An Analysis of Critical Factors Affecting the Success of Open Innovation Strategies in High-Tech Firms: The Case of South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Open Innovation Strategy
2.2. Critical Factors Affecting Open Innovation Strategy
3. Methods
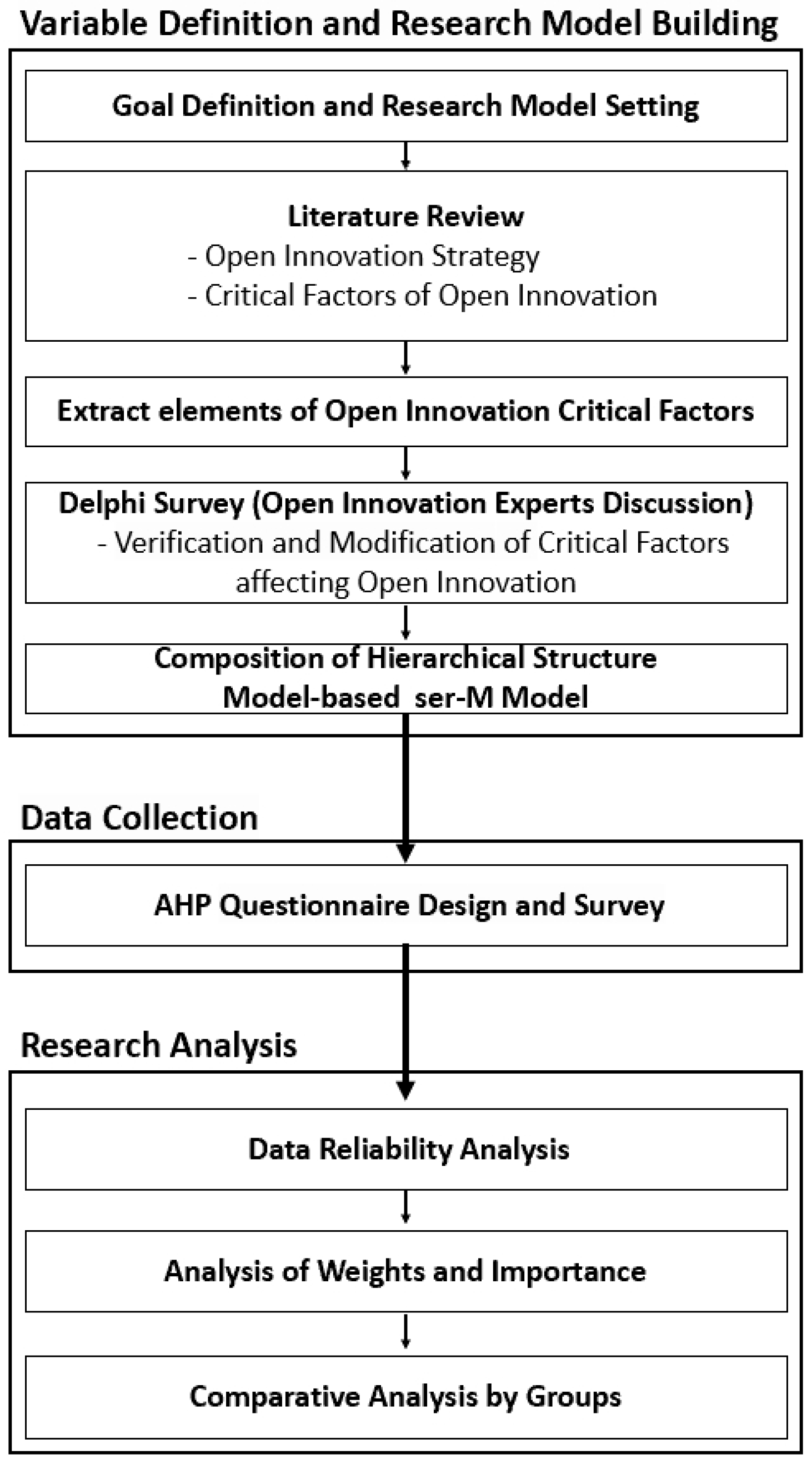
3.1. Research Design
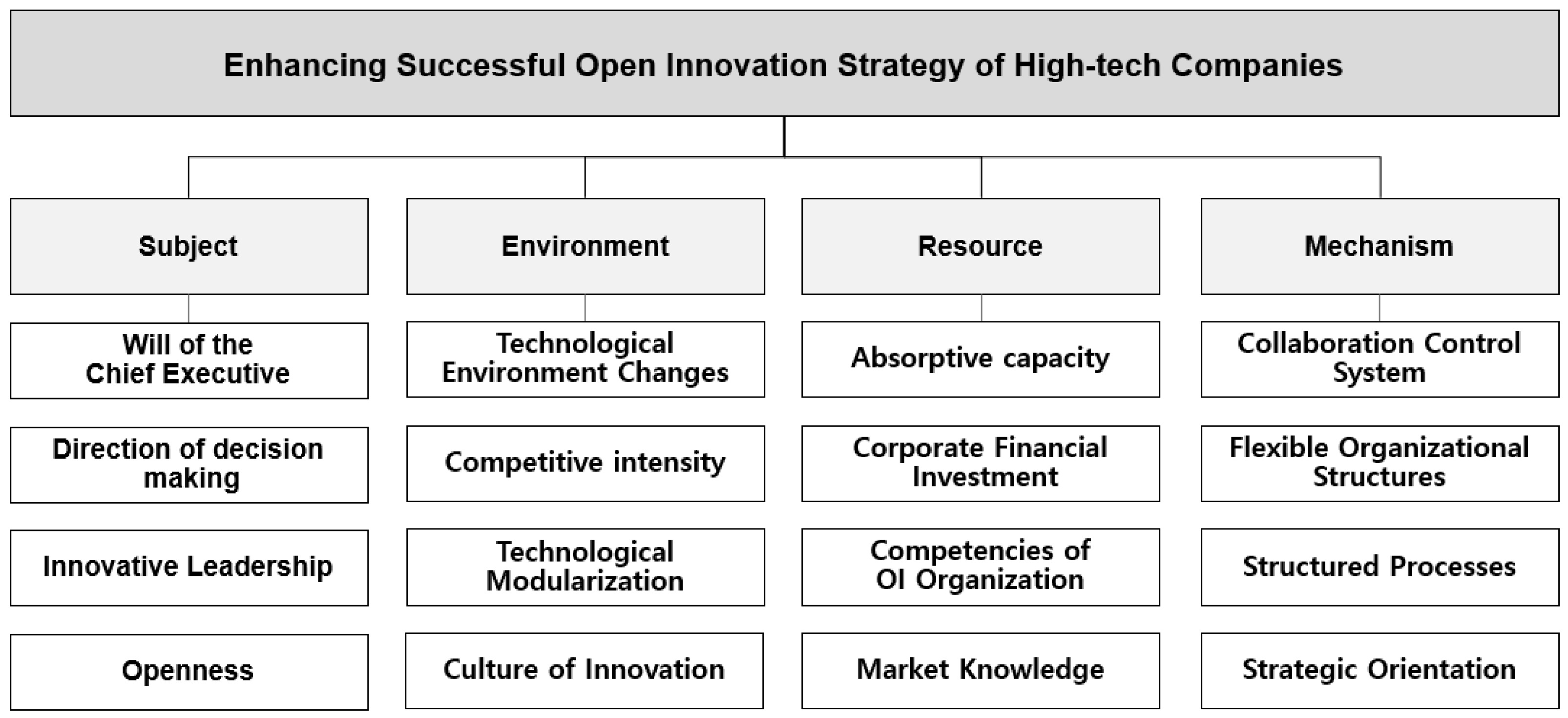
3.2. Research Model
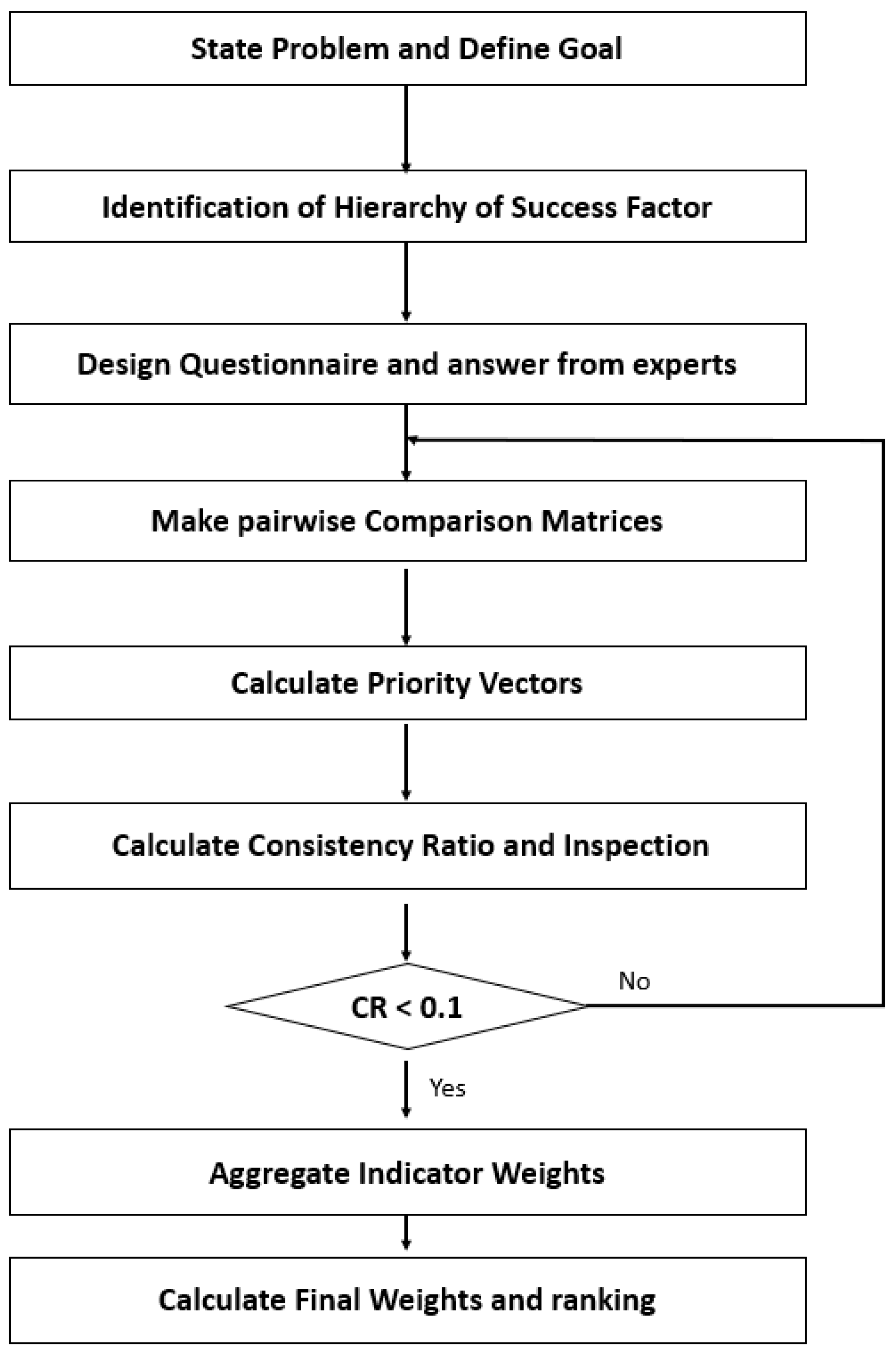
3.3. AHP Analysis
3.4. Data Collection and Process
4. Results
4.1. Comparison of Evaluation Variables
4.2. Comparison of Evaluation Areas Between Business Group and Professional Group
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
6.1. Implications
6.2. Research Limitations and Future Plans
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Sample of the Questionnaire

References
- Abastante, Francesca, Salvatore Corrente, Salvatore Greco, Alessio Ishizaka, and Isabella M. Lami. 2019. A new parsimonious AHP methodology: Assigning priorities to many objects by comparing pairwise few reference objects. Expert Systems with Applications 127: 109–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Joon Mo, Tim Minshall, and Letizia Mortara. 2017. Understanding the human side of openness: The fit between open innovation modes and CEO characteristics. R&D Management 47: 727–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, Joon Mo, Tim Minshall, and Letizia Mortara. 2018. How do entrepreneurial leaders promote open innovation adoption in small firms? In Researching Open Innovation in SMEs. Singapore: World Scientific, pp. 137–77. [Google Scholar]
- Arora, Ashish. 2004. Markets for Technology: The Economics of Innovation and Corporate Strategy. Cambridge: MIT Press. [Google Scholar]
- Asad, Muzaffar, Muhammad Uzair Asif, Mohammed Ali Bait Ali Sulaiman, Mir Shahid Satar, and Ghadah Alarifi. 2023. Open innovation: The missing nexus between entrepreneurial orientation, total quality management, and performance of SMEs. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship 12: 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audretsch, B. David, and Maksim Belitski. 2023. The limits to open innovation and its impact on innovation performance. Technovation 119: 102519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bejarano, José Bestier Padilla, Jhon Wilder Zartha Sossa, Carlos Ocampo-López, and Margarita Ramírez-Carmona. 2023. Open innovation: A technology transfer alternative from universities. A systematic literature review. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 9: 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertello, Alberto, Paola De Bernardi, and Francesca Ricciardi. 2024. Open innovation: Status quo and quo vadis-an analysis of a research field. Review of Managerial Science 18: 633–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, Marcel, Ann-Kristin Zobel, Allan Afuah, Esteve Almirall, Sabine Brunswicker, Linus Dahlander, Lars Frederiksen, Annabelle Gawer, Marc Gruber, and Stefan Haefliger. 2017. The open innovation research landscape: Established perspectives and emerging themes across different levels of analysis. Industry and Innovation 24: 8–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogers, Marcel, Henry Chesbrough, Sohvi Heaton, and David J. Teece. 2019. Strategic management of open innovation: A dynamic capabilities perspective. California Management Review 62: 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, Francesco, Jesús Contreras, and Josefa Hernandez. 2010. Enterprise 2.0 and semantic technologies: A technological framework for open innovation support. Paper presented at the 11th European Conference on Knowledge Management, Vila Nova de Famalicao, Portugal, September 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, Francesco, Jesús Contreras, Josefa Z. Hernández, and Jose Manuel Gomez-Perez. 2012. Open Innovation in an Enterprise 3.0 framework: Three case studies. Expert Systems with Applications 39: 8929–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesbrough, Henry. 2003. Open Innovation: The New Imperative for Creating and Profiting from Technology. Boston: Harvard Business School Publishing Company. [Google Scholar]
- Chesbrough, Henry. 2006a. Open innovation: Researching a new paradigm. Oxford University Press Google Schola 2: 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Chesbrough, Henry. 2006b. Open Business Models: How to Thrive in the New Innovation Landscape. Boston: Harvard Business Press. [Google Scholar]
- Chesbrough, Henry. 2007. Why Companies Should Have Open Business Models. MIT Sloan Management Review. Available online: https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/why-companies-should-have-open-business-models/ (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Chesbrough, Henry, and Adrienne Kardon Crowther. 2006. Beyond high tech: Early adopters of open innovation in other industries. R&D Management 36: 229–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chesbrough, Henry, and Marcel Bogers. 2014. Explicating open innovation: Clarifying an emerging paradigm for understanding innovation. In New Frontiers in Open Innovation. Oxford: Oxford University Press, pp. 3–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, DongSung. 2014. Mechanism-Based View: A New Strategy Paradigm for Holistics Management. Seoul: Seoul Econoic Management Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, Clayton M. 1997. Marketing strategy: Learning by doing. Harvard Business Review 75: 141–51. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, Wesley M., and Daniel A. Levinthal. 1990. Absorptive capacity: A new perspective on learning and innovation. Administrative Science Quarterly 35: 128–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, Massimo G., Terttu Luukkonen, Philippe Mustar, and Mike Wright. 2010. Venture capital and high-tech start-ups. Venture Capital 12: 261–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cricelli, Livio, Roberto Mauriello, and Serena Strazzullo. 2023. Preventing open innovation failures: A managerial framework. Technovation 127: 102833. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlander, Linus, and David M. Gann. 2010. How open is innovation? Research Policy 39: 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Faria, Pedro, Florian Noseleit, and Bart Los. 2020. The influence of internal barriers on open innovation. Industry and Innovation 27: 205–09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilrukshi, M. G. M., C. N. Wickramasinghe, and S. D. Edirisinghe. 2022. Impact of open innovation on firm performance: A literature review. South Asian Journal of Business Insights 2: 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgson, Mark, David Gann, and Ammon Salter. 2006. The role of technology in the shift towards open innovation: The case of Procter & Gamble. R&D Management 36: 333–46. [Google Scholar]
- Drechsler, Wenzel, and Martin Natter. 2012. Understanding a firm’s openness decisions in innovation. Journal of Business Research 65: 438–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dries, Liesbeth, Stefano Pascucci, Áron Török, and Jozsef Toth. 2013. Open innovation: A case-study of the Hungarian wine sector. EuroChoices 12: 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkel, Ellen, John Bell, and Hannah Hogenkamp. 2011. Open innovation maturity framework. International Journal of Innovation Management 15: 1161–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enkel, Ellen, Oliver Gassmann, and Henry Chesbrough. 2009. Open R&D and open innovation: Exploring the phenomenon. R&D Management 39: 311–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ettlinger, Nancy. 2017. Open innovation and its discontents. Geoforum 80: 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felin, Teppo, and Todd R. Zenger. 2014. Closed or open innovation? Problem solving and the governance choice. Research Policy 43: 914–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaspary, Eliana, Gilnei Luiz De Moura, and Douglas Wegner. 2020. How does the organisational structure influence a work environment for innovation? International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation Management 24: 132–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, Oliver, Ellen Enkel, and Henry Chesbrough. 2010. The future of open innovation. R&D Management 40: 213–21. [Google Scholar]
- Getz, Kenneth A., and Kenneth I. Kaitin. 2012. Open innovation: The new face of pharmaceutical research and development. Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology 5: 481–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grama-Vigouroux, Simona, Sana Saidi, Anne Berthinier-Poncet, Wim Vanhaverbeke, and Allane Madanamoothoo. 2020. From closed to open: A comparative stakeholder approach for developing open innovation activities in SMEs. Journal of Business Research 119: 230–44. [Google Scholar]
- Haefliger, Stefan. 2019. Orientations of open strategy: From resistance to transformation. In Handbook of Open Strategy. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 151–66. [Google Scholar]
- Harker, Patrick T., and Luis G. Vagras. 1990. Reply to “Remarks on the analytic hierarchy process” by J.S. Dyer. Management Science 36: 269–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasnas, Irina, Luca Lambertini, and Arsen Palestini. 2014. Open Innovation in a dynamic Cournot duopoly. Economic Modelling 36: 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Yuetong, and Xiaohui Liu. 2011. The influence of openness to innovation performance. Paper presented at the 2011 International Conference on Information Management, Innovation Management and Industrial Engineering, Shenzhen, China, November 26–27. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, He, Geoffrey Parker, Yinliang Ricky Tan, and Hongyan Xu. 2020. Altruism or Shrewd Business? Implications of Technology Openness on Innovations and Competition. MIS Quarterly 44: 1049–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, Kuang-Peng, and Christine Chou. 2013. The impact of open innovation on firm performance: The moderating effects of internal R&D and environmental turbulence. Technovation 33: 368–80. [Google Scholar]
- Huston, Larry, and Nabil Sakkab. 2006. Connect and develop. Harvard Business Review 84: 58–66. [Google Scholar]
- INSEAD and Ipsos. 2023. Surviving the Strom: How Corporate-Startup Collaborations Is the Key to Thriving Amid Economic Turbulence. Open Innovation Report 2023. Sydney: INSEAD and Ipsos. [Google Scholar]
- Jespersen, Kristina Risom. 2010. User-involvement and open innovation: The case of decision-maker openness. International Journal of Innovation Management 14: 471–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keupp, Marcus Matthias, and Oliver Gassmann. 2009. The past and the future of international entrepreneurship: A review and suggestions for developing the field. Journal of Management 35: 600–33. [Google Scholar]
- Kuschel, Jonas, Björn Remneland, and Magnus Holmqvist Kuschel. 2011. Open innovation and control: A case from Volvo. International Journal of Networking and Virtual Organisations 9: 123–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamberti, Emilia, Francesca Michelino, Antonello Cammarano, and Mauro Caputo. 2017. Open innovation scorecard: A managerial tool. Business Process Management Journal 23: 1216–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, Keld, and Ammon Salter. 2006. Open for innovation: The role of openness in explaining innovation performance among UK manufacturing firms. Strategic Management Journal 27: 131–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarenko, Yuliia. 2019. Open innovation practice: Exploring opportunities and potential risks. Baltic Journal of Economic Studies 5: 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, Gonzalo, Alberto Tejero, José N. Franco-Riquelme, John J. Kline, and Raquel E. Campos-Macha. 2019. Proximity metrics for selecting R&D partners in international open innovation processes. IEEE Access 7: 79737–57. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenthaler, Ulrich. 2009. Outbound open innovation and its effect on firm performance: Examining environmental influences. R&D Management 39: 317–30. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenthaler, Ulrich, and Eckhard Lichtenthaler. 2009. A capability-based framework for open innovation: Complementing absorptive capacity. Journal of Management Studies 46: 1315–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Zheng, Yongjiang Shi, and Bo Yang. 2022. Open innovation in times of crisis: An overview of the healthcare sector in response to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market and Complexity 8: 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Chen, Zhiying Liu, Yi Xu, Suqin Liao, and Lihua Fu. 2022. How TMT diversity influences open innovation: An empirical study on biopharmaceutical firms in China. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management 34: 151–65. [Google Scholar]
- Marullo, Cristina, Elena Casprini, Alberto Di Minin, and Andrea Piccaluga. 2018. Ready for take-off’: How open Innovation influences startup success. Creativity and Innovation Management 27: 476–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matt, Christian, Thomas Hess, and Alexander Benlian. 2015. Digital transformation strategies. Business & Information Systems Engineering 57: 339–43. [Google Scholar]
- Michelino, Francesca, Antonello Cammarano, Emilia Lamberti, and Mauro Caputo. 2017. Open innovation for start-ups: A patent-based analysis of bio-pharmaceutical firms at the knowledge domain level. European Journal of Innovation Management 20: 112–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, Saima, Asif Mahmood, and Hassan Waqar. 2022. The interplay of open innovation and strategic innovation: Unpacking the role of organizational learning ability and absorptive capacity. International Journal of Engineering Business Management 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyao, Manabu, Hiroyuki Ozaki, Stefano Tobia, Antonio Messeni Petruzzelli, and Federico Frattini. 2022. The role of open innovation hubs and perceived collective efficacy on individual behaviour in open innovation projects. Creativity and Innovation Management 31: 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortara, Letizia, and Tim Minshall. 2011. How do large multinational companies implement open innovation? Technovation 31: 586–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier, Nolberto, and Eloy Hontoria. 2021. Uses and Limitations of the AHP Method. Cham: Springer International Publishing. [Google Scholar]
- Naqshbandi, M Muzamil, Ibrahim Tabche, and Neetu Choudhary. 2019. Managing open innovation: The roles of empowering leadership and employee involvement climate. Management Decision 57: 703–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebi, Maleknaz, and Guenther Ruhe. 2014. An open innovation approach in support of product release decisions. Paper presented at the 7th International Workshop on Cooperative and Human Aspects of Software Engineering, Hyderabad, India, June 2–3. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Xiaoyu. 2022. A Research on Open Innovation of High-tech Enterprises in the New Era. Journal of Innovation and Development 1: 32–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ober, Józef. 2022. Open innovation in the ICT industry: Substantiation from Poland. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 8: 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozman, Muge. 2011. Modularity, industry life cycle and open innovation. Journal of Technology Management & Innovation 6: 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Parida, Vinit, Mats Westerberg, and Johan Frishammar. 2012. Inbound open innovation activities in high-tech SMEs: The impact on innovation performance. Journal of Small Business Management 50: 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, Gary, and David J. Teece. 2008. Collaborative Arrangements and Global Technology Strategy: Some Evidence from the Telecommunications Equipment Industry. Hackensack: World Scientific Publishing, pp. 145–74. [Google Scholar]
- Podvezko, Valentinas. 2009. Application of AHP technique. Journal of Business Economics and Management 2: 181–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, Michael E. 1991. Towards a dynamic theory of strategy. Strategic Management Journal 12: 95–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziwon, Agnieszka, and Marcel Bogers. 2019. Open innovation in SMEs: Exploring inter-organizational relationships in an ecosystem. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 146: 573–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziwon, Agnieszka, Marcel Bogers, Henry Chesbrough, and Timo Minssen. 2022. Ecosystem effectuation: Creating new value through open innovation during a pandemic. R&d Managemen 52: 376–90. [Google Scholar]
- Reiss, Julian. 2007. Do we need mechanisms in the social sciences? Philosophy of the Social Sciences 37: 163–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertsone, Galina, and Inga Lapiņa. 2023. Digital transformation as a catalyst for sustainability and open innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 9: 100017. [Google Scholar]
- Rogo, Francesco, Livio Cricelli, and Michele Grimaldi. 2014. Assessing the performance of open innovation practices: A case study of a community of innovation. Technology in Society 38: 60–80. [Google Scholar]
- Rumanti, Augustina Asih, Afrin Fauzya Rizana, Fadillah Ramadhan, and Rocky Reynaldo. 2021. The impact of open innovation preparation on organizational performance: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access 9: 126952–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, Thomas L. 1972. An Eigenvalue Allocation Model for Prioritization and Planning. Philadelphia: Energy Management and Policy Center, University of Pennsylvania, vol. 28, p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Saaty, Thomas L. 1980. The analytic hierarchy process (AHP). The Journal of the Operational Research Society 41: 1073–76. [Google Scholar]
- Saebi, Tina, and Nicolai J. Foss. 2015. Business models for open innovation: Matching heterogeneous open innovation strategies with business model dimensions. European Management Journal 33: 201–13. [Google Scholar]
- Salter, Ammon, Paola Criscuolo, and Anne L. J. Ter Wal. 2014. Coping with open innovation: Responding to the challenges of external engagement in R&D. California Management Review 56: 77–94. [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeier, Patricia, Nadia Jamali, Carmen Kobe, Ellen Enkel, Oliver Gassmann, and Markus Meier. 2004. Towards a structured and integrative front-end of product innovation. Paper presented at the R and D Management Conference (RADMA), Lisbon, Portugal, July 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Satta, Giovanni, Francesco Parola, Lara Penco, and Salvatore Esposito de Falco. 2016. Insights to technological alliances and financial resources as antecedents of high-tech firms’ innovative performance. R&D Management 46: 127–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sá, Tiago, João J. M. Ferreira, and Shital Jayantilal. 2023. Open innovation strategy: A systematic literature review. European Journal of Innovation Management. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieg, Jan Henrik, Martin W. Wallin, and Georg Von Krogh. 2010. Managerial challenges in open innovation: A study of innovation intermediation in the chemical industry. R&D Management 40: 281–91. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, Marisa, Marco Busi, Peter Ball, and Robert Van Der Meer. 2008. Factors influencing an organisation’s ability to manage innovation: A structured literature review and conceptual model. International Journal of Innovation Management 12: 655–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sovacool, Benjamin K., Jakob Jeppesen, Jesper Bandsholm, Joakim Asmussen, Rakulan Balachandran, Simon Vestergaard, Thomas Hauerslev Andersen, Thomas Klode Sørensen, and Frans Bjørn-Thygesen. 2017. Navigating the “paradox of openness” in energy and transport innovation: Insights from eight corporate clean technology research and development case studies. Energy Policy 105: 236–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spithoven, André, Bart Clarysse, and Mirjam Knockaert. 2011. Building absorptive capacity to organise inbound open innovation in traditional industries. Technovation 31: 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staack, Volker, and Branton Cole. 2020. Reinventing Innovation Five Findings to Guide Strategy through Execution; Key Insights from PwC’s Innovation Benchmark. London: PWC. [Google Scholar]
- Strazzullo, Serena, Roberto Mauriello, Vincenzo Corvello, Livio Cricelli, and Michele Grimaldi. 2023. How open innovation can improve companies’ corporate social responsibility performance? Business Ethics, the Environment & Responsibility. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stroh, Timothy Eric. 2019. A practitioners perspective on the benefits of open innovation. Journal of Innovation Management 7: 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, David J. 2010. Business models, business strategy and innovation. Long Range Planning 43: 172–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, David J. 2020. Hand in glove: Open innovation and the dynamic capabilities framework. Strategic Management Review 1: 233–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabucchi, Daniel, Tommaso Buganza, Claudio Dell’Era, and Elena Pellizzoni. 2018. Exploring the inbound and outbound strategies enabled by user generated big data: Evidence from leading smartphone applications. Creativity and Innovation Management 27: 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, Godwin G. 2000. Using analytic hierarchy process to analyze the information technology outsourcing decision. Industrial Management & Data Systems 100: 421–29. [Google Scholar]
- Urbinati, Andrea, Luca Manelli, Federico Frattini, and Marcel L. A. M. Bogers. 2022. The digital transformation of the innovation process: Orchestration mechanisms and future research directions. Innovation 24: 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van de Vrande, Vareska, Jeroen P. De Jong, Wim Vanhaverbeke, and Maurice De Rochemont. 2009. Open Innovation in SMEs: Trends, Motives and Management Challenges. Technovation 29: 423–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhaverbeke, Wim, Vareska Van de Vrande, and Henry Chesbrough. 2008. Understanding the advantages of open innovation practices in corporate venturing in terms of real options. Creativity and Innovation Management 17: 251–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Chong, Peter W Cardon, Ci-Rong Li, and Chun-Xuan Li. 2023. The influences of open communication by senior leaders and legitimacy judgments on effective open innovation. International Journal of Business Communication 60: 912–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Chun-Hsien, and Xiaohong Iris Quan. 2019. The role of external technology scouting in inbound open innovation generation: Evidence from high-technology industries. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management 68: 1558–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, Joel, and Marcel Bogers. 2014. Leveraging external sources of innovation: A review of research on open innovation. Journal of Product Innovation Management 31: 814–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, Andy Wai Kan, Atanas G. Atanasov, Helen Sheridan, Elisabeth Klager, Fabian Eibensteiner, Sabine Völkl-Kernsock, Maria Kletecka-Pulker, Harald Willschke, and Eva Schaden. 2021. Open innovation in medical and pharmaceutical research: A literature landscape analysis. Frontiers in Pharmacology 11: 587526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yudanov, Andrey. 2012. What is an Innovative firm? Вoпрoсы экoнoмики 7: 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yulianto, Edy, and Supriono. 2023. Effect of open innovation on firm performance through type of innovation: Evidence from SMES in Malang City, East Java, Indonesia. Cogent Business & Management 10: 2262671. [Google Scholar]
- Zarzewska-Bielawska, Agnieszka. 2012. The strategic dilemmas of innovative enterprises: Proposals for high-technology sectors. R&D Management 42: 303–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Hao, Zengguang Ma, Xiaoning Liang, and Tony C. Garrett. 2024. Antecedents and outcomes of open innovation over the past 20 years: A framework and meta-analysis. Journal of Product Innovation Management 41: 793–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Xiaobin, Zhaofang Chu, Lei Ren, and Jianguo Xing. 2023. Open innovation and sustainable competitive advantage: The role of organizational learning. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 186: 122114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zincir, Oya, and Diana Rus. 2019. Understanding Knowledge Absorption for Inbound Open Innovation Practices: How Do Knowledge Antecedents Influence the Process? In The Role of Knowledge Transfer in Open Innovation. Hershey: IGI Global, pp. 97–117. [Google Scholar]
- Ziviani, Fabricio, Hugo Tadeu Braga, Renata de Souza França, and Fabio Correa. 2022. Open Innovation as a Strategy for Creating Value in Technology-based companies: Value creation; Innovation; Innovation Profile; Knowledge networks; Open innovation. Revista de Negócios 27: 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
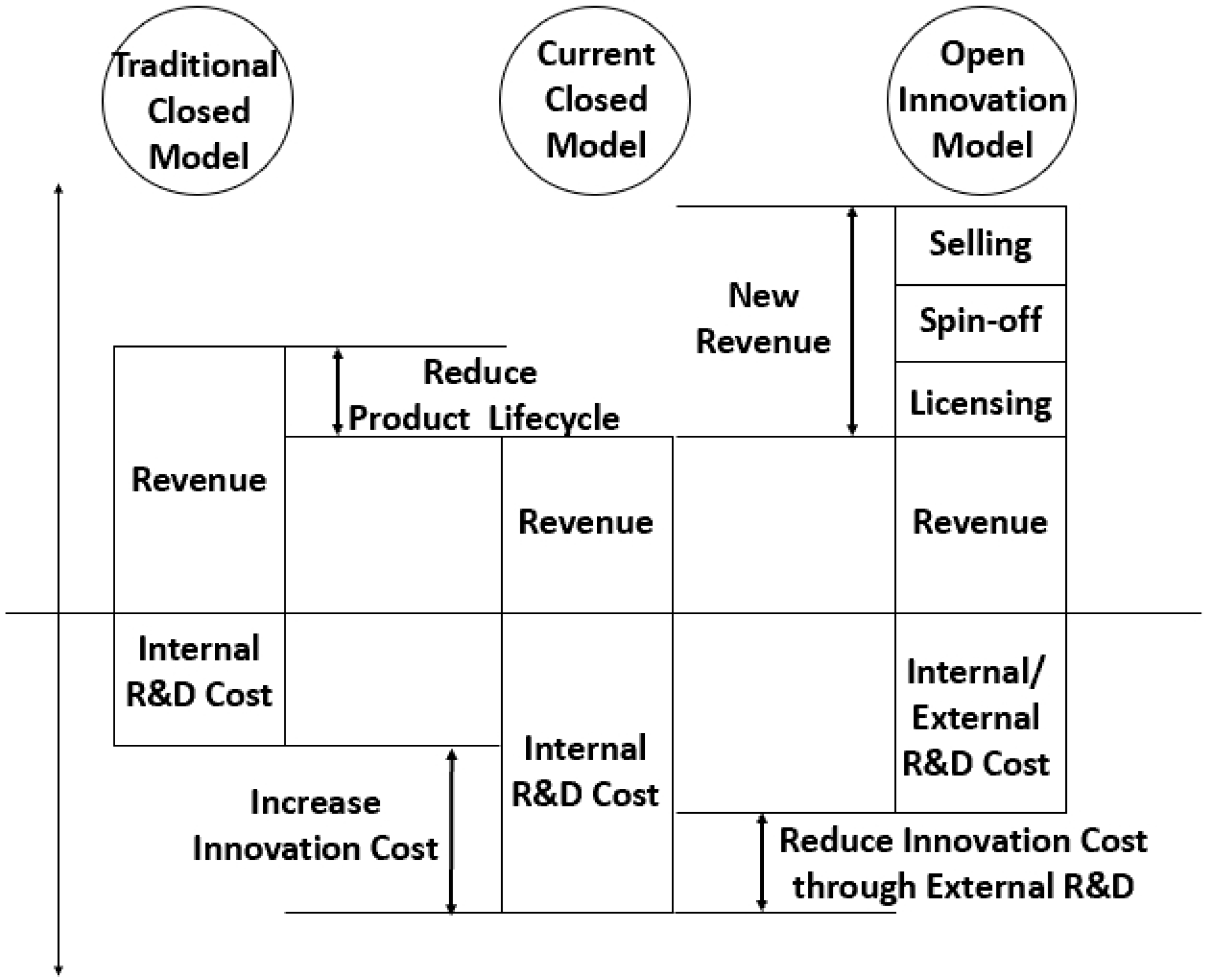

| Separation | Concepts | Innovation Process Highlights | Company Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inbound | Expand its own knowledge base and increase innovation through the introduction of external knowledge |
|
|
| Outbound | Exporting its own technology to external parties and monetizing it through other channels |
|
|
| Coupled | Integrate inbound and outbound open innovation by partnering with complementary partners |
|
|
| Evaluation Area | Evaluation Factor | Definition | Related Studies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subject | Will of the Chief Executive | The establishment of a clear vision and active support from chief executives is essential for the effective implementation of open innovation processes. | Ahn et al. (2017); Bogers et al. (2019); Drechsler and Natter (2012); Enkel et al. (2011); Naqshbandi et al. (2019); Rumanti et al. (2021); Teece (2020) |
| Direction of Decision-Making | The effective integration of external ideas and resources, coupled with the capacity to make innovative decisions that reflect diverse perspectives, is a crucial skill in any field. | ||
| Innovative Leadership | Leadership that cultivates a culture of creativity and innovation and that provides an environment conducive to the implementation of novel ideas. | ||
| Openness | The capacity to recognize and accept novel insights and experiences from external sources is a crucial aspect of organizational awareness and attitude. | ||
| Environment | Technological Environment Changes | The evolution of R&D and market environments in response to new technological advancements and innovations. | Arora (2004); Gassmann et al. (2010); Keupp and Gassmann (2009); Lichtenthaler (2009); Ozman (2011); Sá et al. (2023); He and Liu (2011) |
| Competitive Intensity | The degree of competition among companies in an industry and market and the extent to which competition exerts influence over operations. | ||
| Technological Modularization | An R&D approach that entails the independent design of system and product technology according to functional specifications, with the objective of facilitating interchangeability and reusability. | ||
| Culture of Innovation | The prevailing culture within the industry facilitates the adoption of external technology and knowledge, rather than the perpetuation of proprietary solutions. | ||
| Resource | Absorptive Capacity | The ability of an organization/individual to identify, assimilate, transform, and exploit knowledge from its environment. | Chesbrough (2006b); Cohen and Levinthal (1990); Hung and Chou (2013); Mirza et al. (2022); Miyao et al. (2022); Spithoven et al. (2011); West and Bogers (2014) |
| Corporate Financial Investment | Corporate-level financial support to drive open innovation, such as CVCs and corporate funds. | ||
| Competencies of Open Innovation Organization | An organization’s ability to strategically manage open innovation, collaborate with external partners, and integrate new ideas internally. | ||
| Market Knowledge | Information and knowledge about the market that are shared internally within the organization. | ||
| Mechanism | Collaboration Control System | An organizational structure that enables different organizations to effectively collaborate and innovate during open innovation. | Carbone et al. (2010); Chesbrough (2007); Colombo et al. (2010); Cricelli et al. (2023); Dries et al. (2013); Gaspary et al. (2020); Haefliger (2019) |
| Flexible Organizational Structures | A structure that enables an organization to respond quickly to changing environments and to capture and leverage innovative ideas from inside and outside the organization. | ||
| Structured Processes | A system for quickly responding to and systematically resolving problems in the execution of open innovation. | ||
| Strategic Orientation | The alignment of strategic behaviors and attitudes in an organization to achieve open innovation goals. |
| Section | Sample Size | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 27 | 90 |
| Female | 3 | 10 | |
| Age | 30s | 2 | 7 |
| 40s | 15 | 50 | |
| 50s | 13 | 43 | |
| Job Experience | 10–20 Years | 7 | 23 |
| 20–30 Years | 19 | 63 | |
| 30 Years | 4 | 13 | |
| Job Area | Engineers | 15 | 50 |
| Open Innovation Professionals | 15 | 50 | |
| Position | Team Member | 3 | 10 |
| Director | 19 | 63 | |
| Executive | 8 | 27 | |
| Evaluation Areas | The Weights of Areas | Evaluation Factors | The Weights of Evaluation Factors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local | Local * | Priority | Global ** | Priority | ||
| Subject | 0.556 | Will of Chief Executives | 0.373 | 1 | 0.207 | 1 |
| Direction of Decision-Making | 0.370 | 2 | 0.205 | 2 | ||
| Innovation Leadership | 0.184 | 3 | 0.102 | 4 | ||
| Openness | 0.073 | 4 | 0.041 | 7 | ||
| Environment | 0.263 | Technological Environment Changes | 0.560 | 1 | 0.147 | 3 |
| Competitive Intensity | 0.262 | 2 | 0.069 | 6 | ||
| Technological Modularization | 0.112 | 3 | 0.029 | 8 | ||
| Culture of Innovation | 0.067 | 4 | 0.018 | 12 | ||
| Resource | 0.121 | Absorptive Capacity | 0.569 | 1 | 0.069 | 5 |
| Corporate Financial Investment | 0.241 | 2 | 0.029 | 9 | ||
| Competencies of Open Innovation Organization | 0.118 | 3 | 0.014 | 13 | ||
| Market Knowledge | 0.071 | 4 | 0.009 | 14 | ||
| Mechanism | 0.060 | Collaboration Control System | 0.475 | 1 | 0.029 | 10 |
| Flexible Organizational Structure | 0.306 | 2 | 0.018 | 11 | ||
| Structured Processes | 0.135 | 3 | 0.008 | 15 | ||
| Strategic Orientation | 0.084 | 4 | 0.005 | 16 | ||
| Total | 1.000 | 4.000 | 1.000 | |||
| Evaluation Factors | Weights of Evaluation Factors | Priority of Factors (by Global) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local | Global | |||||
| Engineer Group | Professional Support Group | Engineer Group | Professional Support Group | Engineer Group | Professional Support Group | |
| Will of Chief Executives | 0.362 | 0.370 | 0.205 | 0.203 | 2 | 2 |
| Direction of Decision-Making | 0.389 | 0.372 | 0.220 | 0.205 | 1 | 1 |
| Innovation Leadership | 0.177 | 0.172 | 0.100 | 0.094 | 4 | 4 |
| Openness | 0.072 | 0.086 | 0.041 | 0.047 | 7 | 7 |
| Technological Environment Changes | 0.577 | 0.548 | 0.152 | 0.143 | 3 | 3 |
| Competitive Intensity | 0.249 | 0.280 | 0.066 | 0.073 | 5 | 5 |
| Technological Modularization | 0.107 | 0.110 | 0.028 | 0.029 | 9 | 10 |
| Culture of Innovation | 0.066 | 0.062 | 0.017 | 0.016 | 12 | 12 |
| Absorptive Capacity | 0.578 | 0.566 | 0.065 | 0.072 | 6 | 6 |
| Corporate Financial Investment | 0.237 | 0.244 | 0.027 | 0.031 | 10 | 8 |
| Competencies of Open Innovation Organization | 0.127 | 0.104 | 0.014 | 0.013 | 13 | 13 |
| Market Knowledge | 0.058 | 0.087 | 0.006 | 0.011 | 15 | 14 |
| Collaboration Control System | 0.472 | 0.495 | 0.028 | 0.031 | 8 | 9 |
| Flexible Organizational Structure | 0.297 | 0.295 | 0.018 | 0.018 | 11 | 11 |
| Structured Processes | 0.123 | 0.140 | 0.007 | 0.009 | 14 | 15 |
| Strategic Orientation | 0.108 | 0.069 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 16 | 16 |
| Total | 4.000 | 4.00 | 1.000 | 1.000 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, M.; Kim, B. An Analysis of Critical Factors Affecting the Success of Open Innovation Strategies in High-Tech Firms: The Case of South Korea. Adm. Sci. 2024, 14, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14110274
Song M, Kim B. An Analysis of Critical Factors Affecting the Success of Open Innovation Strategies in High-Tech Firms: The Case of South Korea. Administrative Sciences. 2024; 14(11):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14110274
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Minkyu, and Boyoung Kim. 2024. "An Analysis of Critical Factors Affecting the Success of Open Innovation Strategies in High-Tech Firms: The Case of South Korea" Administrative Sciences 14, no. 11: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14110274
APA StyleSong, M., & Kim, B. (2024). An Analysis of Critical Factors Affecting the Success of Open Innovation Strategies in High-Tech Firms: The Case of South Korea. Administrative Sciences, 14(11), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci14110274



_김_(김).png)


