Identification of Gene Expression and Splicing QTLs in Porcine Muscle Associated with Meat Quality Traits
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
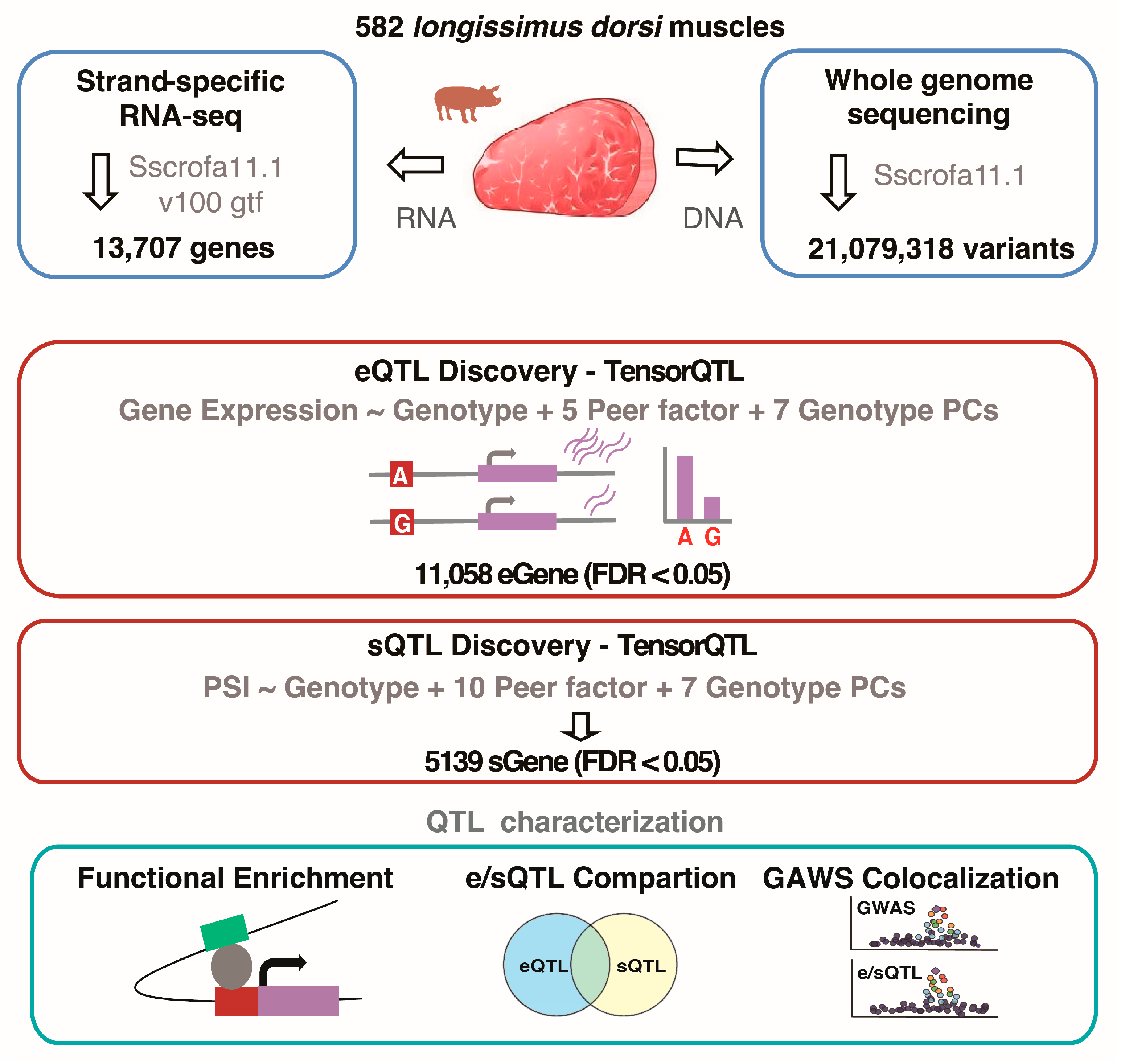
2.1. Animal Sampling and Sequencing
2.2. DNA Alignment and Variant Calling
2.3. Expression and Splicing Quantification
2.4. Covariate Selection
2.5. Estimating Cis-Heritability of Gene Expression and Intron Excision Ratio
2.6. Cis-eQTL and Cis-sQTL Mapping
2.7. GWAS of Meat Quality Traits
2.8. Colocalization and Quantitative Trait Transcripts (QTT) Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Data Process and Quality
3.2. Cis-Heritability of Gene Expression and Intron Excision Ratios
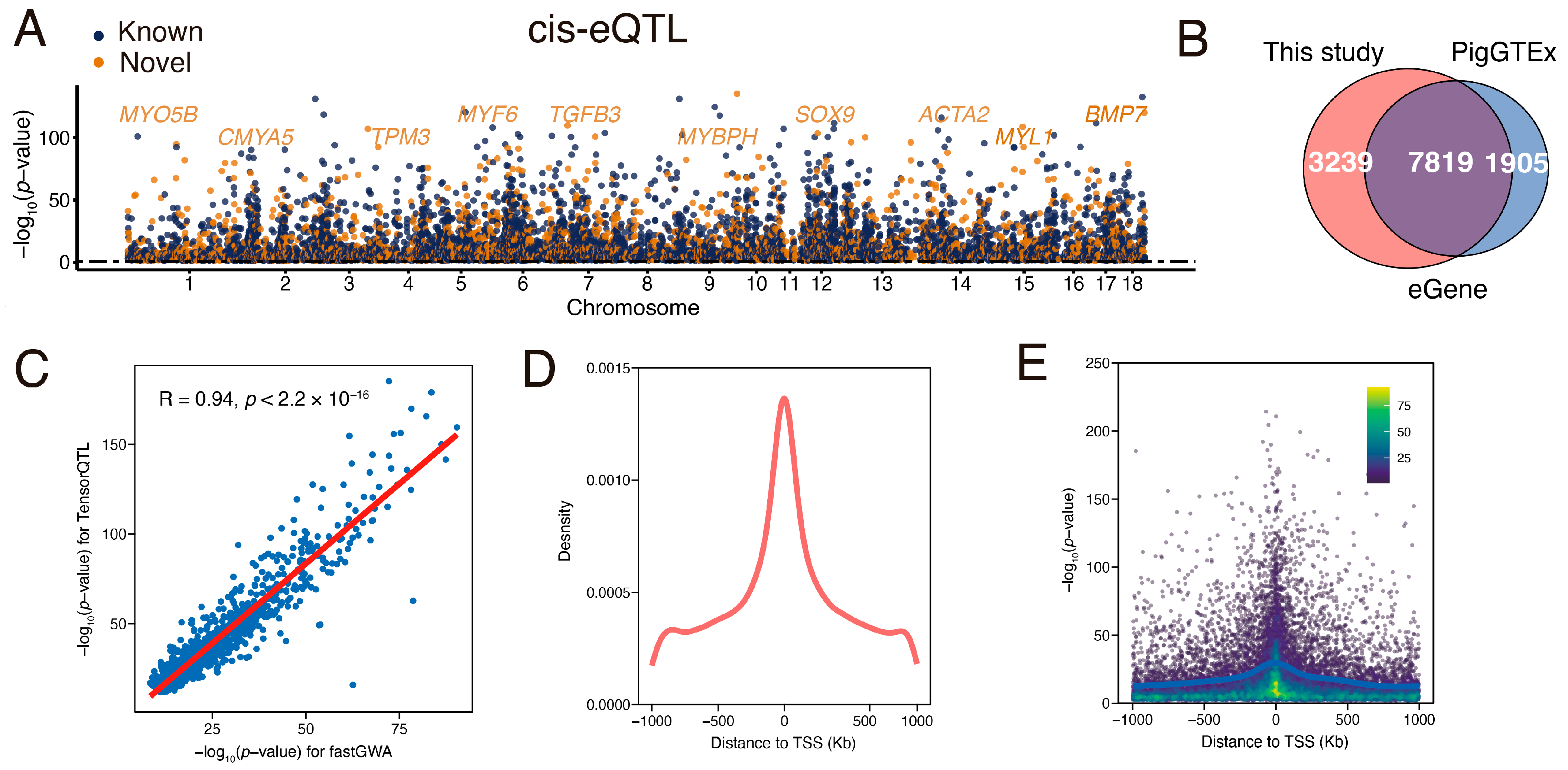
3.3. Identification and Characterization of Muscle eQTL
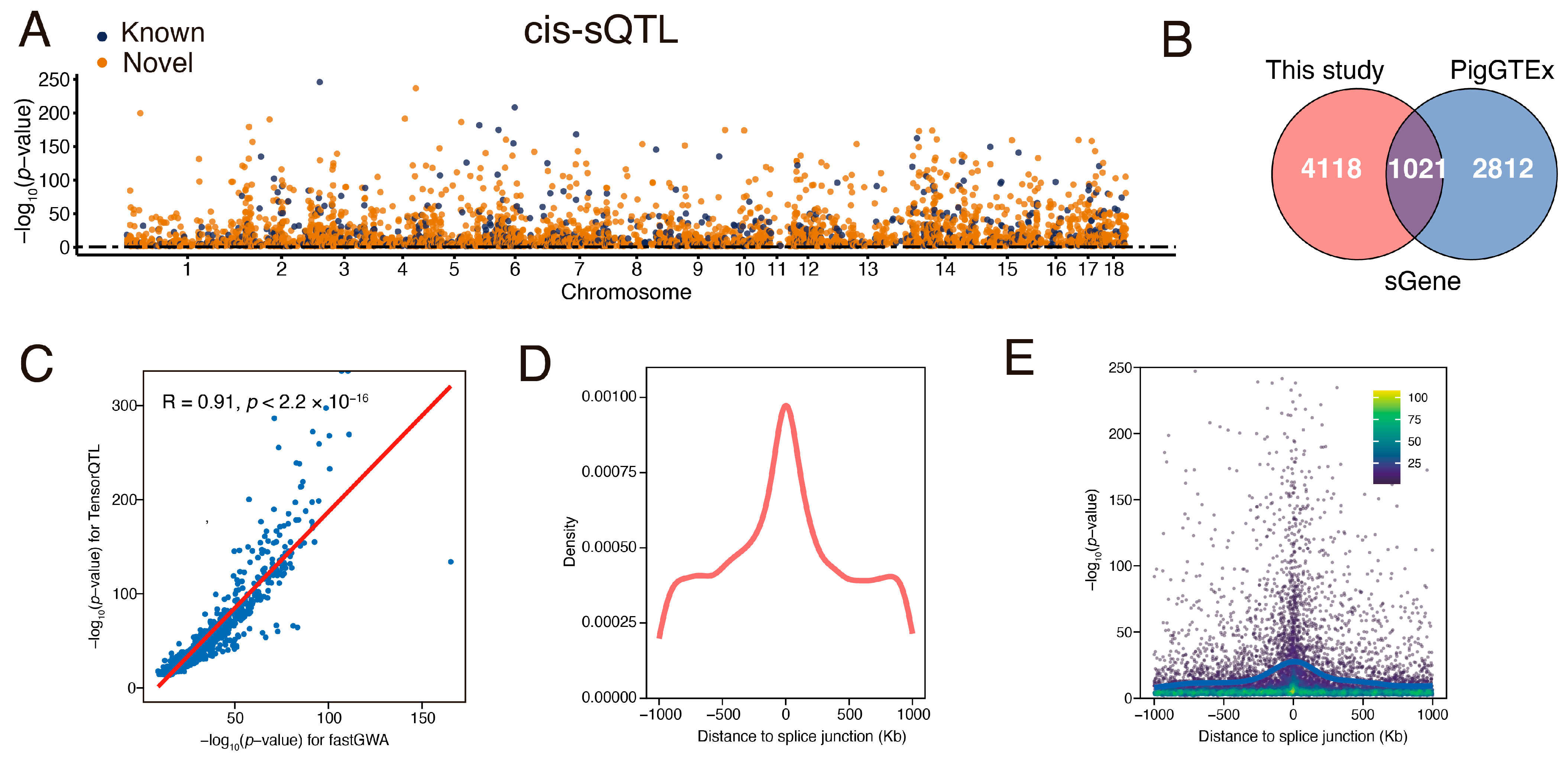
3.4. Identification and Characterization of Muscle sQTL
3.5. Independent Regulation of eQTLs and sQTLs
3.6. Colocalization Analysis of eQTL and sQTL with GWAS Locus
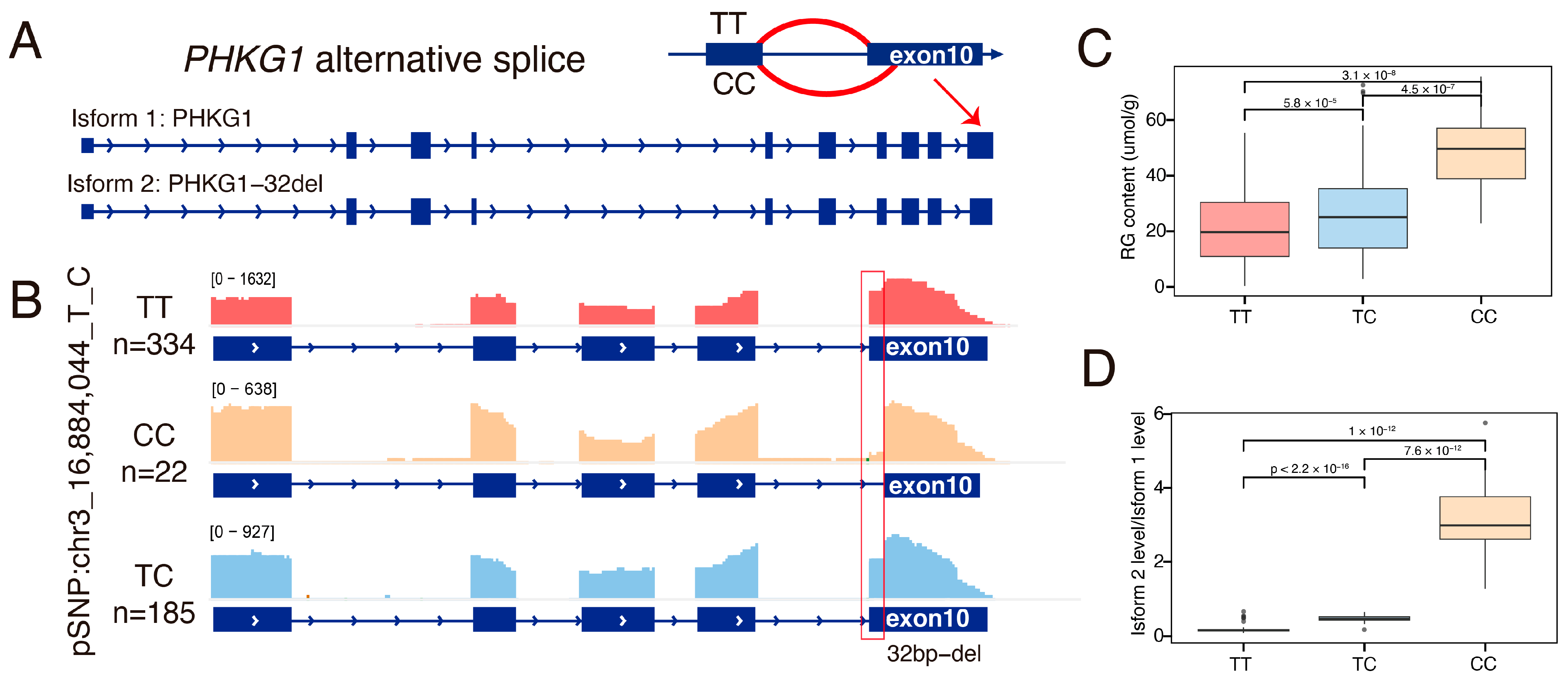
3.7. The Alternative Splicing of Exon 10 of the PHKG1 Affects Glycogen Metabolism
3.8. The PHKG1 Splice Site Usage Is Significantly Associated with GP-Related Meat Quality Traits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| eQTL | Expression quantitative trait loci |
| sQTL | Splice quantitative trait loci |
| GWAS | Genome-wide associated studies |
| RG | Residual glycogen content |
| TG | Total glycogen content |
| WGS | Whole-genome sequencing |
| TSS | Transcription start site |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| FDR | False discovery rate |
References
- Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, X.; Chen, C.; Xing, Y.; Duan, Y.; Xiao, S.; Yang, B.; Ma, J. An integrative analysis of transcriptome and GWAS data to identify potential candidate genes influencing meat quality traits in pigs. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 748070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, L.; Georges, M. Domestic-animal genomics: Deciphering the genetics of complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 5, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-L.; Park, C.A.; Wu, X.-L.; Reecy, J.M. Animal QTLdb: An improved database tool for livestock animal QTL/association data dissemination in the post-genome era. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D871–D879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visscher, P.M.; Wray, N.R.; Zhang, Q.; Sklar, P.; McCarthy, M.I.; Brown, M.A.; Yang, J. 10 years of GWAS discovery: Biology, function, and translation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaid, D.J.; Chen, W.; Larson, N.B. From genome-wide associations to candidate causal variants by statistical fine-mapping. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2018, 19, 491–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Zhao, H. A review of post-GWAS prioritization approaches. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandiedonck, C. Genetic association of molecular traits: A help to identify causative variants in complex diseases. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-A.; Przytycka, T.M. Bridging the gap between genotype and phenotype via network approaches. Front. Genet. 2013, 3, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consortium, G. The GTEx Consortium atlas of genetic regulatory effects across human tissues. Science 2020, 369, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, Y.; Canela-Xandri, O.; Wang, S.; Yu, Y.; Cai, W.; Li, B.; Xiang, R.; Chamberlain, A.J.; Pairo-Castineira, E. A multi-tissue atlas of regulatory variants in cattle. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, D.; Bai, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhong, C.; Hou, Y.; Consortium, C.; Lan, F.; Diao, S.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, B. The ChickenGTEx pilot analysis: A reference of regulatory variants across 28 chicken tissues. bioRxiv 2023. bioRxiv:2023.546670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Gao, Y.; Yin, H.; Bai, Z.; Liu, S.; Zeng, H.; Consortium, P.; Bai, L.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, B. A compendium of genetic regulatory effects across pig tissues. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay, N.R.; Gloudemans, M.; Antonio, M.L.; Abell, N.S.; Balliu, B.; Park, Y.; Martin, A.R.; Musharoff, S.; Rao, A.S.; Aguet, F. Impact of admixture and ancestry on eQTL analysis and GWAS colocalization in GTEx. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Gao, S.; Muegge, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, B. Advanced applications of RNA sequencing and challenges. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2015, 9, BBI.S28991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, B.; Chen, Y.; Gao, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, H. The eQTL colocalization and transcriptome-wide association study identify potentially causal genes responsible for economic traits in Simmental beef cattle. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Tang, Q.; Hu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.; Zeng, B.; Wang, Y.; He, M.; Li, Y.; Gui, L. A pig BodyMap transcriptome reveals diverse tissue physiologies and evolutionary dynamics of transcription. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Qin, J.; Rao, L.; Cui, D.; Tang, X.; Chen, L.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, L. Genetic dissection and genomic prediction for pork cuts and carcass morphology traits in pig. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukund, K.; Subramaniam, S. Skeletal muscle: A review of molecular structure and function, in health and disease. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2020, 12, e1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Shi, X.e.; Lu, H.; Xia, B.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, G. RNA-seq transcriptome analysis of extensor digitorum longus and soleus muscles in large white pigs. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2016, 291, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoa, V.B.; Seong, P.-N.; Cho, S.-H.; Kang, S.-M.; Kim, Y.-S.; Moon, S.-S.; Choi, Y.-M.; Kim, J.-H.; Seol, K.-H. Quality characteristics and flavor compounds of pork meat as a function of carcass quality grade. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Ma, T.; Liu, Y.; Long, H.; Cheng, H.; Fang, M.; Gong, J.; Li, X. Genome-wide analysis of expression QTL (eQTL) and allele-specific expression (ASE) in pig muscle identifies candidate genes for meat quality traits. Genet. Sel. Evol. 2020, 52, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez-Irizarry, D.; Casiro, S.; Daza, K.R.; Bates, R.O.; Raney, N.E.; Steibel, J.P.; Ernst, C.W. Genetic control of longissimus dorsi muscle gene expression variation and joint analysis with phenotypic quantitative trait loci in pigs. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. SNP-Based and Kmer-Based eQTL Analysis Using Transcriptome Data. Animals 2024, 14, 2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Mao, H.; Ren, J.; Yan, X.; Duan, Y.; Yang, G.; Ren, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, B.; Ouyang, J. A linkage map of the porcine genome from a large-scale White Duroc× Erhualian resource population and evaluation of factors affecting recombination rates. Anim. Genet. 2009, 40, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warr, A.; Affara, N.; Aken, B.; Beiki, H.; Bickhart, D.M.; Billis, K.; Chow, W.; Eory, L.; Finlayson, H.A.; Flicek, P. An improved pig reference genome sequence to enable pig genetics and genomics research. Gigascience 2020, 9, giaa051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Han, D. BWA-MEME: BWA-MEM emulated with a machine learning approach. Bioinformatics 2022, 38, 2404–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A.; Vilella, A.J.; Cuppen, E.; Nijman, I.J.; Prins, P. Sambamba: Fast processing of NGS alignment formats. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2032–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, A.; Hanna, M.; Banks, E.; Sivachenko, A.; Cibulskis, K.; Kernytsky, A.; Garimella, K.; Altshuler, D.; Gabriel, S.; Daly, M. The Genome Analysis Toolkit: A MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, T.; Li, H.; Chang, P.C.; Lin, M.F.; Carroll, A.; McLean, C.Y. Accurate, scalable cohort variant calls using DeepVariant and GLnexus. Bioinformatics 2021, 36, 5582–5589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. featureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shumate, A.; Wong, B.; Pertea, G.; Pertea, M. Improved transcriptome assembly using a hybrid of long and short reads with StringTie. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2022, 18, e1009730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolayeva, O.; Robinson, M.D. edgeR for differential RNA-seq and ChIP-seq analysis: An application to stem cell biology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1150, 45–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.I.; Knowles, D.A.; Humphrey, J.; Barbeira, A.N.; Dickinson, S.P.; Im, H.K.; Pritchard, J.K. Annotation-free quantification of RNA splicing using LeafCutter. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegle, O.; Parts, L.; Piipari, M.; Winn, J.; Durbin, R. Using probabilistic estimation of expression residuals (PEER) to obtain increased power and interpretability of gene expression analyses. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; de Bakker, P.I.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lee, S.H.; Goddard, M.E.; Visscher, P.M. GCTA: A tool for genome-wide complex trait analysis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor-Weiner, A.; Aguet, F.; Haradhvala, N.J.; Gosai, S.; Anand, S.; Kim, J.; Ardlie, K.; Van Allen, E.M.; Getz, G. Scaling computational genomics to millions of individuals with GPUs. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, J.; Zhou, L.; Ren, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, H.; Xie, X. A splice mutation in the PHKG1 gene causes high glycogen content and low meat quality in pig skeletal muscle. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Stephens, M. Genome-wide efficient mixed-model analysis for association studies. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 821–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giambartolomei, C.; Vukcevic, D.; Schadt, E.E.; Franke, L.; Hingorani, A.D.; Wallace, C.; Plagnol, V. Bayesian test for colocalisation between pairs of genetic association studies using summary statistics. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Wu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, Q.; Ke, S.; He, M.; Fu, H. ABO genotype alters the gut microbiota by regulating GalNAc levels in pigs. Nature 2022, 606, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Gong, H.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, T.; Lin, Z.; Li, J.; Xiao, S.; Yang, B.; Huang, L. Mapping short tandem repeats for liver gene expression traits helps prioritize potential causal variants for complex traits in pigs. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.R.; Gussoni, E. Tropomyosin 3 (TPM3) function in skeletal muscle and in myopathy. Skelet. Muscle 2023, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropka-Molik, K.; Eckert, R.; Piórkowska, K. The expression pattern of myogenic regulatory factors MyoD, Myf6 and Pax7 in postnatal porcine skeletal muscles. Gene Expr. Patterns 2011, 11, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagakura, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Jeong, J.; Hinata, N.; Katori, Y.; Chang, W.-J.; Abe, S. Switching of Sox9 expression during musculoskeletal system development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, X.-y.; Guo, P.; Wang, D.-l. MYBPC2 and MYL1 as significant gene markers for rhabdomyosarcoma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 1533033820979669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Yao, Y.; Yin, H.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; Kern, C.; Halstead, M.; Chanthavixay, G.; Trakooljul, N. Pig genome functional annotation enhances the biological interpretation of complex traits and human disease. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Wu, Y.; Fang, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, S.; Zeng, J.; Yang, J. Genetic control of RNA splicing and its distinct role in complex trait variation. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R.; Fang, L.; Liu, S.; Macleod, I.M.; Liu, Z.; Breen, E.J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, G.E.; Tenesa, A.; Mason, B.A. Gene expression and RNA splicing explain large proportions of the heritability for complex traits in cattle. Cell Genom. 2023, 3, 100385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Velez-Irizarry, D.; Ernst, C.W.; Huang, W. Mapping splice QTLs reveals distinct transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulatory variation of gene expression and identifies putative alternative splicing variation mediating complex trait variation in pigs. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.E.; Charenton, C.; Nagai, K. RNA splicing by the spliceosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapel, X.M.; Kadri, N.K.; Leonard, A.S.; He, Q.; Lloret-Villas, A.; Bhati, M.; Hiltpold, M.; Pausch, H. Molecular quantitative trait loci in reproductive tissues impact male fertility in cattle. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominic Mills, J.; Kawahara, Y.; Janitz, M. Strand-specific RNA-Seq provides greater resolution of transcriptome profiling. Curr. Genom. 2013, 14, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liberman, L.M.; Mukherjee, N.; Benfey, P.N.; Ohler, U. Integrated detection of natural antisense transcripts using strand-specific RNA sequencing data. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 1730–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, J.-i.; Suzuki, Y.; Sakate, R.; Sato, Y.; Seki, M.; Irie, T.; Takeuchi, N.; Ueda, T.; Nakao, M.; Sugano, S. Low conservation and species-specific evolution of alternative splicing in humans and mice: Comparative genomics analysis using well-annotated full-length cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 6386–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Abbreviation | Traits | R2 | p-Value | T-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proximal splice site: chr3:16,830,087:16,830,325: clu_20067 | ||||
| LDRG | Residual Glycogen, mmol/g | 0.15 | 9.59 × 10−21 | −9.73 |
| LDTG | Total Glycogen, mmol/g | 0.08 | 1.57 × 10−11 | −6.89 |
| LDpH24h | pH 24 h of LM | 0.01 | 1.03 × 10−2 | 2.57 |
| LDL24h | Minolta L value 24 h of LM | 0.01 | 4.56 × 10−2 | −2.00 |
| LDEZ24h | 24-h drip loss of LM, % | 0.00 | 1.98 × 10−1 | −1.29 |
| LDintFAT | Intramuscular fat content of LM | 0.00 | 6.65 × 10−1 | 0.43 |
| Distal splice site: chr3:16,830,087:16,830,357: clu_20067 (32-del) | ||||
| LDRG | Residual Glycogen, mmol/g | 0.15 | 4.74 × 10−21 | 9.82 |
| LDTG | Total Glycogen, mmol/g | 0.08 | 1.85 × 10−11 | 6.86 |
| LDpH24h | pH 24 h of LD | 0.01 | 1.25 × 10−2 | −2.51 |
| LDL24h | Minolta L value 24 h of LD | 0.01 | 5.78 × 10−2 | 1.90 |
| LDEZ24h | 24-h drip loss of LD, % | 0.00 | 2.08 × 10−1 | 1.26 |
| LDintFAT | Intramuscular fat content of LD | 0.00 | 6.68 × 10−1 | −0.40 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Ling, C.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, Z. Identification of Gene Expression and Splicing QTLs in Porcine Muscle Associated with Meat Quality Traits. Animals 2025, 15, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091209
Zhou M, Ling C, Xiao H, Zhang Z. Identification of Gene Expression and Splicing QTLs in Porcine Muscle Associated with Meat Quality Traits. Animals. 2025; 15(9):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091209
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Meng, Chenjin Ling, Hui Xiao, and Zhiyan Zhang. 2025. "Identification of Gene Expression and Splicing QTLs in Porcine Muscle Associated with Meat Quality Traits" Animals 15, no. 9: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091209
APA StyleZhou, M., Ling, C., Xiao, H., & Zhang, Z. (2025). Identification of Gene Expression and Splicing QTLs in Porcine Muscle Associated with Meat Quality Traits. Animals, 15(9), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani15091209





