Abstract
We start by exploring how the interplay of soft power and learning levers helps firms address competitive uncertainty in innovation-intensive environments (IIEs). We then theorize that firms’ motivation to pursue a specific combination of soft power and learning tactics in IIEs is shaped by CEO regulatory focus. The analysis of a panel of IIE firms supports our theorizing and reveals that accounting for CEO regulatory focus is elemental to the understanding of firms’ performance heterogeneity in such environments. We conclude that a perspective focused on a combination of soft power and learning tactics is better fitted to explain firms’ performance in environments plagued by extreme uncertainty compared to traditional theoretical lenses. Our main contribution is to the study of performance in innovation-intensive environments.
1. Introduction
Researchers are increasingly realizing that there is not a single model that adequately depicts firm performance in all market contexts or all innovation regimes (James et al. 2013; Kaplan and Murray 2010; Santos and Eisenhardt 2009; Volberda et al. 2013). The predominant perspectives that explain firm performance in innovation-intensive environments—further referred to as IIEs—are typically rooted in resources (Cozzolino and Rothaermel 2018; Rothaermel and Deeds 2004), learning (Bingham and Davis 2012; Stettner and Lavie 2014), or competencies (Birkinshaw et al. 2008; Teece 2019; Volberda et al. 2013). Scholars view IIEs as markets with a fluid structure (Davis et al. 2009), and markets plagued by uncertainty (Leiponen and Helfat 2010) and disruption (Kaplan and Vakili 2015). In IIEs, innovation growth, either disruptive or non-disruptive (Kim and Mauborgne 2019), internal or external (Di Guardo and Harrigan 2016; Hess and Rothaermel 2011; Lavie et al. 2011; Yamakawa et al. 2011; Yang et al. 2011), represents the most widely used means to sustain and promote firm performance (Kim and Mauborgne 2019). However, mixed findings show that firms that gather the most resources, learn and apply the best practices, and develop appropriate competencies do not necessarily perform better in highly ambiguous environments such as IIEs (Stettner and Lavie 2014). Instead, political science scholars emphasize the role of achieving cognitive and competitive market dominance as imperative for performance in highly uncertain environments (Nye 2004, 2013). In this paper, we integrate mainstream theorizing on the role of learning in IIEs with more recent soft power theorizing on the importance of market control under high uncertainty. We adopt a power-learning perspective that integrates firms’ ability to control the pace of innovation growth with the ability to learn on the go. We claim that a power-learning view better explains the differences in IIE firms’ performance than individual views can.
Borrowed from the political sciences field of research (Nye 2004), the soft power perspective explains how firms in highly uncertain environments establish cognitive and competitive dominance by claiming, demarcating, and controlling the market (Santos and Eisenhardt 2009). We view soft power as elemental in IIEs. Under the pressure of uncertainty introduced by innovation transitions (Adner and Kapoor 2016), hard power reflected in coercion and control is significantly diluted (Drees and Heugens 2013; Santos and Eisenhardt 2009), being replaced by softer mechanisms. We identify two power-building mechanisms that stand apart in IIEs and that can clarify most of the uncertainty surrounding the value of firms’ innovation (Santos and Eisenhardt 2009): (1) creating the illusion of power, and (2) exploiting others’ tendency to stick to the familiar. IIE firms applying these soft power levers contour themselves as powerful players, establishing cognitive dominance in a noisy environment.
The degree to which innovation growth affects performance in IIEs depends on IIE firms’ ability to learn as well (Anand et al. 2016; Bingham and Davis 2012; Musaji et al. 2020). The innovation process is in itself a learning process (Kale and Singh 2007) shaped by characteristics of the environment (Yang et al. 2011), of the competition (Kim and Miner 2007; Lavie et al. 2011), and of the firm (James et al. 2013; Kale and Singh 2007; Kaplan and Vakili 2015). IIEs are ambiguous and fast-paced (Adner and Kapoor 2016; Kim and Mauborgne 2019), and have frequent innovation events but few similar cases (Eisenhardt 1989; Wirtz et al. 2007). They expose firms to faulty learning (Anand et al. 2016; Di Guardo and Harrigan 2016), information overload (Dahlin et al. 2018), limited or incorrect feedback (Anand et al. 2016; Kim et al. 2009), and insufficient time to reflect on the process (Musaji et al. 2020). Learning in IIEs pertains to learning from limited experiences (Bingham et al. 2015; Dahlin et al. 2018). The frequent changes, fast pace, and high uncertainty of IIEs present firms with high learning failure rates (Desai 2011; Edmondson et al. 2001). The benefits of learning from experience at a low innovation pace are traded for costs as the innovation pace increases (Vermeulen and Barkema 2002). The benefits and costs of learning in IIEs complement firms’ ability to use soft power to improve performance as spurious learning necessitates more illusions of power to be created by firms in order to achieve the same performance outcome.
The high uncertainty that IIE firms are exposed to brings into play the motivation that firms have to pursue certain innovative behaviors. Behavioral strategy scholars showed that CEOs’ intrinsic impetus to either maximize positive outcomes (promotion focus) or minimize losses (prevention focus) shapes the degree to which firm-level factors drive firm outcomes (Das and Kumar 2010; Galinsky et al. 2005). Essential to individual decision-making (Brockner et al. 2004), self-regulation potentially shapes firms’ proclivity to enact certain power-learning mechanisms over others. Under the fast pace and extreme uncertainty of IIEs, CEOs’ preference for achievement over safety (Crowe and Higgins 1997; Higgins 1998) shapes their preference for using certain soft power levers as well as the way firms accumulate and deploy knowledge. We expect CEOs’ individual self-regulation to bound firms’ performance through the choice of power-learning levers enacted.
Integrating power-learning and self-regulation, this paper proposes a moderated model predicting firms’ performance in IIEs. We propose that the performance of IIE firms is determined by the pace of innovation and that this process is shaped by firm leaders’ individual preference for achievement or safety. We integrate soft power and learning mechanisms and propose a moderated benefit–cost model for the innovation pace–performance relationship. The benefit–cost analysis builds on the joint consideration of soft power and learning levers and is shaped by the individual-level motivation to pursue these strategic actions. We ask: How does CEOs’ self-regulation shape the innovation–performance relationship in IIEs?
The core theoretical contribution of our study is a framework that explains firm market performance through a power-learning lens and places it in the context of decision-makers’ motivation for action. The performance heterogeneity of IIE firms highlights the need for a new perspective on firm innovation, one focused on the benefits and costs of innovation growth and pace. The joint consideration of soft power and learning mechanisms opens intriguing avenues for both innovation and strategy research. In what follows, we provide a comprehensive background on the literature related to soft power, learning, and CEO motivation behind strategic action in IIEs. We formulate and test hypotheses. We find that innovation growth drives IIE firms’ performance following an inverse U-shape and lowers performance as pace increases. CEO regulation strongly moderates both relationships, highlighting the role of individual motivation in IIEs. Lastly, we discuss implications and suggestions for future research.
2. Soft Power, Learning, and CEO Self-Regulation in IIEs
IIEs are rapidly growing markets with blurred boundaries (Adner and Kapoor 2016; Ahuja et al. 2008) that lack a clear sense of what relationships and competencies are valuable (Bingham and Davis 2012), have fluid business models (Suarez et al. 2015; Teece 2000; Vermeulen and Barkema 2002) and possibly unreliable patterns of behavior (Pentland and Feldman 2008), and are plagued by learning discontinuities (Anand et al. 2016) and sporadic changes in demand, players, and regulations (Eisenhardt 1989; Hargadon and Douglas 2001). Governed by extreme uncertainty, IIEs are unpredictable. Firms are not only unable to predict the future that their innovations might bring, but they may also be confused about the value of their own physical (Bingham and Eisenhardt 2011) or learning resources (Anand et al. 2016; Bingham and Davis 2012), and about the meaning of their own actions (Davis et al. 2009). IIEs are also hypercompetitive (Cozzolino and Rothaermel 2018; Pacheco-de-Almeida 2010). The innovation pace dictates the performance outcome (Adner and Kapoor 2016; James et al. 2013) and strategizing how to learn brings substantial benefits (Behrens and Patzelt 2018; Dahlin et al. 2018; Eisenhardt 1989; Vlas et al. 2023; Vermeulen and Barkema 2002).
The only certainty of IIEs is the need for innovation. Internal innovation reflects IIE firms’ organic efforts to gain power by lowering resource dependencies (Drees and Heugens 2013), developing new knowledge (Grillitsch et al. 2019; Kaplan and Vakili 2015), or expanding into new markets (Cozzolino and Rothaermel 2018; James et al. 2013; Vlas et al. 2022; Yang et al. 2011). Under high uncertainty, internal innovation can help firms gain a powerful position from which to draw performance benefits (Keil et al. 2008).
While the importance of innovation for the performance of IIE firms is unquestionable, the role of innovation growth and pace may be (Musaji et al. 2020; Shan et al. 2016). Only recently, researchers paid attention to the pace of certain business activities and found that pace has both positive and negative performance effects (Nadkarni et al. 2016; Pacheco-de-Almeida et al. 2015; Shan et al. 2016). How much and how fast seems to matter, and faster is not necessarily always better (Musaji et al. 2020; Shan et al. 2016). Borrowing from this literature, we focus on the magnitude and pace of innovation growth and investigate their role on IIE firms’ market performance through power-learning lenses.
Consistent to the soft power perspective (Nye 2004, 2013; Santos and Eisenhardt 2009), the mechanisms that affect IIE firms’ market performance are based on what matters most to those effectuating the valuation—the investors, the analysts, the stakeholders at large. The underlying power mechanisms that drive investors’ valuation of performance are related to a firm’s ability to establish cognitive dominance by becoming a referent for that market (Santos and Eisenhardt 2009). The market performance of the firm in IIEs is thus a reflection of the firms’ ability to reduce uncertainty for others by using two soft power mechanisms: creating the illusion of power and exploiting others’ tendency for familiarity (Santos and Eisenhardt 2009).
According to this perspective, soft power helps firms overcome the fact that the accumulated hard power may not be applicable in uncertainty-plagued IIEs after innovation discontinuities happen (Adner and Kapoor 2016; Nye 2013). In discontinuity-plagued IIEs, the optimal combination of soft power mechanisms that firms need to adopt affects their market performance directly, with more mechanisms adopted having a higher power to affect the firm-level outcome. Of course, what soft power mechanisms are applied depends on the type of innovation that is pursued. Also, the effects of the mechanisms that are applied affect firms’ market performance to different degrees. For example, incremental innovations may make it easier for firms to exploit others’ tendency to stick to something familiar (Hess and Rothaermel 2011; Kim and Mauborgne 2019), but radical innovations may drive higher illusions of power (Behrens and Patzelt 2018; Kaplan and Vakili 2015). While in this study we do not differentiate innovation behavior by the type of innovation, we point to the fact together, these soft power mechanisms define firms’ innovation behavior in IIEs. Ultimately, this behavior establishes the firm as a reference point for others, lowering the uncertainty of its future market performance.
Beyond the soft power that IIE firms may enact to drive a higher valuation of performance, learning has been identified as a key driver of performance (Anand et al. 2016; Stettner and Lavie 2014). Firms’ learning in IIEs is viewed as essential because it helps overcome inertia (Gilbert 2005; Haunschild et al. 2015; Levinthal and March 1993), contributes to new capability development (Bingham et al. 2015; Kale and Singh 2007), improves adaptability (Bingham et al. 2015; Kale and Singh 2007), and supports resource and routine renewal (Bresman 2013; Edmondson et al. 2001; Pentland and Feldman 2008; Teece 2019). While the key premise of organizational learning research is that firm-level outcomes improve with experience (Cyert and March 1963; Lieberman 1987), the usefulness of experience in changing contexts is limited (Anand et al. 2016; Annosi et al. 2020; Di Guardo and Harrigan 2016; Kim et al. 2009). The risks of learning when experience is limited stem from spurious successes and failures that the changing environment causes (Dahlin et al. 2018). Among the problems, scholars highlight negative transfer (O’Grady and Lane 1996), reduced motivation to learn (Haunschild et al. 2015), interpretability and confusion (Dahlin et al. 2018), false lessons (Anand et al. 2016), a lack of patterns leading to the replacement of reliable routines (Annosi et al. 2020; Kim et al. 2009), confounding inferences and generalizations (Kim et al. 2009), unreliable data leading to superstitious learning (Dahlin et al. 2018; March et al. 1991), a lack of causality, and an unclear relationship with performance (Argote and Miron-Spektor 2011). To complicate learning, the fast pace of events intrinsic to IIEs (Adner and Kapoor 2016) shrinks the pool of experiences that can be used to learn from (Argote et al. 2003; Kim et al. 2009). A faster pace introduces selection errors (Anand et al. 2016; Argote et al. 2003; Dahlin et al. 2018) and information asymmetries (Kim and Miner 2007) that make learning problematic. Fast paced innovation creates a high cognitive burden on decision-makers to learn/unlearn (Zhao and Olivera 2006). Overall, the ambiguity of IIEs poses a learning challenge to firms competing in these contexts, limiting the pool of useful experiences to draw from and impacting firms’ ability to streamline activities in the short run.
Behavioral researchers have long argued that the efficiency of mechanisms enacted by firms to drive higher performance varies with firm characteristics (Hambrick et al. 2015; Higgins and Spiegel 2004; Hmieleski and Baron 2008). Regulatory focus theory (Crowe and Higgins 1997; Higgins 1998; Higgins and Spiegel 2004) views the motivation that firms’ leaders have to pursue certain courses of action as having a profound impact on organizational decision-making and behavior. The term regulatory focus refers to an individual’s tendency to either achieve positive outcomes by being sensitive to accomplishments and aspirations (promotion focus) or avoid negative outcomes by paying attention to safety and obligations (prevention focus) (Crowe and Higgins 1997; Higgins 1998). Regulatory focus pertains to self-regulation and goal attainment and encompasses the motivation that drives individuals with power to decide such as the CEO (Lanaj et al. 2012) to prefer certain courses of action over others (Johnson et al. 2010). This has special relevance for firms navigating environments with extreme uncertainty because the responsibility for the success or failure of innovation falls on the one person at the top (Galinsky et al. 2005; Gamache et al. 2015; Hambrick et al. 2015; Neukam and Bollinger 2022). Due to the intrinsic specifics of each type, CEOs’ self-regulation has the potential to either enhance or hinder the performance effect of power-learning mechanisms, thus mitigating or exacerbating the uncertainty surrounding firms’ strategic action in IIEs.
3. Hypothesis Development
3.1. Benefits and Costs of Innovation Growth in IIEs
In the following, the additive effects of latent mechanisms based on soft power and learning perspectives help us explain an inverted U-shape relationship between innovation growth and market performance in IIEs. We argue that innovation growth facilitates the enactment of soft power mechanisms that drive a positive market performance and, at the same time, increases the costs of learning by limiting the experiences that IIE firms may use to streamline performance.
The soft power perspective argues that under extreme uncertainty, creating the illusion of power and exploiting others’ tendency to stick to something familiar reduces uncertainty by lowering the information asymmetries obscuring the true value of the firm (Santos and Eisenhardt 2009). By growing their innovation pools, IIE firms improve their potential for commercialization (Leiponen and Helfat 2010) and limit their likelihood for failure (James et al. 2013). Enlarged innovation pools open up the opportunity to signal power and to carve a distinct market space for the IIE firm. Innovation growth provides increased recombinatory potential (Kaplan and Vakili 2015; Yayavaram and Chen 2015) that allows for the reuse or repurpose of older innovations, lowering the chance for diminishing returns (Rothaermel and Deeds 2004). Appending the innovation base with new innovations projects self-serving illusions of power as firms’ knowledge base is refreshed and, at the same time, nourishes some degree of certainty about firms’ market potential that results from blending in older innovations. The blend of something old and something new, familiarity and novelty, has been associated with comfort and acceptance (Hargadon and Douglas 2001). Associated with positive investor sentiments (Arthurs et al. 2009), the balancing of soft power mechanisms of illusion and the exploitation of others’ tendencies lowers the overwhelming information asymmetries related to IIE firms’ power. Investors feel that they become better informed about firms’ potential, triggering a higher market valuation of IIE firms’ performance.
While the soft power benefits of growing innovation accumulate as more mechanisms are implemented, so do the learning costs. In IIEs, growing the innovation pool adds complexity, and the uncertainty of the environment makes experiences episodic and feedback ambiguous (Anand et al. 2016; Annosi et al. 2020). Given the degree of noise, the applicability of learned experiences is low (Musaji et al. 2020) and the chance for negative learning is high (O’Grady and Lane 1996). The increase in complexity incrementally exposes firms to information overload that further limits learning (Dahlin et al. 2018). It creates confusion about the value of new innovations and opens the door to false lessons (Dahlin et al. 2018; Di Guardo and Harrigan 2016). The increase in complexity of the innovation pool created through recombination imposes limits on firms’ understanding of cause and effect (Argote and Miron-Spektor 2011; March et al. 1991). The lack of understanding in causality surges as the volume of innovations increases, triggering a sharp increase in the costs associated with improper implementation. At high innovation growth levels, IIE firms risk replacing reliable routines (Bresman 2013; Edmondson et al. 2001; Pentland and Feldman 2008) and risk confounding inferences because of unreliable data (Kim et al. 2009; Zollo and Winter 2002). The learning costs of innovation growth accumulate with limited understanding of causality and the implementation process, with limited applicability of experiences, and with the risks of negative learning, imposing limits on how well IIE firms perform.
Overall, we suggest that in IIEs, firms’ market performance depends on their ability to grow their innovation pools in such a way that very low or very high growth negatively affects value by imposing limits on either power or learning, but medium growth balances the power benefits and the learning costs to maximize firms’ performance. Specifically:
Hypothesis 1.
Innovation growth exhibits an inverted U-shape relationship to IIE firms’ future market performance.
3.2. Innovation Pace and Market Performance in IIEs
Previously, researchers investigated the role of pace in the decision-making process to more accurately understand the mechanisms that drive firm performance (Eisenhardt 1989; Kessler and Chakrabarti 1996; Vermeulen and Barkema 2002). That literature attributes an essential role to the temporal dimensions of the process, and explains outcome heterogeneity through lenses of accumulation, processing, and the implementation of knowledge in such a context (Nadolska and Barkema 2014; Pacheco-de-Almeida et al. 2015). In IIEs, innovation scholars identify pace as the key attribute of the learning process (Bingham et al. 2015; Haunschild et al. 2015; Laamanen and Keil 2008). Innovation pace is particularly relevant in IIEs because IIEs represent contexts with frequent innovation events (Eisenhardt 1989), accentuated information recency (Haunschild et al. 2015), and fast-paced decision-making (Davis et al. 2009; Nadolska and Barkema 2014). On the positive side, a higher innovation pace allows for more information to be accumulated in a shorter amount of time, which, all other factors being constant, should help firms learn faster. However, the quality, redundancy, and feedback of what is learned has a high potential to be isolated and spurious (Dahlin et al. 2018). A higher innovation pace thus imposes limits on firms’ learning by shortening the time to process information and feedback. These limitations of idiosyncratic experiences are reinforcing in nature as spurious failures and successes cause negative learning (Dahlin et al. 2018; O’Grady and Lane 1996).
A high innovation pace involves frequent events (Laamanen and Keil 2008; Nadolska and Barkema 2014), which add to the complexity of information that firms have to process (Dahlin et al. 2018). It increases ambiguity and noise (Laamanen and Keil 2008) and requires firms to devote increased resources and time to understand and process the cause–effect relationships (Argote and Miron-Spektor 2011; Musaji et al. 2020; Yayavaram and Chen 2015). Causality becomes unclear (Dahlin et al. 2018), increasing the likelihood of mistakes. Performance feedback is ambiguous as well (Anand et al. 2016), and is likely to be misguided as firms attribute failures to chance (Zhao and Olivera 2006), overlook the importance of “near misses” (Kim and Miner 2007), and hold onto flawed beliefs (Kale and Singh 2007).
The reinforcing nature of limited experience (Zhao and Olivera 2006) causes poor lessons that further limit firm performance as innovation pace continues to increase. Spurious failures and successes lead firms down inaccurate or even erroneous paths (Laamanen and Keil 2008) and cause them to incorrectly modify best practices and routines (Dahlin et al. 2018). This negative transfer of knowledge from accurate experiences to spurious ones happens when managers lack crucial information about events and are forced to make decisions under the pressure of time or performance (O’Grady and Lane 1996; Stettner and Lavie 2014). Managers’ cognitive burden as they have to continuously rework their assumptions, generalize, and make inferences (Kim et al. 2009) leads to myopic lessons (Levinthal and March 1993) and causes incorrect overriding of effective routines, leading to more faulty lessons and spurious successes. The negative performance effect accentuates as pace increases. In sum, we claim that a higher innovation pace increases firms’ learning cost, which further impedes performance.
Hypothesis 2.
Innovation pace negatively affects IIE firms’ future market performance.
3.3. The Moderating Effects of CEO Self-Regulation
We start by investigating the boundary role that CEO regulatory focus, as an independent characteristic of CEOs’ personality (Johnson et al. 2010), has on the innovation growth–firm performance relationship. We expect that CEO regulatory foci (promotion and prevention) affect the two latent mechanisms—soft power and learning—that together lead to the inverse U-shape relationship hypothesized. By affecting the soft power mechanisms, CEO regulatory foci shift the maximum performance right or left, allowing IIE firms to achieve the same market performance with more or less innovation growth. By affecting the learning mechanisms, CEO regulatory foci shift the maximum performance up or down, allowing IIE firms to achieve a different level of performance with the same investment in innovation. In the following, we draw from the regulatory focus theory (Higgins 1998) to explain how individual self-regulation manifests itself in the relationship between innovation growth and performance.
The regulatory focus theory establishes promotion and prevention foci as motivational characteristics that guide an individual’s behavior toward either achievement or safety (Brockner et al. 2004; Higgins and Spiegel 2004). The achievement orientation of promotion-focused CEOs gives these individuals the inner motivation to overvalue innovation by seeing chances in opportunities as opposed to risks (Hmieleski and Baron 2008) and by evaluating risks more leniently (Das and Kumar 2010). Such CEOs undervalue the subtle soft power practices and do not see the need for them. Prevention-focused CEOs’ aversion for risk and uncertainty motivates them toward safer decisions (Hmieleski and Baron 2008) that minimize their losses. They adopt illusions as a way to minimize their risks (Galinsky et al. 2005) and create rich stories to justify their actions (Galinsky et al. 2005). Their preference for soft power is rooted in their high preference for safety and for systematic decisions characterized by high levels of due diligence (Brockner et al. 2004). Overall, we expect different self-regulation to attribute different values to the use of soft power, with prevention being more likely to adopt it.
CEOs’ self-regulation also affects firms’ motivation for learning in IIEs. The IIEs’ context exposes firms to spurious successes and failures (Dahlin et al. 2018) and frequent events (Haunschild et al. 2015). Promotion-focused CEOs rejoice at the benefits of the higher salience of the learning opportunity, which fuels their motivation for achievement. Primarily concerned with maximizing possible returns, they tend to downplay possible negative outcomes of learning from spurious successes or failures associated with frequent innovations (Das and Kumar 2010), while not being worried about the lack of time to process information or the opportunism that the situation presents. Tempted by the opportunity, they will embrace spurious learning, thus increasing the costs of learning in IIEs. On the other hand, prevention-focused CEOs’ preference for safer practices and reliable routines (Gamache et al. 2015) makes them reluctant to adopt spurious successes and failures. The information content ambiguity (Zhao and Olivera 2006) and the lack of a proper understanding of cause and effect (Dahlin et al. 2018) shake the stability of the playfield they enjoy. Their preference for safety overemphasizes the risks of spurious learning and limit prevention-focused CEOs’ outcomes from engaging in innovation. Their preference for avoiding uncertainty altogether favors the reuse of established routines (Gilbert 2005), impeding the implementation of new practices or the modification of known routines as required by innovation growth (Annosi et al. 2020; Pentland and Feldman 2008). A similar point is made by Burger-Helmchen (2007), indicating that the routines and heuristics of CEOs can be dependent on the tools they use to make their decisions. As opposed to promotion focus, prevention focus seems to decrease the costs of learning in IIEs.
Overall, we argue that promotion focus will inhibit the use of soft power while adopting limited experiences with more leniency. First, this decreases the benefits of soft power and increases the costs of learning, flattening the curvilinear relationship between innovation growth and firms’ market performance. Second, it shifts the point of maximum performance to be achieved with less growth. At the same time, we argue that prevention focus increases the use of soft power but impedes learning from limited experience. The benefits of soft power increase and the costs of learning decrease, steepening the curvilinear relationship between innovation growth and firms’ market performance. Additionally, it shifts the point of maximum performance to be achieved with significantly less growth.
Hypothesis 3a.
CEO promotion focus negatively moderates the relationship between IIE firms’ innovation growth and future market performance.
Hypothesis 3b.
CEO prevention focus positively moderates the relationship between IIE firms’ innovation growth and future market performance.
CEO promotion and prevention foci also change the magnitude of the pace–performance relationship. Promotion-focused individuals’ comfort with uncertainty and risks vis-à-vis strategic action (Johnson et al. 2010) coupled with their achievement orientation (Galinsky et al. 2005) gives these individuals more trust that they can navigate the risks and challenges of IIEs, allowing them to accumulate experience faster. Less worried about making a mistake and more worried about losing an opportunity (Cowden and Bendickson 2018; Johnson et al. 2010), promotion-focused CEOs are likely to experience small failures and successes more often (Galinsky et al. 2005). The high recency of events motivates them to act first (Haunschild et al. 2015) and consequently commit more and smaller errors. Their path to learning allows for incremental adjustments that correct their firm’s performance at each step and lowers the costs of learning from limited experiences (Anand et al. 2016). By contrast, prevention focus is a risk-averse self-regulation mechanism that sensitizes individuals to possible losses (Crowe and Higgins 1997). In response to this concern, prevention-focused CEOs adopt a conservative attitude that minimizes the vulnerabilities and risks to which they are exposed (Higgins 1998). Their need for stability and safety is satisfied through careful planning and the systematic consideration of decisions (Gamache et al. 2015), which makes them delay decisions until sufficient experience has been accumulated. They experience failures and successes less often and the associated learning costs are higher (Anand et al. 2016). They spend more time trying to identify and understand the best path to success, which even if identified is likely to be irrelevant as the environment changes too often. Overall, their behavior increases learning costs.
Hypothesis 4a.
CEO promotion focus mitigates the negative effect of innovation pace on IIE firms’ future market performance.
Hypothesis 4b.
CEO prevention focus accentuates the negative effect of innovation pace on IIE firms’ future market performance.
4. Methodology
4.1. Data and Sample
Because our study focuses on the role of innovation growth for firms’ market valuation, we collect data between 2005 and 2018, including from U.S. firms operating in traditional and information technology manufacturing industries (SIC 2000–3999 and SIC 7370–7379), as well as a variety of service industries (SIC 4510–6320) such as telecommunications, data security, or drug proprietaries. This multi-industry context is relevant for three reasons. Firms in these industries display the most active innovation behavior and for them, our innovation growth and pace measures are particularly relevant. These industries have been dominated by U.S.-based firms with publicly available data, which is the reason many previous innovation studies have been based in these industries (Bresman 2013; Rothaermel and Deeds 2004; Stettner and Lavie 2014), making the study highly relevant to previous work. Last, most of these firms are large, with more than two thirds ranked in Fortune 500 in 2019, making them more likely to be diverse in terms of leadership (Lanaj et al. 2012), thus representing a proper context in which to test our moderating effects.
We integrate three main data sources. The United States Patents and Trademark Office (USPTO) is used to identify firms’ innovation behavior. WRDS Compustat provides the financial data necessary to compute firms’ market performance and the financial controls. EDGAR Online and companies’ official websites provide access to firms’ letters to shareholders, which are used to extract CEO regulatory focus. We use the General Architecture for Text Engineering (GATE) tool (Vlas and Robinson 2012) to extract CEO regulatory focus from each firm’s letter to shareholders. Our final data set is a panel of 80 firms that have on average 6 observations per firm, giving us the chance to analyze 476 such instances.
4.2. Variables
- Market performance. Based on previous research (Stettner and Lavie 2014; Yamakawa et al. 2011), our dependent variable reflects firms’ market value computed as the product between firms’ stock closing price and the number of common shares outstanding. We compensate for the volatility of this measure by averaging the four end-of-quarter values (in millions). Market performance is preferable to traditional accounting measures such as ROA because it captures investors’ ex-ante expectation about firms’ future financial performance as opposed to slowly adjusting accounting-based performance measures that capture firms’ ex-post performance. It addresses the issue of different standards used to measure performance while effectively capturing the expected proceeds from innovation growth, and it captures both short-term performance and long-term prospects in a single variable (Uotila et al. 2009).
- Innovation growth. Our first predictor reflects firms’ yearly growth in patenting. Following previous innovation research (Kaplan and Vakili 2015; Yayavaram and Chen 2015), we measure firms’ innovation with a citation-weighted measure of granted patents (De Rassenfosse and Jaffe 2018). Growth rate is measured as the annual percentage change in citation-weighted patents granted in the current year compared to previous year. The measure is first normalized to avoid losing observations and then logged to address skewedness.
- Innovation pace. Our second predictor reflects firms’ commitment to innovation. We operationalize pace with a difference between two consecutive years’ rates of growth. A positive difference reflects an increase in firms’ innovation growth rate and therefore an increased commitment to innovation. A valid data point requires firms to patent for three consecutive years. We assign a zero to years with no patents to avoid losing data points.
- CEO regulatory foci. We capture both promotion and prevention foci of firms’ CEOs using a content capture technique. Individuals’ regulatory focus is reflected in individuals’ language (Johnson et al. 2010) and is therefore reflected in the content of individuals’ written communication. The fact that individuals may not be fully aware of their own regulatory focus (Gamache et al. 2015) makes this approach more appropriate compared to interviews. Letters to shareholders represent a consistent form of communication that CEOs use, which are non-intrusive and publicly available. Using GATE (Vlas and Robinson 2012), we automatically track and count promotion and prevention words in each letter. We create our moderating measures by weighting the counts against the total word count of each letter and scaling up to facilitate interpretation.
- Controls. To minimize possible alternative explanations, we include firm-level and CEO-level controls in both regression stages and add controls for intertemporal trends (year dummies) and for interindustry variation (SIC 3-digit codes). Specifically, in the first stage regression, we include factors that might confound the motivation for innovation growth. Strategic change represents firms’ flexibility, which is essential when following a high-innovation-growth strategy and is reflected by firms’ allocations in a number of strategic dimensions (Triana et al. 2013). Firm size, coded 1 for firms with total assets value above average and 0 otherwise, can influence firms’ innovation growth, with large firms being more capable of sustaining high innovation growth rates (Stettner and Lavie 2014). R&D intensity, measured as the log-transformed ratio of R&D expenses to total revenue, represents firms’ absorptive capacity used to enhance the value of innovation. Slack (log-transformed ratio of firms’ total debt in revenue) represents the rent-generating potential of firms. Innovation coverage reflects firms’ potential for knowledge recombination and is measured as the average number of subclasses per class of patents filed over the last five-year window. CEO salary increase captures CEOs’ monetary motivation to promote future innovation growth, and CEO underreporting captures CEOs’ tendency for miscommunication (Boudt and Thewissen 2019). We measure the latter as the log-transformed difference between the total actual and the SEC-reported compensation.
4.3. Model Specification
To test our hypotheses, we estimate a linear random-effects model with year and industry controls. Innovation behavior usually has unobservable mechanisms (Stettner and Lavie 2014; Uotila et al. 2009; Vermeulen and Barkema 2002) that influence the innovation preference but not the innovation outcome, and therefore need to be accounted for (Wolfolds and Siegel 2019). We address this possible endogeneity using a two-stage model (Heckman 1979). We use the second-stage models to test the hypotheses. We build five models by sequentially adding variables to avoid an increase in multicollinearity (Yang et al. 2011). We address potential interdependence among observations by lagging all variables by one year relative to the dependent variable. The Hausman test (Hausman 1978) reveals that the random-effects specification is appropriate for innovation growth models (chi-squared = 38.72, p = 0.227) and the fixed-effects specification is appropriate for innovation pace models (chi-squared = 80.36, p < 0.001).
In the second-stage regressions, we control for factors that might explain the performance outcome irrespective of firms’ innovation growth or pace, while including first-stage inverse Mills ratios and year effects. Previous performance is measured as the log-transformed value of total sales in the preceding year. Firm age (logged number of years from the incorporation event) can affect market performance as older firms have a heightened ability to innovate at high rates. Firm solvency, measured as the log-transformed ratio of cash to total debt, reflects firms’ resources available to sustain innovation growth over time. The firm external mode helps us isolate the effect that other modes of operation may have on firms’ financial performance and the ability to sustain high innovation growth rates (Stettner and Lavie 2014). Patenting experience, which is the log-transformed total number of patents granted in the preceding five years and modeled to be preserved at 90 percent per year (Stettner and Lavie 2014), controls for firms’ experience with patenting innovations with the patenting office, which may enable firms familiar with the process to realize higher innovation growth. Innovation newness (log-transformed average number of claims per patent) reflects the complexity of firms’ innovation, which may protect from future infringement. Innovation focus (average number of patents filed per subclass of innovation over a five-year window) represents the concentration of firms’ innovation in certain clusters of knowledge which might facilitate extracting higher rents from innovation growth. CEO age reflects individual experience (log-transformed), with more experienced CEOs being more comfortable with higher innovation rates (Volberda et al. 2013). CEO tenure may trade off against focused innovation, and CEO gender may be suggestive of others’ acceptance of an individual’s innovation (Triana et al. 2013). CEO duality may facilitate innovative behavior, and CEO compensation controls for CEOs’ acceptance of risk (Hambrick et al. 2015).
5. Findings
Table 1 presents descriptive statistics for both the innovation growth (N = 476) and innovation pace (N = 205) models. Over the timeframe studied, the average firm has a market value of $10.37 billion that is positively correlated with firm sales, age, patenting experience, number of acquisitions, and CEO characteristics. Investors, in other words, increase their performance expectations as firms perform well, become more mature, have an active patenting behavior, or are led by CEOs who are older, have longer tenure with the firm, are white males, lead the board of directors as well, and have more visible compensation packages (salary and bonuses). Market performance is also positively correlated with CEO promotion focus (r = 0.14; p < 0.05) and negatively correlated with CEO prevention focus (r = −0.03).

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics.
In the first stage, we run separate Probit regressions for innovation growth and innovation pace models. We use the predicted values from this stage to generate the inverse Mills ratios for the second-stage models. Table 2 reports the results of the second-stage panel regression for the innovation growth models. The main effect (H1) and the moderating effects (H3a–b) for innovation growth are tested in Models 1–4.

Table 2.
Regression of innovation growth on IIE firms’ market performance.
We start with a baseline model with controls. Model 1 tests Hypothesis 1 claiming that innovation growth has an inverse U-shape effect on firms’ market value. The first-degree coefficient is significant and positive (β = 1.267, p < 0.01) and the second-degree coefficient is significant and negative (β = −0.730, p < 0.001). To claim support for this hypothesis, we go beyond regression results and test the inverted U-shape with the Stata U-test (Lind and Mehlum 2010). The test in Table 3 reveals that slope is sufficiently steep at both ends of the range and that the turning point confidence interval is located inside the min–max range of the predictor variable. Table 4 reports the average marginal returns for the entire min–max interval of the predictor showing that the slopes remain significant between ±1 s.d. of the predictor. Figure 1 corroborates the results. We conclude that Hypothesis 1 is supported.

Table 3.
U-test results. Specification: f(x) = x2 Extreme point: 0.8677933. Test: H1: Inverse U-shape vs. H0: Monotone or U-shape.

Table 4.
Average marginal effects of innovation growth.
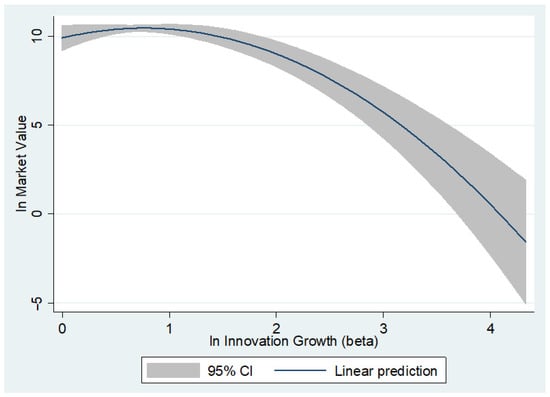
Figure 1.
Innovation growth-market value representation.
Hypotheses 3a–b investigate the effect of CEO regulatory focus on the innovation growth–market performance relationship. Model 2 tests the moderating effect of CEO promotion focus and reveals a negative and significant interaction reflecting a double negative effect (β = 1.217, p < 0.001). Additional analyses show that as CEO promotion focus increases, the inverse U-shaped curve flattens (Figure 2a) and the maximum market performance is achieved sooner (turning point moves to the left) (Table 5). Table 6 shows that the moderating effect holds for the entire ±1 s.d. of both the predictor and the moderator. Hypothesis 3a is supported.
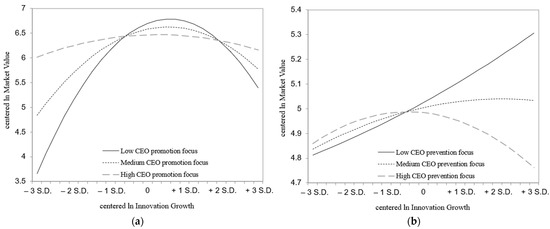
Figure 2.
(a,b) Quadratic three-way innovation growth interaction plots.

Table 5.
Equations of interest.

Table 6.
Marginal effects of innovation growth by CEO promotion focus.
Model 3 tests the moderating effect of CEO prevention focus and reveals only marginal support (β = −0.198, p < 0.1). IIE firms achieve maximum market performance with lower levels of innovation growth (turning point moves to the left) when led by CEOs with a high prevention focus (Table 5). As the prevention orientation accentuates, the inverse U-shape steepens for high but not for low levels of CEO prevention focus (Figure 2b). Overall, we conclude that Hypothesis 3b is not supported.
Model 4 is the full model for all hypotheses on innovation growth. The results are robust.
Table 7 reports the results of the second-stage panel regression for the innovation pace hypotheses. The main effect (H2) and the moderating effects (H4a–b) for innovation pace are tested in Models 5–8. We start with a baseline model with controls. Model 5 tests Hypothesis 2 claiming that innovation pace has a negative effect on IIE firms’ market performance. The coefficient is significant and negative (β = −0.091, p < 0.001). Hypothesis 2 is supported.

Table 7.
Regression of innovation pace on IIE firms’ market performance.
Hypotheses 4a–b investigate the effect of having a promotion (prevention)-focused CEO on the innovation pace–market value relationship. In Table 7, Model 6 tests the moderating effect of CEO promotion focus and reveals that the promotion regulation mechanism mitigates the negative effect of high pace on market performance. The coefficient is positive and significant (β = 0.002, p < 0.001) and the moderating effect holds for the entire ±1 s.d. The graphical representation shows that as CEO promotion focus increases, the negative effect is attenuated (Figure 3a). We conclude that Hypothesis 4a is supported.
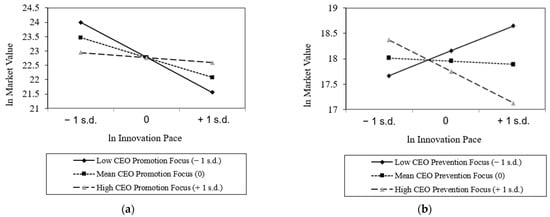
Figure 3.
(a,b) Innovation pace interactions (predictive margins with 95% CI).
In Table 7, Model 7 tests the moderating effect of CEO prevention focus and reveals that the prevention regulation mechanism enhances the negative effect of high pace on IIE firms’ market performance. The coefficient is negative and significant (β = −0.001, p < 0.001). The moderating effect holds for the entire ±1 s.d. of the moderator. The graphical representation shows that as the CEO prevention focus increases, the negative effect is accentuated (Figure 3b). We conclude that Hypothesis 4b is supported.
Model 8 is the full model for all hypotheses on innovation pace. The results are robust.
6. Robustness and Post Hoc Analyses
We test the robustness of the results with several additional tests. First, we conduct a robustness check to confirm that the hypothesized relationship between innovation growth and market performance is indeed quadratic. Adding a cubic innovation growth term does not improve the model fit and tests that the relationship is U-shaped and not S-shaped (Lind and Mehlum 2010). Second, we split the data by the empirically determined turning point (Table 5: turning point = −β1/2β2 = 0.867) and verify if the two linear regressions show slopes consistent with the hypothesized curve. We find that the results are robust. Third, Winsorizing innovation growth at the 1st and 99th percentile of the variable also retrieves very robust results for the inverse U-shaped relationship.
Two additional checks are performed to test whether the predicted relationships hold on various subsamples of the data. We first ran our models on a subsample of software and hardware firms (SIC 357, 367, and 737). These firms (21.4% of firms in the sample) have a different patenting behavior than pharma, telecom, or manufacturing firms in our original data set. The consistent results that we find support our theorizing claiming that the interplay of soft power and learning mechanisms drive the effect on market performance and not firms’ engagement in ambidexterity, as some scholars might claim (Stettner and Lavie 2014). To remove the possible alternative explanation that being ranked in the Fortune 500 drives firms’ market performance more than power-learning mechanisms, we run a second check on a subsample of firms that are not ranked in Fortune 500. We also find that the results hold.
Lastly, we investigate possible (in)congruence effects between the two self-regulation foci and their possible effects on the innovation–market performance relationship. Polynomial regression allows us to investigate predictors’ linear and non-linear effects as well as their interaction (Shanock et al. 2010). Graphical representation in the form of response surface analysis allows us to better interpret and understand the relationships between different configurations of the two moderator variables (promotion and prevention) and the main relationship (innovation growth × market value) (Edwards 1995). A potential (in)congruence effect is denoted by a significant interactive term in the full model (Edwards and Lambert 2007). We find no significant interaction term in the innovation growth models (βPRO × PRE = −0.011, p = 0.918; βPRO × PRE = −0.102, p = 0.601), in the innovation pace (βPRO × PRE = 0.001, p = 0.708), or the innovation growth × innovation pace interaction (βINNG × INNP = −0.519, p = 0.229; βINNG_SQ × INNP = 0.061, p = 0.468). We conclude that there are no (in)congruence effects between the two self-regulation moderators (promotion and prevention) or between the two predictors (innovation growth and innovation pace) that may explain the observed effect on IIE firms’ performance.
7. Discussion
7.1. Theoretical Implications
With a specific focus on IIEs, this research investigates a novel power-learning perspective with potential to explain why and how firms manipulate environmental uncertainty to ensure a positive market performance. Strategy and learning scholars have long been interested in how firms manage uncertainty in various contexts (Santos and Eisenhardt 2009; Wirtz et al. 2007), and a rainbow of explanations from competencies (Bingham et al. 2015; Teece 2019), routines (Annosi et al. 2020; Gilbert 2005; Pentland and Feldman 2008), and knowledge scope (Leiponen and Helfat 2010), to resource combinations (Rothaermel and Deeds 2004; Stettner and Lavie 2014; Uotila et al. 2009), signaling (Arthurs et al. 2009) and competitive dynamics (Cozzolino and Rothaermel 2018; Nadkarni et al. 2016) have been invoked to explain it. Our perspective aims to contribute to this body of literature by (1) extending scholars’ understanding of the process through which the growth and the pace of innovation affects market performance in IIEs, and (2) considering the CEOs’ motivation behind the decisions that fuel this process.
We address the first point by advancing a novel perspective that offers insights into the benefits of using soft power tactics and into the costs of learning from experience when innovating in IIEs. Specifically, testing our theoretical framework on a panel of IIE firms shows strong support for an inverse U-shaped relationship between innovation growth and market value as a measure of performance. Previously, scholars found support for the same type of inverted U relationship when studying the relationship between creativity and entrepreneurship (Lehmann and Seitz 2016). When investigating contingency effects, scholars have found that these relationships are also mitigated by soft power, culture, and heuristics. In addition to previous findings, we observe that maximum performance is achieved when firms’ innovation growth is in the middle of the possible range, and not when firms innovate too little or too much, finding that is in line with prior innovation research in stable environments (James et al. 2013). Further, we investigate the effect of innovation pace and find that speedy innovation is detrimental to performance. The finding resonates with prior research showing that the uncertainty of the IIEs complicates the learning process (Behrens and Patzelt 2018; Pacheco-de-Almeida et al. 2015; Shan et al. 2016) and that fast-paced innovation adds to the ambiguity already nurtured by the environment (Adner and Kapoor 2016; Vermeulen and Barkema 2002).
In addressing the second point, this study investigates why the innovation–performance relationship varies in IIEs, with some firms leading the market and others barely surviving. By incorporating leaders’ motivation for strategic action (Brockner et al. 2004; Cowden and Bendickson 2018; Crowe and Higgins 1997; Higgins 1998), we find that the achievement and the avoidance orientation of firms’ CEOs affect the degree to which innovation growth and innovation pace matter for IIE firms’ performance. The support we find tells us that the motivation for achievement hurts performance in IIEs but the motivation for safety helps it. A deeper investigation into why this happens reveals that the inverted U effect of innovation growth on IIE firms’ performance flips almost immediately after achieving the turning point. The shape flip raises attention on a theoretical implication and an interesting practical implication as well (Haans et al. 2016). From a theoretical standpoint, the shape flip exposes a possibly concave cost function of experience (Argote and Miron-Spektor 2011; Lieberman 1987; Musaji et al. 2020). Table 6 shows that the shape flip happens within the 95% confidence interval of the moderator. We observe that the value at which the shape flips from an inverse U to a U-shape happens almost immediately after innovation growth–performance reaches the maximum point. For IIE firms led by a promotion-focused CEO motivated by gain maximization, the maximum performance is reached when the innovation growth rate is in the middle of the promotion focus range and holds as long as the CEO’s motivation for gain is not extremely high. For CEOs with very high tolerance for risk and uncertainty, the costs of using insufficient or incorrect experiences (Dahlin et al. 2018) increasingly fade relative to the benefits of learning from the resulting failures (Kim and Miner 2007; Musaji et al. 2020). We believe that the CEOs who have a very high promotion focus make almost reckless innovation decisions in IIEs in the absence of sufficient experience, actions that leads them to experience an increased number of small and frequent failures, from which learning occurs. For them, the cost curve associated with intensifying the innovation efforts is progressively bent as the promotion focus of the CEO increases, and this happens to such an extent that the curvature of the experience benefit shape surpasses that of the cost of failure shape and results in a flip of the innovation growth–IIE firm performance relationship.
7.2. Practical Implications
From a practical standpoint, can a higher motivation for gain or safety counteract some of the negative implications of not innovating enough? Empirically, this can be observed by investigating how the turning point changes as the promotion or prevention of the CEO increases. The maximum of the innovation growth–performance function moves to the left in both cases, which means that as the CEO’s motivation for action increases, the innovation growth necessary to achieve the same performance level decreases. In practice, IIE firms motivated by the gains that innovation brings are likely to have more opportunities to learn and will probably learn faster and mostly based on mistakes than successes (Haunschild et al. 2015; Kim et al. 2009; Kim and Miner 2007), and fewer innovations will be needed to achieve high performance levels. IIE firms motivated by safety and minimization of losses are likely to pay close attention to how their innovation strategy unfolds, and fewer but better developed innovations will be needed to learn (Bingham and Eisenhardt 2011; March et al. 1991). The bottom line is that the ambiguity of IIEs cannot guarantee or attribute any definitive benefits to firms’ innovation strategy in the short or long term, and thus firms need to have a strong motivation behind their innovation strategy so that the learning process pays off sooner rather than later.
7.3. Contributions
The proposed power-learning perspective contributes to extending both power and learning research to IIEs. A growing number of scholars showed that in relatively stable environments, ‘over-innovation’ negatively impacts firms’ performance (Hess and Rothaermel 2011; James et al. 2013; Kaplan and Vakili 2015; Yayavaram and Chen 2015). Our framework aims to contribute to this line of scholarly interest emphasizing that the mechanisms that firms enact in IIEs are rooted in a combination of soft power and learning from limited experiences and not in escalating diseconomies such as limitations of complexity (James et al. 2013). Our emphasis on the role of innovation growth and pace also highlights a gap in research investigating the temporal aspects of innovation. While scholars have only recently begun to pay attention to the notion of speed (Behrens and Patzelt 2018; Pacheco-de-Almeida et al. 2015; Shan et al. 2016), the recognition of the importance of innovation pace can be traced back to Kessler and Chakrabarti (1996). Our theorizing only underscores the relevance and importance of this new line of inquiry.
7.4. Limitations and Future Research
With respect to this paper’s limitations, the data structure requirements of this study impelled us to restrict the sample of firms to only IIE firms in certain industries, thus lacking generalizability. Our study covers the analysis of a 15-year period of U.S.-based IIEs such as pharma, telecom, software, hardware, and aircraft. Given that these industries possess unique characteristics required for our theorizing, the findings of this study cannot be generalized to other industries with dissimilar innovation rates. Also, our sample of firms is comprised of mainly large firms on the Fortune 500 list, a limitation imposed by the need to find firms that regularly publish letters to shareholders needed to capture our moderation effects. As such, our findings may not be generalizable to industries dominated by small or medium-sized firms. It would be interesting to see if firms outside of the Fortune 500 list differ in terms of the power-learning tactics they use, and whether such firms achieve similar market performance effects.
8. Conclusions
Overall, our study is among the first to examine both the antecedents and the motivational moderators of firm performance in IIEs. Adopting a novel power-learning perspective, we embark on a challenge to investigate why and how IIE firms differ in terms of market performance. We test and find support for the claim that firm performance under extreme uncertainty requires firms to balance power and learning mechanisms that substantially differ from the ones used in more stable markets. Our theoretical angle is also meant to fuel a recent line of inquiry that focuses on the role of pace in IIEs and to extend scholars’ understanding of the role that leaders’ motivation plays in such environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.O.V. and E.S.; methodology, C.O.V. and E.S.; software, R.E.V.; validation, C.O.V.; formal analysis, C.O.V. and E.S.; data curation, R.E.V.; writing—original draft preparation, C.O.V.; writing—review and editing, E.S. and B.B.d.G.; visualization, C.O.V.; supervision, C.O.V., B.B.d.G. and R.E.V.; project administration, C.O.V.; funding acquisition, C.O.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The APC was funded by [Management Department, Isenberg School of Management, University of Massachusetts Amherst].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adner, Ron, and Rahul Kapoor. 2016. Innovation ecosystems and the pace of substitution, Re-examining technology S-curves. Strategic Management Journal 37: 625–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, Gautam, Curba Morris Lampert, and Vivek Tandon. 2008. Moving beyond Schumpeter, Management research on the determinants of technological innovation. Academy of Management Annals 2: 1–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, Jaideep, Louis Mulotte, and Charlotte R. Ren. 2016. Does experience imply learning? Strategic Management Journal 37: 1395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annosi, Maria Carmela, Antonella Martini, Federica Brunetta, and Lucia Marchegiani. 2020. Learning in an agile setting, A multilevel research study on the evolution of organizational routines. Journal of Business Research 110: 554–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argote, Linda, and Ella Miron-Spektor. 2011. Organizational learning: From experience to knowledge. Organization Science 22: 1123–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argote, Linda, Bill McEvily, and Ray Reagans. 2003. Managing knowledge in organizations: An integrative framework and review of emerging themes. Management Science 49: 571–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthurs, Jonathan D., Lowell W. Busenitz, Robert E. Hoskisson, and Richard A. Johnson. 2009. Signaling and initial public offerings: The use and impact of the lockup period. Journal of Business Venturing 24: 360–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, Judith, and Holger Patzelt. 2018. Incentives, resources and combinations of innovation radicalness and innovation speed. British Journal of Management 29: 691–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, Christopher B., and Jason P. Davis. 2012. Learning sequences: Their existence, effect, and evolution. Academy of Management Journal 55: 611–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, Christopher B., and Kathleen M. Eisenhardt. 2011. Rational heuristics: The ‘simple rules’ that strategists learn from process experience. Strategic Management Journal 32: 1437–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, Christopher B., Koen H. Heimeriks, Mario Schijven, and Stephen Gates. 2015. Concurrent learning: How firms develop multiple dynamic capabilities in parallel. Strategic Management Journal 36: 1802–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkinshaw, Julian, Gary Hamel, and Michael J. Mol. 2008. Management innovation. Academy of Management Review 33: 825–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudt, Kris, and James Thewissen. 2019. Jockeying for position in CEO letters: Impression management and sentiment analytics. Financial Management 48: 77–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresman, Henrik. 2013. Changing routines: A process model of vicarious group learning in pharmaceutical R&D. Academy of Management Journal 56: 35–61. [Google Scholar]
- Brockner, Joel, E. Tory Higgins, and Murray B. Low. 2004. Regulatory focus theory and the entrepreneurial process. Journal of Business Venturing 19: 203–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger-Helmchen, Thierry. 2007. From investment rules of thumb to routines: A real option approach. Problems and Perspectives in Management 6: 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cowden, Birton J., and Joshua S. Bendickson. 2018. Impacts of regulatory focus and institutions on innovation. Management Decision 56: 939–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzolino, Alessio, and Frank T. Rothaermel. 2018. Discontinuities, competition, and cooperation: Coopetitive dynamics between incumbents and entrants. Strategic Management Journal 39: 3053–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, Ellen, and E. Tory Higgins. 1997. Regulatory focus and strategic inclinations: Promotion and prevention in decision-making. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 69: 117–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyert, Richard, and James March. 1963. A Behavioral Theory of the Firm. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall. [Google Scholar]
- Dahlin, Kristina B., You-Ta Chuang, and Thomas J. Roulet. 2018. Opportunity, motivation, and ability to learn from failures and errors: Review, synthesis, and ways to move forward. Academy of Management Annals 12: 252–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, Tushar K., and Rajesh Kumar. 2010. Regulatory focus and opportunism in the alliance development process. Journal of Management 37: 682–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, Jason P., Kathleen M. Eisenhardt, and Christopher B. Bingham. 2009. Optimal structure, market dynamism, and the strategy of simple rules. Administrative Science Quarterly 54: 413–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rassenfosse, Gaétan, and Adam B. Jaffe. 2018. Are patent fees effective at weeding out low-quality patents? Journal of Economics & Management Strategy 27: 134–48. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, Vinit M. 2011. Mass media and massive failures: Determining organizational efforts to defend field legitimacy following crises. Academy of Management Journal 54: 263–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Guardo, Maria Chiara, and K. R. Harrigan. 2016. Shaping the path to inventive activity: The role of past experience in R&D alliances. Journal of Technology Transfer 41: 250–69. [Google Scholar]
- Drees, Johannes M., and Pursey Heugens. 2013. Synthesizing and extending resource dependence theory: A meta-analysis. Journal of Management 39: 1666–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmondson, Amy C., Richard M. Bohmer, and Gary P. Pisano. 2001. Disrupted routines: Team learning and new technology implementation in hospitals. Administrative Science Quarterly 46: 685–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, Jeffrey R. 1995. Alternatives to difference scores as dependent variables in the study of congruence in organizational research. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes 64: 307–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, Jeffrey R., and Lisa Schurer Lambert. 2007. Methods for integrating moderation and mediation: A general analytical framework using moderated path analysis. Psychological Methods 12: 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. 1989. Making fast strategic decisions in high-velocity environments. Academy of Management Journal 32: 543–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galinsky, Adam D., Geoffrey J. Leonardelli, Gerardo A. Okhuysen, and Thomas Mussweiler. 2005. Regulatory focus at the bargaining table: Promoting distributive and integrative success. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin 31: 1087–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamache, Daniel L., Gerry McNamara, Michael J. Mannor, and Russell E. Johnson. 2015. Motivated to acquire? The impact of CEO regulatory focus on firm acquisitions. Academy of Management Journal 58: 1261–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, Clark G. 2005. Unbundling the structure of inertia: Resource versus routine rigidity. Academy of Management Journal 48: 741–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grillitsch, Markus, Torben Schubert, and Martin Srholec. 2019. Knowledge base combinations and firm growth. Research Policy 48: 234–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haans, Richard F. J., Constant Pieters, and Zi-Lin He. 2016. Thinking about U: Theorizing and testing U and inverted U-shaped relationships in strategy research. Strategic Management Journal 37: 1177–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambrick, Donald C., Stephen E. Humphrey, and Abhinav Gupta. 2015. Structural interdependence within top management teams: A key moderator of upper echelons predictions. Strategic Management Journal 36: 449–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargadon, Andrew B., and Yellowlees Douglas. 2001. When innovations meet institutions: Edison and the design of the electric light. Administrative Science Quarterly 46: 476–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haunschild, Pamela R., Francisco Polidoro, Jr., and David Chandler. 2015. Organizational oscillation between learning and forgetting: The dual role of serious errors. Organization Science 26: 1682–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausman, Jerry A. 1978. Specification tests in econometrics. Econometrica 46: 1251–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, James J. 1979. Sample selection bias as a specification error. Econometrica 1: 153–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, Andrew M., and Frank T. Rothaermel. 2011. When are assets complementary? Star scientists, strategic alliances, and innovation in the pharmaceutical industry. Strategic Management Journal 32: 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, E. Tory, and Scott Spiegel. 2004. Promotion and prevention strategies for self-regulation: A motivated cognition perspective. In Handbook of Self-Regulation: Research Theory and Applications. Edited by Kathleen D. Vohs and Roy F. Baumeister. New York: Guilford Press, pp. 171–87. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, E. Tory. 1998. Promotion and prevention: Regulatory focus as a motivational principle. Advances in Experimental Social Psychology 30: 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hmieleski, Keith M., and Robert A. Baron. 2008. Regulatory focus and new venture performance: A study of entrepreneurial opportunity exploitation under conditions of risk versus uncertainty. Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal 2: 285–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, Sharon D., Michael J. Leiblein, and Shaohua Lu. 2013. How firms capture value from their innovations. Journal of Management 39: 1123–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, Russell E., Chu-Hsiang Chang, and Liu-Qin Yang. 2010. Commitment and motivation at work: The relevance of employee identity and regulatory focus. Academy of Management Review 35: 226–45. [Google Scholar]
- Kale, Prashant, and Harbir Singh. 2007. Building firm capabilities through learning: The role of the alliance learning process in alliance capability and firm-level alliance success. Strategic Management Journal 28: 981–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, Sarah, and Fiona Murray. 2010. Entrepreneurship and the construction of value in biotechnology. In Technology and Organization: Essays in Honour of Joan Woodward. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, Sarah, and Keyvan Vakili. 2015. The double-edged sword of recombination in breakthrough innovation. Strategic Management Journal 36: 1435–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keil, Thomas, Markku Maula, Henri Schildt, and Shaker A. Zahra. 2008. The effect of governance modes and relatedness of external business development activities on innovative performance. Strategic Management Journal 29: 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, Eric H., and Alok K. Chakrabarti. 1996. Innovation speed: A conceptual model of context, antecedents, and outcomes. Academy of Management Review 21: 1143–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Ji-Yub, and Anne S. Miner. 2007. Vicarious learning from the failures and near-failures of others: Evidence from the US commercial banking industry. Academy of Management Journal 50: 687–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, June-Young, Ji-Yub Kim, and Anne S. Miner. 2009. Organizational learning from extreme performance experience: The impact of success and recovery experience. Organization Science 20: 958–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W. Chan, and Renée Mauborgne. 2019. Nondisruptive creation: Rethinking innovation and growth. MIT Sloan Management Review 60: 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Laamanen, Tomi, and Thomas Keil. 2008. Performance of serial acquirers: Toward an acquisition program perspective. Strategic Management Journal 29: 663–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaj, Klodiana, Chu-Hsiang Chang, and Russell E. Johnson. 2012. Regulatory focus and work-related outcomes: A review and meta-analysis. Psychological Bulletin 138: 998–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, Dovev, Jingoo Kang, and Lori Rosenkopf. 2011. Balance within and across domains: The performance implications of exploration and exploitation in alliances. Organization Science 22: 1517–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, Erik E., and Nikolaus Seitz. 2016. Creativity and entrepreneurship: Culture, subculture and new venture creation. In The Global Management of Creativity. Edited by Marcus Wagner, Jaume Valls-Pasola and Thierry Burger-Helmchen. London: Routledge, pp. 117–40. [Google Scholar]
- Leiponen, Aija, and Constance E. Helfat. 2010. Innovation objectives, knowledge sources, and the benefits of breadth. Strategic Management Journal 31: 224–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levinthal, Daniel A., and James G. March. 1993. The myopia of learning. Strategic Management Journal 14: 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, Marvin B. 1987. The learning curve, diffusion, and competitive strategy. Strategic Management Journal 8: 441–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lind, Jo Thori, and Halvor Mehlum. 2010. With or without U? The appropriate test for a U-shaped relationship. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics 72: 109–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, James G., Lee S. Sproull, and Michal Tamuz. 1991. Learning from samples of one or fewer. Organization Science 2: 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaji, Serghei, William S. Schulze, and Julio O. De Castro. 2020. How long does it take to get to the learning curve? Academy of Management Journal 63: 205–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadkarni, Sucheta, Tianxu Chen, and Jianhong Chen. 2016. The clock is ticking! Executive temporal depth, industry velocity and competitive aggressiveness. Strategic Management Journal 37: 1132–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadolska, Anna, and Harry G. Barkema. 2014. Good learners: How top management teams affect the success and frequency of acquisitions. Strategic Management Journal 35: 1483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neukam, Marion, and Sophie Bollinger. 2022. Encouraging creative teams to integrate a sustainable approach to technology. Journal of Business Research 150: 354–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nye, Joseph S. 2004. Soft Power: The Means to Success in World Politics. Cambridge: Public Affairs. [Google Scholar]
- Nye, Joseph S. 2013. Hard, Soft, and Smart Power. Oxford: Oxford Handbooks. [Google Scholar]
- O’Grady, Shawna, and Henry W. Lane. 1996. The psychic distance paradox. Journal of International Business Studies 27: 309–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-de-Almeida, Gonçalo, Ashton Hawk, and Bernard Yeung. 2015. The right speed and its value. Strategic Management Journal 36: 159–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-de-Almeida, Gonçalo. 2010. Erosion, time compression, and self-displacement of leaders in hypercompetitive environments. Strategic Management Journal 31: 1498–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentland, Brian T., and Martha S. Feldman. 2008. Designing routines: On the folly of designing artifacts, while hoping for patterns of action. Information and Organization 18: 235–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothaermel, Frank T., and David L. Deeds. 2004. Exploration and exploitation alliances in biotechnology: A system of new product development. Strategic Management Journal 25: 201–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, Filipe M., and Kathleen M. Eisenhardt. 2009. Constructing markets and shaping boundaries: Entrepreneurial power in nascent fields. Academy of Management Journal 52: 643–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Peng, Michael Song, and Xiaofeng Ju. 2016. Entrepreneurial orientation and performance: Is innovation speed a missing link? Journal of Business Research 69: 683–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanock, Linda Rhoades, Benjamin E. Baran, William A. Gentry, Stacy Clever Pattison, and Eric D. Heggestad. 2010. Polynomial regression with response surface analysis: A powerful approach for examining moderation and overcoming limitations of difference scores. Journal of Business and Psychology 25: 543–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stettner, Uriel, and Dovev Lavie. 2014. Ambidexterity under scrutiny: Exploration and exploitation via internal organization, alliances, and acquisitions. Strategic Management Journal 35: 1903–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suarez, Fernando F., Stine Grodal, and Aleksios Gotsopoulos. 2015. Perfect timing? Dominant category, dominant design, and the window of opportunity for firm entry. Strategic Management Journal 36: 437–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, David J. 2000. Strategies for managing knowledge assets: The role of firm structure and industrial context. Long Range Planning 33: 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, David J. 2019. Strategic renewal and dynamic capabilities: Managing uncertainty, irreversibilities, and congruence. In Strategic Renewal: Core Concepts, Antecedents and Micro Foundations. Edited by Aybars Tuncdogan, Adam Lindgreen, Henk Volberda and Frans van den Bosch. London: Routledge, pp. 21–51. [Google Scholar]
- Triana, María del Carmen, Toyah L. Miller, and Tiffany M. Trzebiatowski. 2013. The double-edged nature of board gender diversity: Diversity, firm performance, and the power of women directors as predictors of strategic change. Organization Science 25: 609–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uotila, Juha, Markku Maula, Thomas Keil, and Shaker A. Zahra. 2009. Exploration, exploitation, and financial performance: Analysis of S&P 500 corporations. Strategic Management Journal 30: 221–31. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen, Freek, and Harry Barkema. 2002. Pace, rhythm, and scope: Process dependence in building a profitable multinational corporation. Strategic Management Journal 23: 637–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlas, Cristina O., Orlando C. Richard, Goce Andrevski, Alison M. Konrad, and Yang Yang. 2022. Dynamic capabilities for managing racially diverse workforces: Effects on competitive action variety and firm performance. Journal of Business Research 141: 600–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlas, Cristina O., Radu E. Vlas, William N. Robinson, and Youstina Masoud. 2023. How do external disruptions affect technological knowledge repository diversification? The role of repositories’ historical and social aspiration levels and knowledge footprint. Knowledge and Process Management 30: 110–21. [Google Scholar]
- Vlas, Radu E., and William N. Robinson. 2012. Two rule-based natural language strategies for requirements discovery and classification in open-source software development projects. Journal of Management Information Systems 28: 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volberda, Henk W., Frans AJ Van Den Bosch, and Cornelis V. Heij. 2013. Management innovation: Management as fertile ground for innovation. European Management Review 10: 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirtz, Bernd W., Alexander Mathieu, and Oliver Schilke. 2007. Strategy in high-velocity environments. Long Range Planning 40: 295–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfolds, Sarah E., and Jordan Siegel. 2019. Misaccounting for endogeneity: The peril of relying on the Heckman two-step method without a valid instrument. Strategic Management Journal 40: 432–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, Yasuhiro, Haibin Yang, and Zhiang John Lin. 2011. Exploration versus exploitation in alliance portfolio: Performance implications of organizational, strategic, and environmental fit. Research Policy 40: 287–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Haibin, Zhiang Lin, and Mike W. Peng. 2011. Behind acquisitions of alliance partners: Exploratory learning and network embeddedness. Academy of Management Journal 54: 1069–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayavaram, Sai, and Wei-Ru Chen. 2015. Changes in firm knowledge couplings and firm innovation performance: The moderating role of technological complexity. Strategic Management Journal 36: 377–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Bin, and Fernando Olivera. 2006. Error reporting in organizations. Academy of Management Review 31: 1012–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zollo, Maurizio, and Sidney G. Winter. 2002. Deliberate learning and the evolution of dynamic capabilities. Organization Science 13: 339–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).