Comparison Between Two Methodologies of Sample Preservation for RNA Extraction in Naturally Delivered Ovine Placenta
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Placental Sampling and Preservation
2.3. RNA Extraction
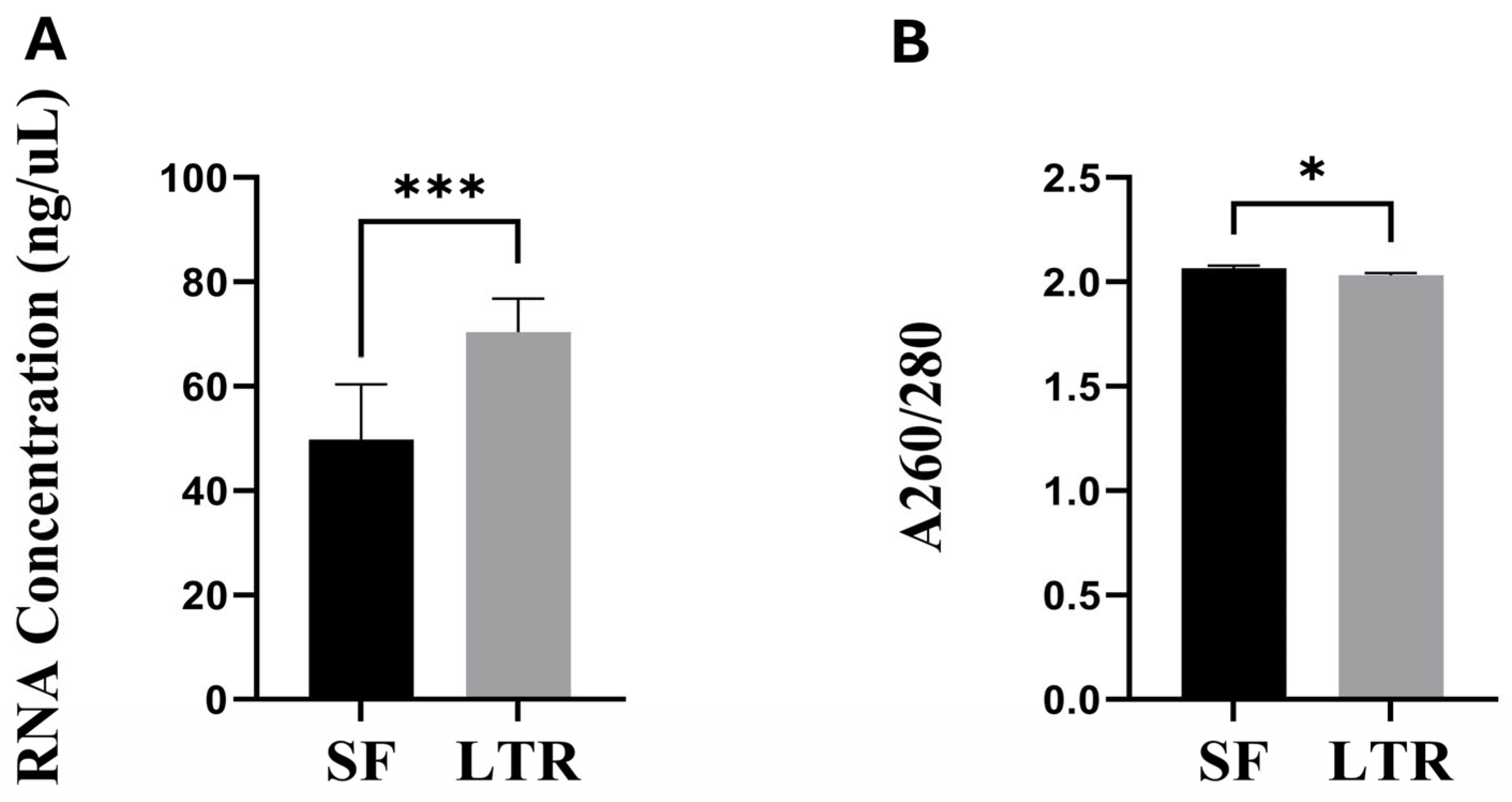
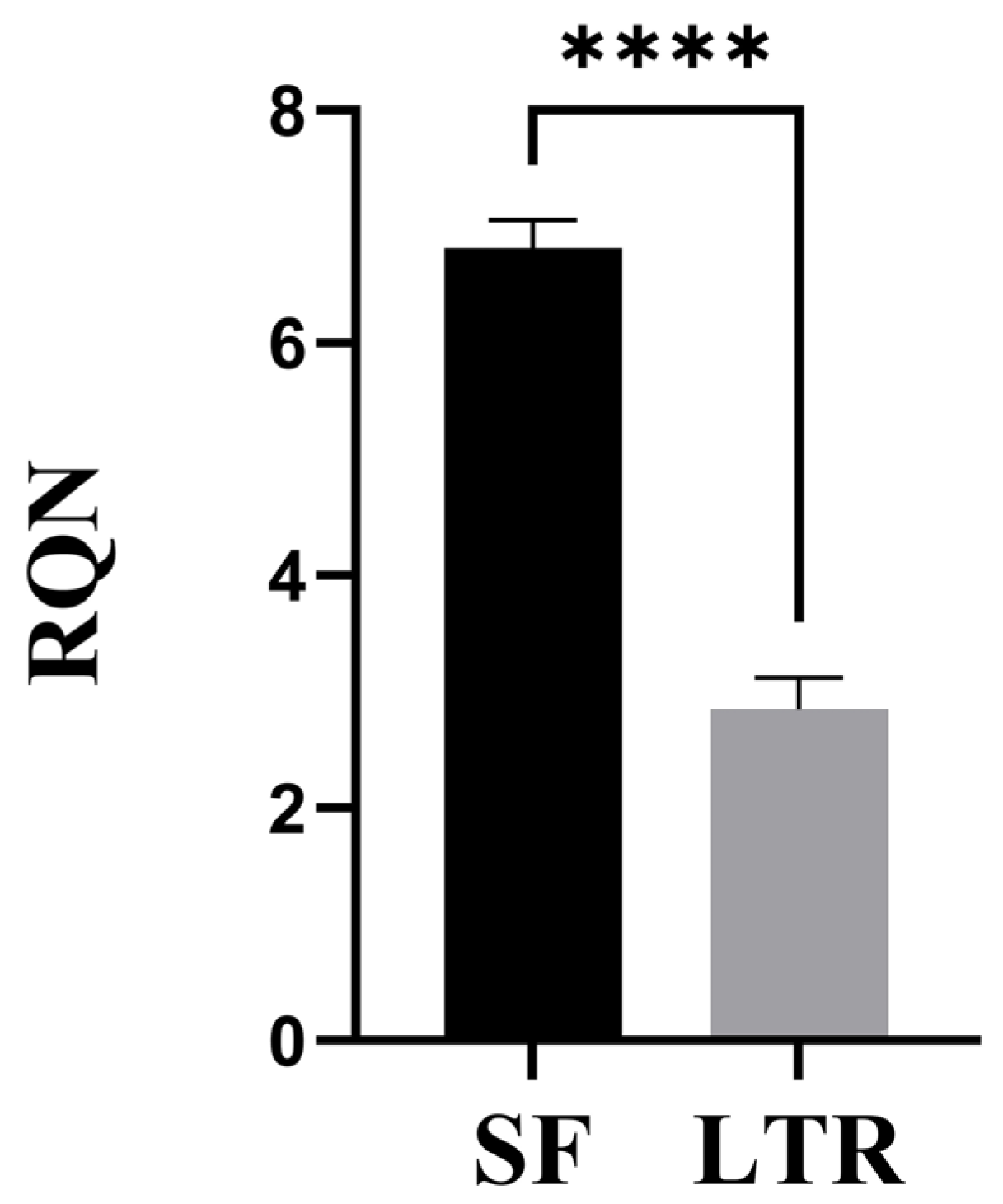
2.4. RNA Quantity and Quality Indicators
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. RNA Concentration and Purity
3.2. RNA Integrity
3.3. Time of Placental Expulsion and Correlation to RNA Quantity and Quality Indicators
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RNA | Ribonucleic Acid |
| GD | Gestational Day |
| SF | Snap-Frozen treatment |
| LTR | RNAlater® treatment |
| RQN | RNA Quality Number |
| RIN | RNA Integrity Number |
References
- Sammin, D.; Markey, B.; Bassett, H.; Buxton, D. The ovine placenta and placentitis-A review. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 135, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, A.R.; Kennedy, V.C.; Lynch, C.S.; Hord, T.K.; Winger, Q.A.; Rozance, P.J.; Anthony, R.V. In vivo investigation of ruminant placenta function and physiology-A review. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthurs, A.L.; McCullough, D.; Williamson, J.M.; Jankovic-Karasoulos, T.; Smith, M.D.; Roberts, C.T. Factors influencing RNA yield from placenta tissue. Placenta 2023, 140, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauser, C.B.; Lambo, C.A.; Askelson, K.; Burns, G.W.; Behura, S.K.; Spencer, T.E.; Bazer, F.W.; Satterfield, M.C. Placental transcriptome adaptations to maternal nutrient restriction in sheep. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, J.S.; Anthony, R.V. The pregnant sheep as a model for human pregnancy. Theriogenology 2008, 69, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banstola, A.; Reynolds, J.N.J. The Sheep as a Large Animal Model for the Investigation and Treatment of Human Disorders. Biology 2022, 11, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiser, R.; Krebs, C.; Ebert, B.; Dantzer, V. Placental vascular corrosion cast studies: A comparison between ruminants and humans. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1997, 38, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, A.M. Recent advances in understanding evolution of the placenta: Insights from transcriptomics. F1000Research 2018, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.L.; Diglisic, S.; Leister, F.; Webster, M.; Yolken, R.H. Evaluating RNA status for RT-PCR in extracts of postmortem human brain tissue. Biotechniques 2004, 36, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidova, M.; Tomankova, S.; Abaffy, P.; Kubista, M.; Sindelka, R. Effects of post-mortem and physical degradation on RNA integrity and quality. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2015, 5, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.; Mueller, O.; Stocker, S.; Salowsky, R.; Leiber, M.; Gassmann, M.; Lightfoot, S.; Menzel, W.; Granzow, M.; Ragg, T. The RIN: An RNA integrity number for assigning integrity values to RNA measurements. BMC Mol. Biol. 2006, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roume, H.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; Muller, E.E.L.; Wilmes, P. Sequential isolation of metabolites, RNA, DNA, and proteins from the same unique sample. In Methods in Enzymology, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 531, pp. 219–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opitz, L.; Salinas-Riester, G.; Grade, M.; Jung, K.; Jo, P.; Emons, G.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Beißbarth, T.; Gaedcke, J. Impact of RNA degradation on gene expression profiling. BMC Med. Genom. 2010, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, N.M.; Cooke, K.M.; Radford, C.C.; Perley, L.E.; Silasi, M.; Flannery, C.A. Time course analysis of RNA quality in placenta preserved by RNA later or flash freezing. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 77, e12637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haimov-Kochman, R.; Fisher, S.J.; Winn, V.D. Modification of the Standard Trizol-Based Technique Improves the Integrity of RNA Isolated from RNase-Rich Placental Tissue. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 159–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, N.A.; Shankar, V. Single-strand-specific nucleases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 26, 457–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peirson, S.N.; Butler, J.N. RNA extraction from mammalian tissues. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007, 362, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajo, P.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Benavides, J.; Sánchez-Sánchez, R.; Amieva, R.; Collantes-Fernández, E.; Pastor-Fernández, I. Ovine placental explants: A new ex vivo model to study host-pathogen interactions in reproductive pathogens. Theriogenology 2023, 212, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erichsen, C.; Heiser, A.; Haack, N.; Maclean, P.; Dwyer, C.M.; McCoard, S. Increasing the Understanding of Nutrient Transport Capacity of the Ovine Placentome. Animals 2024, 14, 1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Allison, B.J.; Brain, K.L.; Patey, O.V.; Niu, Y.; Botting, K.J.; Ford, S.G.; Garrud, T.A.; Wooding, P.F.B.; Lyu, Q.; et al. Placental mitochondrial metabolic adaptation maintains cellular energy balance in pregnancy complicated by gestational hypoxia. J. Physiol. 2025. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambo, C.A.; Edwards, A.K.; Bazer, F.W.; Dunlap, K.; Satterfield, M.C. Development of a surgical procedure for removal of a placentome from a pregnant ewe during gestation. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K.; Rodriguez Perez, C.; Louis-Maerten, E.; Müller, N.; Shaw, D. “Killing in the Name of 3R?” The Ethics of Death in Animal Research. J. Agric. Environ. Ethics 2025, 38, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fthenakis, G.C.; Leontides, L.S.; Amiridis, G.S.; Saratsis, P. Incidence risk and clinical features of retention of foetal membranes in ewes in 28 flocks in southern Greece. Prev. Vet. Med. 2000, 43, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auer, H.; Mobley, J.; Ayers, L.; Bowen, J.; Chuaqui, R.; Johnson, L.; Livolsi, V.; Lubensky, I.; McGarvey, D.; Monovich, L.; et al. effects of frozen tissue storage conditions on the integrity of RNA and protein. Biotech. Histochem. 2014, 89, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, J.; Mackay, R.; de Aguiar Greca, S.-C.; Corti, A.; Silva, E.; Karteris, E.; Ahluwalia, A. The role of the 3rs for understanding and modeling the human placenta. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur Clark, J. The 3Rs in research: A contemporary approach to replacement, reduction and refinement. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, S1–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena-Aguilar, G.; Sánchez-López, A.M.; Barberán-Aceituno, C.; Carrillo-Ávila, J.A.; López-Guerrero, J.A.; Aguilar-Quesada, R. DNA Source Selection for Downstream Applications Based on DNA Quality Indicators Analysis. Biopreserv. Biobank. 2016, 14, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, J.; De Preter, K.; Lefever, S.; Nuytens, J.; De Vloed, F.; Derveaux, S.; Hellemans, J.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. Measurable impact of RNA quality on gene expression results from quantitative PCR. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2011, 39, e63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.G.; Rashid, M.; Verma, T.; Ludbe, M.; Khade, B.; Gera, P.B.; Gupta, S. Establishing a correlation between RIN and A260/280 along with the multivariate evaluation of factors affecting the quality of RNA in cryopreserved cancer bio-specimen. Cell Tissue Bank. 2019, 20, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Baumann, M.; Nikitina, L.; Wenger, F.; Surbek, D.; Körner, M.; Albrecht, C. RNA degradation differentially affects quantitative mRNA measurements of endogenous reference genes in human placenta. Placenta 2013, 34, 544–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobarteh, M.L.; Moore, S.E.; Kennedy, C.; Gambling, L.; McArdle, H.J. The effect of delay in collection and processing on RNA integrity in human placenta: Experiences from rural Africa. Placenta 2014, 35, 72–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- ThermoFisher Scientific. RNAlater Tissue Collection: Stabilization Solution Protocol. Available online: https://tools.thermofisher.com/content/sfs/manuals/cms_056069.pdf (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Ozkan, H.; Kerman, E. Comparative Evaluation of RNAlater Solution and Snap Frozen Methods for Gene Expression Studies in Different Tissues. Rev. Rom. Med. Lab. 2020, 28, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, L.; Thiagarajan, R.; Boscolo, F.; Taché, V.; Coleman, R.; Kim, J.; Kwan, W.; Loring, J.; Parast, M.; Laurent, L. Banking placental tissue: An optimized collection procedure for genome-wide analysis of nucleic acids. Placenta 2014, 35, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, M.; Zhandi, M.; Sharafi, M.; Akbari, A.; Atrabi, M.J.; Totonchi, M. Gene expression profile of placentomes and clinical parameters in the cows with retained placenta. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworska, J.; Janowski, T. Expression of proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6 and TNFα in the retained placenta of mares. Theriogenology 2019, 126, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick, R.; Casey, O.M.; Morris, D.; Smith, T.; Powell, R.; Sreenan, J.M. Postmortem stability of RNA isolated from bovine reproductive tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Struct. Expr. 2002, 1574, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajardy, I.; Moitrot, E.; Vambergue, A.; Vandersippe-Millot, M.; Deruelle, P.; Rousseaux, J. Time course analysis of RNA stability in human placenta. BMC Mol. Biol. 2009, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, A.A.; Smart, B.P.; Keenan-Devlin, L.S.; Romero, J.; Franklin, A.; Borders, A.; Ernst, L.M.; Miller, G.E. Time-dependent changes in placental mRNA expression after delivery due to delayed specimen collection. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2021, 86, e13452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Preservation Method | Indicator | Correlation Coefficient (r2) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snap Frozen (SF) | Concentration (ng/µL) | 0.010 | 0.6125 |
| A260/280 Ratio | 0.063 | 0.2065 | |
| RNA Quality Number (RQN) | 0.002 | 0.7874 | |
| RNAlater® (LTR) | Concentration (ng/µL) | 0.084 | 0.1405 |
| A260/280 Ratio | 0.002 | 0.8058 | |
| RNA Quality Number (RQN) | 0.050 | 0.2615 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aránguiz, F.; Bahamonde, J.; Sales, F.; Araya, M.; Ulloa-Leal, C.; Ratto, M.; Sandoval, C. Comparison Between Two Methodologies of Sample Preservation for RNA Extraction in Naturally Delivered Ovine Placenta. Animals 2025, 15, 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060786
Aránguiz F, Bahamonde J, Sales F, Araya M, Ulloa-Leal C, Ratto M, Sandoval C. Comparison Between Two Methodologies of Sample Preservation for RNA Extraction in Naturally Delivered Ovine Placenta. Animals. 2025; 15(6):786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060786
Chicago/Turabian StyleAránguiz, Florencia, Javiera Bahamonde, Francisco Sales, Matías Araya, César Ulloa-Leal, Marcelo Ratto, and Camila Sandoval. 2025. "Comparison Between Two Methodologies of Sample Preservation for RNA Extraction in Naturally Delivered Ovine Placenta" Animals 15, no. 6: 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060786
APA StyleAránguiz, F., Bahamonde, J., Sales, F., Araya, M., Ulloa-Leal, C., Ratto, M., & Sandoval, C. (2025). Comparison Between Two Methodologies of Sample Preservation for RNA Extraction in Naturally Delivered Ovine Placenta. Animals, 15(6), 786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15060786





