Mechanism of HCB-Modified Asphalt and Dynamic Properties of Mixtures
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Base Asphalt
2.2. Preparation of HCB
2.3. Preparation of HCB-Modified Asphalt
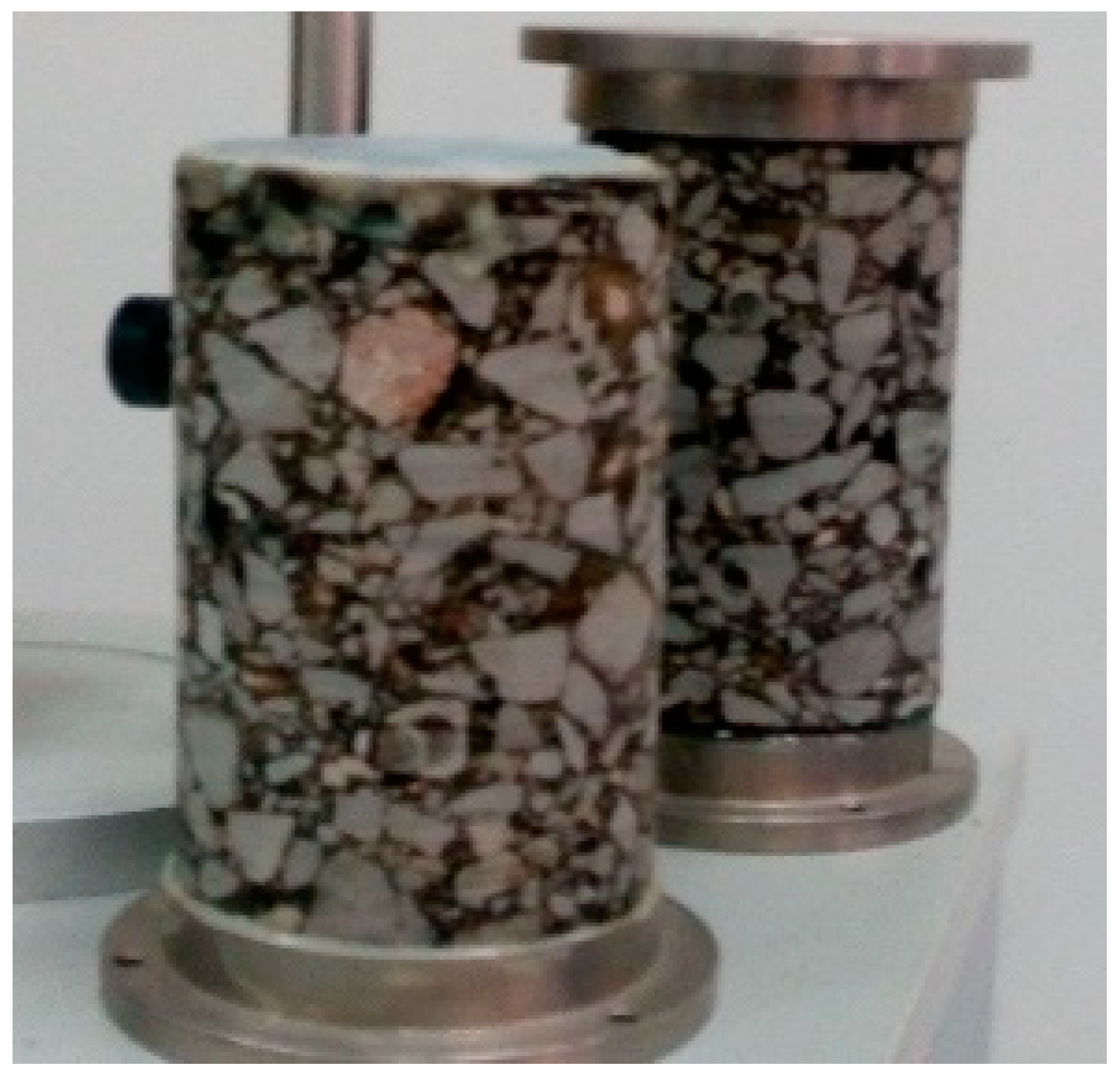
2.4. Preparation of HCB-Modified Asphalt Mixture
3. Test Methods
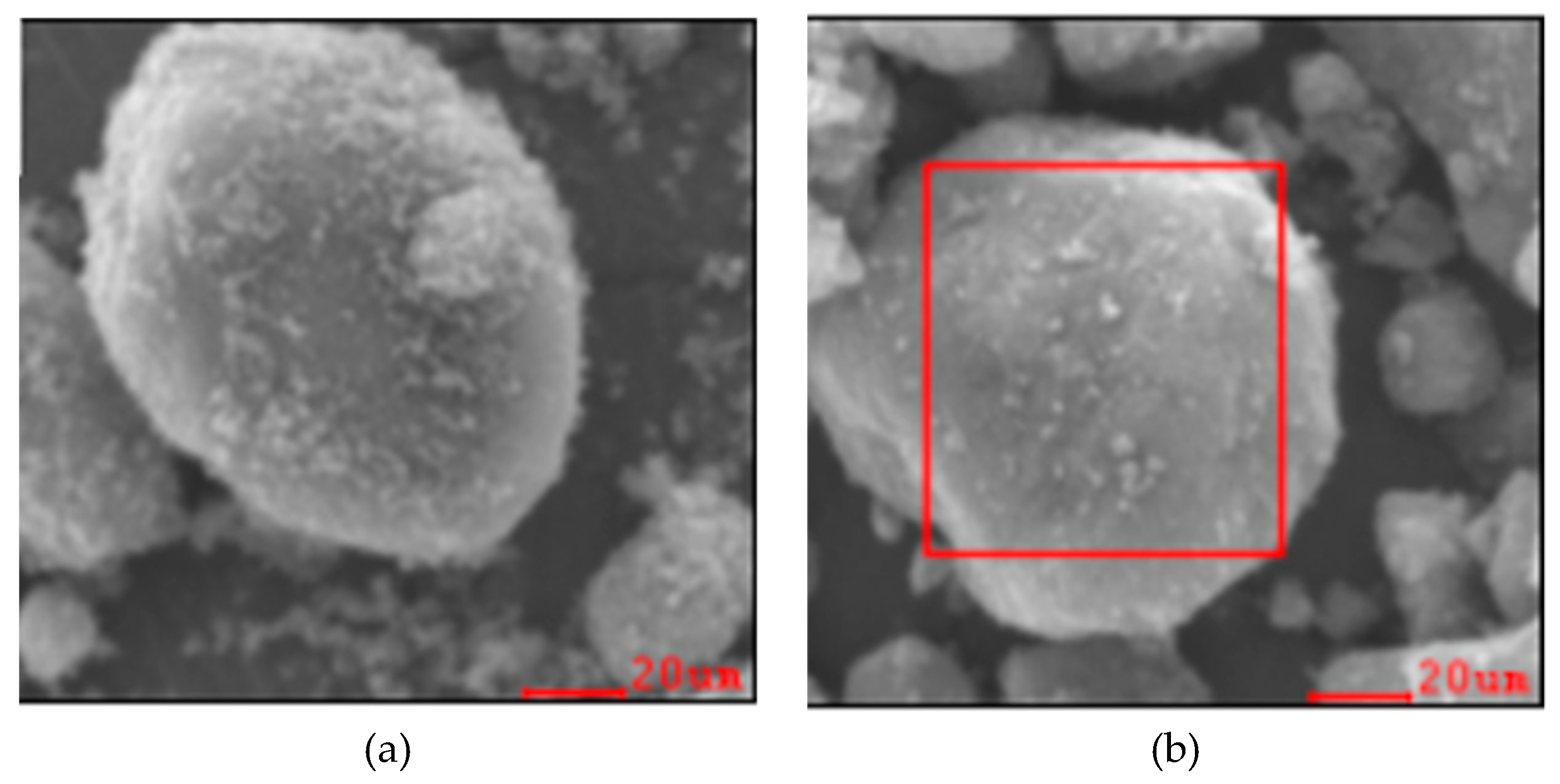
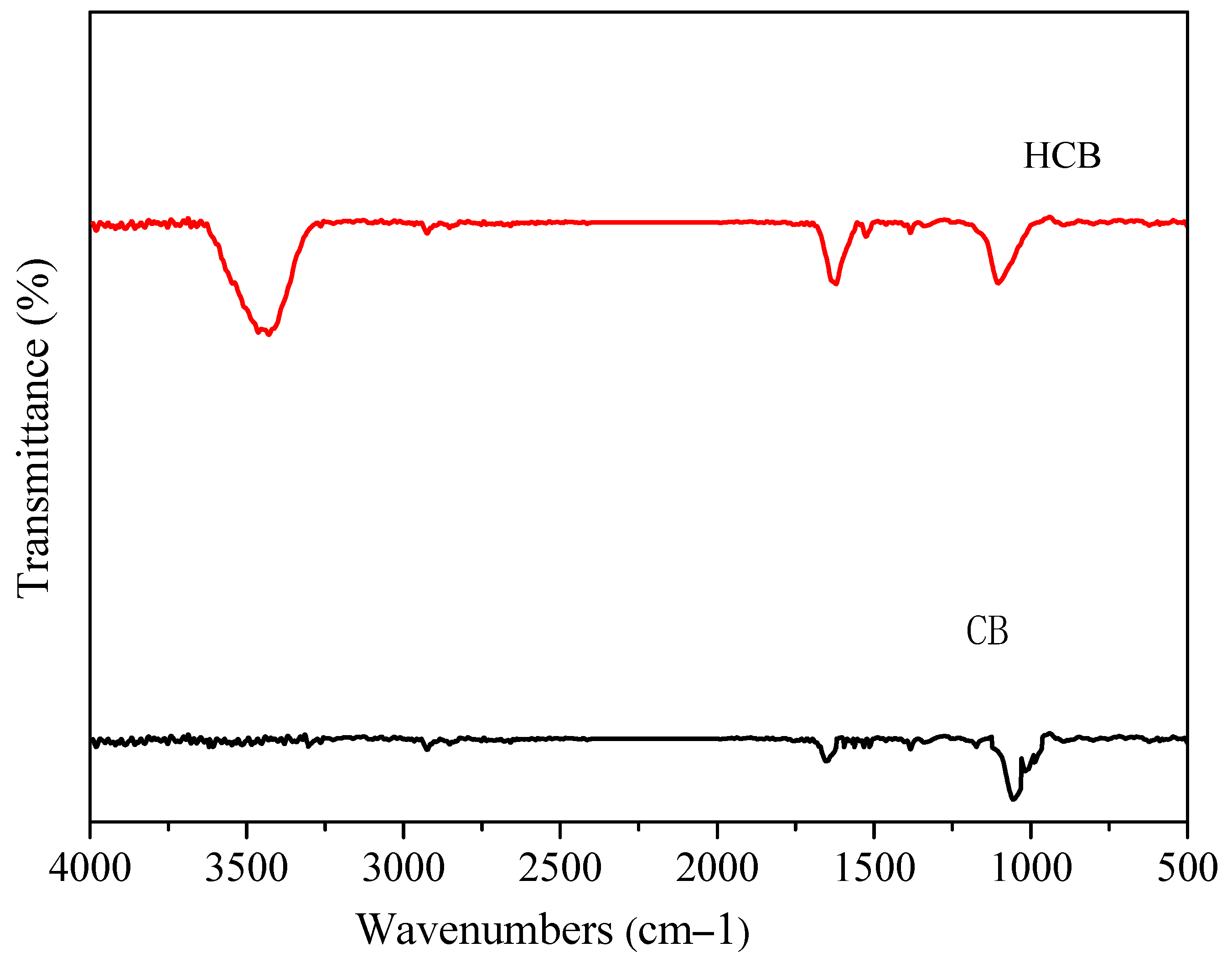
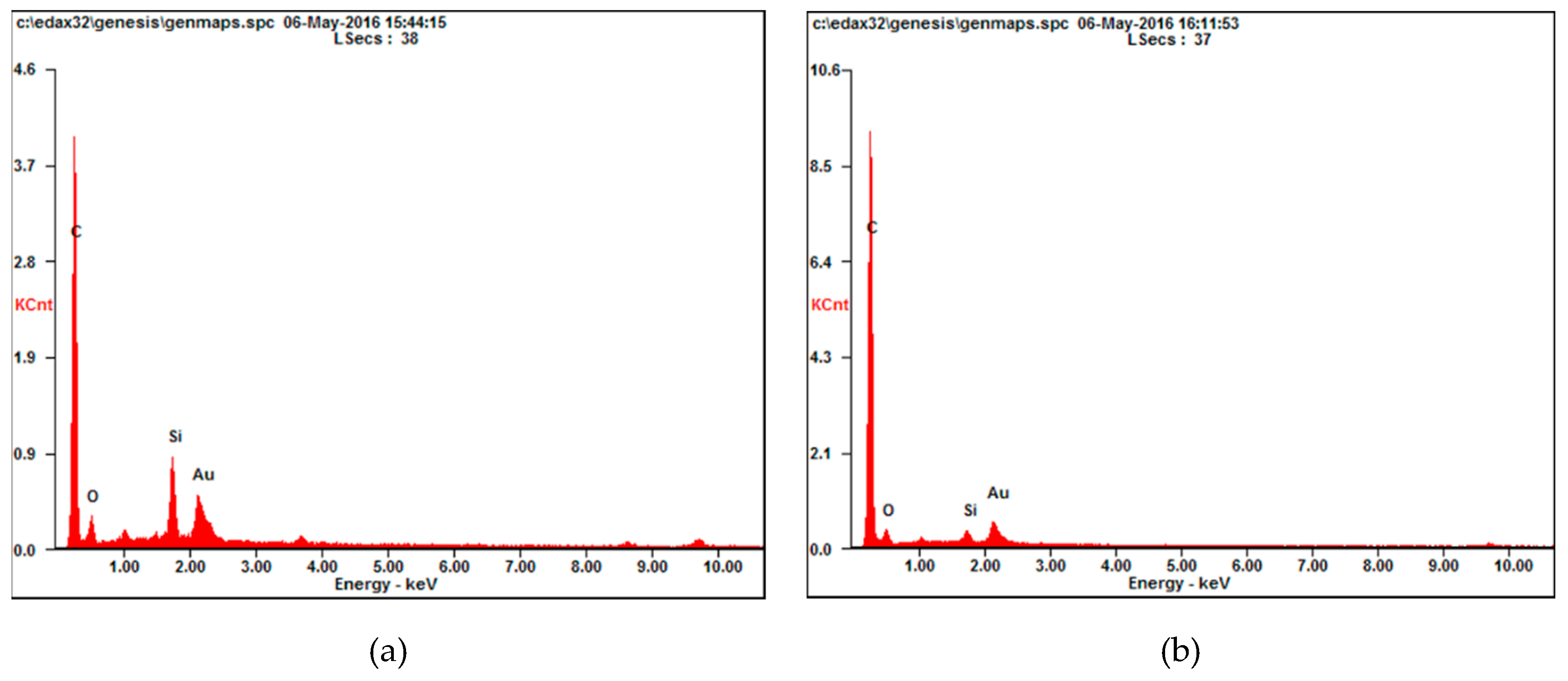
3.1. Microscopic Tests of HCB
3.2. Property Tests of HCB-Modified Asphalt
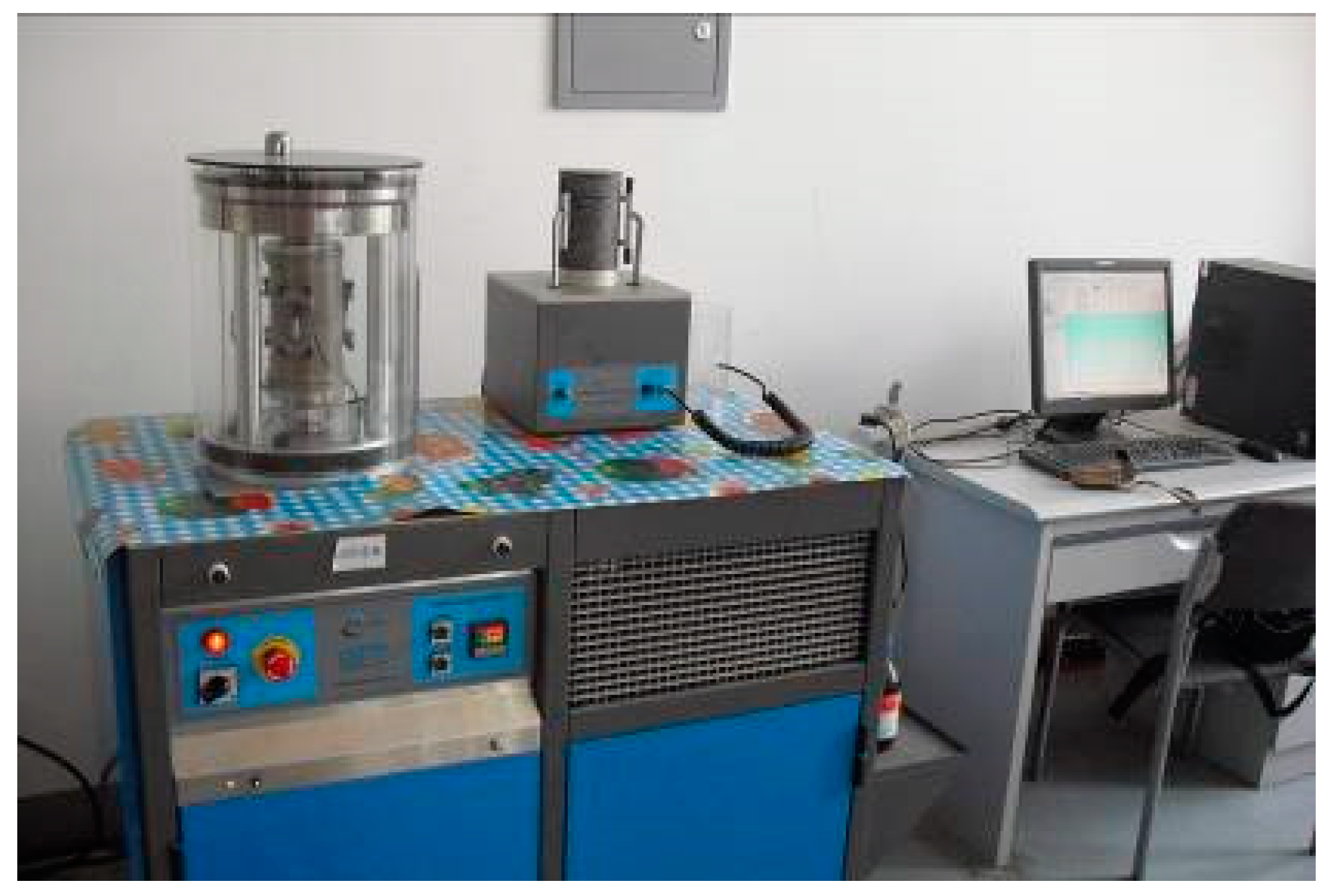
3.3. SPT of HCB-Modified Asphalt Mixture
4. Microstructural Analysis of HCB
5. Analysis of HCB-Modified Asphalt Properties
5.1. Basic Properties
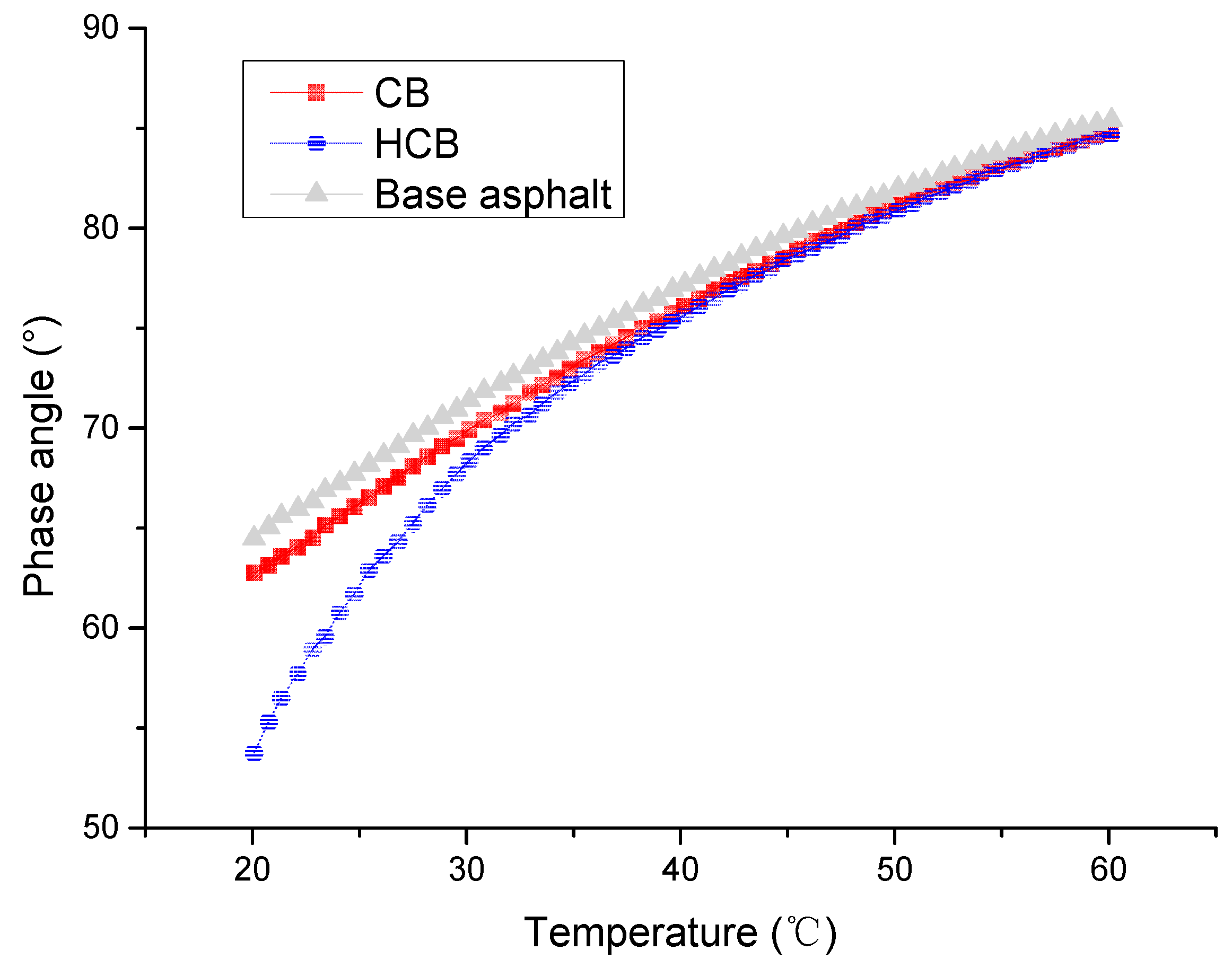
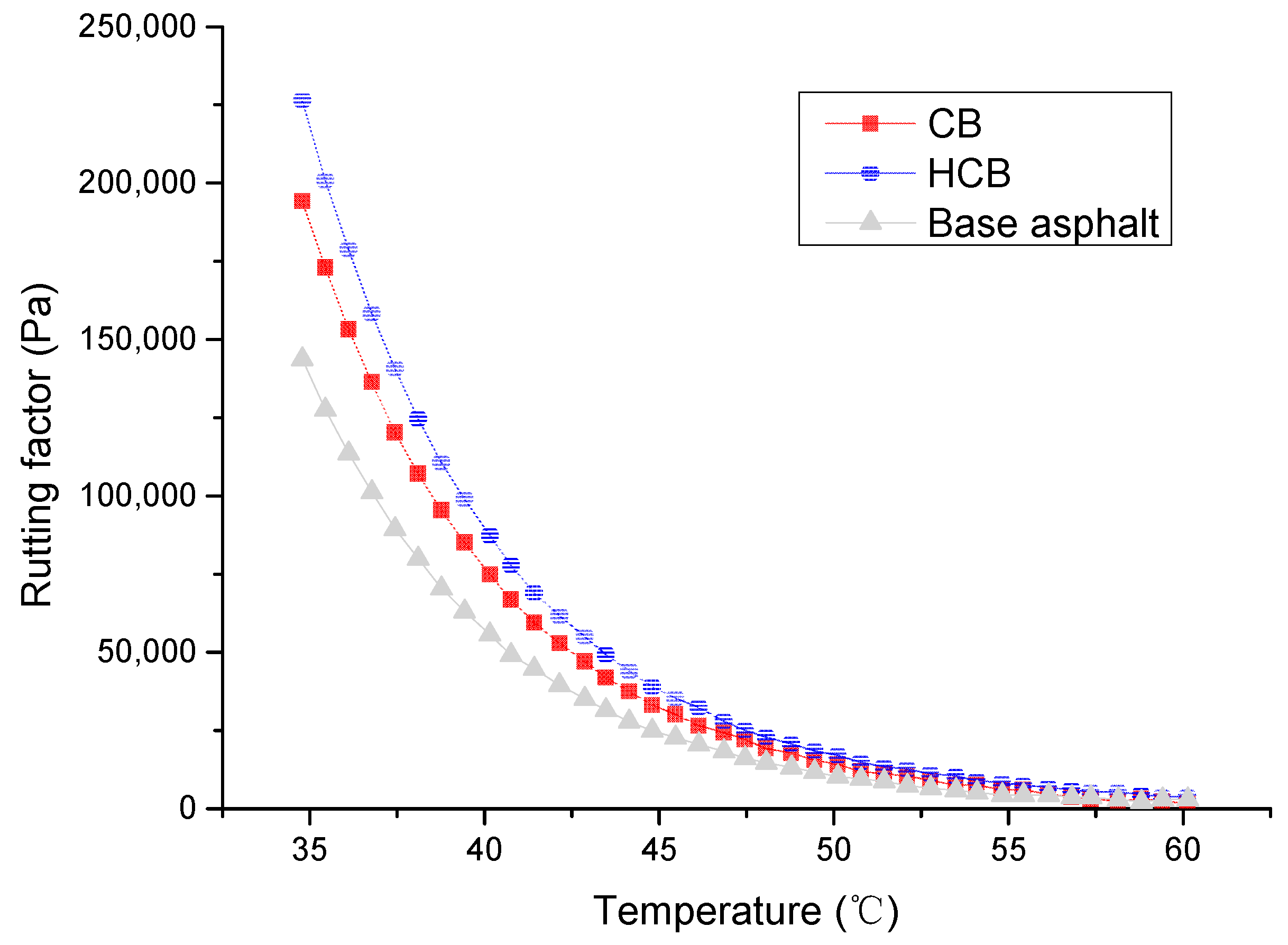
5.2. Rheological Properties
5.3. Aging Properties
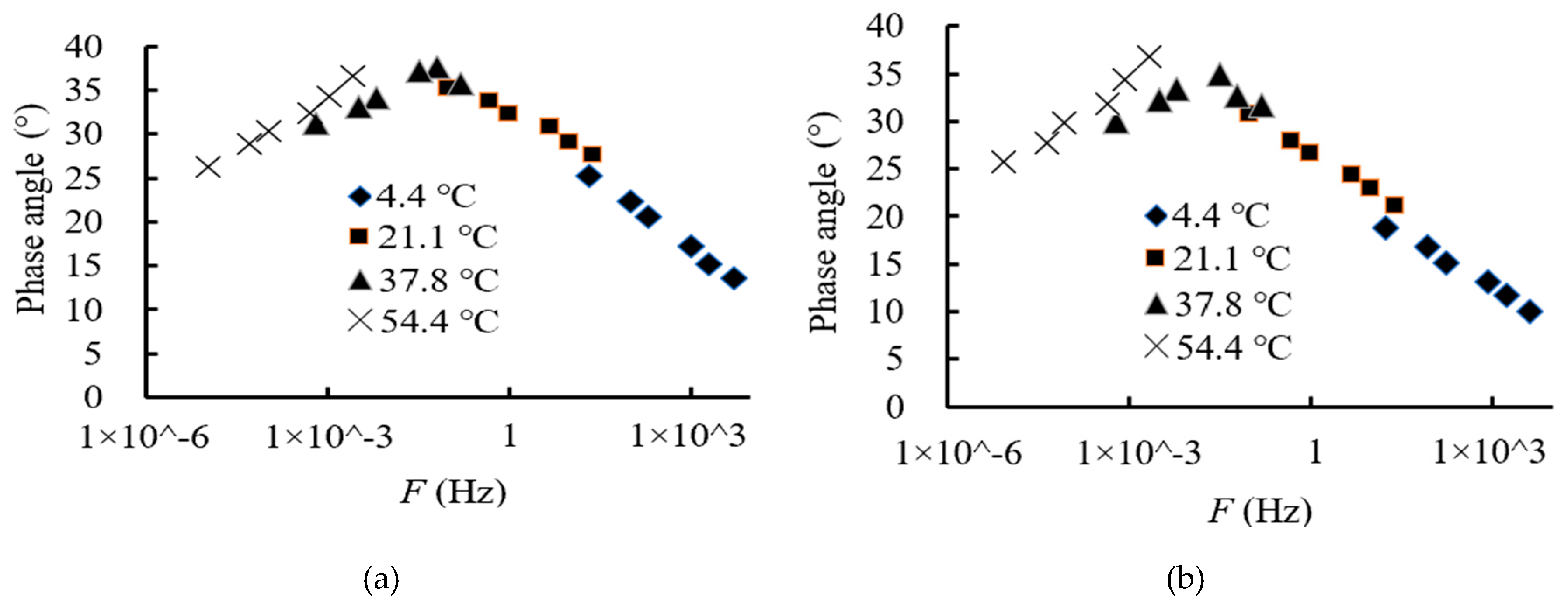
6. Dynamic Properties of HAM
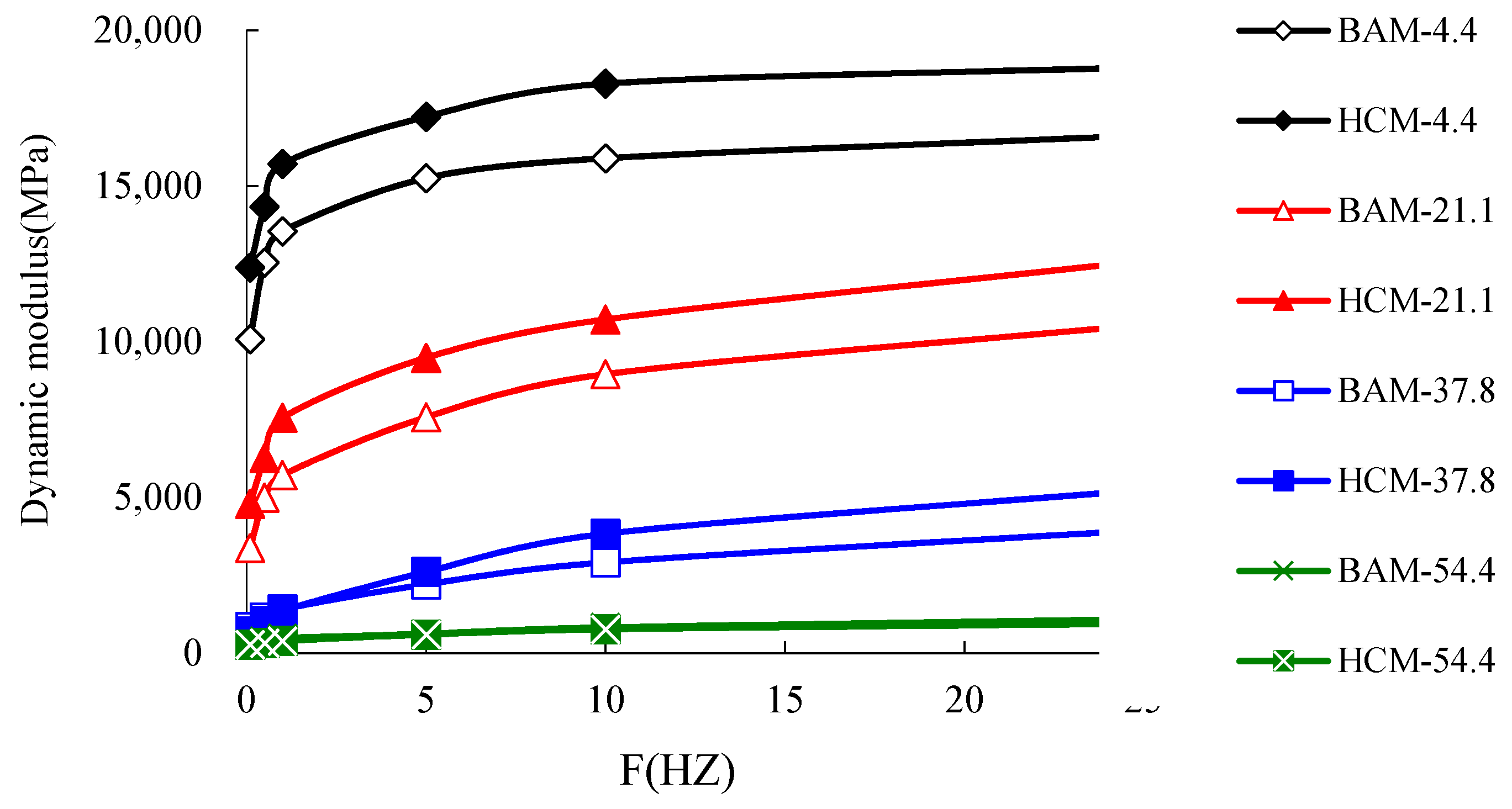
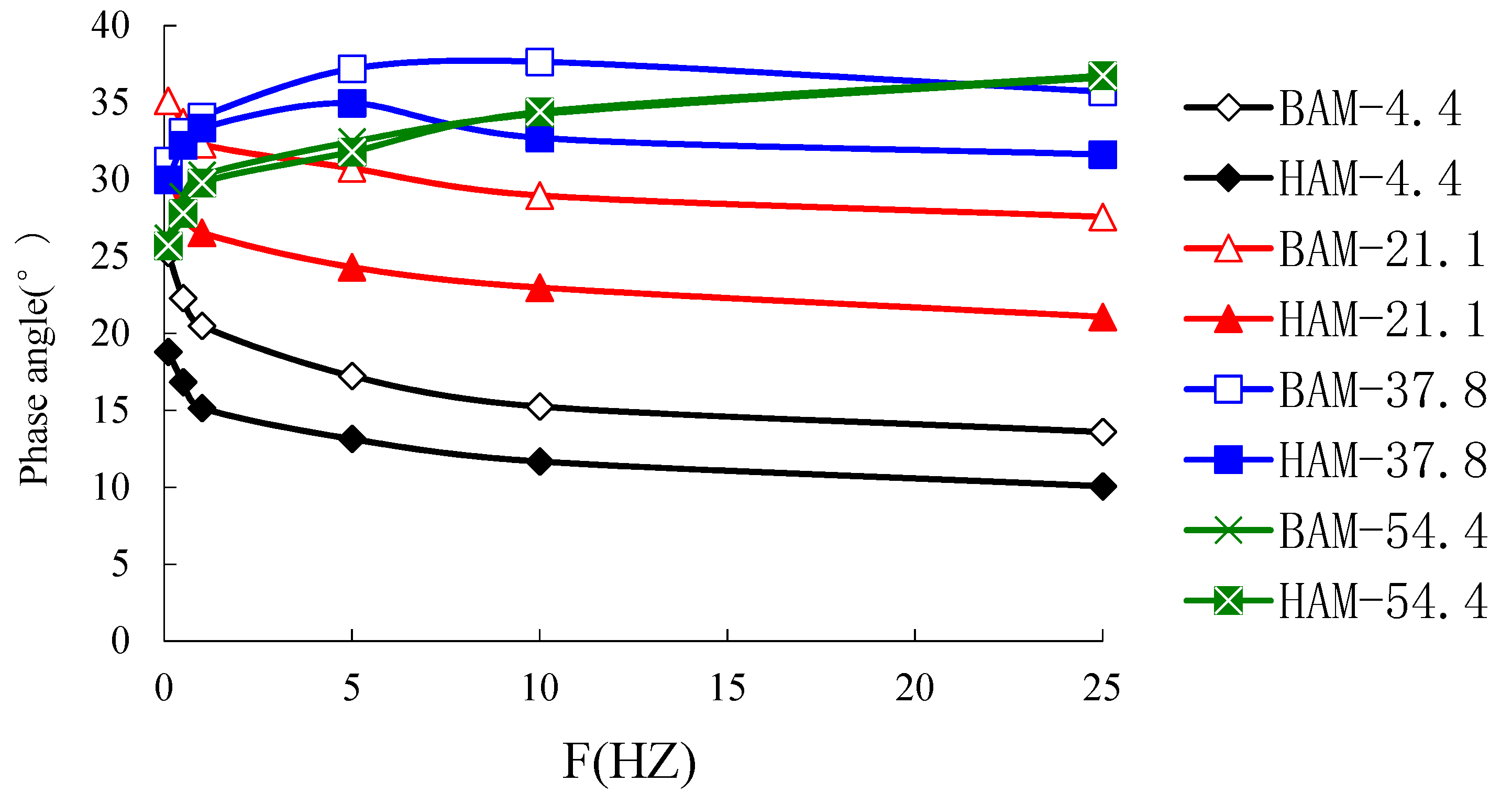
6.1. Dynamic Response Parameter Analysis
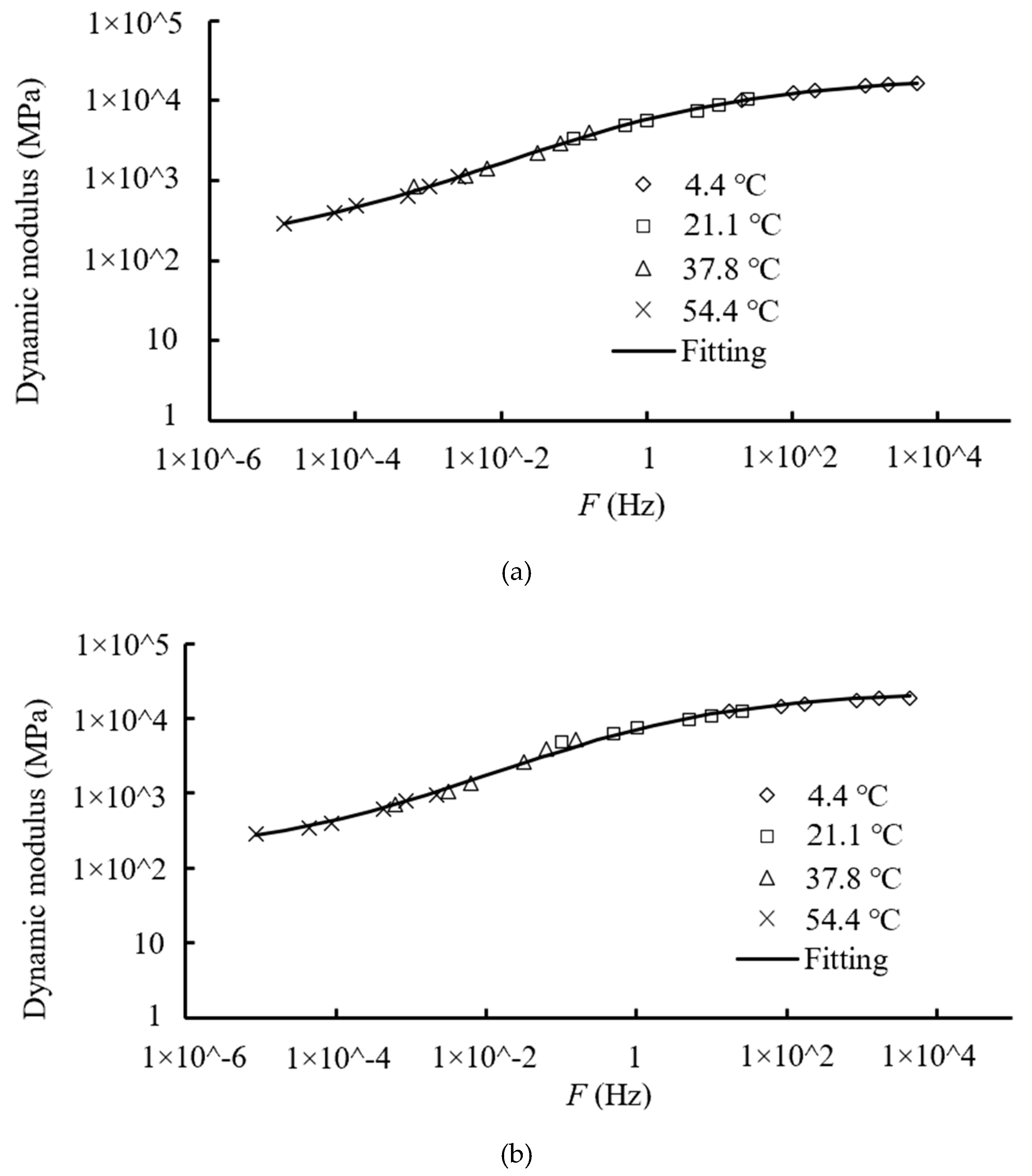
6.2. The Master Curve Analysis of Dynamic Response Parameters
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, W.; Liu, A.H.; Wang, L. Research of in Situ Grafted Carbon Black. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 464, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C. Hazard assessment and regionalization of highway flood disasters in China. Nat. Hazards 2020, 200, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ch’ng, S.Y.; Andriyana, A.; Tee, Y.L.; Verron, E. Effects of Carbon Black and the Presence of Static Mechanical Strain on the Swelling of Elastomers in Solvent. Materials 2015, 8, 884–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kondyurin, A.V.; Eliseeva, A.Y.; Svistkov, A.L. Bound (“Glassy”) Rubber as a Free Radical Cross-linked Rubber Layer on a Carbon Black. Materials 2018, 11, 1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Guo, C.Z.; Ma, Z.L. Inexpensive Ipomoea aquatica Biomass-Modified Carbon Black as an Active Pt-Free Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Reduction Reaction in an Alkaline Medium. Materials 2015, 8, 6658–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raza, M.A.; Asgar, H.; Abdullah, A. Carburising of Low-Carbon Steel Using Carbon Black Nanoparticles. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2016, 41, 4661–4667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Guern, M.; Chailleux, E.; Farcas, F. Physico-chemical analysis of five hard bitumens: Identification of chemical species and molecular organization before and after artificial aging. Fuel 2010, 89, 3330–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, K.; Tada, Y.; Shindo, Y. Thermal conductivity of polymer composites with close-packed structure of nano and micro fillers. Composites 2009, 40, 724–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.C.; Qiao, Z.P. Preparation of fuel oils and charcoal by waste rubber. Environ. Pollut. Control 2001, 28, 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.Q.; Xiao, G.L. Trends in further processing and application of pyrolysis carbon black of used tire. Polym. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2004, 20, 142–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rafi, J.; Kamal, M.A.; Ahmad, N.; Hafeez, M. Performance Evaluation of Carbon Black Nano-Particle Reinforced Asphalt Mixture. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Casado-Barrasa, R.; Lastra-Gonzalez, P.; Indacoechea-Vega, I.; Castro-Fresno, D. Assessment of carbon black modified binder in a sustainable asphalt concrete mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 211, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbakhsh, H.; Karimi, M.M.; Jahangiri, B.; Nejad, F.M. Induction heating and healing of carbon black modified asphalt concrete under microwave radiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.T. Research on the properties of SBS modified asphalt with silica hydrated. New Build. Mater. 2013, 6, 64–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.M.; Fan, Z.R.; Wu, S.P.; Li, Y.Y. Effect of Carbon Black Nanoparticles from the Pyrolysis of Discarded Tires on the Performance of Asphalt and its Mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Little, D.N.; Button, J.W.; Youssef, H. Development of Criteria to Evaluate Uniaxial Creep Data and Asphalt Concrete Permanent Deformation Potential; Transportation Research Record: Washington, DC, USA, 1993; pp. 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.G.; Meegoda, J.N. Micromechanical Simulation of Hot Mix Asphalt. J. Eng. Mech. 1997, 123, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.W.; Gibson, N.H.; Schapery, R.A.; Witczak, M.W. Viscoplasticity Modeling of Asphalt Concrete Behavior. In Proceedings of the 15th ASCE Engineering Mechanics Conference, New York, NY, USA, 2–5 June 2002; pp. 144–159. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.M.; Ning, F.B.; Li, Y.Y. Effect of carbon black on the dynamic moduli of asphalt mixtures and its master curves. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2019, 13, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.R.; Chang, Y.T.; Chen, Z.D. Study on test standard of asphalt mixture dynamic modulus. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2015, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.L.; Jiang, X.M.; Guo, K.; Xue, Y.; Dong, H. Analysis of Viscoelastic Response and Creep Deformation Mechanism of Asphalt Mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 171, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Test Indicators | Base Asphalt | Test Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 5 s, 100 g)/(1/10 mm) | 83 | ASTM D5 |
| Softening point (R&B)/°C | 44.5 | ASTM D36 |
| Ductility (5 °C, 5 cm/min)/cm | 7.4 | ASTM D113 |
| Viscosity (135 °C)/pa.s | 0.370 | ASTM D 4402 |
| Mixture | 16 mm | 13.2 mm | 9.5 mm | 4.75 mm | 2.36 mm | 1.18 mm | 0.6 mm | 0.3 mm | 0.15 mm | 0.075 mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC-13 | 100 | 95.6 | 72.7 | 40.4 | 30 | 19.4 | 14.5 | 10.3 | 8.1 | 5.1 |
| Asphalt Mixture | Optimal Asphalt Content (%) | Volume of Air Voids (%) | Voids in Mineral Aggregate (%) | Voids Filled with Asphalt (%) | Marshall Stability (kN) | Flow Value (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAM | 4.5 | 3.95 | 14.5 | 72.8 | 12.5 | 3.1 |
| HAM | 4.5 | 4.18 | 14.4 | 72.3 | 13.4 | 2.5 |
| Test Indicators | Base Asphalt | CB-Modified Asphalt | HCB-Modified Asphalt |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 5 s, 100 g)/(1/10 mm) | 83 | 81 | 73 |
| Softening point (R&B)/°C | 44.5 | 46.2 | 47.4 |
| Ductility (5 °C, 5 cm/min)/cm | 7.4 | 7.3 | 8.1 |
| Viscosity (135 °C)/pa.s | 0.370 | 0.390 | 0.425 |
| Test Indicators | BA | CB-Modified Asphalt | HCB-Modified Asphalt | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before Aging | After Aging | Before Aging | Before Aging | After Aging | Before Aging | |
| Penetration (25 °C)/(1/10 mm) | 83 | 46 | 81 | 48 | 73 | 47 |
| Ductility (5 °C)/cm | 7.4 | 0 | 7.3 | 0 | 8.1 | 4.5 |
| Softening point (R&B)/°C | 44.5 | 51.5 | 46.2 | 52.4 | 47.4 | 52.8 |
| Penetration ratio (%) | - | 56.4 | - | 62.7 | - | 64.7 |
| Softening point increase (°C) | - | 7.0 | - | 6.2 | - | 5.4 |
| Mixtures | Transition Temperature (°C) | Activation Energy ΔEa (J) | Shift Factor log[α(T)] |
|---|---|---|---|
| BAM | 4.4 | 216631.4 | 2.314 |
| 21.1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 37.8 | 230131.7 | −2.194 | |
| 54.4 | 221054.2 | −3.989 | |
| HAM modified asphalt mixture | 4.4 | 208657.3 | 2.228 |
| 21.1 | 0 | 0 | |
| 37.8 | 231061.2 | −2.203 | |
| 54.4 | 225021.7 | −4.060 |
| Mixtures | α | β | γ | δ | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BAM | 4.32205 | 2.07160 | −1.10936 | −0.53270 | 0.99470 |
| HAM modified asphalt mixture | 4.37454 | 2.18026 | −1.15643 | −0.62096 | 0.99865 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Z.; Su, J.; Li, P.; Bing, H. Mechanism of HCB-Modified Asphalt and Dynamic Properties of Mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4971. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144971
Ding Z, Su J, Li P, Bing H. Mechanism of HCB-Modified Asphalt and Dynamic Properties of Mixtures. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(14):4971. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144971
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Zhan, Jinfei Su, Peilong Li, and Hui Bing. 2020. "Mechanism of HCB-Modified Asphalt and Dynamic Properties of Mixtures" Applied Sciences 10, no. 14: 4971. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144971
APA StyleDing, Z., Su, J., Li, P., & Bing, H. (2020). Mechanism of HCB-Modified Asphalt and Dynamic Properties of Mixtures. Applied Sciences, 10(14), 4971. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10144971







