Effects of Exercise on Physical Fitness in Older Adults with and Without Severe Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Sample
2.3. Inclusion Criteria
2.4. Exclusion Criteria
2.5. Intervention
2.6. Procedure
2.7. Physiological Variables
2.8. Anthropometric Variables
2.9. Physical Ability Tests
2.10. Statistical Analysis
2.11. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
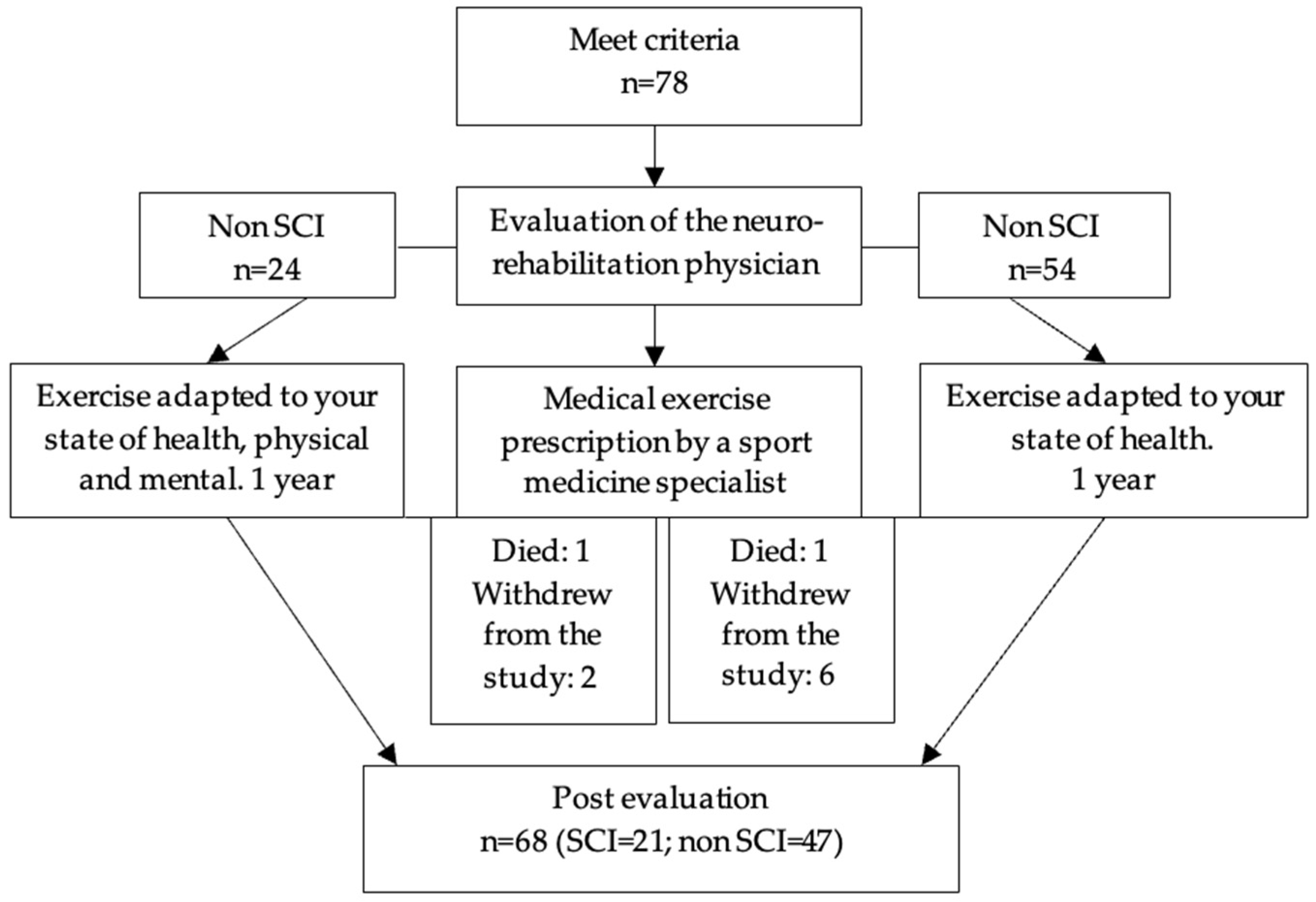
3.1. Characterization of the Population: Flow Chart and Characterization Table
3.2. Results of the Relative Risk of Deterioration by Variables After the Intervention
3.3. Changes in the Variables over Time
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alemán, J. A., de Baranda Andujar, P. S., & Ortín Ortín, E. J. (2014). Guía para la prescripción de ejercicio físico en pacientes con riesgo cardiovascular. Seh-Lelha. [Google Scholar]
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication manual of the american psychological association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, C. (2015). Understanding relative risk, odds ratio, and related terms: As simple as it can get. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 76(7), e857–e861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aráuz-Hernández, A. G., Guzmán-Padilla, S., & Roselló-Araya, M. (2013). La circunferencia abdominal como indicador de riesgo de enfermedad cardiovascular. Acta Médica Costarricense, 55(3), 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballarín-Naya, L., Malo, S., & Moreno-Franco, B. (2021). Efecto de intervenciones basadas en ejercicio físico y dieta sobre la evolución de deterioro cognitivo leve a demencia en sujetos mayores de 45 años. Revisión sistemática. Revista Española de Salud Pública, 95, e202102032. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Borg, G. A. (1982). Psychological bases of perceived exertion. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 14(5), 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Borson, S. (2010). Cognition, aging, and disabilities: Conceptual issues. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Clinics of North America, 21(2), 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, K., Emes, C., & Rogerson, M. (2004). Exercise testing protocols for different abilities in the older population. Activities, Adaptation & Aging, 28(1), 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carral, C., Fernández, C., & Pérez, R. (2000). Condición física y tercera edad: Valores normativos de la batería E.C.F.A. In T. García (Ed.), I Congreso de la asociación española de ciencias del deporte (pp. 391–404). Asociación Española de Ciencias del Deporte. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterji, S., Byles, J., Cutler, D., Seeman, T., & Verdes, E. (2015). Health, functioning, and disability in older adults—Present status and future implications. The Lancet, 385(9967), 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chobanian, A. V., Bakris, G. L., Black, H. R., Cushman, W. C., Green, L. A., Izzo, J. L., Jones, D. W., Materson, B. J., Oparil, S., Wright, J. T., & Roccella, E. J. (2003). Seventh report of the joint national committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension, 42(6), 1206–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofoletti, G., Oliani, M. M., Gobbi, S., Stella, F., Bucken Gobbi, L. T., & Renato Canineu, P. (2008). A controlled clinical trial on the effects of motor intervention on balance and cognition in institutionalized elderly patients with dementia. Clinical Rehabilitation, 22(7), 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colado, J. C., Furtado, G. E., Teixeira, A. M., Flandez, J., & Naclerio, F. (2020). Concurrent and construct validation of a new scale for rating perceived exertion during elastic resistance training in the elderly. Journal of Sports Science & Medicine, 19(1), 175–186. [Google Scholar]
- Colcombe, S. J., Erickson, K. I., Scalf, P. E., Kim, J. S., Prakash, R., McAuley, E., Elavsky, S., Marquez, D. X., Hu, L., & Kramer, A. F. (2006). Aerobic exercise training increases brain volume in aging humans. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences, 61(11), 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colomer, F. A., & Puig-Ribera, A. (2022). Inactividad física y sedentarismo. Los principales problemas de salud. AMF, 18(2), 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Enriquez-del Castillo, L. A., González-Bustos, J. B., Flores, L. A., Domínguez Esparza, S., Cervantes Hernández, N., & Viera Ponce, A. J. (2022). Estilo de vida activo según nuevas directrices de la OMS: ¿una influencia sobre la aptitud física, composición corporal y calidad de vida en mujeres mayores? Revista Ciencias de La Actividad Física, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garatachea, N., Santos-Lozano, A., Hughes, D. C., Gómez-Cabello, A., & Ara, I. (2017). Physical exercise as an effective antiaging intervention. BioMed Research International, 2017, 7317609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garber, C. E., Blissmer, B., Deschenes, M. R., Franklin, B. A., Lamonte, M. J., Lee, I.-M., Nieman, D. C., & Swain, D. P. (2011). Quantity and quality of exercise for developing and maintaining cardiorespiratory, musculoskeletal, and neuromotor fitness in apparently healthy adults. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 43(7), 1334–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadiri, K., Rezaei, M., Tabatabaei, S. M., Shahsavari, M., & Shahsavari, S. (2016). Use of LDA combined with PLS for classification of lung cancer gene expression data. International Journal of Medical Research & Health Sciences, 5(9S), 500–506. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero Teijón, M., González-Sánchez, A., de la Torre, L., & Sánchez Cabaco, A. (2024). Estado cognitivo, emocional y nivel de dependencia en personas adultas y mayores institucionalizadas. Revista Española de Geriatría y Gerontología, 59(3), 101481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenkamp, T. I. M., van Wijck, R., & Evenhuis, H. M. (2010). Physical fitness in older people with ID—Concept and measuring instruments: A review. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 31(5), 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilgenkamp, T. I. M., van Wijck, R., & Evenhuis, H. M. (2012). Feasibility and reliability of physical fitness tests in older adults with intellectual disability: A pilot study. Journal of Intellectual & Developmental Disability, 37(2), 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J. C., Richardson, D., & Hudson, J. M. (2021). The relationship between lateralization patterns from sequence based motor tasks and hemispheric speech dominance. Neuropsychology, 35(2), 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulme, C., & Riddoch, M. J. (1993). Developmental disorders of visual-spatial processing. In D. J. Vaina, & S. K. Halko (Eds.), Space and spatial analysis in neuroscience (pp. 265–298). Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, R., Liang, J., Xu, Y., & Wang, Y. (2019). Effects of physical activity and exercise on the cognitive function of patients with Alzheimer disease: A meta-analysis. BMC Geriatrics, 19(1), 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolliffe, I. T., & Cadima, J. (2016). Principal component analysis: A review and recent developments. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 374(2065), 20150202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katch, V. L., McArdle, W. D., & Katch, F. I. (2015). Fisiología del ejercicio. Fundamentos (4th ed.). Editorial Médica Panamericana. [Google Scholar]
- Lamotte, G., Shah, R. C., Lazarov, O., & Corcos, D. M. (2017). Exercise training for persons with alzheimer’s disease and caregivers: A review of dyadic exercise interventions. Journal of Motor Behavior, 49(4), 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, D. P., Teo, K. K., Rangarajan, S., Lopez-Jaramillo, P., Avezum, A., Jr., Orlandini, A., Seron, P., Ahmed, S. H., Rosengren, A., Kelishadi, R., Rahman, O., Swaminathan, S., Iqbal, R., Gupta, R., Lear, S. A., Oguz, A., Yusoff, K., Zatonska, K., Chifamba, J., … Yusuf, S. (2015). Prognostic value of grip strength: Findings from the Prospective Urban Rural Epidemiology (PURE) study. The Lancet, 386(9990), 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X., Huang, Y., Lo, K., Huang, Y., Chen, J., & Feng, Y. (2021). Quotient of waist circumference and body mass index: A valuable indicator for the high-risk phenotype of obesity. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 12, 697437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, A., Saz, P., & Marcos, G. (2002). MMSE. Examen cognoscitivo mini-mental. TEA Ediciones. [Google Scholar]
- Lobo, J. L., & Vanegas, O. J. (2022). Evaluación de la aptitud física de los usuarios del programa de actividad física “Montelíbano saludable”. GADE: Revista Científica, 2(4), 214–233. [Google Scholar]
- Lohman, T. G., Roche, A. F., & Martorell, R. (1988). Skinfold thicknesses and measurement technique. In G. Harrison, E. R. Buskirk, J. E. Carter, F. E. Johnston, T. G. Lohman, & M. L. Pollock (Eds.), Antropometric standardization reference manual. Human Kinetics. [Google Scholar]
- López, J. C., & Arango, E. F. (2015). Efectos del entrenamiento en superficies inestables sobre el equilibrio y funcionalidad en adultos mayores. Revista Facultad Nacional de Salud Pública, 33(1), 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Miquel, J., & Martí Agustí, G. (2011). Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). Revista Española de Medicina Legal, 37(3), 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, J. M., dos Santos, K. M., Bueno, J. C. A., de Oliveira, C. M., Fernandes, S., & do Nascimento, I. B. (2023). Prática do exercício físico no comprometimento cognitivo e intercorrências neuromusculares na atenção ao idoso: Uma revisão sistemática. Medicina (Ribeirão Preto), 56(4), e-212061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marfell-Jones, M., Olds, T., & Stewart, A. (2006). International standards for anthropometric assessment. ISAK. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, N.-H., Li, C.-I., Liu, C.-S., Lin, C.-H., Chang, C.-K., Chang, H.-W., Yang, C.-W., Li, T.-C., & Lin, C.-C. (2020). Effects of concurrent aerobic and resistance exercise in frail and pre-frail older adults. Medicine, 99(29), e21187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppewal, A., & Hilgenkamp, T. I. M. (2019). Physical fitness is predictive for 5-year survival in older adults with intellectual disabilities. Journal of Applied Research in Intellectual Disabilities, 32(4), 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H., Park, J. H., Na, H. R., Hiroyuki, S., Kim, G. M., Jung, M. K., Kim, W. K., & Park, K. W. (2019). Combined intervention of physical activity, aerobic exercise, and cognitive exercise intervention to prevent cognitive decline for patients with mild cognitive impairment: A randomized controlled clinical study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 8(7), 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, B. K., & Saltin, B. (2015). Exercise as medicine—Evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases. Scandinavian Journal of Medicine & Science in Sports, 25(S3), 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero-Chamizo, R., Gómez-Cabello, A., Mélendez, A., Vila-Maldonado, S., Espino, L., Gusi, N., Villa, G., Casajús, J. A., González-Gross, M., & Ara, I. (2015). Higher levels of physical fitness are associated with a reduced risk of suffering sarcopenic obesity and better perceived health among the elderly. The EXERNET multi-center study. The Journal of Nutrition, Health and Aging, 19(2), 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. (2008). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. [Google Scholar]
- Rikli, R. E., & Jones, C. J. (1999). Functional fitness normative scores for community-residing older adults, ages 60–94. Journal of Aging and Physical Activity, 7(2), 162–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Ramos, N., Romero-Ramos, O., & González Suárez, A. J. (2020). Actividad física y funciones cognitivas en personas mayores: Revisión sistemática de los últimos 5 años (Physical activity and cognitive functions in older people: A systematic review of the last 5 years). Retos, 39, 1017–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schutz, Y., Kyle, U., & Pichard, C. (2002). Fat-free mass index and fat mass index percentiles in Caucasians aged 18–98 y. International Journal of Obesity, 26(7), 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siswadi, Muslim, A., & Bakhtiar, T. (2012). Variable selection using principal component and procrustes analyses and its application in educational data. Journal of Asian Scientific Research, 2(12), 856–865. [Google Scholar]
- Stanish, H. I., Temple, V. A., & Frey, G. C. (2006). Health-promoting physical activity of adults with mental retardation. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 12(1), 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2013). Using multivariate statistics (6th ed.). Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Temple, V. A., Frey, G. C., & Stanish, H. I. (2006). Physical activity of adults with mental retardation: Review and research needs. American Journal of Health Promotion, 21(1), 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verghese, J., Lipton, R. B., Katz, M. J., Hall, C. B., Derby, C. A., Kuslansky, G., Ambrose, A. F., Sliwinski, M., & Buschke, H. (2003). Leisure activities and the risk of dementia in the elderly. New England Journal of Medicine, 348(25), 2508–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T., & Zhao, Y. (2021). Associations between functional fitness and walking speed in older adults. Geriatric Nursing, 42(2), 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M., Guo, Y., Gong, J., Deng, M., Yang, N., & Yan, Y. (2018). Relationships between functional fitness and cognitive impairment in Chinese community-dwelling older adults: A cross-sectional study. BMJ Open, 8(5), e020695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Cognitive Impairment | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SCI | Non-SCI | Total | |
| Total sample | 21 (30.9) | 47 (69.1) | 68 (100) |
| Gender | |||
| Male | 11 (52.4) | 14 (29.8) | 25 (36.7) |
| Female | 10 (47.6) | 33 (70.2) | 43 (63.3) |
| Age group | |||
| <80 years | 9 (42.9) | 23 (48.9) | 32 (47.1) |
| ≥80 years | 12 (57.1) | 24 (51.1) | 36 (52.9) |
| Weekly frequency of exercise | |||
| Two times per week | 10 (47.6) | 32 (68.1) | 42 (61.7) |
| Over three times per week | 11 (52.4) | 15 (31) | 26 (38.3) |
| Comorbidities | |||
| No | 11 (52.4) | 27 (57.4) | 38 (55.9) |
| Yes | 10 (47.6) | 20 (42.6) | 30 (44.1) |
| Cardiopulmonary | 1 (10.0) | 9 (45.0) | 6 (9.8) |
| Neurological | 5 (50.0) | 2 (10.0) | 8 (13.1) |
| Osteom | 4 (40.00) | 9 (45.0) | 14 (22.9) |
| Variables | SCI | Impaired | RR | IC 95% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes, n (%) | No, n (%) | ||||
| SBP | Yes, n = 21 | 2 (9.5) | 19 (90.5) | 0.6 | 0.1–2.8 |
| No, n = 47 | 7 (14.9) | 47 (85.1) | |||
| Total, n = 68 | 9 (13.2) | 59 (86.8) | |||
| DBP | Yes | 1 (4.7) | 20 (95.3) | 0.6 | 0.1–4.7 |
| No | 4 (8.5) | 43 (91.5) | |||
| Total | 5 (7.3) | 63 (92.7) | |||
| BMI | Yes | 3 (14.3) | 18 (85.7) | 1.3 | 0.4– 5.1 |
| No | 5 (10.6) | 42 (89.4) | |||
| Total | 8 (11.8) | 60 (88.2) | |||
| %F | Yes | 1 (4.7) | 20 (95.3) | 1.1 | 0.1–11.7 |
| No | 2 (4.3) | 45 (95.7) | |||
| Total | 3 (4.4) | 65 (95.6) | |||
| FFMI | Yes | 4 (19.0) | 17 (81.1) | 9.0 | 1.1–75.3 * |
| No | 1 (2.1) | 46 (97.9) | |||
| Total | 5 (7.3) | 63 (92.7) | |||
| PerAb | Yes | 1 (4.7) | 20 (95.3) | 0.8 | 0.1–6.8 |
| No | 3 (6.4) | 44 (93.6) | |||
| Total | 4 (5.9) | 64 (94.17) | |||
| ChairSR | Yes | 1 (4.7) | 20 (95.3) | 1.1 | 0.1–11.7 |
| No | 2 (4.3) | 45 (95.7) | |||
| Total | 3 (4.4) | 65 (95.6) | |||
| MGS | Yes | 3 (14.3) | 18 (85.7) | 1.4 | 0.4–5.1 |
| No | 5 (10.6) | 42 (89.4) | |||
| Total | 8 (11.8) | 54 (88.2) | |||
| 30SCHS | Yes | 4 (19.0) | 17 (81.0) | 3.0 | 0.7–12.2 |
| No | 3 (6.4) | 44 (93.6) | |||
| Total | 7 (10.3) | 61 (89.7) | |||
| 6MiWa | Yes | 4 (19.0) | 17 (81.0) | 1.1 | 0.4–3.3 |
| No | 8 (17.0) | 39 (83.0) | |||
| Total | 12 (17.6) | 56 (82.4) | |||
| U&G | Yes | 6 (28.5) | 15 (71.5) | 4.5 | 1.2–16.2 * |
| No | 3 (6.4) | 44 (93.6) | |||
| Total | 9 (13.2) | 59 (86.8) | |||
| RMB | Yes | 2 (9.5) | 19 (90.5) | 2.2 | 0.3–14.8 |
| No | 2 (4.2) | 44 (95.8) | |||
| Total | 4 (5.9) | 64 (94.1) | |||
| LMB | Yes | 4 (19.0) | 17 (81.0) | 2.2 | 0.3–14.8 |
| No | 5 (10.6) | 44 (89.4) | |||
| Total | 9 (13.2) | 59 (86.8) | |||
| SP | Yes | 5 (23.8) | 16 (76.2) | 2.8 | 0.8–9.4 |
| No | 4 (8.5) | 43 (91.5) | |||
| Total | 9 (13.2) | 59 (86.8) | |||
| Variables | Pre | Post |
|---|---|---|
| N = 68 | Median (Q1, Q3) | Median (Q1, Q3) |
| SBP *** | 120 (110, 130) | 110 (110, 130) |
| DBP * | 70 (61, 80) | 70 (60, 70) |
| BMI ** | 25.8 (23.1, 28.5) | 25.6 (22.8, 28.2) |
| %F *** | 35.4 (27.4, 39.4) | 33.9 (26.1, 37.9) |
| FFMI * | 17.4 (15.1, 18.4) | 17.7 (16.0, 18.5) |
| PerAb *** | 92 (87.2, 99.1) | 89.7 (85, 95) |
| ChairSR *** | −19.9 (−29.0, −8.3) | −14 (−23.0, −4.2) |
| MGS | 18.5 (12.8, 23.3) | 17.7 (12.5, 22.9) |
| 30SCHS ** | 10 (7, 13) | 11 (7, 14) |
| 6MiWa * | 311 (203, 466) | 346 (222, 503) |
| U&G *** | 10.7 (7.8, 22.9) | 9.2 (6.7, 16.2) |
| RMB | 3 (0.0, 8.3) | 3.5 (0.0, 9.6) |
| LMB | 2.9 (0.0, 8.3) | 3 (0.0, 9.0) |
| SP * | 20.8 (16.2, 29.4) | 18.5 (14, 26.1) |
| Analysis of Differences in Effects Between Groups: Median (Q1, Q3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-SCI (n = 47) | SCI (n = 21) | |||||
| Variables | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Non-SCI (n = 47) | SCI (n = 21) |
| SBP (mm Hg) | 120 (110, 130) | 110 (110, 120) | 120 (110, 120) | 110 (108, 110) | −2.0 (−10, 0.0) | −10 (−12, 0.0) |
| DBP (mm Hg) | 70 (60, 80) | 70 (60, 70) | 70 (65, 80) | 66 (60, 70) | 0.0 (−10, 0.0) | −10 (−10, 5) |
| BMI (Kg/m2) | 26.2 (23.2, 28.7) | 26.2 (23.1, 28.5) | 24.8 (22.3, 28.3) | 23.5 (21.7, 27.2) | −0.1 (−0.7, 0.4) | −0.6 (−1.9, −0.1) * |
| %F | 36.7 (31.6, 39.4) | 34.3 (28.2, 38.3) | 32.6 (24.4, 39) | 27.1 (21.7, 3.5) | −1.2 (−2.4, 0.0) | −2.7 (−5.1, −1.1) * |
| FFMI (Kg/m2) | 17.4 (15.8, 18.4) | 17.6 (16.1, 18.7) | 17.4 8 (16.3, 18.6) | 17.8 (15.6, 18.4) | 0.2 (−0.2, 0.9) | −0.1 (−0.6, 0.4) |
| PerAb (cm) | 93 (87, 100) | 91.3 (85, 95.7) | 91.4 (87.5, 98) | 88 (54.5, 94) | −2.0 (−5, 0.0) | −3.5 (−6.1, 0.0) |
| ChairSR (cm) | −15 (−25, −5) | −12.0 (−18, −3) ** | −25.0 (−32.5, 14.5) | −23 (−31, −8.5) ** | 2.0 (0.0, 7) | 5 (0.0, 10) |
| MGS (Kg) | 17.9 (12.8, 23.4) | 17.9 (13.0, 23.1) | 19 (13.8, 22.2) | 17.4 (11, 20.2) | 0.1 (−1.1, 1.4) | −0.4 (−2.9, 0.1) * |
| 30SCHS (N°) | 11 (8, 13) | 12 (9, 15) | 9 (5, 12) | 9 (1.5, 11.5) ** | 1.0 (0, 0.3) | 0 (−2, 1.5) * |
| 6MiWa (m) | 354 (218, 483) | 410 (247, 578) | 281 (198, 411) | 288 (119, 443) * | 42.9 (0.0, 101) | 8 (−38.5, 61.6) |
| U&G (s) | 9.4 (7.2, 17.2) | 8 (6, 13) * | 15.3 (11.5, 23.9) | 15.4 (11, 21.5) *** | −1.1 (−2.4, 0.1) | −0.6 (−4.1, 1.8) |
| RMB (s) | 4 (0.0, 9.8) | 4.4 (1, 15) * | 1 (0.0, 3.3) | 0.0 (0.0, 5.7) ** | 0.0 (−1, 4.1) | 0 (−1, 5.1) |
| LMB (s) | 3.4 (0.0, 9.1) | 5 (0, 10) | 2.3 (0.0, 5.5) | 0.0 (0.0, 5.5) * | 0.0 (−1, 3.2) | 0 (−2.6, 0.0) |
| SP (s) | 18.3 (14.8, 23.2) | 15.6 (13.1, 20.7) *** | 48.6 (23.9, 120) | 37 (19, 120) *** | −1.7 (−4.1, 0.0) | −6 (2.7, 2.2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramos-Álvarez, O.; Roldán-Aguilar, E.E.; Altamiranda-Saavedra, M.; Marín, J.C.; Arufe-Giráldez, V. Effects of Exercise on Physical Fitness in Older Adults with and Without Severe Cognitive Impairment. Behav. Sci. 2025, 15, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15030351
Ramos-Álvarez O, Roldán-Aguilar EE, Altamiranda-Saavedra M, Marín JC, Arufe-Giráldez V. Effects of Exercise on Physical Fitness in Older Adults with and Without Severe Cognitive Impairment. Behavioral Sciences. 2025; 15(3):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15030351
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamos-Álvarez, Oliver, Elkin Eduardo Roldán-Aguilar, Mariano Altamiranda-Saavedra, Juan Carlos Marín, and Víctor Arufe-Giráldez. 2025. "Effects of Exercise on Physical Fitness in Older Adults with and Without Severe Cognitive Impairment" Behavioral Sciences 15, no. 3: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15030351
APA StyleRamos-Álvarez, O., Roldán-Aguilar, E. E., Altamiranda-Saavedra, M., Marín, J. C., & Arufe-Giráldez, V. (2025). Effects of Exercise on Physical Fitness in Older Adults with and Without Severe Cognitive Impairment. Behavioral Sciences, 15(3), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15030351








