Toxic Effects of Waterborne Pb Exposure on Hematological Parameters and Plasma Components in Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Fish and Environment
2.2. Lethal Concentration 50% (LC50)
2.3. Hematological Parameters
2.4. Plasma Components
2.5. Statistical Analysis Method
3. Results
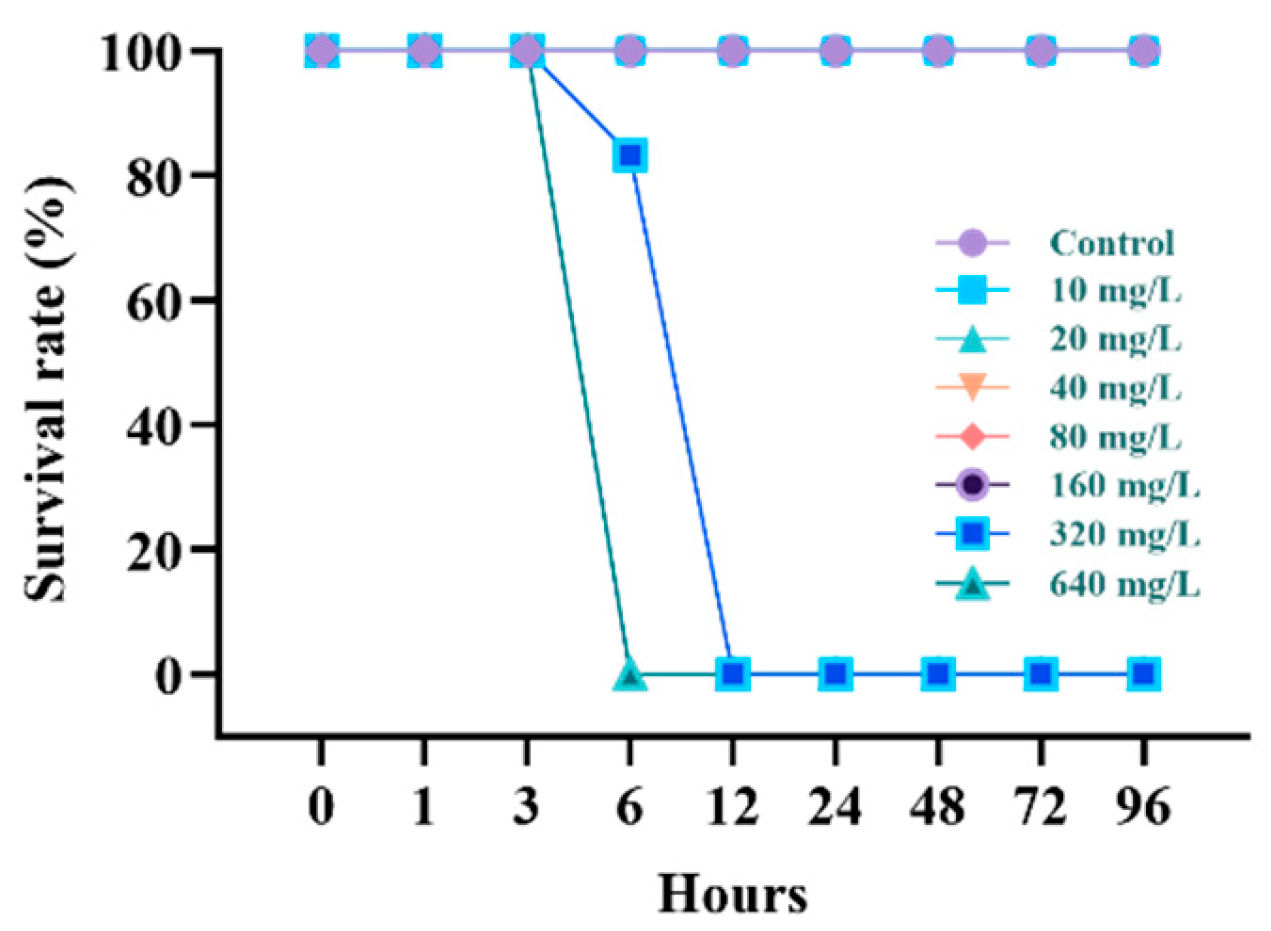
3.1. Survival Rate and Lethal Concentration (LC50)
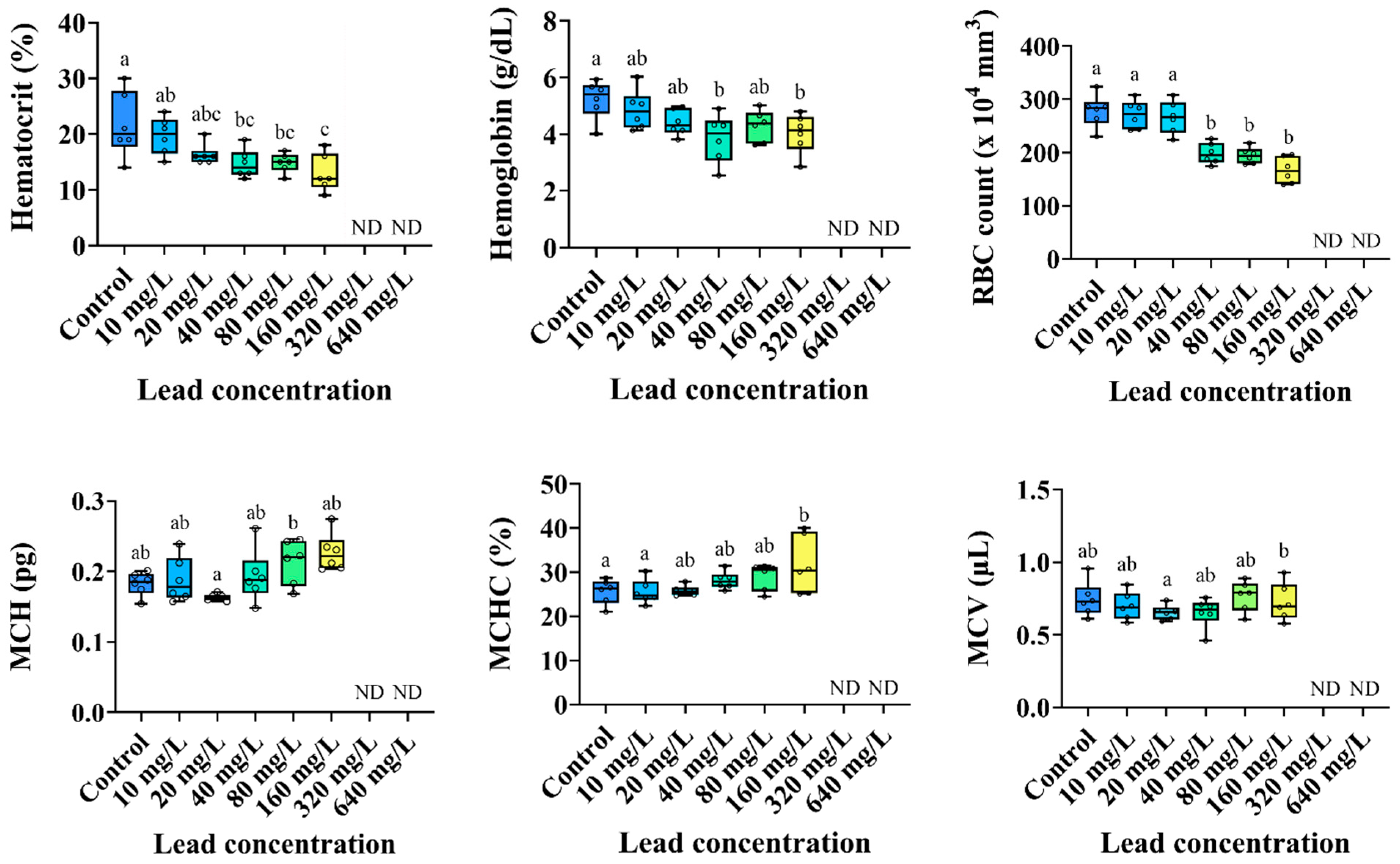
3.2. Hematological Parameters
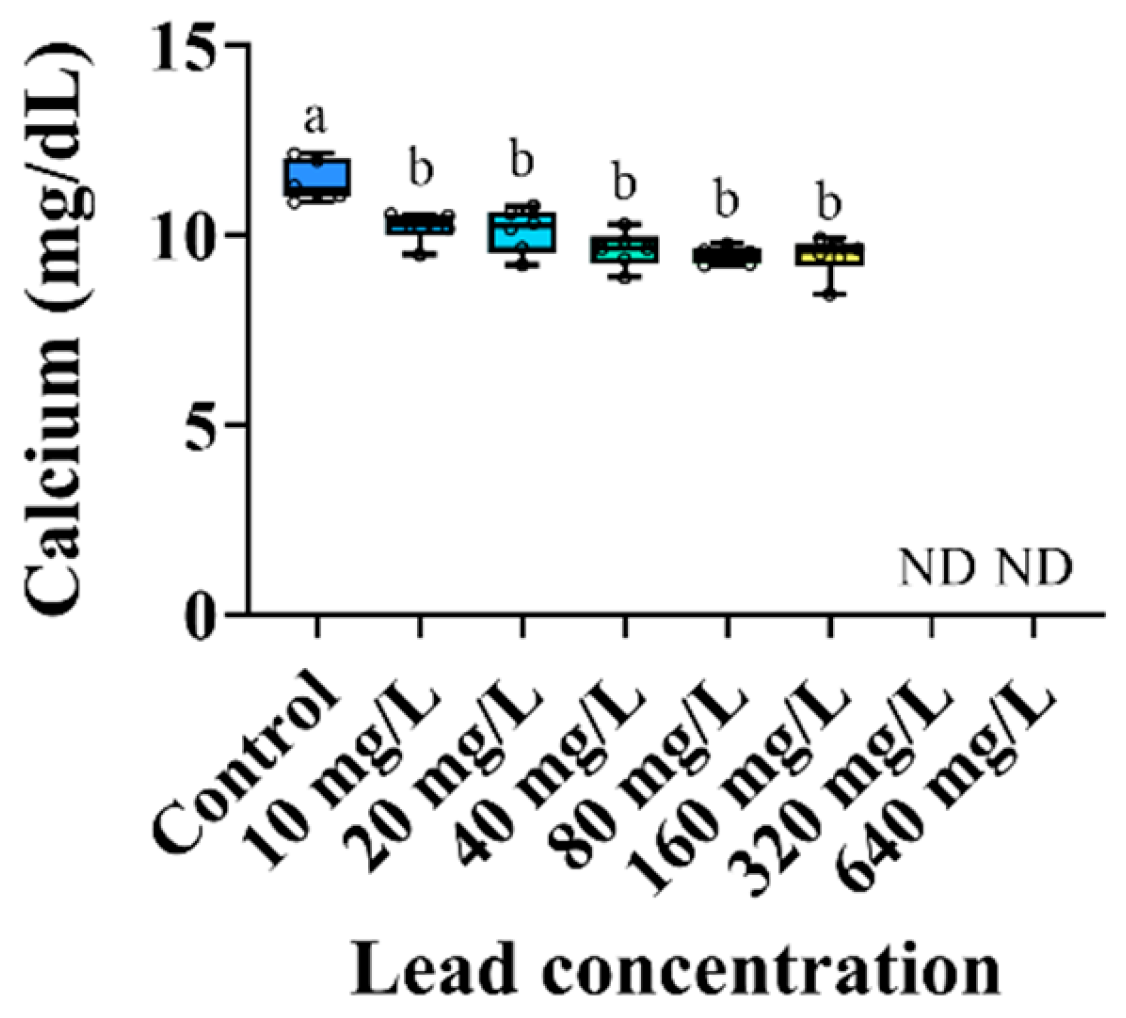
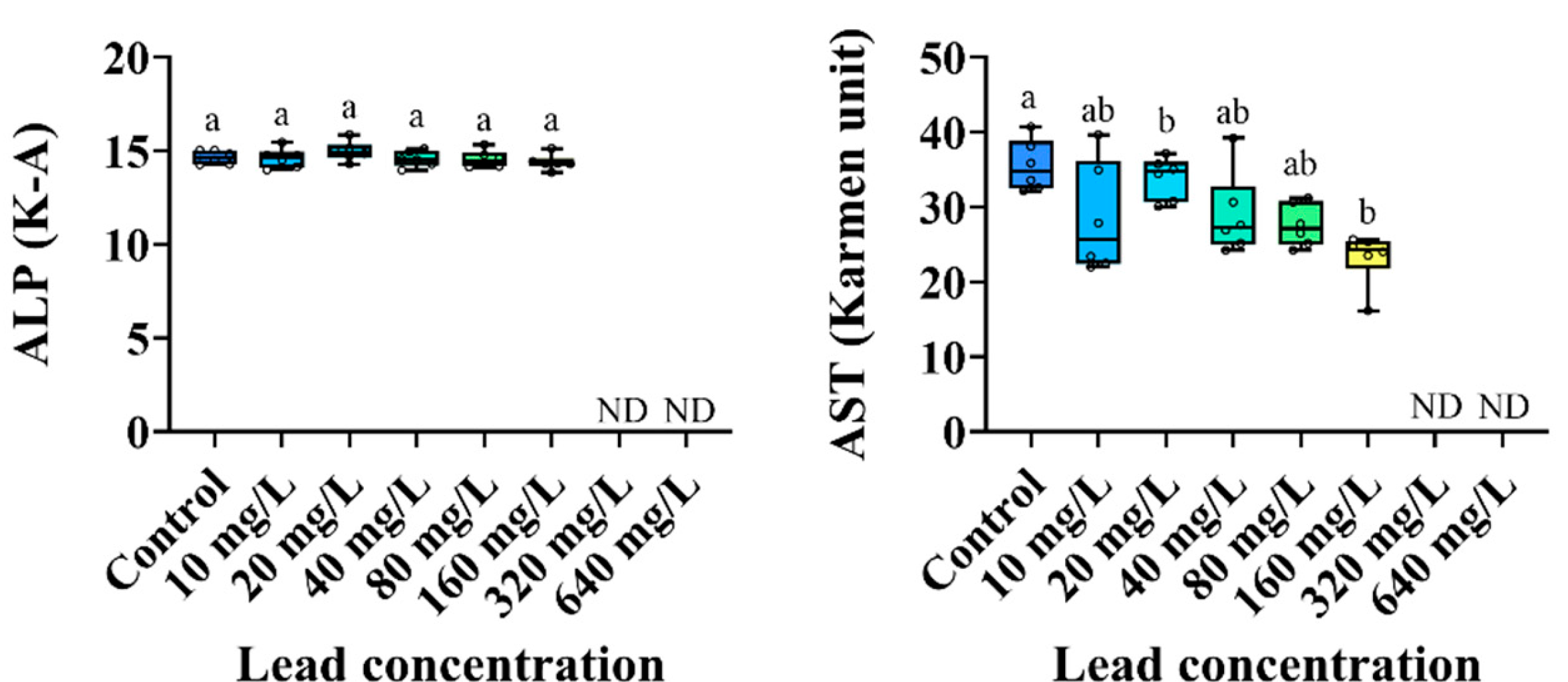
3.3. Plasma Components
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narwal, N.; Kakakhel, M.A.; Katyal, D.; Yadav, S.; Rose, P.K.; Rene, E.R.; Rakib, M.R.J.; Khoo, K.S.; Kataria, N. Interactions between microplastic and heavy metals in the aquatic environment: Implications for toxicity and mitigation strategies. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kang, J.C.; Shin, Y.K.; Ma, K.H.; Chin, P. Histological responses of the flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus exposed to copper. Fish Pathol. 2001, 14, 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Kaya, H.; Akbulut, M. Effects of waterborne lead exposure in mozambique tilapia: Oxidative stress, osmoregulatory responses, and tissue accumulation. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2015, 27, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S. The Mechanism of Waterborne Lead Uptake and Toxicity in Daphnia magna. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ara, A.; Usmani, J.A. Lead toxicity: A review. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2015, 8, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Song, Z.; Bi, Y.; Li, Y.; Lan, X.; Pan, C.; Foulkes, N.; et al. Early-life lead exposure induces long-term toxicity in the central nervous system: From zebrafish larvae to juveniles and adults. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakakhel, M.A.; Narwal, N.; Kataria, N.; Johari, S.A.; Din, S.Z.U.; Jiang, Z.; Khoo, K.S.; Xiaotao, S. Deciphering the dysbiosis caused in the fish microbiota by emerging contaminants and its mitigation strategies—A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 237, 117002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.C.; Glover, C.N.; Wood, C.M. Dietary Pb accumulation in juvenile freshwater rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 51, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Du, H.; Fu, L.; Jin, C.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H. Effects of dietary Pb on accumulation, histopathology, and digestive enzyme activities in the digestive system of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2009, 127, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimi, M.; Mahboobi-Soofiani, N.; Malekpouri, P. Effects of water-borne copper and lead on metabolic and excretion rate of bahaii loach (Turcinoemacheilus bahaii). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2018, 60, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mager, E.M.; Grosell, M. Effects of acute and chronic waterborne lead exposure on the swimming performance and aerobic scope of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 154, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizza, M.; Giusi, G.; Crudo, M.; Canonaco, M.; Facciolo, R.M. Lead-induced neurodegenerative events and abnormal behaviors occur via ORXRergic/GABAARergic mechanisms in a marine teleost. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui Thi, N.H.; Nguyen Thi, N.A.; Audira, G.; Siregar, P.; Liang, S.T.; Huang, J.C.; Hsiao, C.D. Chronic exposure to low concentration lead chloride-induced anxiety and loss of aggression and memory in zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rufli, H. Introduction of moribund category to OECD fish acute test and its effect on suffering and LC50 values. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.N.A.; Elkhadrawy, B.A.; Mansour, A.T.; Abdel-Ghany, H.M.; Yassin, E.M.M.; Elsayyad, A.; Alwutayd, K.M.; Ismail, S.H.; Mahboub, H.H. Alleviating effect of a magnetite (Fe3O4) nanogel against waterborne-lead-induced physiological disturbances, histopathological changes, and lead bioaccumulation in African catfish. Gels 2023, 9, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, M.A.; Ateeq, B.; Ali, M.N.; Sabir, R.; Ahmad, W. Studies on lethal concentrations and toxicity stress of some xenobiotics on aquatic organisms. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, K.; Jaafar, A.M.; Akbar, J. Acute-lethal toxicity (LC50) Effect of Terminalia Catappa Linn. leaves extract on Oreochromis niloticus (Red Nile Tilapia) juveniles under static toxicity exposure. Orient. J. Chem. 2019, 35, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarkhani, R.; Hedayati, A.; Bagheri, T.; Shadi, A.; Khalili, M. Investigation of LC50, NOEC and LOEC of Zebra fish (Danio rerio) in response to common agricultural pesticides in Golestan province, Iran. J. Comp. Clin. Path. Res. 2012, 1, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Warith, A.W.A.; Younis, E.S.M.; Al-Asgah, N.A.; Rady, A.M.; Allam, H.Y. Bioaccumulation of lead nitrate in tissues and its effects on hematological and biochemical parameters of Clarias gariepinus. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 840–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witeska, M.; Kondera, E.; Szymańska, M.; Ostrysz, M. Hematological Changes in Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) after Short-Term Lead (Pb) Exposure. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2010, 19, 825–831. [Google Scholar]
- Rios, F.S.; Oba, E.T.; Fernandes, M.N.; Kalinin, A.L.; Rantin, F.T. Erythrocyte senescence and haematological changes induced by starvation in the neotropical fish traíra, Hoplias malabaricus (Characiformes, Erythrinidae). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 140, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Reshi, Q.M.; Fazio, F. The influence of the endogenous and exogenous factors on hematological parameters in different fish species: A review. Aquac. Int. 2020, 28, 869–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.H.; Lim, H.K.; Chang, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Myeong, J.I. Effects of 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine (T3) on osmoregulation following freshwater acclimation in starry flounder. Dev. Reprod. 2009, 13, 313–320. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H. Responses of Hematological Parameters, Antioxidant and Heat Shock Protein 90 in Starry Flounder (Platichthys stellatus) Exposed to Microplastics. Ph.D. Thesis, Pukyong National University, Busan, Republic of Korea, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, H.K.; Kim, Y.S.; Son, M.H.; Kim, K.D.; Jeong, M.H.; Chang, Y.J. Quality characteristics of starry flounder Platichthys stellatus meat reared in different salinity. J. Fish. Mar. Sci. Educ. 2012, 24, 324–332. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, H.D.; Park, H.J.; Kang, J.C. Change of growth performance, hematological parameters, and plasma component by hexavalent chromium exposure in starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2019, 22, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.; Madhuri, S. Heavy metals causing toxicity in animals and fishes. Res. J. Anim. Vet. Fish. Sci. 2014, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Eyckmans, M.; Lardon, I.; Wood, C.M.; De Boeck, G. Physiological effects of waterborne lead exposure in spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 126, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, P.R.; Sabhanayakam, S.; Krishnakumar, N.; Vadivelu, M. Morphological changes due to lead exposure and the influence of DMSA on the gill tissues of the freshwater fish, Catla catla. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 2440–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekoubin, H.; Gharedaashi, E.; Imanpour, M.R.; Montajami, S. Determination of LC50 of lead nitrate and copper sulfate in Caspian roach (Rutilus rutilus caspicus). Walailak J. Sci. Technol. 2012, 9, 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kshab, A.A.; Yehya, O.Q. Determination of the lethal concentration 50% (LC50) of lead chloride and its accumulation in different organs of Gambusia affinis fish. Iraqi J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 35, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, Z.; Khalesi, M.K.; Kohestan, E.S.; Rahmani, H. Comparison of lethal concentrations (LC50-96 h) of CdCl2, CrCl3, and Pb(NO3)2 in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Sutchi catfish (Pangasius hypophthalmus). Iran. J. Toxicol. 2012, 6, 672–680. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, S.A.J.I.D.; Javed, M.U.H.A.M.M.A.D.; Javid, A.R.S.H.A.D. Studies on acute toxicity of metals to the fish (Labeo rohita). Int. J. Agr. Biol. 2007, 9, 333–337. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, B.O.; Manjeet, K. Determination of LC50 of lead nitrate for a fish, Labeo rohita (Hamilton Buchanan). Int. Res. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 4, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Witeska, M.; Kondera, E.; Bojarski, B. Hematological and hematopoietic analysis in fish toxicology—A review. Animals 2023, 13, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, S.S.; Maqaddas, S.; Fazio, F.; Amouri, R.E.; Shaikh, G.S.; Rahim, A.; Khan, K.; Ullah, J.; Mohany, M.; Parrino, V.; et al. Evaluation of lead exposure effects on tissue accumulation, behavior, morphological and hemato-biochemical changes in common carp (Cyprinus carpio). J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2024, 86, 127523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, V.T.; Le, T.M.L.; Duong, T.Q.A.; Mai, N.A.T.; Thuong, H.N.T. Assessment of lead toxicity in red tilapia Oreochromis sp. through hematological parameters. Asian J. Agric. Biol. 2022, 10, 202101016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, S.; Waheed, N.; Khan, M.F.; Naseer, A.; Noreen, S.; Ahmad, Z.; Nawaz, U.; Ghayyur, S.; Rifu, X. Investigating the Influence of Specific Heavy Metals on the Haemato-Biochemical and Genotoxic Traits of Grass Carp. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2024, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çiftçi, N.; Karayakar, F.; Ay, Ö.; Cicik, B.; Erdem, C. Effects of copper and lead on some hematological parameters of Oreochromis niloticus. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 2771–2775. [Google Scholar]
- Ates, B.; Orun, I.; Talas, Z.S.; Durmaz, G.; Yilmaz, I. Effects of sodium selenite on some biochemical and hematological parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss Walbaum, 1792) exposed to Pb2+ and Cu2+. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 34, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergonul, M.B.; Atasagun, S.; Kocaturk, K. Alterations in the hematological and biochemical parameters and plasma ion concentrations of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L., 1758) after short-term exposure to sub-lethal concentrations of lead. Kafkas Univ. Vet. Fak. Derg. 2012, 18, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, N.S.; Cicik, B.; Erdem, C.; Ay, O. Effects of lead concentrations on sera parameters and hematocrit levels in Anguilla anguilla (Linnaeus, 1758). J. Fish. Sci 2008, 2, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, C.P.K.; Manikandavelu, D.; Arisekar, U.; Albeshr, M.F.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Sudhakar, O.; Keerthana, M.; Packialakshmi, J.S. Toxicological effect of endocrine disrupting heavy metal (Pb) on Mekong silurid Pangasius catfish, Pangasius hypophthalmus. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lall, S.P.; Kaushik, S.J. Nutrition and metabolism of minerals in fish. Animals 2021, 11, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, J.C. The lead accumulation and hematological findings in juvenile rockfish Sebastes schlegelii exposed to the dietary lead (II) concentrations. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 115, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghaed, A.T.; Ghelichpour, M.; Hoseini, S.M.; Amini, K. Hemolysis interference in measuring fish plasma biochemical indicators. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 1143–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastav, A.K.; Rai, R.; Suzuki, N.; Mishra, D.; Srivastav, S.K. Effects of lead on the plasma electrolytes of a freshwater fish, Heteropneustes fossilis. Int. Aquat. Res. 2013, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.M.; Risso, W.E.; Fernandes, M.N.; Martinez, C.B. Lead accumulation and its effects on the branchial physiology of Prochilodus lineatus. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 40, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atli, G.; Canli, M. Enzymatic responses to metal exposures in a freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 145, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagrana, C.C.; Apodaca, D.C.; David, C.P. Toxicity of Cu2+, Cd2+, and Pb2+ metal ions in chironomids and factors that affect metal accumulation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Environment Science and Engineering IPCBEE; LACSIT Press: Singapore, 2011; Volume 8, pp. 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Fiess, J.C.; Kunkel-Patterson, A.; Mathias, L.; Riley, L.G.; Yancey, P.H.; Hirano, T.; Grau, E.G. Effects of environmental salinity and temperature on osmoregulatory ability, organic osmolytes, and plasma hormone profiles in the Mozambique tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 146, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicik, B.; ENGiN, K. The effects of cadmium on levels of glucose in serum and glycogen reserves in the liver and muscle tissues of Cyprinus carpio (L., 1758). Turk. J. Vet. Anim. Sci. 2005, 29, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, C.B.R.; Nagae, M.Y.; Zaia, C.T.B.V.; Zaia, D.A.M. Acute morphological and physiological effects of lead in the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Braz. J. Biol. 2004, 64, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamalam, B.S.; Medale, F.; Panserat, S. Utilisation of dietary carbohydrates in farmed fishes: New insights on influencing factors, biological limitations and future strategies. Aquaculture 2017, 467, 3–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.; Krishnani, K.K.; Kumar, P.; Jha, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Singh, N.P. Dietary zinc promotes immuno-biochemical plasticity and protects fish against multiple stresses. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 62, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, M.; Usmani, N. Stress response of biomolecules (carbohydrate, protein and lipid profiles) in fish Channa punctatus inhabiting river polluted by Thermal Power Plant effluent. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 22, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinodhini, R.; Narayanan, M. The impact of toxic heavy metals on the hematological parameters in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2009, 6, 23–28. [Google Scholar]
- Nirmalan, N.; Nirmalan, M. Hormonal control of metabolism: Regulation of plasma glucose. Anaesth. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 21, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajirezaee, S.; Ajdari, A.; Azhang, B. Metabolite profiling, histological and oxidative stress responses in the grey mullet, Mugil cephalus exposed to the environmentally relevant concentrations of the heavy metal, Pb(NO3)2. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2021, 244, 109004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, H.; Akbulut, M.; Yilmaz, S. Influence of sublethal lead concentrations on glucose, serum enzymes and ion levels in tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies in Agriculture, Food and Environment (HAICTA 2015), Kavala, Greece, 17–20 September 2015; pp. 858–866. [Google Scholar]
- Öner, M.; Atli, G.; Canli, M. Changes in serum biochemical parameters of freshwater fish Oreochromis niloticus following prolonged metal (Ag, Cd, Cr, Cu, Zn) exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Dhara, K.; Chukwuka, A.V.; Pal, P.; Saha, N.C.; Faggio, C. Sub-lethal acute effects of environmental concentrations of inorganic mercury on hematological and biochemical parameters in walking catfish, Clarias batrachus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2023, 264, 109511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Yun, S.; Jun, J.W.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.G.; Kang, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Han, J.S.; Sukumaran, V.; Park, S.C. Therapeutic effect of intestinal autochthonous Lactobacillus reuteri P16 against waterborne lead toxicity in Cyprinus carpio. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluah, N.S.; Ulasi, A.M.; Nwani, C.D. Changes in the leucocyte and serum biochemistry in Clarias gariepinus (Burchfiel) exposed to sublethal lead chloride. Changes 2014, 4, 55–61. [Google Scholar]
- Atli, G.; Ariyurek, S.Y.; Kanak, E.G.; Canli, M. Alterations in the serum biomarkers belonging to different metabolic systems of fish (Oreochromis niloticus) after Cd and Pb exposures. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 40, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunçsoy, M.; Duran, S.; Ay, Ö.; Cicik, B.; Erdem, C. Effects of copper and lead applied singly and in mixture with chitosan on some sera parameters of Clarias gariepinus. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar]
- Fırat, Ö.; Kargın, F. Individual and combined effects of heavy metals on serum biochemistry of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2010, 58, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiseni, M.; Asayesh, S.; Shafiee Bazarnoie, S.; Mohseni, F.; Moradi, N.; Matouri, M.; Mirzaee, N. Biochemical alteration induced by cadmium and lead in common carp via an experimental food chain. Iran. J. Toxicol. 2016, 10, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Li, Z.; Hassan, S.; Ahmad, S.; Guo, X.; Wanghe, K.; Nabi, G. Heavy metals bioaccumulation and subsequent multiple biomarkers based appraisal of toxicity in the critically endangered Tor. putitora. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 113032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyat, M.S.; Ayyat, A.M.; Naiel, M.A.; Al-Sagheer, A.A. Reversal effects of some safe dietary supplements on lead contaminated diet-induced impaired growth and associated parameters in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture 2020, 515, 734580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiti, H.; Bislimi, K.; Bajgora, A.; Rexhepi, A.; Dalo, E. Protective effect of vitamin C against oxidative stress in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) induced by heavy metals. Int. J. Agric. Biosci. 2018, 7, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourian, K.; Baghshani, H.; Shahsavani, D. The effect of vitamin C on lead-induced plasma biochemical alterations in fish, Cyprinus carpio. Iran. J. Toxicol. 2019, 13, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fırat, Ö.; Cogun, H.Y.; Yüzereroğlu, T.A.; Gök, G.; Fırat, Ö.; Kargin, F.; Kötemen, Y. A comparative study on the effects of a pesticide (cypermethrin) and two metals (copper, lead) on serum biochemistry of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Fish. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 37, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccarty, L.S.; Borgert, C.J. Review of the toxicity of chemical mixtures: Theory, policy, and regulatory practice. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2006, 45, 119–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Toxicity of metal compounds: Knowledge and myths. Organometallics 2017, 36, 4071–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Cao, J.; Qin, X.; Qiu, W.; Mei, J.; Xie, J. Toxic effects on bioaccumulation, hematological parameters, oxidative stress, immune responses, and tissue structure in fish exposed to ammonia nitrogen: A review. Animals 2021, 11, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.K.; Kim, K.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kang, J.C. Toxic effects and depuration after the dietary lead (II) exposure on the bioaccumulation and hematological parameters in starry flounder (Platichthys stellatus). Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 45, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çoğun, H.Y.; Şahin, M. The effect of lead and zeolite on hematological and some biochemical parameters in Nile fish (Oreochromis niloticus). Curr. Prog. Biol. Res. 2013, 12, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu, E. The effects of lead-induced toxicity on metabolic biomarkers in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2016, 25, 1419–1427. [Google Scholar]

| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Temperature (°C) | 17.5 ± 0.3 |
| pH | 7.9 ± 0.1 |
| Salinity (‰) | 31.1 ± 0.1 |
| Dissolved Oxygen (mg/L) | 6.3 ± 0.3 |
| Ammonia (µg/L) | 17 ± 2.3 |
| Nitrite (µg/L) | 6.3 ± 0.8 |
| Nitrate (µg/L) | 0.12 ± 0.01 |
| Phosphate (µg/L) | 0.2 ± 0.02 |
| 95% Confidence Limits | |
|---|---|
| Probability | Estimate (mg/L) |
| 0.01 | 160.068 |
| 0.10 | 190.075 |
| 0.20 | 202.710 |
| 0.30 | 211.821 |
| 0.40 | 219.606 |
| 0.50 | 226.882 |
| 0.60 | 234.158 |
| 0.70 | 241.943 |
| 0.80 | 251.054 |
| 0.90 | 263.689 |
| 0.99 | 293.696 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, M.-J.; Lee, K.M.; Hur, S.-P.; Choi, C.Y.; Kim, J.-H. Toxic Effects of Waterborne Pb Exposure on Hematological Parameters and Plasma Components in Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus. Animals 2025, 15, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070932
Kim M-J, Lee KM, Hur S-P, Choi CY, Kim J-H. Toxic Effects of Waterborne Pb Exposure on Hematological Parameters and Plasma Components in Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus. Animals. 2025; 15(7):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070932
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Min-Jung, Kyung Mi Lee, Sung-Pyo Hur, Cheol Young Choi, and Jun-Hwan Kim. 2025. "Toxic Effects of Waterborne Pb Exposure on Hematological Parameters and Plasma Components in Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus" Animals 15, no. 7: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070932
APA StyleKim, M.-J., Lee, K. M., Hur, S.-P., Choi, C. Y., & Kim, J.-H. (2025). Toxic Effects of Waterborne Pb Exposure on Hematological Parameters and Plasma Components in Starry Flounder, Platichthys stellatus. Animals, 15(7), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15070932






