Accessory Ligament of the Deep Digital Flexor Tendon of the Horse Forelimb and Its Relationship with the Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon: A Plastination, Histological, and Morphometry Study
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
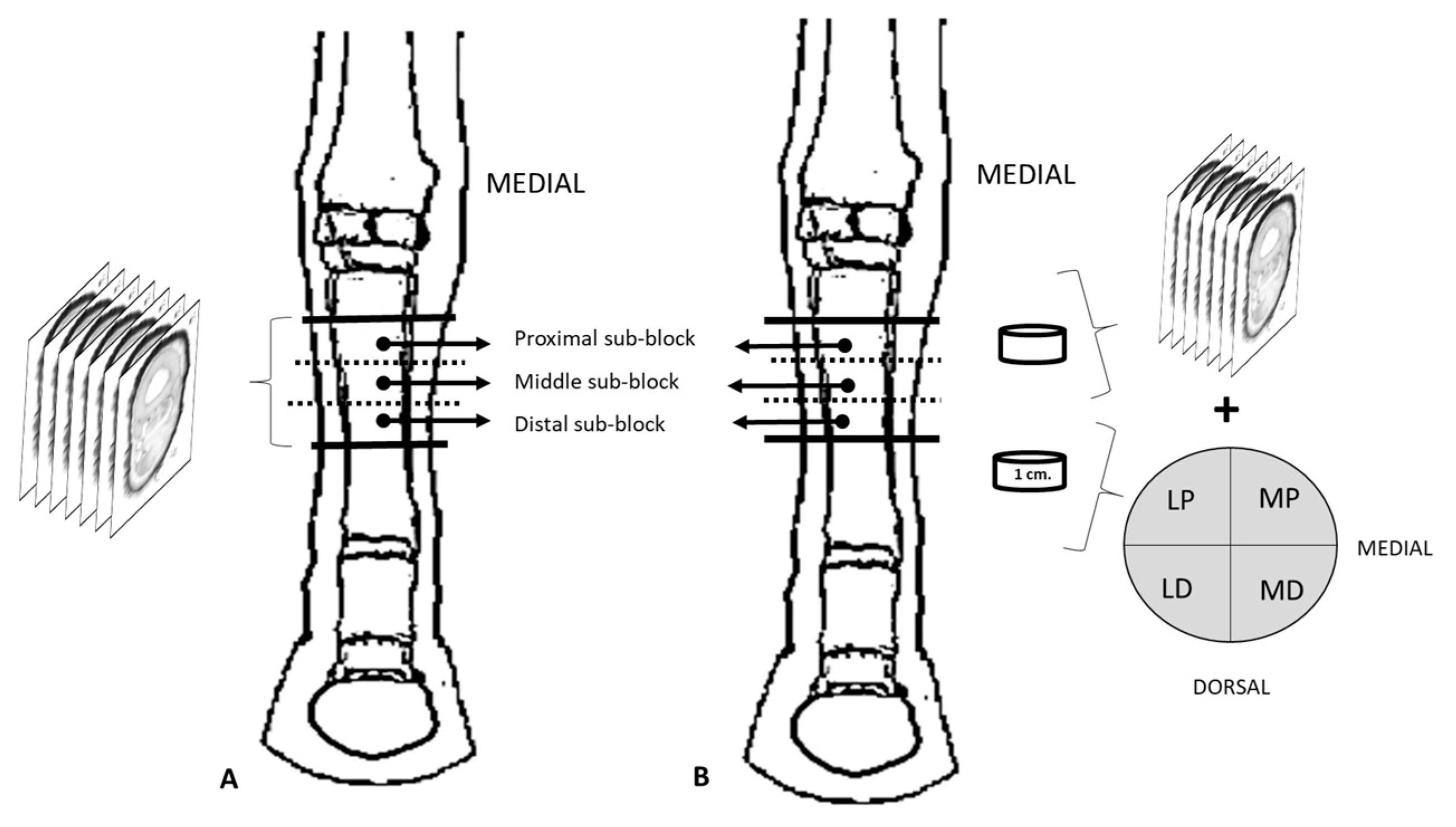
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dissection
2.2. Cryosectionning
2.2.1. Plastination
2.2.2. Histological Processing
2.2.3. Microscopy Viewing
2.3. Morphometry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dissection
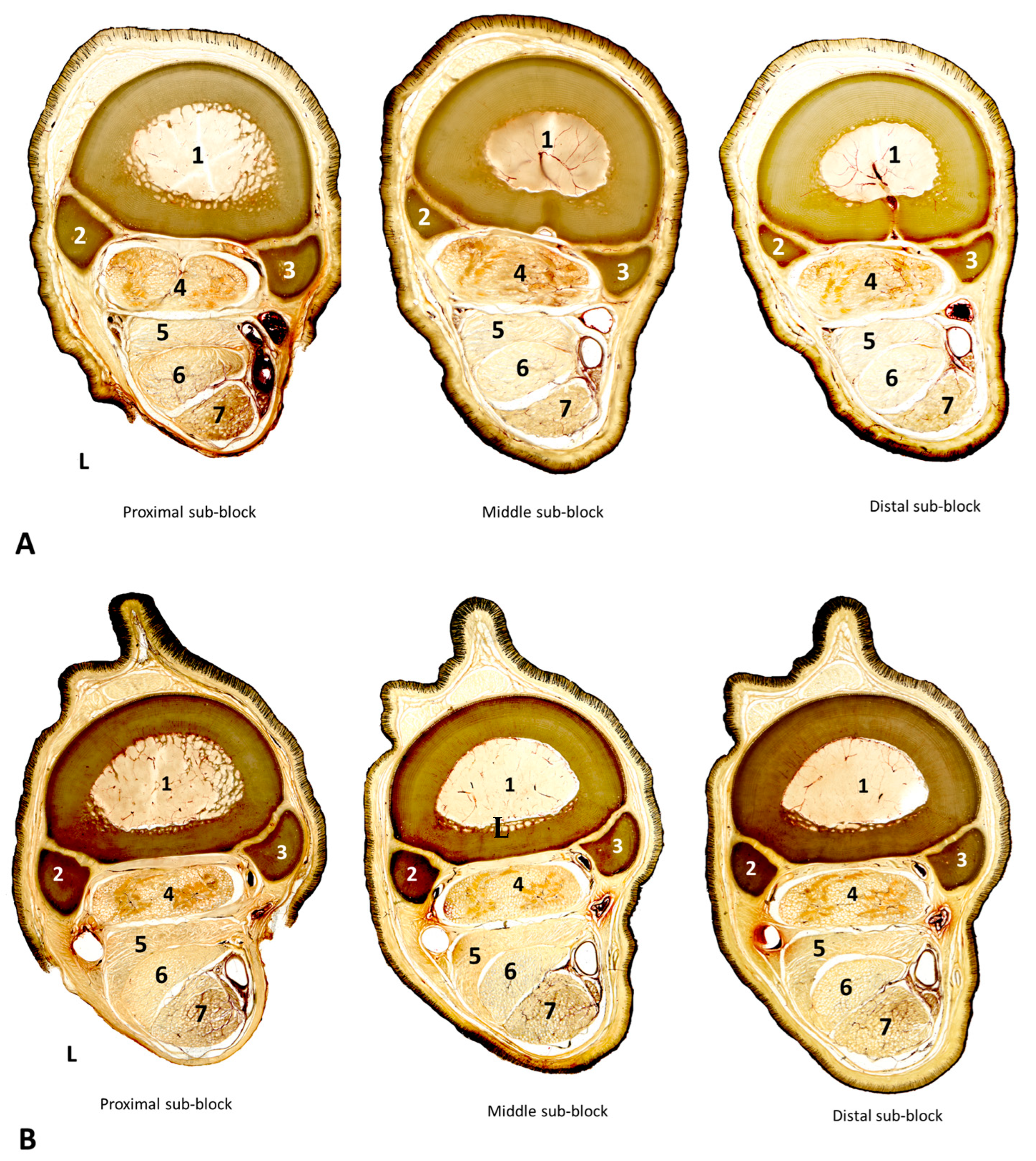
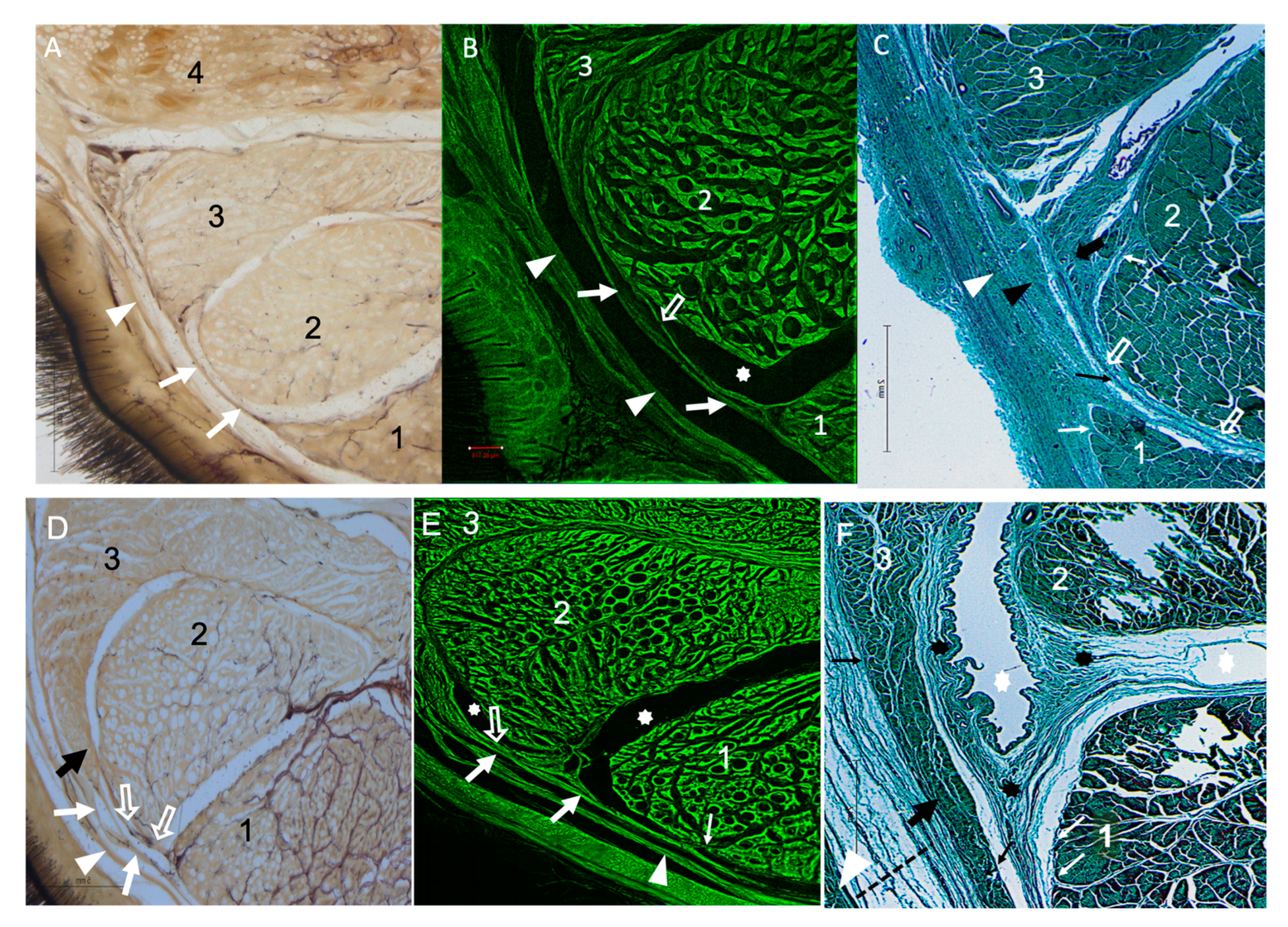
3.2. Cross-Sectional Anatomy
3.3. Morphometric Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nickel, R.; Schummer, A.; Seiferie, E. The anatomy of the domestic animals. In The Locomotor System of the Domestic Mammals; P. Parey: Berlin, Germany, 1986; Volume 1, pp. 358–388. [Google Scholar]
- Denoix, J.M. Functional anatomy of tendons and ligaments in the distal limb (manus and pes). Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 1994, 10, 273–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalec, A.; Egerbacher, M. The deep fascia and retinacula of the equine forelimb—Structure and innervation. J. Anat. 2017, 231, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyce, K.M.; Wensing, C.J.G.; Sack, W.O. The forelimb of the horse. In Textbook of Veterinary Anatomy, 4th ed.; Dyce, K.M., Wensing, C.J.G., Sack, W.O., Eds.; Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2009; pp. 586–623. [Google Scholar]
- Taintor, J.; Caldwell, F.; Almond, G. Aseptic tenosynovitis of the carpal flexor sheath caused by rupture of the accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon. Can. Vet. J. 2013, 54, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Leach, D.; Harland, R.; Burko, B. The anatomy of the carpal tendon sheath of the horse. J. Anat. 1981, 133 Pt 2, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swanstrom, M.D.; Stover, S.M.; Hubbard, M.; Hawkins, D.A. Determination of passive mechanical properties of the superficial and deep digital flexor muscle-ligament- tendon complexes in the forelimbs of horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2004, 65, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, A.; Dyson, S. Anatomical, magnetic resonance imaging and histological findings in the accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon of forelimbs in nonlame horses. Equine Vet. J. 2011, 43, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyson, S. Proximal injuries of the accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon in forelimbs and hindlimbs: 12 horses (2006–2010). Equine Vet. Educ. 2012, 24, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, S.J.; Genovese, R.L. The Suspensory Apparatus. In Diagnosis and Management of Lameness in the Horse; Ross, M., Dyson, S., Eds.; Saunders: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2003; pp. 654–666. [Google Scholar]
- Yiannikouris, S.; Schneider, R.K.; Sampson, S.N.; Roberts, G. Desmotomy of the accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon in the forelimb of 24 horses 2 years and older. Vet. Surg. 2011, 40, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehart, S.; Arndt, G.; Ridermann, G.; Gmachl, M.; Carstanjen, B. Assessment of ultrasonographic morphometric measurements of digital flexor tendons and ligaments of the palmar metacarpal region in Icelandic Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2010, 71, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agut, A.; Martínez, M.L.; Sánchez-Valverde, M.Á.; Soler, M.; Rodríguez, M.J. Ultrasonographic characteristics (cross-sectional area and relative echogenicity) of the digital flexor tendons and ligaments of the metacarpal region in Purebred Spanish horses. Vet. J. 2009, 180, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehart, S.; Arndt, G.; Carstanjen, B. Ultrasonographic morphometric measurements of digital flexor tendons and ligaments of the palmar metacarpal region in Haflinger Horses. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2010, 39, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, N.H.; McCarthy, I.; Birch, H.L. An equine tendon model for studying intra-tendinous shear in tendons that have more than one muscle contribution. Acta Biomater. 2021, 127, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ely, E.R.; Avella, C.S.; Price, J.S.; Smith, R.K.; Wood, J.L.; Verheyen, K.L. Descriptive epidemiology of fracture, tendon and suspensory ligament injuries in National Hunt racehorses in training. Equine Vet. J. 2009, 41, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrle, A.; Lilge, S.; Clegg, P.D.; Maddox, T.W. Equine flexor tendon imaging part 1: Recent developments in ultrasonography, with focus on the superficial digital flexor tendon. Vet. J. 2021, 278, 105764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, C.L. Rehabilitation of tendon and ligament injuries. Proceeding Am. Assoc. Equine Pract. 1997, 43, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb, M.B. Ultrasonographic Evaluation of the metacarpus, metacarpus, and pastern. Clin. Tech. Equine Pract. 2004, 3, 238–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padaliya, N.R.; Ranpariya, J.J.; Kumar, D.; Javia, C.B.; Barvalia, D.R. Ultrasonographic assessment of the equine palmar tendons. Vet. World 2015, 8, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dowling, B.A.; Dart, A.J.; Hodgson, D.R.; Smith, R.K. Superficial digital flexor tendonitis in the horse. Equine Vet. J. 2000, 32, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riemersma, D.J.; van den Bogert, A.J.; Jansen, M.O.; Schamhardt, H.C. Influence of shoeing on ground reaction forces and tendon strains in the forelimbs of ponies. Equine Vet. J. 1996, 28, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, S.E.; Chateau, H.; Pourcelot, P.; Denoix, J.M.; Crevier-Denoix, N. Effect of toe and heel elevation on calculated tendon strains in the horse and the influence of the proximal interphalangeal joint. J. Anat. 2007, 210, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, J.; Hüppler, M.; Geiger, S.; Mäder, D.; Häfner, F. Modifying the height of horseshoes: Effects of wedge shoes, studs, and rocker shoes on the phalangeal alignment, pressure distribution, and hoof-ground contact during motion. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2017, 53, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, R.; de Jong, K.; Sora, M.C.; López-Albors, O.; Baptista, C. E12 technique: Conventional epoxy resin sheet plastination. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2019, 48, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sora, M.C.; von Horst, C.; López-Albors, O.; Latorre, R. Ultra-thin sectioning and grinding of epoxy plastinated tissue. Anat. Histol. Embryol. 2019, 48, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, S.; Oda, T. Estimation of the Effects of Achilles Tendon Geometry on the Magnitude and Distribution of Local Strain: A Finite Element Analysis. Biomechanics 2023, 3, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.J.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, G.; Hu, Y.C.; Lun, D.X. Cross-Sectional Area Measurement Techniques of Soft Tissue: A Literature Review. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 12, 1547–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, S.; Mersmann, F.; Schroll, A.; Mäkitalo, N.; Arampatzis, A. Insufficient accuracy of the ultrasound-based determination of Achilles tendon cross-sectional area. J. Biomech. 2016, 49, 2932–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, A.; Hollnagel, K.; Whitmer, K.; John, C.; Johnson, B.; Godin, J.; Miller, T. Reliability of Magnetic Resonance Imaging Prediction of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Autograft Size and Comparison of Radiologist and Orthopaedic Surgeon Predictions. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2019, 7, 2325967119889593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, J.; White, N.A. Introduction to Equine Tendon Injury. Depth Tendon Ligament Inj. 2008, 54, 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, H.L.; Smith, T.J.; Poulton, C.; Peiffer, D.; Goodship, A.E. Do regional variations in flexor tendons predispose to site-specific injuries? Equine Vet. J. 2002, 34 (Suppl. S34), 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trump, M.A. Retrospective Study of the Prevalence of Injuries to the Suspensory Ligament, Digital Flexor Tendons and Associatedstructures in a Nonracehorse Referral-Hospital Population; University of Zurich: Hobokken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDiarmid, A. Acquired flexural deformity of the metacarpophalangeal joint in five horses associated with tendonous damage in the palmar metacarpus. Vet. Rec. 1999, 144, 475–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, N.; Taylor, C.J.; McGilvray, T.; Tucker, R.; Bathe, A.; Elliott, C.R.B.; Smith, R.K.W. Desmitis of the accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon in the forelimb: A retrospective case study of 91 horses. Equine Vet. J. 2023, 56, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.K.; Lui, Y.H.; Kapacee, Z.; Kadler, K.E.; Ferguson, M.W.; McGrouther, D.A. The cellular biology of flexor tendon adhesion formation: An old problem in a new paradigm. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 1938–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Kang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Bao, R. Tendon Adhesion and Novel Solutions; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Hodgson, D.R.; Rose, R.J. The Athletic Horse: Principles and Practice of Equine Sports Medicine; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1994; pp. 300–301. [Google Scholar]
- Crevier-Denoix, N.; Collobert, C.; Pourcelot, P.; Denoix, J.M.; Sanaa, M.; Geiger, D.; Bernard, N.; Ribot, X.; Bortolussi, C.; Bousseau, B. Mechanical properties of pathological equine superficial digital flexor tendons. Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 1997, 29, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerts, C.; Seifert, C.; Zimmerman, M.; Felix, E.; Suls, M.; Mariën, T.; Broeckx, S.; Spaas, J.H. Desmitis of the Accessory Ligament of the Equine Deep Digital Flexor Tendon: A Regenerative Approach. J. Tissue Sci. Eng. 2013, 4, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Bossa, B.; Medina-Ríos, H.; Cardona-Álvarez, J.A. Evaluation of morphometric measures of tendons and metacarpal ligaments by ultrasonography in Colombian creole horses. Rev. MVZ Cordoba. 2020, 25, e1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, H.L.; McLaughlin, L.; Smith, R.K.; Goodship, A.E. Treadmill exercise-induced tendon hypertrophy: Assessment of tendons with different mechanical functions. Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 1999, 31, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, A.; Baccarin, R. The cross-sectional area of the superficial digital flexor tendon of trained and untrained Thoroughbred racehorses. Ciência Rural 2010, 40, 1786–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco Lopez, D.; Mochal-King, C.; Fontenot, R.; O’Shea, C.M. Ex-vivo evaluation of a percutaneous looped thread desmotomy of the accessory ligament of the deep digital flexor tendon in horses. Vet. Surg. 2024, 53, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köster, A.; Lindner, A.; Gerhards, H. Development of the cross sectional area of flexor tendons in the metacarpal region of 2-year-old horses of different breeds. Pferdeheilkunde 2014, 30, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasashima, Y.; Smith, R.K.; Birch, H.L.; Takahashi, T.; Kusano, K.; Goodship, A.E. Exercise-induced tendon hypertrophy: Cross-sectional area changes during growth are influenced by exercise. Equine Vet. J. Suppl. 2002, 34, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherdchutham, W.; Meershoek, L.S.; van Weeren, P.R.; Barneveld, A. Effects of exercise on biomechanical properties of the superficial digital flexor tendon in foals. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 62, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, P.; Dumont, C.; Barreto Vianna, A.; Maranhão, R.; Okiyama, F.; Nogueira, K.; Lima, E. Effect of age and exercise on morphometric structural changes in surface and deep digital flexor tendons of quarter horses. Onl. J. Vet. Res. 2014, 18, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Patterson-Kane, J.C.; Parry, D.A.D.; Goodship, A.E.; Firth, E.C. Exercise modifies the age-related change in crimp pattern in the core region of the equine superficial digital flexor tendon. N. Z. Vet. J. 1997, 45, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Structures | Proximal Sub-Blocks | Middle Sub-Blocks | Distal Sub-Blocks |
|---|---|---|---|
| AL-DDFT Type I | 73.1 ± 16 Aa | 65.2 ± 12.7 Ab | 68.7 ± 13.9 Ab |
| AL-DDFT Type II | 110.7 ± 4.8 Ba | 105.4 ± 8.7 Ba | 106.1 ± 3.4 Ba |
| AL-DDFT (General) | 82.2 ± 21.5 a | 75.7 ± 21.3 a | 83.7 ± 8.2 a |
| DDFT | 95.5 ± 14.6 a | 82.5 ± 11.5 b | 80.2 ± 21.6 a |
| SDFT | 71.7 ± 19.9 a | 69.1 ± 23.7 a | 78.4 ± 21.7 a |
| SL | 157.3 ±21.7 a | 148.5 ± 19.3 b | 153.2 ± 20.5 ab |
| Metacarpal bone III | 761.8 ± 99.1 a | 676.6 ± 79 b | 706.4 ± 49 b |
| Metacarpal bone II | 64.6 ± 16.4 a | 51.7 ± 11.6 b | 46.8 ± 9.9 c |
| Metacarpal bone IV | 66.9 ± 23.5 a | 46 ± 15.4 b | 38.3 ± 14.4 c |
| Structures | Proximal Sub-Block | Median Sub-Block | Distal Sub-Block |
|---|---|---|---|
| AL-DDFT/DDFT | |||
| Type I AL | 0.8 ± 0.2 Aa | 0.8 ± 0.1 Aa | 0.9 ± 0.2 Ab |
| Type II AL | 1.0 ± 0.1 Ba | 1.1 ± 0.5 Ba | 1.3 ± 0.0 Bb |
| AL-DDFT/SDFT | |||
| Type I AL | 1.2 ± 0.2 Aa | 1.2 ± 0.1 Aa | 1.1 ± 0.2 Ab |
| Type II AL | 1.1 ± 0.5 Aa | 1.0 ± 0.9 Ba | 1.0 ± 0.3 Ab |
| AL-DDFT/SL | |||
| Type I AL | 0.5 ± 0.5 Aa | 0.4 ± 0.4 Aa | 0.4 ± 0.4 Ab |
| Type II AL | 0.7 ± 0.0 Ba | 0.7 ± 0.5 Ba | 0.7 ± 0.0 Bb |
| DDFT/SDFT | 1.4 ± 0.3 a | 1.3 ± 0.3 a | 1.1 ± 0.3 b |
| SL/SDFT | 2.3 ± 0.5 a | 2.3 ± 0.6 a | 2.1 ± 0.6 b |
| SL/DDFT | 1.7 ± 0.3 a | 1.8 ± 0.2 b | 1.9 ± 0.3 c |
| Metacarpal bone III/AL-DDFT | |||
| Type I AL | 10.5 ± 1.5 Aa | 10.2 ± 1.1 Aa | 10.4 ± 1.7 Aa |
| Type II AL | 7.3 ± 0.4 Ba | 7.1 ± 0.4 Ba | 8.8 ± 0.1 Ba |
| Metacarpal bone III/DDFT | 8 ± 0.8 a | 8.2 ± 0.6 a | 8.9 ± 0.6 b |
| Metacarpal bone III/SDFT | 11.2 ± 2.2 a | 10.5 ± 2.3 a | 9.6 ± 2.3 a |
| Metacarpal bone III/SL | 4.9 ± 0.5 a | 4.6 ± 0.4 b | 4.7 ± 0.5 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eren, G.; López-Albors, O.; Guilabert Segura, R.; Jordan Montesinos, J.; Latorre, R. Accessory Ligament of the Deep Digital Flexor Tendon of the Horse Forelimb and Its Relationship with the Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon: A Plastination, Histological, and Morphometry Study. Animals 2024, 14, 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202952
Eren G, López-Albors O, Guilabert Segura R, Jordan Montesinos J, Latorre R. Accessory Ligament of the Deep Digital Flexor Tendon of the Horse Forelimb and Its Relationship with the Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon: A Plastination, Histological, and Morphometry Study. Animals. 2024; 14(20):2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202952
Chicago/Turabian StyleEren, Gulsum, Octavio López-Albors, Ruth Guilabert Segura, Joana Jordan Montesinos, and Rafael Latorre. 2024. "Accessory Ligament of the Deep Digital Flexor Tendon of the Horse Forelimb and Its Relationship with the Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon: A Plastination, Histological, and Morphometry Study" Animals 14, no. 20: 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202952
APA StyleEren, G., López-Albors, O., Guilabert Segura, R., Jordan Montesinos, J., & Latorre, R. (2024). Accessory Ligament of the Deep Digital Flexor Tendon of the Horse Forelimb and Its Relationship with the Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon: A Plastination, Histological, and Morphometry Study. Animals, 14(20), 2952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14202952






