-
 Biologically-Based Notions About Uterine Bleeding During Myomectomy: Reasoning on Tradition and New Concepts
Biologically-Based Notions About Uterine Bleeding During Myomectomy: Reasoning on Tradition and New Concepts -
 The Potential Effects of Sensor-Based Virtual Reality Telerehabilitation on Lower Limb Function in Patients with Chronic Stroke Facing the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Case-Control Study
The Potential Effects of Sensor-Based Virtual Reality Telerehabilitation on Lower Limb Function in Patients with Chronic Stroke Facing the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Case-Control Study
Journal Description
Medical Sciences
Medical Sciences
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal, providing a platform for advances in basic, translational and clinical research, published quarterly online by MDPI. The Korean Society of Physical Medicine (KSPM) is affiliated with Medical Sciences and its members receive discounts on the article processing charges.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within Scopus, ESCI (Web of Science), PubMed, PMC, MEDLINE, CAPlus / SciFinder, and other databases.
- Journal Rank: JCR - Q1 (Medicine, General and Internal) / CiteScore - Q1 (General Medicine)
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 24.3 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 2.9 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: reviewers who provide timely, thorough peer-review reports receive vouchers entitling them to a discount on the APC of their next publication in any MDPI journal, in appreciation of the work done.
- Sections: published in 12 topical sections.
Impact Factor:
4.4 (2024)
Latest Articles
A Novel Method to Determine the Respiratory Compensation Point from Percutaneous Oxygen Saturation of Healthy Adults During a Ramp-Incremental Test: A Cross-Sectional Study
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 192; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030192 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: In exercise testing, the ventilatory threshold 1 (VT1) and ventilatory threshold 2 (VT2) are used in lifestyle-related diseases, cardiac rehabilitation, and athletic training. We investigated a VT2 measuring method using a pulse oximeter. Methods: Thirty-four adults (men: 15; women: 19) performed a
[...] Read more.
Background: In exercise testing, the ventilatory threshold 1 (VT1) and ventilatory threshold 2 (VT2) are used in lifestyle-related diseases, cardiac rehabilitation, and athletic training. We investigated a VT2 measuring method using a pulse oximeter. Methods: Thirty-four adults (men: 15; women: 19) performed a bicycle ergometer Ramp Test. VT1 values were determined using expiratory gas data. The bifurcation of the curve obtained by designating the pulse rate (PR) as an independent variable and SpO2/PR as a dependent variable was calculated using the residual sum of squares and defined as the SpO2 threshold (ST) (SpO2-Slope method). A second bifurcation with ST as the origin was further defined (ST2). ST2 validity was assessed by comparing and analyzing the differences and correlations with each VT2 obtained by expiratory gas analysis. Results: The correlation between ST2 determined by the SpO2-Slope method using PR as an index and VT2 obtained from respiratory gas analysis was significant, showing a positive correlation (r = 0.74~0.92; p < 0.01), with most data points falling within the 1.96 ± SD in the Bland–Altman analysis. Conclusions: ST2 values derived from SpO2 and pulse rate measurements by pulse oximeter may be a valuable VT2 measuring method.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Disease)
►
Show Figures
Open AccessReview
Mapping Cognitive Oncology: A Decade of Trends and Research Fronts
by
Anna Tsiakiri, Akyllina Despoti, Panagiota Koutsimani, Kalliopi Megari, Spyridon Plakias and Angeliki Tsapanou
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 191; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030191 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Cognitive and neuropsychological effects of cancer and its treatments have gained increasing attention over the past decade, with growing evidence of persistent deficits across multiple cancer types. While numerous studies have examined these effects, the literature remains fragmented, and no comprehensive bibliometric
[...] Read more.
Background: Cognitive and neuropsychological effects of cancer and its treatments have gained increasing attention over the past decade, with growing evidence of persistent deficits across multiple cancer types. While numerous studies have examined these effects, the literature remains fragmented, and no comprehensive bibliometric synthesis has been conducted to map the field’s intellectual structure and emerging trends. Methods: A bibliometric and science mapping analysis was performed using the Scopus database to identify peer-reviewed articles published between 2015 and 2025 on neuropsychological or cognitive outcomes in adult cancer populations. Data from 179 eligible publications were analyzed with VOSviewer and Microsoft Power BI, applying performance metrics and network mapping techniques, including co-authorship, bibliographic coupling, co-citation, and keyword co-occurrence analyses. Results: Publication output increased steadily over the decade, with leading contributions from the Journal of Neuro-Oncology, Psycho-Oncology, and Brain Imaging and Behavior. Co-citation analysis identified three core intellectual pillars: (i) clinical characterization of cancer-related cognitive impairment, (ii) mechanistic and neuroimaging-based investigations, and (iii) neurosurgical and neuropathological research in brain tumors. Keyword mapping revealed emerging themes in sleep and circadian rhythm research, biological contributors to cognitive decline, and scalable rehabilitation strategies such as web-based cognitive training. Collaborative networks, while showing dense local clusters, remained moderately fragmented across disciplines. Conclusions: This review provides the first quantitative, decade-spanning map of cognitive oncology research, highlighting both consolidated knowledge areas and underexplored domains. Future efforts should prioritize methodological standardization, cross-disciplinary collaboration, and integration of cognitive endpoints into survivorship care, with the ultimate aim of improving functional outcomes and quality of life for cancer survivors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Section Cancer and Cancer-Related Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Advances in Adoptive Cell Therapies in Cancer: From Mechanistic Breakthroughs to Clinical Frontiers and Overcoming Barriers
by
Syed Arman Rabbani, Mohamed El-Tanani, Yahia El-Tanani, Rakesh Kumar, Shrestha Sharma, Mohammad Ahmed Khan, Suhel Parvez, Alaa A. A. Aljabali, Mohammad I. Matalka and Manfredi Rizzo
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 190; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030190 - 15 Sep 2025
Abstract
Adoptive cell therapies (ACTs) have revolutionized cancer treatment by harnessing the specificity and potency of T lymphocytes. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells have achieved landmark successes in B-cell malignancies and multiple myeloma. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and T-cell receptor (TCR)-engineered T cells offer complementary
[...] Read more.
Adoptive cell therapies (ACTs) have revolutionized cancer treatment by harnessing the specificity and potency of T lymphocytes. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cells have achieved landmark successes in B-cell malignancies and multiple myeloma. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and T-cell receptor (TCR)-engineered T cells offer complementary strategies to target solid tumors and intracellular antigens. Despite these advances, ACTs face challenges including cytokine release syndrome, neurotoxicity, on-target/off-tumor effects, manufacturing scalability, and immunosuppressive tumor microenvironments. Innovative strategies, such as dual-antigen targeting, localized delivery, checkpoint blockade combinations, gene-editing, and machine-learning-guided antigen discovery, are being used to mitigate toxicity, enhance efficacy, and streamline production. As CAR-T, TIL, and TCR modalities converge with advances in manufacturing and computational biology, the next generation of “living drugs” promises broader applicability across hematologic and solid tumors, improved safety profiles, and better treatment outcomes for patients. This review details the evolution of ACTs from first-generation CAR constructs to next-generation “armored” designs. It also focuses on the development and clinical deployment of TIL and TCR therapies. Furthermore, it synthesizes mechanisms, pivotal clinical trial outcomes, and ongoing challenges of ACTs. It also highlights strategies that will drive broader, safer, and more durable applications of these therapies across hematologic and solid tumors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Section Cancer and Cancer-Related Diseases)
Open AccessArticle
Outcomes of Kidney Transplantation from Deceased Donors with Severe Acute Kidney Injury (AKIN Stage 3): A Preliminary Single-Centre Analysis
by
Juan A. Encarnación, Elisabeth Coll, Clara Manso, Santiago Llorente, Francisco Morales, Isabel Saura, Pedro López-Cubillana, Pablo Luis Guzman Martínez-Valls, Gloria Martínez, Isabel De la Fuente, Enrique Cárdenas, Jose L. Alonso-Romero, Paula Ruiz, José Moya, Beatriz Domínguez-Gil and Mario Royo-Villanova
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 188; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030188 - 14 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: The shortage of donor kidneys has prompted interest in using organs from donors with severe acute kidney injury (AKI), but robust data on outcomes from donors with AKIN stage 3 remain limited. Methods: This single-centre, retrospective cohort study compared outcomes of kidney
[...] Read more.
Background: The shortage of donor kidneys has prompted interest in using organs from donors with severe acute kidney injury (AKI), but robust data on outcomes from donors with AKIN stage 3 remain limited. Methods: This single-centre, retrospective cohort study compared outcomes of kidney transplants from deceased donors with AKIN stage 3 AKI to matched non-AKI donors (n = 57 per group; matched by donor age ±5 years, year of transplant, and major cardiovascular risk factors). Primary outcomes were delayed graft function (DGF), death-censored graft survival, and patient survival. Secondary outcomes included renal function at follow-up. Results: DGF occurred in 54.4% (31/57) of AKIN 3 recipients vs. 33.3% (19/57) of non-AKI recipients (risk difference 21.1%, 95% CI 3.1–39.2; p = 0.037). Five-year death-censored graft survival was 94.7% vs. 96.4% (HR 1.28, 95% CI 0.25–6.52; p = 0.645). Five-year patient survival was 84.8% vs. 84.0% (HR 0.96, 95% CI 0.30–3.05; p = 0.979). Median follow-up was 32 months. Conclusions: In this preliminary, selected kidneys from AKIN stage 3 donors yielded similar medium-term graft and patient survival to non-AKI donors, despite higher DGF incidence. Findings should be interpreted cautiously and confirmed in adequately powered, multicentre studies with extended follow-up.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Nephrology and Urology)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Bone Mineral Density and Serum Levels of Bone Remodeling Markers in Ankylosing Spondylitis Treated with Anti TNF-α Agents
by
Efren Gerardo Alvarez-Ayala, Jorge Ivan Gamez-Nava, Ana Miriam Saldaña-Cruz, Fabiola Gonzalez-Ponce, Betsabe Contreras-Haro, Melissa Ramirez-Villafaña, Edsaul Emilio Perez-Guerrero, Miriam Fabiola Alcaraz-Lopez, Eli Efrain Gomez-Ramirez, Juan Manuel Ponce-Guarneros, Norma Alejandra Rodriguez-Jimenez, Sylvia Elena Totsuka-Sutto, Alberto Daniel Rocha-Muñoz, Luis Alfonso Muñoz-Miranda, Laura Gonzalez-Lopez and Cesar Arturo Nava-Valdivia
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 189; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030189 - 13 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic autoinflammatory rheumatic disease mainly affecting the sacroiliac joints and spine, causing altered bone remodeling. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-17 contribute to bone loss by modulating pathways including Wnt/β-catenin, which is inhibited by proteins like
[...] Read more.
Background: Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic autoinflammatory rheumatic disease mainly affecting the sacroiliac joints and spine, causing altered bone remodeling. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-17 contribute to bone loss by modulating pathways including Wnt/β-catenin, which is inhibited by proteins like Dickkopf-1 (DKK-1) and sclerostin (SOST). Bone morphogenetic protein-6 (BMP-6) promotes osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. This study evaluated the association between serum levels of DKK-1, SOST, BMP-6, and bone mineral density (BMD) in AS patients treated with anti-TNF agents and conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs). Methods: A cross-sectional study included 76 AS patients diagnosed by modified New York criteria and 30 healthy donors matched by age and sex. BMD at the lumbar spine and hips was assessed by DXA in all participants. Disease activity (BASDAI) and functional index (BASFI) were measured in AS patients. Serum levels of DKK-1, SOST, BMP-6, TNF-α, and IL-17 were quantified by ELISA in both groups. AS patients were divided into two treatment groups: combined anti-TNFα and csDMARD therapy (n = 38), and only csDMARDs (n = 38). Results: Bone mineral density showed no significant statistical differences between the spine (p = 0.930) and hips (p = 0.876) in AS patients compared to healthy controls. The activity (BASDAI) and functionality (BASFI) scores were similar in both treatment groups (p = 0.161 and p = 0.271, respectively). No significant differences were found in serum levels of DKK-1 (p = 0.815), SOST (p = 0.771), BMP-6 (p = 0.451), or IL-17 (p = 0.335) between combined anti-TNFα and csDMARD therapy versus monotherapy with csDMARD. Conclusions: The combination of anti-TNF bDMARD therapy and csDMARD therapy is not significantly associated with serum levels of DKK-1, SOST, BMP-6, and BMD compared to those treated with csDMARD monotherapy in patients with AS. This study provides novel and clinically relevant evidence on how anti-TNF bDMARDs and csDMARDs differentially affect bone turnover biomarkers and bone health in patients with AS, contributing to a better understanding of therapeutic strategies and guiding future research and clinical decision-making.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Translational Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Transcriptomic and Metagenomic Biomarkers in Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review, Diagnostic Meta-Analysis, and Functional Meta-Synthesis
by
Carlos M. Ardila, Eliana Pineda-Vélez and Anny M. Vivares-Builes
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 187; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030187 - 12 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Evidence from transcriptomic and histopathologic studies has revealed that peri-implantitis lesions are characterized by deeper inflammatory infiltration, increased immune cell accumulation, and distinctive molecular signatures. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and pathophysiological potential of transcriptomic, metagenomic, and bioinformatic biomarkers
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Evidence from transcriptomic and histopathologic studies has revealed that peri-implantitis lesions are characterized by deeper inflammatory infiltration, increased immune cell accumulation, and distinctive molecular signatures. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the diagnostic and pathophysiological potential of transcriptomic, metagenomic, and bioinformatic biomarkers in peri-implantitis by integrating findings from bioinformatics and machine learning-based studies. The dual objective was to identify biologically relevant markers and assess the accuracy of predictive models, addressing diagnostic gaps in peri-implant disease management. Methods: Eligible designs included cross-sectional, case–control, and cohort studies. Literature searches were conducted across PubMed, EMBASE, Scielo, and Scopus, with independent screening, data extraction, and quality assessment. Functional meta-synthesis was used to thematically organize biomarkers and pathways, while diagnostic meta-analysis pooled ROC-AUC values to assess model performance. Results: Eleven studies met the inclusion criteria. Functional synthesis revealed five recurring biomarker themes: innate and adaptive immune responses, immune cell infiltration, fibroblast activation, and ceRNA regulation. A meta-analysis of six studies reported a pooled AUC of 0.91 (95% CI: 0.88–0.93) with I2 = 0%, indicating no heterogeneity, supporting the reliability of ML-based models in distinguishing peri-implantitis from healthy conditions. Sources of variation included differences in validation strategies and data preprocessing. Conclusions: Integrating transcriptomic, metagenomic, and bioinformatic biomarkers with machine learning may enable earlier and more accurate diagnosis of peri-implantitis. The identified biomarkers highlight molecular and microbial pathways linked to inflammation and tissue remodeling, underscoring their potential as diagnostic indicators and therapeutic targets with translational relevance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Translational Medicine)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Clinical Evaluation of a Pollen-Extract-Based Phytotherapy Compared to Conventional Therapies in Chronic Prostatitis and Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
by
Marius Ivănuță, Dragoș Puia, Alin Adrian Cumpănaș, Ana-Maria Ivănuță, Veaceslav Groza and Cătălin Pricop
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 186; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030186 - 11 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is a prevalent condition characterized by pelvic pain and urinary symptoms with multifactorial aetiology. Standard treatments, including alpha-blockers, often have limited long-term effectiveness. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a standardized pollen
[...] Read more.
Background: Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CP/CPPS) is a prevalent condition characterized by pelvic pain and urinary symptoms with multifactorial aetiology. Standard treatments, including alpha-blockers, often have limited long-term effectiveness. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a standardized pollen extract (Deprox® 500), alone or in combination with alpha-blockers, in reducing CP/CPPS symptoms and the need for rescue medication. Methods: This prospective, multicentre study included 207 male patients with CP/CPPS treated at two Romanian urology centres between January 2023 and January 2025. Patients were divided into three groups: Group A—alpha-blocker monotherapy; Group B—standardized pollen extract monotherapy; and Group C—combination therapy with standardized pollen extract and alpha-blocker. Symptom severity and treatment response were evaluated using the validated English versions of the NIH Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), and International Index of Erectile Function-5 (IIEF-5), all of which were translated into Romanian for use in this study. Results: Groups B and C both demonstrated significantly greater reductions in pelvic pain and urinary symptoms compared to Group A (p = 0.01), with marked improvements in NIH-CPSI and IPSS. Conclusions: A standardized pollen extract used alone or in combination with an alpha-blocker significantly improved CP/CPPS symptoms and reduced the need for NSAID rescue medication. These findings support its potential as a safe and effective therapeutic option.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Mitral Valve Prolapse and Sudden Cardiac Death—A Puzzle with Missing Pieces: Review of the Literature and Case Report
by
Diana Roxana Opris, Marius Mihai Harpa, David-Emanuel Anitei, Paul Calburean and Roxana Rudzik
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 185; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030185 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Mitral valve prolapse is a common valvular heart disorder, usually associated with a benign prognosis in the absence of significant mitral regurgitation. However, a subset of patients is at increased risk for complex ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Identifying these high-risk
[...] Read more.
Background: Mitral valve prolapse is a common valvular heart disorder, usually associated with a benign prognosis in the absence of significant mitral regurgitation. However, a subset of patients is at increased risk for complex ventricular arrhythmias and sudden cardiac death. Identifying these high-risk individuals remains a major clinical challenge. Case Summary: We present the case of a 71-year-old female patient with recurrent syncopal episodes, a strong family history of sudden cardiac death, and complex ventricular ectopy. Multimodality imaging revealed bileaflet mitral valve prolapse, severe mitral regurgitation, mitral annular disjunction, and the Pickelhaube sign, with no evidence of myocardial fibrosis on cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. The patient underwent minimally invasive mitral valve repair and received an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator for primary prevention of sudden cardiac death. Follow-up revealed significant reverse cardiac remodeling, marked reduction in arrhythmic burden, and restoration of mitral valve function. Family screening identified mitral annular disjunction in both of her daughters, who were asymptomatic and without arrhythmias. Discussion: Mitral annular disjunction has emerged as a potentially arrhythmogenic substrate, especially in patients with familial clustering, raising the possibility of a genetic predisposition. Risk stratification remains difficult, as no individual clinical, electrocardiographic, or imaging marker has demonstrated consistent predictive value. Surgical correction of mitral valve prolapse with associated mitral annular disjunction may lead to a reduction in arrhythmic risk and promote favorable structural remodeling. Conclusions: This case-based review emphasizes the importance of advanced imaging techniques in the identification and management of high-risk mitral valve prolapse phenotypes. Early surgical intervention and close arrhythmic surveillance may improve outcomes, although further research is necessary to define risk assessment tools and explore the genetic background of arrhythmogenic mitral valve disease.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Traditional Surgery and Minimally Invasive Approaches to Valvular Heart Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Proteome Differences in Smooth Muscle Cells from Diabetic and Non-Diabetic Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Patients Reveal Metformin-Induced Mechanisms
by
Tara A. R. van Merrienboer, Karlijn B. Rombouts, Albert C. W. A. van Wijk, Jaco C. Knol, Thang V. Pham, Sander R. Piersma, Connie R. Jimenez, Ron Balm, Kak K. Yeung and Vivian de Waard
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 184; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030184 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Aims: Surgery remains the only definitive treatment option for abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), as no conclusive evidence supports drug effectiveness in preventing AAA growth. Although type 2 diabetes (T2D) is an important cardiovascular risk factor, patients with T2D show reduced AAA presence
[...] Read more.
Aims: Surgery remains the only definitive treatment option for abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), as no conclusive evidence supports drug effectiveness in preventing AAA growth. Although type 2 diabetes (T2D) is an important cardiovascular risk factor, patients with T2D show reduced AAA presence and growth, associated with metformin use. We aimed to investigate the potential benefits of metformin on AAA using proteomics and in vitro experiments. Methods: Proteomics analysis using tandem mass spectrometry was performed on aortic smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from non-pathological controls (C-SMC, n = 8), non-diabetic (ND, n = 19) and diabetic (D, n = 5) AAA patients. Key findings were subsequently validated in aortic tissue using mass spectrometry-based proteomics. SMCs were cultured with/without metformin and analyzed. Results: Comparison of the proteome of SMCs from ND-AAA patients with controls revealed a reduction in proteins associated with metabolic processes and mitochondrial function. Cytoskeletal and extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins were elevated in ND-AAA-SMCs versus C-SMCs, with a similar cluster of mechanosensitive proteins being increased in ND-AAA-SMCs versus D-AAA-SMCs. D-AAA-SMCs showed an improved metabolic and antioxidant profile, enriched in pentose phosphate pathway proteins responsible for NAD(P)H generation (G6PD, PGD) and NAD(P)H-dependent antioxidants (NQO1, CBR1, AKR1C1, AKR1B1, GSTM1), all regulated by NRF2, an antioxidant transcription factor. Over half of the proteins identified in the protein–protein interaction network, constructed from proteins with higher expression in D-AAA SMCs versus ND-AAA SMCs, were verified in D-AAA aortic tissue. In vitro, metformin causes a shift from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism, increased AMPK activation and elevated mitochondrial biogenesis, indicated by increased PGC-1α expression. Metformin increased the gene expression of PGD, CBR1 and the protein expression of NQO1, with enhanced translocation of pNRF2 to the nucleus, due to reduced KEAP1 as negative regulator of NRF2. Consequently, metformin enhanced the gene expression of well-known antioxidant regulators SOD2 and CAT. Conclusions: This study identified significant differences in the proteome of SMCs derived from controls, ND-AAA and D-AAA patients. It highlights distinct pathways in relation to mechanosensing, metabolism and redox balance as therapeutic targets of metformin that may underlie its inhibition of AAA progression.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Renal Failure and Systolic Heart Failure Have Synergistic Effect on In-Hospital All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Normotensive Acute Pulmonary Embolism
by
Mirjana Mijuskovic, Brankica Terzic, Sonja Salinger, Jovan Matijasevic, Sandra Pekovic, Tamara Preradovic-Kovacevic, Ljiljana Kos, Bjanka Bozovic, Irena Mitevska, Bojan Mitrovic, Aleksandar Neskovic, Ema Jevtic, Vladimir Miloradovic, Boris Dzudovic and Slobodan Obradovic
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 183; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030183 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Renal failure (RF) and systolic heart failure (sHF) are very often associated with each other, and their synergistic influence can affect the prognosis of acute pulmonary embolism (aPE) patients. The aim of this study is to evaluate the associations between RF,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Renal failure (RF) and systolic heart failure (sHF) are very often associated with each other, and their synergistic influence can affect the prognosis of acute pulmonary embolism (aPE) patients. The aim of this study is to evaluate the associations between RF, sHF, and in-hospital mortality in patients with normotensive aPE. Methods: We analyzed data from the Regional PE Registry (REPER), and 1968 patients with CT pulmonary angiography-confirmed aPE who had a systolic blood pressure of 100 mmHg and higher, and for whom creatinine blood levels and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) were measured at admission to hospital were enrolled. The patients were divided into four groups: the first group comprised patients without renal and systolic heart failure, the second those with RF (creatinine clearance less than 60 mL/min), the third those with sHF (LVEF less than 50%), and the fourth those with both RF and sHF. The primary endpoint of this study was in-hospital all-cause mortality. Results: There are significant differences between in-hospital mortality among the groups: 38/1247 (3.0%) vs. 63/514 (12.9%) vs. 10/99 (10.1%) vs. 20/108 (18.5%) (p < 0.001). In the multivariable regression model adjusted for age, right ventricular dysfunction, and troponin levels, the presence of renal failure, sHF, and both were independently associated with in-hospital all-cause mortality with ORs of 3.59 (95%CI 2.04–6.30, p < 0.001) vs. 3.97 (1.71–9.25, p = 0.001) vs. 6.39 (3.15–12.99, p < 0.001), respectively. Conclusions: The association of renal failure and systolic heart failure has a deleterious prognosis in patients with normotensive aPE.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Obesity and Pregnancy: Impact on Childbirth Timing, Delivery Mode, and Maternal Recovery: An Update
by
Angeliki Gerede, Maria Danavasi, Sofoklis Stavros, Anastasios Potiris, Athanasios Zikopoulos, Efthalia Moustakli, Charikleia Skentou, Ekaterini Domali, Nikolaos Nikolettos and Makarios Eleftheriades
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 182; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030182 - 10 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review explores the impact of maternal obesity on pregnancy outcomes, emphasizing its significant global health challenge and profound implications for both mothers and infants. It influences the timing and mode of childbirth, elevating the risk of conditions like hypertensive disorders, cesarean delivery,
[...] Read more.
This review explores the impact of maternal obesity on pregnancy outcomes, emphasizing its significant global health challenge and profound implications for both mothers and infants. It influences the timing and mode of childbirth, elevating the risk of conditions like hypertensive disorders, cesarean delivery, and gestational diabetes mellitus. The review focuses on analyzing how maternal obesity affects postpartum recovery, birth timing, and delivery methods. Relevant studies were identified using PubMed and Scopus. Findings indicate that obese pregnant women are at higher risk for medically indicated preterm birth, scheduled and emergency cesarean sections, and labor induction. Postpartum recovery is often prolonged due to breastfeeding challenges, infection risks, and delayed wound healing. Additionally, maternal obesity increases the likelihood of fetal complications such as macrosomia and long-term metabolic disorders. These results highlight the importance of personalized treatments and early weight control to improve the health of both mother and baby. A comprehensive approach integrating clinical care, public health initiatives, and policy measures is essential to reduce pregnancy complications associated with obesity.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Decoding Fear: Analysis and Prognosis of Preoperatory Stress Level Through Advanced Statistical Modelling—A Prospective Study Across Multiple Surgical Specialties
by
Cristina Gena Dascălu, Andrei Ionut Cucu, Andreea Vovciuc, Sorin Axinte, Serban Turliuc, Amelian Madalin Bobu, Camelia Tamas, Vlad Porumb, Emilia Patrascanu, Catalin Mihai Buzduga, Paula Alexandra Blanaru, Anca Petruta Morosan, Iulian Prutianu, Roxana Covali, Andreea Ioana Pruteanu, Claudia Florida Costea and Alexandru Carauleanu
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 181; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030181 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Preoperative stress is a multifactorial phenomenon shaped by physiological, psychological, and social influences, with a substantial impact on postoperative recovery. This study aimed to quantify preoperative stress levels, identify associated factors, and rank their predictive importance. Methods: A prospective study was conducted
[...] Read more.
Background: Preoperative stress is a multifactorial phenomenon shaped by physiological, psychological, and social influences, with a substantial impact on postoperative recovery. This study aimed to quantify preoperative stress levels, identify associated factors, and rank their predictive importance. Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 197 patients scheduled for general surgery, orthopedics, neurosurgery, or otorhinolaryngology procedures between December 2024 and June 2025 at Suceava County Emergency Clinical Hospital. Stress levels were assessed using the Brief Measure of Emotional Preoperative Stress (B-MEPS), translated and culturally adapted into Romanian. Statistical analyses included nonparametric tests, generalized linear modeling, and Random Forest regression. Results: The mean B-MEPS score was 21.42 ± 6.04 (range: 11–34), indicating a moderate level of preoperative stress. Higher stress scores were significantly associated with female sex (p < 0.001), lower educational attainment (p = 0.003), divorced marital status (p = 0.007), a history of cancer (p = 0.002), and the type of surgical intervention (p = 0.003). Random Forest analysis identified the type of surgery, educational level, and sex as the strongest predictors. Conclusions: Preoperative stress is chiefly influenced by the type of surgical procedure, educational level, and sex, with potential synergistic effects among these factors. Early identification of high-risk patients enables targeted, personalized interventions to mitigate anxiety and improve perioperative outcomes. Further research should include formal validation of the Romanian version of B-MEPS and the integration of additional psychosocial variables.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Metabolic Reprogramming Through Polyphenol Networks: A Systems Approach to Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance
by
Shakila Jahan Shimu, Jawad Ul Karim Mahir, Fardin Al Fahad Shakib, Arafath Amin Ridoy, Ratin Al Samir, Nadia Jahan, Md Fahim Hasan, Sadman Sazzad, Shamima Akter, Mohammad Sarif Mohiuddin, Md Jalal Ahmed Shawon, Mohammad Hossain Shariare, Mohammad Mohabbulla Mohib and Mohammad Borhan Uddin
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 180; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030180 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
Obesity-induced insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) represent complex systemic disorders marked by chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. These pathophysiological processes disrupt insulin signaling and β-cell function, leading to impaired glucose homeostasis across multiple organs.
[...] Read more.
Obesity-induced insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) represent complex systemic disorders marked by chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. These pathophysiological processes disrupt insulin signaling and β-cell function, leading to impaired glucose homeostasis across multiple organs. Conventional therapies often target isolated pathways, overlooking the intricate molecular crosstalk and organelle-level disturbances driving disease progression. Citrus-derived polyphenols—including hesperidin, naringenin, nobiletin, and tangeretin—have emerged as promising agents capable of orchestrating a multi-targeted “metabolic reprogramming.” These compounds modulate key signaling pathways, including AMPK, PI3K/Akt, NF-κB, and Nrf2, thereby enhancing insulin sensitivity, reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, and restoring redox balance. Furthermore, they improve mitochondrial biogenesis, stabilize membrane potential, and alleviate ER stress by modulating the unfolded protein response (UPR), thus supporting cellular energy homeostasis and protein folding capacity. Evidence from preclinical studies and select clinical trials suggests that citrus polyphenols can significantly improve glycemic control, reduce oxidative and inflammatory markers, and preserve β-cell function. Their pleiotropic actions across molecular and organ-level targets position them as integrative metabolic modulators. This review presents a systems-level synthesis of how citrus polyphenols rewire metabolic signaling networks and organelle resilience, offering a holistic therapeutic strategy to mitigate the root causes of obesity-induced insulin resistance.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Total-Arterial Revascularization Is Superior in Heart Failure Patients with Reduced Ejection Fraction—A Propensity Score Matched Retrospective Multicenter Analysis
by
Christian Jörg Rustenbach, Julia Schano, Christoph Salewski, Helene Häberle, Kristian-Christos Ngamsri, Ilija Djordjevic, Stefanie Wendt, Tulio Caldonazo, Ibrahim Saqer, Shekhar Saha, Philipp Schnackenburg, Lina Maria Serna-Higuita, Torsten Doenst, Christian Hagl, Thorsten Wahlers, Christian Schlensak and Stefan Reichert
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 179; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030179 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Total arterial revascularization (TAR) may improve outcomes in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Methods: We retrospectively screened 574 adults with HFrEF (LVEF < 40%) undergoing isolated CABG across four German centers (2017–2023). After 1:1 propensity
[...] Read more.
Background: Total arterial revascularization (TAR) may improve outcomes in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Methods: We retrospectively screened 574 adults with HFrEF (LVEF < 40%) undergoing isolated CABG across four German centers (2017–2023). After 1:1 propensity score matching, 240 patients were analyzed (120 TAR vs. 120 NTAR). The primary endpoint was in-hospital MACCE (death, MI, stroke). Key secondary endpoints included ICU/hospital length-of-stay, ventilation time, delirium, transfusion requirements, and acute kidney injury. Results: MACCE occurred in 4.1% (TAR) vs. 14.2% (NTAR) (p = 0.007). TAR was associated with shorter ICU stay (median 44.5 h vs. 90 h, p < 0.001), shorter hospital stay (10 d vs. 12 d, p = 0.002), reduced ventilation time (8 h vs. 12 h, p < 0.001), lower delirium (5.0% vs. 14.2%, p = 0.016), and fewer RBC transfusions intra-operatively (0.13 ± 0.45 vs. 0.31 ± 0.58 units, p = 0.028) and during the entire stay (0.70 ± 1.33 vs. 1.77 ± 2.91 units, p < 0.001). Conclusions: In this multicenter propensity-matched cohort, TAR was associated with lower in-hospital MACCE and more favorable perioperative outcomes compared with NTAR. Prospective studies are warranted to confirm causality and long-term benefits.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Disease)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Integrated Genomic Analysis Reveals the Synergistic Role of PNPLA3 and ABCC8 Variants in Diabetic MASLD in Pakistan
by
Asma Shabbir, Ambrina Khatoon, Zaigham Abbas, Sucheta Srivastava and Talat Mirza
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 178; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030178 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously termed as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a growing global health concern, particularly in South Asia. While PNPLA3 is a well-recognized genetic contributor to MASLD, the role of other metabolic genes, such
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Metabolic dysfunction associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), previously termed as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a growing global health concern, particularly in South Asia. While PNPLA3 is a well-recognized genetic contributor to MASLD, the role of other metabolic genes, such as ABCC8, remains unexplored in South Asian populations. In this study, we aim to investigate the genetic association and potential synergy between PNPLA3 (rs738409) and ABCC8 (rs146378237) variants in MASLD pathogenesis in a Pakistani cohort. Methods: A two-phased case–control study was conducted. Whole Exome Sequencing (WES) was performed on 6 MASLD cases and 6 healthy controls to identify relevant variants, followed by validation via Sanger sequencing in an extended MASLD cohort (n = 52). Variant frequencies were compared with 96 ethnically matched controls from the 1000 Genomes Project. Furthermore, the association of the variants with clinical, biochemical, and fibrotic parameters was assessed. Results: The PNPLA3 rs738409 G allele (MAF = 0.47) and ABCC8 rs146378237 T allele (MAF = 0.36) were significantly enriched in MASLD cases and strongly associated with cirrhosis. The TT genotype of ABCC8 was also linked to T2DM and low HDL levels. Importantly, eight MASLD patients harbored both GG (PNPLA3) and TT (ABCC8) genotype, and all were known cases of diabetes, suggesting a synergistic genetic interaction. Conclusions: This is the first report of ABCC8 rs146378237 in a South Asian MASLD cohort, revealing population-specific risk and a gene–gene interaction that may inform targeted screening and personalized management of MASLD in high-risk diabetic individuals.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Hepatic and Gastroenterology Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Pediatric Medication Prescribing Across Urgent Care Visits: An Epidemiologic View from a Primary Care Setting in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
by
Reem S. AlOmar, Nouf A. AlShamlan, Ahmed A. Al Yateem, Abdulrahman A. Al-Abdulazeem, Ahmed M. Al-Turki, Reema J. Alghamdi, Najla A. Alhamed, Sameerah Motabgani, Adam F. Aldhawyan and Malak A. Al Shammari
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 177; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030177 - 5 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: Urgent care clinics (UCCs) embedded within primary healthcare settings play a vital role in managing acute, non-life-threatening conditions in children. However, limited data exist on medication prescribing patterns in such settings in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), particularly regarding antibiotic use.
[...] Read more.
Background: Urgent care clinics (UCCs) embedded within primary healthcare settings play a vital role in managing acute, non-life-threatening conditions in children. However, limited data exist on medication prescribing patterns in such settings in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), particularly regarding antibiotic use. This study aimed to describe the epidemiology of pediatric urgent care visits and identify factors associated with prescribing within a model primary healthcare (PHC) center. Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted for all urgent care visits made by pediatric patients (<14 years) at a model PHC center in the KSA for all visits in 2024. Sociodemographic variables, visit timing, diagnosis, and prescription data were extracted from electronic health records. Multivariable logistic regression was used to analyze predictors of medication prescribing. Results: Of the 1016 pediatric urgent care visits, 62.5% resulted in medication prescriptions, and 23.62% of those visits included at least one antibiotic, primarily penicillins (71.33%). Cephalosporins and tetracyclines were not prescribed. Prescriptions were 67% more likely among adolescents and 70% less likely among infants when compared to school-aged children (95% CI = 1.04–2.67 and 95% CI = 0.15–0.61, respectively). Respiratory and ENT-related diagnoses accounted for most prescriptions. No significant sex-based differences in prescribing were observed. Conclusions: The epidemiological patterns observed indicate that respiratory and ENT conditions, as well as seasonal peaks in autumn and winter, are the main drivers of prescribing in pediatric urgent care. These findings have implications for strengthening disease surveillance, anticipating service demand, guiding preventive interventions such as vaccination and health education, and supporting evidence-based planning of primary care resources.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Beyond Obesity
by
George A. Bray and Donna H. Ryan
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 176; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030176 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Diagnosis of clinical obesity has been highlighted by the recent publication from a Commission Report in The Lancet, suggesting the addition of a new diagnostic category, “Preclinical Obesity,” to the already existing ones. Diagnostic criteria for obesity began in the first half
[...] Read more.
Diagnosis of clinical obesity has been highlighted by the recent publication from a Commission Report in The Lancet, suggesting the addition of a new diagnostic category, “Preclinical Obesity,” to the already existing ones. Diagnostic criteria for obesity began in the first half of the 20th century, when life insurance companies provided information tables of ideal body weight levels and/or desirable body weight levels based on actuarial associations with mortality. This was replaced by the body mass index or BMI in the third quarter of the 20th century. This tool documented the epidemic of obesity in the US in the last three decades of the 20th century. The recognition of the importance of fat distribution, pioneered by the work of Jean Vague in France, provided a new understanding of obesity. The limitations of BMI and the availability of effective new treatments have heightened the need for new diagnostic guidelines. Obesity represents an increase in body fat and an alteration in its distribution and function. But at the same time, obesity is a stigmatized word and a pejorative term. This communication discusses ways to better diagnose the increase in body fat and its abnormal distribution. We ask whether there is an alternative word to replace obesity and suggest that adiposity or healthy weight could be options.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Peritoneal Effluent and Ascitic Fluid for Early Detection of Peritonitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
by
Manuel Luis Prieto-Magallanes, José David González-Barajas, Violeta Aidee Camarena-Arteaga, Bladimir Díaz-Villavicencio, Juan Alberto Gómez-Fregoso, Ana María López-Yáñez, Ruth Rodríguez-Montaño, Judith Carolina De Arcos-Jiménez and Jaime Briseno-Ramírez
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 175; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030175 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background: Peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis and cirrhosis remains common and leads to morbidity. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) has been evaluated as a rapid adjunctive biomarker. Methods: Following PRISMA-DTA and PROSPERO registration (CRD420251105563), we searched MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Library, LILACS, Scopus, and Web of
[...] Read more.
Background: Peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis and cirrhosis remains common and leads to morbidity. Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) has been evaluated as a rapid adjunctive biomarker. Methods: Following PRISMA-DTA and PROSPERO registration (CRD420251105563), we searched MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane Library, LILACS, Scopus, and Web of Science from inception to 31 December 2024, and ran an update on 30 June 2025 (no additional eligible studies). Diagnostic accuracy studies measuring NGAL in peritoneal/ascitic fluid against guideline reference standards were included. When 2 × 2 data were not reported, we reconstructed cell counts from published metrics using a prespecified, tolerance-bounded algorithm (two studies). Accuracy was synthesized with a bivariate random effects (Reitsma) model; 95% prediction intervals (PIs) were used to express heterogeneity; small-study effects were assessed by Deeks’ test. Results: Thirteen studies were included qualitatively and ten were entered into a meta-analysis (573 cases; 833 controls). The pooled sensitivity was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.90–0.97) and specificity was 0.86 (0.70–0.94); likelihood ratios were LR+ ≈7.0 and LR− 0.06. Between-study variability was concentrated on specificity: the PI for a new setting was 0.75–0.98 for sensitivity and 0.23–0.99 for specificity. Deeks’ test showed evidence of small-study effects in the primary analysis; assay/platform and thresholding contributed materially to heterogeneity. Conclusions: NGAL in peritoneal/ascitic fluid demonstrates high pooled sensitivity but variable specificity across settings. Given the wide prediction intervals and the signal for small-study effects, NGAL should be interpreted as an adjunct to guideline-based criteria—not as a stand-alone rule-out test. Standardization of pre-analytics and assay-specific, locally verified thresholds, together with prospective multicenter validations and impact/economic evaluations, are needed to define its clinical role.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Hepatic and Gastroenterology Diseases)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Pregnancy
by
Angeliki Gerede, Efthymios Oikonomou, Sofoklis Stavros, Anastasios Potiris, Panagiota Papasozomenou, Menelaos Zafrakas, Ekaterini Domali, Nikolaos Nikolettos and Makarios Eleutheriades
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 174; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030174 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background/Objectives: The reciprocal relationship between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and pregnancy continues to elude the scientific community’s approaches for a clear understanding. Multiple studies have reached dissimilar results regarding the impact that SLE exerts on pregnancy, whilst the potential risks of lupus pregnancies
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: The reciprocal relationship between Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and pregnancy continues to elude the scientific community’s approaches for a clear understanding. Multiple studies have reached dissimilar results regarding the impact that SLE exerts on pregnancy, whilst the potential risks of lupus pregnancies continue to encumber women of childbearing age. Whether SLE predisposes to a complicated pregnancy and conversely whether pregnancy impacts the progression of the disease is aimed to be assessed by this systematic review. Methods: A thorough search of original research articles was conducted using online databases (PubMed, Google Scholar), initially identifying 877 potential studies. Results: Upon further assessment for relevance and eligibility, 65 articles were selected for detailed analysis. Conclusions: We concluded that, even though advanced approaches have optimized SLE prognosis and treatment, the complexity of the disease requires further extensive study in order to grasp the mechanism behind the susceptibility to adverse complications. SLE pregnancy cannot be considered without risk. Comprehensive, multidisciplinary, and continuous monitoring of the disease course prior to, during, and after pregnancy is necessary to ensure optimal recovery and minimal maternal and fetal complications. Tailored treatments and novel biomarkers would move us towards precise patient-centered care that addresses each patient’s unique disease profile and pregnancy needs, ultimately improving both maternal and fetal outcomes in women with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Full article
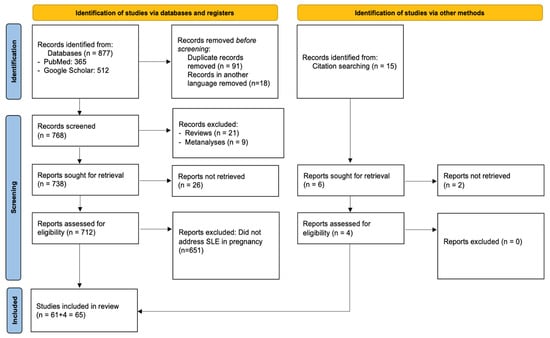
Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Minimally Invasive Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation: A Systematic Review of Current Evidence on Clinical Outcomes and Surgical Approaches
by
Baglan Turtabayev, Seitkhan Joshibayev, Umit Kervan, Samat Zharmenov, Yerbol Ustemirov, Almas Begdildayev and Gali Iskakbayev
Med. Sci. 2025, 13(3), 173; https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci13030173 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
Background/Objectives: Minimally invasive cardiac surgical (MICS) approaches to the implantation of left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) have gained increasing interest as alternatives to full median sternotomy (FS), particularly in patients with prior cardiac surgeries or elevated surgical risk. However, evidence regarding their safety,
[...] Read more.
Background/Objectives: Minimally invasive cardiac surgical (MICS) approaches to the implantation of left ventricular assist devices (LVADs) have gained increasing interest as alternatives to full median sternotomy (FS), particularly in patients with prior cardiac surgeries or elevated surgical risk. However, evidence regarding their safety, feasibility, and clinical outcomes remains fragmented. This systematic review aimed to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of minimally invasive techniques for LVAD implantation in comparison to standard sternotomy, with a focus on mortality, perioperative complications, intensive care unit (ICU) stay, and infection rates. Methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted in PubMed, Web of Science, Science Direct, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar up to 1 January 2025. Studies were included if they reported on adult patients undergoing LVAD implantation via minimally invasive thoracotomy or sternotomy-sparing approaches, with or without comparator groups. Data were extracted and synthesized qualitatively; the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) was applied to assess the methodological quality of the included cohort and retrospective comparative studies. Results: A total of 12 studies involving 1448 patients were included (584 received MICS and 862 received FS). MICS techniques have demonstrated comparable short and mid-term survival outcomes, with trends toward reduced ICU stay, fewer reoperations for bleeding, and lower incidence of driveline infections. Some studies reported longer operative and cardiopulmonary bypass times in the MICS group. Among high-risk cohorts, such as patients with prior sternotomies or significant comorbidities, MICS was associated with lower morbidity and acceptable safety profiles. However, heterogeneity in patient selection, surgical protocols, and outcome definitions limited quantitative synthesis. Conclusions: Minimally invasive LVAD implantation is a viable alternative to conventional sternotomy in selected patient populations. While current data suggest favorable perioperative outcomes and equivalent survival, high-quality prospective studies are needed to confirm long-term benefits and to guide patient selection. MICS approaches should be considered within multidisciplinary teams experienced in advanced heart failure surgery.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Section Cardiovascular Disease)
►▼
Show Figures
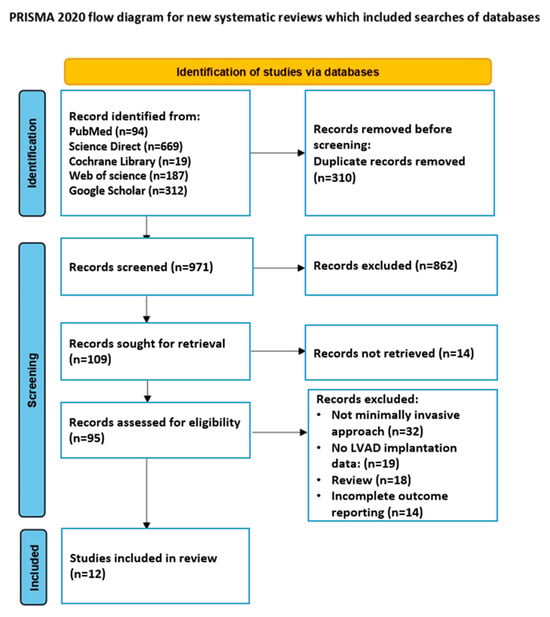
Figure 1

Journal Menu
► ▼ Journal Menu-
- Medical Sciences Home
- Aims & Scope
- Editorial Board
- Reviewer Board
- Instructions for Authors
- Special Issues
- Topics
- Sections & Collections
- Article Processing Charge
- Indexing & Archiving
- Most Cited & Viewed
- Journal Statistics
- Journal History
- Journal Awards
- Society Collaborations
- Conferences
- Editorial Office
Journal Browser
► ▼ Journal BrowserHighly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics
Topic in
Cancers, Diagnostics, JCM, Life, Medical Sciences, Current Oncology
Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Genetic Vulnerabilities and Emerging Targets for Precision Oncology
Topic Editors: Tatiana de Almeida Simão, Sheila Coelho Soares-LimaDeadline: 30 November 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Medical Sciences
The Impact of Temporomandibular Disorders on the Wellbeing
Guest Editor: Oana AlmasanDeadline: 31 December 2025
Special Issue in
Medical Sciences
Feature Papers in Section Cancer and Cancer-Related Diseases
Guest Editor: Ravi P. SahuDeadline: 31 March 2026
Special Issue in
Medical Sciences
Frontier Exploration of Immune Tolerance Induction After Liver Transplantation
Guest Editor: Luit PenningaDeadline: 1 April 2026
Special Issue in
Medical Sciences
Advances and Challenges in Headache and Migraine Management: A Global Perspective
Guest Editor: Faraidoon HaghdoostDeadline: 31 May 2026
Topical Collections
Topical Collection in
Medical Sciences
Advances in the Pathogenesis of Neurodegenerative Diseases
Collection Editor: Maria Liguori
Topical Collection in
Medical Sciences
Advances in Skin Wound Healing
Collection Editors: Heiko Sorg, Daniel J. Tilkorn









