The Influence of Microplastics from Ground Tyres on the Acute, Subchronical Toxicity and Microbial Respiration of Soil
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
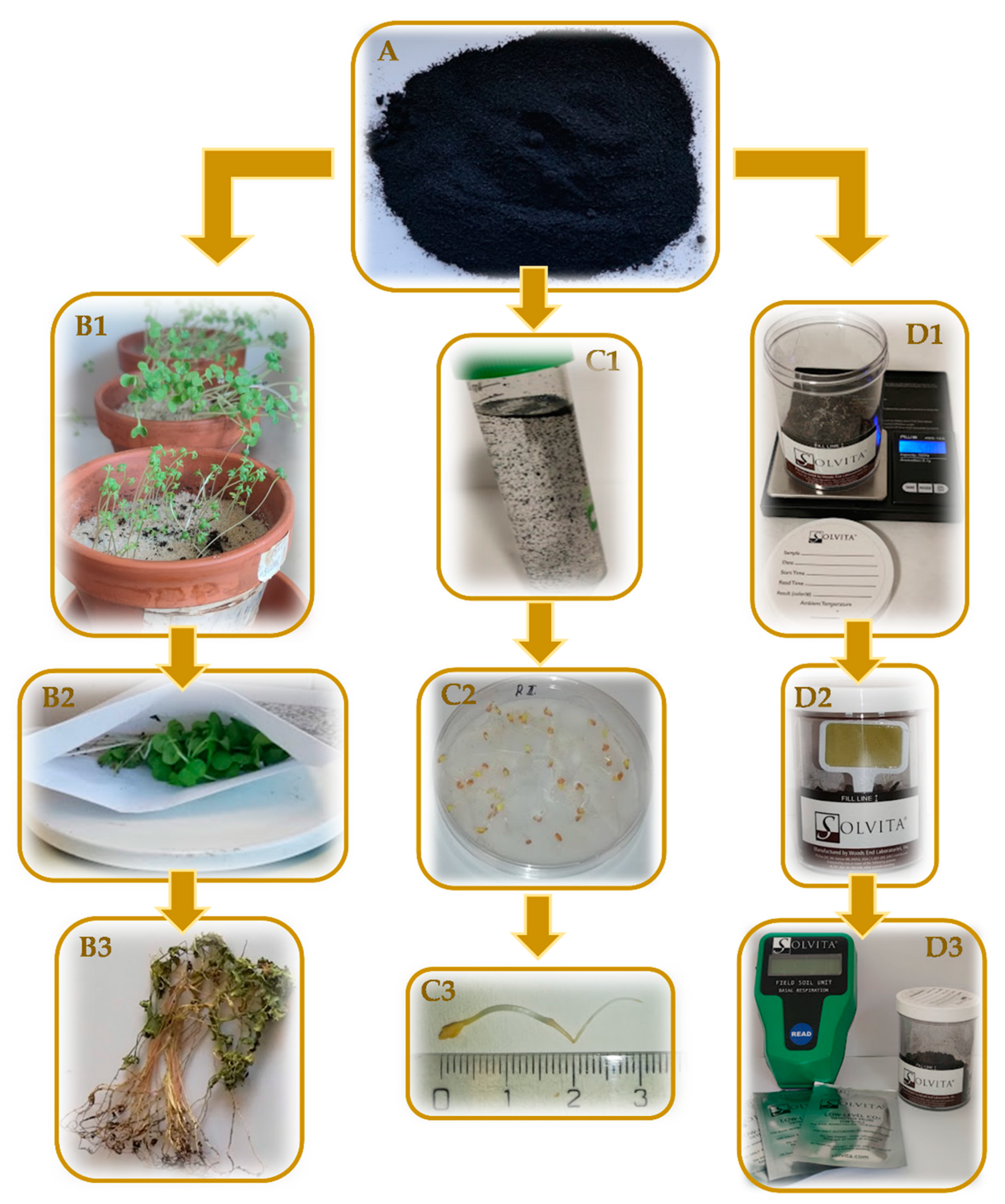
2.1. Subchronical Toxicity of Abrasion Products from Tyres
- PT—number of germinated seeds/plants growing in the tested substrate;
- PC—number of germinated seeds/plants growing in the control substrate.
2.2. Determination of Biomass Weight from the Experiment of Subchronical Toxicity
2.3. Biological Test of Tyres Abrasion Products
- NS—number of seeds germinated in the tested extract;
- NC—number of seeds germinated in the control sample;
- NS—average root length in the tested extract;
- NC—average root length in the control sample.
2.4. Respiration Activity of Soil with the Content of Tyre Abrasion Products
3. Results
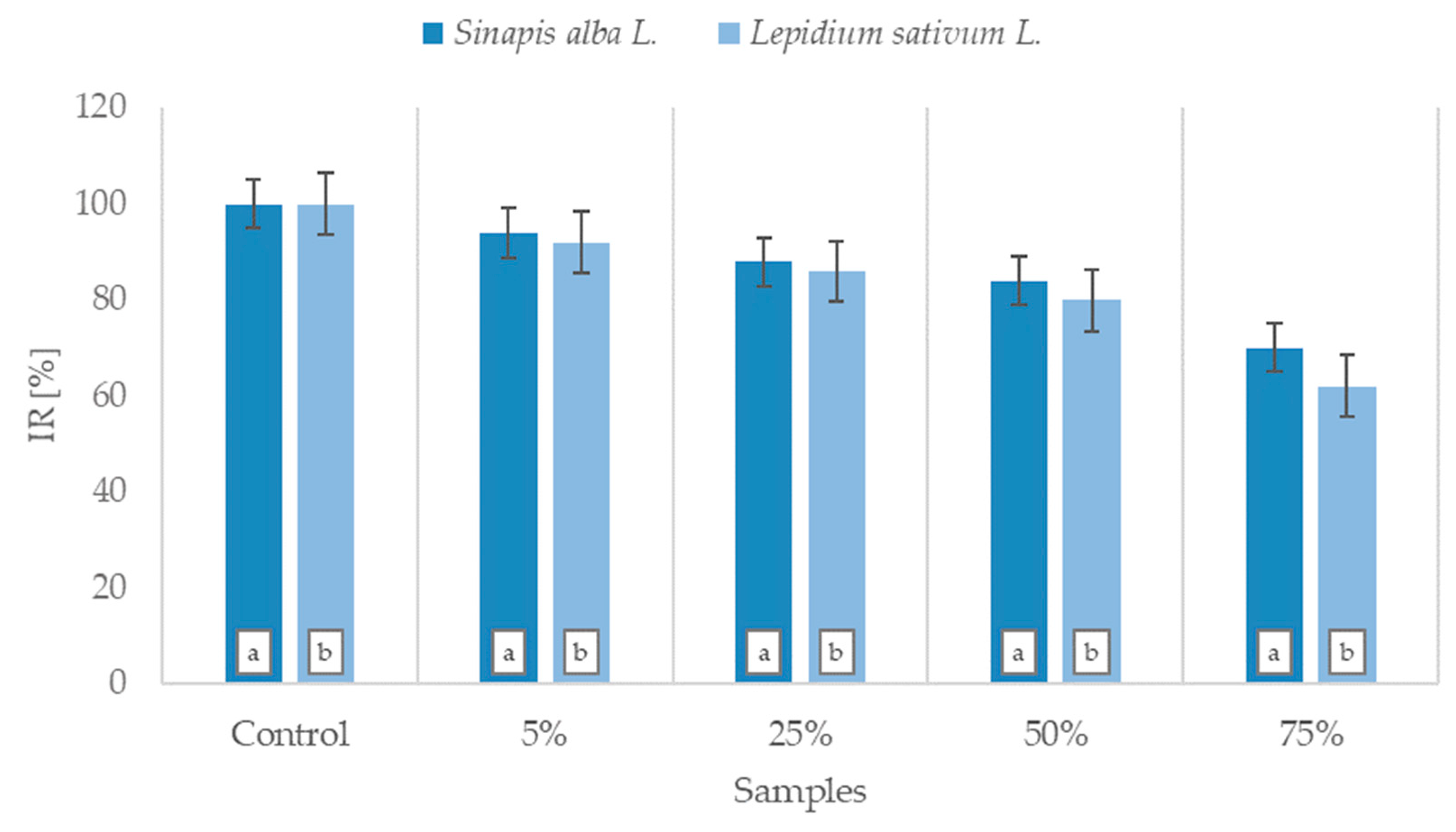
3.1. Subchronical Toxicity of Abrasion Products from Tyres
3.2. Biomass Weight from the Experiment of Subchronical Toxicity
3.3. Biological Test of Tyre Abrasion Products
3.4. Respiration Activity of Soil with the Content of Tyre Abrasion Products
4. Discussion
4.1. Subchronical Toxicity of Abrasion Products from Tyres
4.2. Biomass Weight from the Experiment of Subchronical Toxicity
4.3. Biological Test of tyre Abrasion Products
4.4. Respiration Activity of Soil with Content of Tyre Abrasion Products
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bostock, J. Global Industry Tire Volume to Reach 2.7 Bilion Units by 2022. Smithers. © 2021. Available online: https://www.smithers.com/resources/2017/dec/global-industry-tire-volume-to-reach-2-7-billion (accessed on 2 October 2021).
- Dong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hossain, U.; He, Y.; Liu, P. Life cycle assessment of vehicle tires: A systematic review. Clean. Environ. Syst. 2021, 2, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kořínek, R. Assessment of Selected Methods of Material and Energy Use of a Passenger Tire within Its Entire Life Cycle Using the LCA Method. Ph.D. Thesis, VŠB—Technical University of Ostrava, Faculty of Mining and Geology, Ostrava, Czech Republic, 2012. Available online: http://dspace.vsb.cz/bitstream/handle/10084/100564/KOR089_HGF_P2102_2102V009_2013.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Khan, F.R.; Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A. Acute and long-term toxicity of micronized car tire wear particles to Hyalella Azteca. Aquat. Toxicol. 2019, 213, 105216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Zhou, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Zhou, S.; Xu, E.G.; Xing, B. Environmental occurrence, fate, impact, and potential solution of tire microplastics: Similarities and differences with tire wear particles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halle, L.L.; Palmqvist, A.; Kampmann, K.; Khan, F.R. Ecotoxicology of micronized tire rubber: Past, present and future considerations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, E.; Jung, U.; Choi, S.-S. Quantification of tire tread wear particles in microparticles produced on the road using oleamide as a novel marker. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, P.J.; Löhr, A.J.; Van Belleghem, F.G.A.J.; Ragas, A.M.J. Wear and Tear of Tyres: A Stealthy Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verschoor, A.J. Towards a Definition of Microplastics—Considerations for the Specification of Physico-Chemical Properties; National Institute for Public Health and the Environment: Bilthoven, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 42. Available online: https://www.rivm.nl/bibliotheek/rapporten/2015-0116.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Gwinnerr, C. How Your Car Sheds Microplastics into the Ocean Thousands of Miles Away. The Conversation. 2020. Available online: https://theconversation.com/how-your-car-sheds-microplastics-into-the-ocean-thousands-of-miles-away-142614 (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Järlskog, I.; Strömvall, A.-M.; Magnusson, K.; Gustafsson, M.; Polukarova, M.; Galfi, H.; Aronsson, M.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Occurrence of tire and bitumen wear microplastics on urban streets and in sweepsand and washwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommer, F.; Dietze, V.; Baum, A.; Sauer, J.; Gilge, S.; Maschowski, C.; Gieré, R. Tire Abrasion as a Major Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, C. Tiny Pieces of Plastic Found in Arctic Snow. National Geographic. 2019. Available online: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/microplastics-found-in-arctic-snow (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Basak, S. Are We Breathing In Microplastics?—A Soft Touch Perspective. Medium. 2019. Available online: https://medium.com/@sayanbasak/are-we-breathing-in-microplastics-a-soft-touch-perspective-433767fcb04e (accessed on 18 October 2021).
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Fu, L.; Zhao, C.; Jia, A. Land use conversion influences soil respiration across a desert-oasis ecoregion in Northwest China, with consideration of cold season CO2 efflux and its significance. CATENA 2020, 188, 104460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Bradford, M.A.; Carey, J.; Crowther, T.W.; Machmuller, M.B.; Mohan, J.E.; Tood-Brown, K. Temperature sensitivity of soil carbon. Ecosys. Conseq. Soil Warm. 2019, 175–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, X. Modeling Synthesis and Analysis. In Soil Respiration and the Environment; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 215–246. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780120887828500103 (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Shi, P.; Qin, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, T.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Ren, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F. Soil respiration and response of carbon source changes to vegetation restoration in the Loess Plateau, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 707, 135507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, C.; Baumgarten, A.; Bass, R.; Wever, G.; Lohr, D. Analytical Methods Used with Soilless Substrates. In Soilless Culture, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 509–564. [Google Scholar]
- Šourková, M. Evaluation of the Phytotoxicity of Leachate from Municipal Solid Waste Landfill Bukov. Diploma Thesis, Mendel University in Brno, Faculty of Agronomy, Brno, Czech Republic, 2019. Available online: https://theses.cz/id/nwv7×9/ (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Kočí, V.; Mocová, K. Ecotoxicology for Chemists; University of Chemical Technology: Prague, Czech Republic, 2009; ISBN 978-80-7080-699-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jozífková, Z. Use of Phytotoxicity Contact Tests in the Evaluation of Energy By-Product. Ph.D. Thesis, Brno University of Technology, Faculty of Chemistry, Brno, Czech Republic, 2011. Available online: https://dspace.vutbr.cz/xmlui/bitstream/handle/11012/5671/final-thesis.pdf?sequence=6&isAllowed=y (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- MicroBioTests Inc. Phytotoxkit. Seed Germination and Early Growth Microbiotest with Higher Plants; Standard Operation Procedure: Nazareth, Belgium, 2004; Available online: https://www.microbiotests.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Phytotoxicity-test_Phytotoxkit-solid-samples_Standard-Operating-Procedure.pdf (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Turner, A.; Rice, L. Toxicity of tire wear particle leachate to the marine macroalga, Ulva lactuca. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3650–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ČSN EN 13432 Annex E (normative). Determination of Ecotoxic Effects to Higher Plants; Office for Technical Standards, Metrology and State Testing: Prague, Czech Republic, 2001; Classification Mark 77 0153. [Google Scholar]
- Šourková, M.; Adamcová, D.; Zloch, J.; Skutnik, Z.; Vaverková, M.D. Evaluation of the Phytotoxicity of Leachate from a Municipal Solid Waste Landfill: The Case Study of Bukov Landfill. Environments 2020, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, A.; Tarnawski, M. Phytotoxkit/Phytoteskit and Microtox® as tools for toxicity assessment of sediments. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 98, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamcová, D.; Vaverková, M.D.; Hermanová, S.; Voběrková, S. Ecotoxicity of Composts Containing Aliphatic-Aromatic Copolyesters. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar]
- Šourková, M.; Adamcová, D.; Winkler, J.; Vaverková, M.D. Phytotoxicity of Tires Evaluated in Simulated Conditions. Environments 2021, 8, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouda, T.; Formánková, M. Determination of Competitive Phytotoxicity—Growth Inhibition Keying and Independence Index of Lepidium sativum. Ekomonitor 2014. Available online: http://www.ekomonitor.cz/sites/default/files/filepath/prezentace/13_bouda.pdf (accessed on 19 October 2021). (In Czech).
- Inteko Innovative Composting. Inovation of Technology for Standardization of Compost Quality. Project ATCZ42 INTEKO. 2019. Available online: https://www.at-cz.eu/data/projects/f/17/385.pdf (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Kopačka, M. Possibilities, Methods and Technological Procedures in Biomass Composting. Bachelor’s Thesis, South Bohemian University, Faculty of Agriculture, České Budějovice, Czech Republic, 2009. Available online: https://theses.cz/id/5j3qid/downloadPraceContent_adipIdno_8890 (accessed on 14 October 2021). (In Czech).
- SOLVITA Instructions. Narural Soil Respiration. 2019. Available online: https://solvita.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/03/Solvita-Natural-Soil-Respiration-Instructions_SOP-Version-2019.2.1.pdf (accessed on 5 October 2021).
- Leifheit, E.F.; Kissener, H.L.; Faltin, E.; Ryo, M.; Rilling, M.C. Tire abrasion particles negatively affect plant growth even at low concentrations and alter soil biogeochemical cycling. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selonen, S.; Dolar, A.; Kokalj, A.J.; Sackey, L.N.A.; Skalar, T.; Fernandes, V.C.; Rede, D.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Hurley, R.; Nizzetto, L.; et al. Exploring the impacts of microplastics and associated chemicals in the terrestrial environment—Exposure of soil invertebrates to tire particles. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Parihar, P.; Singh, R.; Singh, V.P.; Prasad, S.M. Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants: Role of Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics, and Ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 6, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emamverdian, A.; Ding, Y.; Mokhberdoran, F.; Xie, Y. Heavy metal stress and some mechanisms of plant defense response. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 756120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.K. Heavy metals toxicity in plants: An overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. S. Afr. J. Botany 2010, 76, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharma, P.; Dubey, R.S. Lead toxicity in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Councell, T.B.; Duckenfield, K.U.; Landa, E.R.; Callender, E. Tire-Wear Particles as a Source of Zinc to the Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 4206–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendl, J. You Would Not Believe How Much Emissions from Tire Wear, Asphalt and Brakes We Breathe. 2011. Available online: https://ekolist.cz/cz/publicistika/nazory-a-komentare/jiri-bendl-to-byste-neverili-kolik-emisi-z-oteru-pneumatik-asfaltu-a-brzd-dychame?sel_ids=1&ids%5Bx9b5d99e810946e6f571c50d69d54a181%5D=1 (accessed on 20 October 2021). (In Czech).
- Halsband, C.; Sørensen, L.; Booth, A.M.; Herzke, D. Car Tire Crumb Rubber: Does Leaching Produce a Toxic Chemical Cocktail in Coastal Marine Systems? Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossa, A.-W.; Young, S.D.; Crout, N.M.J. Zinc uptake and phyto-toxicity: Comparing intensity- and capacity-based drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-F.; Gray, C.; Mico, K.; Zhao, F.-J.; McGrath, S.P. Phytotoxicity and bioavailability of cobalt to plants in a range of soils. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Cizdziel, J.V.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Ecotoxicological effects of micronized care tire wear particles and their heavy metals on the earthworn (Eisenia fetidia) in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plíva, P.; Banout, J.; Habart, J.; Jelínek, A.; Kollárová, M.; Roy, A.; Tomanová, D. Establishment, Course and Management of the Composting Process, 1st ed.; Research Institute of Agricultural Technology: Prague, Czech Republic, 2006; Available online: https://docplayer.cz/2333105-Vyzkumny-ustav-zemedelske-techniky-praha-zakladani-prubeh-a-rizeni-kompostovaciho-procesu.html (accessed on 15 October 2021). (In Czech)
- Wik, A.; Dave, G. Acute toxicity of leachates of tire wear material to Daphnia magna—Variability and toxic components. Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1777–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wik, A.; Nilsson, E.; Källqvist, T.; Tobiesen, A.; Dave, G. Toxicity assessment of sequential leachates of tire powder using a battery of toxicity tests and toxicity identification evaluations. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreider, M.L.; Panko, J.M.; McAtee, B.L.; Sweet, L.I.; Finley, B.L. Physical and chemical characterization of tire-related particles: Comparison of particles generated using different methodologies. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Hüffer, T.; Klöckner, P.; Wehrhahn, M.; Hofmann, T.; Reemtsma, T. Tire wear particles in the aquatic environment—A review on generation, analysis, occurrence, fate and effects. Water Res. 2018, 139, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rilling, M.C.; Leifheitová, E.; Lehmann, J. Microplastic effects on carbon cycling processes in soils. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001130. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski, K.; Rutkowska, G.; Szczesny, K. Effect of recycled styrofoam granules on selected physical and mechanical properties of regular concrete. Acta Sci. Pol. Arch. 2015, 14, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, A.; Sobala, D.; Siwowski, T. Tests of the shear strength of geocomposites made from packages of pressed worn tyres and filling material. Acta Sci. Pol. Arch. 2017, 16, 3–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gülser, F.; Erdoğan, E. The effects of heavy metal pollution on enzyme activities and basal soil respiration of roadside soils. Environ. Monit. Assess 2008, 145, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameter | Unit | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Benzo(a)Pyrene | mg·kg−1 | 0.19 |
| Benzo(e)Pyrene | mg·kg−1 | 0.79 |
| Pyrene | mg·kg−1 | 19.00 |
| Naphthalene | mg·kg−1 | 0.39 |
| After 24 h | Abrasion Products in Substrate | Gel Colour | Biological Activity | Estimated Emissions of CO2-C (kg·ha−1) |
| 0% | Colour 5.52 Light yellow | Very high | 96.6 | |
| 5% | Colour 5.8 Light yellow | Very high | 127 | |
| 25% | Colour 6.09 Light yellow | Very high | 170 | |
| 50% | Colour 4.96 Yellow | Medium high | 55.1 | |
| 75% | Colour 4.53 Yellow | Medium high | 35.5 | |
| After 672 h (28 days) | Abrasion Products in Substrate | Gel Colour | Biological Activity | Estimated Emissions of CO2-C (kg·ha−1) |
| 0% | Colour 5.46 Light yellow | Very high | 90.5 | |
| 5% | Colour 5.9 Light yellow | Very high | 148 | |
| 25% | Colour 5.94 Light yellow | Very high | 186 | |
| 50% | Colour a 5.38 Light yellow | Very high | 83.7 | |
| 75% | Colour 4.95 Yellow | Medium high | 59.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Šourková, M.; Adamcová, D.; Vaverková, M.D. The Influence of Microplastics from Ground Tyres on the Acute, Subchronical Toxicity and Microbial Respiration of Soil. Environments 2021, 8, 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110128
Šourková M, Adamcová D, Vaverková MD. The Influence of Microplastics from Ground Tyres on the Acute, Subchronical Toxicity and Microbial Respiration of Soil. Environments. 2021; 8(11):128. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110128
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠourková, Markéta, Dana Adamcová, and Magdalena Daria Vaverková. 2021. "The Influence of Microplastics from Ground Tyres on the Acute, Subchronical Toxicity and Microbial Respiration of Soil" Environments 8, no. 11: 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110128
APA StyleŠourková, M., Adamcová, D., & Vaverková, M. D. (2021). The Influence of Microplastics from Ground Tyres on the Acute, Subchronical Toxicity and Microbial Respiration of Soil. Environments, 8(11), 128. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments8110128







