The Mediating Effect of Parental Involvement on School Climate and Behavior Problems: School Personnel Perceptions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Relationships between School Climate, Behaviour Problems and Parental Involvement
1.2. Aims of the Study
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Variables and Measures
2.3. Procedures
2.4. Ethical Approval
2.5. Data Analyses Strategy
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Analyses (SC, PI and BP)
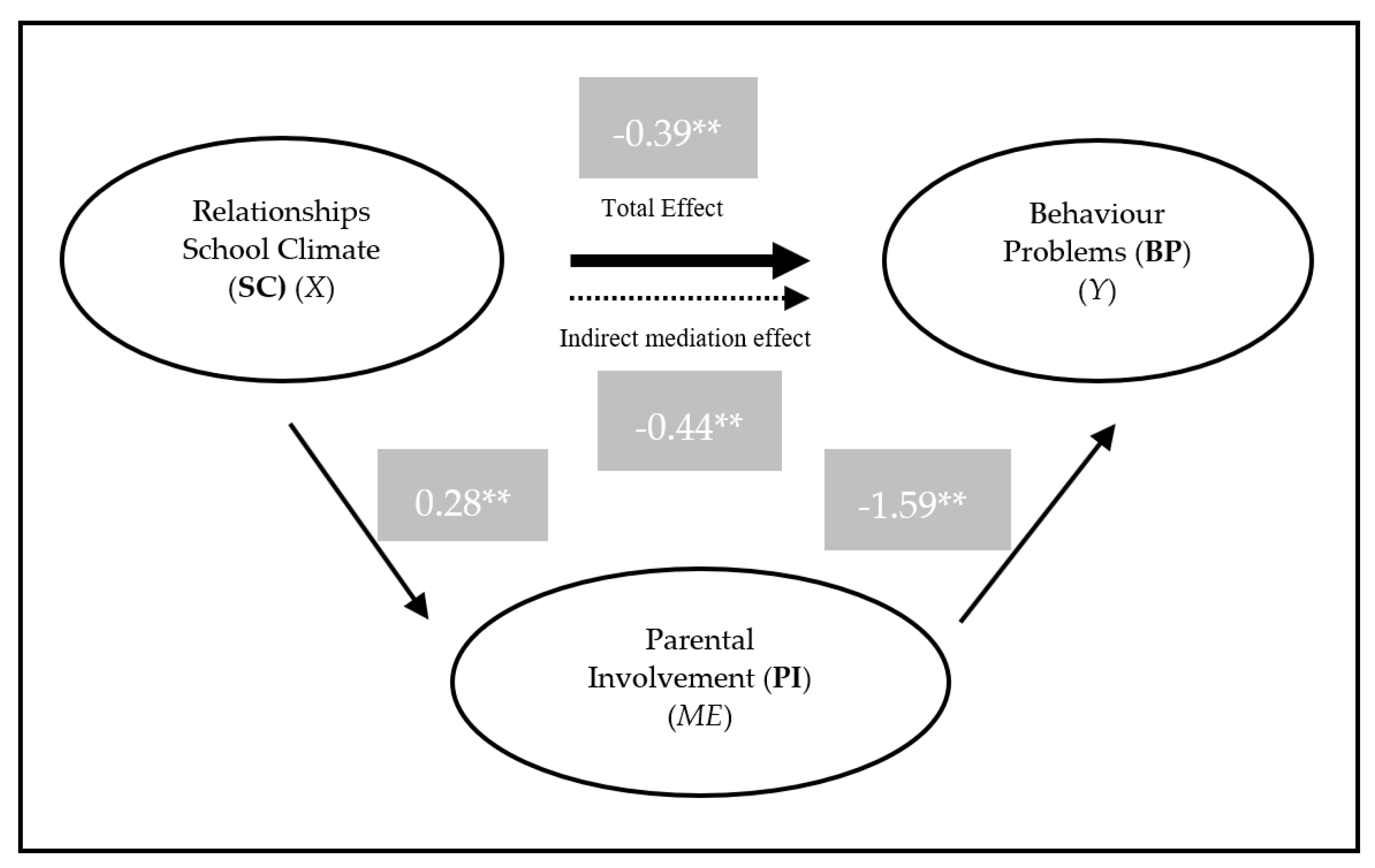
3.2. Relationships between SC and BP: The Mediating Effect of PI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Practical Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aldridge, J.; McChesney, K. The relationship between school climate and adolescent mental health and wellbeing: A systematic literature review. Int. J. Educ. Res. 2018, 88, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Degol, J. School climate: A review of the construct, measurement, and impact on student outcomes. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2016, 28, 315–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuperminc, G.; Leadbeater, B.; Emmons, C.; Blatt, S. Perceived school climate and difficulties in the social adjustment of middle school students. Appl. Dev. Sci. 1997, 1, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Solis, M.; Colunga-Rodriguez, C.; Vazquez-Colunga, J.; Vazquez-Juarez, C.; Angel-Gonzalez, M.; Johnson, S.; Bradshaw, C. Characterization of school climate perception in Mexican middle school students. Psychology 2016, 7, 1562–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen, J.; McCabe, E.; Michelli, N.; Pickeral, T. School climate: Research, policy, practice, and teacher education. Teach. Coll. Rec. 2009, 111, 180–213. [Google Scholar]
- National School Climate Center (NSCC). The 12 Dimensions of School Climate Measured. 2012. Available online: https://www.schoolclimate.org (accessed on 5 May 2020).
- Thapa, A.; Cohen, J.; Guffey, S.; Higgins-D’Alessandro, A. A review of school climate research. Rev. Educ. Res. 2013, 83, 357–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohl, D.; Recchia, S.; Steffgen, G. Measuring school climate: An overview of measurement scales. Educ. Res. 2013, 55, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, S. Improving the school environment to reduce school violence: A review of the literature. J. Sch. Health 2009, 79, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reaves, S.; McMahon, S.; Duffy, S.; Ruiz, L. The test of time: A meta-analytic review of the relation between school climate and problem behaviour. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2018, 39, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewno-Dumdie, B.M.; Mason, B.A.; Hajovsky, D.B.; Villeneuve, E.F. Student-Report Measures of School Climate: A Dimensional Review. Sch. Ment. Health 2019, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridade, S.; Nunes, L.; Sani, A. School diagnostic: Perceptions of educational professionals. Psychol. Community Health 2015, 4, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caridade, S.; Martins, A.C.; Nunes, L. Estilo de vida dos jovens e comportamentos desviantes e delinquentes: Vivências familiares, escolares e individuais [Youth lifestyle and deviant and delinquent behaviors: Family, school and individual experiences]. Revista Portuguesa de Investigação Comportamental e Social 2019, 5, 52–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valois, R.F. Adolescent Problem Behavior (Encyclopedia of Quality of Life and Well-Being Research); Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, L.; Caridade, S.; Sani, A. Avaliação do meio escolar: Um estudo exploratório [School evaluation: An exploratory study]. Revista Lusófona de Educação 2015, 30, 141–158. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, L.; Beça, S.; Dinis, A. Drug abuse and trafficking in universities: An emerging social phenomenon. In Advances in Sociology Research; Jaworski, J.A., Ed.; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 179–192. [Google Scholar]
- Radliff, K.M.; Wheaton, J.E.; Robinson, K.; Morris, J. Illuminating the relationship between bullying and substance use among middle and high school youth. Addict. Behav. 2012, 37, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufur, M.J.; Hoffmann, J.P.; Braudt, D.; Parcel, T.L.; Spence, K. Examining the effects of family and school social Capital on delinquent behavior. Deviant Behav. 2015, 26, 511–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, L.; Caridade, S.; Sani, A.I. Incivilities and delinquency in schools: An analysis of a social phenomenon. In Advances in Sociology Research; Jaworski, J.A., Ed.; Nova Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 193–208. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Stone, S.; Holloway, S. School-based parental involvement as a predictor of achievement and school learning environment: An elementary school-level analysis. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2017, 82, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.L.; Salinas, K.C. Partnering with families and communities. Educ. Leadersh. 2004, 61, 12–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lavenda, O. Parental involvement in school: A test of hoover-dempsey and sandler’s model among jewish and arab parents in Israel. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2011, 33, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourrajab, M.; Roustaee, R.; Talebloo, B.; Kasmaienezhadfard, S.; Ghani, M.F.B. School climate and parental involvement: The perception of Iranian teachers. Glob. J. Commer. Manag. Perspect. 2015, 4, 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Farrell, A.F.; Collier, M.A. School personnel’s perceptions of family-school communication: A qualitative study. Improv. Sch. 2010, 13, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.L. Parent Involvement. Educ. Urban Soc. 1987, 19, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDA). School Connectedness: Strategies for Increasing Protective Factors among Youth. 2009. Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/HealthyYouth/AdolescentHealth/pdf/connectedness.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2020).
- Van Eck, K.; Johnson, S.; Bettencourt, A.; Johnson, S. How school climate relates to chronic absence: A multi-level latent profile analysis. J. Sch. Psychol. 2017, 61, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, A.; Cornell, D.; Fan, X.; Sheras, P.; Shih, T.; Huang, F. Authoritative school discipline: High school practices associated with lower student bullying and victimization. J. Educ. Psychol. 2010, 102, 483–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffgen, G.; Recchia, S.; Viechtbauer, W. The link between school climate and violence in school: A meta-analytic review. Aggress. Violent Behav. 2013, 18, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorio, N.; Clark, K.; Demaray, M.; Doll, E. School climate counts: A longitudinal analysis of school Climate and middle school bullying behaviors. Int. J. Bullying Prev. 2019, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Way, N.; Reddy, R.; Rhodes, J. Students’ perceptions of school climate during the middle school years: Associations with trajectories of psychological and behavioral adjustment. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2007, 40, 194–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagi, K.; Stevens, M.; Simon, T.; Basile, K.; Carter, S.; Carter, S. Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) characteristics associated with violence and safety in middle schools. J. Sch. Health 2018, 88, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, J.M.; McChesney, K.; Afari, E. Relationships between school climate, bullying and delinquent behaviours. Learn. Environ. Res. 2017, 21, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnaar, L.; Arends, F.; Beku, U. Reducing bullying in schools by focusing on school climate and school socio-economic status. S. Afr. J. Educ. 2018, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, R. Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design; Sage Publications: Beverly Hills, CA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Lamoreaux, D.; Sulkowski, M. An alternative to fortified schools: Using Crime Prevention Through Environmental Design (CPTED) to balance student safety and psychological well-being. Psychol. Sch. 2020, 57, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horner, R.H.; Sugai, G.; Anderson, C.M. Examining the evidence base for school-wide positive behavior support. Focus Except. Child. 2010, 42, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienen, A.; Reijnders, I.; Aggelen, M.V.; Bos, E.H.; Batstra, L.; Jonge, P. The relative impact of school-wide positive behavior support on teachers’ perceptions of student behavior across schools, teachers, and students. Psychol. Sch. 2019, 56, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitiyo, M.; May, M.E.; Chitiyo, G. An assessment of the evidence-base for school-wide positive behavior support. Educ. Treat. Child. 2012, 35, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Nokali, N.; Bachman, H.; Votruba-Drzal, E. Parent involvement and children’s academic and social development in elementary school. Child Dev. 2010, 81, 988–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Epstein, J. School/family/community partnerships: Caring for the children we share. Phi Delta Kappan 2010, 92, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.; Herman, K.; Stormont, M.; Reinke, W.; Webster-Stratton, C. Impact of Incredible Years® on teacher perceptions of parental involvement: A latent transition analysis. J. Sch. Psychol. 2017, 62, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caridade, S.; Azevedo, V.; Dinis, M.A.; Sani, A.; Nunes, L. School personnel perception on school climate and students’ behaviour problems in Portugal. Psychol. Sch. 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Pourrajab, M.; Ghani, M.F.; Panahi, A. The mediating effect of parental involvement on school climate and continuous improvement. Malays. Online J. Educ. Manag. (MOJEM) 2018, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kõiv, K. Comparison and Connections Between School Climate, School Safety and Adolescents’ Antisocial Behavior Across three Types of Schools. Soc. Ugdym. 2014, 38, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carvalho, M.; Alão, P.; Magalhães, J. Da indisciplina ao clima de escola: A voz dos alunos [From indiscipline to school climate: The voice of students]. Revista Portuguesa de Investigação Educacional 2017, 17, 42–60. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, H. School social workers’ perception of school climate: An ecological system perspective. Int. J. Sch. Soc. Work 2017, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berkowitz, R.; Iachini, A.; Moore, H.; Capp, G.; Astor, R.A.; Pitner, R.; Benbenishty, R. School climate. In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Education; Noblit, G., Ed.; Oxford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Field, A. Discovering Statistics Using IBM SPSS Statistic, 2nd ed.; North American Edition; Sage: Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Child, D. The Essentials of Factor Analysis, 2nd ed.; Cassel Educational: New York, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Norusis, M.J. SPSS for Windows. SPSS, Ed.; SPSS Inc.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corporation Released IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25; IBM Corp.: Armonk, NY, USA, 2018.
- Hayes, A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1–692. [Google Scholar]
- Jeynes, W.H. A meta-analysis: The relationship between parental involvement and African American school outcomes. J. Black Stud. 2016, 47, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variables | Percentage (n) |
|---|---|
| Sex | |
| Female | 79.0 (260) |
| Male | 20.4 (67) |
| Education | |
| 1st–4th year | 2.1 (7) |
| 5th–6th year | 1.5 (5) |
| 7th–9th year | 5.2 (17) |
| 10th–12th year | 17.6 (58) |
| Higher Education | 73.6 (242) |
| School function | |
| Teacher | 71.4 (235) |
| Non-teacher | 28.3 (93) |
| School geographic location | |
| Lisbon | 22.8 (75) |
| Porto | 38.3 (126) |
| Other areas | 38.9 (128) |
| Variables/Dimensions | Mean (SD) | Total Mean (M) | Standard Deviation (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total School Climate (SC) | 20.38 | 2.97 | |
| Environmental–structural | 11.14 (1.84) | ||
| Relationships | 9.24 (1.749) | ||
| Behavior Problems (BP) | 6.05 | 2.69 | |
| Absenteeism | 2.60 (0.97) | ||
| Disruptive Behavior | 2.99 (1.76) | ||
| Incivilities | 2.51 (1.07) | ||
| Parental Involvement (PI) | 1.68 (0.65) | 1.68 | 0.651 |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Total School Climate (SC) | ||||||||
| 2. Environmental–Structural SC | 0.835 ** | |||||||
| 3. Relationships SC | 0.815 ** | 0.363 ** | ||||||
| 4. Behavior Problems (BP) | −0.242 ** | −0.152 ** | −0.251 ** | |||||
| 5. Absenteeism | −0.140 * | −0.032 | −0.203 ** | 0.552 ** | ||||
| 6. Disruptive Behavior | −0.199 ** | −0.130 ** | −0.201 ** | 0.918 ** | 0.417 ** | |||
| 7. Incivilities | −0.216 ** | −0.144 ** | −0.215 ** | 0.787 ** | 0.309 ** | 0.527 ** | ||
| 8. Parental Involvement (PI) | 0.533 ** | 0.155 ** | 0.740 ** | −0.359 ** | −0.317 ** | −0.310 ** | −0.276 ** |
| Predictor Variable Model | F(1327) | R2 | B | β | t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parental Involvement (PI) | 48.387 ** | 0.129 | −1.483 | −0.359 | −6.956 ** |
| Total School Climate (SC) | 20.379 ** | 0.059 | −0.220 | −0.242 | −4.514 ** |
| Environmental–Structural SC | 7.734 * | 0.023 | −0.222 | −0.152 | −2.781 ** |
| Relationships SC | 21.899 ** | 0.063 | −0.385 | −0.251 | −4.68 ** |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caridade, S.M.M.; Sousa, H.F.P.e.; Pimenta Dinis, M.A. The Mediating Effect of Parental Involvement on School Climate and Behavior Problems: School Personnel Perceptions. Behav. Sci. 2020, 10, 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10080129
Caridade SMM, Sousa HFPe, Pimenta Dinis MA. The Mediating Effect of Parental Involvement on School Climate and Behavior Problems: School Personnel Perceptions. Behavioral Sciences. 2020; 10(8):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10080129
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaridade, Sónia Maria Martins, Hélder Fernando Pedrosa e Sousa, and Maria Alzira Pimenta Dinis. 2020. "The Mediating Effect of Parental Involvement on School Climate and Behavior Problems: School Personnel Perceptions" Behavioral Sciences 10, no. 8: 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10080129
APA StyleCaridade, S. M. M., Sousa, H. F. P. e., & Pimenta Dinis, M. A. (2020). The Mediating Effect of Parental Involvement on School Climate and Behavior Problems: School Personnel Perceptions. Behavioral Sciences, 10(8), 129. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10080129







