The Effects of Picloram and Clopyralid on Ocimum Basilicum (Basil)—A Study of the Uptake, Distribution and Translocation of Synthetic Auxins from Soil to Plant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Plant Material and Growth
2.3. Experimental Procedure Conditions
2.4. LC-MS/MS Instrument
2.5. Extraction of Synthetic Auxins from Soil and Plants
2.6. QA&QC
2.7. Bioconcentration and Translocation Factors
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of LC-MS/MS Conditions
3.2. Optimization of UEA Procedure
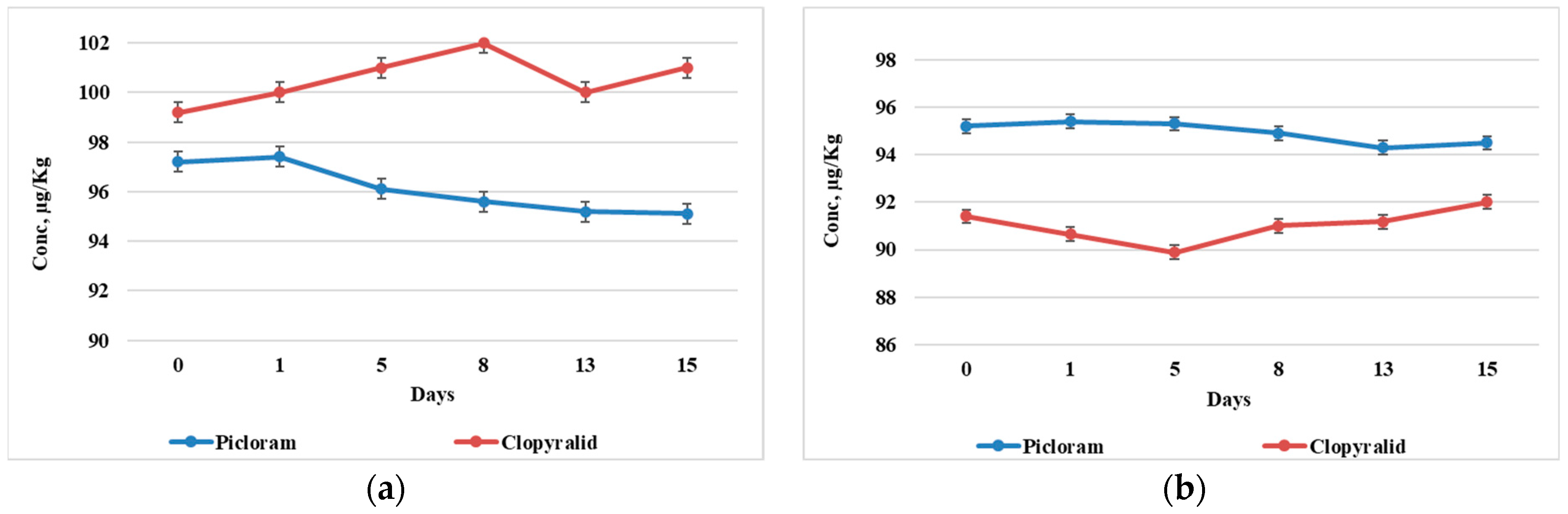
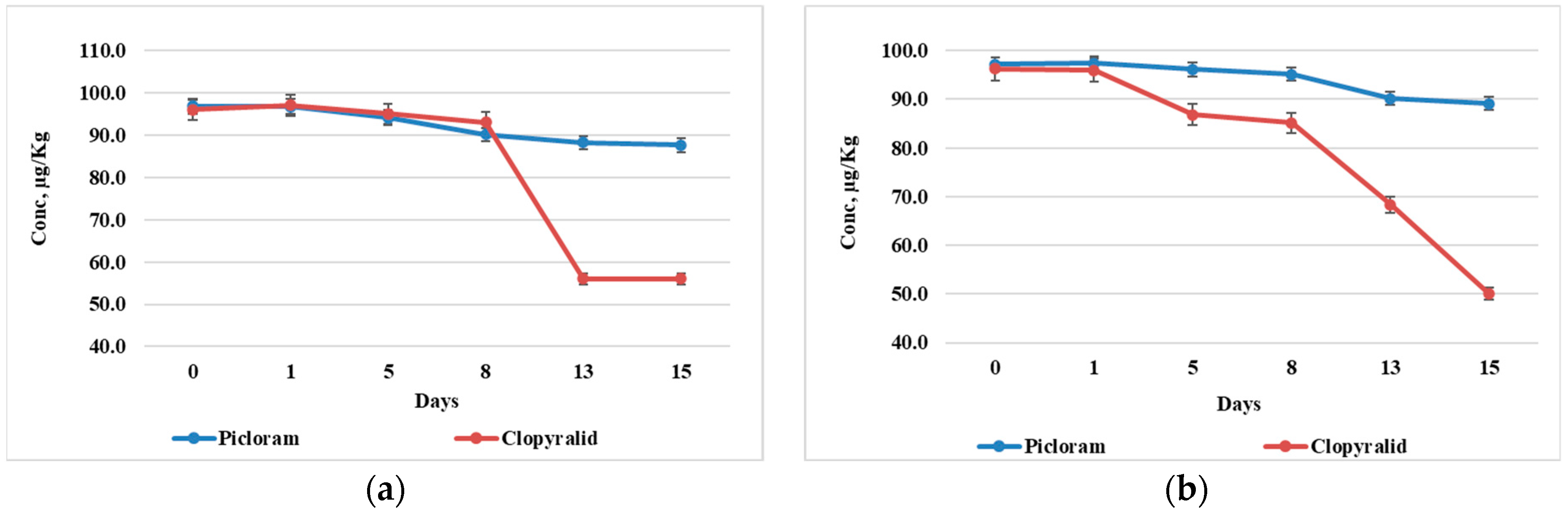
3.3. The Uptake of Clopyralid and Picloram in Plant Organs
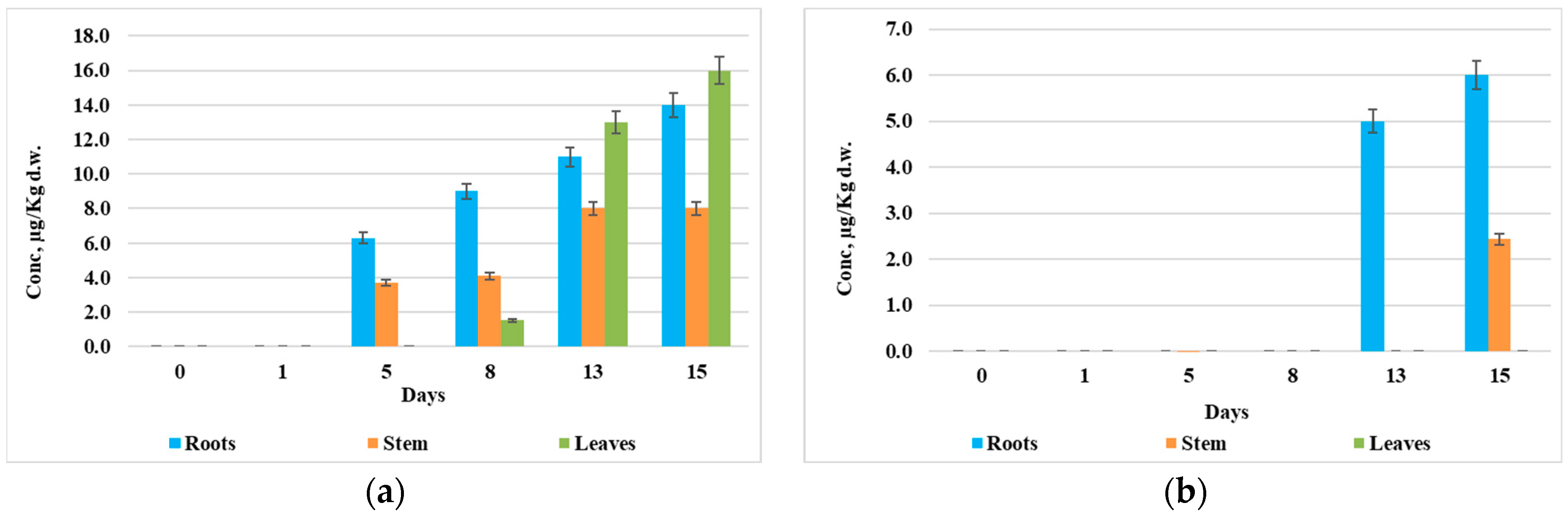
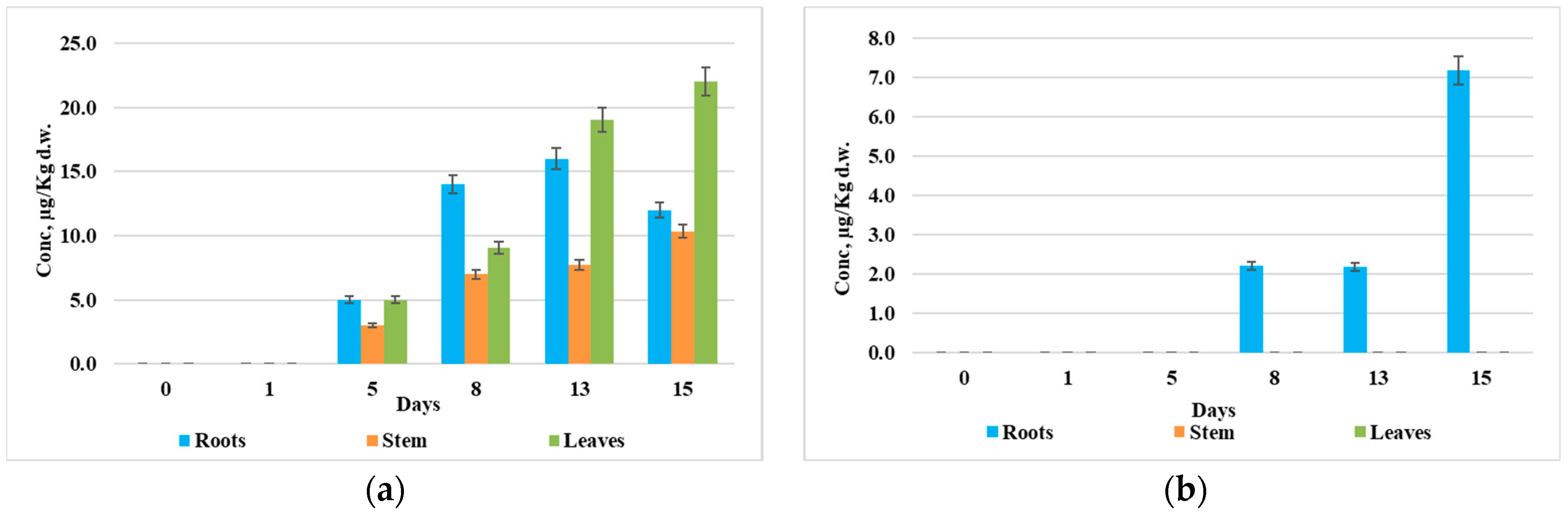
3.4. Distribution of Synthetic Auxins in Plant Organs
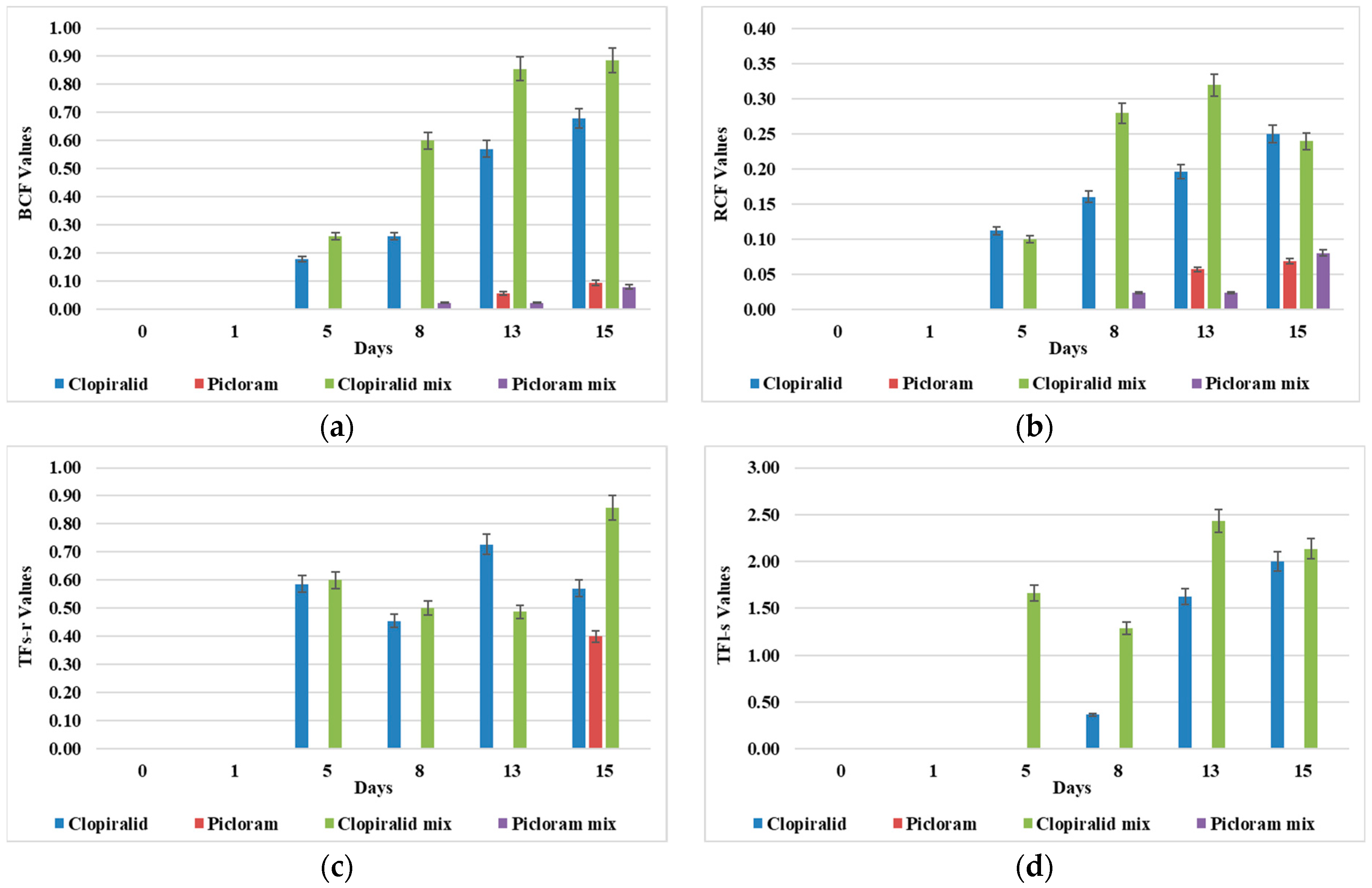
3.5. Bioconcentration and Translocation Capacity of Organic Compounds to Plants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shoenberger, E.D.; Jungers, J.M.; Law, E.P.; Keene, C.L.; DiTommaso, A.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Wyse, D.L.; Picasso, V.D.; Stoltenberg, D.E. Synthetic auxin herbicides do not injure intermediate wheatgrass or affect grain yield. Weed Technol. 2023, 37, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, D.; Paisley-Jone, C. Pesticides Industry Sales and Usage, 2008–2012 Market Estimates. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2017-01/documents/pesticides-industry-sales-usage-2016_0.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Rolando, C.A.; Scott, M.B.; Baillie, B.R.; Dean, F.; Todoroki, C.L.; Paul, T.S.H. Persistence of triclopyr, dicamba, and picloram in the environment following aerial spraying for control of dense pine invasion. Invasive Plant Sci. Manag. 2023, 16, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusinska, J.; Uzunova, V.; Schmitzer, P.; Weimer, M.; Bell, J.; Napier, R.M. The differential binding and biological efficacy of auxin herbicides. Pest Manag. Sci. 2022, 78, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ensminger, M.P.; Budd, R.; Kelley, K.C.; Goh, K.S. Pesticide occurrence and aquatic benchmark exceedances in urban surface waters and sediments in three urban areas of California, USA, 2008–2011. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 3697–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. The Use of Plant Protection Products in the European Union Data 1992–2003, Statistical Books. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/products-statistical-books/-/ks-76-06-669 (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Wolf, A.; Bergmann, A.; Wilken, R.D.; Gao, X.; Bi, Y.; Chen, H.; Schüth, C. Occurrence and distribution of organic trace substances in waters from the Three Gorges Reservoir, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 7124–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, V.L.; Vinocur, A.; Sabio y García, C.A.; Allend, L.; Cristose, D.S.; Rojas, D.; Wolansky, M.; Pizarro, H. Effects of glyphosate and 2,4-D mixture on freshwater phytoplankton and periphyton communities: A microcosms approach. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, S.; Perret, D.; Gentili, A.; D’Ascenzo, G.; Faberi, A. Determination of phenoxyacid herbicides and their phenolic metabolite in drinking water and surface water. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 16, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, A.; Okoh, O.O.; Agunbiade, F.O.; Okoh, A.I. Occurrence of phenolic derivatives in Buffalo River of Eastern Cape South Africa: Exposure risk evaluation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 171, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiron, S.; Comoretto, L.; Rinaldi, E.; Maurino, V.; Minero, C.; Vione, D. Pesticide by-products in the Rhône delta (Southern France). The case of 4-chloro-2-methylphenol and its nitroderivative. Chemosphere 2009, 74, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Costa, F.B.; Fenton, O.; Jordan, P.; Fennell, C.; Mellander, P.E. Using a multi-dimensional approach for catchment scale herbicide pollution assessments. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, K. Auxin herbicides: Current status of mechanism and mode of action. Pest Manag. Sci. 2010, 66, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance picloram. EFSA J. 2009, 7, 1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszko, T.; Muszyński, P.; Materska, M.; Bojanowska, M.; Kostecka, M.; Jackowska, I. Adsorption and degradation of phenoxyalkanoic acid herbicides in soils: A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gressel, J. Evolving understanding of the evolution of herbicide resistance. Pest Manag. Sci. 2009, 65, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; An, Q.; Pan, C.; Zou, N. Exogenous salicylic acid alleviates the accumulation of pesticides and mitigates pesticide-induced oxidative stress in cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 208, 111654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Jiang, L.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; An, S.; Zhang, X. Uptake, accumulation, and translocation mechanisms of steroid estrogens in plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, R.; Dong, S.; Yao, S.; Wang, F.; Cao, D.; Xu, S.; Fang, H.; Yu, Y. Upward translocation of acetochlor and atrazine in wheat plants depends on their distribution in roots. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 135636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Li, H.; Ryser, E.T.; Zhang, W. Comparing root concentration factors of antibiotics for lettuce (Lactuca sativa) measured in rhizosphere and bulk soils. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 127677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glüge, J.; Escher, B.I.; Scheringer, M. How error-prone bioaccumulation experiments affect the risk assessment of hydrophobic chemicals and what could be improved. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2023, 19, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayampathi, T.; Atugoda, T.; Jayasinghe, C. Uptake and accumulation of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in leafy vegetables. In Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products: Waste Management and Treatment Technology, 1st ed.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2019; pp. 87–113. [Google Scholar]
- Kacalkova, L.; Tlustos, P. The uptake of persistent organic pollutants by plants. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2011, 6, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, S.; Wang, X.; Akram, M.A.; Hu, W.; Dong, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, H.; Degen, A.A.; Xiong, J.; et al. Concentrations and bioconcentration factors of leaf microelements in response to environmental gradients in drylands of China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1143442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Lv, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Plant uptake and accumulation of emerging contaminants: Emerging understanding, challenges, and future prospects. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.G.; Borglin, S.E.; Green, F.B.; Grayson, A.; Wozei, E.; Stringfellow, W.T. Biologically directed environmental monitoring, fate, and transport of estrogenic endocrine disrupting compounds in water: A review. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodgen, L.K.; Ueda, A.; Wu, X.; Parker, D.R.; Gan, J. Uptake and accumulation of four PPCP/EDCs in two leafy vegetables. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panseri, S.; Chiesa, L.M.; Arioli, F.; Pavlovic, R.; Villa, R.; Lavazza, A. Occurrence of selected steroid hormones and hormone residues in Italian dairy products. Food Control 2011, 22, 1843–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Gong, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, L.; Feng, C.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Y. Distribution and accumulation characteristics of typical organic pollutants in sediment–plant system of freshwater aquatic ecosystem: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukun, B.; Gaines, T.A.; Nissen, S.J.; Westra, P.; Brunk, G.; Shaner, D.L.; Sleugh, B.B.; Peterson, V.F. Aminopyralid and Clopyralid Absorption and Translocation in Canada Thistle (Cirsium arvense). Weed Sci. 2009, 57, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koskinen, W.C.; Clay, S.A. Pesticide sorption–desorption in soils and sediments. In Handbook of Residue Analytical Methods for Agrochemicals, 1st ed.; Lee, P.W., Aizawa, H., Barefoot, A.C., Miyamoto, J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Wauchope, R.D.; Yeh, S.; Linders, J.B.H.J.; Kloskowski, R.; Tanaka, K.; Rubin, B.; Katayama, A.; Kördel, W.; Gerstl, Z.; Lane, M.; et al. Pesticide soil sorption parameters: Theory, measurement, uses, limitations and reliability. Pest Manag. Sci. 2002, 58, 419–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolai, M.; Pellissier, L.; Bovet, N.; Renaud, J.; Mazet, M. Pesticide residues in drinking water: A global overview. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flury, M. Experimental evidence of transport of pesticides through field soils—A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1996, 25, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, C.S.; Hjelmsø, M.H. Agricultural soils, pesticides and microbial diversity. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.K.; Quince, C.; Macdonald, C.A.; Khachane, A.; Thomas, N.; Al-Soud, W.A.; Sørensen, S.J.; He, Z.; White, D.; Sinclair, A.; et al. Loss of microbial diversity in soils is coincident with reductions in some specialized functions. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2408–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanizadeh, H.; Li, F.; He, L.; Harrington, K.C. Characterization of clopyralid resistance in lawn burweed (Soliva sessilis). PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0253934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riah, W.; Laval, K.; Laroche-Ajzenberg, E.; Mougin, C.; Latour, X.; Trinsoutrot-Gattin, I. Effects of pesticides on soil enzymes: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Pan, Y.; Meng, W. A review of the ecotoxicological effects of pesticide residues in freshwater ecosystem. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.P. Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Powles, S. Metabolism-Based Herbicide Resistance and Cross-Resistance in Crop Weeds: A Threat to Herbicide Sustainability and Global Crop Production. Plant Physiol. 2014, 166, 1106–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cycon, M.; Mrozik, A.; Piotrowska-Seget, Z. Bioaugmentation as a strategy for the remediation of pesticide-polluted soil: A review. Chemosphere 2017, 172, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test Samples | BCF | RCF | TFs-r | TFl-s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clopyralid | 0.68 ± 0.022 | 0.25 ± 0.008 | 0.57 ± 0.018 | 2.02 ± 0.064 |
| Picloram | 0.11 ± 0.003 | 0.07 ± 0.002 | 0.41 ± 0.013 | - |
| Clopyralid—Mix | 0.89 ± 0.028 | 0.24 ± 0.008 | 0.86 ± 0.027 | 2.13 ± 0.068 |
| Picloram—Mix | 0.08 ± 0.003 | 0.08 ± 0.003 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scutariu, R.E.; Petre, V.A.; Tatarus, A.; Puiu, D.M.; Chiriac, F.L. The Effects of Picloram and Clopyralid on Ocimum Basilicum (Basil)—A Study of the Uptake, Distribution and Translocation of Synthetic Auxins from Soil to Plant. Environments 2025, 12, 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050144
Scutariu RE, Petre VA, Tatarus A, Puiu DM, Chiriac FL. The Effects of Picloram and Clopyralid on Ocimum Basilicum (Basil)—A Study of the Uptake, Distribution and Translocation of Synthetic Auxins from Soil to Plant. Environments. 2025; 12(5):144. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050144
Chicago/Turabian StyleScutariu, Roxana Elena, Valentina Andreea Petre, Alina Tatarus, Diana Maria Puiu, and Florentina Laura Chiriac. 2025. "The Effects of Picloram and Clopyralid on Ocimum Basilicum (Basil)—A Study of the Uptake, Distribution and Translocation of Synthetic Auxins from Soil to Plant" Environments 12, no. 5: 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050144
APA StyleScutariu, R. E., Petre, V. A., Tatarus, A., Puiu, D. M., & Chiriac, F. L. (2025). The Effects of Picloram and Clopyralid on Ocimum Basilicum (Basil)—A Study of the Uptake, Distribution and Translocation of Synthetic Auxins from Soil to Plant. Environments, 12(5), 144. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments12050144







