Trends in Animal Shelter Management, Adoption, and Animal Death in Taiwan from 2012 to 2020
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population and Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
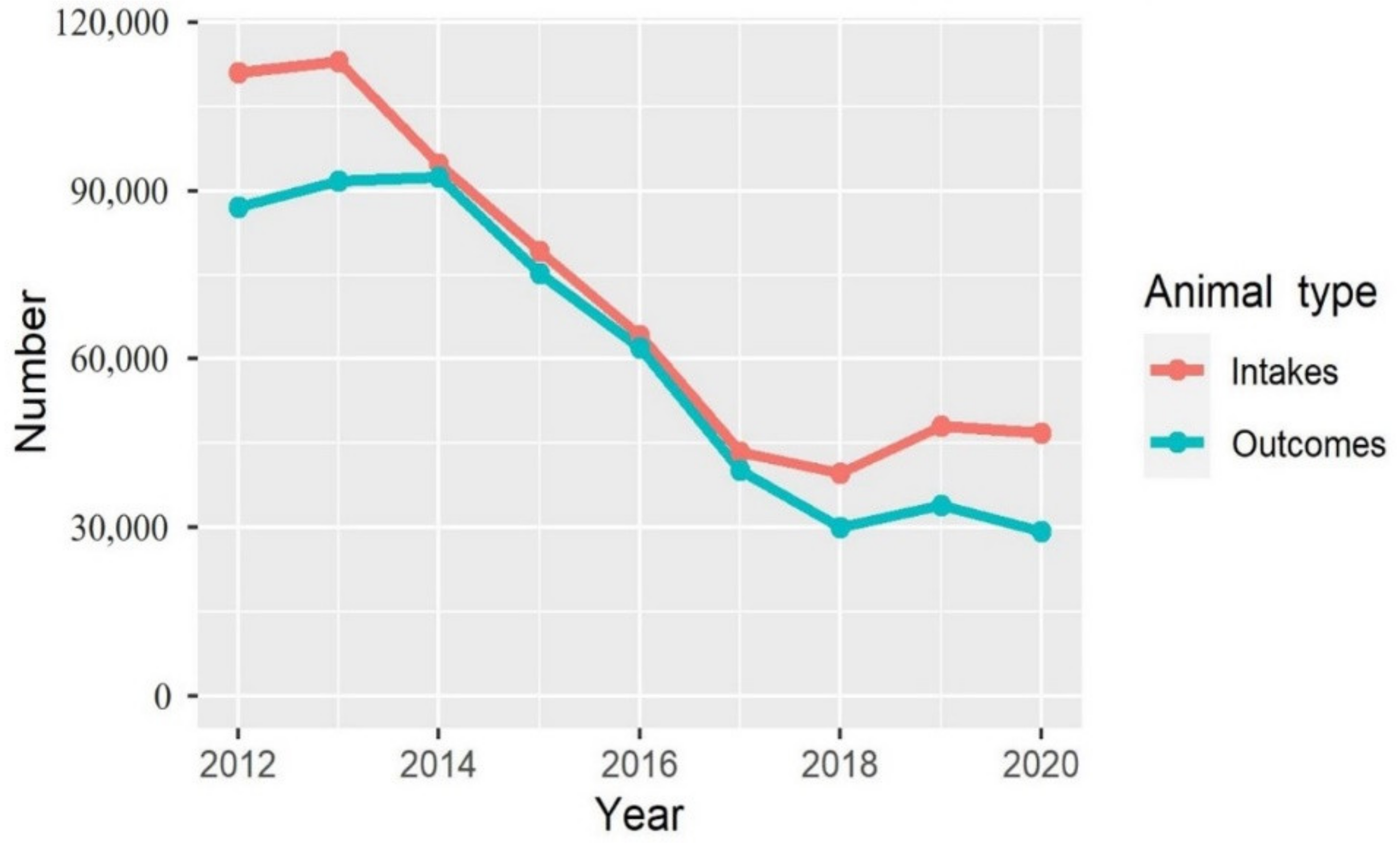
3.1. Overall Shelter Flow
3.2. Specific Reasons for Animal Intakes and Outcomes
3.3. Risk Factors for Overall and Specific Animal Intakes and Outcomes
3.3.1. Univariable Linear Regression Results
3.3.2. Multivariable Linear Regression Results
3.4. Workload of Shelter Veterinarians
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atlas, R.M. One Health: Its Origins and Future. In One Health: The Human-Animal-Environment Interfaces in Emerging Infectious Diseases: The Concept and Examples of a One Health Approach; Mackenzie, J.S., Jeggo, M., Daszak, P., Richt, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, R.; Ji, S.; Su, S.; Zhou, J. One Health strategies for rabies control in rural areas of China. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, 365–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.M.; Hartmann, S.; Munteanu, A.M.; Dalla Villa, P.; Quinnell, R.J.; Collins, L.M. The Effectiveness of Dog Population Management: A Systematic Review. Animals 2019, 9, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, K.F.; Levy, J.K. Rethinking the Animal Shelter’s Role in Free-Roaming Cat Management. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jessup, D.A. The welfare of feral cats and wildlife. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 225, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, T.S.; Dickman, C.R.; Glen, A.S.; Newsome, T.M.; Nimmo, D.G.; Ritchie, E.G.; Vanak, A.T.; Wirsing, A.J. The global impacts of domestic dogs on threatened vertebrates. Biol. Conserv. 2017, 210, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.S.; Glen, A.S.; Nimmo, D.G.; Ritchie, E.G.; Dickman, C.R. Invasive predators and global biodiversity loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 11261–11265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commonwealth of Australia. Threat Abatement Plan for Predation by Feral Cats. 2015. Available online: https://www.awe.gov.au/environment/biodiversity/threatened/publications/tap/threat-abatement-plan-feral-cats (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Henderson, W. ; Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Centre (Australia) Pathogens in Vertebrate Pests in Australia; Invasive Animals Cooperative Research Centre: Canberra, Australia, 2009; ISBN 978-0-9806716-4-3. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, C.H. Pangolin Conservation Model Students Dodge Smuggling, But Still Can’t Escape the Threat of Stray Dogs. Ten Years of Injury Rescue Trends Reveal Mysteries. Environmental Information Center. 2022. Available online: https://e-info.org.tw/node/233245 (accessed on 16 August 2022).
- Wang, S.-L.; Tu, Y.-C.; Lee, M.-S.; Wu, L.-H.; Chen, T.-Y.; Wu, C.-H.; Tsao, E.H.-S.; Chin, S.-C.; Li, W.-T. Fatal canine parvovirus-2 (CPV-2) infection in a rescued free-ranging Taiwanese pangolin (Manis pentadactyla pentadactyla). Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morters, M.K.; McKinley, T.J.; Restif, O.; Conlan AJ, K.; Cleaveland, S.; Hampson, K.; Whay, H.R.; Damriyasa, I.M.; Wood JL, N. The demography of free-roaming dog populations and applications to disease and population control. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 51, 1096–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Rabies Epidemiology and Burden. 2021. Available online: https://www.who.int/activities/improving-data-on-rabies/rabies-epidemiology-and-burden (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- World Organisation for Animal Health. Toxoplasma gondii (Infection with)—WOAH—World Organisation for Animal Health. 2022. Available online: https://www.woah.org/en/document/toxoplasma-gondii-infection-with/ (accessed on 3 February 2022).
- Hamilton, F. Implementing Nonlethal Solutions for Free-Roaming Cat Management in a County in the Southeastern United States. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Høgåsen, H.R.; Er, C.; Di Nardo, A.; Dalla Villa, P. Free-roaming dog populations: A cost-benefit model for different management options, applied to Abruzzo, Italy. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 112, 401–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy BP, A.; Cumming, B.; Brown, W.Y. Global Strategies for Population Management of Domestic Cats (Felis catus): A Systematic Review to Inform Best Practice Management for Remote Indigenous Communities in Australia. Animals 2020, 10, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisiel, L.M. Using a Dog Demography Field Study to Inform the Development of An Agent-Based Computer Simulation. Evaluating Owned Dog Population Control Interventions in a Small, Semi-Urban Community in Mexico; The University of Guelph: Guelph, ON, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yoak, A.J.; Reece, J.F.; Gehrt, S.D.; Hamilton, I.M. Optimizing free-roaming dog control programs using agent-based models. Ecol. Model. 2016, 341, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totton, S.C.; Wandeler, A.I.; Ribble, C.S.; Rosatte, R.C.; McEwen, S.A. Stray dog population health in Jodhpur, India in the wake of an animal birth control (ABC) program. Prev. Vet. Med. 2011, 98, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoak, A.J.; Reece, J.F.; Gehrt, S.D.; Hamilton, I.M. Disease control through fertility control: Secondary benefits of animal birth control in Indian street dogs. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 113, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, F.E. Leading and Organizing Social Change for Companion Animals. Anthrozoös 2010, 23, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faith for Animals. Faith for Animal Work Report 2018 to 2021. 2022. Available online: https://www.faithforanimals.org.tw/uploads/achievement/06/index.htm (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Peng, S.J.-L.; Lee, L.Y.-T.; Fei, A.C.-Y. Shelter animal management and trends in Taiwan. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. JAAWS 2012, 15, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laws and Regulations Database of Taiwan. Animal Protection Act. 2021. Available online: https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=M0060027 (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Daly, N.; Why Animal Shelters Are Facing a New Crisis. Animals. 2021. Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/animals/article/why-animal-shelters-are-facing-a-new-crisis (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- Lin, C.N. Animal Shelters Crowded Due to Poll Focus: Activist—Taipei Times. 2019. Available online: https://www.taipeitimes.com/News/taiwan/archives/2019/01/13/2003707855 (accessed on 16 April 2022).
- American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals. Characteristics, Challenges of the Shelter Environment. ASPCApro. 2015. Available online: https://www.aspcapro.org/characteristics-challenges-shelter-environment (accessed on 22 April 2022).
- Barnard, S.; Pedernera, C.; Candeloro, L.; Ferri, N.; Velarde, A.; Dalla Villa, P. Development of a new welfare assessment protocol for practical application in long-term dog shelters. Vet. Rec. 2016, 178, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protopopova, A. Effects of sheltering on physiology, immune function, behavior, and the welfare of dogs. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 159, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Wagner, D.C.; Kass, P.H.; Hurley, K.F. Associations among weight loss, stress, and upper respiratory tract infection in shelter cats. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2012, 240, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vojtkovská, V.; Voslářová, E.; Večerek, V. Methods of Assessment of the Welfare of Shelter Cats: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.A.; Brandt, J.C.; Lord, L.K.; Miles, E.A. Euthanasia in Animal Shelters: Management’s Perspective on Staff Reactions and Support Programs. Anthrozoös 2013, 26, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, B.E.; Rogelberg, S.G.; Carello Lopina, E.; Allen, J.A.; Spitzmüller, C.; Bergman, M. Shouldering a silent burden: The toll of dirty tasks. Hum. Relat. 2012, 65, 597–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotney, R.L.; McLaughlin, D.; Keates, H.L. A systematic review of the effects of euthanasia and occupational stress in personnel working with animals in animal shelters, veterinary clinics, and biomedical research facilities. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2015, 247, 1121–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laws and Regulations Database of Taiwan. Guideline of the Organization of Animal Shelters. 2015. Available online: https://law.moj.gov.tw/LawClass/LawAll.aspx?pcode=M0130029 (accessed on 12 March 2022).
- Salman, M.D.; Hutchison, J.; Ruch-Gallie, R.; Kogan, L.; New, J.C.; Kass, P.H.; Scarlett, J.M. Behavioral Reasons for Relinquishment of Dogs and Cats to 12 Shelters. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. 2000, 3, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurson, S.A.; Serpell, J.A.; Hart, B.L. Evaluation of a behavioral assessment questionnaire for use in the characterization of behavioral problems of dogs relinquished to animal shelters. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 227, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesel, G.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Brodbelt, D. Factors affecting the success of rehoming dogs in the UK during 2005. Prev. Vet. Med. 2008, 84, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesel, G.; Brodbelt, D.; Pfeiffer, D.U. Characteristics of relinquished dogs and their owners at 14 rehoming centers in the United Kingdom. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. JAAWS 2010, 13, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinzin, K.; Stevenson, M.; Probert, D.; Bird, R.; Jackson, R.; French, N.; Weir, J. Free-roaming and surrendered dogs and cats submitted to a humane shelter in Wellington, New Zealand, 1999–2006. New Zealand Vet. J. 2008, 56, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.; Severinghaus, L.L.; Serpell, J.A. Dog keeping in Taiwan: Its contribution to the problem of free-roaming dogs. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. JAAWS 2003, 6, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puurunen, J.; Hakanen, E.; Salonen, M.K.; Mikkola, S.; Sulkama, S.; Araujo, C.; Lohi, H. Inadequate socialisation, inactivity, and urban living environment are associated with social fearfulness in pet dogs. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, E.; Mohan-Gibbons, H.; Zawistowski, S. Animal Behavior for Shelter Veterinarians and Staff; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Council of Agriculture Executive Yuan. National Animal Sheltering System. 2017. Available online: https://asms.coa.gov.tw/Amlapp/App/PetsMapFront.aspx (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- National Statistics. Statistics from Statistical Bureau. 2021. Available online: https://winsta.dgbas.gov.tw/DgbasWeb/ZWeb/StateFile_ZWeb.aspx (accessed on 28 October 2021).
- Council of Agriculture Executive Yuan. Statistics of Dogs and Cats in Each County and City. 2020. Available online: https://animal.coa.gov.tw/Frontend/Know/AnimalResource#tab2 (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Office of the President Taiwan. Government Organizations. 2022. Available online: https://english.president.gov.tw/Page/106 (accessed on 19 February 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. 2021. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. RStudio. PBC. 2021. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.D.; Francois, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Francois, R.; Henry, L.; Muller, K. dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=dplyr (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Bivand, R.; Keitt, T.; Rowlingson, B. rgdal: Bindings for the ‘Geospatial’ Data Abstraction Library (R Package Version 1.5-23). 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rgdal (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Bivand, R.; Rundel, C. Rgeos: Interface to Geometry Engine—Open Source (‘GEOS’) (R Package Version 0.5-5). 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=rgeos (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Bivand, R.; Lewin-Koh, N. maptools: Tools for Handling Spatial Objects (R Package Version 1.1-2). 2021. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=maptools (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Pebesma, E. Simple Features for R: Standardized Support for Spatial Vector Data. R J. 2018, 10, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auguie, B. gridExtra: Miscellaneous Functions for ‘Grid’ Graphics (R Package Version 2.3). 2017. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=gridExtra (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Grolemund, G.; Wickham, H. Dates and Times Made Easy with lubridate. J. Stat. Softw. 2011, 40, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H.; Seidel, D. scales: Scale Functions for Visualization (R package version 1.1.1). 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=scales (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Kassambara, A. ggpubr: ‘ggplot2′ Based Publication Ready Plots (R Package Version 0.4.0). 2020. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Buendia, A.; Teng, K.T.-Y.; Camino, E.; Dominguez, L.; Cruz-Lopez, F. Influence of multiple factors on hematologic reference intervals in horses residing in livery yards in Spain. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2021, 50, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, M.; Wickham, H. Tidymodels: A Collection of Packages for Modeling and Machine Learning Using Tidyverse Principles. 2020. Available online: https://www.tidymodels.org (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An {R} Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd, ed.; Sage: Newcastle on Tyne, UK, 2019; Available online: https://socialsciences.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Books/Companion/ (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- Akaike, H. Information Theory and an Extension of the Maximum Likelihood Principle. In Breakthroughs in Statistics: Foundations and Basic Theory; Kotz, S., Johnson, N.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 610–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council of Agriculture Executive Yuan. Animal Welfare White Paper. 2019. Available online: https://animal.coa.gov.tw/Frontend/Know/AnimalResource#tab1 (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Hawes, S.M.; Camacho, B.A.; Tedeschi, P.; Morris, K.N. Temporal trends in intake and outcome data for animal shelter and rescue facilities in Colorado from 2000 through 2015. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2019, 254, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanowski, G.N. A Fresh Look at Spay/Neuter Legislation: The Journey to a Middle Ground. J. Public Health Manag. Pract. 2012, 18, E24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L. Research and Analysis on the Enforcement of Animal Protection Law through Pet Registration and Sterilization. 2018. Available online: https://www.ly.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=6590&pid=170970 (accessed on 29 January 2022).
- Weiss, E.; Slater, M.; Garrison, L.; Drain, N.; Dolan, E.; Scarlett, J.M.; Zawistowsk, S.L. Large dog relinquishment to two municipal facilities in New York City and Washington, DC: Identifying targets for intervention. Animals 2014, 4, 409–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.-T. Many Pet Owners Abandon Their Pets, Claiming to Have Found Them. 2015. Available online: https://www.apatw.org/project-article/3739 (accessed on 28 March 2023).
- Morris, K.N.; Gies, D.L. Trends in intake and outcome data for animal shelters in a large U.S. Metropolitan area, 1989 to 2010. J. Appl. Anim. Welf. Sci. JAAWS 2014, 17, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taitung County Government. The Taitung County Animal Shelter and Animal Protection Education Center Opened. 2017. Available online: https://www.taitung.gov.tw/News_Content.aspx?n=13370&s=46449 (accessed on 31 August 2022).
- Taitung County Government. Operation Specifications of Stray Animal Shelter Management in Taitung County. 2018. Available online: https://law.taitung.gov.tw/LawContent.aspx?id=GL000070 (accessed on 25 March 2022).
- Fawcett, A. Is a One Welfare approach the key to addressing unintended harms and maximising benefits associated with animal shelters? J. Appl. Anim. Ethics Res. 2019, 1, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, J.S. Occupational Stress in Animal Shelter Workers. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bartram, D.J.; Baldwin, D.S. Veterinary surgeons and suicide: A structured review of possible influences on increased risk. Vet. Rec. 2010, 166, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, E.M.; LaLonde, C.M.; Reese, L.A. Compassion fatigue in animal care workers. Traumatology 2020, 26, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlf, V.I. Interventions for occupational stress and compassion fatigue in animal care professionals—A systematic review. Traumatology 2018, 24, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiesman, H.M.; Konda, S.; Hartley, D.; Menéndez, C.C.; Ridenour, M.; Hendricks, S. Suicide in US workplaces, 2003–2010: A comparison with non-workplace suicides. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 48, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy-Gerlach, J.; Ojha, M.; Arkow, P. Social workers in animal shelters: A strategy toward reducing occupational stress among animal shelter workers. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 734396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Indicators | Equations | Covariates |
|---|---|---|
| PI | (a) year, (b) county, (c) administrative division, (d) geographical divisions, (e) GDP, (f) population, (g) higher education, (h) plain area of a county, (i) population density over the plain area, (j) population density, (k) fertility rate, and (l) euthanasia | |
| PO | ||
| PA | ||
| PD | (a) year, (b) county, (c) administrative division, (d) geographical divisions, (e) higher education, and (f) euthanasia |
| Indicators | Equations | Covariates |
|---|---|---|
| PI | (a) year, (b) month, (c) county, (d) administrative division, (e) geographical divisions, (f) GDP, (g) population, (h) higher education, (i) plain area of a county, (j) population density over the plain area, (k) population density, (l) fertility rate, (m) stray dogs, (n) total pets, (o) total managers, (p) total ACOs, (q) total vets, (r) working day | |
| PO | ||
| PA | ||
| WV | (a) year, (b) month, (c) county, (d) administrative division, (e) geographical divisions |
| Covariate | Category | Estimate (95% CI 1) | p-Value | p-Value for the Covariate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Intercept | 146.56 (127.02 to 166.09) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Year | −15.70 (−19.81 to −11.60) | <0.001 | ||
| County | Intercept (Taipei) | 56.38 (12.71 to 100.05) | 0.012 | <0.001 |
| Chiayi County | 114.41 (52.65 to 176.17) | <0.001 | ||
| Chiayi City | −3.69 (−65.45 to 58.07) | 0.907 | ||
| Changhua County | 47.53 (−14.23 to 109.30) | 0.133 | ||
| Hsinchu County | 49.37 (−12.40 to 111.13) | 0.119 | ||
| Hsinchu City | −37.07 (−98.83 to 24.70) | 0.241 | ||
| Hualien County | 69.70 (7.94 to 131.46) | 0.028 | ||
| Kaohsiung | −0.71 (−62.47 to 61.05) | 0.982 | ||
| Keelung County | 7.58 (−54.18 to 69.34) | 0.810 | ||
| Kinmen and Lienchiang County | −32.01 (−93.77 to 29.75) | 0.311 | ||
| Miaoli County | 3.90 (−57.86 to 65.66) | 0.902 | ||
| Nantou County | 10.20 (−51.56 to 71.96) | 0.747 | ||
| New Taipei | −16.68 (−78.44 to 45.08) | 0.597 | ||
| Penghu County | −40.66 (−102.42 to 21.11) | 0.199 | ||
| Pingtung County | 211.52 (149.76 to 273.28) | <0.001 | ||
| Taichung | 69.70 (7.94 to 131.46) | 0.028 | ||
| Tainan | 43.29 (−18.47 to 105.05) | 0.171 | ||
| Taitung County | 51.43 (−10.33 to 113.20) | 0.105 | ||
| Taoyuan | 9.74 (−52.02 to 71.51) | 0.758 | ||
| Yilan County | 9.20 (−52.56 to 70.96) | 0.771 | ||
| Yunlin County | 7.90 (−53.86 to 69.66) | 0.802 | ||
| Administrative division 2 | Intercept (County) | 113.89 (97.66 to 130.13) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| City | −68.58 (−102.38 to −34.77) | <0.001 | ||
| Metropolis | −39.96 (−66.48 to −13.44) | 0.004 | ||
| Outer island | −93.85 (−133.63 to −54.07) | <0.001 | ||
| Geographical division 3 | Intercept (West) | 84.22 (61.43 to 107.02) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| East | 32.72 (−9.92 to 75.36) | 0.134 | ||
| North | −24.68 (−54.52 to 5.16) | 0.107 | ||
| Outer island | −64.18 (−106.82 to −21.54) | 0.004 | ||
| South | 45.12 (12.89 to 77.35) | 0.007 | ||
| GDP 4 | Intercept | 545.72 (423.40 to 668.04) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Every 1000 New Taiwan Dollar | −0.63 (−0.79 to −0.46) | <0.001 | ||
| Population | Intercept | 86.51 (69.21 to 103.81) | <0.001 | 0.662 |
| Every 100,000 people | −0.25 (−1.35 to 0.86) | 0.662 | ||
| Higher education 5 | Intercept | 172.33 (132.46 to 212.20) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| % | −2.31 (−3.30 to −1.31) | <0.001 | ||
| Plain area of a county | Intercept | 49.51 (31.91 to 67.11) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| 10 km2 | 0.74 (0.45 to 1.03) | <0.001 | ||
| Population density over the plain area | Intercept | 90.60 (76.88 to 104.33) | <0.001 | 0.048 |
| 100,000 people/1 km2 | −1.14 (−2.25E to −0.02) | 0.048 | ||
| Population density | Intercept | 96.23 (81.73 to 110.72) | <0.001 | 0.004 |
| Person/1 km2 | −0.01 (−0.01 to −2.59E−03) | 0.004 | ||
| Fertility rate | Intercept | 144.94 (81.29 to 208.60) | <0.001 | 0.057 |
| ‰ | −1.90 (−3.84 to 0.04) | 0.057 | ||
| Euthanasia 6 | Intercept (No) | 40.55 (24.44 to 56.66) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Yes | 77.75 (56.14 to 99.36) | <0.001 |
| Dataset 1 (2012–2020) | ||
| Indicators | Covariates | Adjusted R2 |
| PI | (a) year (estimate: −0.08, 95% CI: −0.12 to −0.05) | 0.88 |
| (b) county | ||
| (c) euthanasia (estimate: 0.19, 95% CI: −0.26 to 0.63) | ||
| (d) county: euthanasia | ||
| PO | (a) year (estimate: −0.09, 95% CI: −0.11 to −0.06) | 0.93 |
| (b) county | ||
| (c) euthanasia (estimate: 0.11, 95% CI: −0.25 to 0.47) | ||
| (d) county: euthanasia | ||
| PA | (a) year (estimate: 5.11, 95% CI: 3.79 to 6.43) | 0.47 |
| (b) county | ||
| (c) fertility rate (estimate: 1.10, 95% CI: 0.21 to 2.00) | ||
| PD | (a) year (estimate: −0.06, 95% CI: −0.34 to 0.21) | 0.66 |
| (b) county | ||
| (c) year: county | ||
| Dataset 2 (2018–2020) | ||
| Indicators | Covariates | Adjusted R2 |
| PI | (a) year (estimate: 0.04, 95% CI: −0.53 to 0.62) | 0.76 |
| (b) county | ||
| (c) working day (estimate: 0.05, 95% CI: 0.04 to 0.06) | ||
| (d) year2 (estimate: −0.07, 95% CI: −0.34 to 0.21) | ||
| (e) year: county | ||
| (f) year2: county | ||
| PO | (a) year (estimate: −0.06, 95% CI: −0.67 to 0.54) | 0.76 |
| (b) county | ||
| (c) working day (estimate: 0.05, 95% CI: 0.03 to 0.06) | ||
| (d) year2 (estimate: −3.04E−03, 95% CI: −0.29 to 0.29) | ||
| (e) year: county | ||
| (f) year2: county | ||
| PA | (a) year (estimate: −0.76, 95% CI: −1.77 to 0.26) | 0.77 |
| (b) county | ||
| (c) working day (estimate: 0.03, 95% CI: 0.01 to 0.06) | ||
| (d) year2 (estimate: 0.15, 95% CI: −0.34 to 0.63) | ||
| (e) year: county | ||
| (f) year2: county | ||
| WV | (a) year (estimate: −0.13, 95% CI: −0.29 to 0.03) | 0.70 |
| (b) month | ||
| (c) county | ||
| (d) year: county | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, T.-Y.; Teng, K.T.-y. Trends in Animal Shelter Management, Adoption, and Animal Death in Taiwan from 2012 to 2020. Animals 2023, 13, 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091451
Yan T-Y, Teng KT-y. Trends in Animal Shelter Management, Adoption, and Animal Death in Taiwan from 2012 to 2020. Animals. 2023; 13(9):1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091451
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Tzu-Yun, and Kendy Tzu-yun Teng. 2023. "Trends in Animal Shelter Management, Adoption, and Animal Death in Taiwan from 2012 to 2020" Animals 13, no. 9: 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091451
APA StyleYan, T.-Y., & Teng, K. T.-y. (2023). Trends in Animal Shelter Management, Adoption, and Animal Death in Taiwan from 2012 to 2020. Animals, 13(9), 1451. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091451





