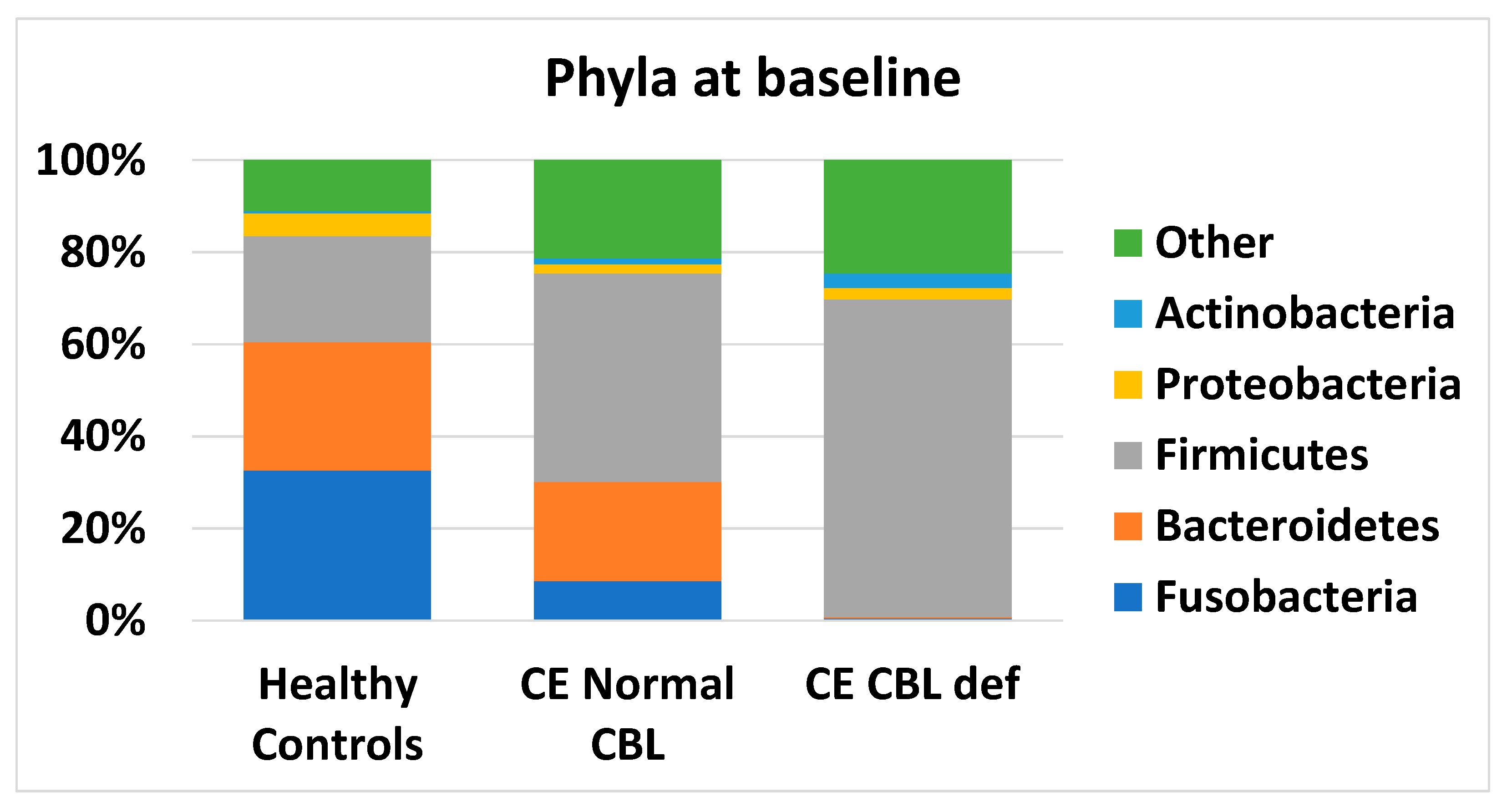
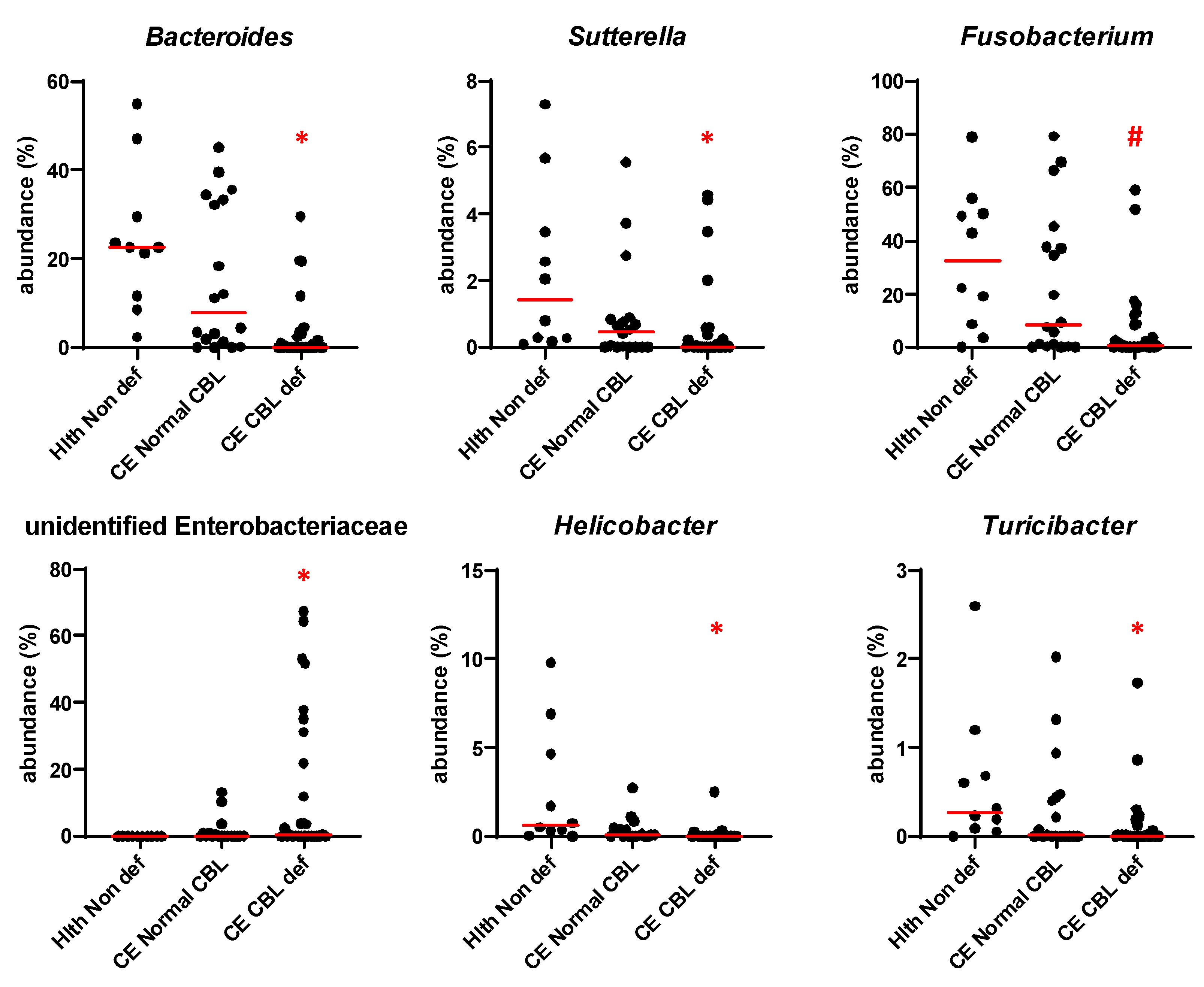
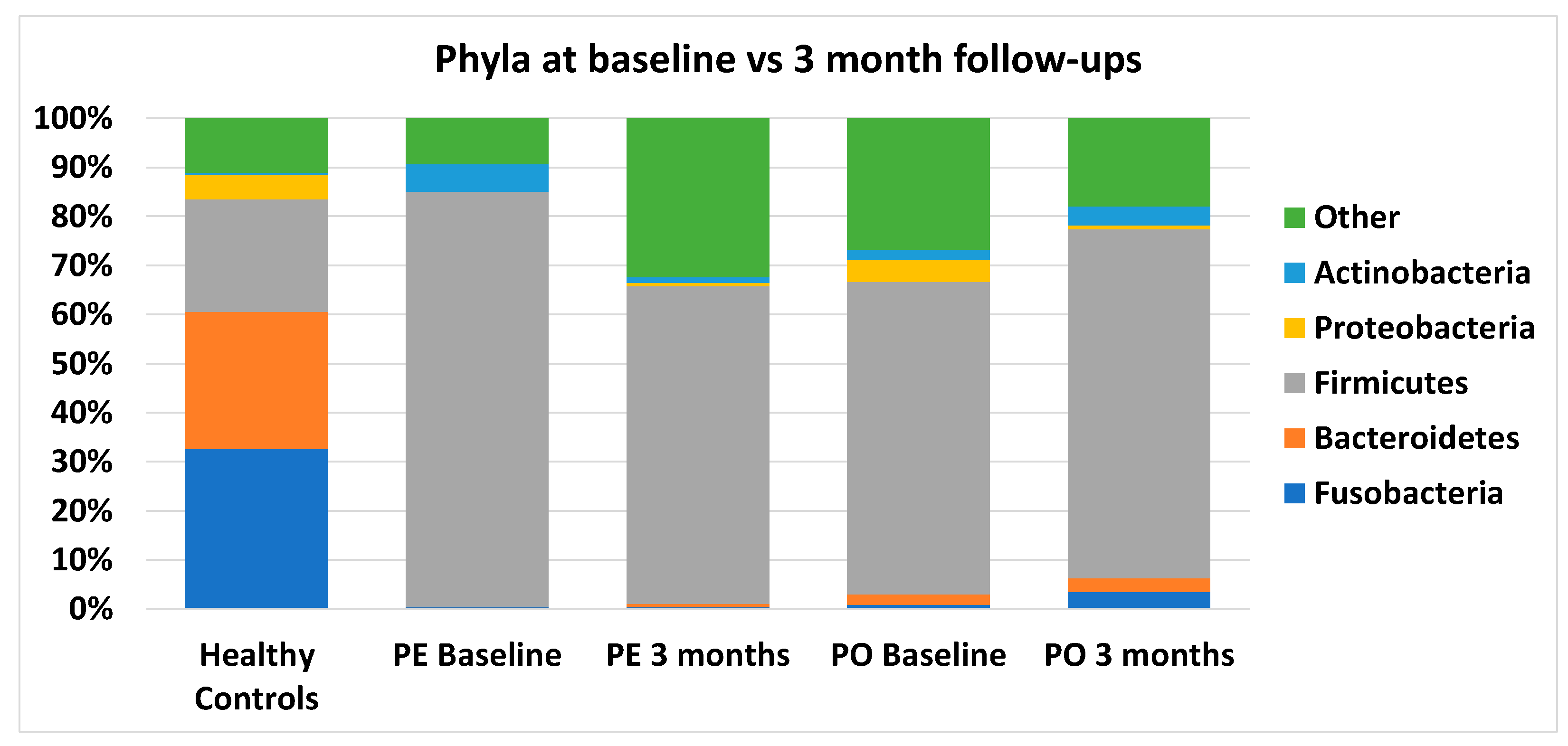
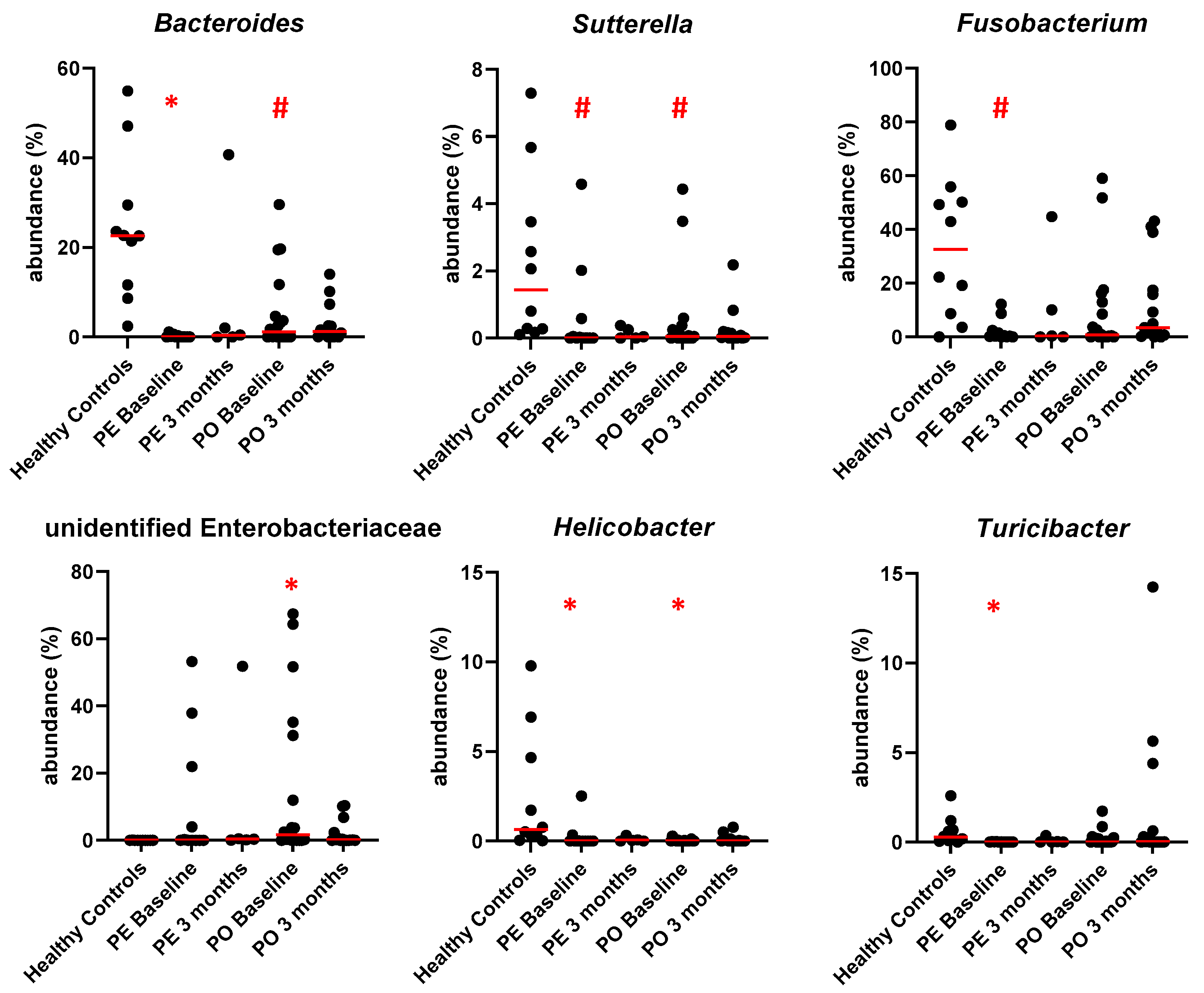
3.5. Microbiome Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allenspach, K.; Wieland, B.; Grone, A.; Gaschen, F. Chronic enteropathies in dogs: Evaluation of risk factors for negative outcome. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craven, M.; Simpson, J.W.; Ridyard, A.E.; Chandler, M.L. Canine inflammatory bowel disease: Retrospective analysis of diagnosis and outcome in 80 cases (1995–2002). J. Small Anim. Pract. 2004, 45, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, A.J.; Day, M.J.; Ruaux, C.G.; Steiner, J.M.; Williams, D.A.; Hall, E.J. Comparison of direct and indirect tests for small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and antibiotic-responsive diarrhea in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2003, 17, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, M.; Steiner, J.M.; Fosgate, G.T.; Zentek, J.; Hartmann, S.; Kohn, B. Chronic Diarrhea in Dogs-Retrospective Study in 136 Cases. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2017, 31, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruaux, C.G. Cobalamin in companion animals: Diagnostic marker, deficiency states and therapeutic implications. Vet. J. 2013, 196, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, P.H.; Barry, N.A.; Mok, K.C.; Taga, M.E.; Goodman, A.L. Human gut microbes use multiple transporters to distinguish vitamin B(1)(2) analogs and compete in the gut. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, R. B12 trafficking in mammals: A for coenzyme escort service. ACS Chem. Biol. 2006, 1, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnusdottir, S.; Ravcheev, D.; de Crecy-Lagard, V.; Thiele, I. Systematic genome assessment of B-vitamin biosynthesis suggests co-operation among gut microbes. Front. Genet. 2015, 6, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannella, R.A.; Broitman, S.A.; Zamcheck, N. Vitamin B12 uptake by intestinal microorganisms: Mechanism and relevance to syndromes of intestinal bacterial overgrowth. J. Clin. Investig. 1971, 50, 1100–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannella, R.A.; Zamcheck, N.; Broitman, S.A. Competition between Bacteria and Intrinsic-Factor for Vitamin-B12-Implications for Vitamin-B12 Malabsorption in Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth. Gastroenterology 1972, 62, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degnan, P.H.; Taga, M.E.; Goodman, A.L. Vitamin B12 as a modulator of gut microbial ecology. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 769–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guetterman, H.M.; Huey, S.L.; Knight, R.; Fox, A.M.; Mehta, S.; Finkelstein, J.L. Vitamin B-12 and the Gastrointestinal Microbiome: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 13, 530–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurwara, S.; Ajami, N.J.; Jang, A.; Hessel, F.C.; Chen, L.; Plew, S.; Wang, Z.; Graham, D.Y.; Hair, C.; White, D.L.; et al. Dietary Nutrients Involved in One-Carbon Metabolism and Colonic Mucosa-Associated Gut Microbiome in Individuals with an Endoscopically Normal Colon. Nutrients 2019, 11, 613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrothers, J.M.; York, M.A.; Brooker, S.L.; Lackey, K.A.; Williams, J.E.; Shafii, B.; Price, W.J.; Settles, M.L.; McGuire, M.A.; McGuire, M.K. Fecal Microbial Community Structure Is Stable over Time and Related to Variation in Macronutrient and Micronutrient Intakes in Lactating Women. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2379–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boran, P.; Baris, H.E.; Kepenekli, E.; Erzik, C.; Soysal, A.; Dinh, D.M. The impact of vitamin B12 deficiency on infant gut microbiota. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2020, 179, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, D.R.; Rhoades, N.; Mercado, J.; Argueta, P.; Lopez, U.; Flores, G.E. Dietary Habits of 2- to 9-Year-Old American Children Are Associated with Gut Microbiome Composition. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 120, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xiang, S.; Feng, X.; Wang, H.; Tian, S.; Xu, Y.; Shi, L.; Yang, L.; Li, M.; Shen, Y.; et al. Impact of Cyanocobalamin and Methylcobalamin on Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Intestinal Microbiota Composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xiang, S.; Ye, K.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y. Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) Induced a Shift in Microbial Composition and Metabolic Activity in an in vitro Colon Simulation. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shou, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xu, Y.; Shi, L.; Xiang, S.; Feng, X.; Han, J. Stability of vitamin B12 with the protection of whey proteins and their effects on the gut microbiome. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.J.; Alexeev, E.E.; Farb, L.; Vickery, T.W.; Zheng, L.; Eric, L.C.; Kitzenberg, D.A.; Battista, K.D.; Kominsky, D.J.; Robertson, C.E.; et al. Oral vitamin B(12) supplement is delivered to the distal gut, altering the corrinoid profile and selectively depleting Bacteroides in C57BL/6 mice. Gut Microbes 2019, 10, 654–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurz, E.; Horne, R.G.; Maattanen, P.; Wu, R.Y.; Botts, S.R.; Li, B.; Rossi, L.; Johnson-Henry, K.C.; Pierro, A.; Surette, M.G.; et al. Vitamin B12 Deficiency Alters the Gut Microbiota in a Murine Model of Colitis. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kang, S.; Sol Kim, D. Folate and vitamin B-12 deficiencies additively impaire memory function and disturb the gut microbiota in amyloid-beta infused rats. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2022, 92, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.; Guard, B.C.; Blake, A.B.; Ackermann, M.; Webb, C.; Hill, S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Long-Term Recovery of the Fecal Microbiome and Metabolome of Dogs with Steroid-Responsive Enteropathy. Animals 2021, 11, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Role of the Canine Gut Microbiome and Metabolome in Health and Gastrointestinal Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Markel, M.E.; Garcia-Mazcorro, J.F.; Unterer, S.; Heilmann, R.M.; Dowd, S.E.; Kachroo, P.; Ivanov, I.; Minamoto, Y.; Dillman, E.M.; et al. The fecal microbiome in dogs with acute diarrhea and idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batt, R.M.; Carter, M.W.; Peters, T.J. Biochemical changes in the jejunal mucosa of dogs with a naturally occurring enteropathy associated with bacterial overgrowth. Gut 1984, 25, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutgers, H.C.; Batt, R.M.; Elwood, C.M.; Lamport, A. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in dogs with chronic intestinal disease. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1995, 206, 187–193. [Google Scholar]
- Willard, M.D.; Simpson, R.B.; Fossum, T.W.; Cohen, N.D.; Delles, E.K.; Kolp, D.L.; Carey, D.P.; Reinhart, G.A. Characterization of naturally developing small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in 16 German shepherd dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1994, 204, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Suchodolski, J.S.; Dowd, S.E.; Wilke, V.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E. 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing reveals bacterial dysbiosis in the duodenum of dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlShawaqfeh, M.K.; Wajid, B.; Minamoto, Y.; Markel, M.; Lidbury, J.A.; Steiner, J.M.; Serpedin, E.; Suchodolski, J.S. A dysbiosis index to assess microbial changes in fecal samples of dogs with chronic inflammatory enteropathy. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toresson, L.; Steiner, J.M.; Razdan, P.; Spodsberg, E.; Olmedal, G.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Spillmann, T. Comparison of efficacy of oral and parenteral cobalamin supplementation in normalising low cobalamin concentrations in dogs: A randomised controlled study. Vet. J. 2018, 232, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obeid, R.; Kuhlmann, M.K.; Kohler, H.; Herrmann, W. Response of homocysteine, cystathionine, and methylmalonic acid to vitamin treatment in dialysis patients. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, W.; Obeid, R. Causes and early diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2008, 105, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briani, C.; Dalla Torre, C.; Citton, V.; Manara, R.; Pompanin, S.; Binotto, G.; Adami, F. Cobalamin deficiency: Clinical picture and radiological findings. Nutrients 2013, 5, 4521–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toresson, L.; Steiner, J.M.; Spodsberg, E.; Olmedal, G.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Lidbury, J.A.; Spillmann, T. Effects of oral versus parenteral cobalamin supplementation on methylmalonic acid and homocysteine concentrations in dogs with chronic enteropathies and low cobalamin concentrations. Vet. J. 2019, 243, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jergens, A.E.; Schreiner, C.A.; Frank, D.E.; Niyo, Y.; Ahrens, F.E.; Eckersall, P.D.; Benson, T.J.; Evans, R. A scoring index for disease activity in canine inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2003, 17, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drammeh, B.S.; Schleicher, R.L.; Pfeiffer, C.M.; Jain, R.B.; Zhang, M.; Nguyen, P.H. Effects of delayed sample processing and freezing on serum concentrations of selected nutritional indicators. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1883–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruaux, C.G.; Steiner, J.M.; Williams, D.A. Metabolism of amino acids in cats with severe cobalamin deficiency. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parada, A.E.; Needham, D.M.; Fuhrman, J.A. Every base matters: Assessing small subunit rRNA primers for marine microbiomes with mock communities, time series and global field samples. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1403–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apprill, A.; McNally, S.; Parsons, R.; Weber, L. Minor revision to V4 region SSU rRNA 806R gene primer greatly increases detection of SAR11 bacterioplankton. Aquatic. Microbial. Ecol. 2015, 75, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate-A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Madsen, M.; Kilkenney, A.; Gregory, B.; Christensen, E.I.; Vorum, H.; Hojrup, P.; Schaffer, A.A.; Kirkness, E.F.; Tanner, S.M.; et al. Amnionless function is required for cubilin brush-border expression and intrinsic factor-cobalamin (vitamin B12) absorption in vivo. Blood 2005, 106, 1447–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, F.; Minamoto, Y.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Galiazzo, G.; Vecchiato, C.G.; Pinna, C.; Biagi, G.; Pietra, M. Effect of an extruded animal protein-free diet on fecal microbiota of dogs with food-responsive enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamoto, Y.; Otoni, C.C.; Steelman, S.M.; Buyukleblebici, O.; Steiner, J.M.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. Alteration of the fecal microbiota and serum metabolite profiles in dogs with idiopathic inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. Microbes 2015, 6, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honneffer, J.B.; Minamoto, Y.; Suchodolski, J.S. Microbiota alterations in acute and chronic gastrointestinal inflammation of cats and dogs. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 16489–16497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xenoulis, P.G.; Palculict, B.; Allenspach, K.; Steiner, J.M.; Van House, A.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial communities imbalances in the small intestine of dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2008, 66, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.J.; Pilla, R.; Panta, A.; Pandey, S.; Sarawichitr, B.; Suchodolski, J.; Sohrabji, F. Reproductive Senescence and Ischemic Stroke Remodel the Gut Microbiome and Modulate the Effects of Estrogen Treatment in Female Rats. Transl. Stroke Res. 2020, 11, 812–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, N.D.; Barker, A.K.; Alcott, C.J.; Levine, J.M.; Meren, I.; Wengert, J.; Jergens, A.E.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Association of Specific Constituents of the Fecal Microbiota with Immune-Mediated Brain Disease in Dogs. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minamoto, Y.; Minamoto, T.; Isaiah, A.; Sattasathuchana, P.; Buono, A.; Rangachari, V.R.; McNeely, I.H.; Lidbury, J.; Steiner, J.M.; Suchodolski, J.S. Fecal short-chain fatty acid concentrations and dysbiosis in dogs with chronic enteropathy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, M.; Gao, J.; Rizzo, M.; Harrison, T.; Tiedje, J.M. Diet is a major factor governing the fecal butyrate-producing community structure across Mammalia, Aves and Reptilia. ISME J. 2015, 9, 832–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghoff, N.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Association between serum cobalamin and methylmalonic acid concentrations in dogs. Vet. J. 2012, 191, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter (Range; Median) | CE + cbl a Deficiency | CE; Normal cbl | Healthy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of dogs | 29 | 18 | 10 |
| Age (years) | 1.5–13.1 (6.1) | 0.5–12.5 (5.2) | 2.1–10.3 (5.0) |
| BW b (kg) at inclusion | 4.1–49.0 (11.8) | 8.9–32.7 (20.9) | 3.6–30.8 (7.6) |
| BCS c at inclusion (X/9) | 3–7 (4) | 2–7 (4) | 4–6 (5) |
| Sex (m/MN/F/FN) | 12/6/6/5 | 11/2/2/3 | 0/4/4/2 |
| Serum alb d concentration (g/L); RI e 29–39 | 14–37 (30) | 27–38 (31) | 31–39 (33) |
| Serum cbl concentration (pmol/L) at inclusion; RI 180–708 | <111–210 (183) | 350–>738 (492) | 350–658 (475) |
| Serum cbl concentration (pmol/L) after cbl supplementation; RI 180–708 | 434–2894 (727) | n/a | n/a |
| Serum MMA f concentration (nmol/L) at inclusion; RI 414–1193 | 566–2468 (934) | n/a | 470–972 (746) |
| Serum MMA concentration (nmol/L) at follow-up; RI 414–1193 | 450–1221 (626) | n/a | n/a |
| Diet at inclusion | |||
| KD g; maintenance diet | 8 | 1 | 8 |
| KD: ‘Intestinal’ | 5 | 8 | 1 |
| KD; single protein | 8 | 3 | 1 |
| KD; hydrolyzed | 1 | 6 | n/a |
| KD + Home-cooked | 2 | n/a | n/a |
| Home-cooked | 5 h | n/a | n/a |
| Treatment at inclusion: | |||
| Corticosteroids | 8 i | 10 j | n/a |
| Cyclosporine | 3 k | n/a | n/a |
| Prebiotics | 3 l | 3 m | n/a |
| Probiotics | 3 n | 5 o | n/a |
| Miscellaneous | 9 p | 4 q | n/a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toresson, L.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Spillmann, T.; Lopes, B.C.; Shih, J.; Steiner, J.M.; Pilla, R. The Intestinal Microbiome in Dogs with Chronic Enteropathies and Cobalamin Deficiency or Normocobalaminemia—A Comparative Study. Animals 2023, 13, 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081378
Toresson L, Suchodolski JS, Spillmann T, Lopes BC, Shih J, Steiner JM, Pilla R. The Intestinal Microbiome in Dogs with Chronic Enteropathies and Cobalamin Deficiency or Normocobalaminemia—A Comparative Study. Animals. 2023; 13(8):1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081378
Chicago/Turabian StyleToresson, Linda, Jan S. Suchodolski, Thomas Spillmann, Bruna C. Lopes, Johnathan Shih, Jörg M. Steiner, and Rachel Pilla. 2023. "The Intestinal Microbiome in Dogs with Chronic Enteropathies and Cobalamin Deficiency or Normocobalaminemia—A Comparative Study" Animals 13, no. 8: 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081378
APA StyleToresson, L., Suchodolski, J. S., Spillmann, T., Lopes, B. C., Shih, J., Steiner, J. M., & Pilla, R. (2023). The Intestinal Microbiome in Dogs with Chronic Enteropathies and Cobalamin Deficiency or Normocobalaminemia—A Comparative Study. Animals, 13(8), 1378. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081378







