Abstract
In this paper, new scientific insights in relation to the re-compaction of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC; Avicel®® PH-101) under specific compaction conditions are reported. MCC was subjected to multiple compaction cycles (1st, 2nd, and 3rd) under high compaction pressures, up to 20,000 kPa, using a roller compactor of 100 kg/h capacity. Initially, granules from the 1st and 2nd compaction cycles produced tablets with lower crushing strength compared to those made from the original non-compacted MCC. Tablet weakness was found to be correlated to the generation of a higher intra-granular pore size (diameter) and hence higher tablet porosity compared to that of the original MCC particles. Using Kawakita and Heckel compression analyses, it is suggested that such behavior is attributed to the formation of harder granules of re-compressed powder with a larger diameter than non-compacted MCC particles. Moreover, these granules resulted in a reduction in powder bed volume after the powders were subjected to the 1st and 2nd compaction cycles. Surprisingly, granules resulting from the 3rd compaction cycle produced tablets displaying a higher crushing force than non-compacted MCC. Results from compression analysis indicated a reduction in both the intra-granular pore size (diameter) and in tablet porosity of Avicel PH-101-3rd compaction cycle compared to that of the original non-compacted MCC. It is concluded that intense compression causes shedding of one or more layer from MCC fibers exposing new surfaces with strong binding ability. The foregoing results infer that intensified roller compaction can be employed to improve MCC powder compactibility without any deleterious effects on compact strength.
1. Introduction
Cellulose is a linear polymer which consists of hundreds to thousands of linked D-glucose units having β-(1-4)-glycosidic bonds with a general formula (C6H10O5)n. These units are inter-connected through hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces to form fibrils [1]. This polysaccharide is found in cells of all plants, in addition to hemicellulose, lignin, and other comparably small amounts of extractives. Cellulose exists in plant cells in the form of fibers with a high axial stiffness and which can be separated into nanocellulose fibers (NCF). This transformation can be carried out either by chemical or mechanical treatments; the former use enzymes or chemicals such as mineral acids e.g., sulfuric or hydrochloric acids, while the latter using mechanical stress methods such as ball milling or homogenization. These mechanical stressing methods may be preceded by chemical or enzymatic treatment as has been described by Nechyporchuck et al. [2]. However, these methods generally produce fibrils with different dimensions. The same transformation may occur during industrial processing that applies mechanical stress e.g., ball milling [3,4,5]. This structure renders the cellulose polymer with crystalline and amorphous parts. The balance between these two parts and the de-polymerization of the biopolymer have played a key role in the manufacturing of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) as the most widely used excipient in pharmaceutical applications [6,7,8]. MCC is manufactured by de-polymerization using acid hydrolysis (HCl or H2SO4) of α-cellulose obtained from the pulp of fibrous plant materials, such as cotton wool [9]. Hydrolysis in this manner produces a hydrocellulose which is subjected to filtration then to spray drying to form dry, porous particles of various sizes with increased crystallinity compared to the original raw cellulose [10]. The high recognition of MCC is attributed to its distinctive multifunction and direct compression features. From this perspective, MCC shows superiority with strong binding, flowability, and disintegrant characteristics and uniform particle size, in addition to compatibility with other excipients or drugs [11].
The motivation for using MCC in various solid dosage form preparations is its ability to be compressed and compacted, which is due to its extended porous structure, surface roughness, and plastic deformation [12]. High porosity results in a higher interior particle space which in turn facilitates higher compactibility in the resulted product. This is an advantage compared to other available non-cellulosic direct compression (DC) excipients used in pharmaceutical solid dosage form preparations [13,14]. For a plastically deforming material with such high porosity, an applied pressure facilitates bonding and interlocking between its differently sized and irregularly shaped particles [15,16,17,18]. This observation was outlined by Johansson et al. [19] who showed that the degree of deformation of MCC granules is substantially increased upon increasing their original intra-granular porosity.
Despite numerous benefits of MCC in compactibility of solid powders, a number of shortcomings in the processing of powder mixtures containing MCC exist. These are mostly related to MCC low bulk density, high sensitivity to lubrication, and loss of excipient functionality upon re-workability [20,21,22]. Low bulk density, which has been attributed to the highly porous structure of MCC, leads to a decrease in flowability [23]. This is regarded as a major processing drawback when preparing solid dosage forms because processing of powder mixtures containing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) must have a certain bulk density to facilitate their processing. Thus, volume reduction techniques through slugging or roller compaction are necessary. These processes may need to be repeated where such repetition causes a reduction in powder binding in compacts [24]. The majority of research on the workability of MCC has shown that the excipient loses its binding ability when the slugged or compacted powders are subjected to re-workability [25,26]. Furthermore, there is consensus among pharmaceutical technologists that re-compression of MCC after slugging should be avoided. The root cause of these shortcomings remains unknown. In this regard, the extent of dislocation generated at weak points of plastically deforming materials increases with increasing compaction pressure [27]. This suggestion was further extended to include a work hardening premise by Malkowska and Khan [28] who examined the re-compression properties of slugged MCC granules. In their hypothesis they suggested that after slugging the resistance of MCC granules to permanent deformation increases and this causes a decrease in surface bonding upon re-workability. A recent investigation by Patel et al. [29] confirmed that the effect of work hardening is predominantly responsible for the decrease in workability of slugged granules. Furthermore, they reported that their deduction was more insightful than the granule-size enlargement hypothesis reported by Sun and Himmelspach [30]. This proposal suggests that slugging at low compression/compaction pressures enables the formation of large granules which display a high degree of fragmentation. These fragments are made of individual MCC particles which have strong binding abilities and therefore maintain the strength of the tablets produced. As a result, small granules produced at higher compaction pressures have a lower extent of fragmentation and thus tablet strength is sharply reduced. Therefore, increasing the slugging pressure reduces the granule size and concurrently the specific surface area available for surface bonding.
Nevertheless, workability brings about major improvements in MCC flowability due to the increase in bulk density. However, the weakening in binding ability is a serious challenge to MCC reprocessing. In tests of multiple roller compaction of MCC powder, the binding ability of MCC was weakened further, thereby making material processing and handling more complicated [25,26,31].
Recently, roller compaction has been tested under high pressure conditions and/or under multi-compaction processing for the modification of non-DC excipients in order to convert them into materials exhibiting excellent binding properties [32,33,34,35]. Such high compaction operating conditions have been found to successfully produce DC excipients from starch, lactose, and chitin.
The present work was carried out to test the reworking of MCC powder when subjected to high compaction force using a multiple roller compaction process to overcome the serious challenges outlined above. Powder properties and compression analysis were utilized to assist in the understanding of changes contributing to weakening or hardening of the produced tablets.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
A sample of MCC (Avicel®® PH-101) tested according to Ph Eur., and supplied by FMC BioPolymer (FMC BioPolymer, Philadelphia, PA, USA) with a d(0.5) = 40–75 μm and moisture content of 4.115% (w/w) as per the material specification data sheet supplied by the manufacturer was used.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of Avicel PH-101 powder
Roller Compaction
Five kilograms of pure Avicel PH-101 was compacted using a production scale roller compactor (TFC-520 Roller Compactor, Vector Corporation, Freund Group Company, Marion, IA, USA). Compaction parameters were used under high pressure conditions, i.e., compaction pressure of 20,000 kPa, a roll gap of 2.0 mm, and the ratio of screw to roller speed was fixed at 5. Compaction was repeated using the same sample up to three times. The sheets produced were initially collected in a container then scooped into a Quadro mill (Vector Corporation, Freund Group Company, Marion, IA, USA) equipped with a 2000 μm sieve. Milling was run continuously for 15–20 min until all of the roller-compacted material had been ground into a powder. Analyses were performed on the materials collected downstream of the sieve. All cellulose samples were preserved in well-sealed desiccators containing silica gel. The water content of the MCC powder was between 3.972 and 4.103% (w/w) when tested prior to use, as ascertained using a Karl Fischer volumetric titrator (Mettler Toledo, Hamburg, Germany).
Ball Milling
An amorphous form of Avicel PH-101 was prepared by ball milling process. One kilogram of Avicel PH-101 was milled using an Erweka ball mill (Langen, Germany) that contained porcelain balls (30 to 50 mm diameter). Ball milling was carried out for four successive days (9 h/day).
2.2.2. Powder Characterization
Bulk Density Measurement
An appropriate amount of powder samples of the raw (un-compacted) and roller compacted (1st, 2nd, and 3rd cycles) Avicel PH-101 was carefully poured, in triplicate, into a 100 mL graduated cylinder. The volume was then read directly from the cylinder and used to calculate the bulk density according to the relationship: mass/volume.
True Density Measurement
The true density of the powders (un-compacted and compacted Avicel PH-101) was determined by placing approximately one gram of the powder sample in a small sample cell in a helium gas pycnometer followed by pressurizing the system between 15 and 17 psi with helium. The true density was then calculated by dividing the mass of the material by its volume (the mean of five readings for each sample was obtained). All weight measurements were performed using an analytical balance with a resolution of ± 0.1 mg.
Particle Size and Particle Size Distribution
Particle size distribution was established based on the ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) sieve analysis method, using a sieve shaker equipped with a series of eight sieves of 63, 90, 125, 180, 250, 425, 500, and 600 µm openings. Fifty-gram samples of un-compacted and compacted Avicel PH-101 powder were tested with an amplitude setting of 1.5 mm and 5 min total sifting time. Powder particles from each sieve were collected and weighed using an electronic balance. Cumulative curves were constructed based on the weight percent of remaining powder particles in the sieves versus mean diameter of powder particles.
Porosity of Powders
Total pore volume, total pore surface area, and total and median pore sizes of powders representing un-compacted and compacted (1st, 2nd, and 3rd cycles) Avicel PH-101 were determined using a mercury porosimeter (PoreMaster PM-60-13, Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA). A representative sample of 0.1 g was accurately weighed and placed in a calibrated glass cell, which was installed in a low-pressure mercury chamber for measurement of particles in the size range of 4–200 µm. Gas was evacuated from the sample cell, and mercury was then transferred into the sample cell; the intrusion pressure was increased and the corresponding volume of mercury injected into the cells was recorded. The range of pressure applied to force mercury into the sample cell was 1–50 Pa. As a result of the analyses, intrusion curves and parameters describing the pore structure of the samples were obtained.
Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis
Powder samples of the raw (un-compacted) and roller compacted (1st, 2nd, and 3rd cycles) Avicel PH-101 were analyzed using Scanning Electron Microscopy, SEM (Inspect F50, FEI, Eindhoven, Netherlands). The powder samples were fixed on aluminum stubs and then coated with gold in a low-vacuum sputter coating chamber (Emitech K550X, Quorum Technology England, Lewes, UK) using a beam current of 20 mA/dm3 for 105 s.
X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
Raw (un-compacted) Avicel®® PH-101, Avicel®® PH-101 subjected to 1st, 2nd, and 3rd compaction cycles were tested using an X-ray powder diffractometer (Bruker, Karlsruhe, Germany) in 2θ reflection mode and a range of 2–40°. The X-ray compartment used consisted of a D2 Phaser in a ceramic sealed X-ray tube with Cr, Co, Cu radiation operating at 30 kV/10 mA. DIFFRAC.SUITE™ computer software was used to measure and analyze the data.
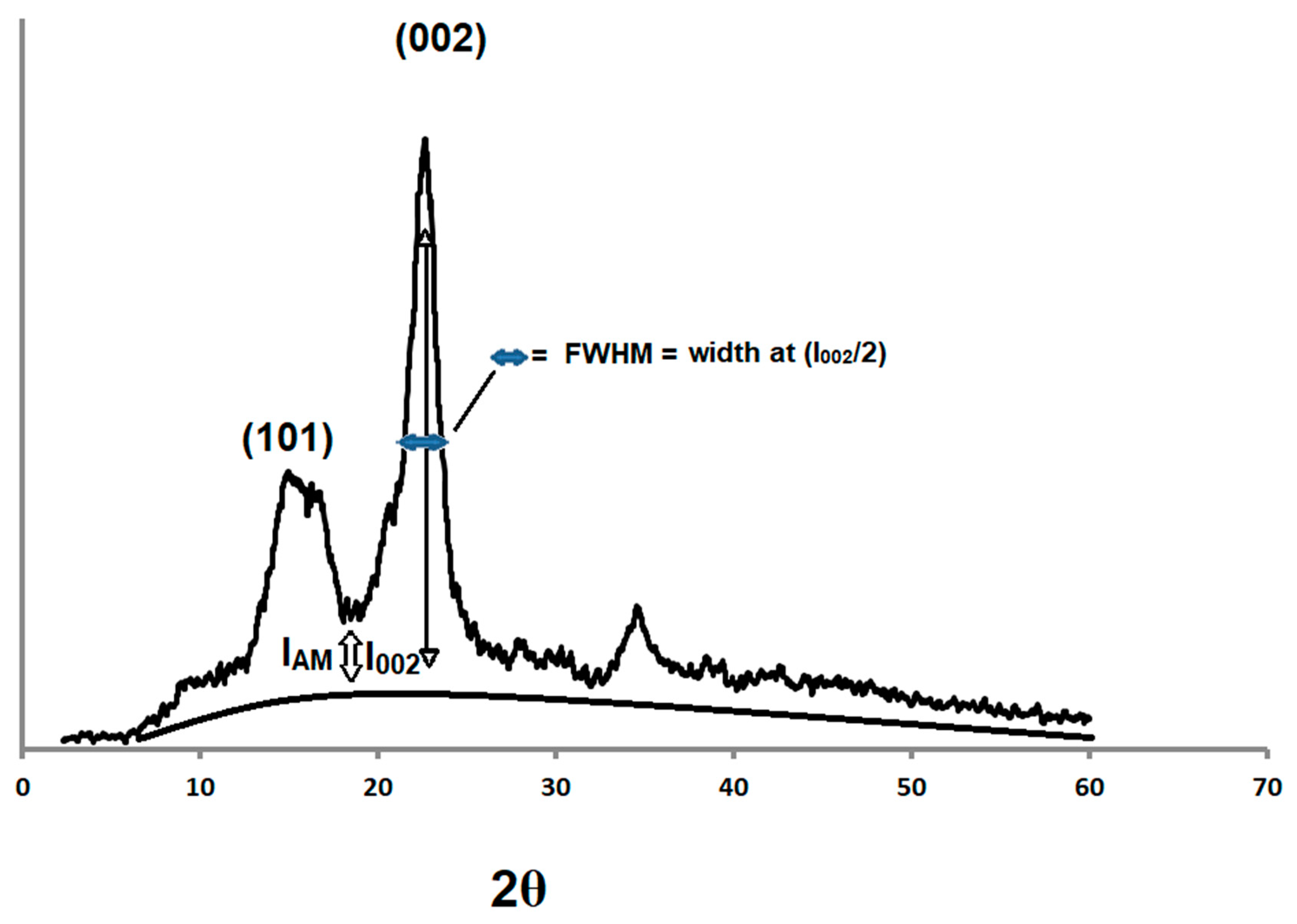
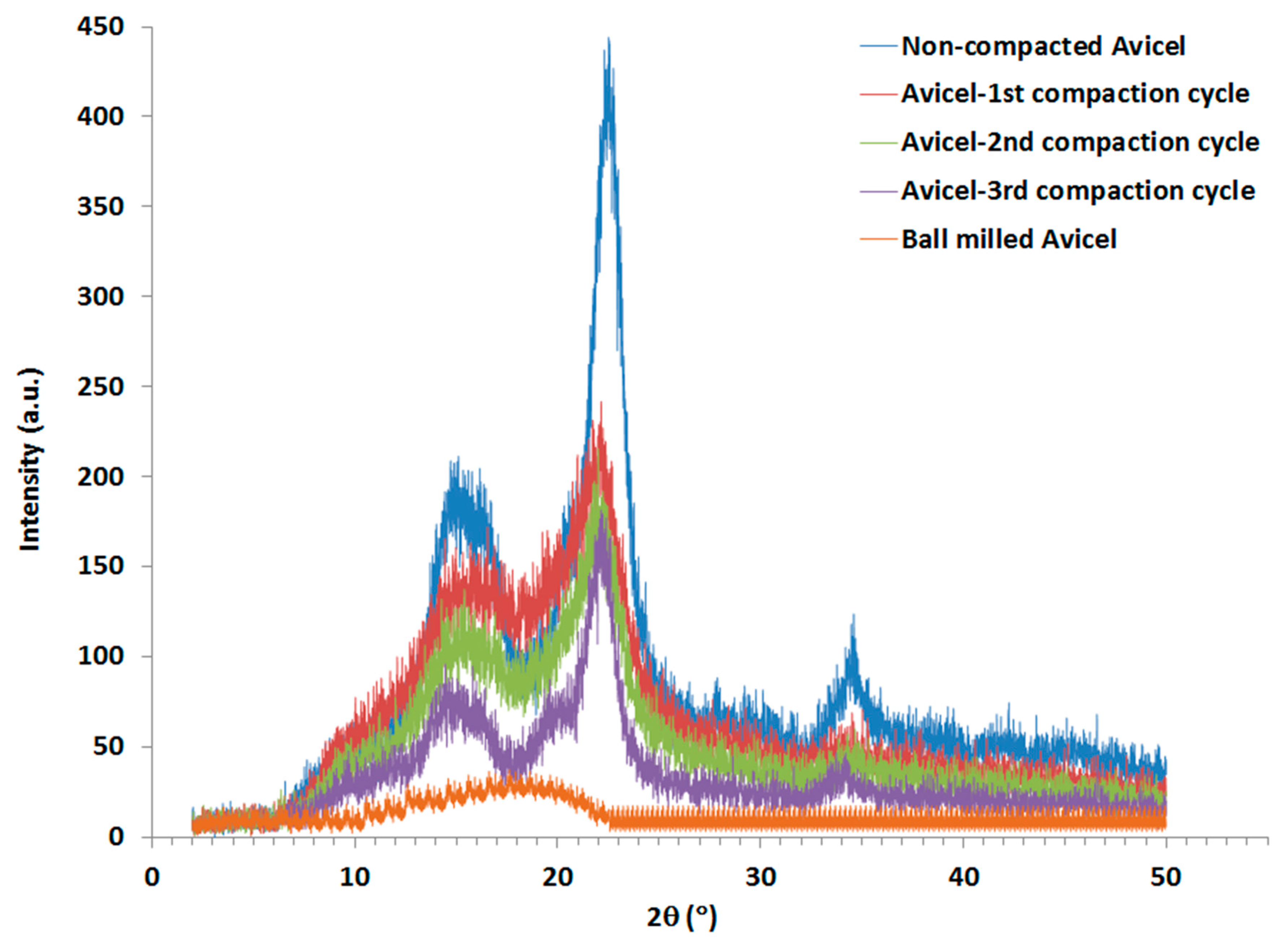
The XRPD spectra of the compacted and non-compacted Avicel PH-101 powders were compared with ball milled Avicel PH-101as a reference. It is evident that the ball milled Avicel PH-101 yielded a clear amorphous pattern (Figure 1). The relative amount of crystallinity in cellulose samples was estimated using a method described by Segal and coworkers [36] to calculate the crystallinity index (CrI). CrI was calculated from the ratio of the height of the 002 peak (I002) and the height of the minimum (IAM) between the 002 and the 101 peaks illustrated in a demonstrative sketch in Figure 1. However, when the difference between CrI values is relatively insignificant, particularly for samples of a broad diffraction spectrum, the full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) is expected to provide a reasonable (indication) estimate of crystallinity.
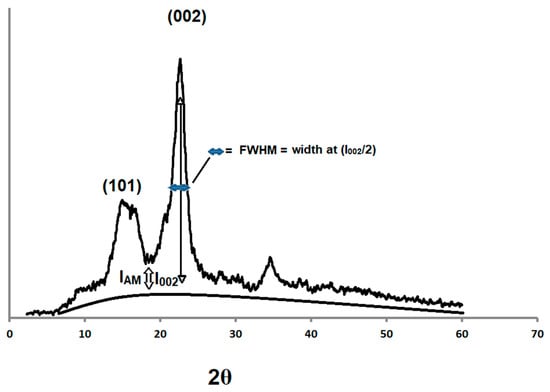
Figure 1.
Illustrative demonstration of the peak heights of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) used for the calculation of the CrI and full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) values.
2.2.3. Compact Characterization (Analysis)
Crushing Strength
Samples of Avicel PH-101, Avicel PH-101 subjected to 1st, 2nd, and 3rd compaction cycles were compressed (500 mg each) into tablets using a single punch tablet press (Manesty F3 single stroke tablet press; West Pharma services Ltd., Dorset, UK) at an applied pressure of 35 units on the scale of the machine. The fitted die was flat, round and 12 mm in diameter. The crushing force of the tablets produced was tested using a hardness tester (Pharma Test PTB 311E, Hainburg, Germany).
Compression Analysis Using Heckel and Kawakita Models
Samples of non-compacted Avicel PH-101 and Avicel PH-101 subjected to 1st, 2nd, and 3rd compaction cycles were compressed into tablets using an instrumental tablet press (GTP-1, Gamlen Tablet Press Ltd., Nottingham, UK). The compression speed was fixed at 60 mm/min for five applied loads; 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500 kg. The samples, 100 ± 1 mg, were poured into 6 mm dies. Kawakita and Heckel models were utilized in order to describe the compression behavior of the powders [31,32,33].
(a) Heckel Analysis
The most universally accepted method used to describe the porosity of a powder bed during compaction and the applied pressure is the Heckel model (Equation (1)) [37]:
where P is the pressure applied, D is the relative density (compact density at pressure P/powder true density), A is a constant, and K is the slope of the linear portion of the Heckel plot [37]. True density was measured using a gas pycnometer (Ultrapycnometer 1000, Quantachrome, Boynton Beach, FL, USA). The average of 5 readings for each sample was used.
Heckel curves were then constructed by plotting ln(1/1 − D), the variation of powder porosity, and P (compression pressure in MPa). The reciprocal of the slope of the linear portion of the Heckel curve is referred to as the yield pressure (Py) that indicates the mechanism occurring during compression and measured deformability.
When D0 is considered as the relative loose powder density at zero pressure describing the initial rearrangement of the powder during die filling, it is equal to the point of intersection of the Heckel plot with the y-axis representing the left-hand side of Equation (1) [37,38]. From the intercept of the linear portion of the Heckel plot, the relative density parameter, Da, can be obtained as follows [38]:
Da = 1 − e−A
The relative density of a powder at low pressure (Db) can then be obtained:
Db = Da − D0
Db is the difference in the actual relative densities between the powder at zero pressure (measured as the intercept of the Heckel curve at P = 0.0 MPa) and extrapolated from the linear portion of the Heckel plot. The relative density, Db, describes the rearrangement phase of particles during the initial stages of compression [38,39]. The PY value is a measure of the extent of plastic deformation. This extent increases when the PY value decreases. In contrast, materials undergo fragmentation by brittle-fracture if the value increases.
(b) Kawakita Analysis
The Kawakita equation describes the relationship between the volume reduction and applied pressure as follows (Equation (4)) [40]:
where P is the applied pressure; a and b are constants characteristic of the powder being compressed. C is the degree of volume reduction, as defined in (Equation (5)).
where V0 is the initial bulk volume and V is the volume at pressure of P [40,41].
From the graphical presentation of P/C versus P, the constants can be evaluated. The constant “a”, is the reciprocal of the slope from the linear portion of the plot and represents the compressibility index, which is related to the total volume reduction for the powder bed; 1/ab is the intercept used to calculate the constant “b” which is termed the coefficient of compression and relates the resistant forces (friction/cohesion) to compression [40]. Moreover, the product of ab has been reported to represent the extent of particle rearrangement under compression pressure [42].
3. Results
3.1. Bulk Density
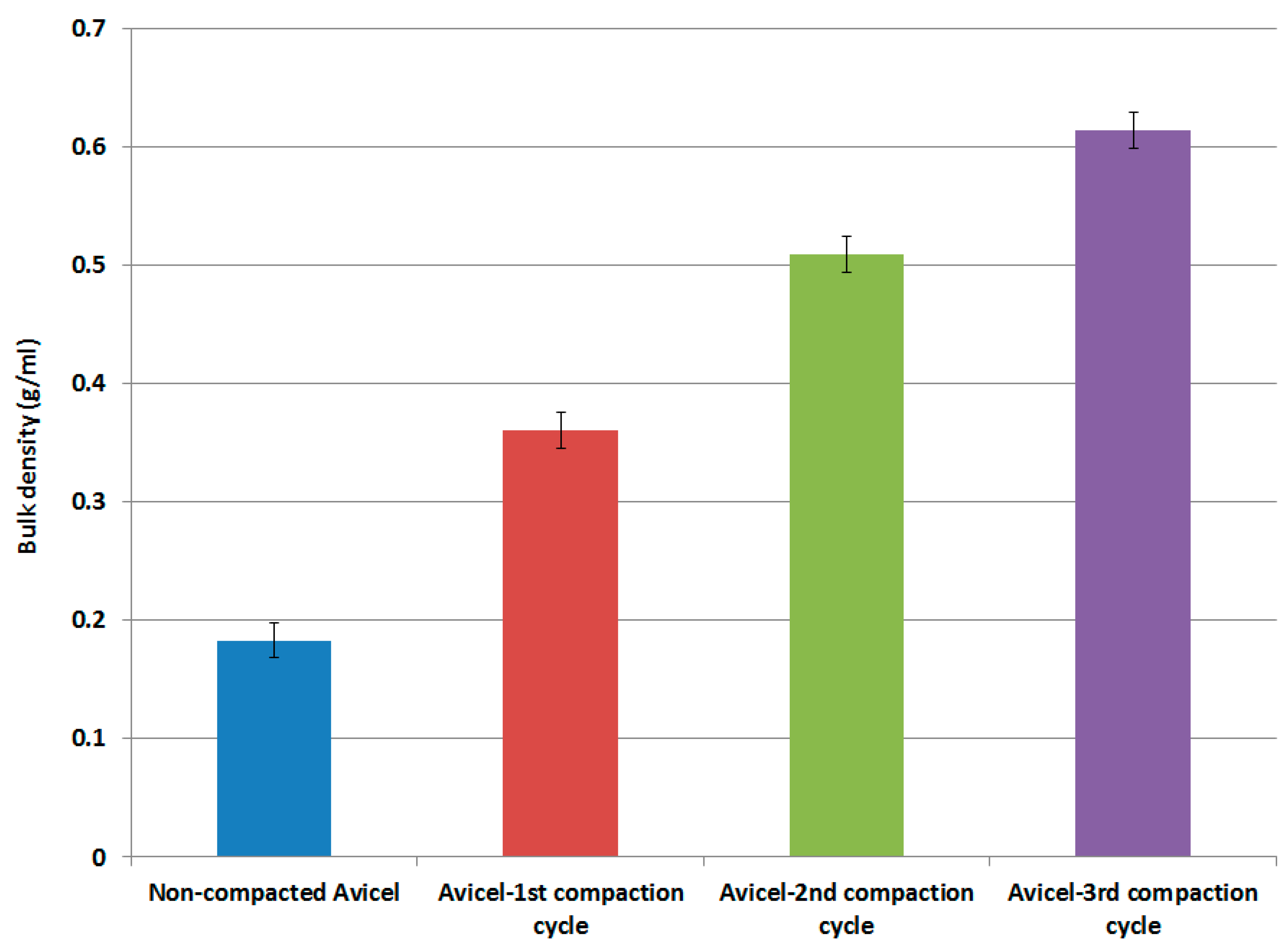
Results of the bulk density of non-compacted Avicel PH-101 and compacted Avicel PH-101 (1st, 2nd, and 3rd compaction cycles) are presented in Figure 2. Generally, the bulk density of MCC is low compared to other common DC excipients [43,44]. In this work, Figure 2 indicates that high-pressure roller compaction of Avicel PH-101 can increase its bulk density from 0.18 g/mL up to a value of about 0.61 g/mL which is ideal for compression machines [32,34].
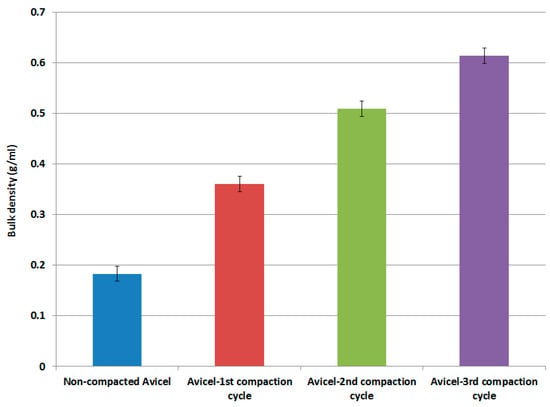
Figure 2.
Bulk density as a function of compaction cycles.
3.2. Particle Size
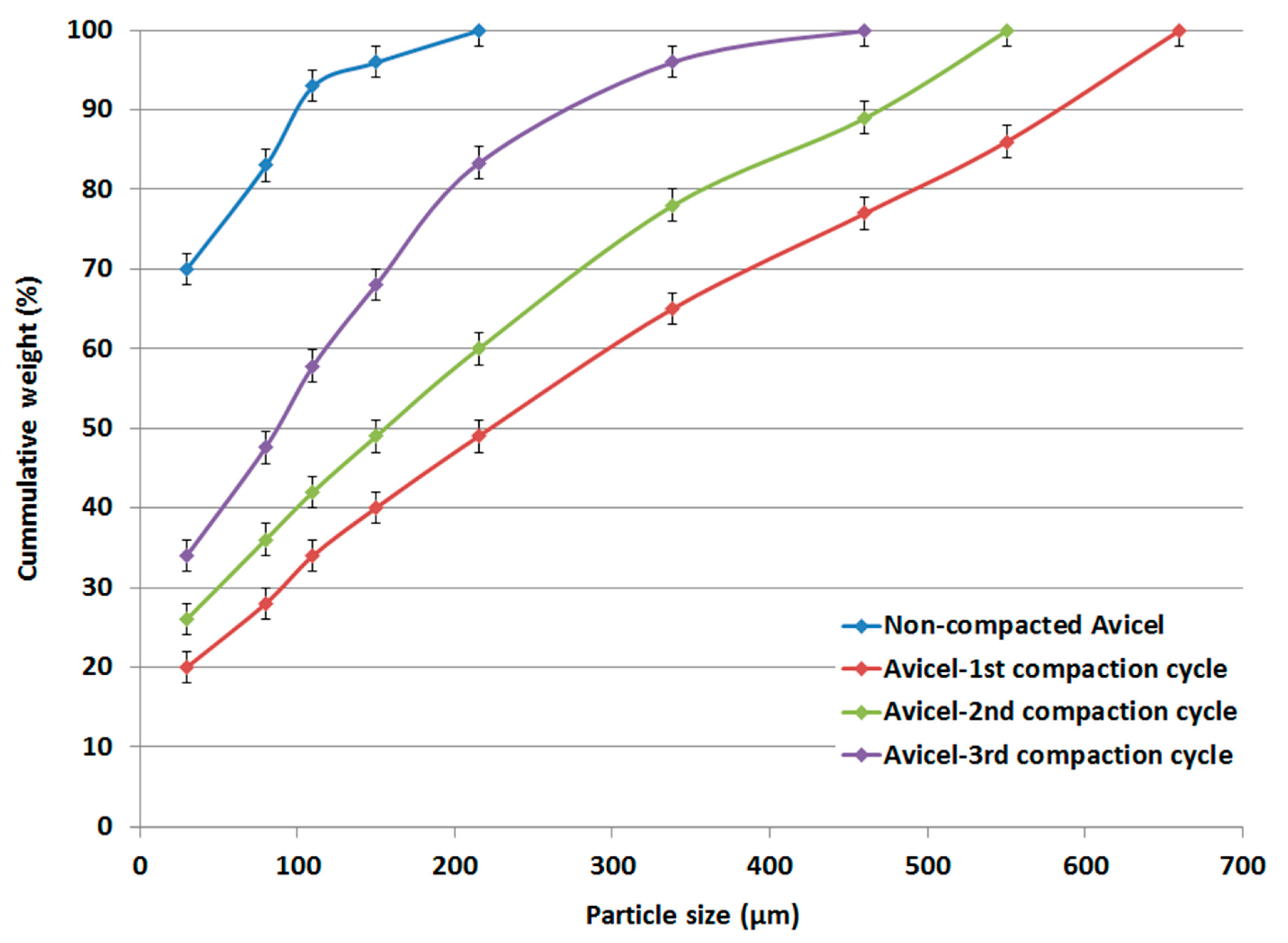
The particle size distributions of compacted and original non-compacted Avicel PH-101 powders obtained by the sieve method displayed cumulative curves based on the weight percent of powders remaining on the sieves. These are presented in the data in Figure 3 as a function of mean particle size.
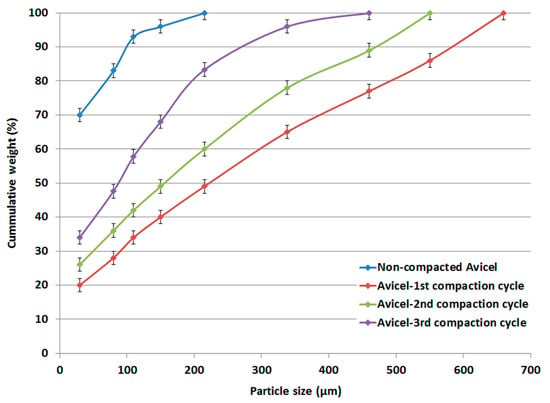
Figure 3.
Particle size distribution of non-compacted and compacted Avicel PH-101.
The particle size distributions of Avicel PH-101 showed a typical narrow range. Interestingly, the data in Figure 3 further show a broader distribution when Avicel PH-101 was subjected to the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd compaction cycles using roller compaction. However, a higher number of compaction cycles causes the particle size to decrease.
3.3. Porosity of Powders
The porosity parameters of un-compacted and compacted Avicel PH-101 powder are shown in Table 1. The pore surface area and pore volume of Avicel PH-101 decreased when the powder was subjected to roller compaction comprising the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd compaction cycles. However, the pore diameter underwent a large increase for the 1st and 2nd compaction cycles followed by a decrease after the 3rd compaction cycle to values that are even lower than that of non-compacted powder.

Table 1.
Porosity characteristics of non-compacted and compacted Avicel®® PH-101.
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
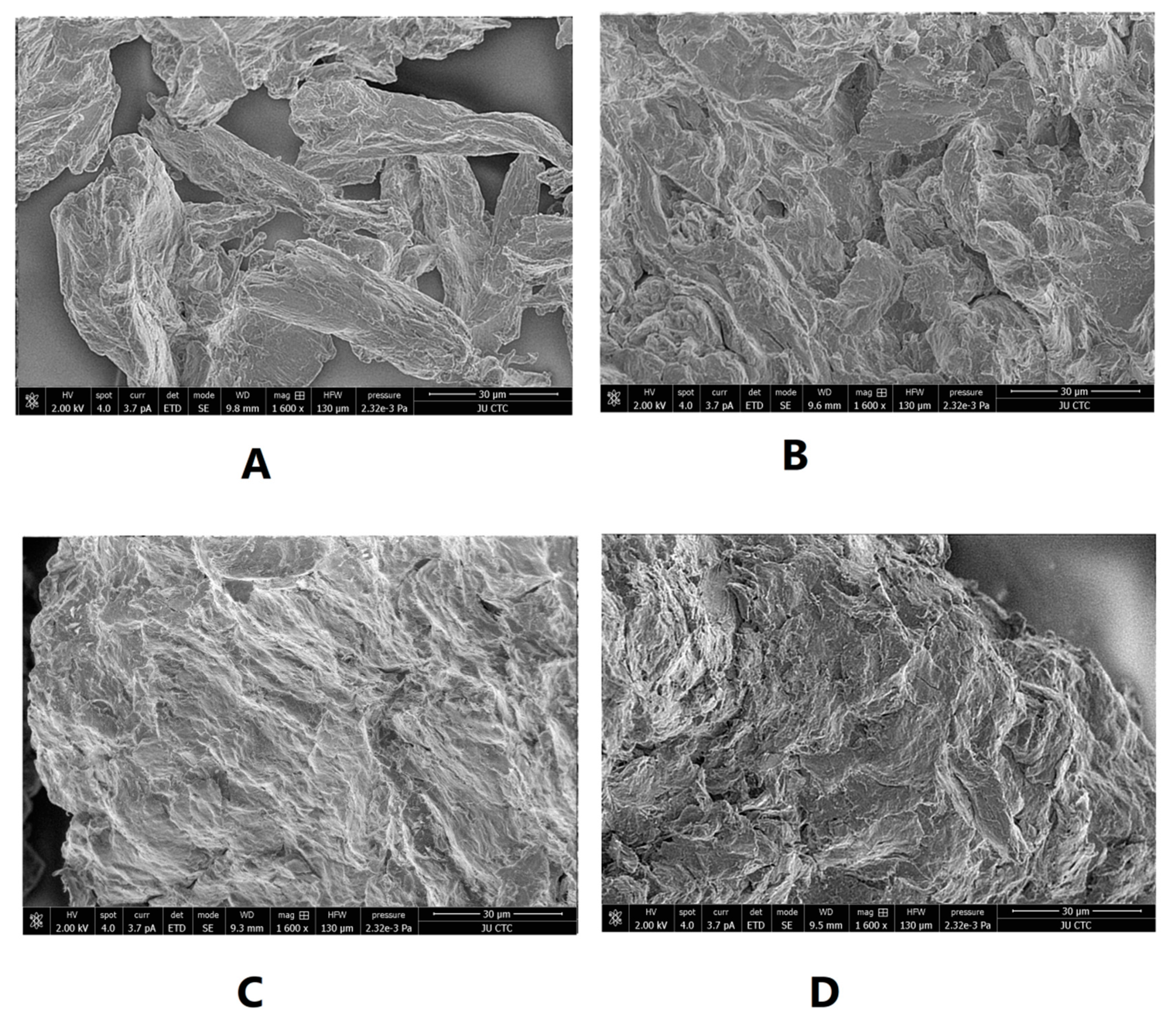
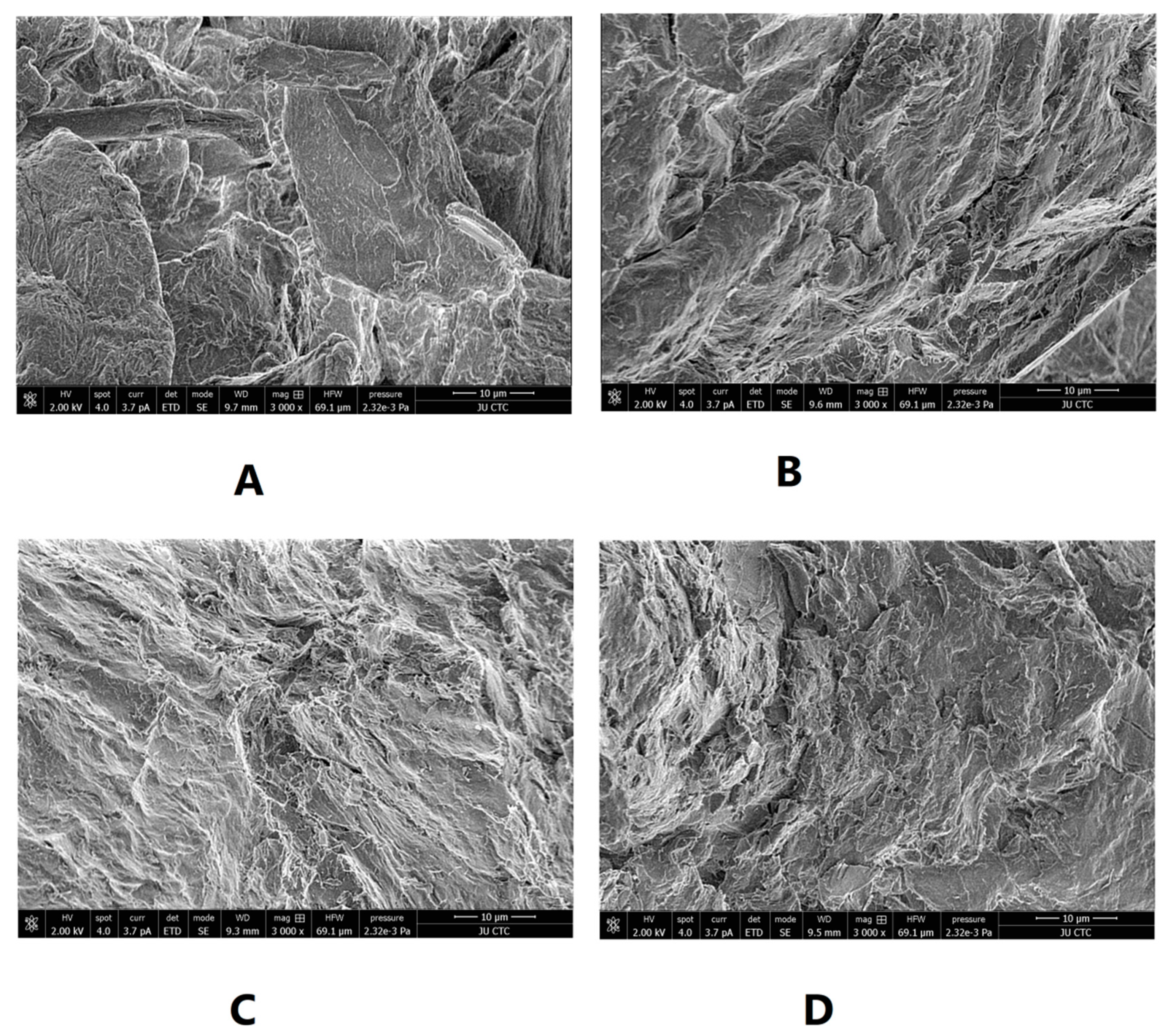
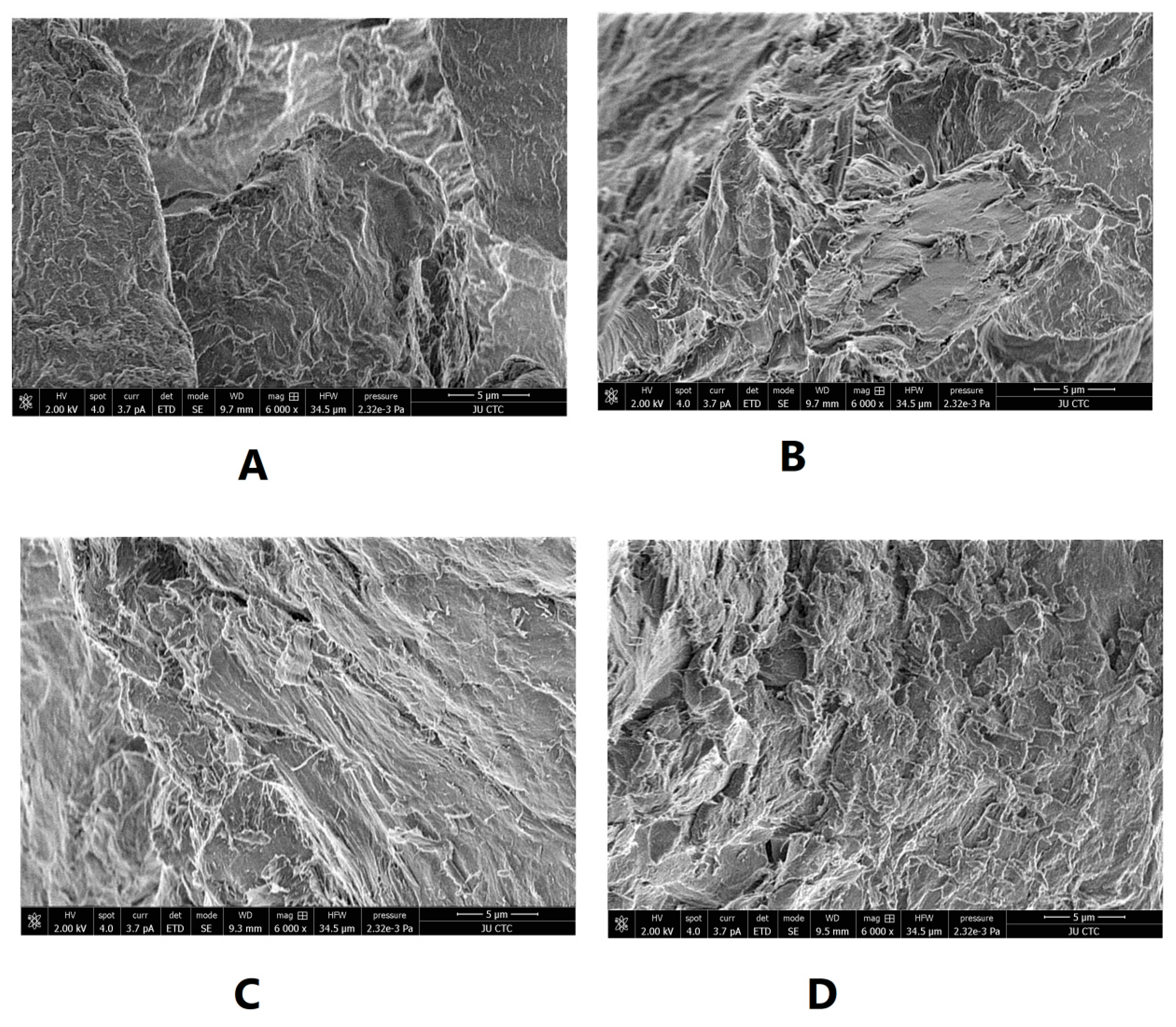
SEM was used to illustrate the effect of intensified compaction on micro-irregularities in Avicel PH101 powder surface. The data in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 presents the SEM of non-compacted Avicel PH-101 (A), roller compacted Avicel-1st compaction cycle (B), roller compacted Avicel-2nd compaction cycle (C), and roller compacted Avicel-3rd compaction cycle (D) at magnifications of 1600×, 3000×, and 6000×. The resulting images indicate how the surface of MCC is transformed from irregular layered lumps into smoother and more fused surfaces. Some kind of irregularities appears on powder compacts under the third compaction cycle. This is due to deformation under this intensified compaction which appears at magnification of 6000×. Such magnification, unfortunately, does not allow us to allocate single NCF rods. It is evident from these images that roller compaction converted the fibrous, multi-layered granules into fused smoother surfaces which appeared in the 2nd compaction cycle. The long fibers became shorter on intensification of compaction. This facilitates binding of Avicel granules into a fused surface and appears after the third compaction cycle.
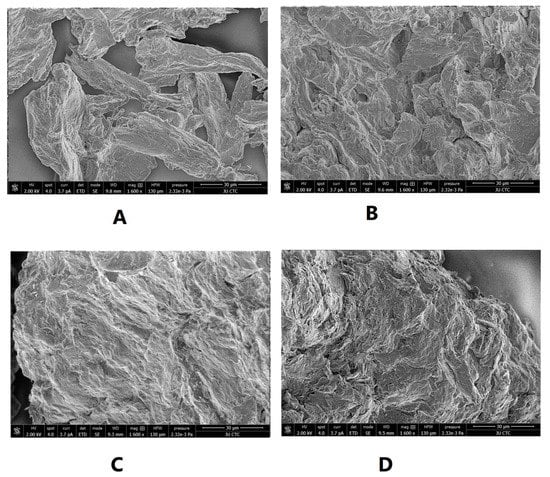
Figure 4.
SEM of non-compacted Avicel PH-101 101 (A), roller compacted Avicel-1st compaction cycle (B), roller compacted Avicel-2nd compaction cycle (C), and roller compacted Avicel-3rd compaction cycle (D) at magnification of 1600×.
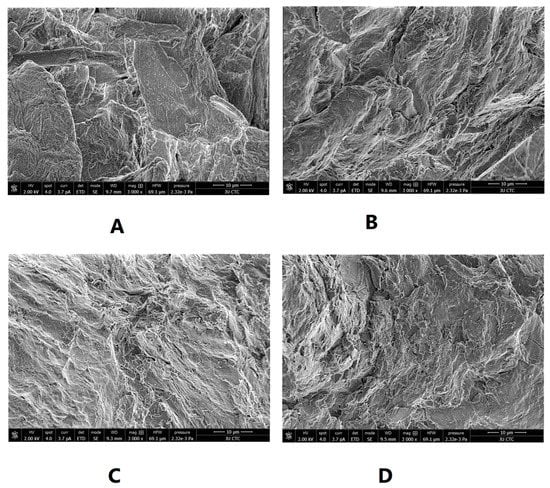
Figure 5.
SEM of non-compacted Avicel PH-101 101 (A), roller compacted Avicel-1st compaction cycle (B), roller compacted Avicel-2nd compaction cycle (C), and roller compacted Avicel-3rd compaction cycle (D) at magnification of 3000×.
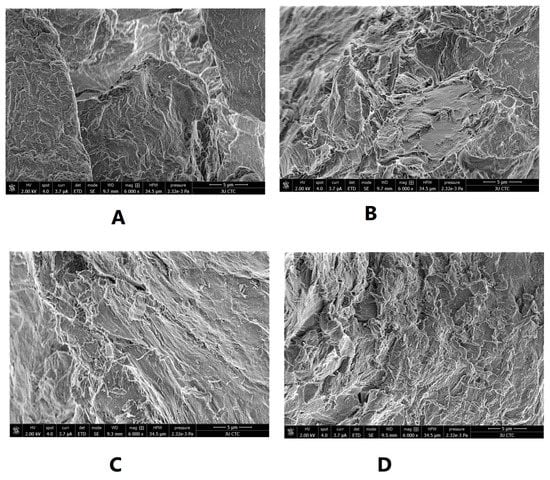
Figure 6.
SEM of non-compacted Avicel PH-101 101 (A), roller compacted Avicel-1st compaction cycle (B), roller compacted Avicel-2nd compaction cycle (C), and roller compacted Avicel-3rd compaction cycle (D) at magnification of 6000×.
3.5. X-ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) Analyses
Non-compacted Avicel PH-101 and granules resulting from the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd high-pressure compaction cycles of the roller compactor were subjected to XRPD analysis (Figure 7). The crystallinity index was calculated using the peak height ratios relative to amorphous cellulose produced by the ball milling technique. CrI results are presented in Table 2 for each type of powder. The CrI values of Avicel PH-101 encountered a non-significant decrease when the number of compaction cycles was increased. Thus, the FWHM was also calculated and values are given in Table 2. According to the Scherrer equation [45,46], which states that peak width is inversely proportional to crystallite size, it is obvious that a high decrease in crystal size occurred in the 1st compaction cycle compared to the raw Avicel, then the crystal size encountered a noticeable increase and a further increase for the 2nd and 3rd compaction cycles.
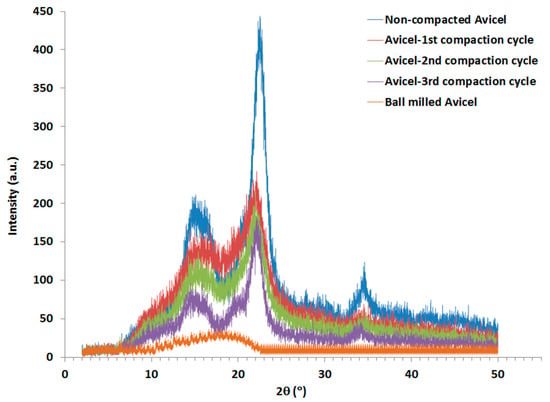
Figure 7.
XRPD spectra of non-compacted, compacted, and ball-milled Avicel PH-101.

Table 2.
CrI and FWHM values for non-compacted and compacted samples.
3.6. Compact (Tablet) Crushing Strength
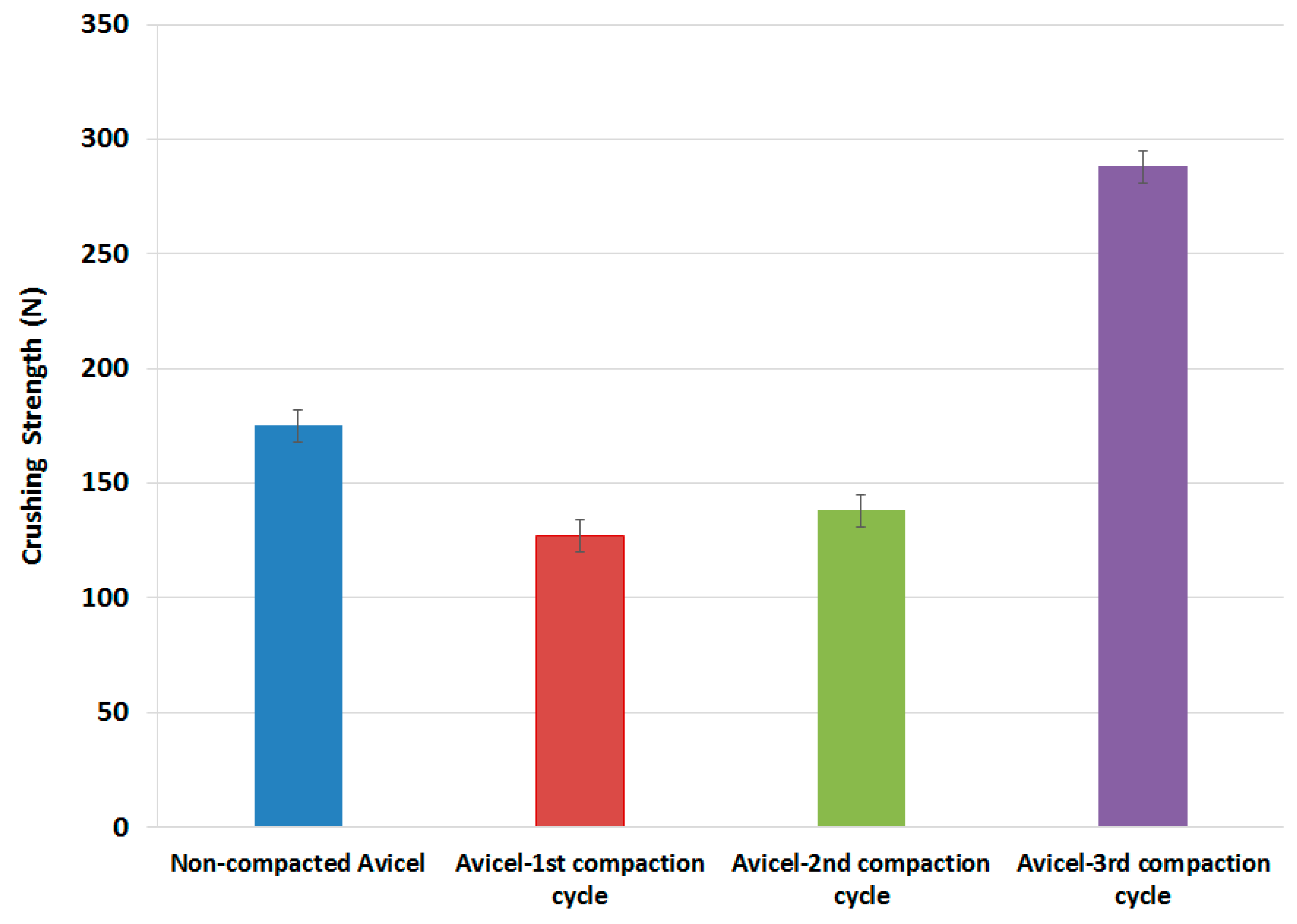
All tested powders were compressed using a single punch tablet machine; the crushing force of all the tablets produced is presented in the data in Figure 8. Compacts produced from granules resulting from the 1st high-pressure compaction cycle of the roller compactor were weaker than those of the original non-compacted powder. The crushing force started to increase for the granules resulting from the 2nd high-pressure compaction cycle. However, the tablet hardness was still lower than that of un-compacted powder. Surprisingly, the granules of the 3rd compaction cycle resulted in tablets with a crushing force much higher than that of the original non-compacted powder.
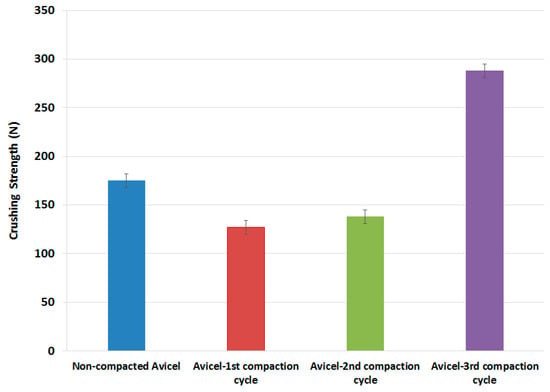
Figure 8.
Tablet crushing strength as a function of compaction cycles.
3.7. Compacts Porosity
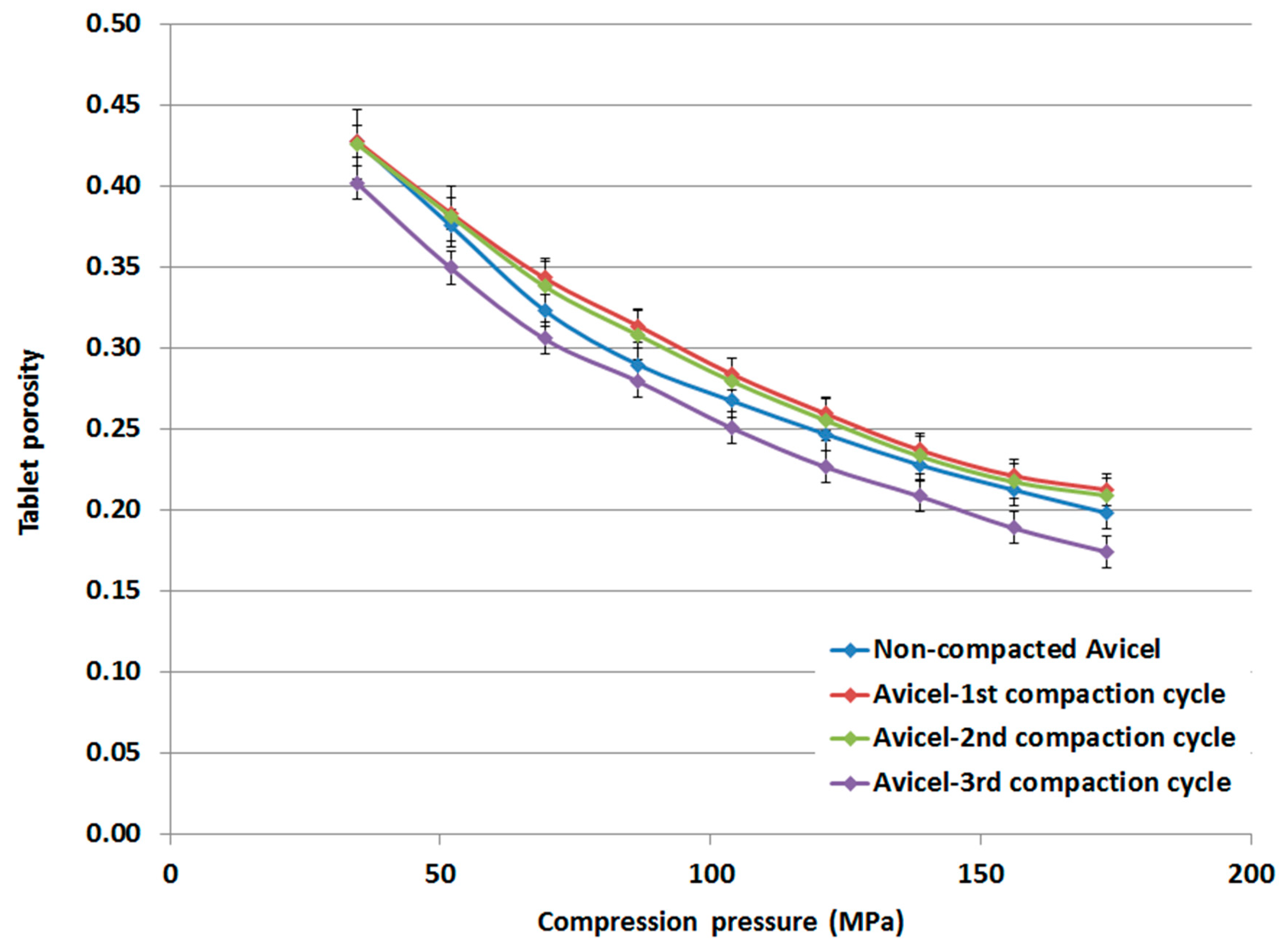
The tablet porosity, determined from its thickness, is presented for the compacts made from non-compacted Avicel PH-101, compacted-1st cycle Avicel PH-101, compacted-2nd cycle Avicel PH-101, and compacted-3rd cycle Avicel PH-101 (Figure 9). The porosity of tablets made of compacted powder representing the 1st and 2nd compaction cycles is higher than that of tablets made of non-compacted powder. However, tablet porosity was found to decrease to values lower than that for the non-compacted powder when the powder representing the 3rd compaction cycle was compressed.
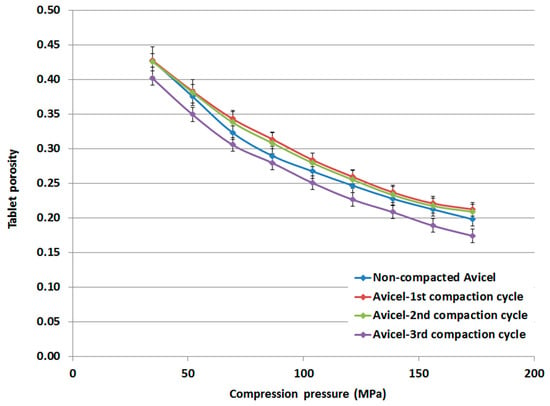
Figure 9.
Porosity of tablets made of non-compacted and compacted Avicel PH-101.
3.8. Compression Analyses
3.8.1. Heckel Analysis
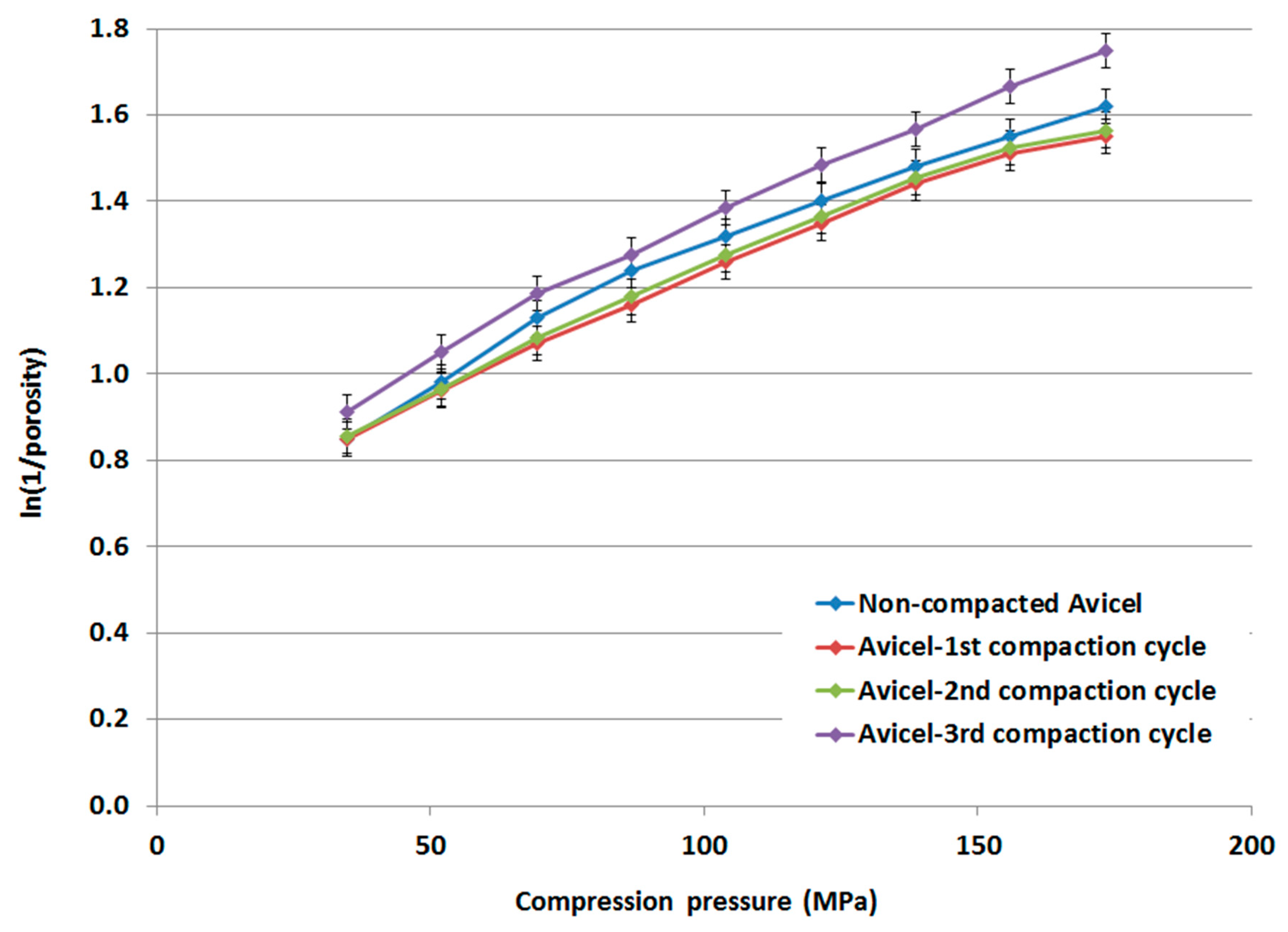
Based on the measured true densities, for which no significant change within the range 1.643–1.648 g/mL was detected, for compacted and non-compacted Avicel PH-101 powders, Heckel plots and Heckel parameters were determined for non-compacted Avicel PH-101, compacted-1st cycle Avicel PH-101, compacted-2nd cycle Avicel PH-101, and compacted-3rd cycle Avicel PH-101. Results are presented in Figure 10 and Table 3, respectively. The linear portion of the Heckel plots was selected in the compression pressure range from 104 to 156 MPa. The extent of plastic deformation of compacted Avicel PH-101 is higher (as Py is lower) than the non-compacted original form. In fact, the extent of Avicel’s plastic deformation increases as a function of the number of times the compaction is repeated. However, the Db value undergoes a decrease for the powders comprising the 1st and 2nd compared to the Db value of the 1st compaction cycle. For the 3rd cycle, the Db value underwent a slight increase and was slightly higher than the Db value of the 1st compaction cycle.
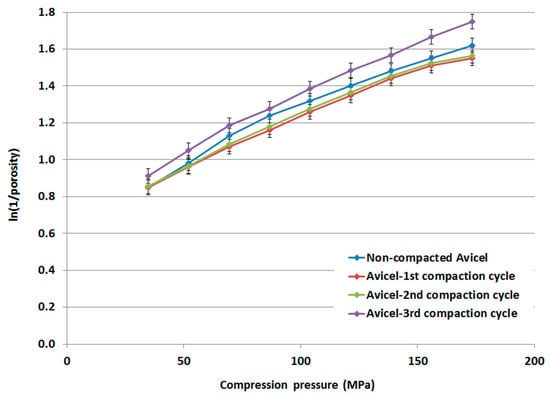
Figure 10.
Heckel plot of non-compacted and compacted Avicel PH-101.

Table 3.
Parameters derived from the Heckel plots of non-compacted and compacted Avicel®® PH-101.
3.8.2. Kawakita Analysis
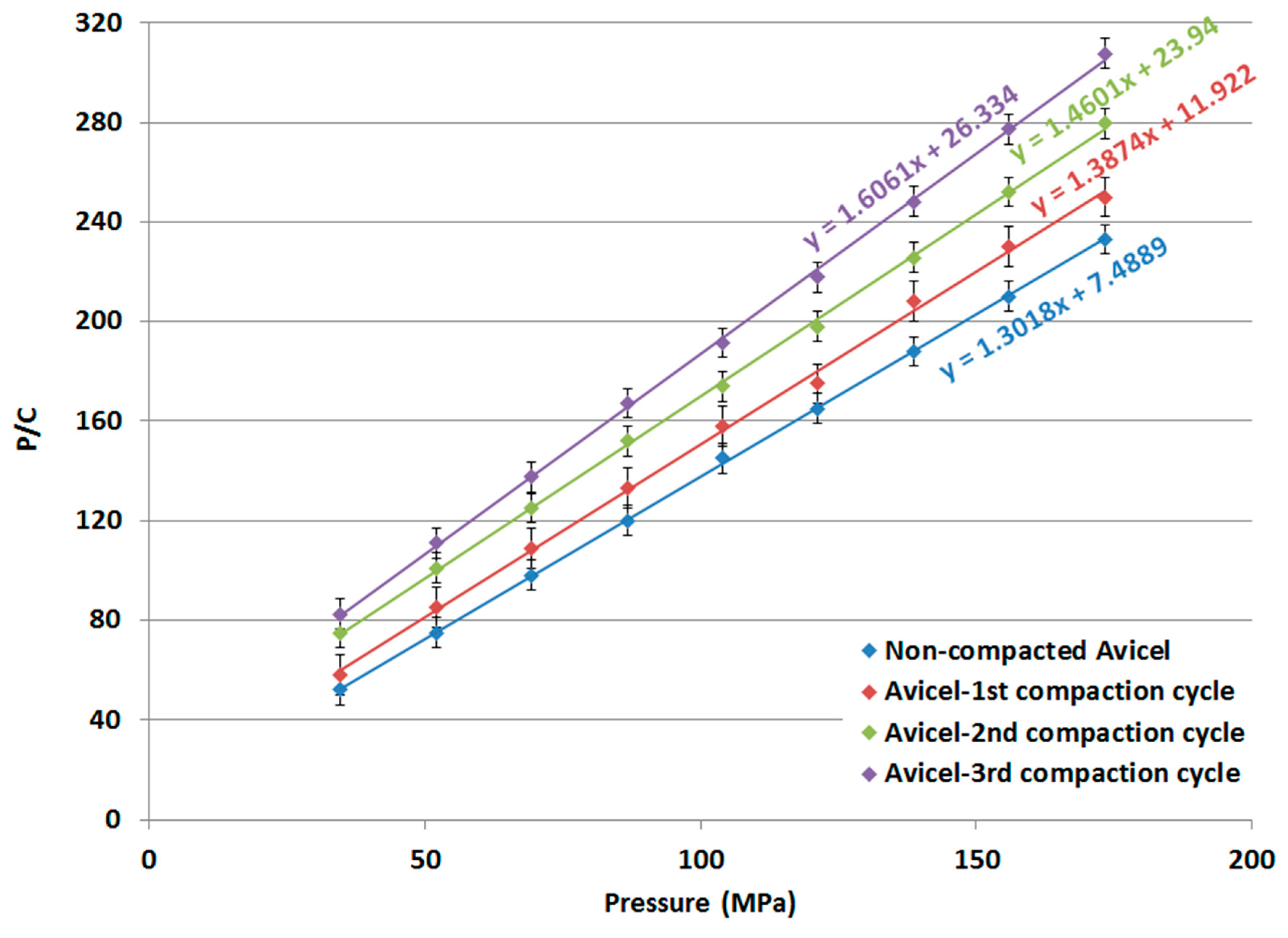
Kawakita plots and Kawakita parameters for non-compacted Avicel PH-101, compacted-1st cycle Avicel PH-101, compacted-2nd cycle Avicel PH-101, and compacted-3rd cycle Avicel PH-101 are presented in Figure 11 and Table 4, respectively.
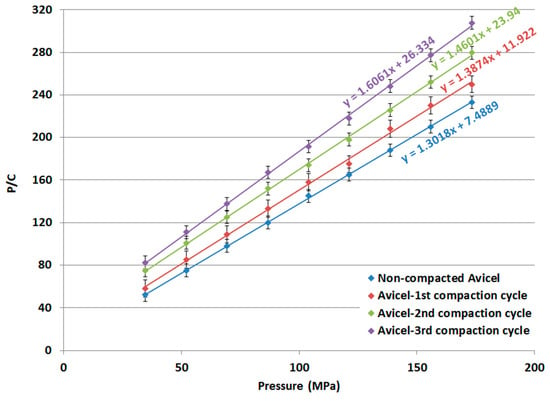
Figure 11.
Kawakita plot of non-compacted and compacted Avicel PH-101.

Table 4.
Parameters derived from the Kawakita plots of non-compacted and compacted Avicel®® PH-101.
The 1/b parameter obtained from the Kawakita analysis is indicative of the force required for a reduction in the powder bed volume [47]. The value increases for Avicel PH-101 with a higher number of compaction cycles, particularly during the 1st and 2nd compaction cycles. Thus, the granules from the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd compaction cycles of Avicel PH-101 are hard enough to impose resistance to a compression/compaction force. The compaction of powders for repeated compaction cycles renders the granules more highly resistive to compression as their 1/b value increases. Similarly, the foregoing resistance can be interpreted from the reduced a parameter when the powder undergoes compaction. This parameter, which reflects the maximum powder volume reduction, is reduced to lower values as compression is carried out on powders using a higher number of compaction cycles. Moreover, the extent of particle re-arrangement (ab) undergoes a decrease for powders of higher compaction cycles in comparison to the raw excipient itself (Table 4).
4. Discussion
The objective of the present work was to explore if the MCC shortcoming of losing the intensity of its binding power following reprocessing or reworking can be alleviated. This investigation was focused on applying immense compaction force using a roller compactor. In the present work, one of the most used excipients in preparations of pharmaceutical solid dosage forms was selected as the investigational model, that is, Avicel PH101. This MCC (Avicel PH-101) is the most commonly used grade in tablet manufacturing among different branded grades of MCC produced by FMC (FMC BioPolymer, Philadelphia, PA, USA). Furthermore, the present choice of Avicel PH-101 was primarily aimed to compare the obtained results with previously published research in which this grade was used [27,28,29,30]. This may assist in the understanding of the mechanism underlying Avicel PH101 loss of binding in reworking during tablet making. It is worth mentioning that, as a spray-dried material, Avicel PH101 is highly porous with low bulk density which results in poor flowability, as is clear from Figure 2.
Initially, the outcome of the Kawakita analysis gives a clear indication that once Avicel PH101 is subjected to certain roller compaction it hinders further compression. This finding is deduced from higher resistance of the granules under the applied compression force (1/b) and, concurrently, by the lower volume reduction for powders (a) and lower particle re-arrangement (ab) for powders resulting from a higher number of compaction cycles. This behavior is more likely to be attributed to physical modification resulting from the increase in density of granules with compacted cycle repetition. However, Kawakita analysis did not give any indication as to why the tablet crushing force underwent a decrease and then an increase when the compressed powder was made of compacted Avicel PH-101 comprising the 1st (decrease), 2nd (decrease), and the 3rd (increase) compaction cycles. The compacts resulting from the first and second cycles resulted in similar values of crushing strength, indicating that compacts have similar properties under these two cycles because their porous structures stay within the same vicinity. This makes it necessary to test particle size, flow properties, and compression behaviors to clarify the increase in tablet crushing strength under a third compaction cycle.
Initially, high compression/compaction pressures do not alter the chemical structure of microcrystalline cellulose [48]. The increase in the extent of plasticity of Avicel PH-101 (as indicated by the decrease in PY values) when the powder is compacted is more likely to be attributed to the presence of more deforming surfaces upon compaction. In the current case, densification upon processing of Avicel PH-101 via roller compaction is believed to be a major contributor to the extensive presence of new particle surfaces. In contrast, the decrease in Db values for powders comprising the 1st and 2nd compaction cycles highlights a notable difference in powder density as the compaction force is increased (Table 3). This behavior is most probably due to the difference in particle surface irregularities and pore sizes of the powder bed subjected to compression. In this regard, the 1st and 2nd compacted powders are made of larger granules with higher pore size (diameter) than non-compacted powder and the material under compaction preserves its plasticity (Figure 3 and Table 1). In addition, it can be interpreted in terms of low powder re-arrangement, as lower Db was depicted when granules become denser and larger upon compaction [49]. This low powder re-arrangement, as results of Heckel analysis indicated, is equivalent to the lower maximum volume reduction parameter, i.e., a, calculated from the Kawakita equation for compacted samples when compared to non-compacted powders (Table 4). These highly densified granules presented a higher resistance to compression pressure than those of non-compacted powder.
The increase in granule size (Figure 3) for the 1st and 2nd compacted powders is in accord with the conclusions drawn by Sun and Himmelspach, in addition to Patel et al. [30,50]. However, they showed that granules produced at higher slugging/or compaction pressures have high resistance to plastic deformation due to work hardening which was evident in the appearance of hard binding centers on the particle surfaces. This is in conformity with the currently detected increase in plastic deformation, as indicated by Heckel analysis, for the powders throughout roller compaction. Consequently, the highest extent of deformation (lowest Py) and higher rearrangement (higher Db) resulted from 1st and 2nd compaction cycles compared with the 3rd compacted powder justify the increase in the crushing strength of the resulted compacts. The slight increase in the Db value for the 3rd compacted powder compared to the 1st and 2nd is more likely to be an indication of the increase in granule density when the compaction pressure is increased. It is suggested that the highly packed nature of the granules is attributed to the fact that the powder comprising the 3rd compaction cycle had the lower particle size and pore size than the powders from the 1st and 2nd compaction cycles (Figure 3 and Table 1).
The initial decrease in pore area and volume when mercury intrusion porosimetry was employed on all types of compacted and non-compacted powders is attributed to the fact that particles from powders subjected to roller compaction are either much bigger in size (1st and 2nd compaction cycles) or consist of lower surface micro-irregularities (3rd compaction cycle) than non-compacted powder (Figure 3). In contrast, powders from the 3rd compaction cycle are more densified (Figure 2), almost closer in particle size (Figure 3), and have lower intra-granular pore size (diameter) (Table 1) than the powders made from the 1st and 2nd compaction cycles. The increase (for 1st and 2nd compaction cycles) and decrease (for 3rd compaction cycle) of powder pore size is in agreement with the increase and decrease of compact porosity presented in Figure 9. The high porosity for powders comprising 1st and 2nd compaction cycles enables the presence of weak points within the tablets rendering them easy to break when a crushing force is induced, while compact porosity of the 3rd compaction cycle powder decreased to values lower than non-compacted Avicel PH-101. Accordingly, powders comprising the 3rd compaction cycle are expected to be made of tightly packed material of Avicel PH-101 with a particle size closer to non-compacted Avicel PH-101. Such a conclusion is not in agreement with the finding by Bultmann [31] who emphasized that multiple compaction of Avicel PH-101 induces a reduction in the tensile strength of its compacts. It is suggested that this contradiction is attributed to the fact that Avicel PH-101, in the work by Bultmann [31], was not subjected to an intensified compaction pressure which was enough to cause a dramatic change through compaction by roller compactor. The decrease in the relative amount of crystalline material in Avicel PH-101 and the change in crystallite size, as measured by the decrease in its CrI value and the change in FWHM values upon roller compaction (Table 2), give an indication of the extent of compaction pressure that should be used to obtain a significant change in the compression behavior of Avicel PH-101. It is worth noting that MCC preserved its crystallinity with lower magnitude compared with the non-compacted Avicel PH101. However, Vaca-Medina et al. [51] and Kumar and Kothari [52] reported that MCC undergoes an increase in crystallinity when a pressure is induced, whereas Ek et al. [53] reported an initial slight increase followed by a decrease in crystallinity. The tablets they produced were of 12 g weight, 50 × 50 mm square shape, and 0.5 g weight, 17 mm circular shape. When examining the cases for the increase in crystallinity, it was noticed that compression was carried out on tablets of thickness and/or surface area (punch diameter) much higher than that provided by roller compactors. In the current work, the compactor had a roller gap of 2.0 mm, which suggests a mechanically rendered intensive distribution of the compaction force, i.e., 25 MPa, onto individual powder particles. This hypothesis is supported by the findings of Ek et al. [53], who compressed thinner and smaller tablets (estimated not greater than 100 mg tablet weight, 5.5 mm circular shape) than those of the two aforementioned cases which are associated with the increase in crystallinity with pressure. In contrast, the broadening of the diffraction peak at 2θ = 13–17 is equivalent to a previous finding by Rogovina et al. [54] who applied high stress/pressure conditions to powdered cellulose. In this regard, the aforementioned broadening was explained on the basis of amorphization of the specimen or a decrease in the degree of polymerization of cellulose [54].
From the foregoing results and discussion, it is evident that multiple compaction cycles using a roller compactor are capable of altering some of the physical parameters of the tested powder of Avicel PH101. This was evident due to the significant increase in bulk density from 0.18 g/mL to over 0.6 g/mL. This improves powder flow and facilitates its passage in a tableting machine. It can be noted that granules from the first and second compaction cycles behaved similarly but differently from granules of the third compaction cycle. The pore diameters for Avicel PH-101 and from the first and second cycles of compaction were larger than those of granules resulting from the third cycle of compaction. This can be an indication of the appearance of a new surface of MCC fiber. Indeed, pore diameter was smaller than the non-compacted Avicel PH-101 pore diameter, which was evident from porosity measurements. Such observations lead to the conclusion that new fiber surfaces appear due to the applied mechanical stress during roller compaction. This force is capable of destroying or disintegrating the outer layer of MCC fibers exposing the internal layer in the same fashion as used in obtaining nanosize crystalline cellulose fibers. This was reported by Necyporchuck who confirmed the appearance of NCF upon wet grinding [55]. It can be safely concluded that the intense compaction acted as a mechanical force leading to the appearance of smaller sized grains of cellulose fibers (NCFs) and is clearly demonstrated by giving rise to new surfaces capable of bonding. This results in a crushing strength that is even higher than that of non-compacted MCC (Avicel PH-101). In contrast, SEM after the 1st compaction cycle shows a consolidation of individual particles appearing on the surface and forming bigger granules. For the 2nd compaction cycle, consolidation becomes intensified as the individual particles of Avicel PH-101 cannot be seen on the surface of the particles. For the 3rd compaction cycle, the surface of the particles is, again, highly consolidated and consists of individual particles with high surface deformation. Such overall behavior visualized using SEM for Avicel PH-101 under roller compaction is somehow different than that seen in other mechanical stress-inducing techniques such as homogenization, extrusion, blending, and ball milling. These techniques are capable of providing sufficient shear forces necessary to induce delamination of the fibers in the form of nanofibers (nanofibrillated cellulose). In contrast, roller compaction provides the stress-inducing forces necessary for the densification of powders into granules of lower internal porosity compared to the raw material. Hence, the appearance of such nanofibers under the current compaction parameters, as indicated by SEM analysis, did not occur.
These comments are clearly supported by the fact that the tablet crushing strength increases after the third compaction cycle. The exposure of Avicel PH101 to a compaction force using a roller compactor resulted in granules that show a reduced volume under the applied compaction force. This follows the Heckle plot but their binding power is less than that of the non-compacted Avicel PH101. Surprisingly, intensifying the compaction force overcomes the loss of binding power of Avicel PH101 following the re-processing of tableting powder or in densifying powder in solid dosage form manufacturing. The powder surface is slightly fragmented when compared with lower compaction. This final result shows that the loss of MCC functionality after reprocessing can be retained using a roller compactor tuned to a higher compaction force.
5. Conclusions
Re-compaction of MCC leads to an increase in its bulk density, thereby facilitating tablet manufacturing. Different compaction cycles using an industrial roller compactor cause a reduction in binding power of MCC such as Avicel PH101. When multiple compaction cycles were applied to already dry granulated Avicel PH-101 using a roller compactor, the re-compacted Avicel PH-101 regained its binding power for compacts with crushing strength even higher than that of initially processed Avicel PH-101. Such a finding allows reworking or reprocessing of MCC in tablet making.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.A.F., I.R. and A.A.B.; Data curation, I.R. and L.A.-H.; Formal analysis, D.A.F., L.A.-H. and A.A.B.; Investigation, D.A.F., I.R. and L.A.-H.; Methodology, D.A.F.; Project administration, A.A.B.; Software, L.A.-H; Supervision, D.A.F.; Writing–original draft, D.A.F. and I.R.; Writing-review & editing, B.Z.C. and A.A.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank The University of Jordan and University of Greenwich for their ongoing support. The authors also wish to thank the Jordanian Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Co. (JPM) for providing materials, laboratory and testing facilities.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The Jordanian Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Company (JPM) did not have any role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Fittolani, G.; Seeberger, P.H.; Delbianco, M. Helical polysaccharides. Pept. Sci. 2020, 112, e2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechyporchuk, O.; Belgacem, M.N.; Bras, J. Production of cellulose nanofibrils: A review of recent advances. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 93, 2–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasmania, L.; Thielemans, W. Preparation of nanocellulose and its potential application. Int. J. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. Nanomed. 2018, 4, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayeb, A.H.; Amini, E.; Ghasemi, S.; Tajvidi, M. Cellulose Nanomaterials—Binding Properties and Applications: A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Sabapathi, S.N. Cellulose nanocrystals: Synthesis, functional properties, and applications. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2015, 8, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfa, J.; Chukwu, A.; Udeala, O.K. Compression and Compaction Behaviour of Microcrystalline Cellulose from Sorghum and Andropogon Stalks. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2017, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, J.; Knop, K.; Kleinebudde, P. Brand-to-brand and batch-to-batch uniformity of microcrystalline cellulose in direct tableting with a pneumohydraulic tablet press. Pharm. Ind. 2006, 68, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, T.; Nakagami, H. Effect of crystallinity of microcrystalline cellulose on the compactibility and dissolution of tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1999, 47, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumattaqiin, F.; Chonkaew, W. Preparation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) by acid hydrolysis using microwave assisted method from cotton wool. Macromol. Symp. 2015, 354, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioelovich, M. Study of fractal dimensions of microcrystalline cellulose obtained by the spray-drying method. Fractal Fract. 2019, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Law, Y.; Chakrabarti, S. Physical properties and compact analysis of commonly used direct compression binders. Am. Assoc. Pharm. Sci. PharmSciTech. 2003, 4, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoorens, G.; Krier, F.; Leclercq, B.; Carlin, B.; Evrard, B. Microcrystalline cellulose, a direct compression binder in a quality by design environment—A review. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 473, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlin, B. Direct compression and the role of filler-binders. In Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms-Tablets; Augsburger, L.L., Augsburger, L.L., Hoag, S.W., Hoag, S.W., Eds.; Informa: London, UK, 2008; pp. 173–216. [Google Scholar]
- Haware, R.V.; Tho, I.; Bauer-Brandl, A. Application of multivariate methods to compression behavior evaluation of directly compressible materials. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 72, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, S.; Alshihabi, F.; Betz, G. Investigating the effect of particle size and shape on high speed tableting through radial die-wall pressure monitoring. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 413, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, J.; Liang, X.; Zhong, S. Multivariate analysis approach for correlations between material properties and tablet tensile strength of microcrystalline cellulose. Pharmazie 2012, 67, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pönni, R.; Vuorinen, T.; Kontturi, E. Proposed nano-scale coalescence of cellulose in chemical pulp fibers during technical treatments. BioResource 2012, 7, 6077–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westermarck, S.; Juppo, AM.; Kervinen, L.; Yliruusi, J. Microcrystalline cellulose and its microstructure in pharmaceutical processing. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 1999, 481, 99–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, B.; Alderborn, G. The effect of shape and porosity on the compression behaviour and tablet forming ability of granular materials formed from microcrystalline cellulose. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2001, 52, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hentzschel, C. M, Sakmann A, Leopold, C.S. Comparison of traditional and novel tableting excipients: Physical and compaction properties. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2012, 17, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wen, H.; Desai, D. Lubrication in tablet formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2010, 75, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Secreast, P.J.; Amidon, G.E. Mechanistic study of the effect of roller compaction and lubricant on tablet mechanical strength. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 1342–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoorens, G.; Krier, F.; Rozet, E.; Carlin, B.; Evrard, B. Understanding the impact of microcrystalline cellulose physicochemical properties on tabletability. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 490, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhumal, S.; Kulkarni, P.A.; Kashikar, V.S.; Baweja, J.; Thottasseri, M. A Review: Roller Compaction for Tablet Dosage Form Development. Res. Rev. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 2, 68–73. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, R.W. Roller Compaction Technology. In Handbook of Pharmaceutical Granulation Technology, 3rd ed.; Parikh, D.M., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 163–182. [Google Scholar]
- He, X. Application of roller compaction in solid formulation development. Am. Pharm. Rev. 2003, 6, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, W.; Gilman, J. Dislocation velocities, dislocation densities and plastic flow in lithium fluoride crystals. J. Appl. Phys. 1959, 30, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkowska, S.; Khan, K.A. Effect of re-conpression on the properties of tablets prepared by dry granulation. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1983, 9, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Dahiya, S.; Sun, CC.; Bansa, A. Understanding size enlargement and hardening of granules on tabletability of unlubricated granules prepared by dry granulation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 758–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.C.; Himmelspach, M.W. Reduced tabletability of roller compacted granules as a result of granule size enlargement. J. Pharm. Sci. 2006, 95, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultmann, J.M. Multiple compaction of microcrystalline cellulose in a roller compactor. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 54, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Fara, D.; Al-Hmoud, L.; Rashid, I.; Chowdhry, B.Z.; Badwan, A. Understanding the Performance of a Novel Direct Compression Excipient Comprising Roller Compacted Chitin. Mar. Drugs. 2020, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fara, D.A. A comparison of industrial lactose obtained by roller compaction with spray dried lactose and α-lactose monohydrate using compression analysis techniques. J. Excip. Food Chem. 2019, 10, 41–54. [Google Scholar]
- Abu Fara, D.; Rashid, I.; Alkhamis, K.; Al-Omari, M.; Chowdhry, B.; Badwan, A. Modification of a-lactose monohydrate as a direct compression excipient using roller compaction. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2018, 44, 2038–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, I.; Al-Remawi, M.; Leharne, S.A.; Chowdhry, B.Z.; Badwan, A. A novel multifunctional pharmaceutical excipient: Modification of the permeability of starch by processing with magnesium silicate. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 411, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, L.; Creely, J.J.; Martin, A.E.; Conrad, C.M. An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text. Res. J. 1962, 29, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, R.W. An analysis of powder compaction phenomena. Trans. Metall. Soc. Am. Inst. Mech. Eng. AIME. 1961, 221, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.H.; Kim, N.A.; Chu, K.R.; Jung, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Jeong, S.H. Material properties and compressibility using heckel and kawakita equation with commonly used pharmaceutical excipients. J. Pharm. Invest. 2010, 40, 237–244. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Venkatesh, G.; Fassihi, R. Compactibility characterization of granular pectin for tableting operation using a compaction simulator. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 161, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, K.; Lüdde, K.H. Some considerations on powder compression equations. Powder Technol. 1971, 4, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Muller, F.; Augsburger, L. Evaluation of the plug formation process of silicified microcrystalline cellulose. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 233, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordström, J.; Klevan, I.; Alderborn, G. A particle rearrangement index ased on the kawakita powder compression equation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, B.C.; Colvin, J.T.; Mullarney, M.P.; Zinchuk, A.V. The relative densities of pharmaceutical powders, blends, dry granulations, and immediate-release tablet. Pharm. Technol. 2003, 27, 64–80. [Google Scholar]
- Doelker, E. Comparative compaction properties of various microcrystalline cellulose types and generic products. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1993, 19, 2399–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherrer, P. Bestimmung der Grösse und der inneren Struktur von Kolloidteilchen mittels Röntgenstrahlen. Nachr. Ges. Wiss. Göttingen. 1918, 26, 98–100. [Google Scholar]
- Langford, J.I.; Wilson, A.J.C. Scherrer after sixty years: A survey and some new results in the determination of crystallite size. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1978, 11, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, J.; Kumar, V. Comparative evaluation of silicified microcrystalline cellulose II as a direct compression vehicle. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, Y.; Fukuoka, E.; Nakajima, S.; Hasegawa, J. Crystallinity and physical characteristics of microcrystalline cellulose. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1977, 25, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alebiowu, G.; Osinoiki, KA. Assessment of tapioca starches obtained after different steeping periods as binders in a paracetamol tablet formulation. Farmacia 2010, 58, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Kaushal, A.M.; Bansal, A.K. Compression physics in the formulation development of tablets. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2006, 23, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaca-Medina, G.; Jallabert, B.; Viet, D.; Peydecastaing, J.; Rouilly, A. Effect of temperature on high pressure cellulose compression. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2311–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kothari, S.H. Effect of compressional force on the crystallinity of directly compressible cellulose excipients. Int. J. Pharm. 1999, 177, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ek, R.; Wormald, P.; östelius, J.; Iversen, T.; Nyström, C. Crystallinity index of microcrystalline cellulose particles compressed into tablets. Int. J. Pharm. 1995, 125, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogovina, S.Z.; Zhorin, V.A.; Shashkin, D.P.; Yenikolopyan, N.S. X-ray diffraction study of cellulose after plastic flow under pressure. Polym. Sci. USSR 1989, 31, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechyporchuk, O.; Pignon, F.D.; Belgacem, M.N. Morphological properties of nanofibrillated cellulose produced using wet grinding as an ultimate fibrillation process. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).