Expression of Markers Ki-67, Nestin, VEGF, CD34 and Apoptosis in Relatively Healthy Lung Tissue with Non-Changed and Metaplastic Bronchial Epithelium
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Microscopy
2.2.1. Routine Microscopy
2.2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.2.3. Immunohistochemistry Evaluation
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
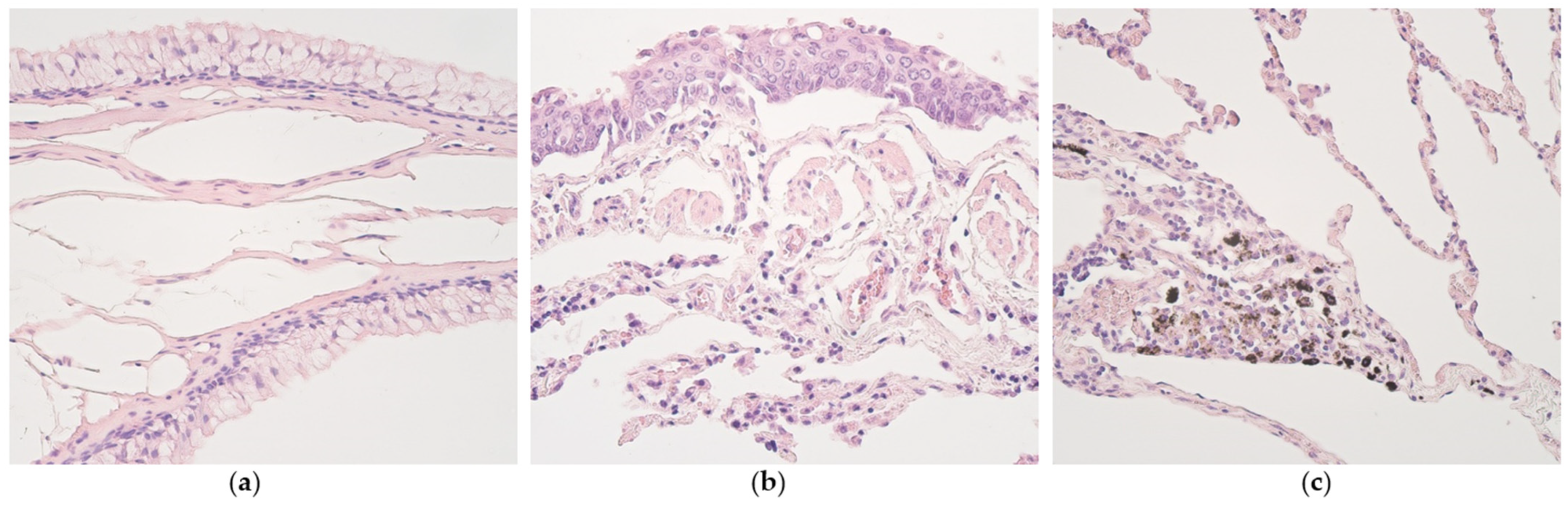
3.1. Routine Histology
3.2. Immunohistochemistry
3.3. Statistical Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Proliferative activity and programmed cell death are not prominent events in normal lung tissue with pseudostratified epithelium and in most cases of lungs with metaplastic epithelium. An exception is alveolar epithelium where apoptosis intensifies seemingly due to the specific aero-hematic barrier role.
- A moderate number of nestin-positive cells in the alveolar epithelium and cartilage of bronchi with pseudostratified ciliated epithelium suggests a significant role of neuronal origin cells in these structures, to be intensified in metaplastic bronchial epithelium.
- A practically non-changed number of CD34-positive cells excludes any difference in stimulation of endothelial origin cells between lungs with different types of epithelium, while an increase in VEGF in structures with metaplastic epithelium suggests the presence/influence of tissue ischemia impact on possible development/maintenance of metaplasia.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kotton, D.N.; Morrisey, E.E. Lung regeneration: Mechanisms, applications and emerging stem cell populations. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, Y.Y.; Cao, W.W.; Li, L.; Li, S.P.; Liu, T.; Wan, H.Y.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Tang, H. MicroRNA-519d targets MKi67 and suppresses cell growth in the hepatocellular carcinoma cell line QGY-7703. Cancer Lett. 2011, 28, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inwald, E.C.; Klinkhammer-Schalke, M.; Hofstädter, F.; Zeman, F.; Koller, M.; Gerstenhauer, M.; Ortmann, O. Ki-67 is a prognostic parameter in breast cancer patients: Results of a large population-based cohort of a cancer registry. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 139, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sorbye, S.W.; Kilvaer, T.K.; Valkov, A.; Donnem, T.; Smeland, E.; Al-Shibli, K.; Bremnes, R.M.; Busund, L.T. Prognostic impact of Jab1, p16, p21, p62, Ki67 and Skp2 in soft tissue sarcomas. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e470682012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciancio, N.; Galasso, M.G.; Campisi, R.; Bivona, L.; Migliore, M.; Di Maria, G.U. Prognostic value of p53 and Ki67 expression in fiberoptic bronchial biopsies of patients with non small cell lung cancer. Multidiscip. Respir. Med. 2012, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobecki, M.; Mrouj, K.; Camasses, A.; Parisis, N.; Nicolas, E.; Llères, D.; Gerbe, F.; Prieto, S.; Krasinska, L.; David, A.; et al. The cell proliferation antigen Ki-67 organises heterochromatin. eLife 2016, 5, e13722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, A.; Susaki, M.; Takano, Y.; Mizusawa, M.; Mishima, M.; Iijima, M.; Kuroda, S.; Okada, T.; Nakamura, C. The Structural Function of Nestin in Cell Body Softening is Correlated with Cancer Cell Metastasis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, D.; Xiang, A.P.; Mao, F.F.; Zhang, L.; Di, C.G.; Liu, X.M.; Shao, Y.; Ma, B.F.; Lee, J.H.; Ha, K.S.; et al. Nestin is required for the proper self-renewal of neural stem cells. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 2162–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupkova, O., Jr.; Loja, T.; Zambo, I.; Veselska, R. Nestin expression in human tumors and tumor cell lines. Neoplasma 2010, 57, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, N.; Ono, W.; Mizoguchi, T.; Nagasawa, T.; Frenette, P.S.; Kronenberg, H.M. Vasculature-associated cells expressing nestin in developing bones encompass early cells in the osteoblast and endothelial lineage. Dev. Cell 2014, 29, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.H.; Cai, B.; Tuo, Y.; Wang, J.; Zang, Z.J.; Tu, X.; Gao, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, W.; Li, G.; et al. Characterization of Nestin-positive stem Leydig cells as a potential source for the treatment of testicular Leydig cell dysfunction. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1466–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Day, K.; Shefer, G.; Richardson, J.B.; Enikolopov, G.; Yablonka-Reuveni, Z. Nestin-GFP reporter expression defines the quiescent state of skeletal muscle satellite cells. Dev. Biol. 2007, 304, 246–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, D.O. Vascular endothelial growth factors and vascular permeability. Cardiovasc. Res. 2010, 87, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrara, N.; Gerber, H.P.; LeCouter, J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, S.L.; Flower, V.A.; Pauling, J.D.; Millar, A.B. VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) and Fibrotic Lung Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barratt, S.L.; Blythe, T.; Jarrett, C.; Ourradi, K.; Shelley-Fraser, G.; Day, M.J.; Qiu, Y.; Harper, S.; Maher, T.M.; Oltean, S.; et al. Differential Expression of VEGF-Axxx Isoforms Is Critical for Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sidney, L.E.; Branch, M.J.; Dunphy, S.E.; Dua, H.S.; Hopkinson, A. Concise review: Evidence for CD34 as a common marker for diverse progenitors. Stem Cells 2014, 32, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.S.; Ning, H.; Lin, G.; Lue, T.F. Is CD34 truly a negative marker for mesenchymal stromal cells? Cytotherapy 2012, 14, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, J.S.; McNagny, K.M. Novel functions of the CD34 family. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121 Pt 22, 3683–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nielsen, J.S.; McNagny, K.M. CD34 is a key regulator of hematopoietic stem cell trafficking to bone marrow and mast cell progenitor trafficking in the periphery. Microcirculation 2009, 16, 487–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, P.; Volpe, M.C.; Jacob, J.; Maiocchi, S.; Salton, F.; Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, M.; Braga, L. Regeneration or Repair? The Role of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Cells 2022, 11, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Jiang, K.; Zeng, C.; Zhu, R.; Chu, H.; Liu, H.; Du, J. Synergism of TNF-α and IFN-β triggers human airway epithelial cells death by apoptosis and pyroptosis. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 153, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyrylkova, K.; Kyryachenko, S.; Leid, M.; Kioussi, C. Detection of apoptosis by TUNEL assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 887, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arons, M.; Pilmane, M.; Bhaskar, A.; Kopsky, D.J.; Romanenko, V.; Rohof, O. Pulsed Radiofrequency Increases Nestin and Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 Expression in Porcine Lumbar Dorsal Root Ganglion. Anesthesiol. Pain Med. 2022, 12, e110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilmane, M.; Sumerags, D.; Jain, N.; Jain, S.; Sumeraga, G. Singer’s Nodules: Investigating the Etiopathogenetic Markers Progressing Their Pathogenesis and Clinical Manifestations. Biology 2021, 10, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnizone, M.; Vartina, E.; Pilmane, M. Morphologic comparison of blood vessels used for coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Folia Morphol. 2022, 81, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Imamura, Y.; Yoshimura, H.; Kobayashi, M. Induction of High Endothelial Venule-like Vessels in Oral and Cutaneous Lichen Planus: A Comparative Study. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2020, 68, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukaka, M.M. Statistics corner: A guide to appropriate use of correlation coefficient in medical research. Malawi Med. J. 2012, 24, 69–71. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.E.X.; Tarsi, J.; Ramkumar, T.; Horiuchi, T.K.; Cochran, R.; DeMartino, S.; Schechtman, K.B.; Hussain, I.; Holtzman, M.J.; Castro, M. NHLBI Severe Asthma Research Program (SARP). Epithelial cell proliferation contributes to airway remodeling in severe asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigden, H.M.; Alias, A.; Havelock, T.; O’Donnell, R.; Djukanovic, R.; Davies, D.E.; Wilson, S.J. Squamous Metaplasia Is Increased in the Bronchial Epithelium of Smokers with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciardolo, F.L.; Di Stefano, A.; van Krieken, J.H.; Sont, J.K.; van Schadewijk, A.; Rabe, K.F.; Donner, C.F.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Sterk, P.J.; Mauad, T. Proliferation and inflammation in bronchial epithelium after allergen in atopic asthmatics. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, Y.E.; Blatchford, P.; Hyun, D.S.; Keith, R.L.; Kennedy, T.C.; Wolf, H.; Byers, T.; Bunn, P.A., Jr.; Lewis, M.T.; Franklin, W.A.; et al. Bronchial epithelial Ki-67 index is related to histology, smoking, and gender, but not lung cancer or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 2425–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jeremy George, P.; Banerjee, A.K.; Read, C.A.; O’Sullivan, C.; Falzon, M.; Pezzella, F.; Nicholson, A.G.; Shaw, P.; Laurent, G.; Rabbitts, P.H. Surveillance for the detection of early lung cancer in patients with bronchial dysplasia. Thorax 2007, 62, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.F.; Lai, M.D.; Yang, R.R.; Chen, P.H.; Su, Y.Y.; Lv, B.J.; Sun, L.P.; Huang, Q.; Chen, S.Z. Histological types and significance of bronchial epithelial dysplasia. Mod. Pathol. 2006, 19, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giroux, V.; Rustgi, A.K. Metaplasia: Tissue injury adaptation and a precursor to the dysplasia-cancer sequence. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilmane, M.; Sidhoma, E.; Akota, I.; Kazoka, D. Characterization of Cytokines and Proliferation Marker Ki67 in Cleft Affected Lip Tissue. Medicina 2019, 55, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, D.C.; Gonçalves, A.K.; Cobucci, R.N.; Mendonça, R.C.; Lima, P.H.; Cavalcanti, G. Júnior. Immunohistochemical expression of p16, Ki-67 and p53 in cervical lesions—A systematic review. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera, M.; Wickramasinghe, K.; Brynes, R.; Bu, X.; Ma, Y.; Chandrasoma, P. Ki67 expression in different epithelial types in columnar lined oesophagus indicates varying levels of expanded and aberrant proliferative patterns. Histopathology 2005, 47, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.R.; Hagimoto, N.; Nakamura, M.; Matute-Bello, G. Apoptosis and epithelial injury in the lungs. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2005, 2, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Matute-Bello, G.; Liles, W.C.; Hayashi, S.; Kajikawa, O.; Lin, S.M.; Frevert, C.W.; Martin, T.R. Differential response of human lung epithelial cells to fas-induced apoptosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1949–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Héraud, F.; Héraud, A.; Harmand, M.F. Apoptosis in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaramillo-Rangel, G.; Chávez-Briones, M.D.; Ancer-Arellano, A.; Ortega-Martínez, M. Nestin-Expressing Cells in the Lung: The Bad and the Good Parts. Cells 2021, 10, 3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Martínez, M.; de-la-Garza-González, C.; Ancer-Rodríguez, J.; Jaramillo-Rangel, G. Nestin-positive Stem Cells Participate in Chondrocyte Renewal in Healthy Adult Lung Cartilage. Int. J. Morphol. 2014, 32, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortega-Martínez, M.; Romero-Núñez, E.; Niderhauser-García, A.; de-la-Garza-González, C.; Ancer-Rodríguez, J.; Jaramillo-Rangel, G. Evidence of chondrocyte turnover in lung cartilage, with the probable participation of nestin-positive cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 37, 239–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Martínez, M.; Rodríguez-Flores, L.E.; de-la-Garza-González, C.; Ancer-Rodríguez, J.; Jaramillo-Rangel, G. Detection of a novel stem cell probably involved in normal turnover of the lung airway epithelium. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2015, 19, 2679–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lai, X.; Yao, S.; Chen, H.; Cai, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wei, X.; et al. Nestin promotes pulmonary fibrosis via facilitating recycling of TGF-β receptor I. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2003721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, T.; Du, N. Hypoxia-Induced Nestin Regulates Viability and Metabolism of Lung Cancer by Targeting Transcriptional Factor Nrf2, STAT3, and SOX2. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 12, 9811905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Li, H.; Qian, Y.L.; Quan, R.L.; Chen, X.X.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, P.H.; Meng, X.M.; Jing, X.L.; et al. Nestin represents a potential marker of pulmonary vascular remodeling in pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with congenital heart disease. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2020, 149, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhagwani, A.R.; Hultman, S.; Farkas, D.; Moncayo, R.; Dandamudi, K.; Zadu, A.K.; Cool, C.D.; Farkas, L. Endothelial cells are a source of Nestin expression in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. PloS ONE 2019, 14, e0213890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koyama, S.; Sato, E.; Tsukadaira, A.; Haniuda, M.; Numanami, H.; Kurai, M.; Nagai, S.; Izumi, T. Vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA and protein expression in airway epithelial cell lines in vitro. Eur. Respir. J. 2002, 20, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voelkel, N.F.; Vandivier, R.W.; Tuder, R.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor in the lung. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2006, 290, L209-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medford, A.R.; Millar, A.B. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS): Paradox or paradigm? Thorax 2006, 61, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bates, D.O.; Beazley-Long, N.; Benest, A.V.; Ye, X.; Ved, N.; Hulse, R.P.; Barratt, S.; Machado, M.J.; Donaldson, L.F.; Harper, S.J.; et al. Physiological Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors as Homeostatic Regulators. Compr. Physiol. 2018, 8, 955–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peach, C.J.; Mignone, V.W.; Arruda, M.A.; Alcobia, D.C.; Hill, S.J.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Woolard, J. Molecular Pharmacology of VEGF-A Isoforms: Binding and Signalling at VEGFR2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varet, J.; Douglas, S.K.; Gilmartin, L.; Medford, A.R.; Bates, D.O.; Harper, S.J.; Millar, A.B. VEGF in the lung: A role for novel isoforms. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2010, 298, L768–L774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boussat, S.; Eddahibi, S.; Coste, A.; Fataccioli, V.; Gouge, M.; Housset, B.; Adnot, S.; Maitre, B. Expression and regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor in human pulmonary epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2000, 279, L371–L378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stuttfeld, E.; Ballmer-Hofer, K. Structure and function of VEGF receptors. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, T.; Kanoh, S.; Moskowitz, W.B.; Rubin, B.K. Cardiac asthma: Transforming growth factor-β from the failing heart leads to squamous metaplasia in human airway cells and in the murine lung. Chest 2012, 142, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karseladze, A.I. Impairment of vascularization of the surface covering epithelium induces ischemia and promotes malignization: A new hypothesis of a possible mechanism of cancer pathogenesis. Clin. Transl. Oncol. Off. Publ. Fed. Span. Oncol. Soc. Natl. Cancer Inst. Mex. 2015, 17, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pusztaszeri, M.P.; Seelentag, W.; Bosman, F.T. Immunohistochemical expression of endothelial markers CD31, CD34, von Willebrand factor, and Fli-1 in normal human tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, A.M.; Nesslinger, M.; Skipka, G.; Müller, K.M. Expression of CD34 in pulmonary endothelial cells in vivo. Pathobiology 2002, 70, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, B.C.; Gold, M.J.; Scheer, S.; Hughes, M.R.; Cait, J.; Debruin, E.; Chu, F.S.F.; Walker, D.C.; Soliman, H.; Rossi, F.M.; et al. Loss of Vascular CD34 Results in Increased Sensitivity to Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2017, 57, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| NESTIN | TUNEL | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bronchial Epithelium | Alveolar Epithelium | Cartilage | Bronchial Epithelium | Alveolar Epithelium | Cartilage | |
| Patients with non-changed bronchial and alveolar epithelium | ||||||
| Mean value | 0/+ | ++ | ++ | 0 | ++ | + |
| Patients with metaplastic bronchial epithelium | ||||||
| Mean value | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | ++ | 0/+ |
| VEGF | CD34 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bronchial Epithelium | Subepithelial Blood Vessels | Alveolar Blood Vessels | Subepithelial Blood Vessels | Alveolar Blood Vessels | |
| Patients with non-changed bronchial and alveolar epithelium | |||||
| Mean value | 0/+ | 0 | ++ | Variable | + |
| Patients with metaplastic bronchial epithelium | |||||
| Mean value | ++ | + | ++ | + | + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarina, K.Z.; Pilmane, M. Expression of Markers Ki-67, Nestin, VEGF, CD34 and Apoptosis in Relatively Healthy Lung Tissue with Non-Changed and Metaplastic Bronchial Epithelium. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11010007
Zarina KZ, Pilmane M. Expression of Markers Ki-67, Nestin, VEGF, CD34 and Apoptosis in Relatively Healthy Lung Tissue with Non-Changed and Metaplastic Bronchial Epithelium. Medical Sciences. 2023; 11(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarina, Kaiva Zile, and Mara Pilmane. 2023. "Expression of Markers Ki-67, Nestin, VEGF, CD34 and Apoptosis in Relatively Healthy Lung Tissue with Non-Changed and Metaplastic Bronchial Epithelium" Medical Sciences 11, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11010007
APA StyleZarina, K. Z., & Pilmane, M. (2023). Expression of Markers Ki-67, Nestin, VEGF, CD34 and Apoptosis in Relatively Healthy Lung Tissue with Non-Changed and Metaplastic Bronchial Epithelium. Medical Sciences, 11(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci11010007







