Cathodic Protection Using Aluminum Metal in Chloride Molten Salts as Thermal Energy Storage Material in Concentrating Solar Power Plants
Abstract
:Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
- By adding Al metal into chloride molten salts (cathodic protection), the reduction potential of the alloy can be controlled. The most thermodynamically stable form of chromium in the alloys tested is hence the metallic chromium, meaning that selective oxidation of chromium in the Cr-containing alloys did not occur.
- This behavior can be explained by the formation of Al2O3 in the alloy surface which can generate a passivation layer and hence a reduction of the electrolysis current and lower corrosion rates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehos, M.; Turchi, C.; Vidal, J.; Wagner, M.; Ma, Z.; Ho, C.; Kolb, W.; Andraka, C.; Kruizenga, A. Concentrating Solar Power Gen3 Demonstration Roadmap; Technical Report; NREL: Golden, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Gomez-Vidal, J.; Bonk, A.; Bauer, T. Molten chloride salts for next generation CSP plants: Electrolytical salt purification for reducing corrosive impurity level. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 199, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabadi, B.A.T.; Weidner, J.W.; Garcia-Diaz, B.; Martinez-Rodriguez, M.; Olson, L.; Shimpalee, S. Modeling the Effect of Cathodic Protection on Superalloys Inside High Temperature Molten Salt Systems. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, C171–C179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, G.; Hou, J.; Zeng, C. Electrochemical Study of the Corrosion of a Ni-based Alloy GH3535 in Molten (Li,Na,K)F at 700°C. J. Fluor. Chem. 2015, 178, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zeng, C. Galvanic Corrosion of Pure Metals in Molten Fluorides. J. Fluor. Chem. 2014, 165, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Shi, H.; Xiu, Y.; Bonk, A.; Weisenburger, A.; Jianu, A.; Bauer, T. Molten chloride salts for next generation concentrated solar power plants: Mitigation strategies against corrosion of structural materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2018, 184, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumpelt, M.; Fischer, J.; Johnson, I. The Reaction of Magnesium Metal with Magnesium Chloride. J. Phys. Chem. 1968, 72, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrabadi, B.; Weidner, J.W.; Garcia-Diaz, B.; Martinez-Rodriguez, M.; Olson, L.; Shimpalee, S. Multidimensional Modeling of Nickel Alloy Corrosion inside High Temperature Molten Salt Systems. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2016, 163, C830–C838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Bonk, A.; Bauer, T. Corrosion behavior of metallic alloys in molten chloride salts for thermal energy storage in concentrated solar power plants: A review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2018, 12, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, A.G.; Cabeza, L.F. Corrosion evaluation of eutectic chloride molten salt for new generation of CSP plants. Part 1: Thermal treatment assessment. J. Energy Storage 2020, 27, 101125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisza, A. The capacitance of the diffuse layer of electric double layer of electrodes in molten salts. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 2315–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orazem, M.E. An integrated approach to electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7360–7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.L.; Wang, W.; Wu, W.T. Electrochemical impedance models for molten salt corrosion. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.G.; Cabeza, L.F. Anodic protection assessment using alumina forming alloys in chloride molten salt for CSP plants. Coatings 2020, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández, A.G.; Cabeza, L.F. Corrosion evaluation of eutectic chloride molten salt for new generation of CSP plants. Part 2: Materials screening performance. J. Energy Storage 2020, 29, 101381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.G.; Muñoz-Sanchez, B.; Maestre, J.N. Garcia-Romero, High temperature corrosion behavior on molten nitrate salt based nanofluid for CSP plants. Renew. Energy 2019, 130, 902–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Klammer, N.; Gomez-Vidal, J. Purification strategy and effect of impurities on corrosivity of dehydrated carnallite for thermal solar applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41664–41671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klammer, N.; Engtrakul, C.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Vidal, J. A method to determine MgO and MgOHCl in chloride molten salts. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 3598–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Orabona, N.E.; Dale, O.R.; Okabe, P.; Inman, C.; Simpson, M.F. Effect of Mg dissolution on cyclic voltammetry and open circuit potentiometry of molten MgCl2–KCl–NaCl candidate heat transfer fluid for concentrating solar power. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2019, 202, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Bonk, A.; Gussone, J.; Bauer, T. Electrochemical measurement of corrosive impurities in molten chlorides for thermal energy storage. J. Energy Storage 2020, 15, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
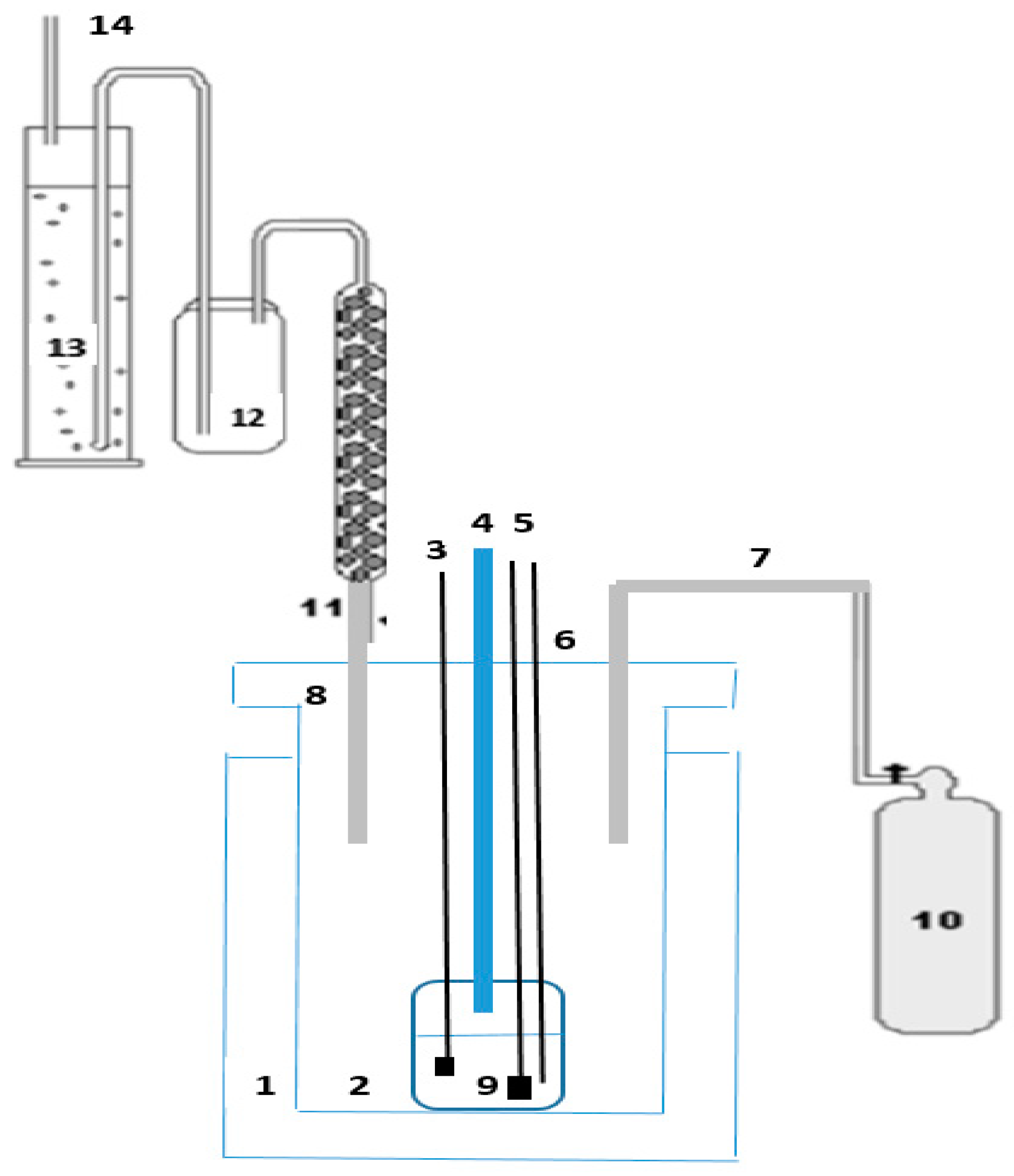
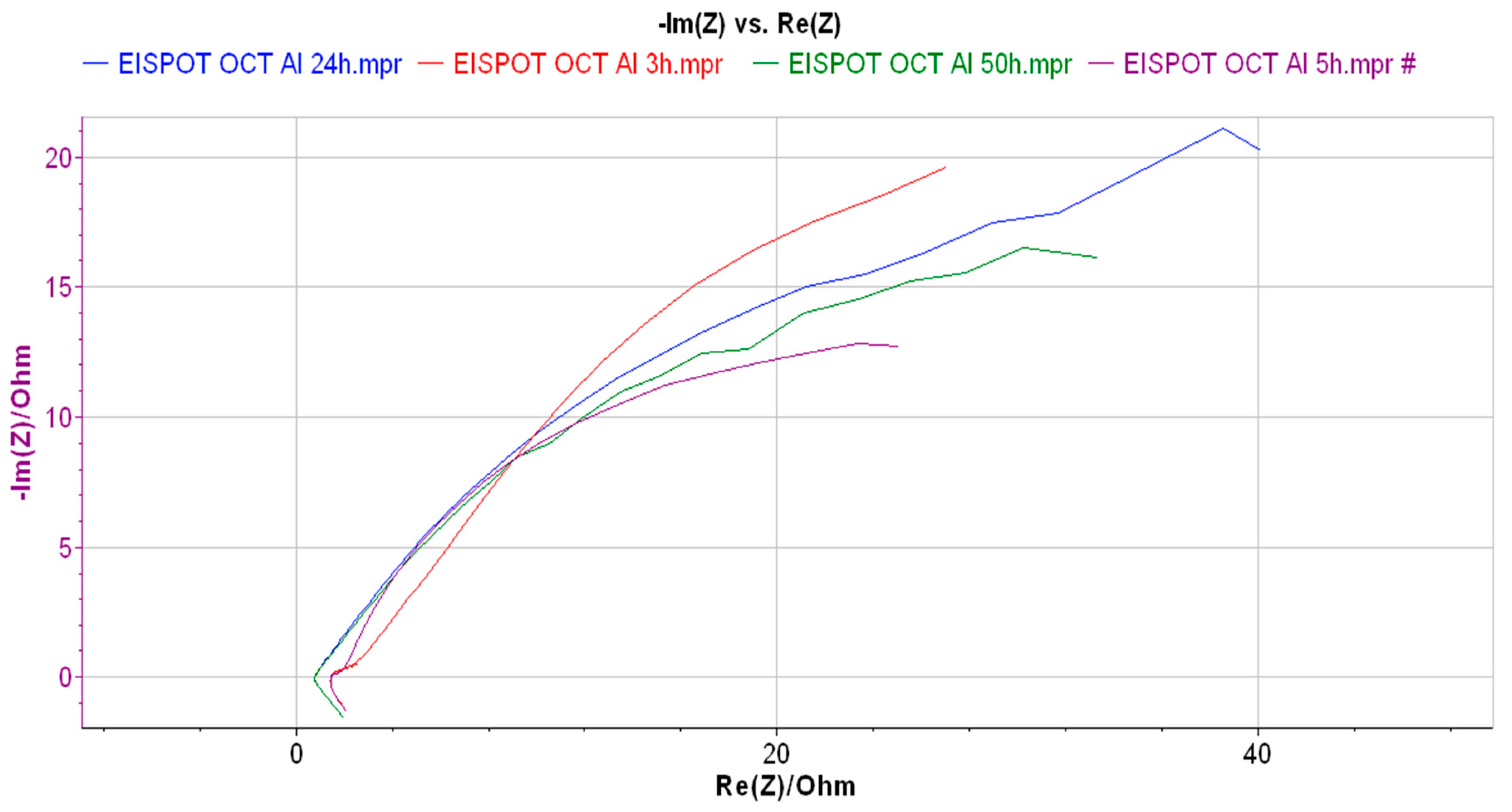
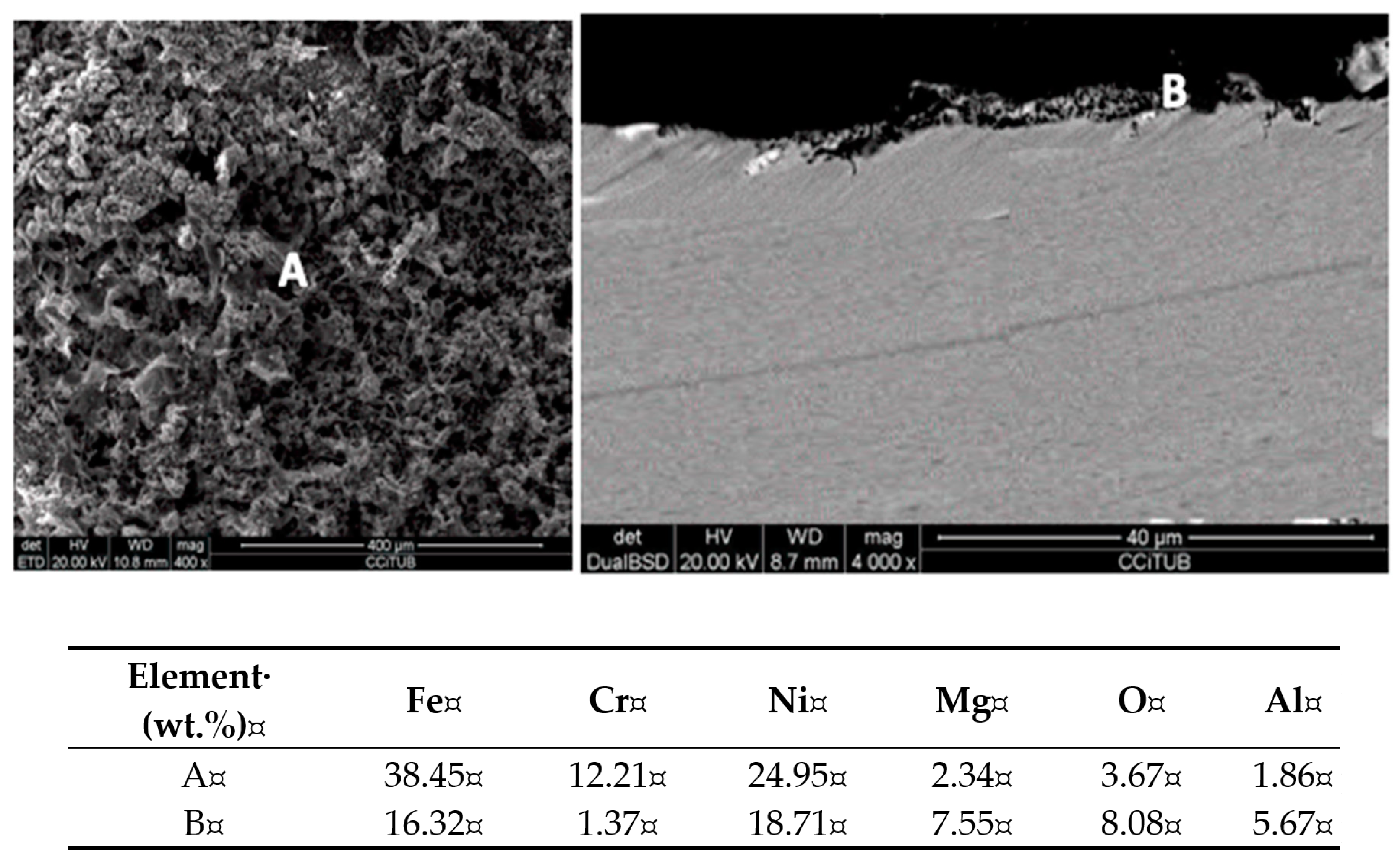



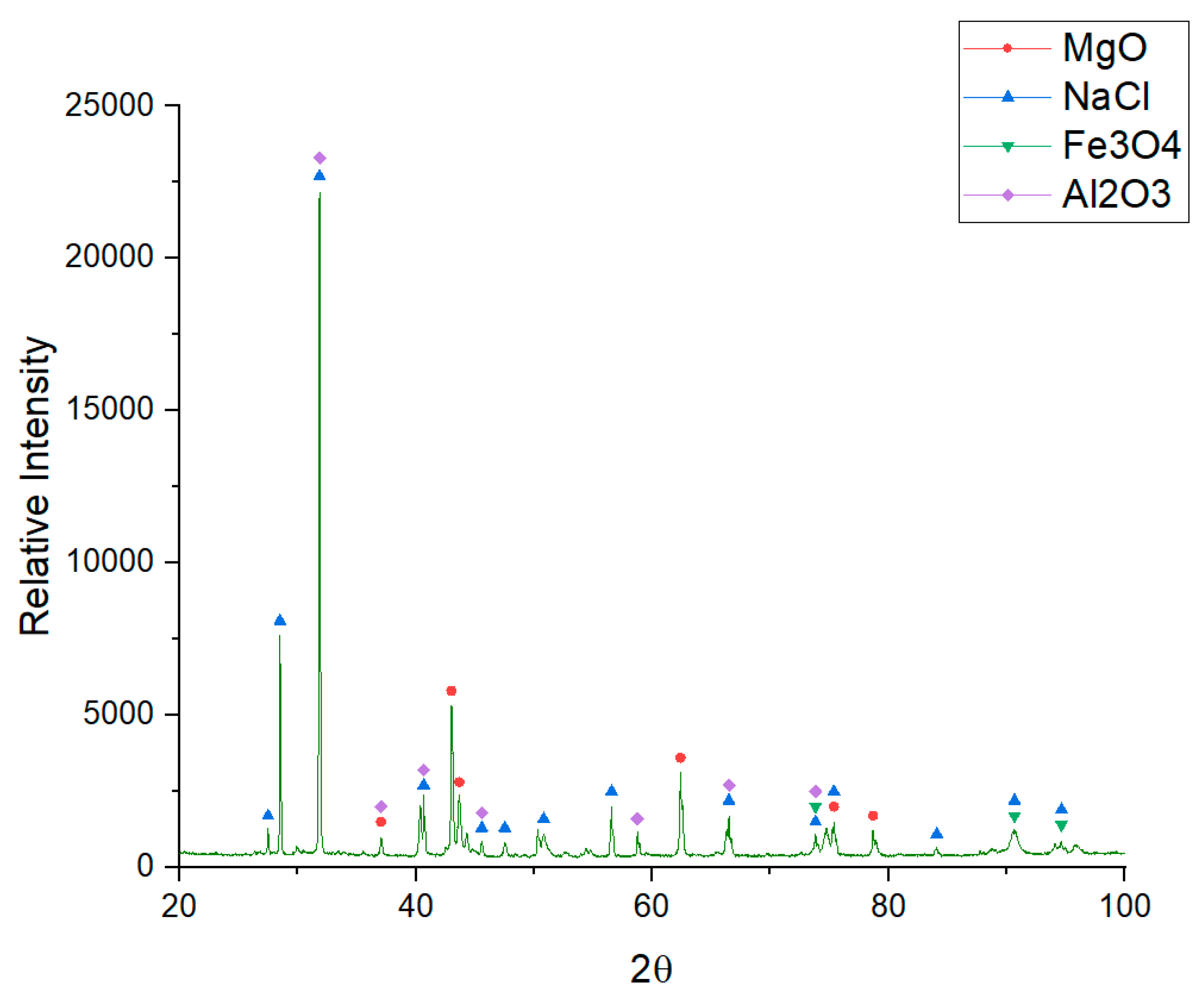
| Alloys | wt.% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nb | Mn | Cr | Ti | Co | Mo | Ni | Al | Fe | |
| OCT | 3 | - | 14 | 2 | - | - | 35 | 3 | Balance |
| HR224 | - | 0.5 | 20 | 0.3 | 2 | 0.5 | 47 | 3.8 | 27.5 |
| Element | R3 (Ohm) | Q1 (F/s) | R5 (Ohm) | Q2 (F/s) | R7 (Ohm) | Equivalent Circuit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 h | 1.507 | 0.325 | 36.21 | 0.183 | 59.45 | 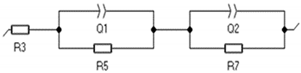 |
| 5 h | 1.561 | 0.243 | 15.56 | 0.289 | 232.07 | |
| 24 h | 0.853 | 0.007 | 0.06 | 0.056 | 63.56 | |
| 50 h | 0.855 | 0.079 | 32.9 | 0.477 | 167.8 |
| Element | R3 (Ohm) | Q1 (F/s) | R5 (Ohm) | Q2 (F/s) | R7 (Ohm) | Equivalent Circuit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 h | 1.762 | 0.272 | 2.39 | 0.098 | 37.89 | 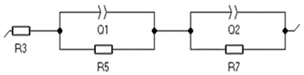 |
| 5 h | 1.896 | 2.508 | 15.55 | 0.072 | 27.39 | |
| 24 h | 1.968 | 0.073 | 24.98 | 1.536 | 18.04 | |
| 50 h | 2.051 | 0.171 | 63.14 | 0.130 | 8.101 |
| Alloys | Ecorr (mV) | Icorr (mA) | βc (mV) | βa (mV) | A (cm2) | CR (mm/y) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCT | −87.32 | 2098.62 | 280.8 | 465.6 | 4.20 | 4.37 |
| HR224 | −31.16 | 210.62 | 239.7 | 241.3 | 6.75 | 0.27 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernández, A.G.; Cabeza, L.F. Cathodic Protection Using Aluminum Metal in Chloride Molten Salts as Thermal Energy Storage Material in Concentrating Solar Power Plants. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113724
Fernández AG, Cabeza LF. Cathodic Protection Using Aluminum Metal in Chloride Molten Salts as Thermal Energy Storage Material in Concentrating Solar Power Plants. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(11):3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113724
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernández, Angel G., and Luisa F. Cabeza. 2020. "Cathodic Protection Using Aluminum Metal in Chloride Molten Salts as Thermal Energy Storage Material in Concentrating Solar Power Plants" Applied Sciences 10, no. 11: 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113724
APA StyleFernández, A. G., & Cabeza, L. F. (2020). Cathodic Protection Using Aluminum Metal in Chloride Molten Salts as Thermal Energy Storage Material in Concentrating Solar Power Plants. Applied Sciences, 10(11), 3724. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10113724






