Two-Stream Bidirectional Interaction Network Based on RGB-D Images for Duck Weight Estimation
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We construct an RGB-D duck weight dataset named SCAU-DuckWT to aid in the research of duck weight estimation. The dataset includes RGB-D images of ducks captured from the bird-eye perspective and the corresponding weight data.
- We present a two-stream RGB-D network for estimating duck weights that can utilize the spatial information of depth images and the texture appearance information of RGB simultaneously.
- We utilize an encoder–decoder architecture with a bidirectional interaction module in the encoder. This allows us to learn a shared representation by capturing the interactions between RGB and depth images. Next, the decoder combines the multi-scale features from both modalities.
- The proposed method provides the best performance for duck estimation when compared to other methods, with an MAE of only 0.1550.
2. Materials and Methods
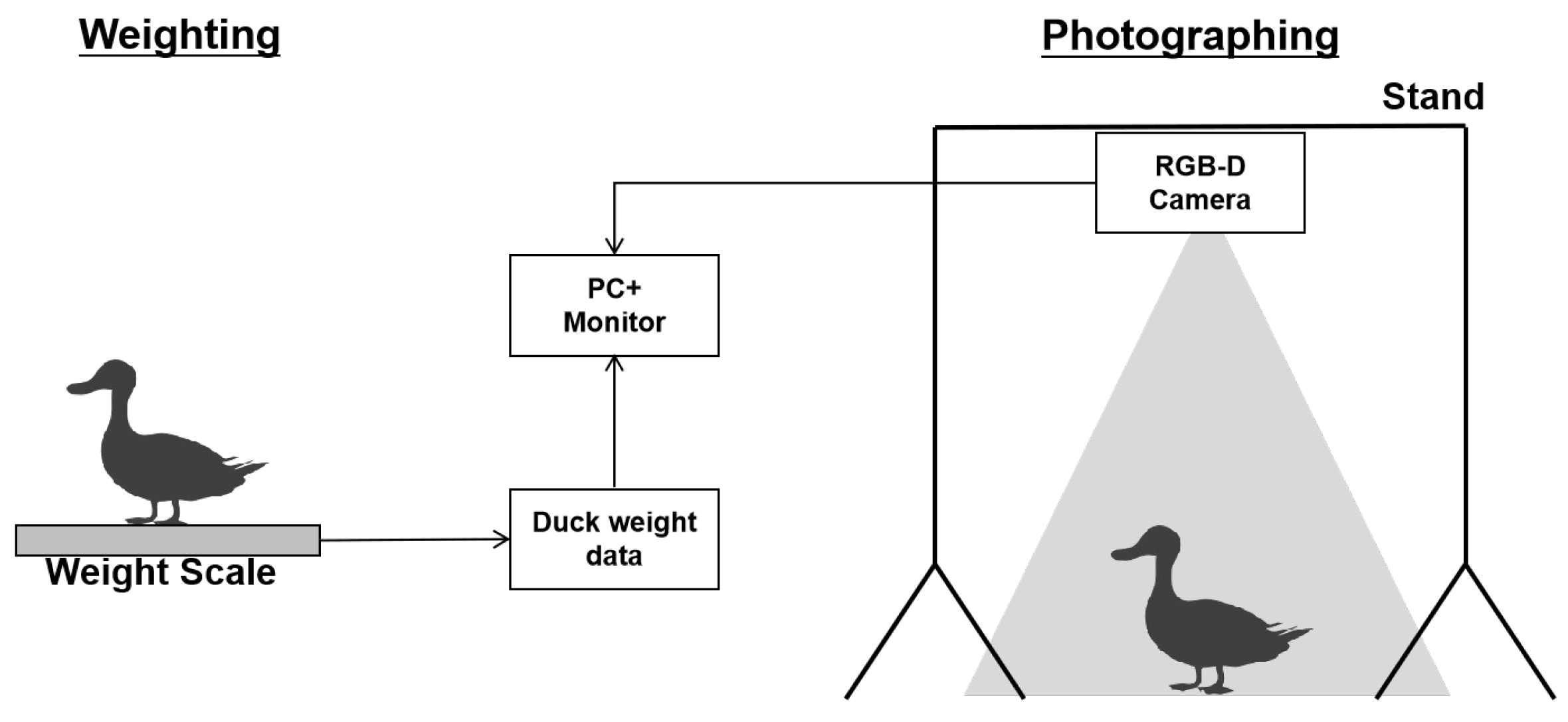
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Overview of Proposed Method
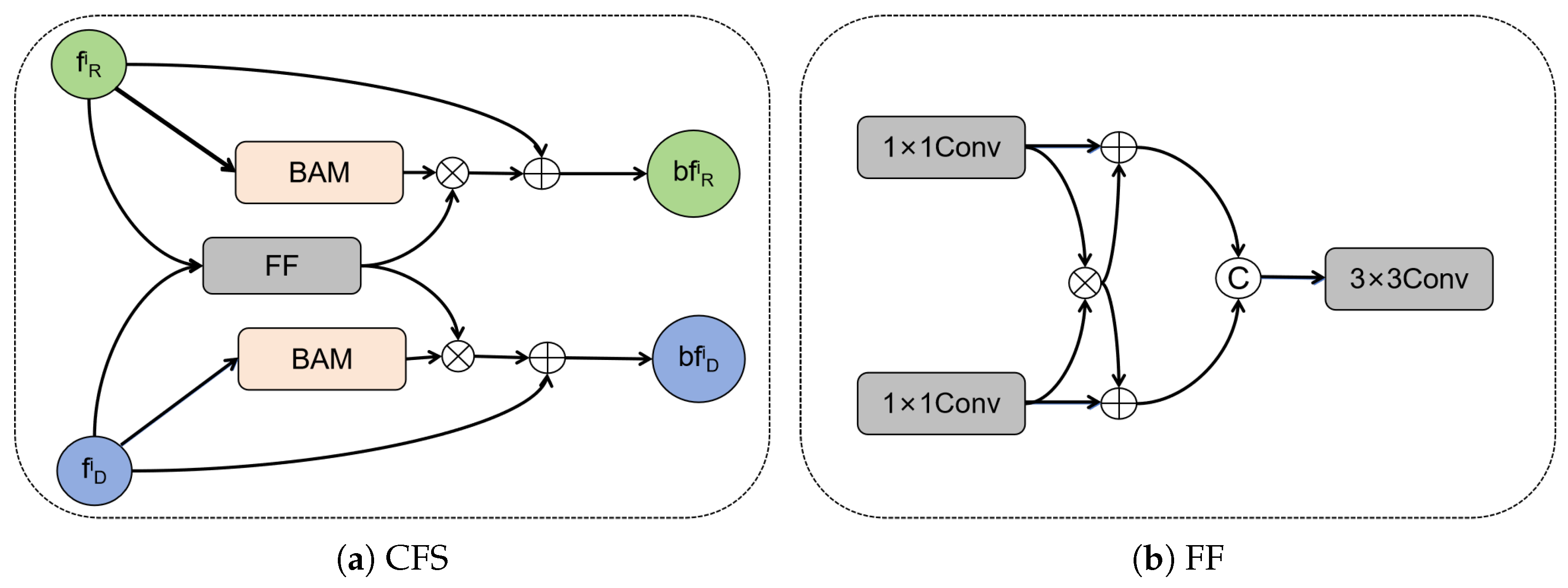
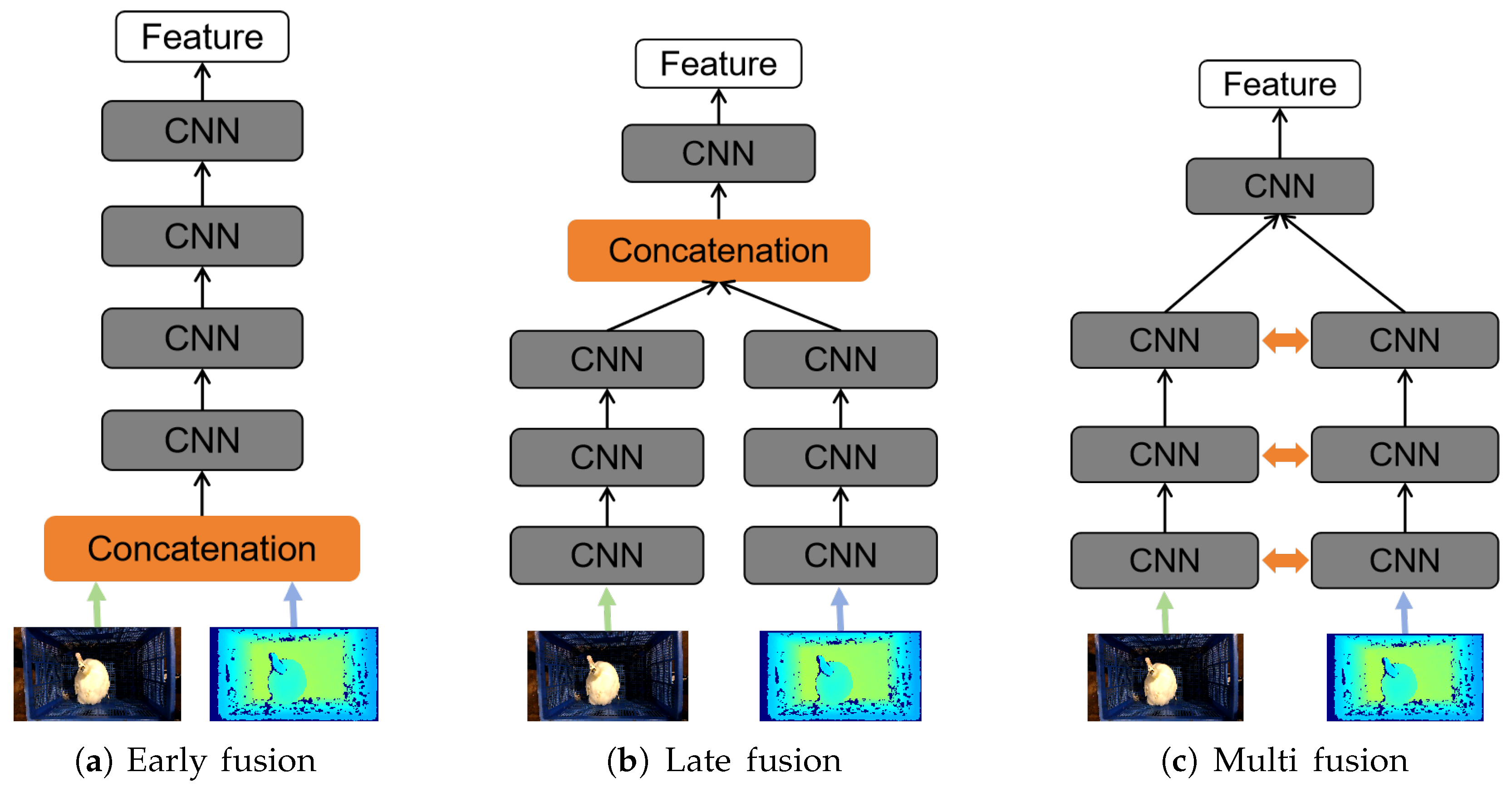
2.2.2. Cross-Modal Feature Extraction Encoder
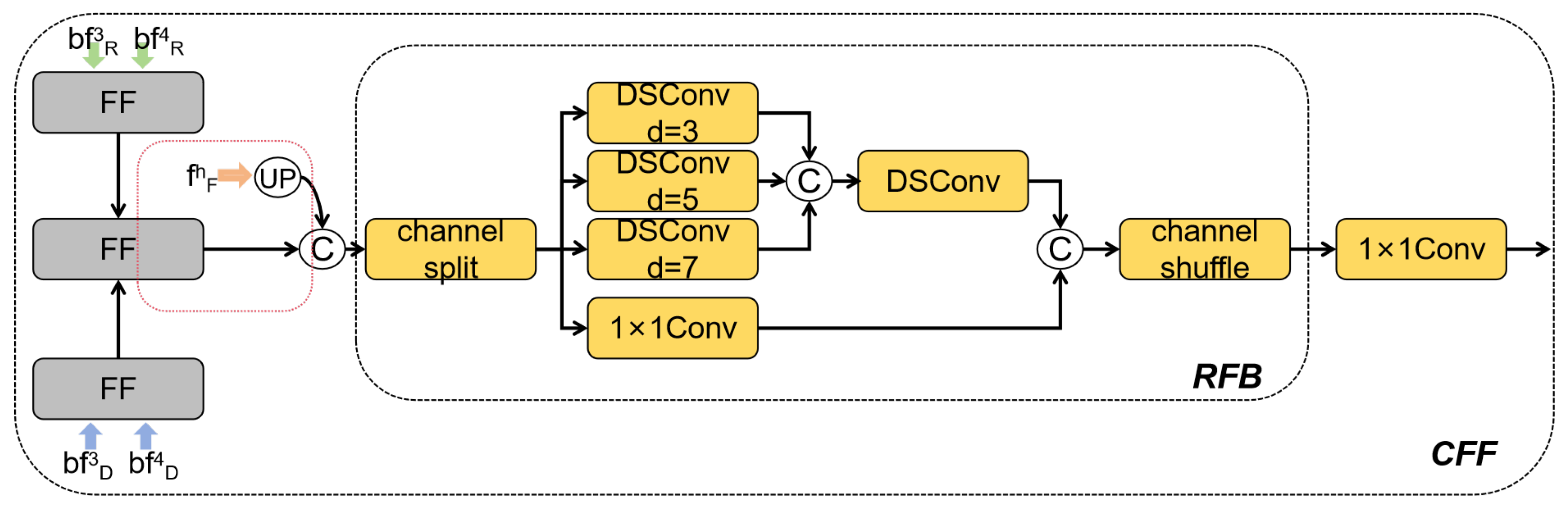
2.2.3. Cross-Modality Feature Aggregation Decoder
2.3. Training Details
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison with Single-Modality Methods
3.2. Comparison with Multi-Modality Methods
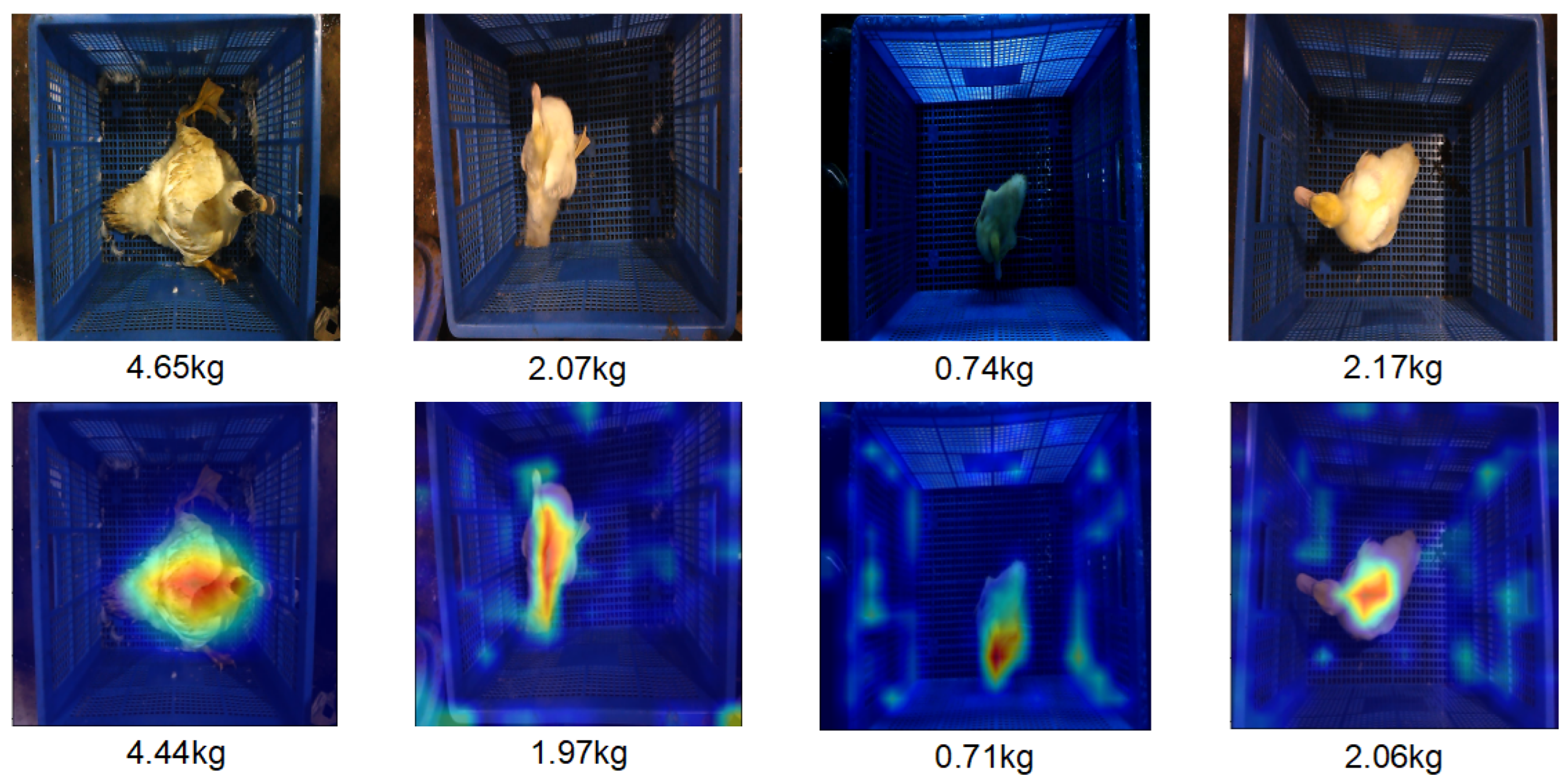
3.3. Visualizations and Analysis
3.4. Discussion
3.4.1. Result Analysis
3.4.2. Impact of CFS
3.4.3. Impact of CFF
3.4.4. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jalaludeen, A.; Churchil, R.R. Duck Production: An Overview. In Duck Production and Management Strategies; Jalaludeen, A., Churchil, R.R., Baéza, E., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2022; pp. 1–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Téguia, A.; Ngandjou, H.M.; Defang, H.; Tchoumboue, J. Study of the live body weight and body characteristics of the African Muscovy duck (Caraina moschata). Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2008, 40, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Purswell, J.L.; Du, Q.; Chesser, G.D.; Lowe, J.W. Analysis of feeding and drinking behaviors of group-reared broilers via image processing. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, W.; Li, H. DHSW-YOLO: A duck flock daily behavior recognition model adaptable to bright and dark conditions. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogah, D.M.; Yakubu, A.; Momoh, M.O.; Dim, N.I. Relationship between some body measurements and live weight in adult Muscovy ducks using path analysis. Trakia J. Sci. 2011, 9, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Lieng, P.; Sangpradit, K. Study on duck weight estimation by using image processing. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, Nakhon Rakchasima, Thailand, 30–31 July 2020; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2020; Volume 187, p. 02001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Sha, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, G.; Li, W.J. Online estimating weight of white Pekin duck carcass by computer vision. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzuolo, A.; Guarino, M.; Sartori, L.; González, L.A.; Marinello, F. On-barn pig weight estimation based on body measurements by a Kinect v1 depth camera. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 148, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cang, Y.; He, H.; Qiao, Y. An intelligent pig weights estimate method based on deep learning in sow stall environments. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 164867–164875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Qiao, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X. Automatic weight measurement of pigs based on 3D images and regression network. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakakis, M.; April, T.; Bailey, M.; Bernhard, M.; Bursztein, E.; Cochran, J.; Durumeric, Z.; Halderman, J.A.; Invernizzi, L.; Kallitsis, M.; et al. Understanding the mirai botnet. In Proceedings of the 26th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 17), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 16–18 August 2017; pp. 1093–1110. [Google Scholar]
- He, C.; Qiao, Y.; Mao, R.; Li, M.; Wang, M. Enhanced LiteHRNet based sheep weight estimation using RGB-D images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 206, 107667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Mi, Y.; Ding, X.; Liu, G.; Li, T. Two-stream cross-attention vision Transformer based on RGB-D images for pig weight estimation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 107986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Fan, D.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. RGB-D salient object detection: A survey. Comput. Vis. Media 2021, 7, 37–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.; He, S.; Zhang, J.; Tian, J.; Tang, Y.; Yang, Q. RGBD salient object detection via deep fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 2274–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Chen, H.; Liu, N.; Yan, C.; Li, X. CNNs-based RGB-D saliency detection via cross-view transfer and multiview fusion. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 48, 3171–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Su, D. Multi-modal fusion network with multi-scale multi-path and cross-modal interactions for RGB-D salient object detection. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 86, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Three-stage bidirectional interaction network for efficient RGB-D salient object detection. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Macao, China, 4–8 December 2022; pp. 3672–3689. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/ACCV2022/html/Wang_Three-Stage_Bidirectional_Interaction_Network_for_Efficient_RGB-D_Salient_Object_Detection_ACCV_2022_paper.html (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. Available online: http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/html/Howard_Searching_for_MobileNetV3_ICCV_2019_paper.html (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. BAM: Bottleneck Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D. Receptive field block net for accurate and fast object detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (NeurIPS 2019), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Volume 32. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2019/hash/bdbca288fee7f92f2bfa9f7012727740-Abstract.html (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iandola, F.; Moskewicz, M.; Karayev, S.; Girshick, R.; Darrell, T.; Keutzer, K. DenseNet: Implementing Efficient ConvNet Descriptor Pyramids. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1404.1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. Available online: https://www.cv-foundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/html/Szegedy_Rethinking_the_Inception_CVPR_2016_paper.html (accessed on 30 March 2025).
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; PMLR: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-cam: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Method | Modality | FLOPS | Parameters | MAE | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV3 | RGB | 16.26 G | 1.13 M | 0.4095 | 0.6525 | 0.7323 |
| DenseNet | RGB | 87.59 G | 1.01 M | 0.2540 | 0.3848 | 0.9069 |
| ResNet | RGB | 55.20 G | 21.69 M | 0.3403 | 0.5152 | 0.8331 |
| InceptionNet | RGB | 354.51 G | 6.88 M | 0.2971 | 0.4161 | 0.8911 |
| EfficientNet | RGB | 5.35 G | 2.49 M | 0.2723 | 0.3706 | 0.9136 |
| Swin Transformer | RGB | 65.43 G | 28.27 M | 0.3887 | 0.6021 | 0.7721 |
| MobileNetV3 | Depth | 16.20 G | 1.13 M | 0.7086 | 0.8899 | 0.5021 |
| DenseNet | Depth | 85.86 G | 1.01 M | 0.7138 | 0.8779 | 0.5154 |
| ResNet | Depth | 54.02 G | 21.69 M | 0.6164 | 0.7897 | 0.6078 |
| InceptionNet | Depth | 354.42 G | 6.88 M | 0.9377 | 1.0525 | 0.3034 |
| EfficientNet | Depth | 5.24 G | 2.49 M | 0.7542 | 0.9079 | 0.4817 |
| Swin Transformer | Depth | 65.28 G | 28.27 M | 0.7627 | 0.9323 | 0.4535 |
| Proposed Method | RGB + Depth | 37.13 G | 6.83 M | 0.1550 | 0.2250 | 0.9682 |
| Method | FLOPS | Parameters | MAE | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MobileNetV3 (Early) | 16.37 G | 1.13 M | 0.3099 | 0.4668 | 0.863 |
| DenseNet (Early) | 88.42 G | 1.01 M | 0.3015 | 0.4543 | 0.8702 |
| ResNet (Early) | 55.70 G | 21.96 M | 0.3294 | 0.4686 | 0.8619 |
| EfficientNet (Early) | 5.39 G | 2.49 M | 0.2971 | 0.3886 | 0.9051 |
| MobileNetV3 (Late) | 32.48 G | red2.26 M | 0.3203 | 0.4380 | 0.8794 |
| DenseNet (Late) | 173.435 G | 2.03 M | 0.2778 | 0.4190 | 0.8896 |
| ResNet (Late) | 109.209 G | red43.90 M | 0.3096 | 0.4111 | 0.8937 |
| EfficientNet (Late) | 10.575 G | 5.01 M | 0.3341 | 0.4745 | 0.8584 |
| Pig weight net | 8.70 G | 55.0 M | 0.1550 | 0.2250 | 0.9682 |
| (multi fusion) | |||||
| Proposed Method | 16.26 G | 1.13 M | 0.1550 | 0.2250 | 0.9682 |
| Method | MAE | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| two-stream MobileNetv3 w/o CFS | 0.1928 | 0.2581 | 0.9581 |
| two-stream MobileNetv3 w 1CFS | 0.1931 | 0.2685 | 0.9547 |
| two-stream MobileNetv3 w 2CFS | 0.1751 | 0.2355 | 0.9651 |
| two-stream MobileNetv3 w 3CFS | 0.1622 | 0.2347 | 0.9654 |
| two-stream MobileNetv3 w 5CFS | 0.1949 | 0.2703 | 0.9541 |
| two-stream MobileNetv3 w 6CFS | 0.1828 | 0.2500 | 0.9607 |
| Proposed Method | 0.1550 | 0.2250 | 0.9682 |
| Method | MAE | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Addition | 0.1952 | 0.272 | 0.9601 |
| Max | 0.2156 | 0.2948 | 0.9453 |
| Concatenation | 0.2126 | 0.2909 | 0.9468 |
| Proposed Method | 0.1550 | 0.2250 | 0.9682 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, D.; Bian, S.; Xie, X.; Wang, C.; Xiao, D. Two-Stream Bidirectional Interaction Network Based on RGB-D Images for Duck Weight Estimation. Animals 2025, 15, 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071062
Zhu D, Bian S, Xie X, Wang C, Xiao D. Two-Stream Bidirectional Interaction Network Based on RGB-D Images for Duck Weight Estimation. Animals. 2025; 15(7):1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071062
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Diqi, Shan Bian, Xiaofeng Xie, Chuntao Wang, and Deqin Xiao. 2025. "Two-Stream Bidirectional Interaction Network Based on RGB-D Images for Duck Weight Estimation" Animals 15, no. 7: 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071062
APA StyleZhu, D., Bian, S., Xie, X., Wang, C., & Xiao, D. (2025). Two-Stream Bidirectional Interaction Network Based on RGB-D Images for Duck Weight Estimation. Animals, 15(7), 1062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15071062






