Extraction and Elevation of Cell-Free DNA under Mastitis and Heat Stress in Dairy Cattle
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
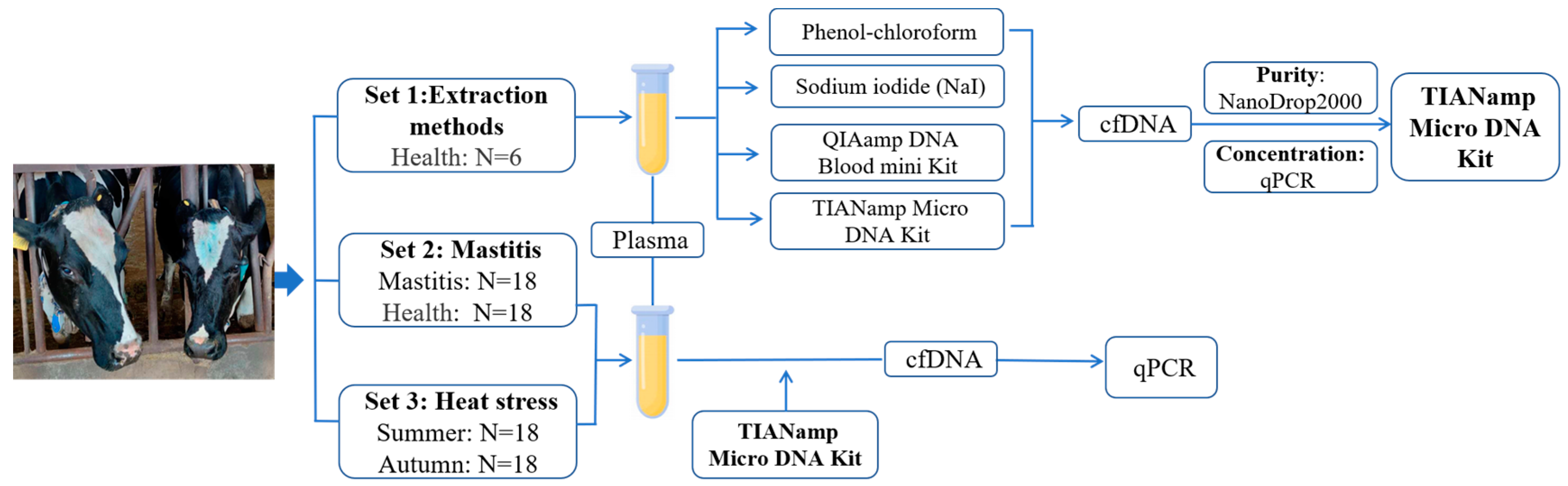
2.1. Animals’ Selection and Sampling
2.2. Extraction of cfDNA
2.3. Quantification of cfDNA
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Extraction Methods for cfDNA from Cattle Blood
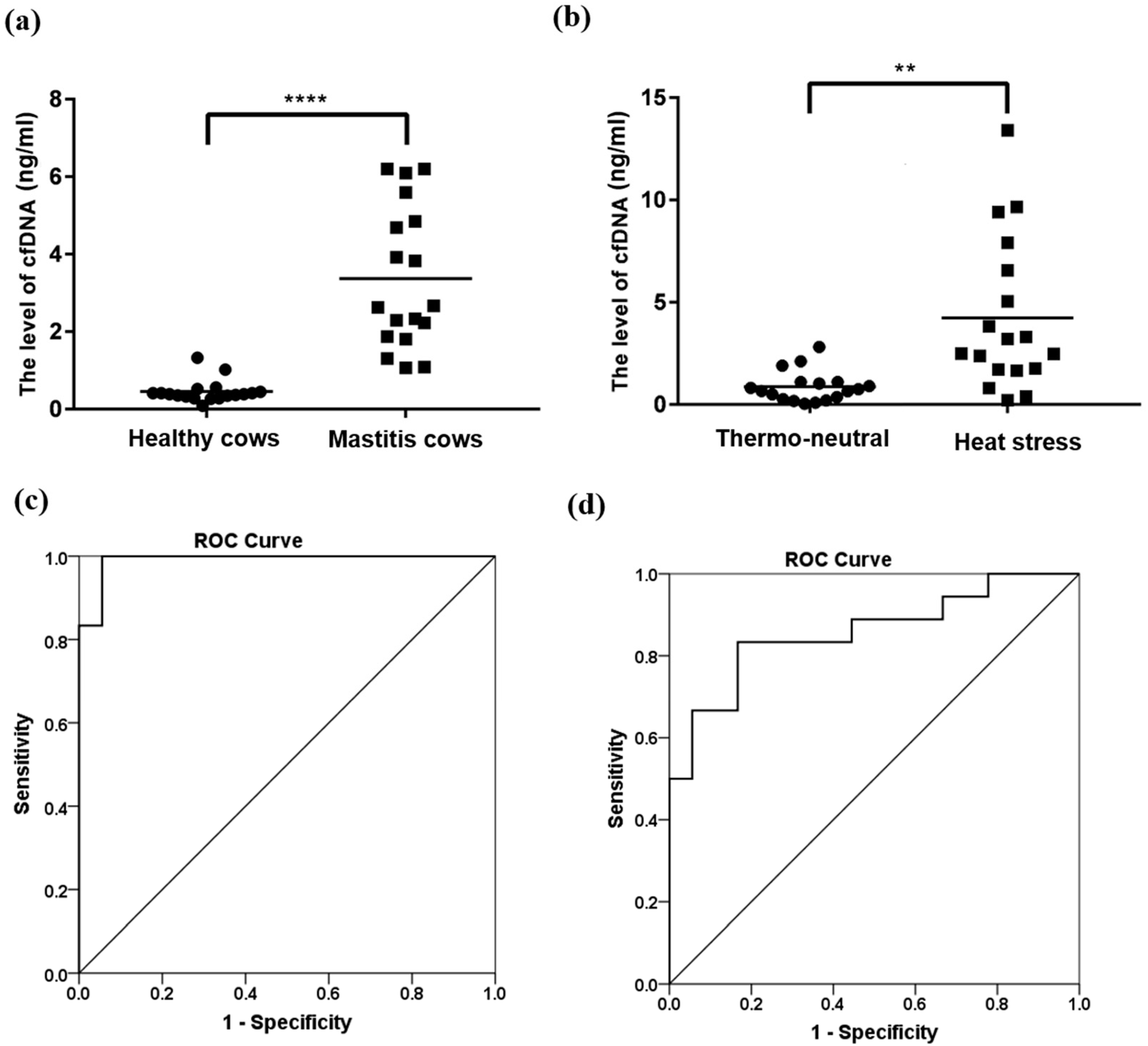
3.2. Effect of Mastitis and Heat Stress on the cfDNA Level in Cattle Blood
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Der Vaart, M.; Pretorius, P.J. The Origin of Circulating Free DNA. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilágyi, M.; Pös, O.; Márton, É.; Buglyó, G.; Soltész, B.; Keserű, J.; Penyige, A.; Szemes, T.; Nagy, B. Circulating Cell-Free Nucleic Acids: Main Characteristics and Clinical Application. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Hills, A.; Page, K.; Hastings, R.K.; Toghill, B.; Goddard, K.S.; Ion, C.; Ogle, O.; Boydell, A.R.; Gleason, K.; et al. Plasma Cell-Free DNA (CfDNA) as a Predictive and Prognostic Marker in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valpione, S.; Gremel, G.; Mundra, P.; Middlehurst, P.; Galvani, E.; Girotti, M.R.; Lee, R.J.; Garner, G.; Dhomen, N.; Lorigan, P.C.; et al. Plasma Total Cell-Free DNA (CfDNA) Is a Surrogate Biomarker for Tumour Burden and a Prognostic Biomarker for Survival in Metastatic Melanoma Patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 88, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldwaser, T.; Klugman, S. Cell-Free DNA for the Detection of Fetal Aneuploidy. Fertil. Steril. 2018, 109, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Liu, Y.; Sun, C.; Liang, H.; Dai, L.; Shen, J.; Wei, S.; Guo, S.; Leong, K.W.; Chen, Y.; et al. Identification of Specific Joint-Inflammatogenic Cell-Free DNA Molecules From Synovial Fluids of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Song, Y.; Chang, J.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Q.; Tian, X.; Li, M.; Zeng, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; et al. High Levels of Circulating Cell-Free DNA Are a Biomarker of Active SLE. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e13015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruegg, P.L. A 100-Year Review: Mastitis Detection, Management, and Prevention. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 10381–10397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjitkar, S.; Bu, D.; Van Wijk, M.; Ma, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhao, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, C.; Xu, J. Will Heat Stress Take Its Toll on Milk Production in China? Clim. Chang. 2020, 161, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.M.; Schur, P.H.; Carr, R.I.; Kunkel, H.G. Deoxybonucleic Acid (DNA) and Antibodies to DNA in the Serum of Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. J. Clin. Investig. 1966, 45, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagath, M.; Krishnan, G.; Devaraj, C.; Rashamol, V.P.; Pragna, P.; Lees, A.M.; Sejian, V. The Impact of Heat Stress on the Immune System in Dairy Cattle: A Review. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 126, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabenishi, H.; Yamazaki, A. Effects of Temperature-Humidity Index on Health and Growth Performance in Japanese Black Calves. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warton, K.; Graham, L.J.; Yuwono, N.; Samimi, G. Comparison of 4 Commercial Kits for the Extraction of Circulating DNA from Plasma. Cancer Genet. 2018, 228–229, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bökenkamp, A.; Wijk, J.V.; Bouman, A.A.; Spreeuwenberg, M.; Stoffel-Wagner, B. The Origin of Circulating Free DNA. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 2215. [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Vaart, M.; Pretorius, P.J. Circulating DNA. Its Origin and Fluctuation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1137, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Teare, M.D.; Holen, I.; Zhu, Y.M.; Woll, P.J. Optimizing the Yield and Utility of Circulating Cell-Free DNA from Plasma and Serum. Clin. Chim. Acta 2009, 404, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischhacker, M.; Schmidt, B.; Weickmann, S.; Fersching, D.M.I.; Leszinski, G.S.; Siegele, B.; Stötzer, O.J.; Nagel, D.; Holdenrieder, S. Methods for Isolation of Cell-Free Plasma DNA Strongly Affect DNA Yield. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 2085–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeze, A.; van der Meer, A.J.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; Ait Soussan, A.; van der Schoot, C.E.; Wuillemin, W.A.; Voermans, C.; van der Poll, T.; Zeerleder, S.S. Systemic Inflammation Induces Release of Cell-Free DNA from Hematopoietic and Parenchymal Cells in Mice and Human. Blood 2018, 132, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Chu, C.; Gui, X.; Li, J.; Chen, Q. The Prognostic Value of Circulating Cell-Free DNA in Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e0197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Bae, H.; Ahn, S.; Shin, S.; Cho, A.; Cho, K.W.; Jung, D.I.; Yu, D.H. Cell-Free DNA as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Dogs With Tumors. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 735682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J.; Beck, J.; Soller, J.T.; Wemheuer, W.; Schütz, E.; Brenig, B. Analysis of Circulating DNA Distribution in Pregnant and Nonpregnant Dairy Cows. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 88, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, J.; Soller, J.T.; Beck, J.; Purwins, V.; Wemheuer, W.; Schütz, E.; Brenig, B. Early Pregnancy Diagnosis in Dairy Cows Using Circulating Nucleic Acids. Theriogenology 2013, 79, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, P.M.K.; Schütz, E.; Beck, J.; Urnovitz, H.B.; Graham, C.; Clark, R.; Dudas, S.; Czub, S.; Sensen, M.; Brenig, B.; et al. Disease-Specific Motifs Can Be Identified in Circulating Nucleic Acids from Live Elk and Cattle Infected with Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manueldas, S.; Benterud, T.; Rueegg, C.S.; Garberg, H.T.; Huun, M.U.; Pankratov, L.; Åsegg-Atneosen, M.; Solberg, R.; Escobar, J.; Saugstad, O.D.; et al. Temporal Patterns of Circulating Cell-Free DNA (CfDNA) in a Newborn Piglet Model of Perinatal Asphyxia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filev, A.D.; Shmarina, G.V.; Ershova, E.S.; Veiko, N.N.; Martynov, A.V.; Borzikova, M.A.; Poletkina, A.A.; Dolgikh, O.A.; Veiko, V.P.; Bekker, A.A.; et al. Oxidized Cell-Free DNA Role in the Antioxidant Defense Mechanisms under Stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1245749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek dos Reis, C.B.; Barreiro, J.R.; Moreno, J.F.G.; Porcionato, M.A.F.; Santos, M.V. Evaluation of Somatic Cell Count Thresholds to Detect Subclinical Mastitis in Gyr Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 4406–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Hu, L.; Fang, H.; Sammad, A.; Kang, L.; Brito, L.F.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y. Association Analysis of Polymorphisms in the 5’ Flanking Region of the HSP70 Gene with Blood Biochemical Parameters of Lactating Holstein Cows under Heat and Cold Stress. Animals 2020, 10, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Kang, L.; Abbas, Z.; Hu, L.; Chen, Y.; Tan, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Q. Identification of Key Genes and Pathways Associated with Thermal Stress in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Holstein Dairy Cattle. Front. Genet. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, R.; Koledić, M.; Maćešić, N.; Benić, M.; Dobranić, V.; Đuričić, D.; Cvetnić, L.; Samardžija, M. Uloga Oksidacijskog Stresa i Upalnog Odgovora u Patogenezi Mastitisa u Mliječnih Krava. Mljekarstvo 2017, 67, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, J.S.; Bhatti, G.K.; Reddy, P.H. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Disorders—A Step towards Mitochondria Based Therapeutic Strategies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 1066–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Li, J.-J.; Wang, D.-Q.; Li, G.-Q.; Wang, G.-L.; Lu, L.-Z. Effects of Heat Stress on Antioxidant Defense System, Inflammatory Injury, and Heat Shock Proteins of Muscovy and Pekin Ducks: Evidence for Differential Thermal Sensitivities. Cell Stress Chaperones 2014, 19, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Method | Quantitative Real-Time PCR | NanoDrop2000 |
|---|---|---|
| cfDNA Yield (Mean ± SD, ng/mL) | cfDNA Purity (A260/280) | |
| Phenol-chloroform | 0.36 ± 0.16 a | 0.67 ± 0.15 a |
| Sodium iodide (NaI) | 0.49 ± 0.13 a | 1.01 ± 0.06 a |
| QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit | 0.79 ± 0.14 b | 1.31 ± 0.17 b |
| TIANamp Micro DNA Kit | 0.84 ± 0.16 b | 1.80 ± 0.25 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Abbas, Z.; Hu, L.; Kang, L.; Tan, X.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y. Extraction and Elevation of Cell-Free DNA under Mastitis and Heat Stress in Dairy Cattle. Animals 2023, 13, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091487
Chen Y, Abbas Z, Hu L, Kang L, Tan X, Xu Q, Wang Y. Extraction and Elevation of Cell-Free DNA under Mastitis and Heat Stress in Dairy Cattle. Animals. 2023; 13(9):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091487
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yumei, Zaheer Abbas, Lirong Hu, Ling Kang, Xiao Tan, Qing Xu, and Yachun Wang. 2023. "Extraction and Elevation of Cell-Free DNA under Mastitis and Heat Stress in Dairy Cattle" Animals 13, no. 9: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091487
APA StyleChen, Y., Abbas, Z., Hu, L., Kang, L., Tan, X., Xu, Q., & Wang, Y. (2023). Extraction and Elevation of Cell-Free DNA under Mastitis and Heat Stress in Dairy Cattle. Animals, 13(9), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani13091487







