Motion Control and External Force Estimation of a Pneumatically Driven Multi-DOF Robotic Forceps
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
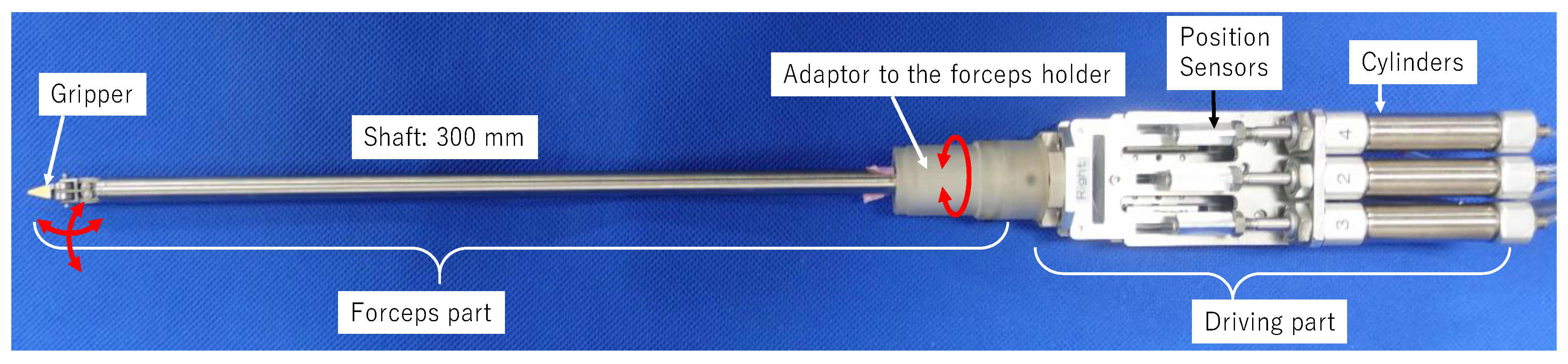
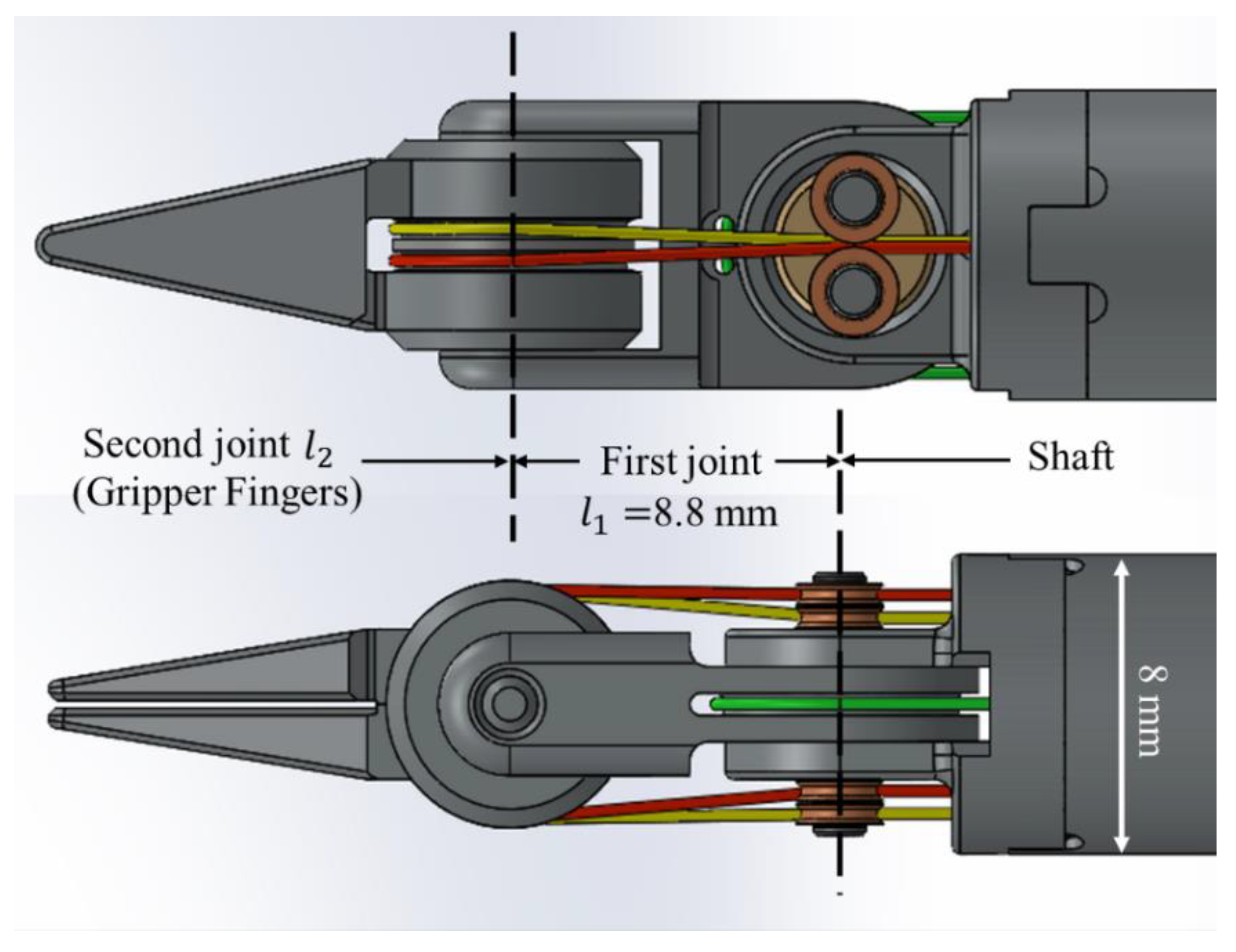
2. Pneumatically Driven Robotic Surgical Forceps
2.1. Overview of the Forceps
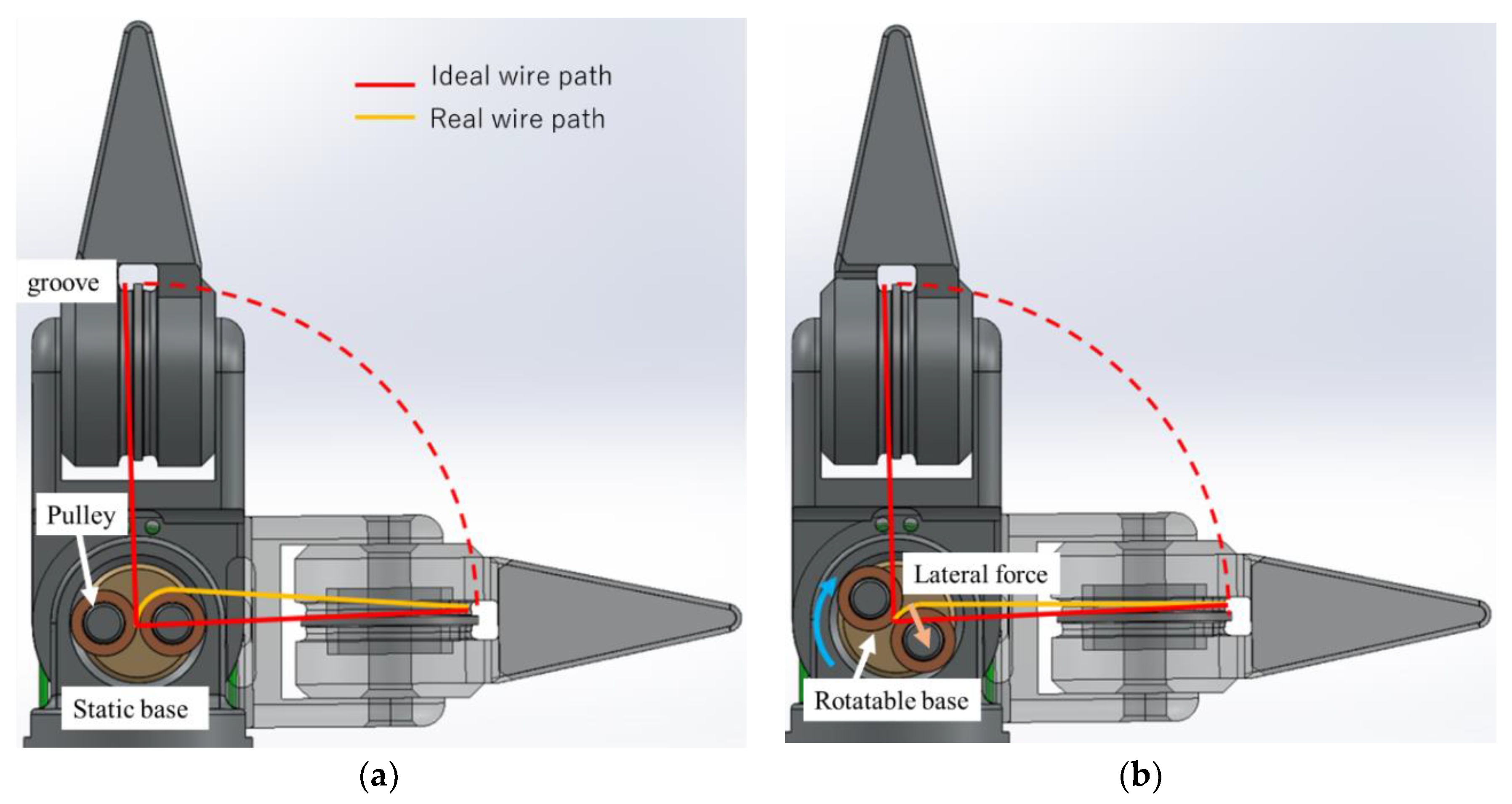
2.2. The Interference Reduction Mechanism
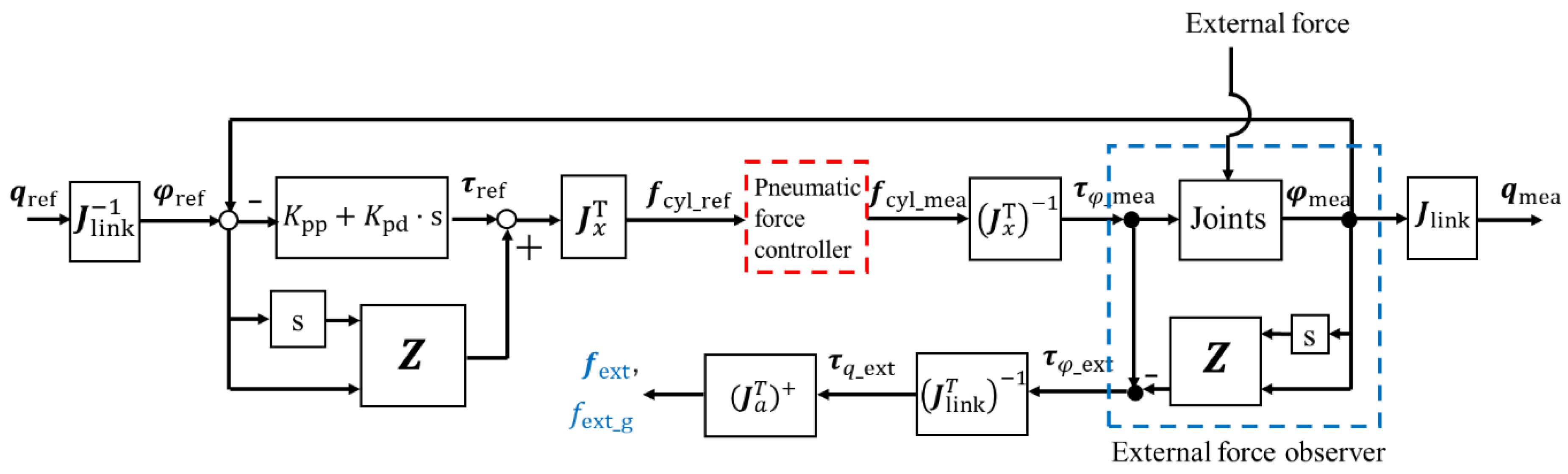
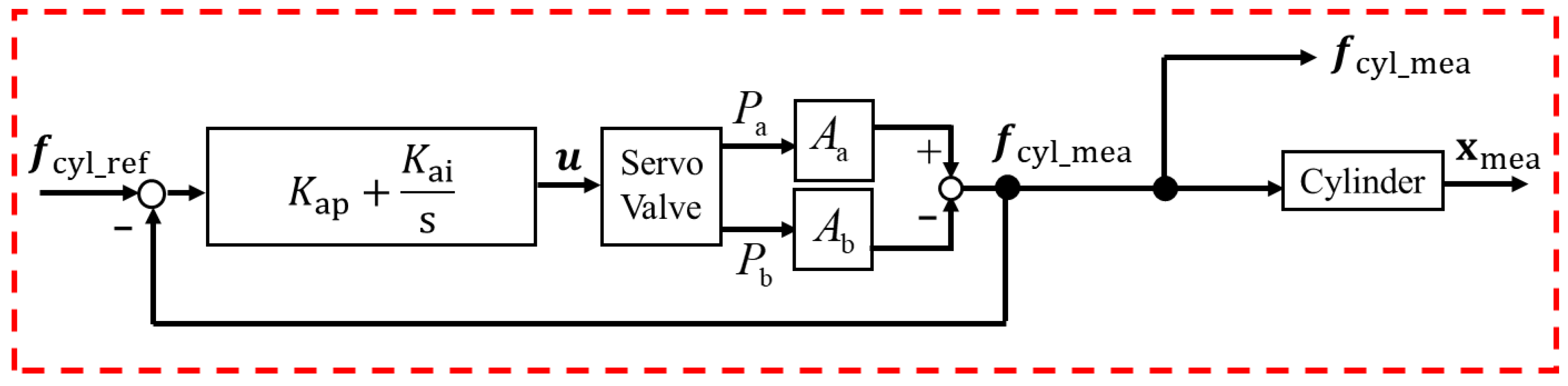
3. Control Scheme
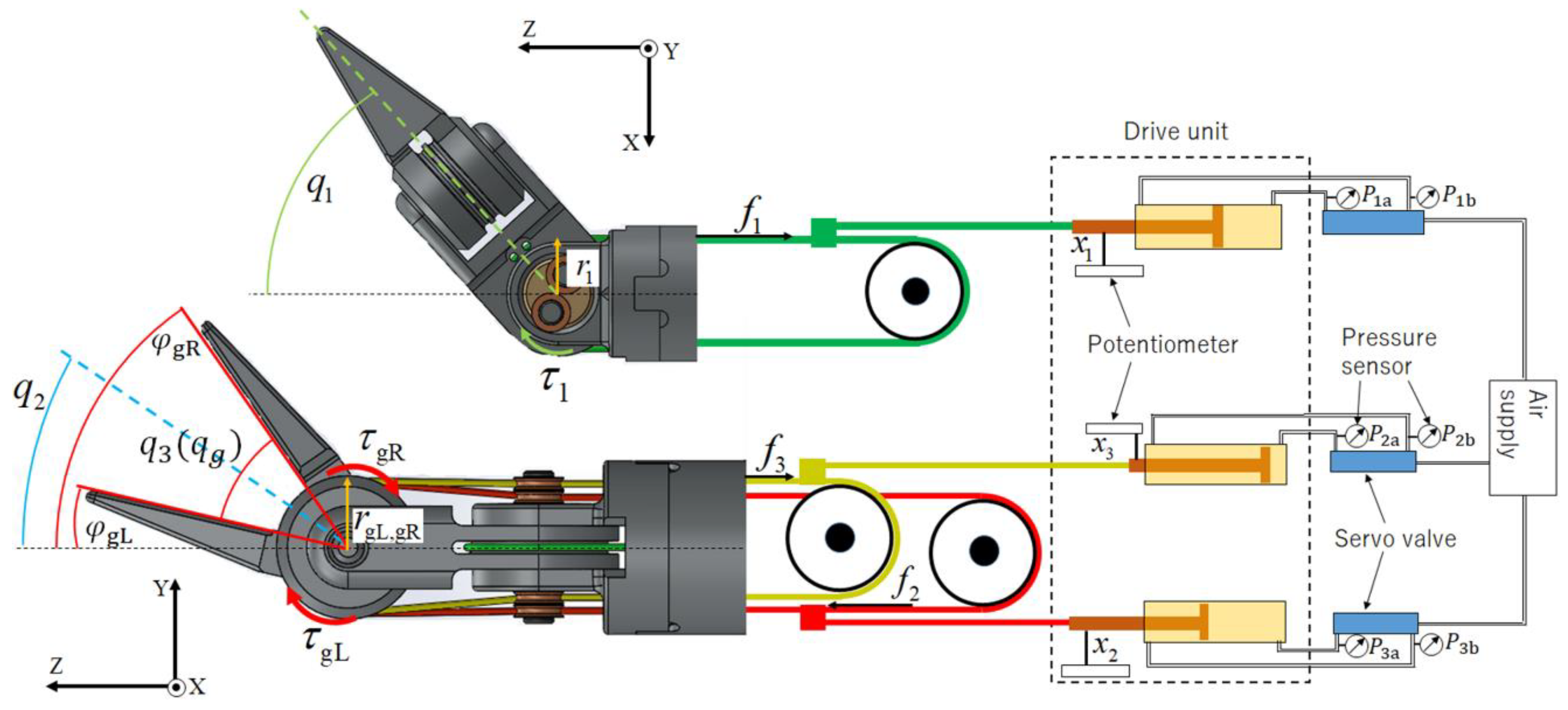
3.1. Kinematics
3.2. Dynamics
3.3. External Force Estimation
3.4. Control System
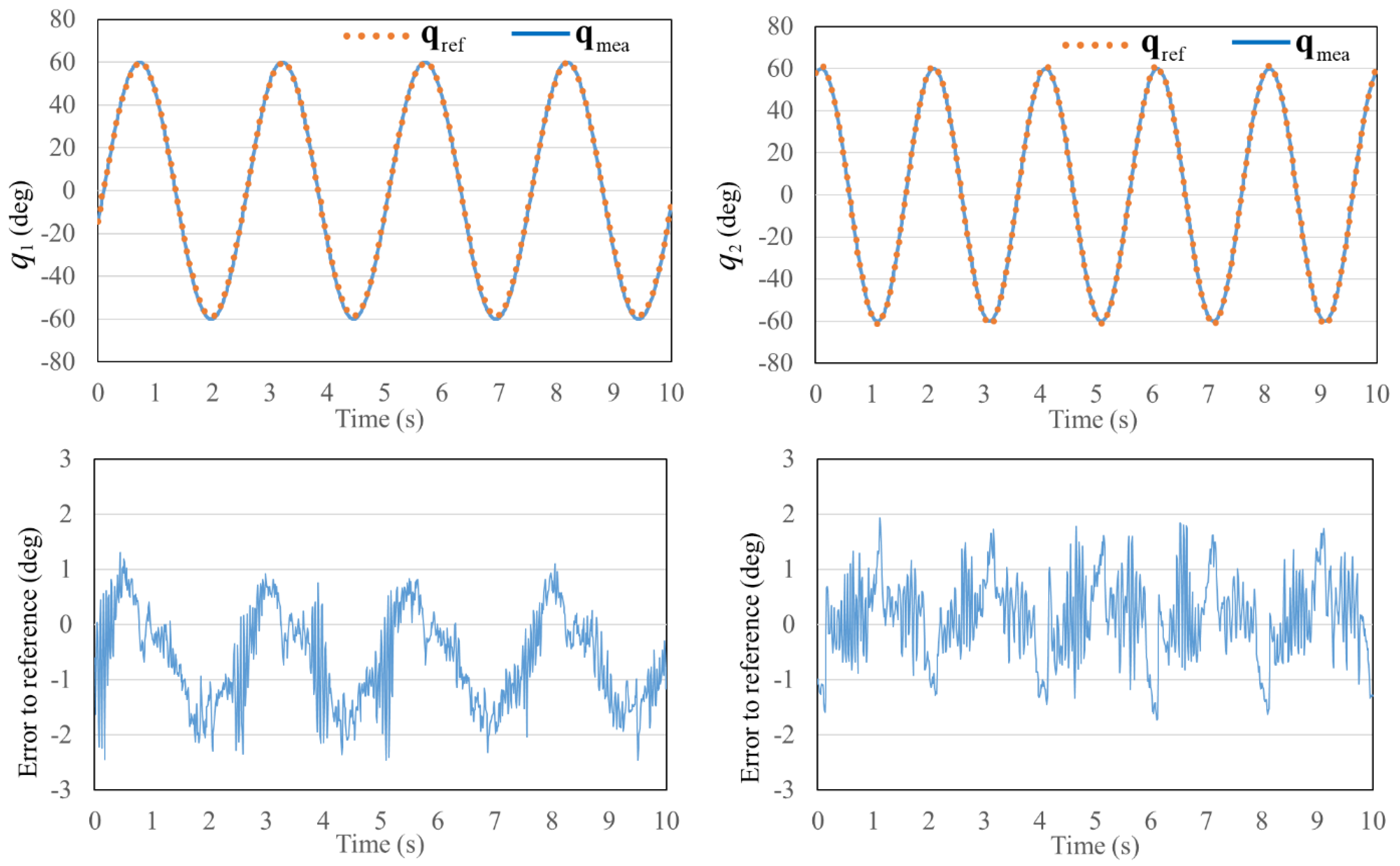
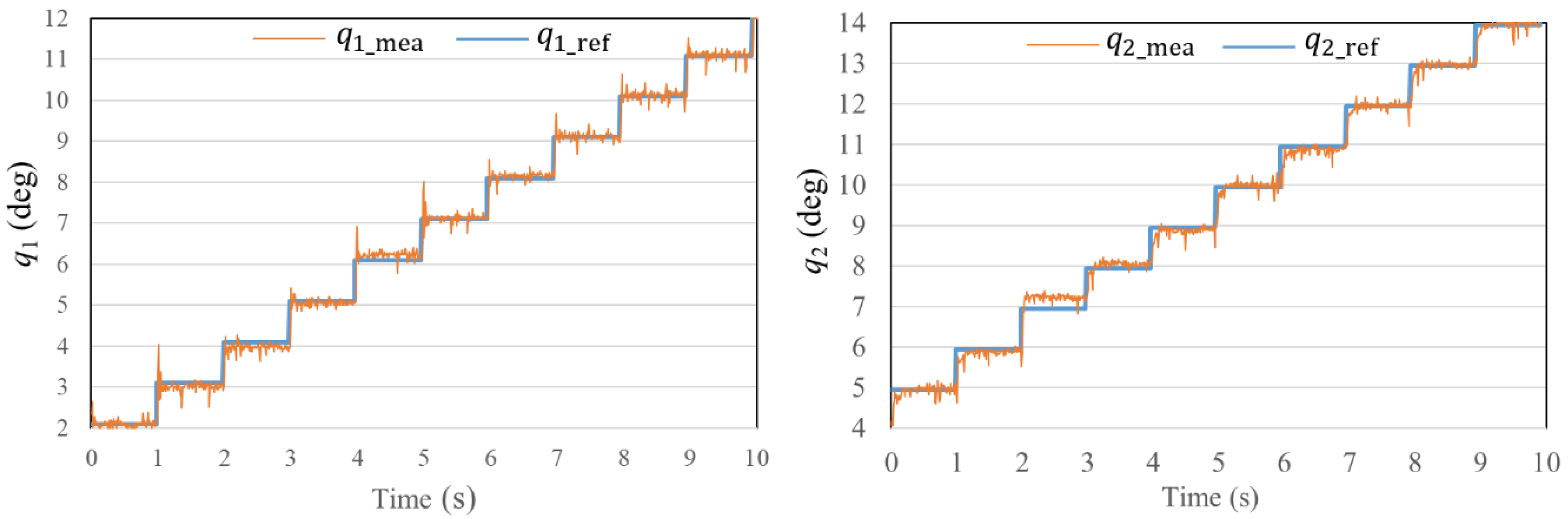
4. Performance Evaluation
4.1. Position Control Performance
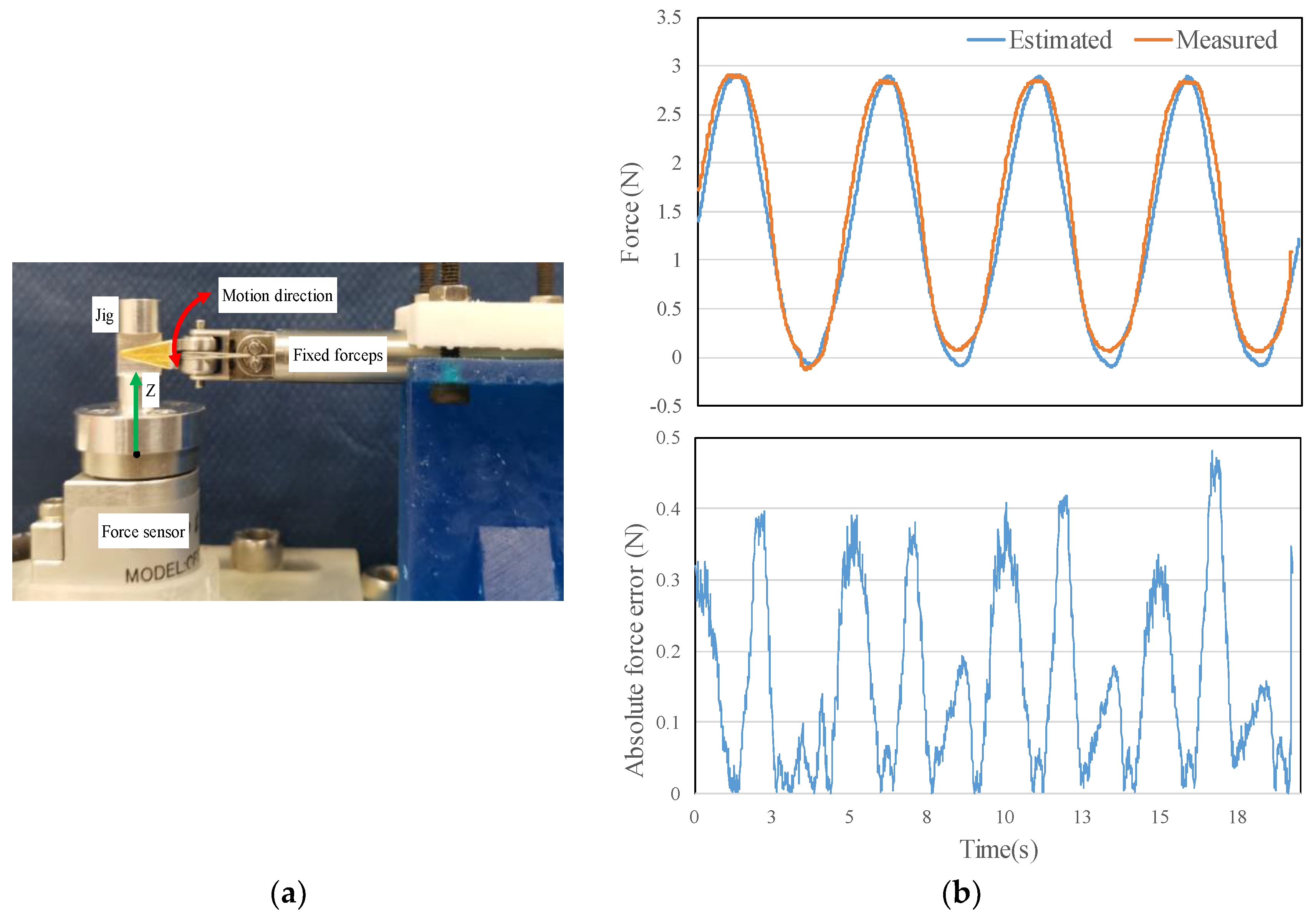
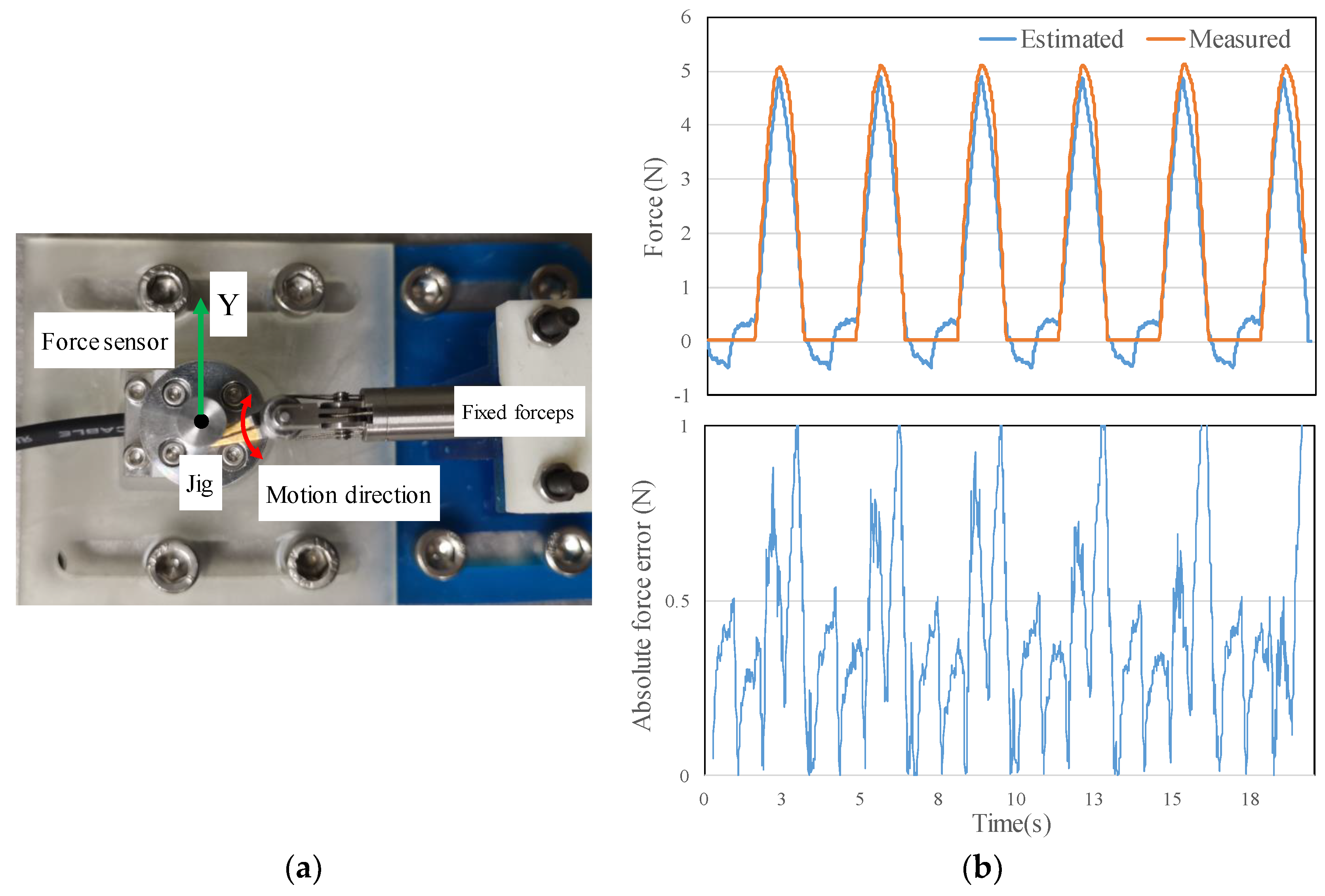
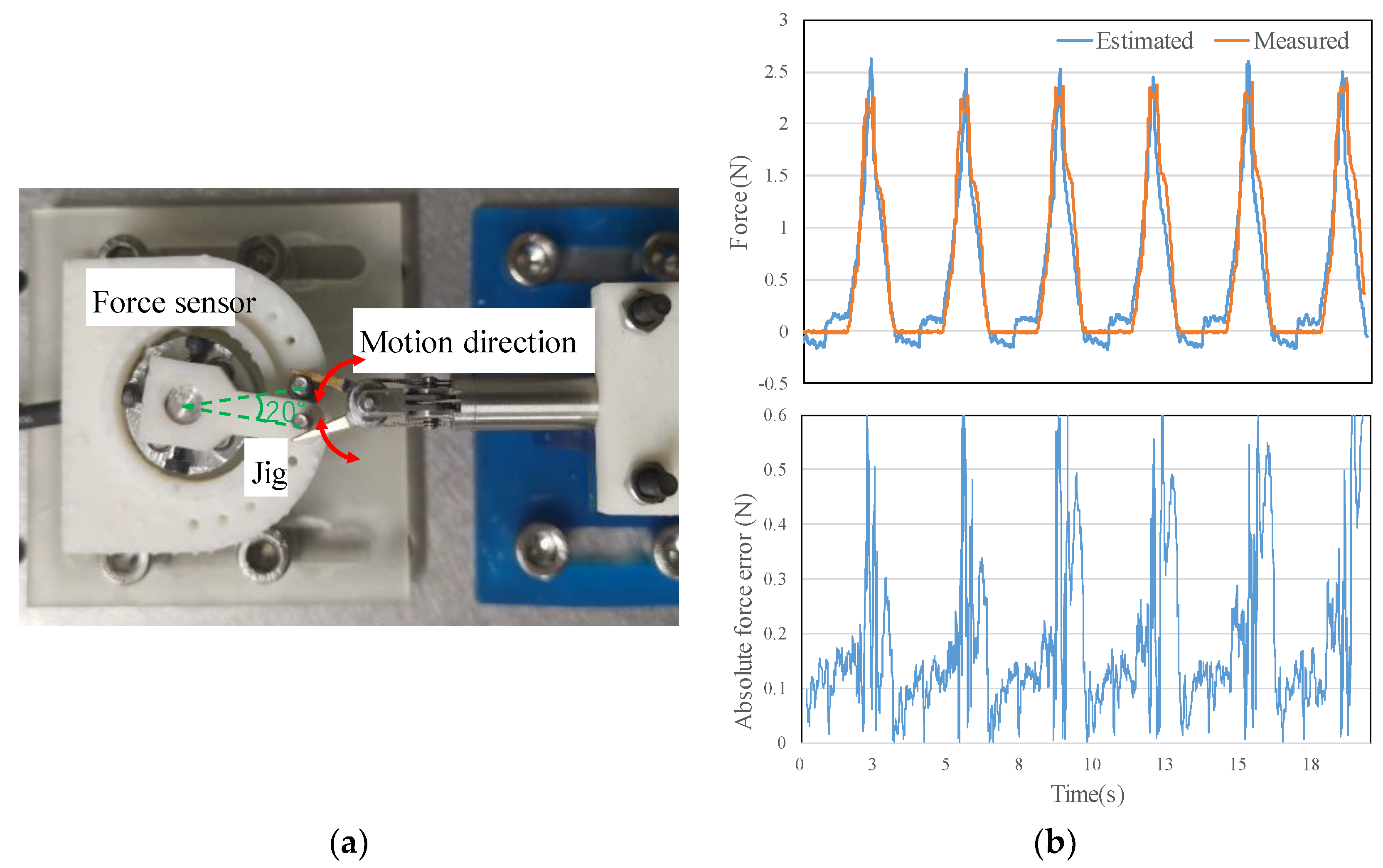
4.2. External Force Estimation Performance
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hu, J.C.; Gu, X.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Barry, M.J.; DAmico, A.V.; Weinberg, A.C.; Keating, N.L. Comparative effectiveness of minimally invasive vs. open radical prostatectomy. JAMA 2009, 302, 1557–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palep, J.H. Robotic assisted minimally invasive surgery. J. Minimal Access Surg. 2009, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, J. Development of the dexterous manipulator and the force sensor for minimally invasive surgery. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Autonomous Robots and Agents, Wellington, New Zealand, 10–12 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz, A.; Treratanakulchai, S.; Berthet-Rayne, P.; Yang, G.-Z. A Rolling-tip Flexible Instrument for Minimally Invasive Surgery; ICRA: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Horeman, T.; Dankelman, J.; Jansen, F.W.; van den Dobbelsteen, J.J. Assessment of laparoscopic skills based on force and motion parameters. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 85–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, M.; Dokko, D.; Okamura, A.M.; Yuh, D.D. Effect of sensory substitution on suture-manipulation forces for robotic surgical systems. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2005, 129, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokrollahi1, E.; Goldenburg, A.A.; Drak, J.M.; Eastwood, K.W.; Kang, M. Development and Control of a Magnetorheological Haptic Device for Robot Assisted Surgery. In Proceedings of the 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Seogwipo, Korea, 11–15 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz, E.; Carlos, M.; Salvador, C. Force Estimation for a Minimally Invasive Robotic Surgery System. U.S. Patent US9855662B2, 2 January 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, U.; Lee, D.-H.; Yoon, W.J.; Hannaford, B.; Choi, H.R. Force sensor integrated surgical forceps for minimally invasive robotic surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonenc, B.; Handa, J.; Gehlbach, P.; Taylor, R.H.; Iordachita, I. Design of 3-DOF force sensing micro-forceps for robot assisted vitreoretinal surgery. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, M.B.; Jo, Y.H. Design and evaluation of 2-DOF compliant forceps with force-sensing capability for minimally invasive robot surgery. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2012, 28, 932–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, H.; Warisawa, S.; Mitsuishi, M.; Arata, J.; Hashizume, M. Development of high dexterity minimally invasive surgical system with augmented force feedback capability. In Proceedings of the First IEEE/RAS-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Pisa, Italy, 20–22 February 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, U.; Kim, Y.B.; So, J.; Seok, D.-Y.; Choi, H.R. Sensorized surgical forceps for robotic-assisted minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 9604–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, D.Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Kim, U.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, H.R. Compensation of environmental influences on sensorized-forceps for practical surgical tasks. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2019, 4, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariyildiz, E.; Ohnishi, K. A guide to design disturbance observer, journal of dynamic systems. Meas. Control 2014, 136, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, R.; Kanno, T.; Kawashima, K. Pneumatically driven surgical instrument capable of estimating translational force and grasping force. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comp. 2019, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intuitive Surgical, Inc. The da Vinci ® Surgical System. Available online: http://www.intuitivesurgical.com/ (accessed on 10 March 2020).
- Jinno, M. Simple noninterference mechanism between the pitch and yaw axes for a wrist mechanism to be employed in robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery. ROBOMECH J. 2019, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu., K.; Simaan, N. Actuation compensaton for flexible surgical snake-like robots with redundant remote actuation. Proc. ICRA 2006, 4143–4148. [Google Scholar]
- Haraguchi, D.; Kanno, T.; Tadano, K.; Kawashima, K. Pneumatically Driven Surgical Manipulator with a Flexible Distal Joint Capable of Force Sensing. IEEE-ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2015, 6, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, M.; Okamura, A.; Bethea, B.; Gott, V.L.; Baumgartner, W.A. Analysis of suture manipulation forces for teleoperation with force feedback. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI, Tokyo, Japan, 25–28 September 2002; pp. 155–162. [Google Scholar]
- Tadano, K. Development of a Haptic Robot System for Laparoscopic Surgery. Ph.D. Thesis, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Tokyo, Japan, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Tadano, K.; Kawashima, K.; Kojima, K.; Tanaka, N. Development of a Pneumatic Surgical Manipulator IBIS IV. J. Robot. Mechatron. 2010, 2, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model Parameter | i = 1 | i = gL, gR |
|---|---|---|
| (mNm·s/rad) | 1.0 | 0.05 |
| (mNm) | 9.0 | 5.0 |
| - | 0.25 |
| Gain | i = 1 | i = gL, gR |
|---|---|---|
| (mNm/rad) | 200 | 150 |
| (mNm/rad) | 3.0 | 2.0 |
| (mNm/rad) | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| (mNm/rad) | 0.5 | 0.5 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, D.; Tadano, K.; Haraguchi, D. Motion Control and External Force Estimation of a Pneumatically Driven Multi-DOF Robotic Forceps. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113679
Zhou D, Tadano K, Haraguchi D. Motion Control and External Force Estimation of a Pneumatically Driven Multi-DOF Robotic Forceps. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(11):3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113679
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Dongbo, Kotaro Tadano, and Daisuke Haraguchi. 2020. "Motion Control and External Force Estimation of a Pneumatically Driven Multi-DOF Robotic Forceps" Applied Sciences 10, no. 11: 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113679
APA StyleZhou, D., Tadano, K., & Haraguchi, D. (2020). Motion Control and External Force Estimation of a Pneumatically Driven Multi-DOF Robotic Forceps. Applied Sciences, 10(11), 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113679





