Establishment of Primary Cell Cultures from Canine Oral Melanomas via Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Novel Tool for Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression Studies
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Cell Characterization
3. Results
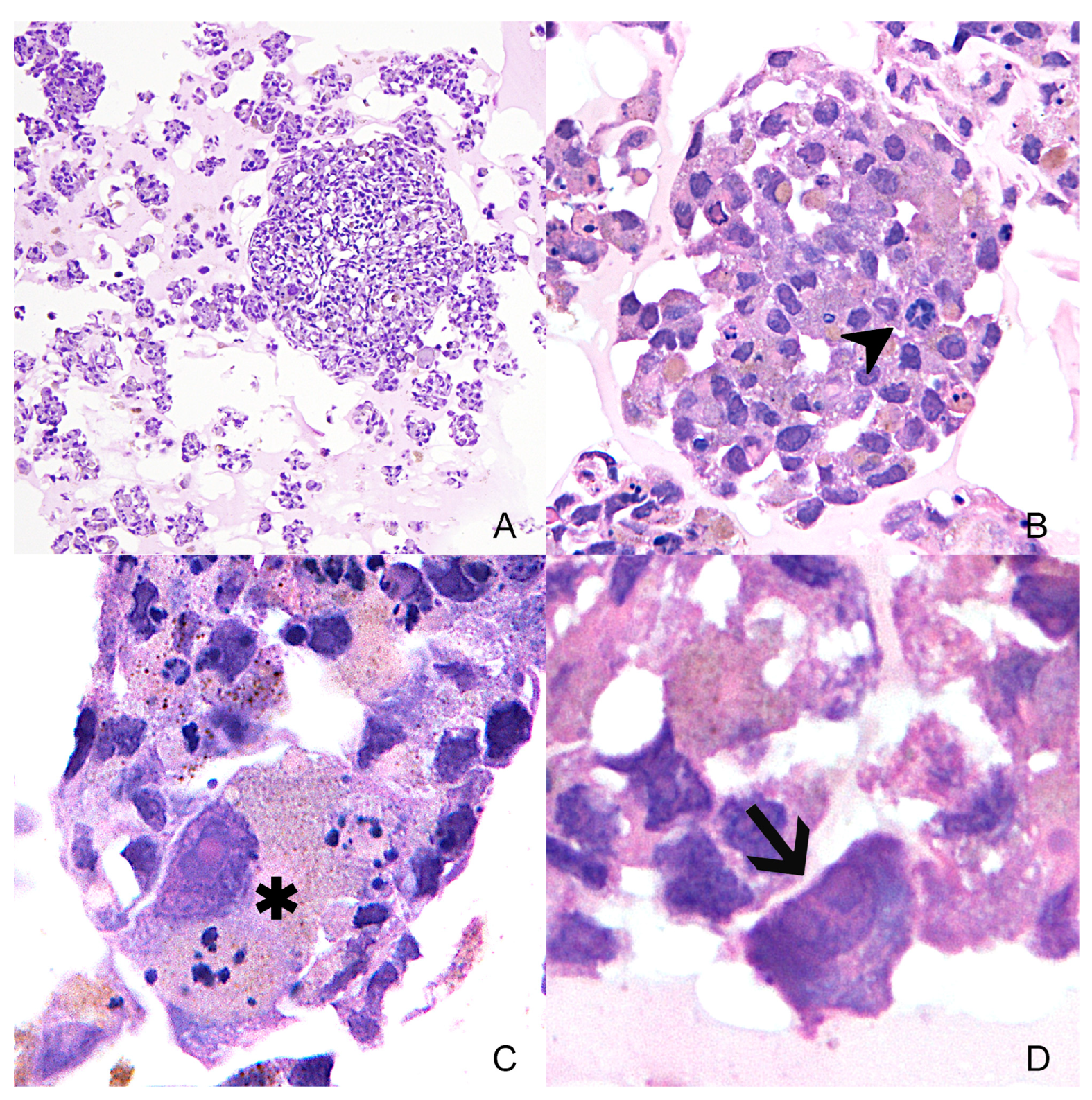
3.1. Case Study
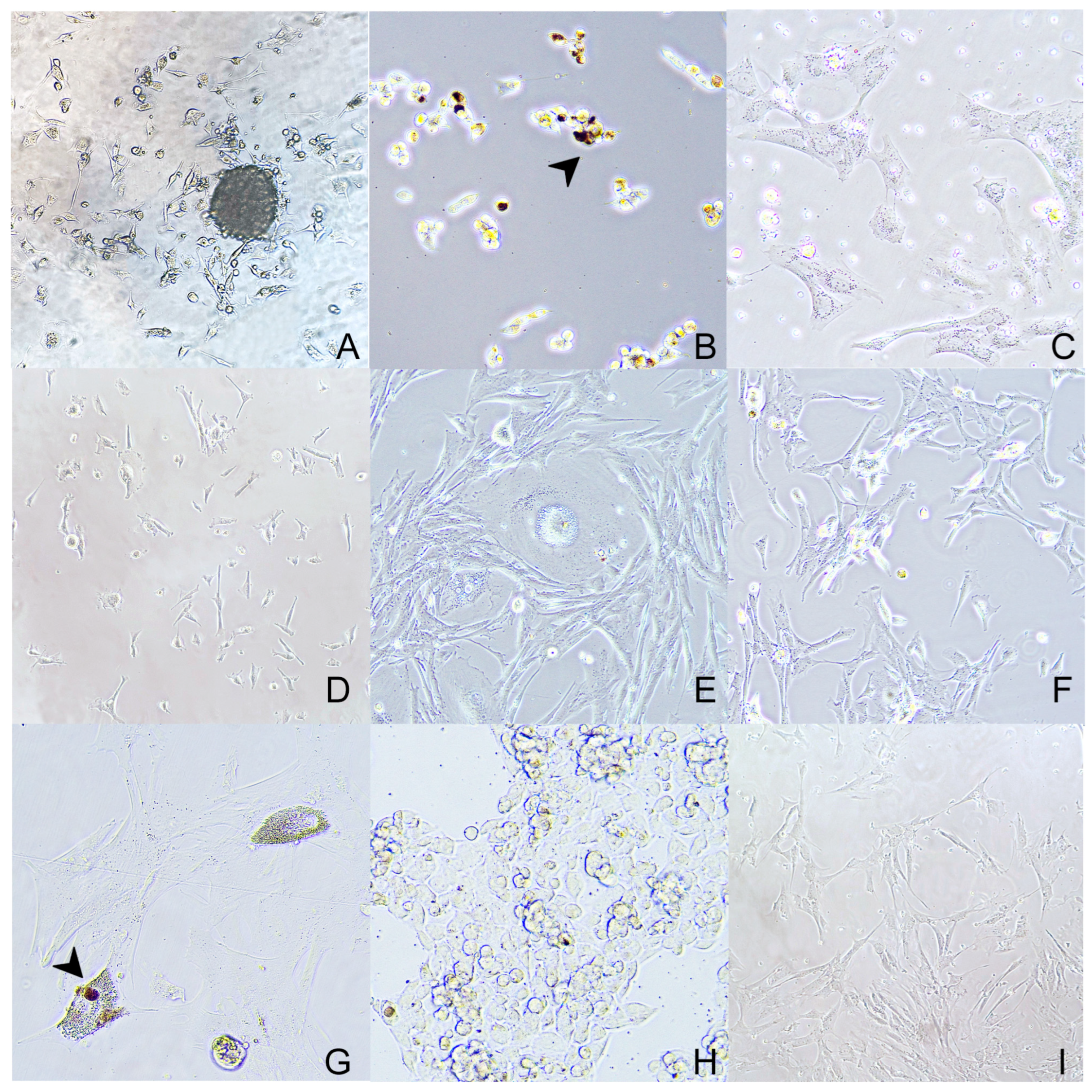
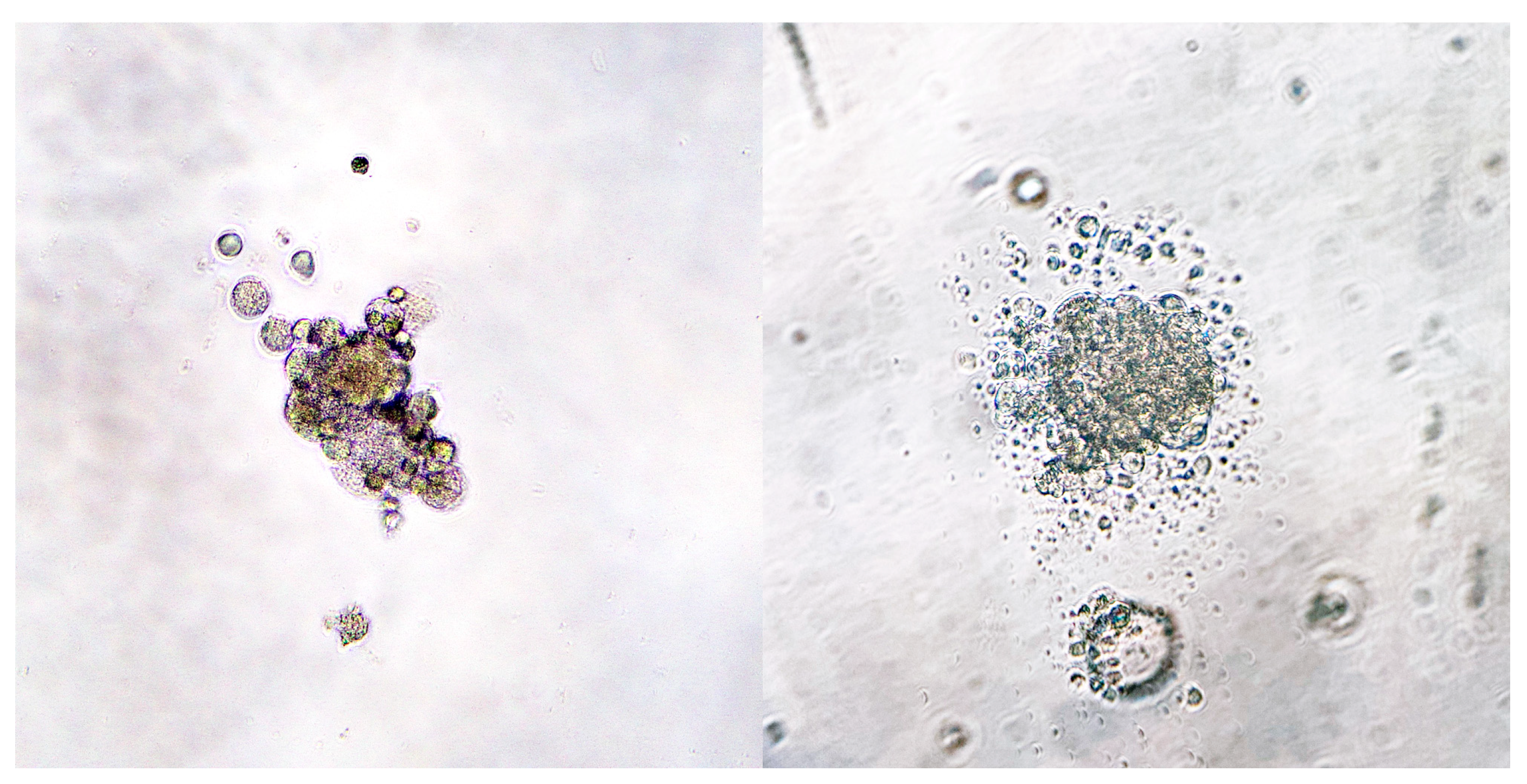
3.2. Primary Cell Culture
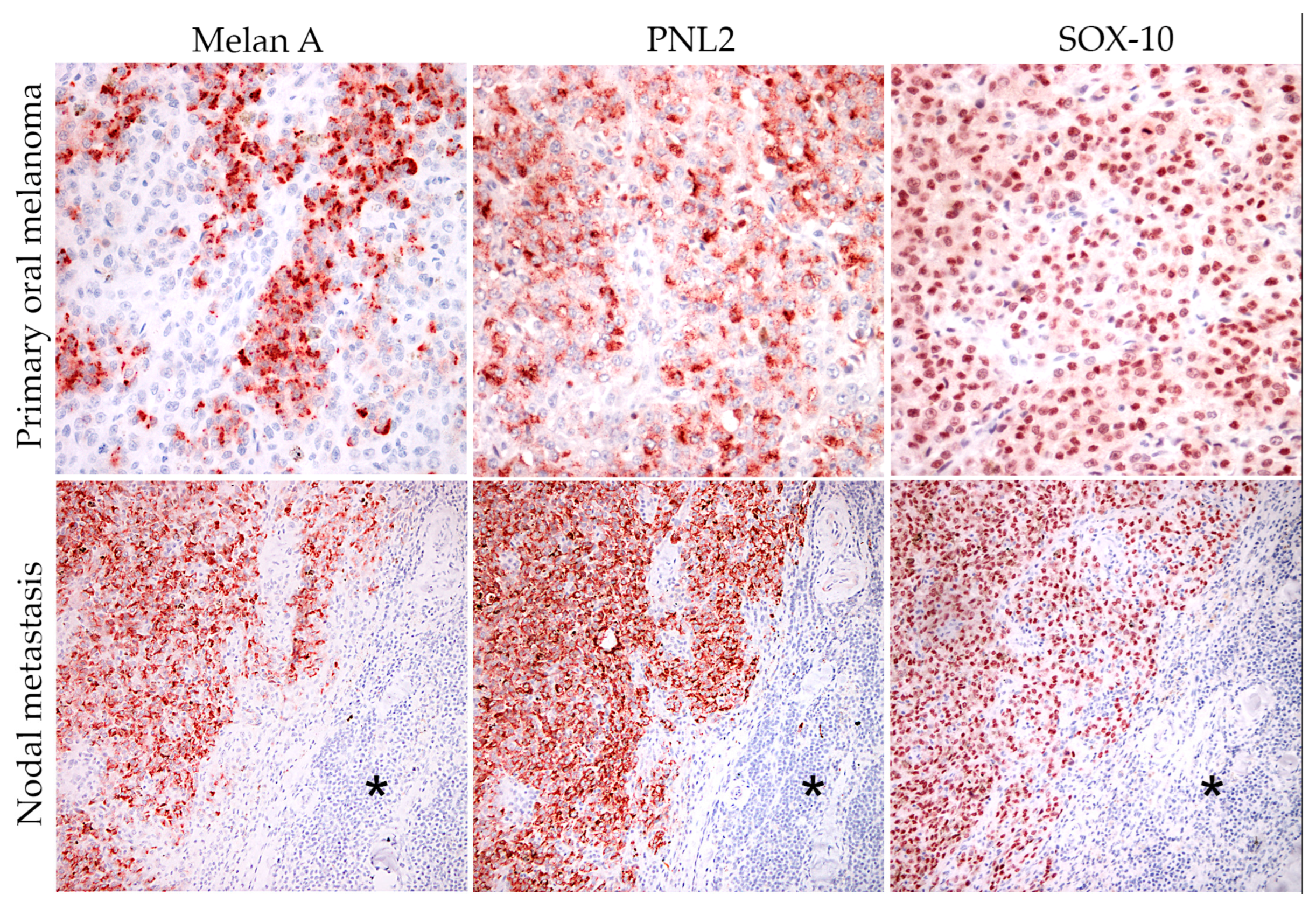
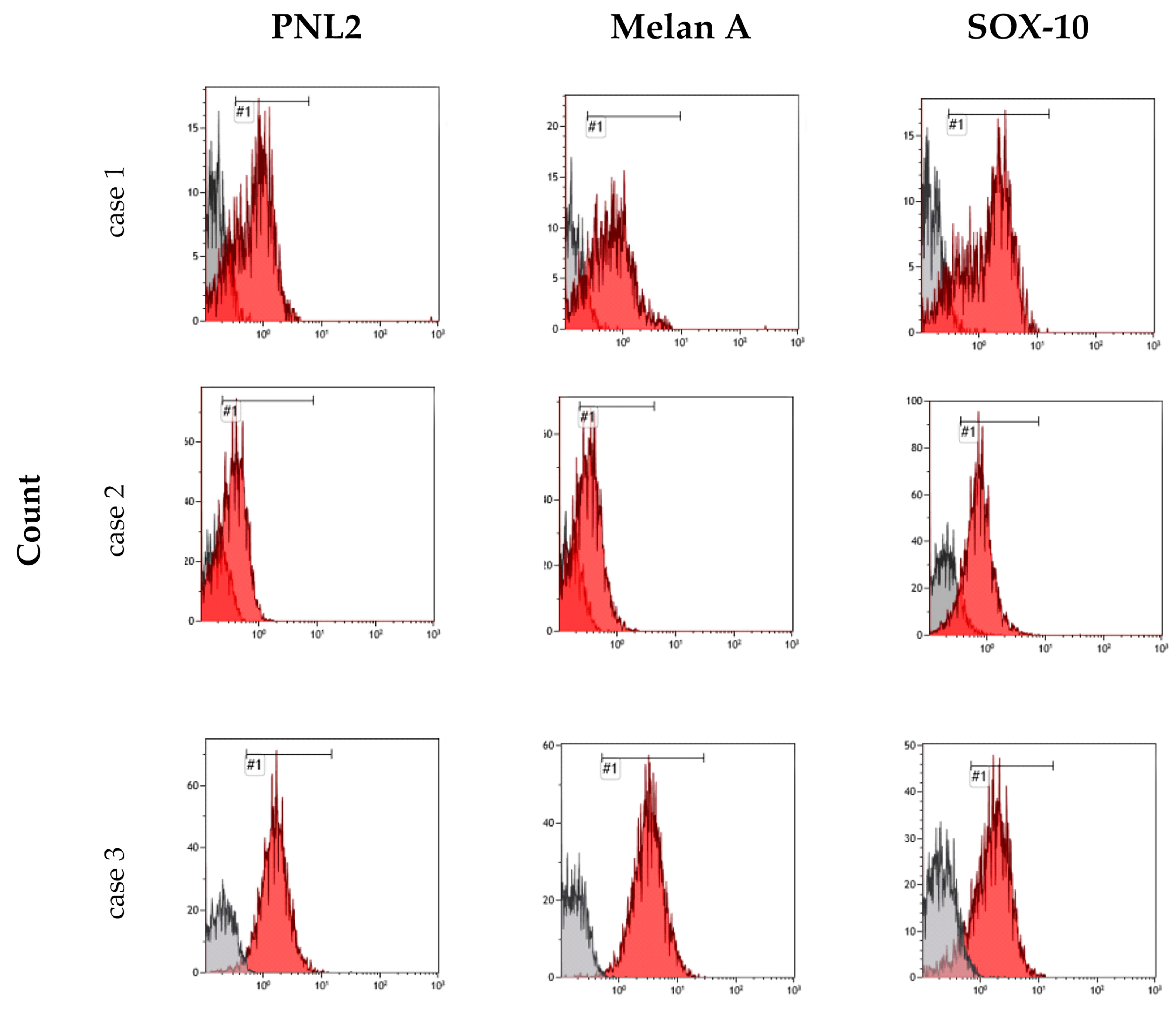
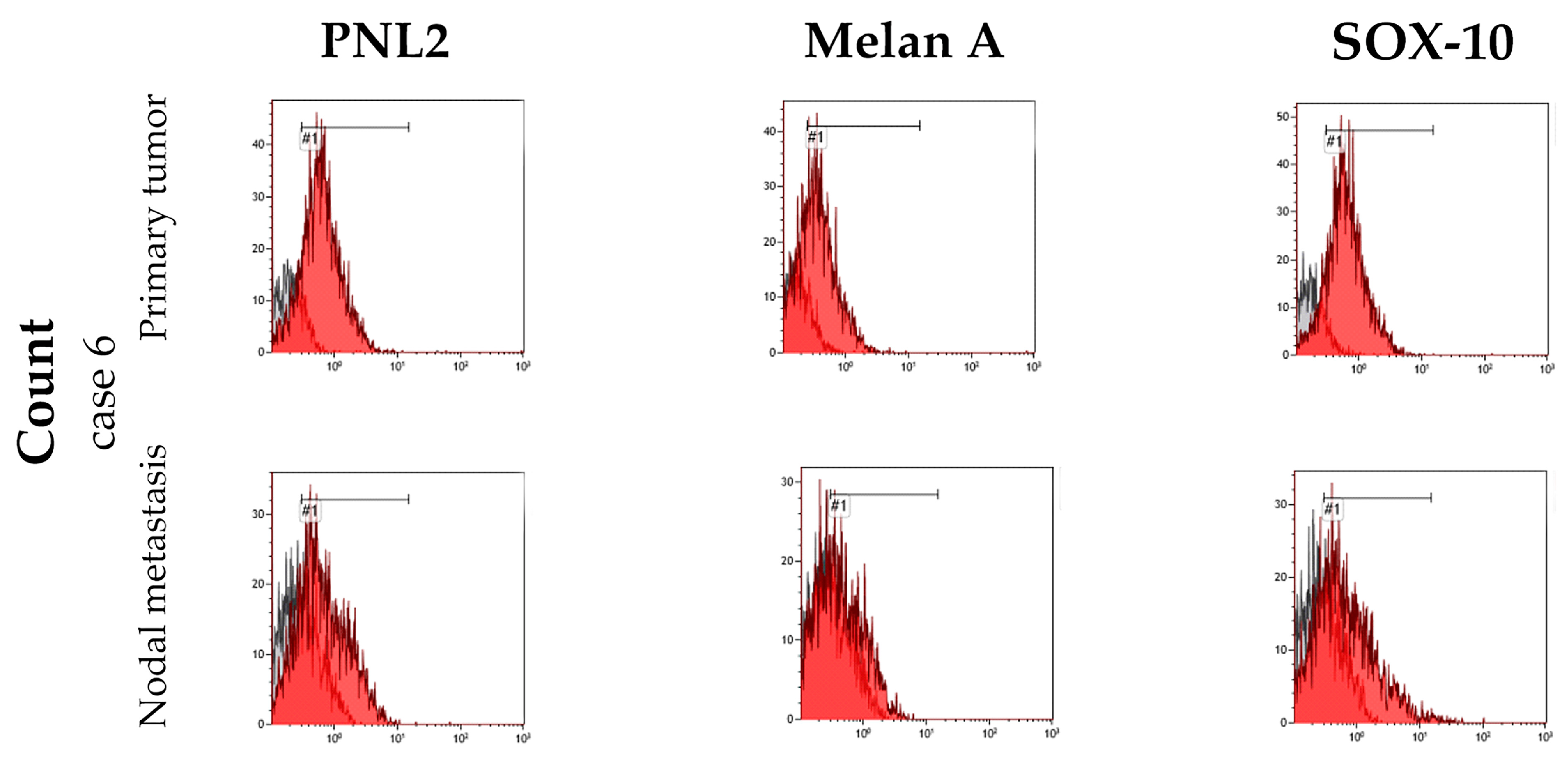
3.3. Cell Culture Characterization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacVean, D.W.; Monlux, A.W.; Anderson, P.S.; Silberg, S.L.; Roszel, J.F. Frequency of Canine and Feline Tumors in a Defined Population. Vet. Pathol. 1978, 15, 700–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cray, M.; Selmic, L.E.; Ruple, A. Demographics of Dogs and Cats with Oral Tumors Presenting to Teaching Hospitals: 1996–2017. J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 21, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, R.C.; Spangler, W.L.; Esplin, D.G.; Kitchell, B.E.; Bergman, P.J.; Ho, H.-Y.; Bergin, I.L.; Kiupel, M. Prognostic Markers for Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms: A Comparative Review of the Literature and Goals for Future Investigation. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.H.; Goldschmidt, M.H.; McManus, P.M. A Comparative Review of Melanocytic Neoplasms. Vet. Pathol. 2002, 39, 651–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, P.J. Canine Oral Melanoma. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 22, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, R.C.; Sebastian, K.; Kiupel, M. Diagnosis and Prognosis of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pazzi, P.; Steenkamp, G.; Rixon, A.J. Treatment of Canine Oral Melanomas: A Critical Review of the Literature. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellado, M.N.; Maglietti, F.H.; Michinski, S.D.; Marshall, G.R.; Signori, E. Electrochemotherapy in Treatment of Canine Oral Malignant Melanoma and Factors Influencing Treatment Outcome. Radiol. Oncol. 2020, 54, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardo, F.; Tarone, L.; Camerino, M.; Giacobino, D.; Iussich, S.; Barutello, G.; Arigoni, M.; Conti, L.; Bolli, E.; Quaglino, E.; et al. Antigen Mimicry as an Effective Strategy to Induce CSPG4-Targeted Immunity in Dogs with Oral Melanoma: A Veterinary Trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A.; Karapetyan, L.; Kirkwood, J.M. Immunotherapy in Melanoma: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Cancers 2023, 15, 1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, L.A.; Riccardo, F.; Iussich, S.; Maniscalco, L.; Gattino, F.; Martano, M.; Morello, E.; Lorda Mayayo, S.; Rolih, V.; Garavaglia, F.; et al. Prolongation of Survival of Dogs with Oral Malignant Melanoma Treated by En Bloc Surgical Resection and Adjuvant CSPG4-antigen Electrovaccination. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 996–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giacobino, D.; Camerino, M.; Riccardo, F.; Cavallo, F.; Tarone, L.; Martano, M.; Dentini, A.; Iussich, S.; Lardone, E.; Franci, P.; et al. Difference in Outcome between Curative Intent vs Marginal Excision as a First Treatment in Dogs with Oral Malignant Melanoma and the Impact of Adjuvant CSPG4-DNA Electrovaccination: A Retrospective Study on 155 Cases. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2021, 19, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turek, M.; LaDue, T.; Looper, J.; Nagata, K.; Shiomitsu, K.; Keyerleber, M.; Buchholz, J.; Gieger, T.; Hetzel, S. Multimodality Treatment Including ONCEPT for Canine Oral Melanoma: A Retrospective Analysis of 131 Dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2020, 61, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, V.B.; Klahn, S.; LeRoith, T.; Huckle, W.R. Canine Melanoma: A Review of Diagnostics and Comparative Mechanisms of Disease and Immunotolerance in the Era of the Immunotherapies. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 9, 1046636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Cardeza, M.L.; Villaverde, M.S.; Fiszman, G.L.; Altamirano, N.A.; Cwirenbaum, R.A.; Glikin, G.C.; Finocchiaro, L.M.E. Suicide Gene Therapy on Spontaneous Canine Melanoma: Correlations between in Vivo Tumors and Their Derived Multicell Spheroids in Vitro. Gene Ther. 2010, 17, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouteau, A.; André, C. Canine Melanomas as Models for Human Melanomas: Clinical, Histological, and Genetic Comparison. Genes 2019, 10, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliano, A. Companion Animal Model in Translational Oncology; Feline Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Canine Oral Melanoma. Biology 2021, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, B.; Adissu, H.; Wei, B.-R.; Michael, H.; Merlino, G.; Simpson, R. Naturally Occurring Canine Melanoma as a Predictive Comparative Oncology Model for Human Mucosal and Other Triple Wild-Type Melanomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarone, L.; Barutello, G.; Iussich, S.; Giacobino, D.; Quaglino, E.; Buracco, P.; Cavallo, F.; Riccardo, F. Naturally Occurring Cancers in Pet Dogs as Pre-Clinical Models for Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 1839–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiya, A.; Massoco, C.; Felizzola, C.; Perlmann, E.; Batschinski, K.; Tedardi, M.; Garcia, J.; Mendonça, P.; Teixeira, T.; Zaidan Dagli, M. Comparative Aspects of Canine Melanoma. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcellato, I.; Sforna, M.; Lo Giudice, A.; Bossi, I.; Musi, A.; Tognoloni, A.; Chiaradia, E.; Mechelli, L.; Brachelente, C. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Canine Oral and Cutaneous Melanomas and Melanocytomas: Phenotypic and Prognostic Assessment. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 878949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcellato, I.; Silvestri, S.; Menchetti, L.; Recupero, F.; Mechelli, L.; Sforna, M.; Iussich, S.; Bongiovanni, L.; Lepri, E.; Brachelente, C. Tumour-infiltrating Lymphocytes in Canine Melanocytic Tumours: An Investigation on the Prognostic Role of CD3+ and CD20+ Lymphocytic Populations. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcellato, I.; Brachelente, C.; De Paolis, L.; Menchetti, L.; Silvestri, S.; Sforna, M.; Vichi, G.; Iussich, S.; Mechelli, L. FoxP3 and IDO in Canine Melanocytic Tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2019, 56, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, N.; Konnai, S.; Asano, Y.; Sajiki, Y.; Deguchi, T.; Okagawa, T.; Watari, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Takagi, S.; Hosoya, K.; et al. Exploration of Serum Biomarkers in Dogs with Malignant Melanoma Receiving Anti-PD-L1 Therapy and Potential of COX-2 Inhibition for Combination Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasumaru, C.C.; Xavier, J.G.; Strefezzi, R.D.F.; Salles-Gomes, C.O.M. Intratumoral T-Lymphocyte Subsets in Canine Oral Melanoma and Their Association with Clinical and Histopathological Parameters. Vet. Pathol. 2021, 58, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, S.H.; Ku, J.-L.; Chun, J.W.; Seo, H.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Paik, W.H.; Ryu, J.K.; Lee, S.K.; et al. Establishment of Patient-Derived Pancreatic Cancer Organoids from Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsies. Gut Liver 2022, 16, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, H.; Chung, M.J.; Park, J.Y.; Park, S.W.; Song, S.Y.; Bang, S. Establishment of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines with Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Biopsy via Conditionally Reprogrammed Cell Culture. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 3339–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergdorf, K.; Phifer, C.; Bharti, V.; Westover, D.; Bauer, J.; Vilgelm, A.; Lee, E.; Weiss, V. High-Throughput Drug Screening of Fine-Needle Aspiration-Derived Cancer Organoids. STAR Protoc. 2020, 1, 100212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baregamian, N.; Sekhar, K.R.; Krystofiak, E.S.; Vinogradova, M.; Thomas, G.; Mannoh, E.; Solórzano, C.C.; Kiernan, C.M.; Mahadevan-Jansen, A.; Abumrad, N.; et al. Engineering Functional 3-Dimensional Patient-Derived Endocrine Organoids for Broad Multiplatform Applications. Surgery 2023, 173, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, A.; Ferrari, S.M.; Fallahi, P.; Berti, P.; Materazzi, G.; Barani, L.; Marchetti, I.; Ferrannini, E.; Miccoli, P. Primary Cell Cultures from Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer Obtained by Fine-needle Aspiration Used for Chemosensitivity Tests. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 69, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.W.; Paiva, V.; Gartner, F.; Amendoeira, I.; Martinez Oliveira, J.; Schmitt, F.C. Fine Needle Aspiration as a Tool To Establish Primary Human Breast Cancer Cultures in Vitro. Acta Cytol. 1999, 43, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, C.; Kusewitt, D.F. Comparison of Tyrosinase-Related Protein-2, S-100, and Melan A Immunoreactivity in Canine Amelanotic Melanomas. Vet. Pathol. 2003, 40, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, C.; Ceciliani, F.; Rondena, M.; Stefanello, D.; Grieco, V. Immunohistochemical Investigation of PNL2 Reactivity of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms and Comparison with Melan A. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedley, R.C.; Lamoureux, J.; Sledge, D.G.; Kiupel, M. Immunohistochemical Diagnosis of Canine Oral Amelanotic Melanocytic Neoplasms. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, M.F.; Thaiwong, T.; Smedley, R.C.; Noland, E.; Kiupel, M. Quantitative Expression of TYR, CD34, and CALD1 Discriminates Between Canine Oral Malignant Melanomas and Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 701457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polton, G.; Borrego, J.F.; Clemente-Vicario, F.; Clifford, C.A.; Jagielski, D.; Kessler, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Lanore, D.; Queiroga, F.L.; Rowe, A.T.; et al. Melanoma of the Dog and Cat: Consensus and Guidelines. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1359426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedley, R.C.; Bongiovanni, L.; Bacmeister, C.; Clifford, C.A.; Christensen, N.; Dreyfus, J.M.; Gary, J.M.; Pavuk, A.; Rowland, P.H.; Swanson, C.; et al. Diagnosis and Histopathologic Prognostication of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms: A Consensus of the Oncology-Pathology Working Group. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraiva, D.P.; Matias, A.T.; Braga, S.; Jacinto, A.; Cabral, M.G. Establishment of a 3D Co-Culture With MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cell Line and Patient-Derived Immune Cells for Application in the Development of Immunotherapies. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Taguchi, M.; Sumi, S.; Oka, K.; Okamura, K. Establishment of a Novel Protocol for Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded Organoids and Spheroids. Biol. Open 2023, 12, bio059882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phifer, C.J.; Bergdorf, K.N.; Bechard, M.E.; Vilgelm, A.; Baregamian, N.; McDonald, O.G.; Lee, E.; Weiss, V.L. Obtaining Patient-Derived Cancer Organoid Cultures via Fine-Needle Aspiration. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilgelm, A.E.; Bergdorf, K.; Wolf, M.; Bharti, V.; Shattuck-Brandt, R.; Blevins, A.; Jones, C.; Phifer, C.; Lee, M.; Lowe, C.; et al. Fine-Needle Aspiration-Based Patient-Derived Cancer Organoids. iScience 2020, 23, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sforna, M.; Chiaradia, E.; Porcellato, I.; Silvestri, S.; Moretti, G.; Mechelli, L.; Brachelente, C. Characterization of Primary Cultures of Normal and Neoplastic Canine Melanocytes. Animals 2021, 11, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segaoula, Z.; Primot, A.; Lepretre, F.; Hedan, B.; Bouchaert, E.; Minier, K.; Marescaux, L.; Serres, F.; Galiègue-Zouitina, S.; André, C.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Two Canine Melanoma Cell Lines: New Models for Comparative Oncology. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Ohashi, E.; Kadosawa, T.; Hong, S.-H.; Matsunaga, S.; Mochizuki, M.; Nishimura, R.; Sasaki, N. Establishment and Characterization of Four Canine Melanoma Cell Lines. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2004, 66, 1437–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonseca-Alves, C.E.; Ferreira, Ê.; De Oliveira Massoco, C.; Strauss, B.E.; Fávaro, W.J.; Durán, N.; Oyafuso Da Cruz, N.; Dos Santos Cunha, S.C.; Castro, J.L.C.; Rangel, M.M.M.; et al. Current Status of Canine Melanoma Diagnosis and Therapy: Report from a Colloquium on Canine Melanoma Organized by ABROVET (Brazilian Association of Veterinary Oncology). Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 707025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisjak, A.; Correa Lopes, B.; Pilla, R.; Nemec, A.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Tozon, N. A Comparison of the Oral Microbiota in Healthy Dogs and Dogs with Oral Tumors. Animals 2023, 13, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-I.; Kim, Y.; Kim, D.-Y.; Na, K.-J. Alteration in E-Cadherin/β-Catenin Expression in Canine Melanotic Tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, S.; Porcellato, I.; Mechelli, L.; Menchetti, L.; Iussich, S.; De Maria, R.; Sforna, M.; Bongiovanni, L.; Brachelente, C. E-Cadherin Expression in Canine Melanocytic Tumors: Histological, Immunohistochemical, and Survival Analysis. Vet. Pathol. 2020, 57, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habanjar, O.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Caldefie-Chezet, F.; Delort, L. 3D Cell Culture Systems: Tumor Application, Advantages, and Disadvantages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
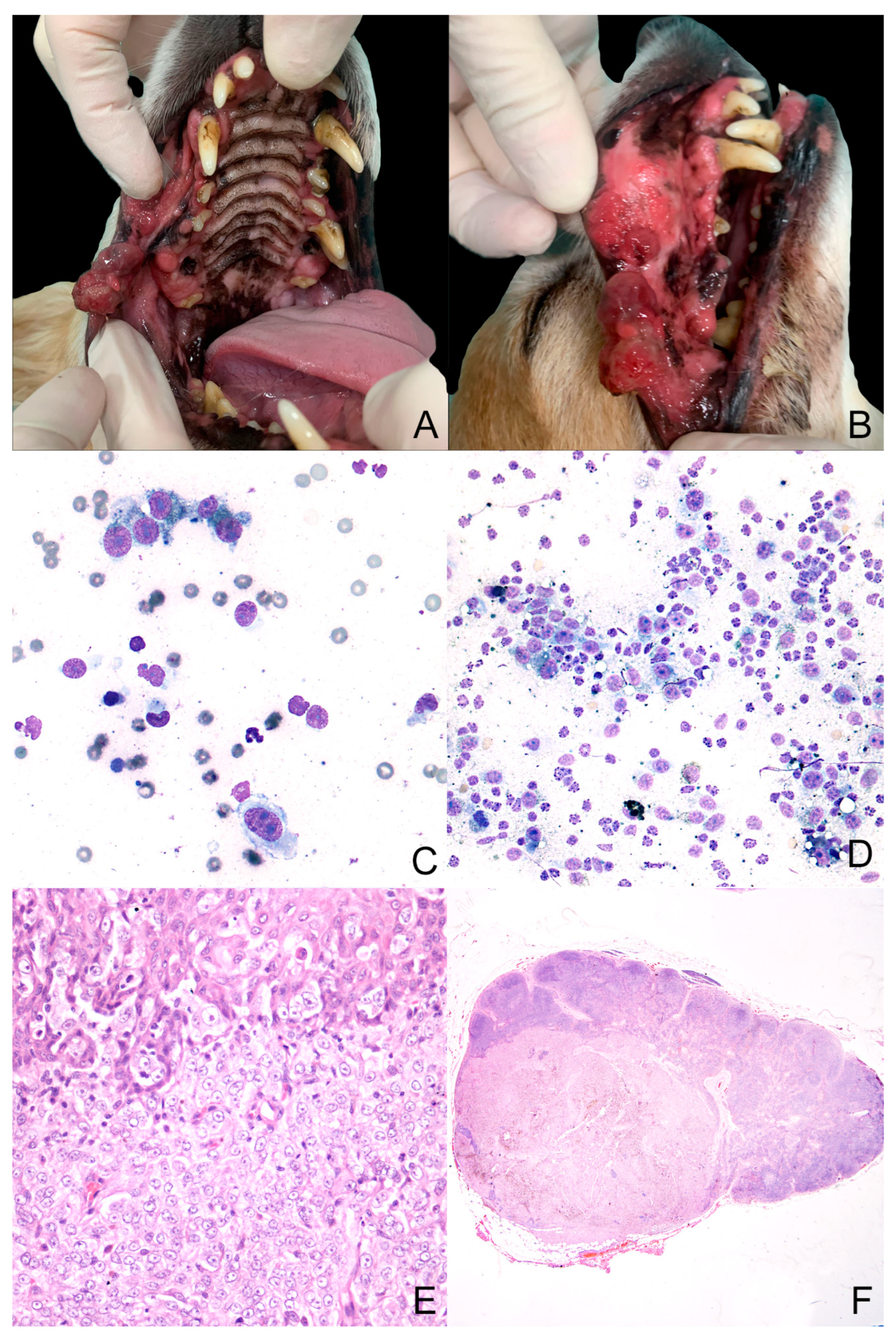


| Case | Dog | Tumor | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breed | Age | Sex | Sampling Site | Diagnosis | ||||
| Primary Tumor | Lymph Node | Cytology | Histology | Immunohistochemistry | ||||
| 1 | Pug | 14 | F | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| 2 | Miniature Pinscher | 12 | F | ✓ | ✓* | ✓* | ✓ | |
| 3 | Mixed breed | 12 | M | ✓ | ✓ | ✓* | ✓* | ✓ |
| 4 | Shih-Tsu | 12 | M | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 5 | Mixed breed | 10 | M | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||
| 6 | Mixed breed | 12 | M | ✓ | ✓ | ✓* | ✓* | ✓ |
| Antigen | Percentage of Positive Cells | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | Case 2 | Case 3 | Case 6 a | Case 6 b | |
| PNL2 | 66.6 | 53.4 | 95.8 | 74 | 43.8 |
| Melan-A | 73.9 | 53.4 | 99 | 48.2 | 19.2 |
| Sox-10 | 85 | 82 | 78.5 | 79.2 | 39.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lo Giudice, A.; Porcellato, I.; Pellegrini, M.; Rottenberg, S.; He, C.; Dentini, A.; Moretti, G.; Cagiola, M.; Mechelli, L.; Chiaradia, E.; et al. Establishment of Primary Cell Cultures from Canine Oral Melanomas via Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Novel Tool for Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression Studies. Animals 2024, 14, 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131948
Lo Giudice A, Porcellato I, Pellegrini M, Rottenberg S, He C, Dentini A, Moretti G, Cagiola M, Mechelli L, Chiaradia E, et al. Establishment of Primary Cell Cultures from Canine Oral Melanomas via Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Novel Tool for Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression Studies. Animals. 2024; 14(13):1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131948
Chicago/Turabian StyleLo Giudice, Adriana, Ilaria Porcellato, Martina Pellegrini, Sven Rottenberg, Chang He, Alfredo Dentini, Giulia Moretti, Monica Cagiola, Luca Mechelli, Elisabetta Chiaradia, and et al. 2024. "Establishment of Primary Cell Cultures from Canine Oral Melanomas via Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Novel Tool for Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression Studies" Animals 14, no. 13: 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131948
APA StyleLo Giudice, A., Porcellato, I., Pellegrini, M., Rottenberg, S., He, C., Dentini, A., Moretti, G., Cagiola, M., Mechelli, L., Chiaradia, E., & Brachelente, C. (2024). Establishment of Primary Cell Cultures from Canine Oral Melanomas via Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Novel Tool for Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression Studies. Animals, 14(13), 1948. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14131948








