Influence of Three Dental Implant Surfaces on Cell Viability and Bone Behavior. An In Vitro and a Histometric Study in a Rabbit Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dental Implant Groups
2.2. Surface Characterization
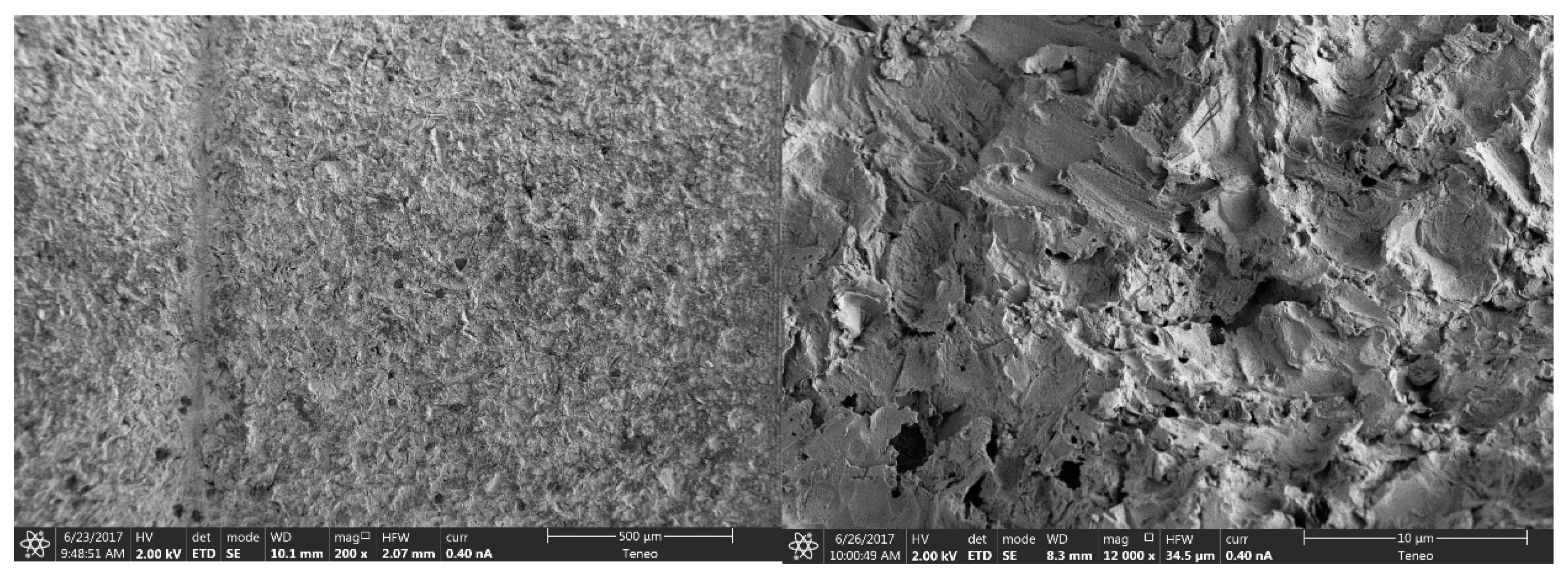
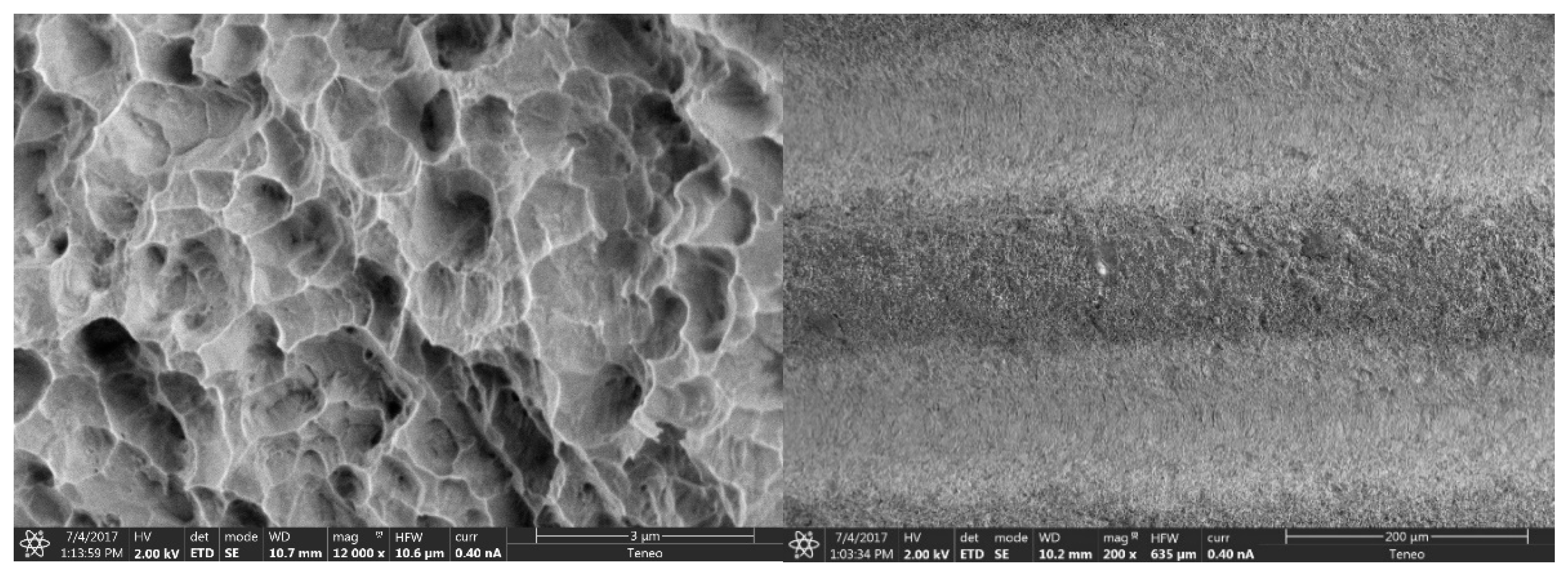
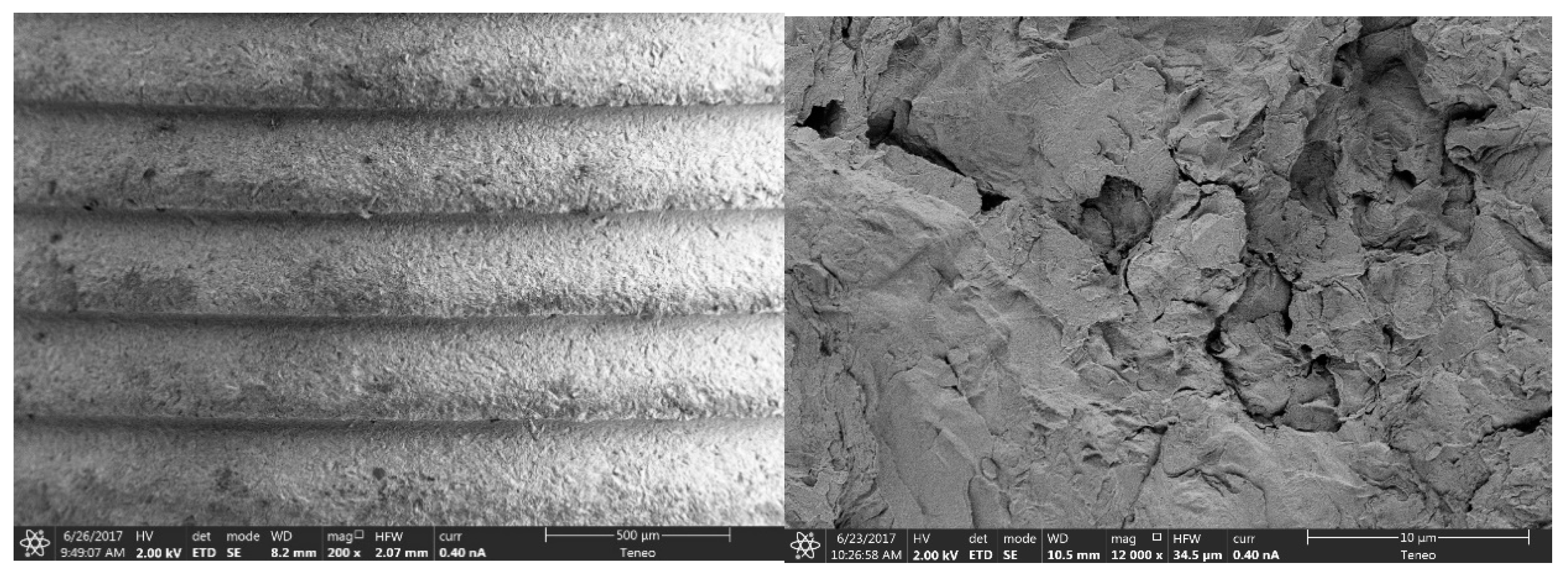
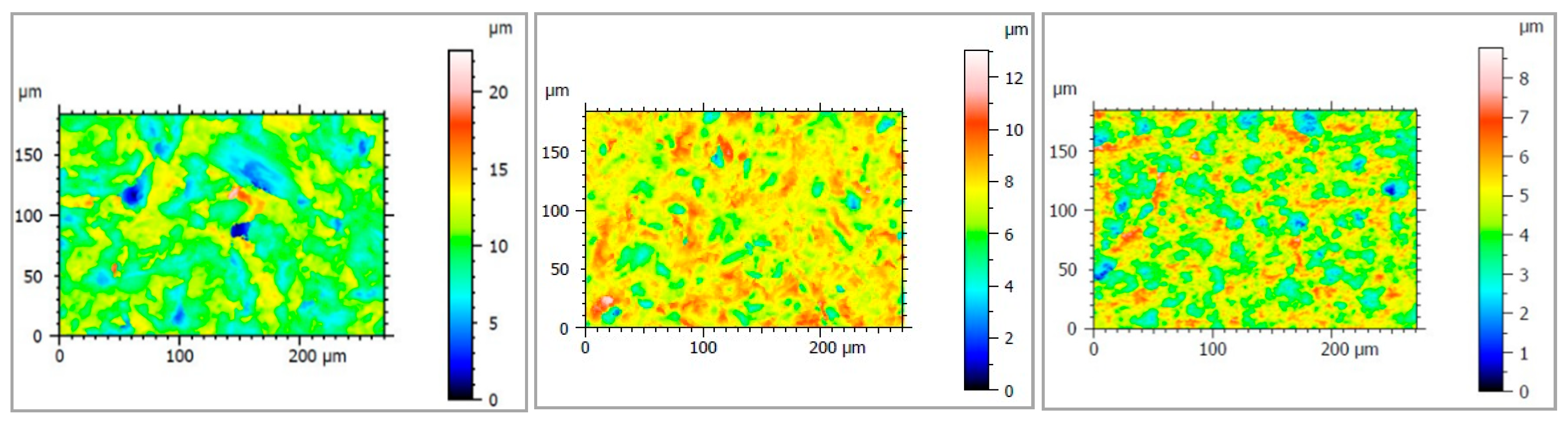
2.2.1. Morphological Analysis of the Surface
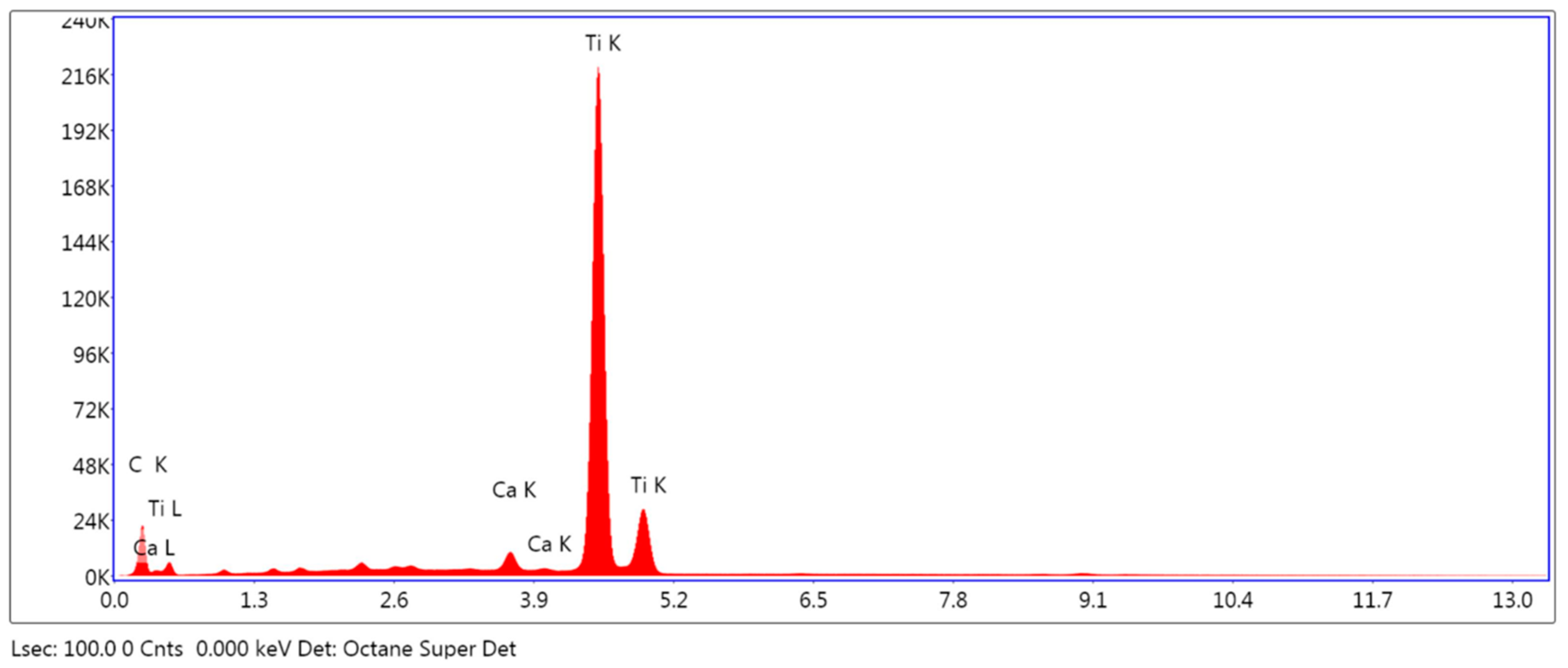
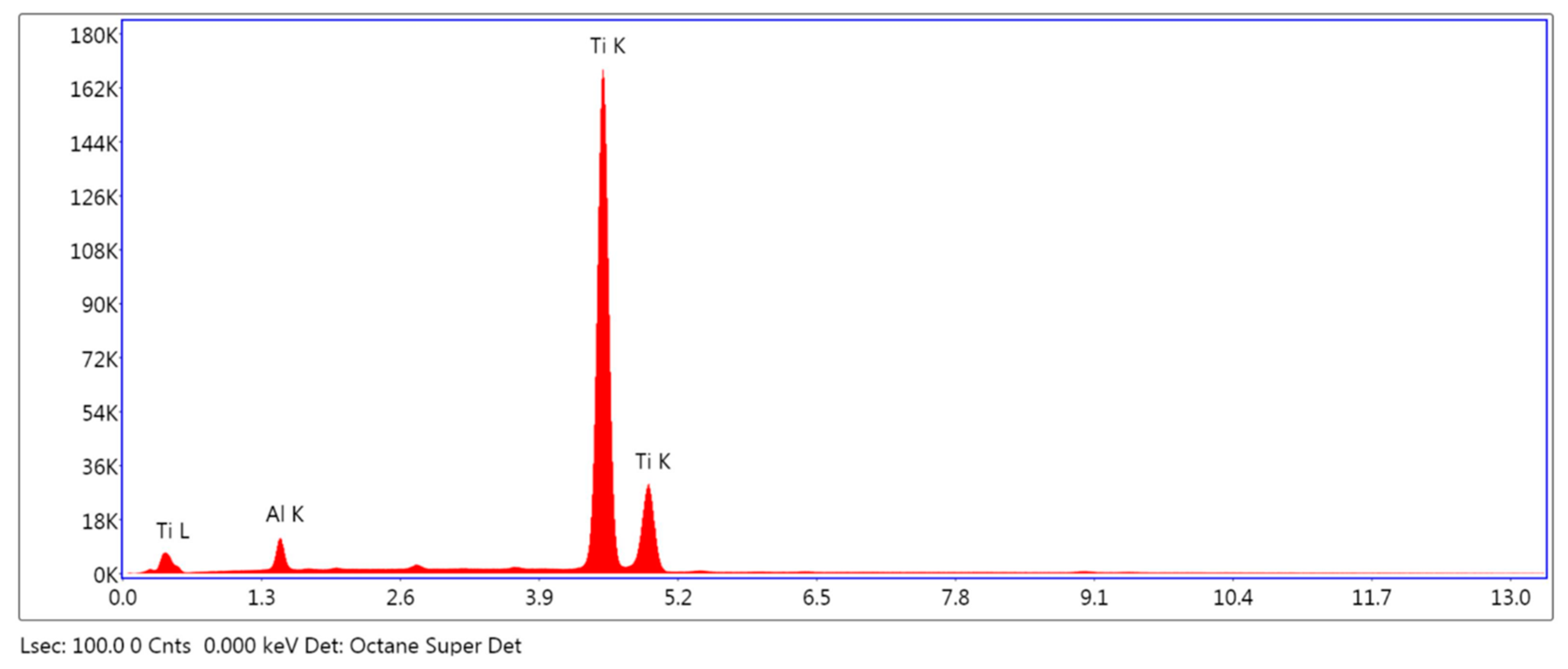
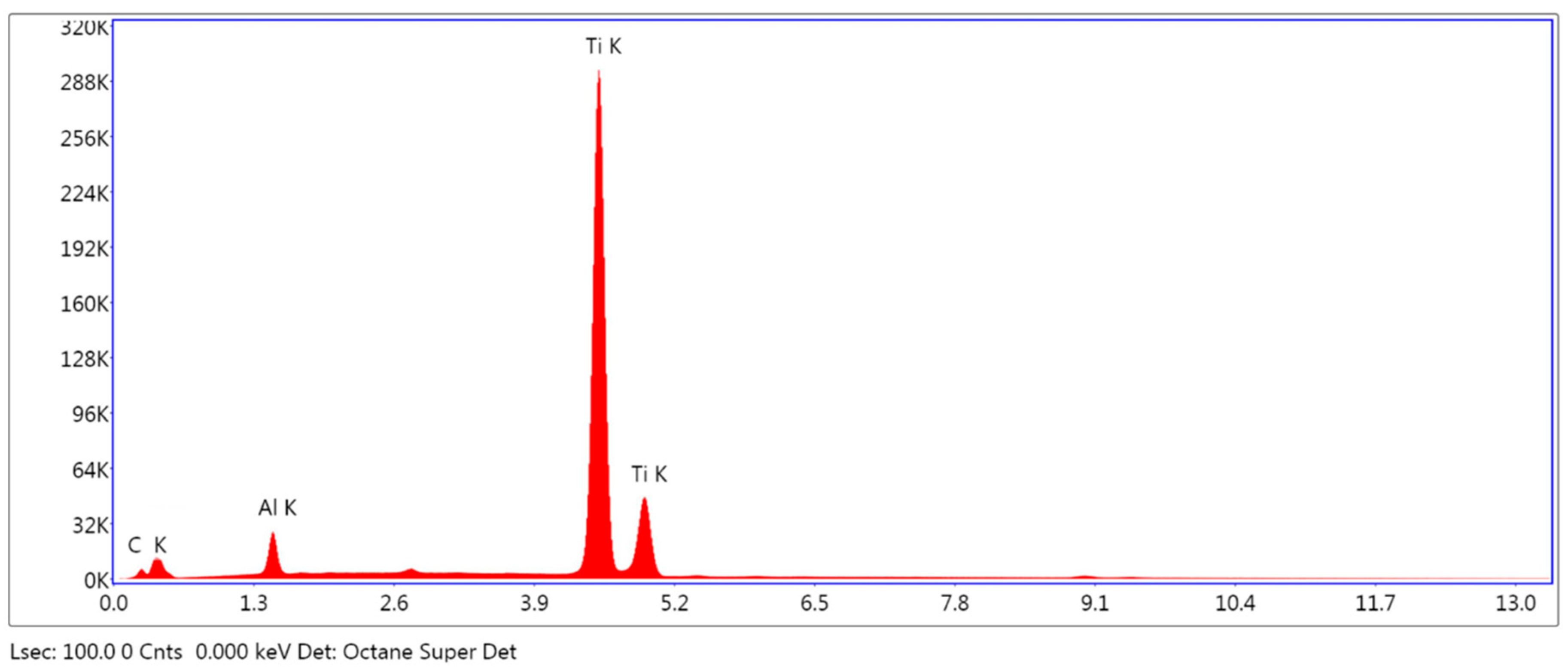
2.2.2. Elemental Analysis of the Surface
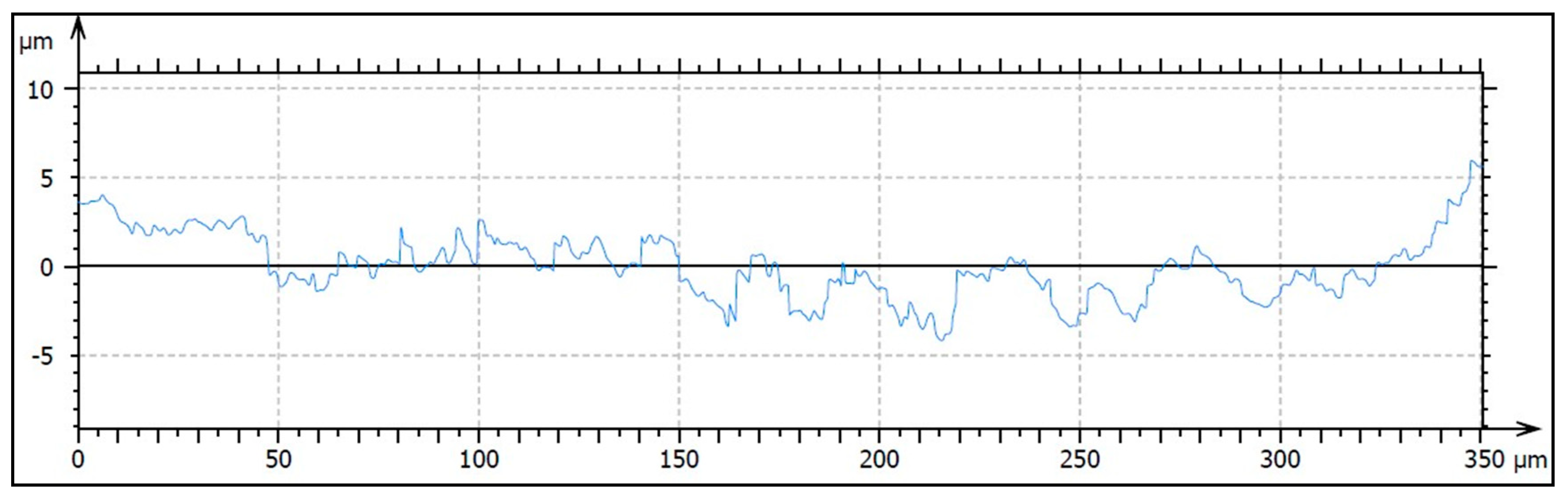
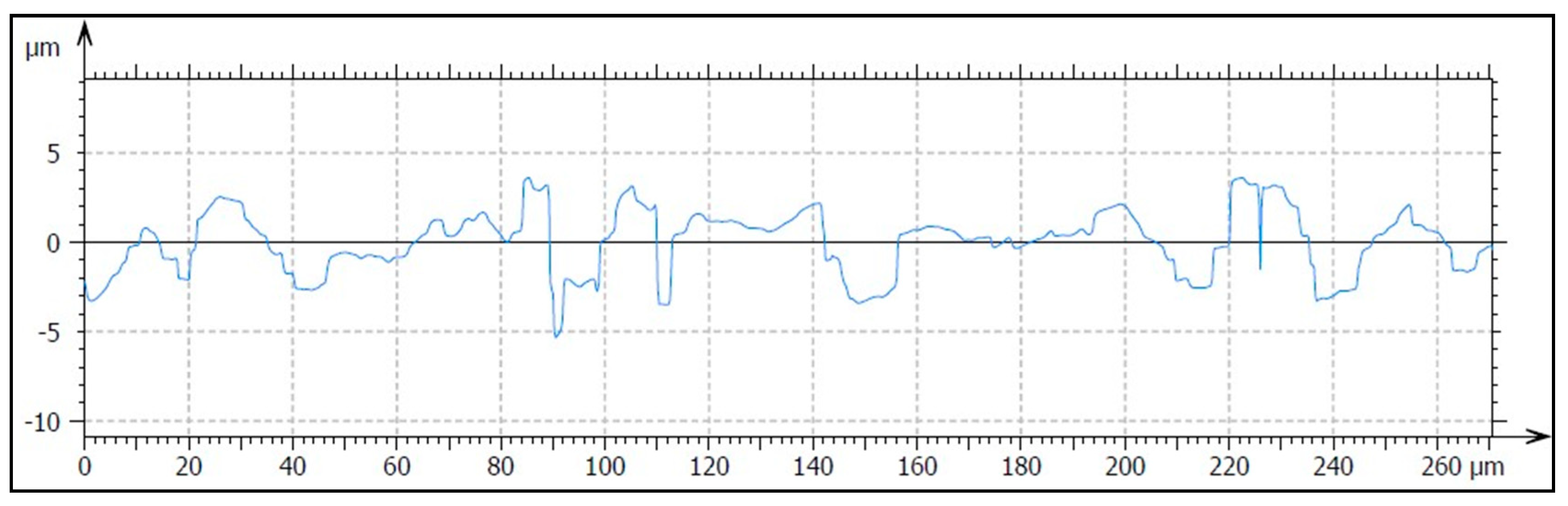
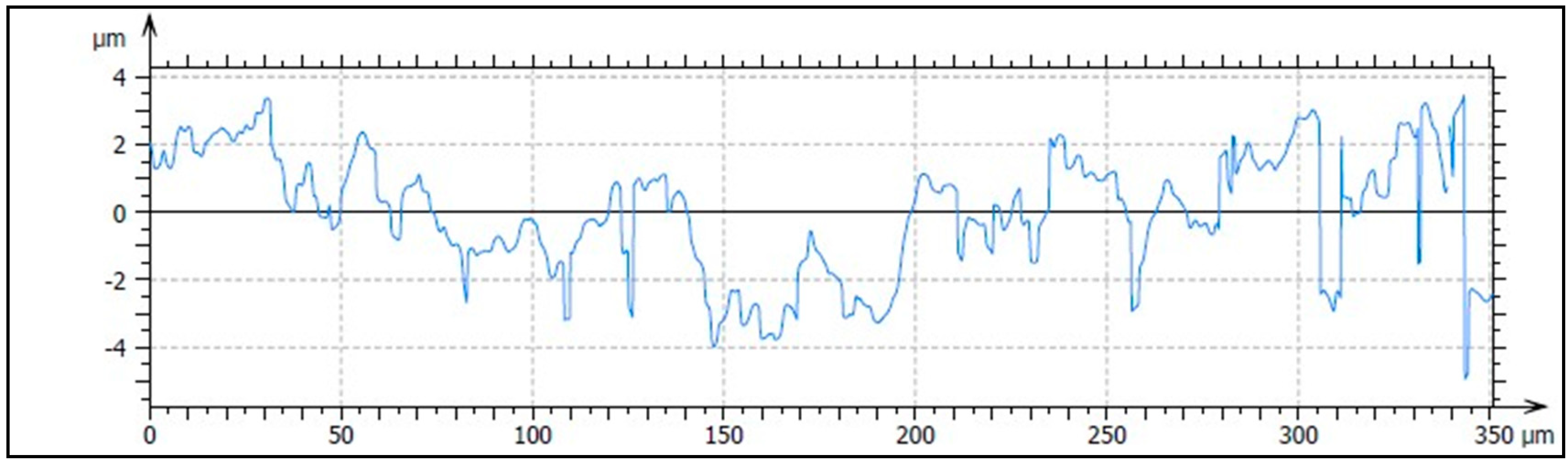
2.2.3. Analysis of Surface Roughness
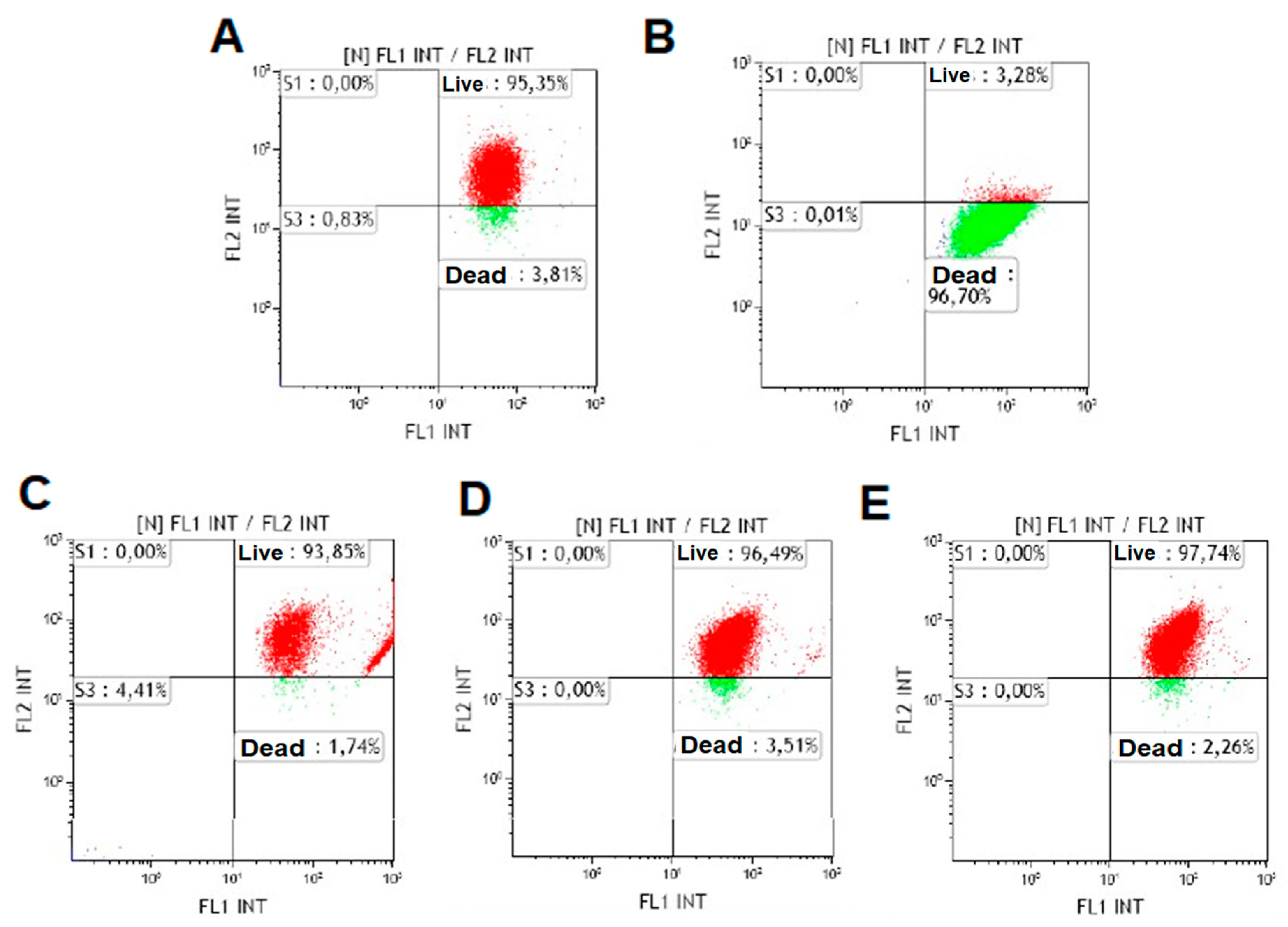
2.3. Cell Viability Study
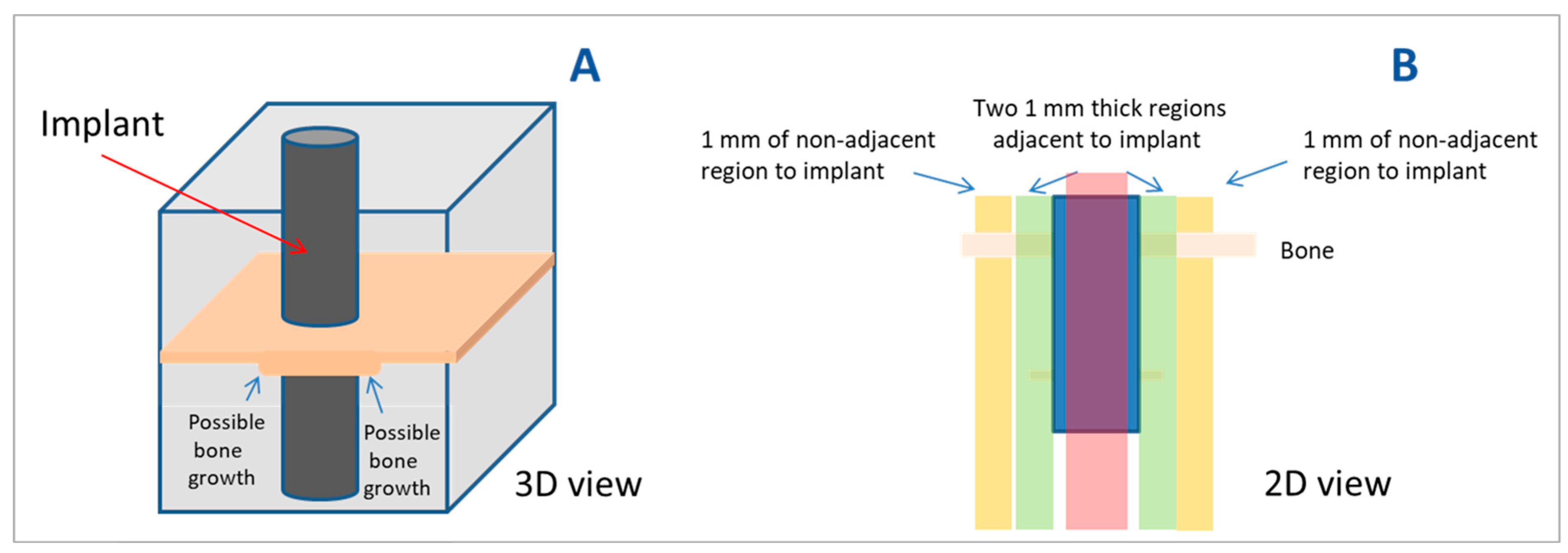
2.4. Experimental Animal Study
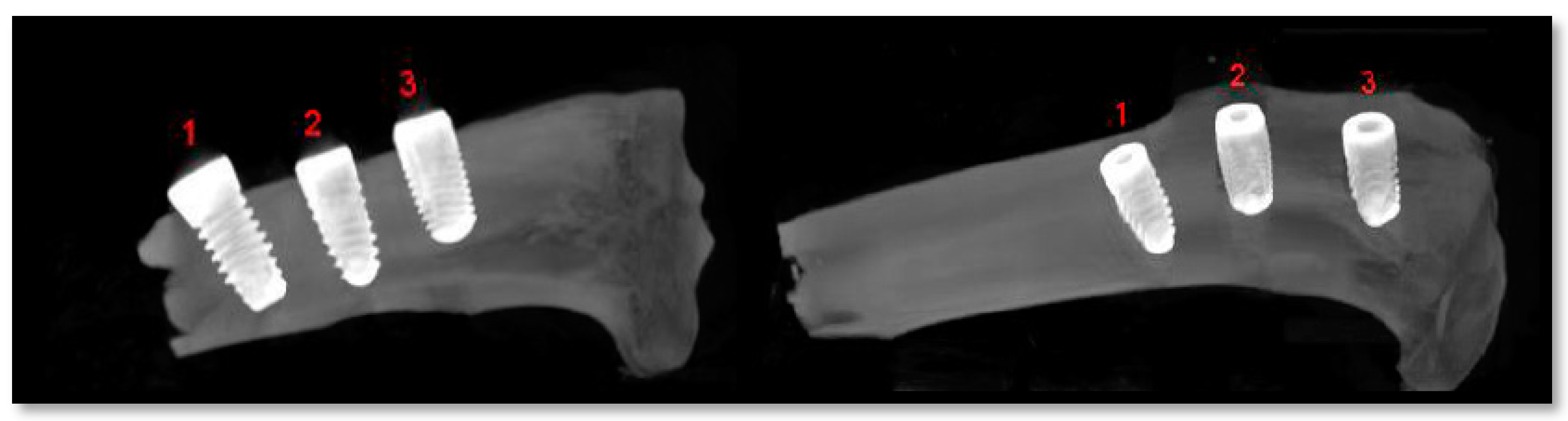
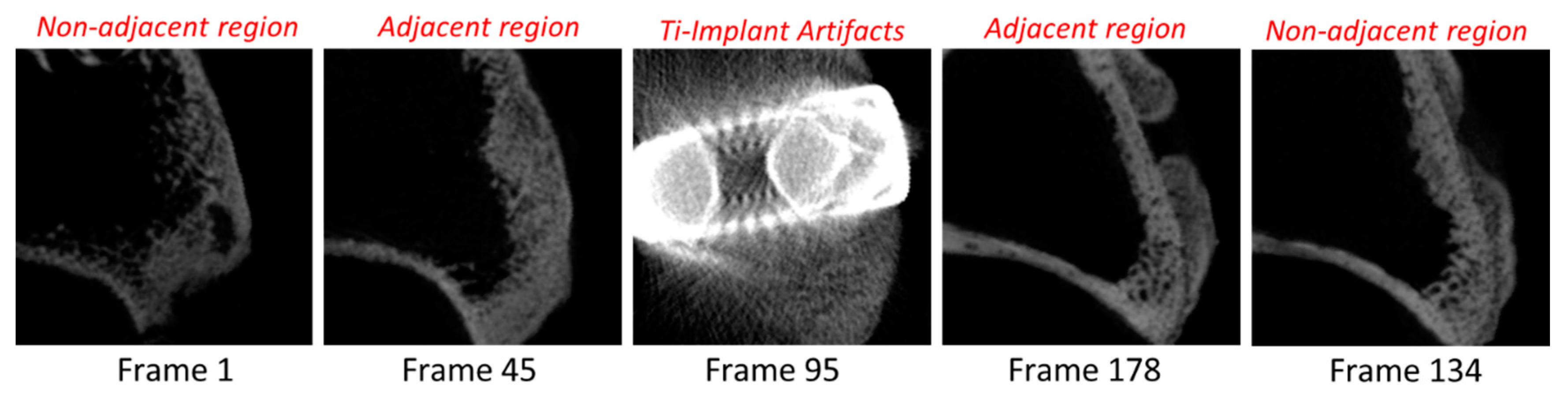
2.5. Radiological Analysis
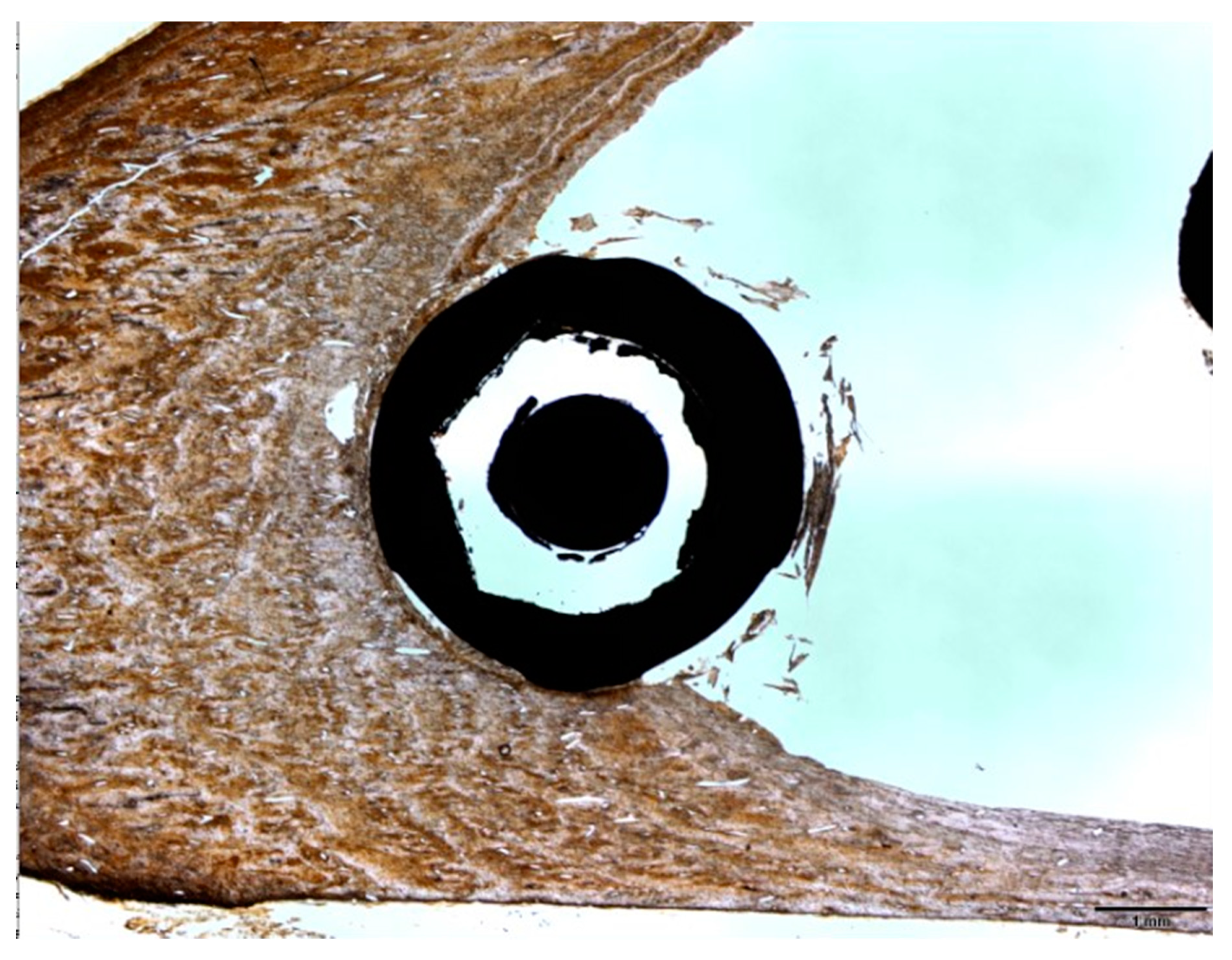
2.6. Histomorphometric Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surface Characterization
3.1.1. Morphological Analysis of the Surface
3.1.2. Elemental Analysis of the Surface
3.1.3. Analysis of Surface Profile
3.2. Cell Viability Study
3.3. Experimental Animal Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21 (Suppl. 1), 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Babík, O.; Czán, A.; Holubjak, J.; Kameník, R.; Pilc, J. Identification of Surface Characteristics Created by Miniature Machining of Dental Implants Made of Titanium Based Materials. Procedia Eng. 2017, 192, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, M.; Singh, Y.; Arora, P.; Arora, V.; Jain, K. Implant biomaterials: A comprehensive review. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, C.N.; Fernandes, D.J.; Resende, C.R.; Roestel, J. Mechanical properties, surface morphology and stability of a modified commercially pure high strength titanium alloy for dental implants. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, e1–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshardt, D.D.; Chappuis, V.; Buser, D. Osseointegration of titanium, titanium alloy and zirconia dental implants: Current knowledge and open questions. Periodontol 2000 2017, 73, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, M.; Guida, L. The Effect of Titanium Surface Modifications on Dental Implant Osseointegration. Front. Oral Biol. 2015, 17, 62–77. [Google Scholar]
- Stanford, C.M. Surface modifications of dental implants. Aust. Dent. J. 2008, 53 (Suppl. 1), S26–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Bhongade, M. Dental Implant Surface Modifications: A Review. J. Dent. Med. Sci. 2016, 15, 132–141. [Google Scholar]
- Jemat, A.; Ghazali, M.J.; Razali, M.; Otsuka, Y. Surface Modifications and Their Effects on Titanium Dental Implants. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 791725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, N.I.; Kerr, M. Chapter 9: Dental Implant Surfaces. In Misch’s Contemporary Implant Dentistry, 4th ed.; Resnik, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; p. 197. [Google Scholar]
- Barfeie, A.; Wilson, J.; Rees, J. Implant surface characteristics and their effect on osseointegration. Br. Dent. J. 2015, 218, E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaro, C.; Rotolo, P.; De Riccardis, F.; Milella, E.; Napoli, A.; Wieland, M.; Textor, M.; Spencer, N.D.; Brunette, D.M. Comparative investigation of the surface properties of commercial titanium dental implants. Part I: Chemical composition. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2002, 13, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smeets, R.; Stadlinger, B.; Schwarz, F.; Beck-Broichsitter, B.; Jung, O.; Precht, C.; Kloss, F.; Gröbe, A.; Heiland, M.; Ebker, T. Impact of Dental Implant Surface Modifications on Osseointegration. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 6285620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemlata, G.; Gaurav, B.; Arvind, G. Implant Surface Modifications: A Review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2012, 6, 319–324. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.Y.; Davies, J.E. Red blood cell and platelet interactions with titanium implant surfaces. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2000, 11, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornstein, M.M.; Reichart, P.A.; Buser, D.; Bosshardt, D.D. Tissue response and wound healing after placement of two types of bioengineered grafts containing vital cells in submucosal maxillary pouches: An experimental pilot study in rabbits. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2011, 26, 768–775. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo-Dalí, G.; Castillo-Oyagüe, R.; Terriza, A.; Saffar, J.L.; Batista-Cruzado, A.; Lynch, C.D.; Sloan, A.J.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.L.; Torres-Lagares, D. Pre-prostheticuseofpoly (lactic–co–glycolicacid) membranes treated with oxygen plasma and TiO2 nanocomposite particles for guided bone regeneration processes. J. Dent. 2016, 47, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouxsein, M.L.; Boyd, S.K.; Christiansen, B.A.; Guldberg, R.E.; Jepsen, K.J.; Müller, R. Guidelines for assessment of bone microstructure in rodents using micro–computed tomography. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2010, 25, 1468–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donath, K.; Breuner, G. A method for the study of undecalcified bones and teeth with attached soft tissues. The Säge-Schliff (sawing and grinding) technique. J. Oral Pathol. 1982, 11, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres-Lagares, D.; Castellanos-Cosano, L.; Serrera-Figallo, M.Á.; García-García, F.J.; López-Santos, C.; Barranco, A.; Rodríguez-Gonzalez Elipe, A.; Rivera-Jiménez, C.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.L. In Vitro and in Vivo Study of Poly (Lactic⁻co⁻Glycolic) (PLGA) Membranes Treated with Oxygen Plasma and Coated with Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite Ultrathin Films for Guided Bone Regeneration Processes. Polymers 2017, 9, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernhardt, R.; Kuhlisch, E.; Schulz, M.C.; Eckelt, U.; Stadlinger, B. Comparison of bone-implant contact and bone-implant volume between 2D-histological sections and 3D-SRµCT slices. Eur. Cell Mater. 2012, 23, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Choi, S.H.; Ryu, J.J.; Koh, S.Y.; Park, J.H.; Lee, I.S. The biocompatibility of SLA-treated titanium implants. Biomed. Mater. 2008, 3, 025011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guehennec, L.; Goyenvalle, E.; Lopez-Heredia, M.A.; Weiss, P.; Amouriq, Y.; Layrolle, P. Histomorphometric analysis of the osseointegration of four different implant surfaces in the femoral epiphyses of rabbits. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, P.G.; Granjeiro, J.M.; Romanos, G.E.; Suzuki, M.; Silva, N.R.; Cardaropoli, G.; Thompson, V.P.; Lemons, J.E. Basic research methods and current trends of dental implant surfaces. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B 2009, 88, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, W.J.; Kim, S.G.; Oh, J.S.; You, J.S.; Jeong, K.I.; Lim, S.C.; Jeong, M.A. Comparative study on the osseointegration of implants in dog mandibles according to the implant surface treatment. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 42, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citeau, A.; Guicheux, J.; Vinatier, C.; Layrolle, P.; Nguyen, T.P.; Pilet, P.; Daculsi, G. In vitro biological effects of titanium rough surface obtained by calcium phosphate grid blasting. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piattelli, A.; Degidi, M.; Paolantonio, M.; Mangano, C.; Scarano, A. Residual aluminum oxide on the surface of titanium implants has no effect on osseointegration. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4081–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehrke, S.A.; Taschieri, S.; Del Fabbro, M.; Coelho, P.G. Positive Biomechanical Effects of Titanium Oxide for Sandblasting Implant Surface as an Alternative to Aluminium Oxide. J. Oral Implantol. 2015, 41, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, M.; Hirsch, J.M.; Lekholm, U.; Thomsen, P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (II). Etiopathogenesis. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 1998, 106, 721–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafie, H.R.; Ballard, M.L. Abutment Preparation Techniques for One-Piece Titanium and Zirconia Implants. In Clinical and Laboratory Manual of Dental Implant Abutments; Shafie, H.R., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sezin, M.; Croharé, L.; Ibañez, J.C. Microscopic Study of Surface Microtopographic Characteristics of Dental Implants. Open Dent. J. 2016, 10, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Oral implant surfaces: Part 1–Review focusing on topographic and chemical properties of different surfaces and in vivo responses to them. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Bachle, M.; Kohal, R.J. A systematic review of the influence of different titanium surfaces on proliferation, differentiation and protein synthesis of osteoblast-like MG63 cells. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2004, 15, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, D.; Broggini, N.; Wieland, M.; Schenk, R.K.; Denzer, A.J.; Cochran, D.L.; Hoffmann, B.; Lussi, A.; Steinemann, S.G. Enhanced bone apposition to a chemically modified SLA titanium surface. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, R.; Ueno, T.; Migita, S.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Doi, H.; Ogawa, T.; Hanawa, T.; Wakabayashi, N. Hydrocarbon Deposition Attenuates Osteoblast Activity on Titanium. J. Dent. Res. 2014, 93, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, T.; Nishimura, I. Different bone integration profiles of turned and acid-etched implants associated with modulated expression of extracellular matrix genes. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2003, 18, 200–210. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, M.B.; Albrektsson, T.; Francischone, C.E.; Schwartz Filho, H.O.; Wennerberg, A. The influence of surface treatment on the implant roughness pattern. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2012, 20, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fabbro, M.D.; Taschieri, S.; Canciani, E.; Addis, A.; Musto, F.; Weinstein, R.; Dellavia, C. Osseointegration of Titanium Implants With Different Rough Surfaces: A Histologic and Histomorphometric Study in an Adult Minipig Model. Implant Dent. 2017, 26, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dundar, S.; Yaman, F.; Bozoglan, A.; Yildirim, T.T.; Kirtay, M.; Ozupek, M.F.; Artas, G. Comparison of Osseointegration of Five Different Surfaced Titanium Implants. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 29, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P.G.; Bonfante, E.A.; Pessoa, R.S.; Marin, C.; Granato, R.; Giro, G.; Witek, L.; Suzuki, M. Characterization of five different implant surfaces and their effect on osseointegration: A study in dogs. J. Periodontol. 2011, 82, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfante, E.A.; Marin, C.; Granato, R.; Suzuki, M.; Hjerppe, J.; Witek, L.; Coelho, P.G. Histologic and biomechanical evaluation of alumina-blasted/acid-etched and resorbable blasting media surfaces. J. Oral Implantol. 2012, 38, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, C.; Granato, R.; Suzuki, M.; Janal, M.N.; Gil, J.N.; Nemcovsky, C.; Bonfante, E.A.; Coelho, P.G. Biomechanical and histomorphometric analysis of etched and non-etched resorbable blasting media processed implant surfaces: An experimental study in dogs. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 3, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszewska-Kuska, M.; Wirstlein, P.; Majchrowski, R.; Dorocka-Bobkowska, B. Osteoblastic cell behaviour on modified titanium surfaces. Micron 2018, 105, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azcarate-Velázquez, F.; Castillo-Oyagüe, R.; Oliveros-López, L.G.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Martínez-González, A.J.; Pérez-Velasco, A.; Lynch, C.D.; Gutiérrez-Pérez, J.L.; Serrera-Figallo, M.A. Influence of bone quality on the mechanical interaction between implant and bone: A finite element analysis. J. Dent. 2019, 88, 103161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Degidi, M.; Perrotti, V.; Degidi, D.; Piattelli, A.; Iezzi, G. Experimental evaluation in rabbits of the effects of thread concavities in bone formation with different titanium implant surfaces. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarano, A.; Lorusso, C.; Di Giulio, C.; Mazzatenta, A. Evaluation of the Sealing Capability of the Implant Healing Screw by Using Real Time Volatile Organic Compounds Analysis: Internal Hexagon Versus Cone Morse. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Implant Manufacturer | Surface Name | Group Name | Titanium Grade | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ziacom | SLA (sandblasted and acid etched) | SLA | Ti grade IV | ZSS4011 |
| BioHorizons | RBT (resorbable hydroxyapatite and tricalcium phosphate (HA and TCP) blast texturing) | HA/TCP | Ti-6Al-4V (grade V) | PGR4009 |
| Zimmer | MTX (microtextured, HA blast, and non-etching acid wash) | HA + AW | Ti-6Al-4V (grade V) | TSVT4B8 |
| Element | Weight % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SLA | HA/TCP | HA + AW | |
| C K | 9.38 (10.23) | 5.23 (8.05) | 3.91 (1.02) |
| Al K | - | 4.60 (4.36) | 3.82 (0.19) |
| Ti K | 89.53 (11.77) | 84.76 (15.59) | 92.27 (0.82) |
| SLA, sandblasted and double acid etched. HA/TCP, hydroxyapatite and tricalcium phosphate blasted. HA + AW, hydroxyapatite blasted and non-etching acid wash. | |||
| Implant | Ra (μm) (SD) | Rq (μm) (SD) | Rp (μm) (SD) | Rv (μm) (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLA | 0.82 (0.10) * | 0.97 (0.08) * | 1.84 (0.04) **, *** | 2.21 (0.01) |
| HA/TCP | 1.11 (0.03) * | 1.45 (0.10) * | 2.97 (0.28) *, *** | 3.38 (1.28) |
| HA + AW | 0.97 (0.17) | 1.18 (0.24) | 2.07 (0.27) *, ** | 3.11 (0.62) |
| Implant | Sa (μm) (SD) | Sq (μm) (SD) | Sp (μm) (SD) | Sv (μm) (SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SLA | 0.76 (0.01) **, *** | 0.97 (0.01) **, *** | 4.20 (0.12) * | 4.62 (0.20) *, ** |
| HA/TCP | 1.61 (0.02) *, *** | 2.05 (0.01) *, *** | 11.69 (1.48) * | 9.35 (4.02) * |
| HA + AW | 0.92 (0.07) *, ** | 1.21 (0.11) *, ** | 10.67 (7.27) | 7.97 (0.68) ** |
| Mean | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Volume (mm3) | SLA | 0.197 | 0.225 |
| HA/TCP | 0.129 | 0.242 | |
| HA + AW | 0.009 | 0.007 | |
| Bone density (HU) | SLA | 642.00 | 149.14 |
| HA/TCP | 505.83 | 212.02 | |
| HA + AW | 442.25 | 235.28 | |
| Accumulated density (HU) | SLA | 4,806,900.00 | 5,857,115.70 |
| HA/TCP | 1,862,223.17 | 3,282,273.12 | |
| HA + AW | 233,098.00 | 225,000.53 | |
| Mean | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Area (mm2) | SLA | 2499 | 2026 |
| HA/TCP | 3147 | 1978 | |
| HA + AW | 1933 | 1022 | |
| BIC (%) | SLA | 40.6 * | 17.77 |
| HA/TCP | 41.28 ** | 11.26 | |
| HA + AW | 27.60 *, ** | 9.62 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizo-Gorrita, M.; Fernandez-Asian, I.; Garcia-de-Frenza, A.; Vazquez-Pachon, C.; Serrera-Figallo, M.-A.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Gutierrez-Perez, J.-L. Influence of Three Dental Implant Surfaces on Cell Viability and Bone Behavior. An In Vitro and a Histometric Study in a Rabbit Model. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144790
Rizo-Gorrita M, Fernandez-Asian I, Garcia-de-Frenza A, Vazquez-Pachon C, Serrera-Figallo M-A, Torres-Lagares D, Gutierrez-Perez J-L. Influence of Three Dental Implant Surfaces on Cell Viability and Bone Behavior. An In Vitro and a Histometric Study in a Rabbit Model. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(14):4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144790
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizo-Gorrita, María, Ignacio Fernandez-Asian, Andreina Garcia-de-Frenza, Celia Vazquez-Pachon, Maria-Angeles Serrera-Figallo, Daniel Torres-Lagares, and Jose-Luis Gutierrez-Perez. 2020. "Influence of Three Dental Implant Surfaces on Cell Viability and Bone Behavior. An In Vitro and a Histometric Study in a Rabbit Model" Applied Sciences 10, no. 14: 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144790
APA StyleRizo-Gorrita, M., Fernandez-Asian, I., Garcia-de-Frenza, A., Vazquez-Pachon, C., Serrera-Figallo, M.-A., Torres-Lagares, D., & Gutierrez-Perez, J.-L. (2020). Influence of Three Dental Implant Surfaces on Cell Viability and Bone Behavior. An In Vitro and a Histometric Study in a Rabbit Model. Applied Sciences, 10(14), 4790. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144790







