Study of the “Oxidation-Complexation” Coordination Composite Ionic Liquid System for Dissolving Precious Metals
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Experimental Procedures
2.2.1. Preparation of Au@SiO2 Catalyst
2.2.2. Analysis of Metal Content in Gold Ore Powder, Waste CPU Pins, and Au@SiO2 Catalyst
2.2.3. General Metal Leaching Procedure by TCCA/N4441Cl
2.2.4. Metal Leaching from Catalyst by TCCA/N4441Cl
2.3. Characterization and Method
3. Results and Discussion
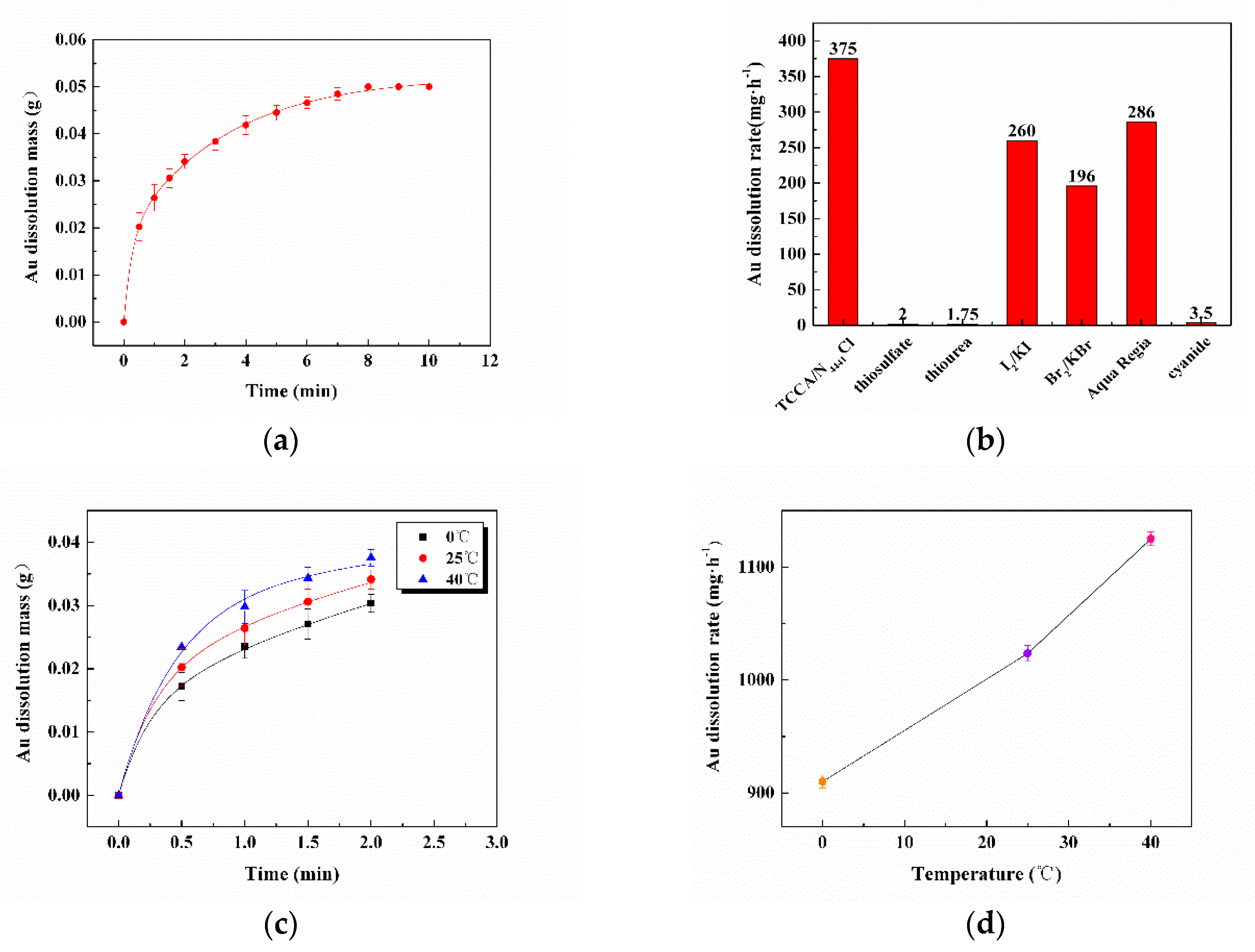
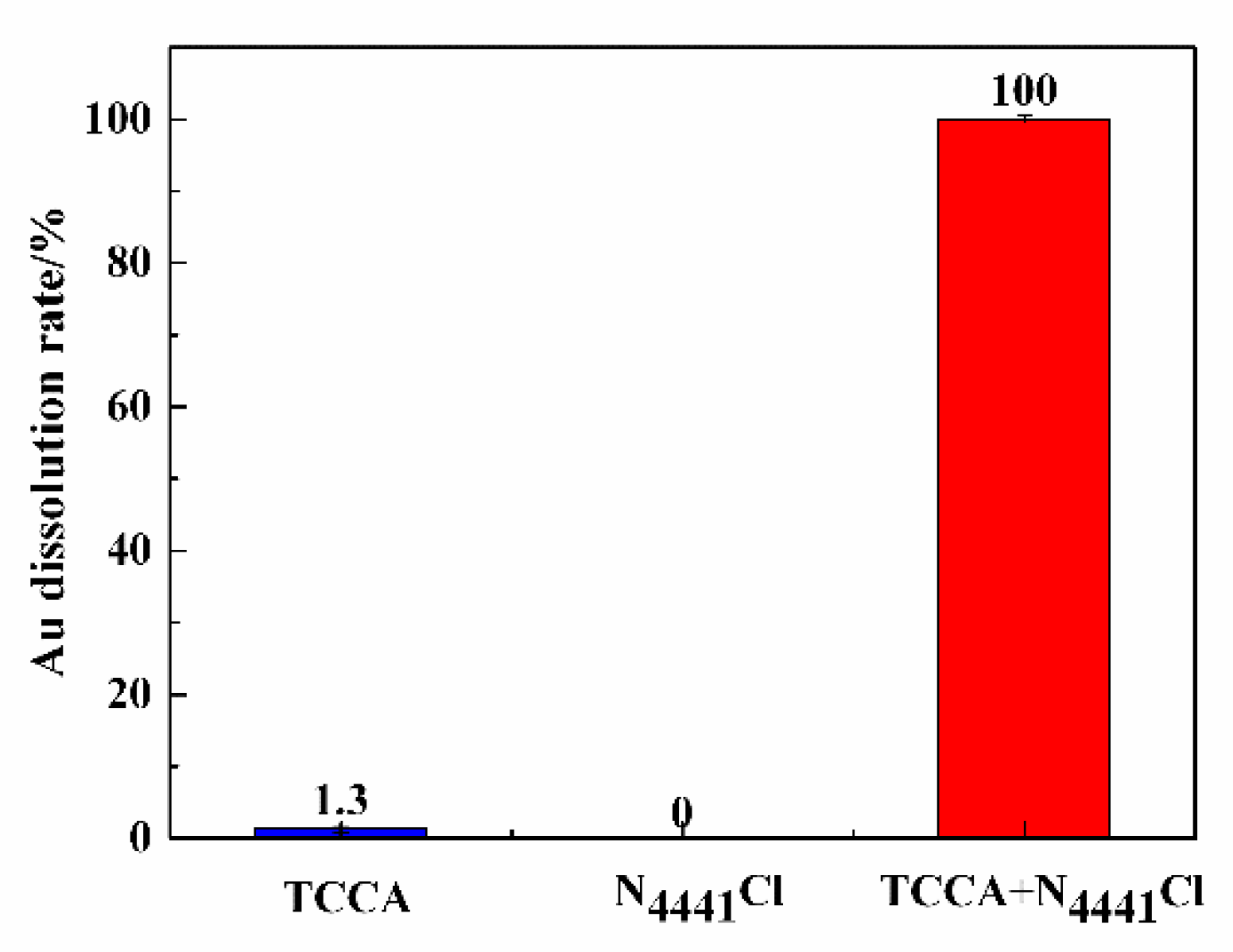
3.1. Metal Dissolving Effect of TCCA/N4441Cl
3.2. The Rate of Dissolving Gold
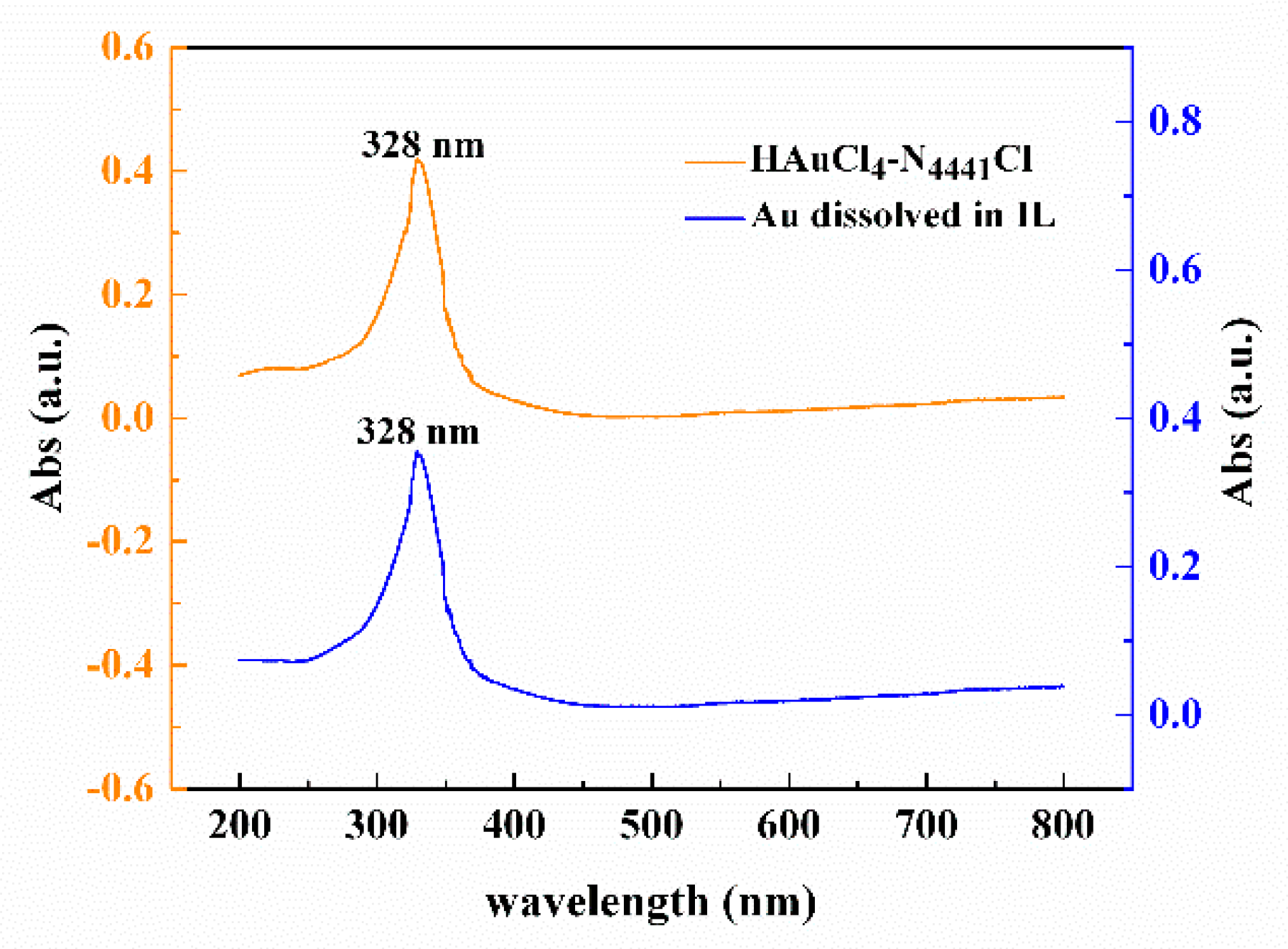
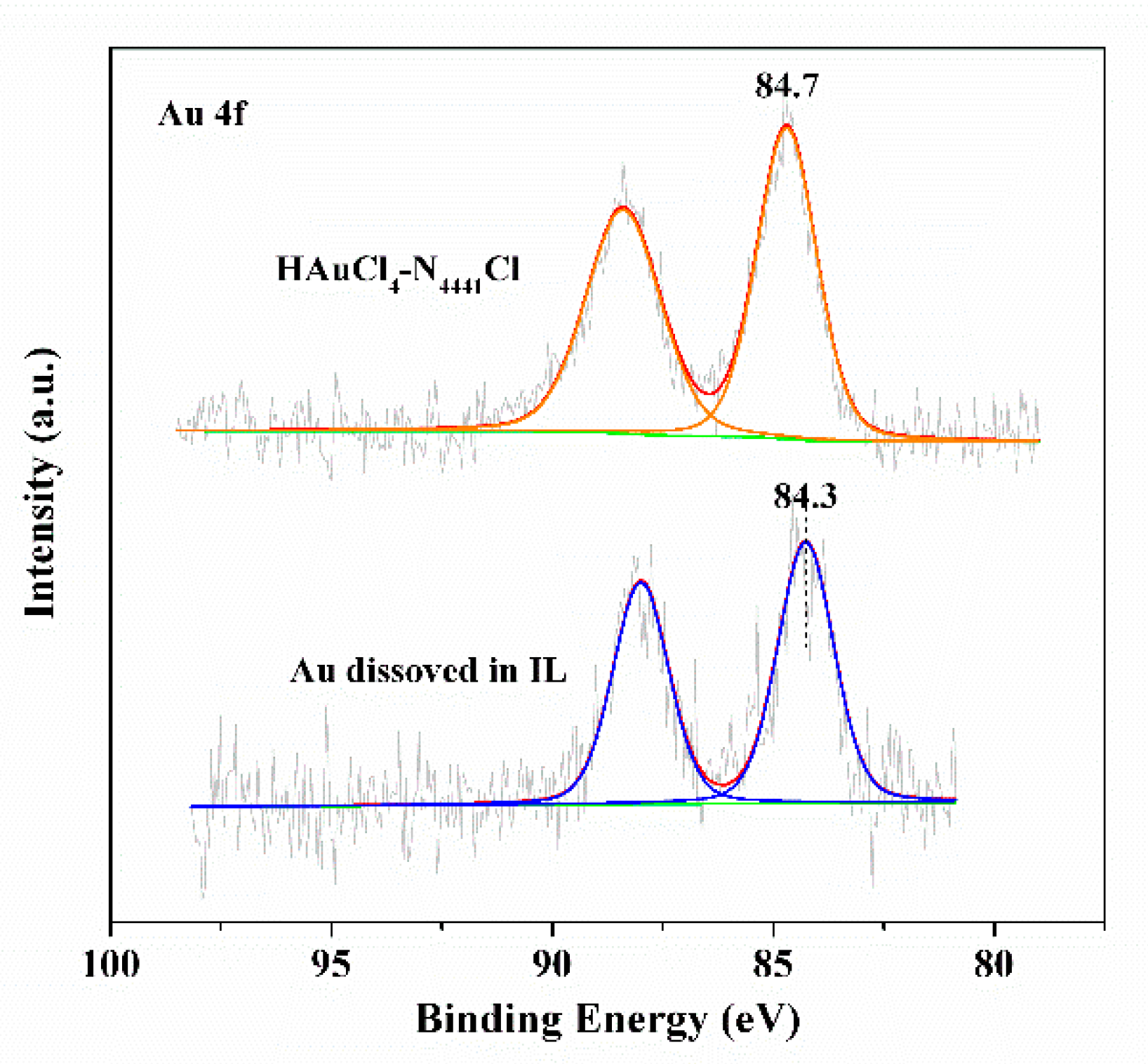
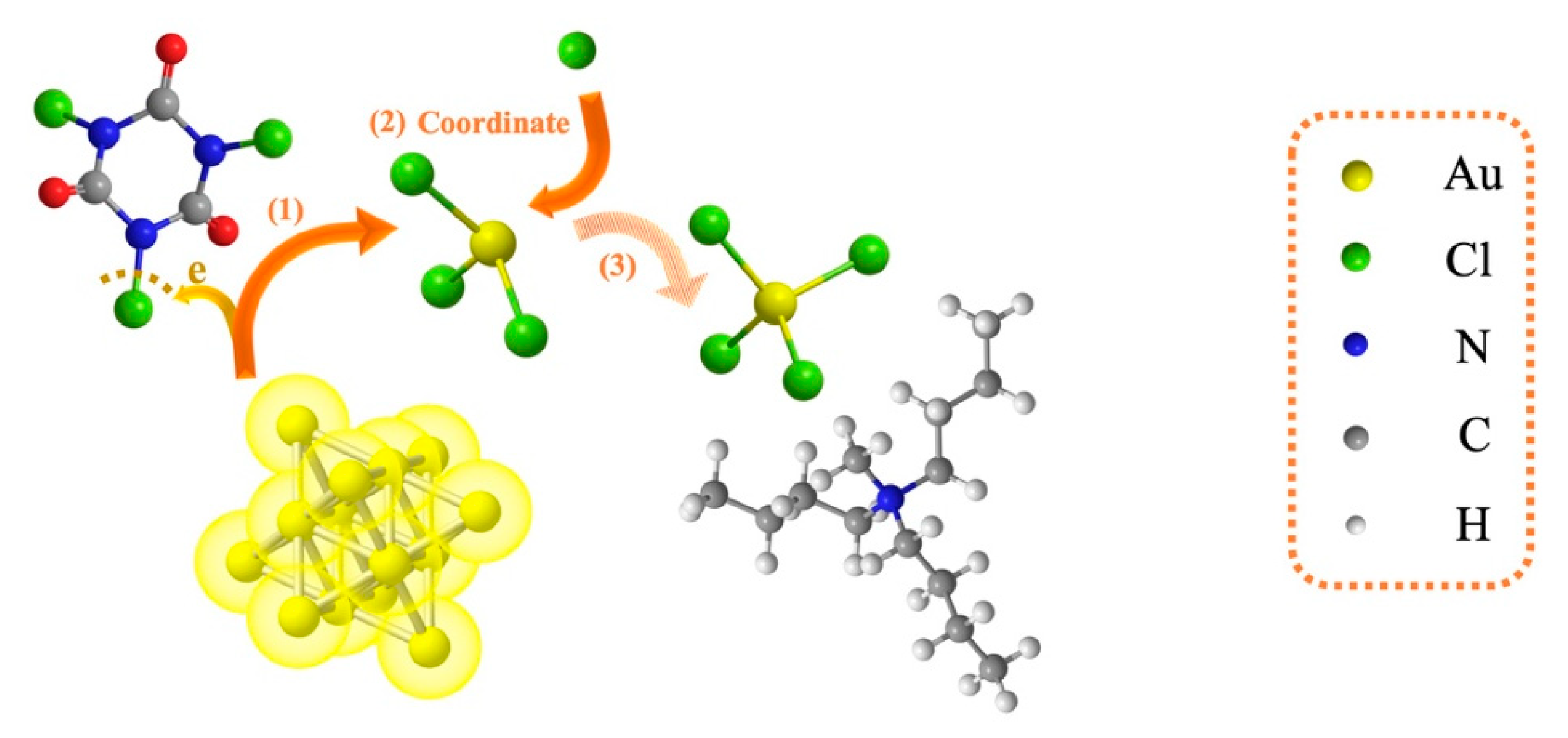
3.3. Reaction Mechanism
4. Application of Precious Metal Extraction
4.1. Extraction from Ores
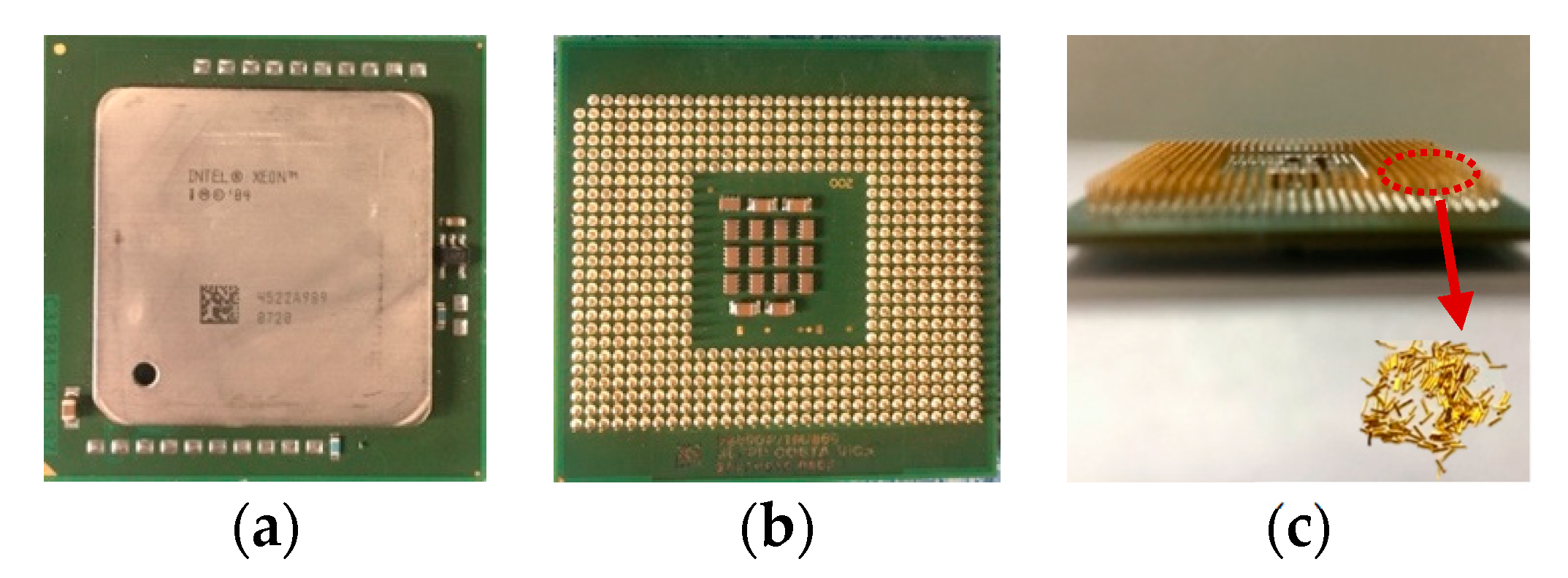
4.2. Extraction from WEEE
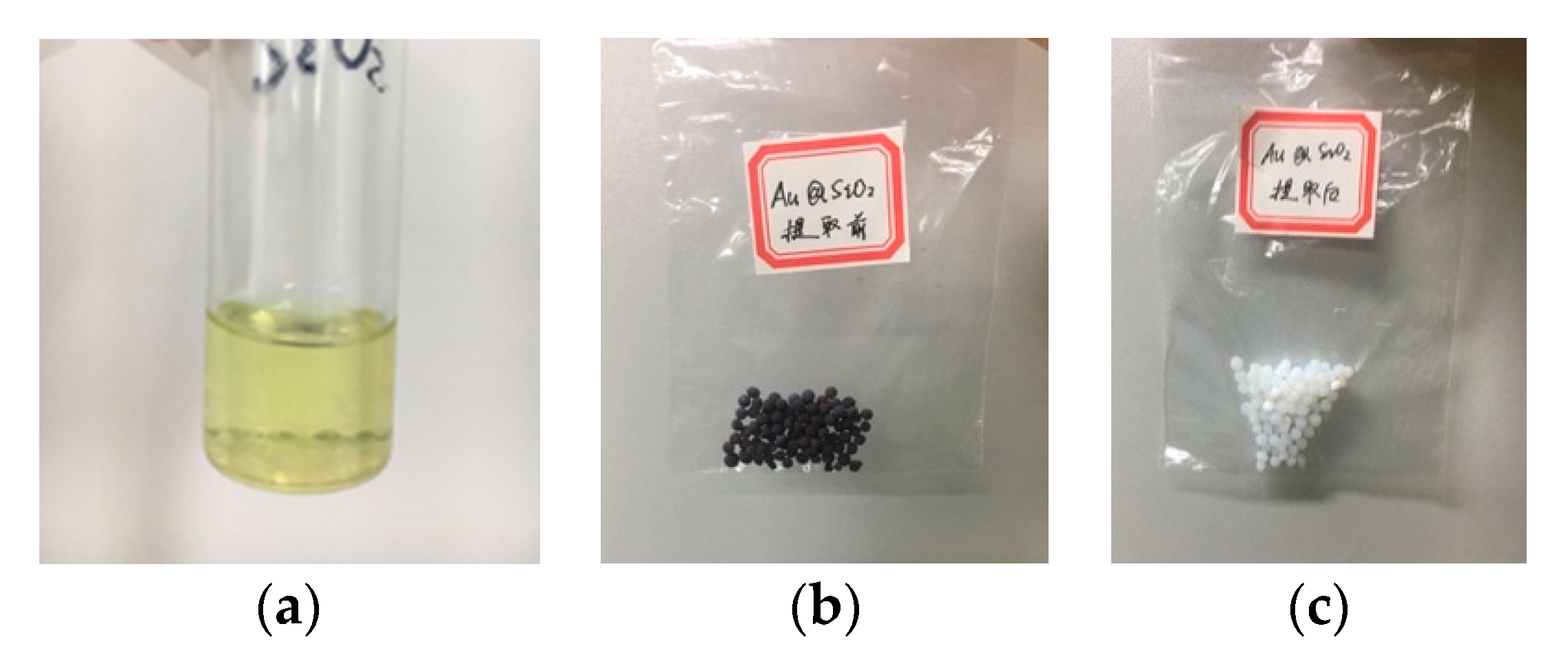
4.3. Extraction from Spent Catalyst
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, D.B. Biomining-Biotechnologies for extracting and recovering metals from ores and waste materials. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 30, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luque-Almagro, V.M.; Moreno-Vivián, C.; Roldán, M.D. Biodegradation of cyanide wastes from mining and jewellery industries. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2016, 38, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berners-Price, S.J.; Filipovska, A. Gold compounds as therapeutic agents for human diseases. Metallomics 2011, 3, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodson, J.R.; Parker, H.L.; García, A.M.; Hicken, A.; Asemave, K.; Farmer, T.J.; He, H.; Clark, J.H.; Hunt, A.J. Bio-derived materials as a green route for precious & critical metal recovery and re-use. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 1951–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Kato, M.; Okinaka, Y. Some recent developments in non-cyanide gold plating for electronics applications. Gold Bull. 2004, 37, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hughes, M.D.; Xu, Y.J.; Jenkins, P.; McMorn, P.; Landon, P.; Enache, D.I.; Carley, A.F.; Attard, G.A.; Hutchings, G.J.; King, F.; et al. Tunable gold catalysts for selective hydrocarbon oxidation under mild conditions. Nature 2005, 437, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G. A golden future. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansurov, Y.N.; Miklin, Y.A.; Miklin, N.A.; Nikol’skii, A.V. Methods and Equipment for Breaking Down Gold-Containing Concentrates from Lean Ores and Mining Industry Waste. Metallurgist 2018, 62, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Tang, H. Pyrometallurgical Recovery of Platinum Group Metals from Spent Catalysts. J. Met. 2017, 69, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willner, J.; Fornalczyk, A.; Cebulski, J.; Janiszewski, K. Preliminary studies on simultaneous recovery of precious metals from different waste materials by pyrometallurgical method. Arch. Metall. Mater. 2014, 59, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, A.K.; Hasan, M.; Mishra, Y.K.; Pandey, A.K.; Tiwary, B.N.; Kuhad, R.C.; Gupta, V.K.; Thakur, V.K. Environmentally sound system for E-waste: Biotechnological perspectives. Curr. Res. Biotechnol. 2019, 1, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzate, A.; López, M.E.; Serna, C. Recovery of gold from waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) using ammonium persulfate. Waste Manag. 2016, 57, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, K.; Beiggy, M.R.; Shirazi, A.G. Platinum recovery from a spent industrial dehydrogenation catalyst using cyanide leaching followed by ion exchange. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2004, 258, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altansukh, B.; Haga, K.; Ariunbolor, N.; Kawamura, S. Leaching and Adsorption of Gold from Waste Printed Circuit Boards Using Iodine-Iodide Solution and Activated Carbon. Eng. J. 2016, 20, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birloaga, I.; De Michelis, I.; Ferella, F.; Buzatu, M.; Vegliò, F. Study on the influence of various factors in the hydrometallurgical processing of waste printed circuit boards for copper and gold recovery. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingying, L.; Xiuli, X.; Wenquan, L. Thiourea leaching gold and silver from the printed circuit boards of waste mobile phones. Waste Manag. 2012, 32, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, M.; Akcil, A.; Erust, C.; Altynbek, S.; Gahan, C.S.; Tuncuk, A. A Potential Alternative for Precious Metal Recovery from E-waste: Iodine Leaching a Potential Alternative for Precious Metal Recovery from E-waste: Iodine Leaching. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, V.H.; Lee, J.; Huynh, T.H.; Jeong, J.; Pandey, B.D. Optimizing the thiosulphate leaching of gold from printed circuit boards of discarded mobile phone. Hydrometallurgy 2014, 149, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, K.N.; Boxall, J.A.; Lichtenthaler, R. Room temperature ionic liquids and their mixtures—A review. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2004, 219, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, A.E.; Swatloski, R.P.; Reichert, W.M.; Mayton, R.; Sheff, S.; Wierzbicki, A.; Davis, J.; Rogers, R.D. Task-specific ionic liquids for the extraction of metal ions from aqueous solutions. Chem. Commun. 2001, 135–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkenani, H.; Taher, M.A. Use of ionic liquid in simultaneous microextraction procedure for determination of gold and silver by ETAAS. Microchem. J. 2012, 103, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, V.M.; Djigailo, D.I.; Momotenko, D.S.; Chernyshov, D.V.; Torocheshnikova, I.I.; Smirnova, S.V.; Pletnev, I.V. Task-specific ionic liquid trioctylmethylammonium salicylate as extraction solvent for transition metal ions. Talanta 2010, 80, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, I.J.B.; Vasam, C.S. Metal-containing ionic liquids and ionic liquid crystals based on imidazolium moiety. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 3498–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheeren, C.W.; Machado, G.; Dupont, J.; Fichtner, P.F.P.; Ribeiro Texeira, S. Nanoscale Pt (O) particles prepared in imidazolium room temperature ionic liquids: Synthesis from an organometallic precursor, characterization, and catalytic properties in hydrogenation reactions. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 42, 4738–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wengert, M.; Sanseverino, A.M.; De Mattos, M.C.S. Trichloroisocyanuric acid: An alternate green route for the transformation of alkenes into epoxides. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2002, 13, 700–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tilstam, U.; Weinmann, H. Trichloroisocyanuric acid: A safe and efficient oxidant. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2002, 6, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Schmalz, C.; Zhou, J.; Zwiener, C.; Chang, V.W.C.; Ge, L.; Wan, M.P. An insight of disinfection by-product (DBP) formation by alternative disinfectants for swimming pool disinfection under tropical conditions. Water Res. 2016, 101, 535–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Zavala, A.; García-Gómez, J.; Gómez-Cortés, A. Study of the structure and selectivity of Pt-Au catalysts supported on Al2O3, TiO2, and SiO2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2000, 167, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, C.; Lamberg, P.; Lindberg, T. Practical way to quantify minerals from chemical assays at Malmberget iron ore operations—An important tool for the geometallurgical program. Miner. Eng. 2013, 49, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallas-Hulin, A.; Kotni, R.K.; Nielsen, M.; Kegnæs, S. Catalytic Oxidation of Allylic Alcohols to Methyl Esters. Top. Catal. 2017, 60, 1380–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Chen, M.; Shu, J.; Shirvani, M.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Sun, S.; Xu, Z.H.; Fu, K.; Chen, S. Copper and gold recovery from CPU sockets by one-step slurry electrolysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 213, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- System, M.; Pacławski, K.; Jaworski, W.; Streszewski, B.; Fitzner, K. Trends in Colloid and Interface Science XXIV. Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2011, 138, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Usher, A.; McPhail, D.C.; Brugger, J. A spectrophotometric study of aqueous Au (III) halide-hydroxide complexes at 25–80 °C. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2009, 73, 3359–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birich, A.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. Kinetic Investigation and Dissolution Behavior of Cyanide Alternative Gold Leaching Reagents. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

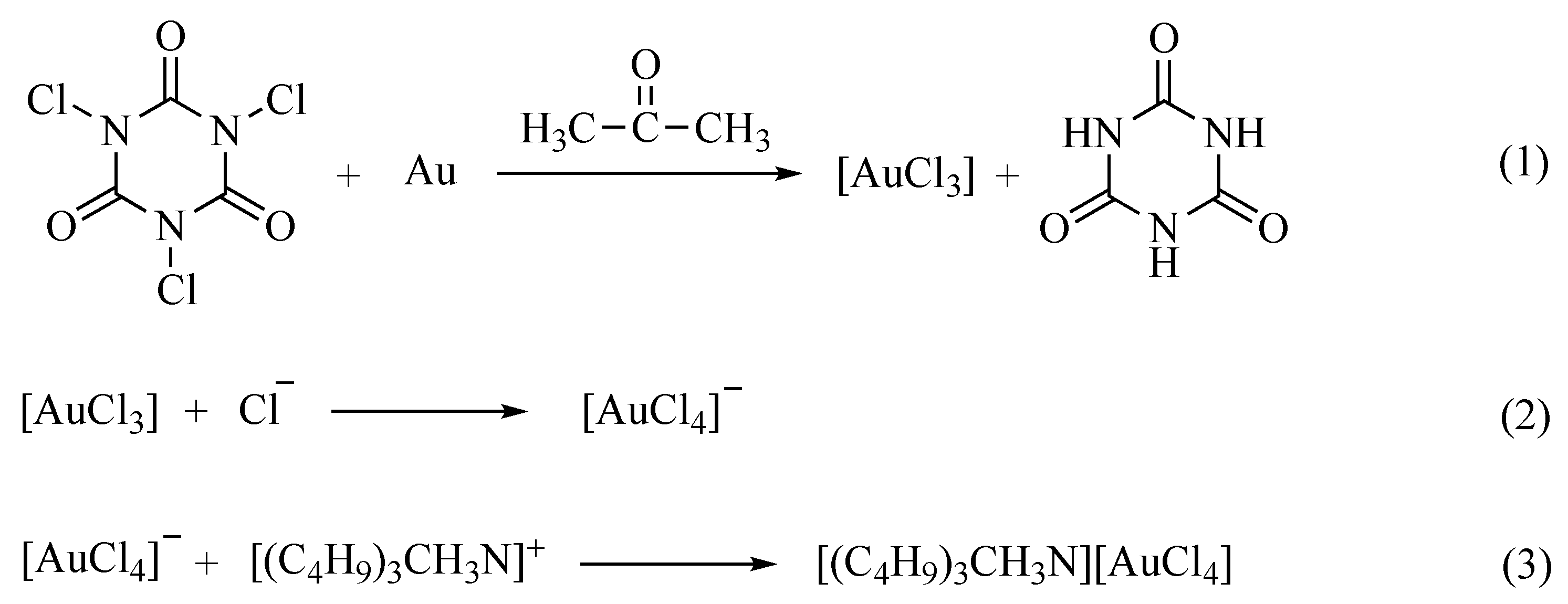


| Metal | Metal Mass/g | AAS Result/g | Leaching Yield/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Au | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100 |
| Pd | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100 |
| Cu | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100 |
| Ag | 0.01 | 0.01 | 100 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, F.; Sun, Y.; Rui, J.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, M.; Wei, L.; Lu, C.; Zhao, J.; et al. Study of the “Oxidation-Complexation” Coordination Composite Ionic Liquid System for Dissolving Precious Metals. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103625
Feng F, Sun Y, Rui J, Yu L, Liu J, Zhang N, Zhao M, Wei L, Lu C, Zhao J, et al. Study of the “Oxidation-Complexation” Coordination Composite Ionic Liquid System for Dissolving Precious Metals. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(10):3625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103625
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Feng, Yanxia Sun, Jiayao Rui, Lu Yu, Jiamei Liu, Ning Zhang, Mingxing Zhao, Linwei Wei, Chunshan Lu, Jia Zhao, and et al. 2020. "Study of the “Oxidation-Complexation” Coordination Composite Ionic Liquid System for Dissolving Precious Metals" Applied Sciences 10, no. 10: 3625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103625
APA StyleFeng, F., Sun, Y., Rui, J., Yu, L., Liu, J., Zhang, N., Zhao, M., Wei, L., Lu, C., Zhao, J., Zhang, Q., & Li, X. (2020). Study of the “Oxidation-Complexation” Coordination Composite Ionic Liquid System for Dissolving Precious Metals. Applied Sciences, 10(10), 3625. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10103625




