Transformational Leadership and Turnover Intentions: The Mediating Role of Employee Performance during the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Research Background and Hypothesis Development
2.1. Transformational Leadership
2.2. Transformational Leadership Predicting Employee Performance and Turnover Intention
2.3. Employee Performance Predicting Turnover Intention
2.4. Employee Performance Mediating the Relationship between Transformational Leadership and Turnover Intention
3. Method
3.1. Sample and Procedures
3.2. Measures
3.2.1. Transformational Leadership (Independent Variable)
3.2.2. Employee Performance (Mediator Variable)
3.2.3. Turnover Intentions (Dependent Variable)
3.2.4. Control Variables
3.3. Common Method Bias Assessment
4. Findings
4.1. Normality Test
4.2. Factor Analysis Findings Related to Scales
4.3. Tests of the Hypotheses
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Discussion
5.2. Conclusions
6. Theoretical Contributions
7. Implications for Practice
8. Limitations and Future Research
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, D. G., and R. W. Griffeth. 1999. Job performance and turnover: A review and integrative multi-route model. Human Resource Management Review 9: 525–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D. G., and R. W. Griffeth. 2001. Test of a mediated performance-turnover relationship highlighting the moderating roles of visibility and reward contingency. Journal of Applied Psychology 86: 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakis, J., B. J. Avolio, and N. Sivasubramaniam. 2003. Context and leadership: An examination of the nine-factor full-range leadership theory using the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire. The Leadership Quarterly 14: 261–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonakis, J., D. V. Day, and B. Schyns. 2012. Leadership and individual differences: At the cusp of a renaissance. The Leadership Quarterly 23: 643–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ariyabuddhiphongs, V., and S. I. Kahn. 2017. Transformational leadership and turnover intention: The mediating effects of trust and job performance on café employees in Thailand. Journal of Human Resources in Hospitality & Tourism 16: 215–33. [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong, M., and S. Taylor. 2014. Armstrong’s Handbook of Human Resource Management Practice, 13th ed. London: Kogan Page. [Google Scholar]
- Aryee, S., and C. W. Chu. 2012. Antecedents and outcomes of challenging job experiences: A social cognitive perspective. Human Performance 25: 215–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryee, S., F. O. Walumbwa, Q. Zhou, and C. A. Hartnell. 2012. Transformational leadership, innovative behavior, and task performance: Test of mediation and moderation processes. Human Performance 25: 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbari, M., A. Purwanto, and P. B. Santoso. 2020. Pengaruh Iklim Organisasi dan Kepemimpinan Transformasional Terhadap Produktivitas Kerja Inovatif Pada Industri Manufaktur di Pati Jawa Tengah. Jurnal Produktivitas: Jurnal Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Muhammadiyah Pontianak 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin-Plunk, C. A., and G. S. Armstrong. 2013. Transformational leadership skills and correlates of prison warden job stress. Criminal Justice and Behavior 40: 551–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avolio, B. J. 1999. Full Leadership Development: Building the Vital Forces in Organizations. Thousand Oaks: Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Avolio, B. J., and B. M. Bass. 1995. Individual consideration viewed at multiple levels of analysis: A multi-level framework for examining the diffusion of transformational leadership. The Leadership Quarterly 6: 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avolio, B. J., W. L. Gardner, F. O. Walumbwa, F. Luthans, and D. R. May. 2004. Unlocking the mask: A look at the process by which authentic leaders impact follower attitudes and behaviors. The Leadership Quarterly 15: 801–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Avolio, B. J., F. O. Walumbwa, and T. J. Weber. 2009. Leadership: Current theories, research, and future directions. Annual Review of Psychology 60: 421–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babin, B. J., and J. S. Boles. 1998. Employee behavior in a service environment: A model and test of potential differences between men and women. Journal of Marketing 62: 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, B. M. 1985. Leadership and Performance beyond Expectations. New York: Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, B. M. 1990. Bass and Stogdili s handbook of leadership. New York: Free Press. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, B. M. 1998. Transformational Leadership: Industrial, Military, and Educational Impact. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, B. M., and B. J. Avolio. 1994. Introduction. In Improving Organizational Effectiveness through Transformational Leadership. Edited by B. M. Bass and B. J. Avolio. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, B. M., and B. J. Avolio. 1997. Full Range Leadership Development: Manual for the Multifactor Leadership Questionnaire. Palo Alto: Mind Garden. [Google Scholar]
- Bass, B. M., and R. E. Riggio. 2006. Transformational Leadership, 2nd ed. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardin, H. J., and J. E. Russell. 2006. Human Resource Management. New York: Tata McGraw-Hill, p. 736. [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum, D., and M. J. Somers. 1993. Fitting job performance into turnover model: An examination of the form of the job performance-turnover relationship and a path model. Journal of Management 19: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, M., and C. Boon. 2013. Performance and turnover intentions: A social exchange perspective. Journal of Managerial Psychology 28: 511–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, J. E., and T. A. Judge. 2003. Self-concordance at work: Toward understanding the motivational effects of transformational leaders. Academy of Management Journal 46: 554–71. [Google Scholar]
- Bothma, C. F., and G. Roodt. 2013. The validation of the turnover intention scale. SA Journal of Human Resource Management 11: 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brislin, R. W. 1980. Translation and content analysis of oral and written material. In Handbook of Cross-Cultural Research. Edited by H. C. Triandis and J. W. Berry. Boston: Allyn & Bacon, vol. 1, pp. 389–444. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J. M. 1978. Leadership. New York: Harper & Row. [Google Scholar]
- Bycio, P., R. D. Hackett, and K. M. Alvares. 1990. Job performance and turnover: A review and meta-analysis. Applied Psychology 39: 47–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W. J. A., Y. S. Wang, and T. C. Huang. 2013. Work design–related antecedents of turnover intention: A multilevel approach. Human Resource Management 52: 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, S. C. S., and S. G. Liang. 2013. When do subordinates’ emotion-regulation strategies matter? Abusive supervision, subordinates’ emotional exhaustion, and work withdrawal. The Leadership Quarterly 24: 125–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J. M., and C. E. Lance. 2010. What reviewers should expect from authors regarding common method bias in organizational research. Journal of Business and Psychology 25: 325–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crampton, S. M., and J. A. Wagner II. 1994. Percept-percept inflation in microorganizational research: An investigation of prevalence and effect. Journal of Applied Psychology 79: 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y. D., Y. Y. Dai, K. Y. Chen, and H. C. Wu. 2013. Transformational vs transactional leadership: Which is better? A study on employees of international tourist hotels in Taipei City. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 25: 760–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, D. R., W. D. Todor, and D. M. Krackhardt. 1982. Turnover overstated: The functional taxonomy. Academy of Management Review 7: 117–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Hartog, D. N., J. J. Van Muijen, and P. L. Koopman. 1997. Transactional versus transformational leadership: An analysis of the MLQ. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology 70: 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, S. D., A. Gupta, K. L. Sotak, K. A. Shirreffs, A. Serban, C. Hao, D. H. Kim, and F. J. Yammarino. 2014. A 25-year perspective on levels of analysis in leadership research. The Leadership Quarterly 25: 6–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupré, K. E., and A. L. Day. 2007. The effects of supportive management and job quality on the turnover intentions and health of military personnel. Human Resource Management: Published in Cooperation with the School of Business Administration, The University of Michigan and in Alliance with the Society of Human Resources Management 46: 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvir, T., D. Eden, B. J. Avolio, and B. Shamir. 2002. Impact of transformational leadership on follower development and performance: A field experiment. Academy of Management Journal 45: 735–44. [Google Scholar]
- Efron, B. 1982. The Jackknife, the Bootstrap and Other Resampling Plans. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics. Monograph 38. Philadelphia: SIAM. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, P. P., A. S. Tsui, J. Liu, and L. Li. 2010. Pursuit of whose happiness? Executive leaders’ transformational behaviors and personal values. Administrative Science Quarterly 55: 222–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, J. B., C. E. Patterson, K. Hester, and D. Y. Stringer. 1996. A quantitative review of research on charismatic leadership. Psychological Reports 78: 271–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giese, W. J., and H. W. Ruter. 1949. An objective analysis of morale. Journal of Applied Psychology 33: 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, A., S. Fitzgerald, S. Bhutani, H. Mand, and S. Sharma. 2010. The relationship between transformational leadership and employee desire for empowerment. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management 22: 263–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, A. E., E. A. Miller, and G. A. Aarons. 2013. Transformational leadership moderates the relationship between emotional exhaustion and turnover intention among community mental health providers. Community Mental Health Journal 49: 373–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gyensare, M. A. 2013. Employee Turnover Intention: Empirical Examination of Antecedent and Outcome Variables. Master’s thesis, Department of Organization and Human Resource Management, University of Ghana, Legon, Ghana. [Google Scholar]
- Gyensare, M. A., O. Anku-Tsede, M. A. Sanda, and C. A. Okpoti. 2016. Transformational leadership and employee turnover intention. World Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Sustainable Development 12: 243–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamstra, M. R., N. W. Van Yperen, B. Wisse, and K. Sassenberg. 2011. Transformational-transactional leadership styles and followers’ regulatory focus. Journal of Personnel Psychology. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harman, H. H. 1976. Modern Factor Analysis. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, A. F. 2017. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis: A Regression-Based Approach. New York: Guilford Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Hinkin, T. R., and J. B. Tracey. 1994. Transformational leadership in the hospitality industry. Hospitality Research Journal 18: 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hochwarter, W. A., G. R. Ferris, A. L. Canty, D. D. Frink, P. L. Perrewea, and H. M. Berkson. 2001. Reconsidering the Job-Performance—Turnover Relationship: The Role of Gender in Form and Magnitude 1. Journal of Applied Social Psychology 31: 2357–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, G. 1980. Culture’s Consequences. Beverly Hills: Sage Publication. [Google Scholar]
- Iverson, R. D., and S. J. Deery. 2000. Job performance and voluntary turnover: An examination of linearity, curvilinearity, and the moderators of time, unemployment rate, and perceived ease of movement using event history analysis. In Academy of Management Proceedings. Briarcliff Manor: Academy of Management, August, vol. 2000, pp. A1–A6. [Google Scholar]
- Jackofsky, E. F. 1984. Turnover and job performance: An integrated process model. Academy of Management Review 9: 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackofsky, E. F., K. R. Ferris, and B. G. Breckenridge. 1986. Evidence for a curvilinear relationship between job performance and turnover. Journal of Management 12: 105–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, T. A., and J. E. Bono. 2000. Five-factor model of personality and transformational leadership. Journal of Applied Psychology 85: 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Judge, T. A., and R. F. Piccolo. 2004. Transformational and transactional leadership: A meta-analytic test of their relative validity. Journal of Applied Psychology 89: 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Judge, T. A., E. Fluegge Woolf, C. Hurst, and B. Livingston. 2006. Charismatic and transformational leadership: A review and an agenda for future research. Zeitschrift für Arbeits-und Organisationspsychologie A&O 50: 203–14. [Google Scholar]
- Kanter, R. M. 1984. Change Masters. Newyork: Simon and Schuster. [Google Scholar]
- Kara, D., M. Uysal, M. J. Sirgy, and G. Lee. 2013. The effects of leadership style on employee well-being in hospitality. International Journal of Hospitality Management 34: 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kark, R., and B. Shamir. 2002. The influence of transformational leadership on followers’ relational versus collective self-concept. In Academy of Management Proceedings. Briarcliff Manor: Academy of Management, August, vol. 2002, pp. D1–D6. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, R. T. 1984. The role of performance and absenteeism in the prediction of turnover. The Academy of Management Journal 27: 176–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerse, G., and A. Naktiyok. 2020. The effect of interactional justice on work engagement through conscientiousness for work. Journal of Economy Culture and Society 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H., and M. Stoner. 2008. Burnout and turnover intention among social workers: Effects of role stress, job autonomy and social support. Administration in Social Work 32: 5–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovjanic, S., S. C. Schuh, and K. Jonas. 2013. Transformational leadership and performance: An experimental investigation of the mediating effects of basic needs satisfaction and work engagement. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology 86: 543–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, H., M. E. Palanski, and T. Simons. 2012. Authentic leadership and behavioral integrity as drivers of follower commitment and performance. Journal of Business Ethics 107: 255–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Little, R. J. 1988. A test of missing completely at random for multivariate data with missing values. Journal of the American Statistical Association 83: 1198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, K. B., K. G. Kroeck, and N. Sivasubramaniam. 1996. Effectiveness correlates of transformational and transactional leadership: A meta-analytic review of the MLQ literature. The Leadership Quarterly 7: 385–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, K. Y., L. C. Chang, and H. L. Wu. 2007. Relationships between professional commitment, job satisfaction, and work stress in public health nurses in Taiwan. Journal of Professional Nursing 23: 110–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKenzie, S. B., P. M. Podsakoff, and G. A. Rich. 2001. Transformational and transactional leadership and salesperson performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 29: 115–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, J. G., and H. A. Simon. 1958. Organizations. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc. [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu, J. E., and J. E. Baratta. 1989. Turnover type as a moderator of the performance-turnover relationship. Human Performance 2: 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, R. L., J. H. Jackson, and S. R. Valentine. 2015. Human Resource Management: Essential Perspectives. Boston: Cengage Learning. [Google Scholar]
- McEvoy, G. M., and W. F. Cascio. 1987. Do good or poor performers leave? A meta-analysis of the relationship between performance and turnover. Academy of Management Journal 30: 744–62. [Google Scholar]
- McShane, S. L., M. A. Y. Von Glinow, and R. Jing. 2000. Organizational Behavior. No. 658/M113. Boston: Irwin/McGraw-Hill. [Google Scholar]
- Mesu, J., K. Sanders, and M. van Riemsdijk. 2015. Transformational leadership and organizational commitment in manufacturing and service small to medium-sized enterprises. Personnel Review 44: 970–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, J. P., D. J. Stanley, L. Herscovitch, and L. Topolnytsky. 2002. Affective, continuance, and normative commitment to the organization: A meta-analysis of antecedents, correlates, and consequences. Journal of Vocational Behavior 61: 20–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, D. P., and N. Landuyt. 2008. Explaining turnover intention in state government: Examining the roles of gender, life cycle, and loyalty. Review of Public Personnel Administration 28: 120–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, F., and K. Nielsen. 2009. Does self-efficacy mediate the relationship between transformational leadership behaviours and healthcare workers’ sleep quality? A longitudinal study. Journal of Advanced Nursing 65: 1833–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsakoff, P. M., S. B. MacKenzie, J.-Y. Lee, and N. P. Podsakoff. 2003. Common method biases in behavioral research: A critical review of the literature and recommended remedies. Journal of Applied Psychology 88: 879–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preacher, K. J., D. D. Rucker, and A. F. Hayes. 2007. Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, methods, and prescriptions. Multivariate Behavioral Research 42: 185–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwanto, A., L. M. Wijayanti, C. C. Hyun, and M. Asbari. 2019. The Effect of Tansformational, Transactional, Authentic and Authoritarian Leadership Style toward Lecture Performance of Private University in Tangerang. Dinasti International Journal of Digital Business Management 1: 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quińones, M. A., J. K. Ford, and M. S. Teachout. 1995. The relationship between work experience and job performance: A conceptual and meta-analytic review. Personnel Psychology 48: 887–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafferty, A. E., and M. A. Griffin. 2004. Dimensions of transformational leadership: Conceptual and empirical extensions. The Leadership Quarterly 15: 329–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rego, A., and M. P. e Cunha. 2008. Authentizotic climates and employee happiness: Pathways to individual performance? Journal of Business Research 61: 739–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N., D. Gomes, and S. Kurian. 2018a. Authentic leadership and performance: The mediating role of employees’ affective commitment. Social Responsibility Journal 14: 213–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, N., İ. Yücel, and D. Gomes. 2018b. How transformational leadership predicts employees’ affective commitment and performance. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management 67: 1901–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riketta, M. 2008. The causal relation between job attitudes and performance: A meta-analysis of panel studies. Journal of Applied Psychology 93: 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, S. P. 2003. Organization Behavior. Saddle River: Prentice-Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Rowold, J., and K. Heinitz. 2007. Transformational and charismatic leadership: Assessing the convergent, divergent and criterion validity of the MLQ and the CKS. The Leadership Quarterly 18: 121–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamin, A., and P. W. Hom. 2005. In search of the elusive U-shaped performance-turnover relationship: Are high performing Swiss bankers more liable to quit? Journal of Applied Psychology 90: 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanda, A., and J. Kuada. 2013. Identification of effective leadership indicators in Ghanaian retail banks using AMOS based confirmatory factor analysis. In Recent Advances in Business Administration, Marketing and Economics. Venice: BAME. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, D. P. 1991. Contextual variables in employee performance-turnover relationships. Academy of Management Journal 34: 966–75. [Google Scholar]
- Shannahan, K. L., A. J. Bush, and R. J. Shannahan. 2013. Are your salespeople coachable? How salesperson coachability, trait competitiveness, and transformational leadership enhance sales performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 41: 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staw, B. M. 1980. The consequences of turnover. Journal of Occupational Behaviour 1: 253–73. [Google Scholar]
- Steel, R. P., and N. K. Ovalle. 1984. A review and meta-analysis of research on the relationship between behavioral intentions and employee turnover. Journal of Applied Psychology 69: 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturman, M. C., and C. O. Trevor. 2001. The implications of linking the dynamic performance and turnover literatures. Journal of Applied Psychology 86: 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sturman, M. C., L. Shao, and J. H. Katz. 2012. The effect of culture on the curvilinear relationship between performance and turnover. Journal of Applied Psychology 97: 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T.C. Sağlık Bakanlığı. 2020a. COVID-19—Yeni Koronavirüs Hastalığı Güncel Durum. Available online: https://covid19bilgi.saglik.gov.tr/tr/ (accessed on 4 February 2021).
- T.C. Sağlık Bakanlığı. 2020b. Türkiye’deki Güncel Durum. Available online: https://covid19.saglik.gov.tr/ (accessed on 12 April 2021).
- Tabachnick, B. G., and L. S. Fidell. 2013. Using Multivariate Statistics, 6th ed. Boston: Pearson. [Google Scholar]
- Top, M., M. Tarcan, S. Tekingündüz, and N. Hikmet. 2013. An analysis of relationships among transformational leadership, job satisfaction, organizational commitment and organizational trust in two Turkish hospitals. The International Journal of Health Planning and Management 28: e217–e241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tracey, J. B., and T. R. Hinkin. 1996. How transformational leaders lead in the hospitality industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management 15: 165–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walumbwa, F. O., and C. A. Hartnell. 2011. Understanding transformational leadership-employee performance links: The role of relational identification and self-efficacy. Journal of Occupational and Organizational Psychology 84: 153–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walumbwa, F. O., B. J. Avolio, and W. Zhu. 2008. How transformational leadership weaves its influence on individual job performance: The role of identification and efficacy beliefs. Personnel Psychology 61: 793–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G., I. S. Oh, S. H. Courtright, and A. E. Colbert. 2011. Transformational leadership and performance across criteria and levels: A meta-analytic review of 25 years of research. Group & Organization Management 36: 223–70. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organisation. 2020. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Outbrake 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novelcoronavirus-2019 (accessed on 18 April 2021).
- Williams, C. R., and L. P. Livingstone. 1994. Another look at the relationship between performance and voluntary turnover. Academy of Management Journal 37: 269–98. [Google Scholar]
- Yücel, İ. 2011. Entrepreneurial orientation, executives’ individualism and firm performance: The moderating role of executives individualism. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Management Science and Engineering Management. Macau: World Academic Union-World Academic Press, pp. 260–64. [Google Scholar]
- Yucel, İ., A. McMillan, and O. C. Richard. 2014. Does CEO transformational leadership influence top executive normative commitment? Journal of Business Research 67: 1170–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel, İ, N. Ribeiro, and D. R. Gomes. 2020. Perceived organizational support and employees’ performance: The mediating role of affective commitment. International Journal of Management and Enterprise Development 19: 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukl, G. 1989. Managerial leadership: A review of theory and research. Journal of Management 15: 251–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukl, G. 1999. An evaluation of conceptual weaknesses in transformational and charismatic leadership theories. The Leadership Quarterly 10: 285–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukl, G. 2006. Leadership in Organizations, 6th ed. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Zaccaro, S. J. 2012. Individual differences and leadership: Contributions to a third tipping point. The Leadership Quarterly 23: 718–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X., J. G. Lynch Jr., and Q. Chen. 2010. Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: Myths and truths about mediation analysis. Journal of Consumer Research 37: 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, R. D., and T. C. Darnold. 2009. The impact of job performance on employee turnover intentions and the voluntary turnover process: A meta-analysis and path model. Personnel Review 38: 142–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Indexes | Reference Value | Transformational Leadership | Employee Performance | Turnover Intention | Research Model | Model without Mediating Variable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMIN/DF | 0 < χ2/sd ≤ 5 | 1.668 | 1.858 | 1.756 | 1.487 | 1.582 |
| RMR | ≤0.10 | 0.005 | 0.034 | 0.014 | 0.029 | 0.018 |
| CFI | ≥0.90 | 0.935 | 0.928 | 0.962 | 0.938 | 0.946 |
| IFI | ≥0.90 | 0.935 | 0.928 | 0.962 | 0.938 | 0.947 |
| NFI | ≥0.90 | 0.948 | 0.925 | 0.964 | 0.941 | 0.957 |
| TLI | ≥0.90 | 0.927 | 0.916 | 0.953 | 0.932 | 0.942 |
| RMSEA | <0.05–0.08≤ | 0.057 | 0.068 | 0.064 | 0.052 | 0.056 |
| Variables | Mean | SS | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—Gender | 1.298 | 0.468 | 1 | |||||
| 2—Age | 2.569 | 1.278 | 0.224 ** | 1 | ||||
| 3—Marital Status | 1.484 | 0.578 | 0.244 ** | −0.547 ** | 1 | |||
| 4—Tenure | 2.876 | 0.896 | 0.048 | 0.365 ** | −0.251 ** | 1 | ||
| 5—Transformational Leadership | 3.876 | 0.985 | −0.03 | −0.142 ** | 0.135 ** | −0.103 * | 1 | |
| 6—Employee Performance | 3.389 | 0.845 | 0.075 | 0.168 ** | −0.084 | 0.098 | 0.492 ** | 1 |
| 7—Turnover Intention | 3.278 | 0.678 | 0.098* | 0.171 ** | −0.096 | 0.167 ** | −0.568 ** | −0.457 ** |
| Standardized | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
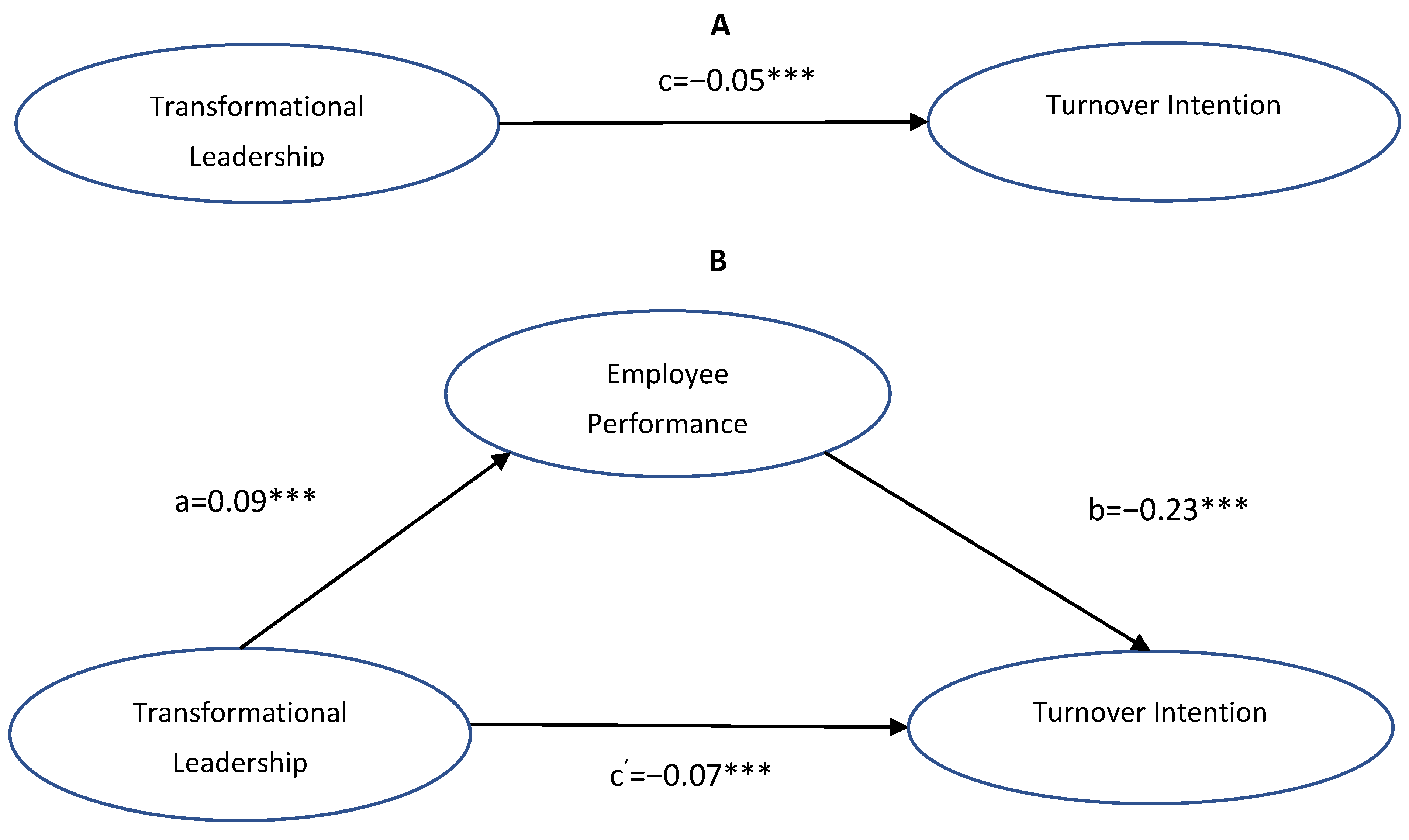
| Path/Effect | β | SE | p | |||||
| c Total effect of Transformational Leadership on Turnover Intention | −0.05 | 0.01 | <0.001 | |||||
a Transformational Leadership  Employee Performance Employee Performance | 0.09 | 0.05 | <0.001 | |||||
b Employee Performance  Turnover Intention Turnover Intention | −0.23 | 0.08 | <0.001 | |||||
c’Transformational Leadership  Turnover Intention Turnover Intention | −0.07 | 0.01 | <0.001 | |||||
| Indirect Effect | ||||||||
TL  EP EP  TI TI | −0.02 | 0.03 | <0.001 | |||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yücel, İ. Transformational Leadership and Turnover Intentions: The Mediating Role of Employee Performance during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Adm. Sci. 2021, 11, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci11030081
Yücel İ. Transformational Leadership and Turnover Intentions: The Mediating Role of Employee Performance during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Administrative Sciences. 2021; 11(3):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci11030081
Chicago/Turabian StyleYücel, İlhami. 2021. "Transformational Leadership and Turnover Intentions: The Mediating Role of Employee Performance during the COVID-19 Pandemic" Administrative Sciences 11, no. 3: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci11030081
APA StyleYücel, İ. (2021). Transformational Leadership and Turnover Intentions: The Mediating Role of Employee Performance during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Administrative Sciences, 11(3), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci11030081





