Concentration of Organotin and Booster Biocides in Sediments of Seagrass Area from Sungai Pulai Estuary, South of Johor, Malaysia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.3.1. Organotin
2.3.2. Booster Biocides
2.4. Instrument Analysis
2.5. Degradation Index Calculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Concentration of Organotin Compounds in Sediments
3.2. Distribution of Booster Biocides in Sediments
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

| Location | MBT | DBT | TBT | MPT | DPT | TPT | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semi-closed Port of Gdynia | 134–1125 | 250–3810 | 1143–6743 | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. | [44] |
| Indonesian coastal waters | 1.5–170 | 0.9–78 | 0.4–350 | 0.2–22 | <0.1–39 | <0.1–19 | [31] |
| Fishing ports along the Chinese coast | <3.6–194 | <2.3–41.5 | <0.7–86 | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. | [45] |
| Southern Baltic coastal zone | 0.54–33.97 | 0.51–38.66 | 0.2–115.2 | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. | [46] |
| Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan | 0.5–83.4 | 0.5–31.6 | 1.2–112 | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. | [47] |
| Shipping and shipbuilding areas in South Korea | 15–6212 | 4–8747 | 3–55,264 | n.r. | n.r. | n.r. | [64] |
| Korean Special Management Sea Areas | <0.1–56.9 | <0.1–160 | <0.1–2304 | <0.1–46.7 | <0.1–2.33 | <0.1–68.5 | [48] |
| Location | Diuron | Dichlofluanid | Chlorothalonil | Irgarol 1051 | M1 | Sea-Nine 211 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| California marinas | <0.3–4.2 | n.r. | n.r. | <0.3–8.9 | <0.3–5.3 | n.r. | [69] |
| Shipping and shipbuilding areas in South Korea | 2.3–62.3 | n.d. | n.r. | n.d.–11.5 | <0.2–0.6 | <0.2–5.5 | [64] |
| Korean Special Management Sea Areas | <0.06–144 | n.r. | n.r. | <0.02–7.79 | <0.07–0.9 | <0.06–117 | [48] |
| Malaysian coastal area | <0.02–4.8 | <0.1 | n.r. | <0.02–14 | <0.1 | <0.04–1.7 | [37] |
| Thailand coastal area | <0.08–25 | n.r. | n.r. | 0.03–3.2 | <1 | 0.09 | [52] |
| Vietnamese coastal areas | 0.11–3.0 | <0.01–13 | n.r. | 0.05–4.0 | <0.1–0.43 | 0.09–1.3 | [66] |
| Indonesian coastal waters | <0.04–740 | <0.04–80 | n.r. | 0.1–76 | 0.4–670 | <0.04–150 | [31] |
| Panamanian marinas | <0.75–14.1 | n.r. | n.r. | <0.08–2.8 | n.r. | <0.38–81.6 | [63] |
| Busan Bay, Korea | 6.89–29.9 | n.r. | 22–1065 | 1.79–73.5 | n.r. | 61.2–269 | [65] |
| Ulsan Bay, Korean | 15.3–39.2 | n.r. | 1.3–422 | <0.02–38.8 | n.r. | <0.02–264 | [65] |
References
- Lewis, J.A. Marine biofouling and its prevention. Mater. Forum 1998, 22, 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, P.D.; De Nys, R.; Kjelleberg, S. Chemical cues for surface colonization. J. Chem. Ecol. 2002, 28, 1935–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, A.; Abel, P.D.; Arnold, D.W.; Milne, A. Cost–benefit analysis of the use of TBT: The case for a treatment approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 258, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.M.; Birchenough, A.C.; Brancato, M.S. The TBT ban: Out of the frying pan into the fire? Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MER. Environmental benefits of TBT antifoulants. Mar. Eng. Rev. 1996, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Hall, L.W., Jr.; Pinkney, A.E. Acute and sublethal effects of organotin compounds on aquatic biota: An interpretative literature evaluation. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1985, 14, 159–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagtap, J.T.; Shejule, K.B.; Jaiswal, D.P. Acute toxicity study of tributyltin chloride on the freshwater bivalve, Lamellidens marginalis. World J. Fish. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 100–103. [Google Scholar]
- Kusk, K.O.; Peterson, S. Acute and chronic toxicity of tributyltin and linear alkylbenzene sulfonate to the marine copepod Acartia tonsa. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1997, 16, 1629–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macken, A.; Giltrap, M.; Foley, B.; McGovern, E.; McHugh, B.; Davoren, M. A model compound study: The ecotoxicological evaluation of five organic contaminants employing a battery of marine bioassays. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 153, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsunemasa, N.; Okamura, H. Effects of organotin alternative antifoulants on oyster embryo. Arc. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 61, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, A.; Antón-Martín, R.; García-Luque, E.; Riba, I.; DelValls, T.A. Distribution of butyltins (TBT, DBT, MBT) in sediments of Gulf of Cádiz (Spain) and its bioaccumulation in the clam Ruditapes philippinarum. Ecotoxicology 2009, 18, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S.; Bhosale, D.; Bhosle, N. Baseline of organotin pollution in fishes, clams, shrimps, squids and crabs collected from the west coast of India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2213–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Wang, J.T.; Chung, K.N.; Leu, M.Y.; Meng, P.J. Distribution and accumulation of organotin species in seawater, sediments and organisms collected from a Taiwan mariculture area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.W.; Chen, C.F.; Ju, Y.R.; Dong, C.D. Assessment of the bioaccumulation and biodegradation of butyltin compounds by Thalamita crenata in Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Brio, F.; Commendatore, M.; Castro, I.B.; Gomes Costa, P.; Fillmann, G.; Bigatti, G. Distribution and bioaccumulation of butyltins in the edible gastropod Odontocymbiola magellanica. Mar. Biol. Res. 2016, 12, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, J.; Nigaya, S.; Takenouchi, A.; Kokushi, E.; Uno, S. Bioaccumulation of environmental organotin compounds in translocated rock shell Thais clavigera in Kagoshima Bay. Fish. Sci. 2016, 82, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, C.; Huang, Q.; Wu, L.; Zhang, W. Organotin contamination in sediments and aquatic organisms from the Yangtze estuary and adjacent marine environments. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017, 34, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.; Laranjeiro, F.; Takahashi, S.; Tanabe, S.; Barroso, C.M.D. Imposex and organotin prevalence in a European post-legislative scenario: Temporal trends from 2003 to 2008. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Ismail, A.; Harino, H.; Yusoff, M.K.; Arai, T. Imposex in Thais gradata as a biomarker for TBT contamination on the southern coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 211, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Ismail, A. Imposex study on Thais tuberosa from port and non-port areas along the west coast of Peninsular Malaysia. J. Trop. Mar. Ecosys. 2011, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Guðmundsdóttir, L.Ó.; Ho, K.K.; Lam, J.C.; Svavarsson, J.; Leung, K.M. Long-term temporal trends (1992–2008) of imposex status associated with organotin contamination in the dogwhelk Nucella lapillus along the Icelandic coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 63, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Prasad, S.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Harino, H.; Yatsuzuka, E.; Inoue, K.; Ismail, A. Status of butyltins contamination in sediments from Kong Kong Laut, Johor after five years of global banning. Pollut. Res. 2016, 35, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, K. Release rate of biocides from antifouling paints. In Ecotoxicology of Antifouling Biocides; Springer: Tokyo, Japan, 2009; Chapter 1; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Konstantinou, I.K.; Albanis, T.A. Worldwide occurrence and effects of antifouling paint booster biocides in the aquatic environment: A review. Environ. Internat. 2004, 30, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomazzi, S.; Cochet, N. Environmental impact of diuron transformation: A review. Chemosphere 2004, 56, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, J.H.; Gunthorpe, L.; Allinson, G.; Duda, S. Effects of antifouling biocides to the germination and growth of the marine macroalga, Hormosira banksii (Turner) Desicaine. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 52, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesworth, J.C.; Donkin, M.E.; Brown, M.T. The interactive effects of the antifouling herbicides Irgarol 1051 and Diuron on the seagrass Zostera marina (L.). Aquat. Toxicol. 2004, 66, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antizar-Ladislao, B. Environmental levels, toxicity and human exposure to tributyltin (TBT)-contaminated marine environment. A review. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 292–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japar, S.B.; Arshad, A.; Hishamuddin, O.; Muta Harah, Z.; Misni, S. Seagrass and macroalgal communities of Sungai Pulai estuary, south-west Johore, Peninsular Malaysia. In Seagrass Biology: Scientific Discussion from an International Workshop, Rottnest Island, Western Australia; Faculty of Science, The University of Western Australia: Nedlands, Australia, 1996; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mukhtar, A.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Ismail, A.; Miyazaki, N. Stable isotope (δ13C and δ15N) analysis as a tool to quantify the food web structure in seagrass area of Pulai River estuary, Johor, Peninsular Malaysia. Malay. Nat. J. 2016, 68, 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Harino, H.; Arifin, Z.; Rumengan, I.F.M.; Arai, T.; Ohji, M.; Miyazaki, N. Distribution of Antifouling Biocides and Perfluoroalkyl Compounds in Sediments from Selected Locations in Indonesian Coastal Waters. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2012, 63, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, E.D.; Phillips, I.R.; Hawker, D.W. In-situ partitioning of butyltin species in estuarine sediments. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez, S.; Albalos, M.; Bayona, J. Organotin contamination in sediments from the Western Mediterranean enclosures following 10 years of TBT regulation. Water Res. 2002, 36, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipkowska, A.; Kowalewska, G.; Pavoni, B.; Łęczyński, L. Organotin compounds in surface sediments from seaports on the Gulf of Gdańsk (southern Baltic coast). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 182, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudaryanto, A.; Takahashi, S.; Iwata, H.; Tanabe, S.; Ismail, A. Contamination of butyltin compounds in Malaysian marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2004, 130, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Carvalho Oliveira, R.; Santelli, R.E. Occurrence and chemical speciation analysis of organotin compounds in the environment: A review. Talanta 2010, 82, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harino, H.; Arai, T.; Ohji, M.; Ismail, A.B.; Miyazaki, N. Contamination profiles of antifouling biocides in selected coastal regions of Malaysia. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2009, 56, 468–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooney, J.J. Organotin compounds and aquatic bacteria: A review. Helgol. Mar. Res. 1995, 49, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooney, J.J. Microbial transformations of tin and tin compounds. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1988, 3, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barug, D. Microbial degradation of bis (tributyltin) oxide. Chemosphere 1981, 10, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowson, P.H.; Bubb, J.M.; Williams, T.P.; Lester, J.N. Degradation of tributyltin in sediment in freshwater and estuarine marine sediments. Water Sci. Technol. 1993, 28, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainbow, P.S. Biomonitoring of heavy metal availability in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1995, 31, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.N.; Rodrigues, P.N.R.; Basto, M.C.P.; Vasconcelos, M.T.S. Butyltin levels in several Portuguese coastal areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 159, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, B.; Wasik, A.; Jewell, L.L.; Piketh, S.; Pączek, U.; Gałuszka, A.; Namieśnik, J. Seasonal changes in organotin compounds in water and sediment samples from the semi-closed Port of Gdynia. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 441, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Shi, J.; He, B.; Xu, W.; Li, X.; Jiang, G. Organotin compounds in surface sediments from selected fishing ports along the Chinese coast. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipkowska, A.; Kowalewska, G.; Pavoni, B. Organotin compounds in surface sediments of the Southern Baltic coastal zone: A study on the main factors for their accumulation and degradation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 2077–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.D.; Chen, C.F.; Chen, C.W. Composition and source of butyltins in sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor, Taiwan. Estuar. Coast. Shelf. Sci. 2015, 156, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, N.H.; Jeong, H.H.; Kang, S.D.; Kim, D.J.; Ju, M.J.; Horiguchi, T.; Cho, H.S. Organotins and new antifouling biocides in water and sediments from three Korean Special Management Sea Areas following ten years of tributyltin regulation: Contamination profiles and risk assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champ, M.A. A review of organotin regulatory strategies, pending actions, related costs and benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 258, 21–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, M. Organotin compounds in the environment—An overview. Appl. Geochem. 2001, 16, 719–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, K.; Lee, R.F. Triphenyltin and its degradation products in foliage and soils from sprayed pecan orchards and in fish from adjacent ponds. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1996, 15, 1492–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harino, H.; Ohji, M.; Wattayakorn, G.; Arai, T.; Rungsupa, S.; Miyazaki, N. Occurrence of antifouling biocides in sediment and green mussels from Thailand. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 51, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harino, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Eguchi, S.; Kawai, S.; Kurokawa, Y.; Arai, T.; Ohji, M.; Okamura, H.; Miyazaki, N. Concentrations of antifouling biocides in sediment and mussel samples collected from Otsuchi Bay, Japan. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2007, 52, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadhav, S. Transformation of triphenyltin by Eubacteria: Fate and effects in environmental system. In Bioprospects of Coastal Eubacteria; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 179–193. [Google Scholar]
- Fent, K. Ecotoxicology of organotin compounds. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 1996, 26, 1–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amouroux, D.; Tessier, E.; Donard, O.F.X. Volatilization of organotin compounds from estuarine and coastal environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.K.; Zhou, G.J.; Xu, E.G.; Wang, X.; Leung, K.M. Long-term spatio-temporal trends of organotin contaminations in the marine environment of Hong Kong. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.S.; Hong, S.H.; Yim, U.H.; Shin, K.H.; Shim, W.J. Temporal changes in TBT pollution in water, sediment, and oyster from Jinhae Bay after the total ban in South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 86, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sant’Anna, B.S.; Santos, D.M.; Marchi, M.R.R.D.; Zara, F.J.; Turra, A. Surface-sediment and hermit-crab contamination by butyltins in southeastern Atlantic estuaries after ban of TBT-based antifouling paints. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 6516–6524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahbib, Y.; Abidli, S.; González, P.R.; Alonso, J.I.G.; El Menif, N.T. Monitoring of organotin pollution in Bizerta Channel (Northern Tunisia): Temporal trend from 2002 to 2010. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2011, 86, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.S.; Hong, S.H.; Shin, K.H.; Shim, W.J. Imposex in Reishia clavigera as an indicator to assess recovery of TBT pollution after a total ban in South Korea. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2017, 73, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanapiah, M.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Shahrun, M.S.; Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Ismail, A.; Harino, H.; Inoe, K. Concentration of antifoulant herbicide, Diuron in the vicinity of Port Klang, Malaysia. In Isu-Isu Terkini Penyelidikan Saintifik Sains Marin di Malaysia; Mohamed, C.A.R., Samsuddin, M., Yatim, A.F.M., Eds.; Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia: Bangi, Malaysia, 2017; pp. 35–38. ISBN 978-983-41358-3-6. [Google Scholar]
- Batista-Andrade, J.A.; Caldas, S.S.; Batista, R.M.; Castro, I.B.; Fillmann, G.; Primel, E.G. From TBT to booster biocides: Levels and impacts of antifouling along coastal areas of Panama. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.S.; Hong, S.H.; An, J.G.; Shin, K.H.; Shim, W.J. Distribution of butyltins and alternative antifouling biocides in sediments from shipping and shipbuilding areas in South Korea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 95, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.N.; Kim, U.J.; Lee, L.S.; Choi, M.K.; Oh, J.E. Assessment of organotin and tin-free antifouling paints contamination in the Korean coastal area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harino, H.; Midorikawa, S.; Arai, T.; Ohji, M.; Cu, N.D.; Miyazaki, N. Concentrations of booster biocides in sediment and clams from Vietnam. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2006, 86, 1163–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L. Occurrence and persistence of antifouling biocide Irgarol 1051 and its main metabolite in the coastal waters of Southern England. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 406, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassi, R.; Tolosa, I.; de Mora, S. A survey of antifoulants in sediments from Ports and Marinas along the French Mediterranean coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2008, 56, 1943–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapozhnikova, Y.; Wirth, E.; Schiff, K.; Fulton, M. Antifouling biocides in water and sediments from California marinas. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 69, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boxall, A.B. Environmental risk assessment of antifouling biocides. Chim. Oggi 2004, 22, 46–49. [Google Scholar]
- Tolosa, I.; Readman, J.W.; Blaevoet, A.; Ghilini, S.; Bartocci, J.; Horvat, M. Contamination of Mediterranean (Cote d’Azur) coastal waters by organotins and Irgarol 1051 used in antifouling paints. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1996, 32, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, I.; Ballesteros, B.; Marco, M.P.; Barceló, D. Pilot survey for determination of the antifouling agent irgarol 1051 in enclosed seawater samples by a direct enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography—diode array detection. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 3530–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunemasa, N.; Yamazaki, H. Concentration of antifouling biocides and metals in sediment core samples in the northern part of Hiroshima Bay. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 9991–10004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.V.; McHugh, M.; Waldock, M. Antifouling paint booster biocides in UK coastal waters: Inputs, occurrence and environmental fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 293, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.V.; Brooks, S. The environmental fate and effects of antifouling paint biocides. Biofouling 2010, 26, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harino, H.; Kitano, M.; Mori, Y.; Mochida, K.; Kakuno, A.; Arima, S. Degradation of antifouling booster biocides in water. J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. UK 2005, 85, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanis, T.A.; Lambropoulou, D.A.; Sakkas, V.A.; Konstantinou, I.K. Antifouling paint booster biocide contamination in Greek marine sediments. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voulvoulis, N.; Scrimshaw, M.D.; Lester, J.N. Occurrence of four biocides utilized in antifouling paints, as alternatives to organotin compounds, in waters and sediments of a commercial estuary in the UK. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2000, 40, 938–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, K.; Ferrer, I.; Barceló, D. Part-per-trillion level determination of antifouling pesticides and their byproducts in seawater samples by off-line solid-phase extraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography–atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 879, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, K.; Ferrer, I.; Hernando, M.D.; Fernández-Alba, A.R.; Marcé, R.M.; Borrull, F.; Barcelo, D. Occurrence of antifouling biocides in the Spanish Mediterranean marine environment. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamwijk, C.; Schouten, A.; Foekema, E.M.; Ravensberg, J.C.; Collombon, M.T.; Schmidt, K.; Kugler, M. Monitoring of the booster biocide dichlofluanid in water and marine sediment of Greek marinas. Chemosphere 2005, 60, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, K.V. The environmental fate and behaviour of antifouling paint booster biocides: A review. Biofouling 2001, 17, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Point | n | MBT | DBT | TBT | MPT | DPT | TPT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | |||||||
| Point 1 | 3 | 6.5 ± 0.3 | 6.1 ± 0.3 | 8.1 ± 0.4 | <0.1 | 89.1 ± 0.5 | 17.1 ± 0.9 |
| Point 2 | 3 | 12.2 ± 0.6 | <0.1 | 10.6 ± 0.5 | <0.1 | 10.2 ± 0.5 | 19.4 ± 1.0 |
| Point 3 | 3 | 7.4 ± 0.4 | <0.1 | 10 ± 0.5 | 16 ± 0.8 | 9.3 ± 0.5 | 17.7 ± 0.9 |
| Point | BDI | PDI |
|---|---|---|
| Point 1 | 1.56 | 5.20 |
| Point 2 | 1.15 | 0.53 |
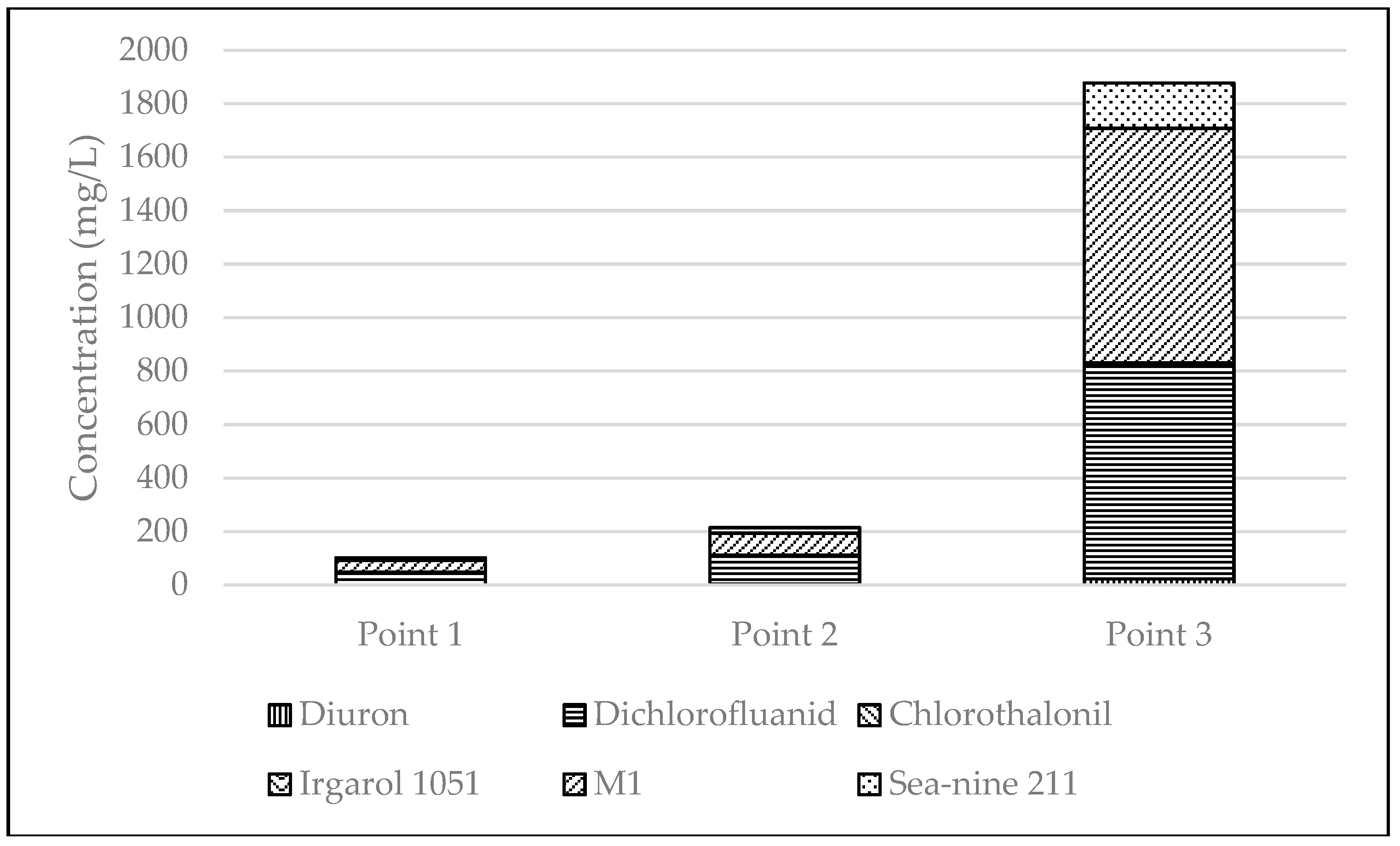
| Point | n | Diuron | Dichlorofluanid | Chlorothalonil | Irgarol 1051 | M1 | Sea-nine 211 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | |||||||
| Point 1 | 3 | <0.1 | 48.7 ± 2.4 | <0.1 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 44 ± 2.2 | 9.1 ± 0.5 |
| Point 2 | 3 | 3.4 ± 0.2 | 108 ± 5.4 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 82.5 ± 4.1 | 20.2 ± 1.0 |
| Point 3 | 3 | 22.9 ± 1.1 | 800 ± 40 | 6.2 ± 0.3 | 1.4 ± 0.1 | 876 ± 44 | 170 ± 8.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukhtar, A.; Mohamat-Yusuff, F.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Harino, H.; Ismail, A.; Inoue, K. Concentration of Organotin and Booster Biocides in Sediments of Seagrass Area from Sungai Pulai Estuary, South of Johor, Malaysia. Environments 2019, 6, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6020026
Mukhtar A, Mohamat-Yusuff F, Zulkifli SZ, Harino H, Ismail A, Inoue K. Concentration of Organotin and Booster Biocides in Sediments of Seagrass Area from Sungai Pulai Estuary, South of Johor, Malaysia. Environments. 2019; 6(2):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6020026
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukhtar, Aqilah, Ferdaus Mohamat-Yusuff, Syaizwan Zahmir Zulkifli, Hiroya Harino, Ahmad Ismail, and Koji Inoue. 2019. "Concentration of Organotin and Booster Biocides in Sediments of Seagrass Area from Sungai Pulai Estuary, South of Johor, Malaysia" Environments 6, no. 2: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6020026
APA StyleMukhtar, A., Mohamat-Yusuff, F., Zulkifli, S. Z., Harino, H., Ismail, A., & Inoue, K. (2019). Concentration of Organotin and Booster Biocides in Sediments of Seagrass Area from Sungai Pulai Estuary, South of Johor, Malaysia. Environments, 6(2), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments6020026




