Trend of Antimicrobial Use in Food-Producing Animals from 2018 to 2020 in Nepal
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
- (a)
- Range of antimicrobials authorized for veterinary use in Nepal
- (b)
- Antimicrobial volumes sourced from pharmaceutical companies
- (c)
- Antimicrobial volumes sourced from veterinary drug importers
- (d)
- Antimicrobial volumes sourced from customs
2.2. Data Collection and Observations
2.3. Trustworthiness of the Source of Data
2.4. Reliability of the Data
2.5. External Validity of the Data
2.6. Internal Validity of the Data
2.7. Data Analysis
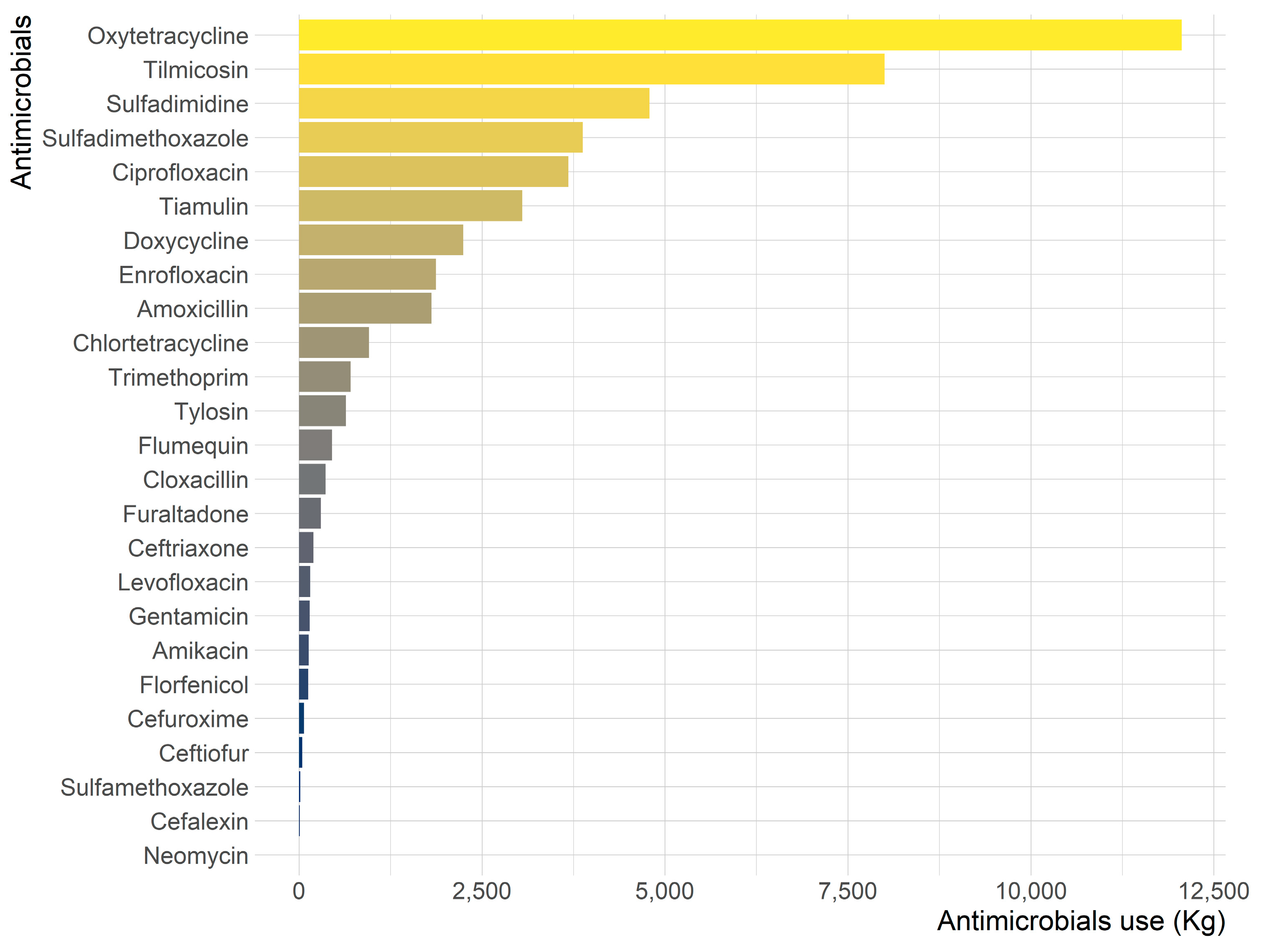
3. Results
3.1. Availability of Authorized Antimicrobials for Veterinary Use in Nepal
3.2. Antimicrobials Imported and Internally Produced for Veterinary Use in Nepal
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MoA. Statistical Information on Nepalese Agriculture 2076/77 (2019/20); Ministry of Agriculture and Livestock Development: Kathmandu, Nepal, 2021.
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#country/149 (accessed on 1 November 2022).
- Neopane, S.P.; Shrestha, B.S.; Gauchan, D. Livestock Contribution to Food and Nutrition Security in Nepal. In Agriculture, Natural Resources and Food Security; Timsina, J., Maraseni, T.N., Gauchan, D., Adhikari, J., Ohja, H., Eds.; Sustainable Development Goals Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, M.A.A.; Rahman, S.; Cohall, D.; Bharatha, A.; Singh, K.; Haque, M.; Gittens-St Hilaire, M. Antimicrobial Stewardship: Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance and Protecting Global Public Health. Infect. Drug Resist. 2020, 13, 4713–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abushaheen, M.A.; Muzaheed Fatani, A.J.; Alosaimi, M.; Mansy, W.; George, M.; Acharya, S.; Rathod, S.; Divakar, D.D.; Jhugroo, C.; Vellappally, S.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance, mechanisms and its clinical significance. Dis. Mon. 2020, 66, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aarestrup, F.M. The livestock reservoir for antimicrobial resistance: A personal view on changing patterns of risks, effects of interventions and the way forward. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2015, 370, 20140085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union Summary Report on Antimicrobial Resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2019–2020. EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, C.; Dixon, R.; Talbot, L.; James, S.J.; Williams, N.; Onarinde, B.A. Assessing the Impact of Heat Treatment of Food on Antimicrobial Resistance Genes and Their Potential Uptake by Other Bacteria-A Critical Review. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiseo, K.; Huber, L.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthe, F.C.J.; Bali, S.R.; Batmanian, G.J. Putting Pandemics Behind Us: Investing in One Health to Reduce Risks of Emerging Infectious Diseases; World-Bank group: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- OIE. The OIE Strategy on Antimicrobial Resistance and the Prudent Use of Antimicrobials; World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE): Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- European Medicines Agency. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2019 and 2020; EMA/58183/2021; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- OIE. OIE Annual Report on Antimicrobial Agents Intended for Use in Animal—Fourth Report; World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE): Paris, France, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- OIE. OIE Annual Report on Antimicrobial Agents Intended for Use in Animals—Fifth Report; World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE): Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mulchandani, R.; Wang, Y.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food-producing animals: 2020 to 2030. PLoS Glob. Public Health 2023, 3, e0001305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DDA. Drugs Act, 2035. Department of Drug Administration, Kathmandu. 1978. Available online: https://www.dda.gov.np/content/drugs-act-2035 (accessed on 2 November 2022).
- Collignon, P.J.; Conly, J.M.; Andremont, A.; McEwen, S.A.; Aidara-Kane, A.; World Health Organization Advisory Group; Bogotá Meeting on Integrated Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance; Agerso, Y.; Andremont, A.; Collignon, P.; et al. World Health Organization Ranking of Antimicrobials According to Their Importance in Human Medicine: A Critical Step for Developing Risk Management Strategies to Control Antimicrobial Resistance From Food Animal Production. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Mapping Supply and Demand for Animal-Source Foods to 2030; Robinson, T.P., Pozzi, F., Eds.; Animal Production and Health Working Paper. No. 2; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Schar, D.; Sommanustweechai, A.; Laxminarayan, R.; Tangcharoensathien, V. Surveillance of antimicrobial consumption in animal production sectors of low- and middle-income countries: Optimizing use and addressing antimicrobial resistance. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.; Hess, C.; Wernsdorf, P.; Kaser, T.; Meitz, S.; Jensen-Jarolim, E.; Hess, M.; Liebhart, D. The systemic multiplication of Gallibacterium anatis in experimentally infected chickens is promoted by immunosuppressive drugs which have a less specific effect on the depletion of leukocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2015, 166, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelhamid, M.K.; Quijada, N.M.; Dzieciol, M.; Hatfaludi, T.; Bilic, I.; Selberherr, E.; Liebhart, D.; Hess, C.; Hess, M.; Paudel, S. Co-infection of Chicken Layers With Histomonas meleagridis and Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Is Associated With Dysbiosis, Cecal Colonization and Translocation of the Bacteria From the Gut Lumen. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 586437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, S.; Ruhnau, D.; Wernsdorf, P.; Liebhart, D.; Hess, M.; Hess, C. Presence of Avibacterium paragallinarum and Histopathologic Lesions Corresponds with Clinical Signs in a Co-infection Model with Gallibacterium anatis. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paudel, S.; Stessl, B.; Hess, C.; Zloch, A.; Hess, M. High genetic diversity among extraintestinal Escherichia coli isolates in pullets and layers revealed by a longitudinal study. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaussmann, B.; Hess, C.; Grafl, B.; Kovacs, M.; Troxler, S.; Stessl, B.; Hess, M.; Paudel, S. Escherichia coli isolates from femoral bone marrow of broilers exhibit diverse pheno- and genotypic characteristics that do not correlate with macroscopic lesions of bacterial chondronecrosis with osteomyelitis. Avian Pathol. 2018, 47, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verraes, C.; Van Boxstael, S.; Van Meervenne, E.; Van Coillie, E.; Butaye, P.; Catry, B.; de Schaetzen, M.A.; Van Huffel, X.; Imberechts, H.; Dierick, K.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance in the food chain: A review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 2643–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhimiukor, O.O.; Odih, E.E.; Donado-Godoy, P.; Okeke, I.N. A bottom-up view of antimicrobial resistance transmission in developing countries. Nat. Microbiol. 2022, 7, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griesbacher, A.; Schliessnig, H.; Weber, S.; Fuchs, K. Antimicrobial use in poultry flocks in Austria between 2013 and 2019. Vet. Rec. 2021, 189, e508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayukekbong, J.A.; Ntemgwa, M.; Atabe, A.N. The threat of antimicrobial resistance in developing countries: Causes and control strategies. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control. 2017, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, K.P.; Wilson, R.T. Antimicrobial Resistance in Nepal. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, C.C.W.; Karmacharya, D.; Bista, M.; Sharma, A.N.; Goldstein, T.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Johnson, C.K. Antibiotic resistance genes of public health importance in livestock and humans in an informal urban community in Nepal. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, A.; Lorenzi, V.; Penasa, M.; Magni, E.; Alborali, G.L.; Bertocchi, L.; De Marchi, M. Effect of welfare standards and biosecurity practices on antimicrobial use in beef cattle. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Rank 1 | Antimicrobial Class | Antimicrobial Use in Kg * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | ||
| I | Cephalosporins | 11,355 | 9061 | 319 |
| I | Aminoglycosides | 4056 | 2820 | 275 |
| I | Amphenicols | 648 | 141 | 125 |
| I | Fluoroquinolones | 10,162 | 6535 | 5702 |
| I | Macrolides | 9329 | 1575 | 8639 |
| II | Penicillins | 8051 | 1296 | 2174 |
| II | Sulfonamides (including TMP) 2 | 15,916 | 12,512 | 9382 |
| II | Tetracyclines | 12,769 | 9696 | 15,257 |
| III | Nitrofurans | 1875 | 1875 | 297 |
| Others 3 | 16,927 | 2184 | 3501 | |
| Total | 91,088 | 47,694 | 45,671 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Upadhyaya, N.; Karki, S.; Rana, S.; Elsohaby, I.; Tiwari, R.; Oli, M.; Paudel, S. Trend of Antimicrobial Use in Food-Producing Animals from 2018 to 2020 in Nepal. Animals 2023, 13, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081377
Upadhyaya N, Karki S, Rana S, Elsohaby I, Tiwari R, Oli M, Paudel S. Trend of Antimicrobial Use in Food-Producing Animals from 2018 to 2020 in Nepal. Animals. 2023; 13(8):1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081377
Chicago/Turabian StyleUpadhyaya, Nabin, Surendra Karki, Sujan Rana, Ibrahim Elsohaby, Ramanandan Tiwari, Manoj Oli, and Surya Paudel. 2023. "Trend of Antimicrobial Use in Food-Producing Animals from 2018 to 2020 in Nepal" Animals 13, no. 8: 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081377
APA StyleUpadhyaya, N., Karki, S., Rana, S., Elsohaby, I., Tiwari, R., Oli, M., & Paudel, S. (2023). Trend of Antimicrobial Use in Food-Producing Animals from 2018 to 2020 in Nepal. Animals, 13(8), 1377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13081377








