Patent Foramen Ovale in Fetal Life, Infancy and Childhood
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. PFO in Fetal Life
3. PFO in Neonates and Infants
4. PFO in Childhood
5. PFO-Associated Medical Diseases
5.1. Residual PFOs in Previously Treated Complex CHD
5.2. Cerebrovascular Accidents (CVAs)/Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs)
5.3. Migraine
5.4. Platypnea-Orthodeoxia Syndrome
5.5. Role of a PFO in Exacerbating Hypoxemia
5.6. Decompression (Caisson’s) Syndrome
5.7. Systemic Embolism
6. Management of PFO
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LA | left atrium |
| RA | right atrium |
| LV | left ventricle |
| RV | right ventricle |
| CHD | congenital heart disease |
| FO | foramen ovale |
| PFO | patent foramen ovale |
| ASD | atrial septal defect |
| ECMO | extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| VAD | ventricular assist device |
| HLHS | hypoplastic left heart syndrome |
| TGA | transposition of great arteries |
| PVR | pulmonary vascular resistance |
| SVR | systemic vascular resistance |
| CVA | cerebrovascular accident |
| TIA | transient ischemic attack |
| TTE | transthoracic echocardiography |
| TEE | transesophageal echocardiography |
| TCD | transcranial Doppler |
| ICE | intracardiac echocardiography |
| CMR | cardiac magnetic resonance |
References
- Sachdeva, R.; Valente, A.M.; Armstrong, A.K.; Cook, S.C.; Han, B.K.; Lopez, L.; Lui, G.K.; Pickard, S.S.; Powell, A.J.; Bhave, N.M.; et al. ACC/AHA/ASE/HRS/ISACHD/SCAI/SCCT /SCMR/AHA/SOPE 2020 appropriate use of criteria for multimodality imaging during the follow-up care of patients with congenital heart disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 657–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, E.P.; Sunde, M.; Costa, M.W.; Rankin, S.A.; Wolstein, O.; Castro, M.L.; Butler, T.L.; Hyun, C.; Guo, G.; Otway, R.; et al. Mutations in cardiac T-box factor gene TBX20 are associated with diverse cardiac pathologies, including defects of septation and vasculogenesis and cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilmshurst, P.T.; Morrison, W.L.; Walsh, K.P. Comparison of the size of persistent foramen ovale and atrial septal defect in divers with shunt-related decompression illness and the general population. Diving Hyperb. Med. 2015, 45, 89–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hagen, P.T.; Scholz, D.G.; Edwards, W.D. Incidence and size of patent foramen ovale during the first 10 decades of life: An autopsy study of 965 normal hearts. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1984, 59, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, H.D.; Shaddy, R.E.; Penny, D.J.; Feltes, T.F.; Cetta, F. Moss and Adams’ Heart Disease in Infants, Children, and Adolescents: Including the Fetus and Young Adult, 9th ed.; Wolters Kluwer: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.; Chan, A.K.; Mondal, T.K.; Paes, B.A. Thrombosis and hemostasis in newborns (THIN) group. Patent foramen ovale and stroke in childhood: A systemic review of the literature. Eur. J. Pediatric Neurol. 2016, 20, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, E.K.; Natrajan, S.; Falkensammer, C.; Beslow, L.A.; Messe, S.R.; Ichord, R.N. Role of patent foramen ovale in first and recurrent childhood cryptogenic arterial ischemic stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, A170. [Google Scholar]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Zaman, M.O.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Mahmoud, A.N.; Patel, N.K.; Agarwal, N.; Tobis, J.M.; Meier, B. Cryptogenic stroke and PFO. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holda, M.K.; Koziej, M. Morphometric features of patent foramen ovale as a risk factor of cerebrovascular accidents: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Cereb. Dis. 2020, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, K.K.; Daniels, C.J.; Aboulhosn, J.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Broberg, C.S.; Coman, J.M.; Crumb, S.R.; Dearani, J.A.; Fuller, S.; Gurvitz, M.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC guidelines for the management of adults with congenital heart disease. Circulation 2019, 139, e698–e800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.H.; Osten, M.; Leventhal, A.; Bach, Y.; Yoo, D.; Mansour, D.; Benson, L.; Wilson, W.M.; Holick, E. Percutaneous intervention to treat platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome: The Toronto experience. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2016, 9, 1928–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Candless, R.T.; Arrington, C.B.; Nielson, D.C.; Bale, J.F.; Minich, L.L. Patent foramen ovale in children with migraine headaches. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.L.; Persaud, V. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 2nd ed.; W.B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kiserud, T.; Rasmussen, S. Ultrasound assessment of the fetal foramen ovale. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2001, 17, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Liu, X.; He, Y. Isolated premature restriction or closure of foramen ovale in fetuses: Echocardiographic characteristics and outcome. Echocardiography 2018, 35, 1189–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowlen, T.T.; Ayres, N.A.; Kearney, D.L.; Nihill, M.R.; Grifka, R.G. Premature closure of foramen ovale associated with aortic stenosis, left ventricular dilation with thrombus, and early mortality. Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 85, 1159–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teroba, S.S.; Oulego, E.; Lobete, P.C.; Alonso, O.P. Intrauterine restriction of foramen ovale: Can cause neonatal pulmonary hypertension. Arch. Argent Pediatr. 2019, 117, e626–e630. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, S.; Vyas, S.; Nicolaides, K.H. Doppler investigation of the fetal circulation. J. Perinat. Med. 1991, 19, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, K.G.; Towretzky, W. Fetal cardiac interventions: Where do we stand? Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 113, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Respondek-Liberska, M.; Płużańska, J.; Słodki, M.; Czichos, E.; Moll, J.; Zych-Krekora, K. Early neonatal surgery for congenital heart defects after prenatal diagnosis of restricted foramen ovale as the priority procedure? Prenat. Cardio 2015, 5, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Songswang, J.; Adatia, I.; Newman, C.; Smallhorn, J.F.; Willaims, W.G.; Freeem, R.M. Mortality in potential arterial switch candidates with transposition of great arteries. J. Am. College Cardiol. 1998, 32, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jantzen, D.W.; Moon-Grady, A.J.; Morris, S.A.; Armstrong, A.K.; Berg, C.; Gangel, J.; Fifer, C.G.; Frommelt, M.; Gembruch, U.; Herberg, U.; et al. Hypoplastic left heart syndrome with intact or restrictive atrial septum. A report from the International Fetal Cardiac Intervention Registry. Circulation 2017, 136, 1346–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubail, Z.; Lemler, M.; Ramciotti, C.; Moore, J.; Ikemba, C. Diagnosing a patent foramen ovale in children. Is transesophageal echocardiography necessary? Stroke 2011, 42, 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, J.L.; Arquizan, C.; Lamy, C.; Zuber, M.; Cabanes, L.; Derumeaux, G.; Coste, J. Recurrent cerebrovascular events associated with patent foramen ovale, atrial septal aneurysm, or both. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 345, 1740–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, S.; Sacco, R.L.; Di Tullio, M.R.; Sciacca, R.R.; Mohr, J.P. Effect of medical treatment in stroke patients with patent foramen ovale. Circulation 2002, 105, 2625–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, K.L.; Seymour, M.; Beshish, A.; Baker, K.R.; Pegelow, D.F.; Lamers, L.J.; Eldridge, M.W.; Bates, M.L. Inspiratory and expiratory resistance cause right-to-left bubble passage through the foramen ovale. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, R.J.; Bartzokis, T.; Yeoh, T.K.; Frogin, H.R.; Choi, D.; Schnitter, J. Enhanced detection of intracardiac sources of cerebral emboli by transesophageal echocardiography. Stroke 1991, 22, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chenzbraun, A.; Pinto, F.J.; Schnittger, I. Biplane transesophageal echocardiography in the diagnosis of patent foramen ovale. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 1993, 6, 417–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestry, F.E. Guidelines for the echocardiographic assessment of atrial septal defect and patent foramen ovale from the American Society of Echocardiography for cardiac angiography and interventions. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2015, 28, 910–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Virmani, R.; Ladich, E.; Mackey-Bojack, S.; Titus, J.; Reisman, M.; Gray, W.; Nakamura, M.; Mooney, M.; Poulose, A.; et al. Patent foramen ovale: Current pathology, pathophysiology, and clinical status. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanley, P.C.; Tajik, A.J.; Hynes, J.K.; Edwards, W.D.; Reeder, G.S.; Hagler, D.J.; Seward, J.B. Diagnosis and classification of atrial septal aneurysm by two-dimensional echocardiography: Report of 80 consecutive cases. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1985, 6, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotani, Y.; Chetan, D.; Rodrigues, W.; Sivarajan, V.B.; Gruenwald, C.; Guerguerian, A.M.; Arsdell, G.S.V.; Honjo, O. Left atrial decompression during venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for left ventricular failure in children: Current strategy and clinical outcomes. Artif. Organs 2013, 37, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacich, D.; Fiorencis, A.; Braggion, G.; Zuin, M.; Rigatelli, G. Patent foramen ovale-related complications in left ventricular assist device patients: A reappraisal for cardiovascular professionals. J. Artif. Organs 2019, 23, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komar, M.; Olszowska, M.; Przewlocki, T.; Podolec, J.; Stepniewski, J.; Sobien, B.; Badacz, R.; Kablak-Ziembicka, A.; Tomkiewicz-Pajak, L.; Podolec, P. Transcranial Doppler ultrasonography should it be the first choice for persistent foramen ovale screening. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound 2014, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Robets, S.C.; Winoker, J.S.; Romero, J.; Goodman-Meza, D.; Gevorgyaan, R.; Tobis, J.M. Accuracy of transcranial Doppler for the diagnosis of intracardiac right to left shunt: A bivariate meta-analysis of prospective studies. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nusser, T.; Hoher, M.; Merkle, N.; Gerbe, O.C.; Spiess, J.; Kestler, H.A.; Rasche, V.; Koch, M.; Hombach, V.; Wohrle, J. Cardiac magnetic resonance imaging and transesophageal echocardiography in patients with transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohrs, O.K.; Petersen, S.E.; Erkapic, D.; Rabel, C.; Schrader, R.; Nowak, B.; Fach, N.A.; Kauczor, H.U.; Voigtlaender, T. Diagnosis of patent foramen ovale using contrast-enhanced dynamic MRI: A pilot study. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, B.S.; Shapiro, L.M.; McCarthy, K.P.; Ho, S.Y. Three-dimensional imaging of the atrial septum and patent foramen ovale anatomy: Defining the morphological phenotypes of patent foramen ovale. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2010, 11, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medford, B.A.; Taggart, N.W.; Cabalka, A.K.; Cetta, F.; Reeder, G.S.; Hagler, D.J.; Johnson, J.N. Intracardiac echocardiography during atrial septal defect and patent foramen ovale device closure in pediatric and adolescent patients. J. Am. Soc. Echocardgr. 2014, 27, 984–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponnuthurai, F.A.; van Gaal, W.J.; Burchell, A.; Mitchell, A.R.; Wilson, N.; Ormerod, O.J. Safety and feasibility of day case patent foramen ovale (PFO) closure facilitated by intracardiac echocardiography. Int. J. Cardiol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.S.; Chandar, J.S.; Sideris, E.B. Role of an inverted buttoned device in trans-catheter occlusion of atrial septal defect or patent foramen ovale with right-to-left shunting associated with previously operated complex congenital cardiac anomalies. Am. J. Cardiol. 1997, 80, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, C.F.H.; Reis, R.L.; Morrow, A.G. Incidence and significance of PFO after the correction of TOF. Ann. Thorac Surg. 1972, 13, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristipino, C.; Sievert, H.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Louis, M.J.; Meier, B.; Scacciatella, P.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Gaita, F.; Toni, D.; Kyrle, P.; et al. Evidence Synthesis Team. Eapci Scientific Documents and Initiatives Committee. International Experts. European position paper on the management of patients with patent foramen ovale. General approach and left circulation thromboembolism. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, M.M.; Ikemba, C.M. Intracardiac shunting and stroke in children: A systemic review. J. Child Neurol. 2011, 26, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbey, E.; Thompson, P.D. Patent foramen ovale: Thromboembolic structure or incidental finding? Conn. Med. 2011, 75, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lantz, M.; Sjostrand, C.; Kostlas, K. Ischemic stroke and patent foramen ovale: Risk factors and genetic profile. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2013, 22, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, G.C.; Sargurupremraj, M.; Velupandian, U.; Gurtu, R.; Trump, D.; Newman, W.; Wang, T.; McCollum, C. Genetics of patent foramen ovale-NKX2-5 and beyond. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2010, 11, 457–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstl, L.; Weinberger, R.; von Kries, R.; Heiner, F.; Schroeder, A.S.; Bonfert, M.V.; Broggraefe, F.; Tracke, M.; Vill, K.; Landgraf, M.N.; et al. Risk factors in childhood arterial ischemic stroke: Findings from a population-based study in Germany. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2018, 22, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrato, P.; Imperiale, D.; Bazzan, M.; Baima, C.; Grasso, M.; Morello, M.; Bergamasco, B. Inherited thrombophilic conditions, patent foramen ovale and juvenile ischemic stroke. Cerbrovasc. Dis. 2001, 11, 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botto, N.; Ait-Ali, L.; Sicari, R.; Spadoni, I.; Andreassi, M.G. Patent foramen ovale: Lies liasons dangereuses between anatomy and genetics. Recenti Prog. Med. 2009, 199, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Giannopoulos, A.; Gavras, C.; Sarioglu, S.; Agathagelou, F.; Kassapogelou, I.; Athanassiadou, F. Atrial septal aneurysms in childhood: Prevalence, classification, and current abnormalities. Cardiol. Young 2014, 24, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, M.M.; Quinn, C.T.; Ramaciotti, C.; Kanter, J.; Osunkwo, I.; Inusa, B.; Iyer, R.; Kwiatkowski, J.L.; Johnson, C.; Rhodes, M.; et al. Increased prevalence of potential right to left shunting in children with sickle cell anemia and stroke. Br. J. Hematol. 2017, 176, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Han, X.; Su, M.; Cao, X.; Wang, G.; Cao, F.; Yu, S. A new perspective of migraine symptoms in patients with congenital heart defect. Headache 2018, 58, 1601–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spalice, A.; Del Balzo, F.; Papetti, L.; Zicari, A.M.; Properzi, E.; Occasi, F.; Nicita, F.; Duse, M. Stroke and migraine is there a possible comorbidity? Ital. J. Pediatr. 2016, 42, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellini, B.; Arruda, M.; Cescut, A.; Saulle, C.; Persico, A.; Carotenuto, M.; Gatta, M.; Nacinovich, R.; Piazza, F.P.; Termine, C.; et al. Headache and comorbidity in children and adolescents. J. Headache Pain 2013, 14, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, D.Y.; Shin, D.H.; Cho, K.H.; Lee, S.P.; Park, S. Migraine with aura: A predictor of patent foramen ovale in children and adolescents. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobis, J.M.; Charles, A.; Siberstein, S.D.; Sorensen, S.; Maini, B.; Horwitz, P.A.; Gurley, J.C. Percutaneous closure of patent foramen ovale in patients with migraine: The PREMIUM trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2766–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, S.; Rao, P.S. Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome: Transcatheter management. In Catheter Based Devices for Treatment of Noncoronary Cardiovascular Disease in Adults and Children; Rao, P.S., Kern, M.J., Eds.; Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; Chapter 15; pp. 2766–2774. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, T.O. Platypnea-orthodeoxia syndrome: Etiology, differential diagnosis, and management. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 1999, 47, 64–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Ohuchi, H.; Hiraumi, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Echigo, S. Effects of postural change on oxygen saturation and respiration in patients after Fontan operation: Platypnea and orthodeoxia. Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 106, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.O. Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale: A definitive treatment for platypnea-orthodeoxia. Catheter. Cardiovasc, Interv. 2000, 100, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojadidi, M.K.; Ruiz, J.C.; Chertoff, J.; Zaman, M.O.; Elgendy, I.Y.; Mohmoud, A.N.; Mohamad, A.A.; Elgendy, A.Y.; Patel, N.K.; Shantha, G.; et al. Patent foramen ovale and hypoxemia. Cardiol. Rev. 2019, 1, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allemann, Y.; Hutter, D.; Lipp, E.; Sartori, C.; Duplian, H.; Egli, M.; Cook, S.; Scherrer, U.; Seiler, C. Patent foramen ovale and high-altitude pulmonary edema. JAMA 2006, 296, 2954–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharan, L.; Stackhouse, K.; Awerbach, J.D.; Bashore, T.M.; Krasuski, R.A. Effect of patent foramen ovale with pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Cardio.l 2018, 122, 505–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, B.D.; Hills, B.A. The lung as a filter for micro bubbles. J. Appl. Physiol. Respir. Environ. Exerc. Physiol. 1979, 47, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilmshurt, P.T.; Byrne, J.C.; Webb-Pepole, M.M. Relation between interatriual shuns and decompression sickness in divers. Lancet 1989, 2, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Rothner, A.D. Migraine with neurological features in a scuba driver with a patent foramen ovale. Headache 2017, 57, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billinger, M.; Zbinden, R.; Mordasini, R.; Windecker, S.; Schmezmann, M.; Meier, B.; Seiler, C. Patent foramen ovale closure in recreational divers: Effect on decompression illness and ischemic brain lesions during long-term follow-up. Heart 2011, 97, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, B.; Hofmann, T.; Justen MHMeinertz, T. Chiari’s network: Normal anatomic variant or risk factor for arterial embolic events. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1995, 26, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigtelli, G.; Dell’avvocata, F.; Braggion, G.; Giordan, M.; Chinaglia, M.; Cardaioli, P. Persistent venous valves correlate with increased shunt and multiple preceding cryptogenic embolic events in patients with patent foramen ovale: An intracardiac echocardiographic study. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2008, 72, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majunke, N.; Sievert, H. ASD/PFO devices: What is in the pipeline? J. Interv. Cardiol. 2007, 20, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

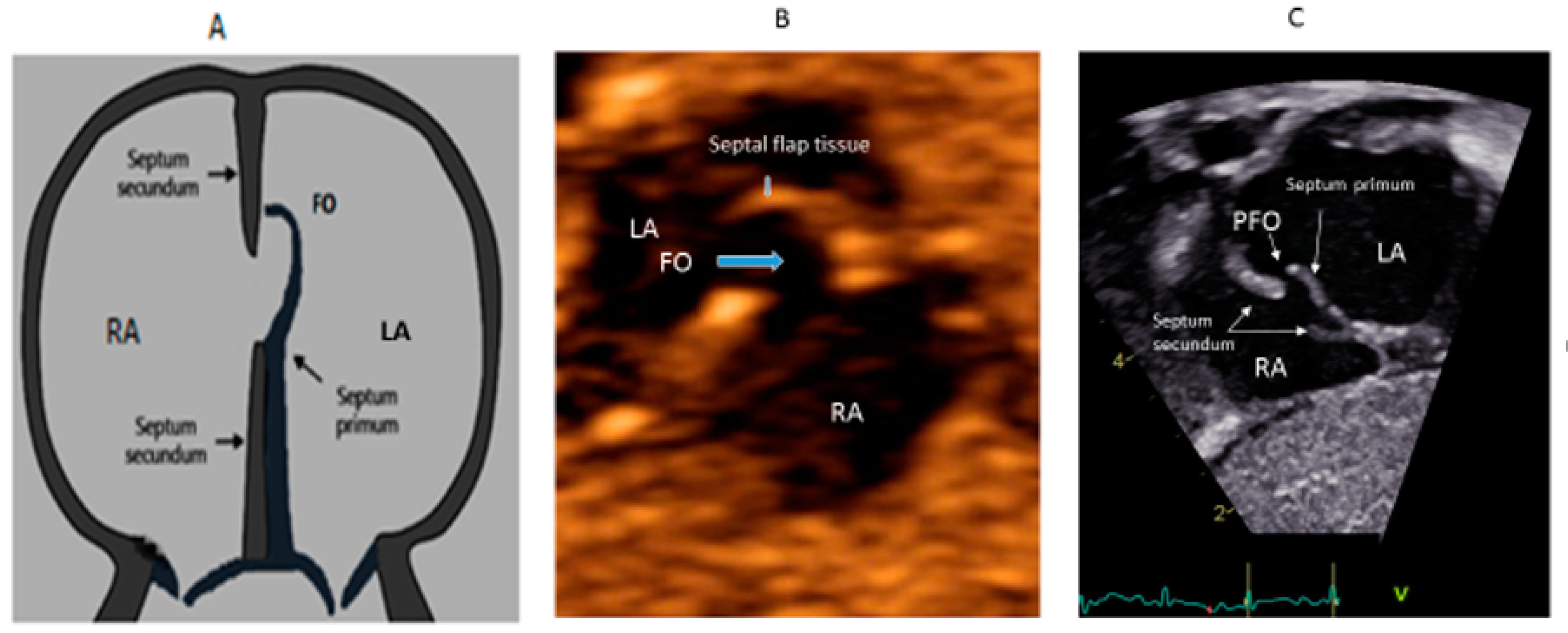
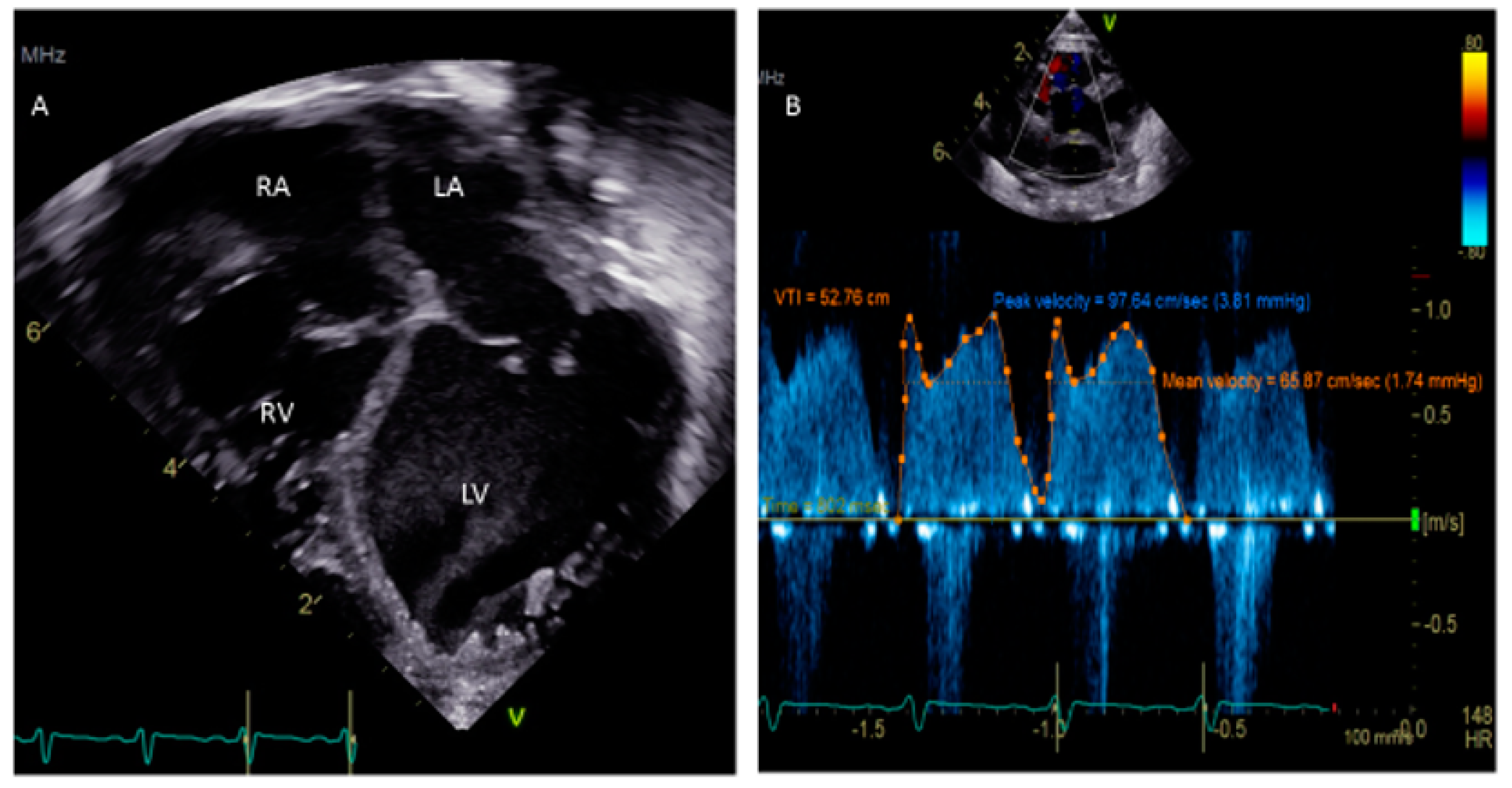

© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, B.B. Patent Foramen Ovale in Fetal Life, Infancy and Childhood. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci8030025
Das BB. Patent Foramen Ovale in Fetal Life, Infancy and Childhood. Medical Sciences. 2020; 8(3):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci8030025
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Bibhuti B. 2020. "Patent Foramen Ovale in Fetal Life, Infancy and Childhood" Medical Sciences 8, no. 3: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci8030025
APA StyleDas, B. B. (2020). Patent Foramen Ovale in Fetal Life, Infancy and Childhood. Medical Sciences, 8(3), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/medsci8030025




