Measurement of Head-Related Transfer Functions: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Principle of HRTF Measurements
2.1. HRTF as a Linear Time Invariant (LTI) System
2.2. Basic HRTF Measurement Methods
2.2.1. HRTF Measurement with Pseudo Random Sequences
MLS/IRS
Golay Codes
- ∘
- : Append to
- ∘
- : Append − to
2.2.2. HRTF Measurement with Sweep Signals
Sweep Generation
- ∘
- Sweep Generation in the Time Domain
- ∘
- Sweep Generation in the Frequency Domain
Properties of Sweep Techniques
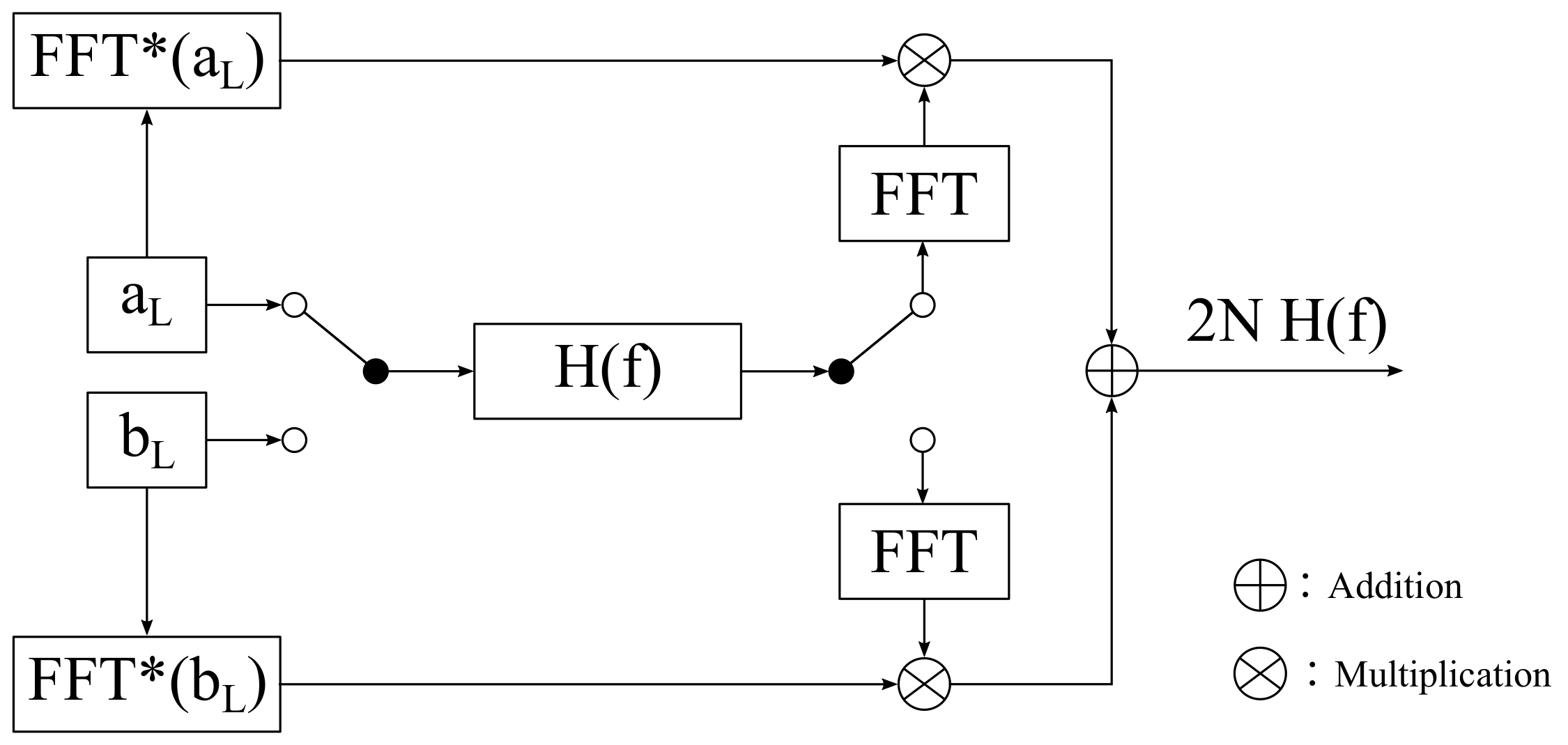
2.2.3. HRTF Measurement with Adaptive Filtering Methods
- (1)
- Calculation of the estimated output signal:
- (2)
- Calculation of the residual error between the measured and the estimated output signal:
- (3)
- Adaptation of the based on the residual error and the input signal:,
2.3. Microphone Position and In-Ear Microphones
2.4. Sound Sources
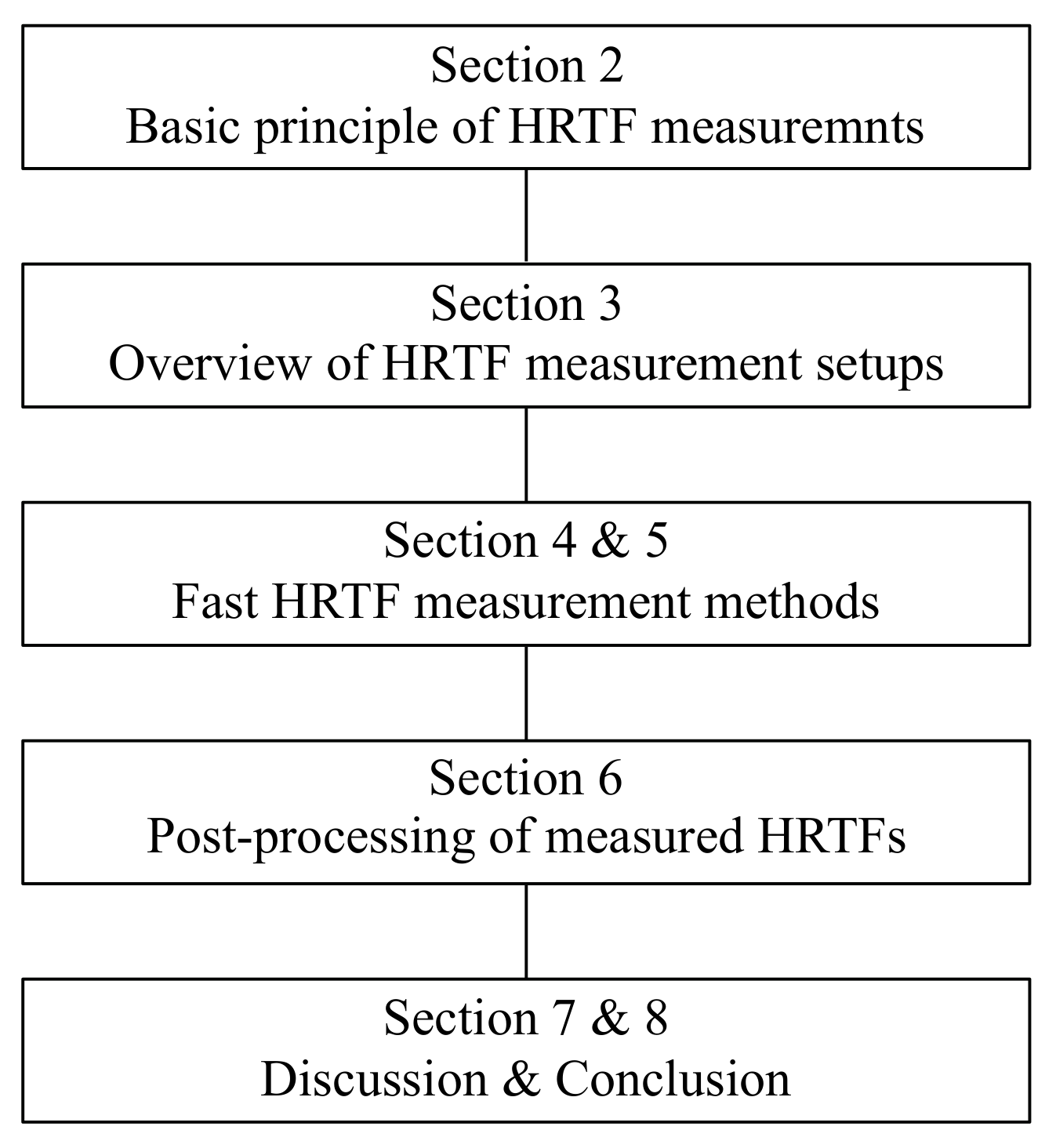
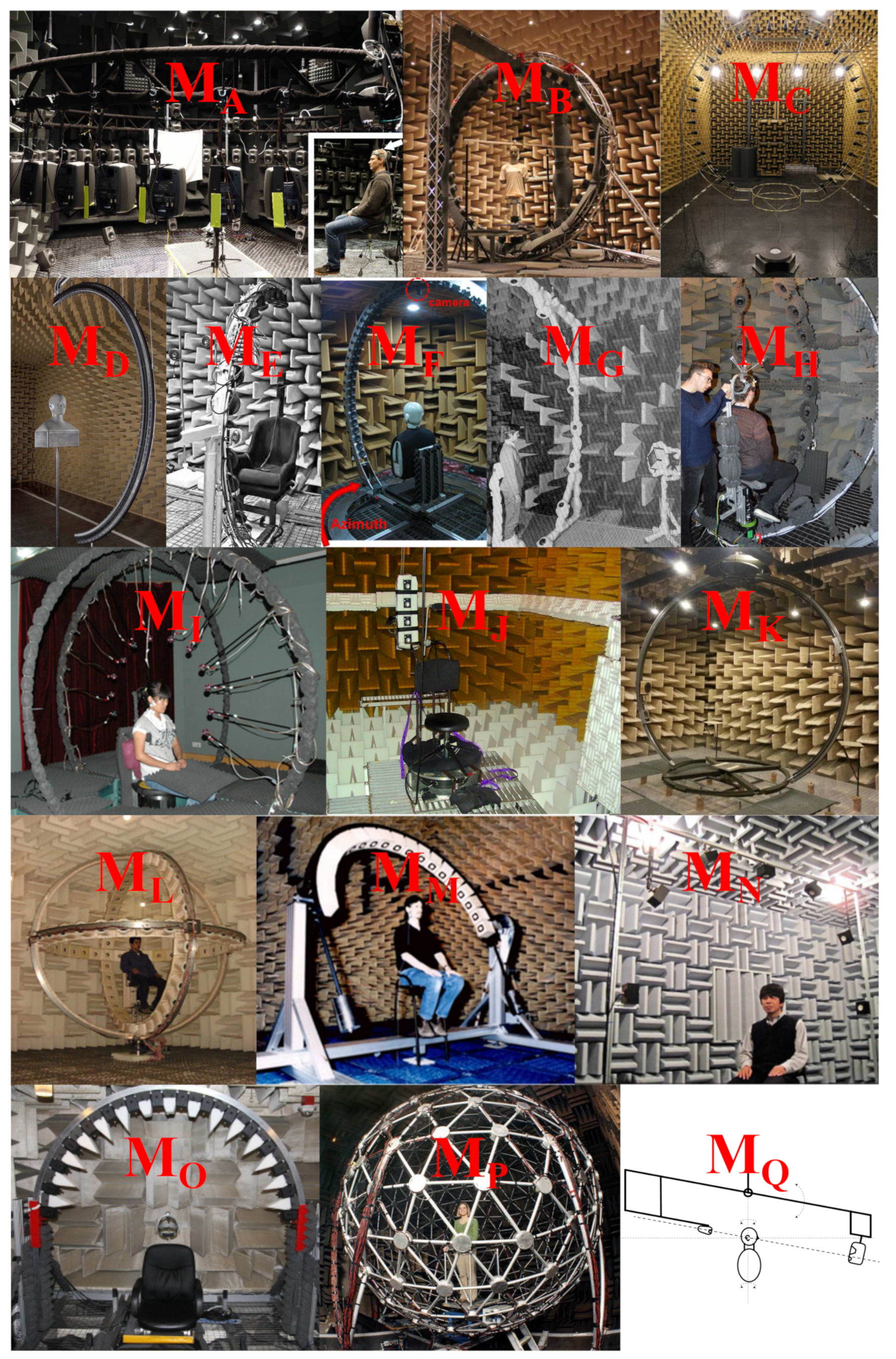
3. Overview of HRTF Measurement Setups
3.1. Multi-Loudspeaker Setups
3.2. Single-Loudspeaker Setups
3.3. Multi-Microphone Setups
3.4. Setups for HRTF Measurements in Non-Anechoic Environments
4. Multi-Loudspeaker-Based Fast HRTF Measurement Methods
4.1. Step-Wise Measurements
4.1.1. Multiple Exponential Sweep Method (MESM)
Interleaving and Overlapping Mechanisms
Optimized MESM
4.2. Continuous Measurements
4.2.1. Continuous MESM
4.2.2. Time-Varying Adaptive Filtering
5. Single-Loudspeaker-Based Fast HRTF Measurement Methods
6. Post-Processing of Measured HRTFs
6.1. Windowing
6.2. Equalization
6.3. Low-Frequency Extension
6.4. Others
7. Discussion
7.1. Measurement Uncertainty
7.2. System Evaluation
7.3. HRTF Format
7.4. Considerations and Trends in HRTF Measurements
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Møller, H. Fundamentals of binaural technology. Appl. Acoust. 1992, 36, 171–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.; Sørensen, M.F.; Hammershøi, D.; Jensen, C.B. Head-Related Transfer Functions of Human Subjects. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1995, 43, 300–321. [Google Scholar]
- Blauert, J. Spatial Hearing: The Psychophysics of Human Sound Localization; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.I.; Wakefield, G.H. Introduction to Head-Related Transfer Functions (HRTFs): Representations of HRTFs in Time, Frequency, and Space. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2001, 49, 231–249. [Google Scholar]
- Hammershøi, D.; Møller, H. Binaural Technique—Basic Methods for Recording, Synthesis, and Reproduction. In Communication Acoustics; Blauert, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 223–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorländer, M. Auralization: Fundamentals of Acoustics, Modelling, Simulation, Algorithms and Acoustic Virtual Reality, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauert, J. (Ed.) The Technology of Binaural Listening; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlebrooks, J.C. Virtual localization improved by scaling nonindividualized external-ear transfer functions in frequency. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 1493–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartmann, W.M.; Wittenberg, A. On the externalization of sound images. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 99, 3678–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begault, D.R.; Wenzel, E.M.; Anderson, M.R. Direct Comparison of the Impact of Head Tracking, Reverberation, and Individualized Head-Related Transfer Functions on the Spatial Perception of a Virtual Speech Source. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2001, 49, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lindau, A.; Hohn, T.; Weinzierl, S. Binaural Resynthesis for Comparative Studies of Acoustical Environments. In Proceedings of the 122nd Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Vienna, Austria, 5–8 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; E, J.; Schlieper, R.; Peissig, J. The Impact of Trajectories of Head and Source Movements on Perceived Externalization of a Frontal Sound Source. In Proceedings of the 144th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Milan, Italy, 23–26 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Schlieper, R.; Peissig, J. The Impact of Head Movement on Perceived Externalization of a Virtual Sound Source with Different BRIR Lengths. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Immersive and Interactive Audio, York, UK, 27–29 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Plinge, A.; Schlecht, S.J.; Thiergart, O.; Robotham, T.; Rummukainen, O.; Habets, E.A.P. Six-Degrees-of-Freedom Binaural Audio Reproduction of First-Order Ambisonics with Distance Information. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Audio for Virtual and Augmented Reality, Redmond, WA, USA, 20–22 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, W.S.; He, J.; Ranjan, R.; Gupta, R. Natural and Augmented Listening for VR, and AR/MR; ICASSP Tutorial: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2018; Available online: https://sigport.org/documents/icassp-2018-tutorial-t11-natual-and-augmented-listening-vrarmr-0 (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Brungart, D.S.; Rabinowitz, W.M. Auditory localization of nearby sources. Head-related transfer functions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1999, 106, 1465–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartung, K.; Braasch, J.; Sterbing, S.J. Comparison of Different Methods for the Interpolation of Head-Related Transfer Functions. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference: Spatial Sound Reproduction, Rovaniemi, Finland, 10–12 April 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kistler, D.J.; Wightman, F.L. A model of head-related transfer functions based on principal components analysis and minimum-phase reconstruction. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 91, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larcher, V.; Warusfel, O.; Jot, J.M.; Guyard, J. Study and Comparison of Efficient Methods for 3D Audio Spatialization Based on Linear Decomposition of HRTF Data. In Proceedings of the 108th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Paris, France, 19–22 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, M.J.; Angus, J.A.S.; Tew, A.I. Analyzing head-related transfer function measurements using surface spherical harmonics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1998, 104, 2400–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zotkin, D.N.; Duraiswaini, R.; Gumerov, N.A. Regularized HRTF fitting using spherical harmonics. In Proceedings of the EEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, New Paltz, NY, USA, 18–21 October 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörschmann, C.; Arend, J.M.; Brinkmann, F. Spatial upsampling of individual sparse head-related transfer function sets by directional equalization. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Congress on Acoustics, Aachen, Germany, 9–13 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Hur, Z.; Alon, D.L.; Mehra, R.; Rafaely, B. Efficient Representation and Sparse Sampling of Head-Related Transfer Functions Using Phase-Correction Based on Ear Alignment. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 2249–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, A.; Jin, C.; van Schaik, A. A psychophysical evaluation of near-field head-related transfer functions synthesized using a distance variation function. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 125, 2233–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraiswaini, R.; Zotkin, D.N.; Gumerov, N.A. Interpolation and range extrapolation of HRTFs. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–21 May 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollow, M.; Nguyen, K.; Warusfel, O.; Carpentier, T.; Müller-Trapet, M.; Vorländer, M.; Noisternig, M. Calculation of Head-Related Transfer Functions for Arbitrary Field Points Using Spherical Harmonics Decomposition. Acta Acust. United Acust. 1998, 1, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnaar, P.; Plogsties, J.; Christensen, F. Directional Resolution of Head-Related Transfer Functions Required in Binaural Synthesis. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2005, 53, 919–929. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Kennedy, R.A.; Abhayapala, T.D. On High-Resolution Head-Related Transfer Function Measurements: An Efficient Sampling Scheme. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2012, 20, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.F. Boundary element method calculation of individual head-related transfer function. I. Rigid model calculation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2001, 110, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeber, B.U.; Fastl, H. Subjective selection of non-individual head-related transfer functions. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Auditory Display, Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 July 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Guezenoc, C.; Séguier, R. HRTF Individualization: A Survey. In Proceedings of the 145th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, New York, NY, USA, 17–20 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zotkin, D.Y.N.; Hwang, J.; Duraiswaini, R.; Davis, L.S. HRTF personalization using anthropometric measurements. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, New Paltz, NY, USA, 19–22 October 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhou, L.; Ma, H.; Wu, Z. HRTF personalization based on artificial neural network in individual virtual auditory space. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomhardt, R.; Braren, H.; Fels, J. Individualization of head-related transfer functions using principal component analysis and anthropometric dimensions. In Proceedings of the 172nd Meeting of the Acoustical Society of America, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA, 28 November–2 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B. Head-Related Transfer Function and Virtual Auditory Display, 2nd ed.; J. Ross Publishing: Plantation, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Enzner, G.; Antweiler, C.; Spors, S. Trends in Acquisition of Individual Head-Related Transfer Functions. In The Technology of Binaural Listening; Blauert, J., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 57–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Massarani, P. Transfer-Function Measurement with Sweeps. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2001, 49, 443–471. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, S. Measuring Transfer-Functions and Impulse Responses. In Handbook of Signal Processing in Acoustics; Havelock, D.I., Kuwano, S., Vorländer, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkeby, O.; Nelson, P.A.; Hamada, H.; Orduna-Bustamante, F. Fast deconvolution of multichannel systems using regularization. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 1998, 6, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, A.T. Methods of Measuring Impulse Responses in Architectural Acoustics. Master’s Thesis, Technical University of Denmark, Kgs. Lyngby, Denmark, 2009. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/reader/41801734 (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Farina, A. Simultaneous Measurement of Impulse Response and Distortion with a Swept-Sine Technique. In Proceedings of the 108th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Paris, France, 19–22 February 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, J.M.; Downey, P. Intensity changes at the ear as a function of the azimuth of a tone source: A comparative study. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1970, 47, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellert, V. Construction of a dummy head after new measurements of thresholds of hearing. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1972, 51, 1359–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, G.B.; Embrechts, J.J.; Archambeau, D. Comparison of Different Impulse Response Measurement Techniques. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2002, 50, 249–262. [Google Scholar]
- Mehrgardt, S.; Mellert, V. Transformation characteristics of the external human ear. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1977, 61, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyser, R.C. Acoustical Measurements by Time Delay Spectrometry. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1967, 15, 370–382. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs, P.A.N.; Godfrey, K.R. Pseudorandom signals for the dynamic analysis of multivariable systems. Proc. Instit. Electr. Eng. 1966, 113, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacWilliams, F.J.; Sloane, N.J.A. Pseudo-random sequences and arrays. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 1715–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.R. Integrated–impulse method measuring sound decay without using impulses. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1979, 66, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borish, J.; Angell, J.B. An Efficient Algorithm for Measuring the Impulse Response Using Pseudorandom Noise. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1983, 31, 478–488. [Google Scholar]
- Mommertz, E.; Müller, S. Measuring impulse responses with digitally pre-emphasized pseudorandom noise derived from maximum-length sequences. Appl. Acoust. 1995, 44, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golay, M. Complementary series. IRE Trans. Inf. Theory 1961, 7, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ream, N. Nonlinear identification using inverse-repeat m sequences. Proc. Instit. Electr. Eng. 1970, 117, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, C.; Hawksford, M.J. Distortion Immunity of MLS-Derived Impulse Response Measurements. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1993, 41, 314–335. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, N. Digital Sequences. In Handbook Of Signal Processing in Acoustics; Havelock, D.I., Kuwano, S., Vorländer, M., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 87–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S.S. Adaptive Filter Theory, 4th ed.; Prentice Hall informations and system sciences series; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Zotkin, D.N.; Duraiswami, R.; Grassi, E.; Gumerov, N.A. Fast head-related transfer function measurement via reciprocity. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 120, 2202–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morse, P.M.; Ingard, K.U. Theoretical Acoustics, 1st ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Sarwate, D.V.; Pursley, M.B. Crosscorrelation properties of pseudorandom and related sequences. Proc. IEEE 1980, 68, 593–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rife, D.D.; Vanderkooy, J. Transfer-Function Measurement with Maximum-Length Sequences. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1989, 37, 419–444. [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooy, J. Aspects of MLS Measuring Systems. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1994, 42, 219–231. [Google Scholar]
- Holters, M.; Corbach, T.; Zölzer, U. Impulse Response Measurement Techniques and their Applicability in the Real World. In Proceedings of the 12th Int. Conference on Digital Audio Effects, Como, Italy, 1–4 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Olesen, S.K.; Plogsties, J.; Minnaar, P.; Christensen, F.; Møller, H. An improved MLS measurement system for acquiring room impulse responses. In Proceedings of the IEEE Nordic Signal Processing Symposium, Kolmården, Sweden, 13–15 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kayser, H.; Ewert, S.D.; Anemüller, J.; Rohdenburg, T.; Hohmann, V.; Kollmeier, B. Database of Multichannel In-Ear and Behind-the-Ear Head-Related and Binaural Room Impulse Responses. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2009, 2009, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, J.N.; Xiang, N. A specialized fast cross-correlation for acoustical measurements using coded sequences. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Green, D.M.; Middlebrooks, J.C. Characterization of external ear impulse responses using Golay codes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 92, 1169–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorik, P. Limitations in using Golay codes for head-related transfer function measurement. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2000, 107, 1793–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craven, P.G.; Gerzon, M.A. Practical Adaptive Room and Loudspeaker Equaliser for Hi-Fi Use. In Proceedings of the 7th AES Conference Digital Signal Processing, London, UK, 14–15 September 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Griesinger, D. Beyond MLS-Occupied Hall Measurement with FFT Techniques. In Proceedings of the 101st Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 8–11 November 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Farina, A. Advancements in Impulse Response Measurements by Sine Sweeps. In Proceedings of the 122nd Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Vienna, Austria, 5–8 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Aoshima, N. Computer–generated pulse signal applied for sound measurement. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1981, 69, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Asano, F.; Kim, H.Y.; Sone, T. An optimum computer–generated pulse signal suitable for the measurement of very long impulse responses. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 1119–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinzierl, S.; Giese, A.; Lindau, A. Generalized Multiple Sweep Measurement. In Proceedings of the 126th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Munich, Germany, 7–10 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Huszty, C.; Sakamoto, S. Time-domain sweeplets for acoustic measurements. Appl. Acoust. 2010, 71, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huszty, C.; Sakamoto, S. Hyperbolic sweep signals for architectural acoustic measurements. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2011, 32, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ochiai, H.; Kaneda, Y. A Recursive Adaptive Method of Impulse Response Measurement with Constant SNR over Target Frequency Band. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2013, 61, 647–655. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, W.; Kennedy, R.A.; Abhayapala, T.D. HRTF measurement on KEMAR manikin. In Proceedings of the Australian Acoustical Society Conference, Adelaide, Australia, 23–25 November 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bernschütz, B. A Spherical Far Field HRIR/HRTF Compilation of the Neumann KU100. In Proceedings of the Tagungsband Fortschritte der Akustik—DAGA, Merano, Italy, 18–21 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Arend, J.M.; Neidhardt, A.; Pörschmann, C. Measurement and Perceptual Evaluation of a Spherical Near-Field HRTF Set. In Proceedings of the 29th Tonmeistertagung—VDT International Convention, Cologne, Germany, 17–20 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Enzner, G. Analysis and optimal control of LMS-type adaptive filtering for continuous-azimuth acquisition of head related impulse responses. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 31 March–4 April 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, A.; Kar, A.; Chandra, M. A technical review on adaptive algorithms for acoustic echo cancellation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing, Melmaruvathur, India, 3–5 April 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.M.; Morgan, D.R. Active noise control: a tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 1999, 87, 943–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.A.; Hamada, H.; Elliott, S.J. Adaptive inverse filters for stereophonic sound reproduction. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1992, 40, 1621–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, M. Simulation and Analysis of Measurement Techniques Simulation and Analysis of Measurement Techniques for the Fast Acquisition of Individual Head-Related Transfer Functions. Master’s Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2014. Available online: https://www2.ak.tu-berlin.de/~akgroup/ak_pub/abschlussarbeiten/2014/FallahiMina_MasA.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Aboulnasr, T.; Mayyas, K. A robust variable step-size LMS-type algorithm: analysis and simulations. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 1997, 45, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, C.K.; Li, S.; Peissig, J. Analysis and Comparison of different Adaptive Filtering Algorithms for Fast Continuous HRTF Measurement. In Proceedings of the Tagungsband Fortschritte der Akustik—DAGA, Kiel, Germany, 6–9 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lüke, H.D. Sequences and arrays with perfect periodic correlation. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1988, 24, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungnickel, D.; Pott, A. Perfect and almost perfect sequences. Discrete Appl. Math. 1999, 95, 331–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antweiler, C.; Telle, A.; Vary, P.; Enzner, G. Perfect-sweep NLMS for time-variant acoustic system identification. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Kyoto, Japan, 25–30 March 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, F.M.; Ross, D.A. The Pressure Distribution in the Auditory Canal in a Progressive Sound Field. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1946, 18, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, C.L.; Braida, L.D.; Cuddy, D.R.; Davis, M.F. Binaural pinna disparity: Another auditory localization cue. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1975, 57, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middlebrooks, J.C.; Makous, J.C.; Green, D.M. Directional sensitivity of sound-pressure levels in the human ear canal. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 86, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djupesland, G.; Zwislocki, J.J. Sound pressure distribution in the outer ear. Acta Oto-Laryngologica 1973, 75, 350–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener, F.M. On the Diffraction of a Progressive Sound Wave by the Human Head. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1947, 19, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, E.A. Earcanal pressure generated by a free sound field. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1966, 39, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhard, M.D.; Sachs, R.M. Anthropometric manikin for acoustic research. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1975, 58, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middlebrooks, J.C. Narrow-band sound localization related to external ear acoustics. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1992, 92, 2607–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wightman, F.L.; Kistler, D.J. Headphone simulation of free-field listening. I: Stimulus synthesis. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1989, 85, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, P.A.; Axelsson, A. Miniature microphone probe tube measurements in the external auditory canal. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1993, 93, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiipakka, M.; Kinnari, T.; Pulkki, V. Estimating head-related transfer functions of human subjects from pressure-velocity measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 4051–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammershøi, D.; Møller, H. Sound transmission to and within the human ear canal. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 408–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Algazi, V.R.; Avendano, C.; Thompson, D. Dependence of Subject and Measurement Position in Binaural Signal Acquisition. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1999, 47, 937–947. [Google Scholar]
- Oberem, J.; Masiero, B.; Fels, J. Experiments on authenticity and plausibility of binaural reproduction via headphones employing different recording methods. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 114, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, F.; Brinkman, F.; Stirnemann, A.; Kollmeier, B. The PIRATE: An anthropometric earPlug with exchangeable microphones for Individual Reliable Acquisition of Transfer functions at the Ear canal entrance. In Proceedings of the Tagungsband Fortschritte der Akustik—DAGA, Rostock, Germany, 18–21 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Durin, V.; Carlile, S.; Guillon, P.; Best, V.; Kalluri, S. Acoustic analysis of the directional information captured by five different hearing aid styles. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, 818–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denk, F.; Ernst, S.M.A.; Ewert, S.D.; Kollmeier, B. Adapting Hearing Devices to the Individual Ear Acoustics: Database and Target Response Correction Functions for Various Device Styles. Trends Hear. 2018, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollow, M.; Masiero, B.; Dietrich, P.; Fels, J.; Vorländer, M. Fast measurement system for spatially continuous individual HRTFs. In Proceedings of the 25th Conference: Spatial Audio in Today’s 3D World, London, UK, 25–27 March 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fuß, A. Entwicklung eines Vollsphärischen Multikanalmesssystems zur Erfassung Individueller Kopfbezogener Übertragungsfunktionen. Master’s Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2014. Available online: https://www2.ak.tu-berlin.de/~akgroup/ak_pub/abschlussarbeiten/2014/FussAlexander_MasA.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Yu, G.; Xie, B.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Analysis on Error Caused by Multi-Scattering of Multiple Sound Sources in HRTF Measurement. In Proceedings of the 132nd Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Budapest, Hungary, 26–29 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nishino, T.; Hosoe, S.; Takeda, K.; Itakura, F. Measurement of the Head Related Transfer Function using the Spark Noise. In Proceedings of the 18th International Congress on Acoustics, Kyoto, Japan, 4–9 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hosoe, S.; Nishino, T.; Itou, K.; Takeda, K. Measurement of Head-Related Transfer Functions in the Proximal Region. In Proceedings of the Forum Acusticum: 4th European Congress on Acustics, Budapest, Hungary, 29 August–2 September 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hosoe, S.; Nishino, T.; Itou, K.; Takeda, K. Development of Micro-Dodecahedral Loudspeaker for Measuring Head-Related Transfer Functions in The Proximal region. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Toulouse, France, 14–19 May 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, Y.; Nishino, T.; Kazuya, T. Development of small sound equipment with micro-dynamic-type loudspeakers for HRTF measurement. In Proceedings of the 19th International Congress on Acoustics, Madrid, Spain, 2–7 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, T.; Xiao, Z.; Gong, M.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, X. Distance-Dependent Head-Related Transfer Functions Measured With High Spatial Resolution Using a Spark Gap. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2009, 17, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Xie, B.; Rao, D. Effect of Sound Source Scattering on Measurement of Near-Field Head-Related Transfer Functions. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2008, 25, 2926–2929. [Google Scholar]
- Bolaños, J.G.; Pulkki, V. HRIR Database with measured actual source direction data. In Proceedings of the 133rd Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–29 October 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G.; Xie, B. Multiple Sound Sources Solution for Near-Field Head-Related Transfer Function Measurements. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Audio for Virtual and Augmented Reality, Redmond, WA, USA, 20–22 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, L.S.; Duraiswami, R.; Grassi, E.; Gumerov, N.A.; Li, Z.; Zotkin, D.N. High Order Spatial Audio Capture and Its Binaural Head-Tracked Playback Over Headphones with HRTF Cues. In Proceedings of the 119th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, New York, NY, USA, 7–10 October 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, A.P.; Khalid, Z.; Kennedy, R.A. Novel Sampling Scheme on the Sphere for Head-Related Transfer Function Measurements. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2015, 23, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tobbala, A.; Peissig, J. Towards Mobile 3D HRTF Measurement. In Proceedings of the 148th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Online Virtual Conference, New York, NY, USA, 2–5 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Denk, F.; Ernst, S.M.A.; Heeren, J.; Ewert, S.D.; Kollmeier, B. The Oldenburg Hearing Device(OlHeaD) HRTF Database; Technical report; University of Oldenburg: Oldenburg, Germany, 2018; Available online: https://uol.de/f/6/dept/mediphysik/ag/mediphysik/download/paper/denk/OlHeaD-HRTF_doc_v1.0.3.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Masiero, B.; Pollow, M.; Fels, J. Design of a Fast Broadband Individual Head-Related Transfer Function Measurement System. In Proceedings of the Forum Acusticum 2011, Aalborg, Denmark, 27 June–1 July 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Richter, J.G.; Fels, J. On the Influence of Continuous Subject Rotation During High-Resolution Head-Related Transfer Function Measurements. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 2019, 27, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrucki, A.; Plaskota, P.; Pruchnicki, P.; Pec, M.; Bujacz, M.; Strumillo, P. Measurement System for Personalized Head-Related Transfer Functions and Its Verification by Virtual Source Localization Trials with Visually Impaired and Sighted Individuals. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2010, 58, 724–738. [Google Scholar]
- Son, D.; Park, Y.; Park, Y.; Jang, S.J. Building Korean Head-related Transfer Function Database. Trans. Korean Soc. Noise Vib. Eng. 2014, 24, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, C.; Thresh, L.; Murphy, D.; Kearney, G. A Perceptual Evaluation of Individual and Non-Individual HRTFs: A Case Study of the SADIE II Database. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Xie, B. Near-field head-related transfer-function measurement and database of human subjects. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2018, 143, EL194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpentier, T.; Bahu, H.; Noisternig, M.; Warusfel, O. Measurement of a head-related transfer function database with high spatial resolution. In Proceedings of the 7th Forum Acusticum, Krakow, Poland, 7–12 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Thiemann, J.; van de Par, S. A multiple model high-resolution head-related impulse response database for aided and unaided ears. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HRTF Measurement System—Tohoku University. Available online: http://www.ais.riec.tohoku.ac.jp/Lab3/localization/index.html (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- HRTF Measurement System—University of Southampton. Available online: http://resource.isvr.soton.ac.uk/FDAG/VAP/html/facilities.html (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Iida, K. Measurement Method for HRTF. In Head-Related Transfer Function and Acoustic Virtual Reality; Iida, K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilinski, P.; Ahrens, J.; Thomas, M.R.P.; Tashev, I.J.; Platt, J.C. HRTF magnitude synthesis via sparse representation of anthropometric features. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, Florence, Italy, 4–9 May 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romigh, G.D.; Brungart, D.S.; Stern, R.M.; Simpson, B.D. Efficient Real Spherical Harmonic Representation of Head-Related Transfer Functions. IEEE J. Select. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindau, A.; Weinzierl, S. FABIAN—An instrument for software-based measurement of binaural room impulse responses in multiple degrees of freedom. In Proceedings of the 24th Tonmeistertagung—VDT International Convention, Leipzig, Germany, 16–19 November 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Bovbjerg, B.P.; Christensen, F.; Minnaar, P.; Chen, X. Measuring the Head-Related Transfer Functions of an Artificial Head with a High-Directional Resolution. In Proceedings of the 109th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 22–25 September 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wierstorf, H.; Geier, M.; Raake, A.; Spors, S. A Free Database of Head Related Impulse Response Measurements in the Horizontal Plane with Multiple Distances. In Proceedings of the 130th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, London, UK, 13–16 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rothbucher, M.; Paukner, P.; Stimpfl, M.; Diepold, K. The TUM-LDV HRTF Database; Technical report; Technische Universität München: München, Germany, 2014; Available online: https://mediatum.ub.tum.de/1206599 (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Hirahara, T.; Sagara, H.; Toshima, I.; Otani, M. Head movement during head-related transfer function measurements. Acoust. Sci. Technol. 2010, 31, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkki, V.; Laitinen, M.V.; Sivonen, V. HRTF Measurements with a Continuously Moving Loudspeaker and Swept Sines. In Proceedings of the 128th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, London, UK, 22–25 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Reijniers, J.; Partoens, B.; Peremans, H. DIY Measurement of Your Personal HRTF at Home: Low-Cost, Fast and Validated. In Proceedings of the 143rd Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, New York, NY, USA, 18–21 October 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Peissig, J. Fast estimation of 2D individual HRTFs with arbitrary head movements. In Proceedings of the 22nd IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, London, UK, 23–25 August 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraiswaini, R.; Zotkin, D.N.; Gumerov, N.A.; O’Donovan, A.E. Capturing and recreating auditory virtual reality. In Principles and Applications of Spatial Hearing; Suzuki, Y., Brungart, D., Iwaya, Y., Iida, K., Cabrera, D., Kato, H., Suzuki, Y., Eds.; World Scientific Pub. Co: Singapore; Hackensack, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 337–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, N.; Hirahara, T. Fast near-field HRTF measurements using reciprocal method. In Proceedings of the 20th International Congress on Acoustics, Sydney, Australia, 23–27 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zaar, J. Vermessung von Außenohrübertragungsfunktionenmit Reziproker Messmethode; Project report; Kunstuniversität Graz: Graz, Austria, 2010; Available online: https://iem.kug.ac.at/fileadmin/media/iem/projects/2010/zaar.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Brungart, D.S.; Nelson, W.T.; Bolia, R.S.; Tannen, R.S. Evaluation of the SNAPSHOT 3D Head-Related Transfer Functions Measurement System; Technical report; University of Cincinnati: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1998; Available online: https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/citations/ADA375508 (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Algazi, V.R.; Duda, R.O.; Thompson, D.M.; Avendano, C. The CIPIC HRTF Database. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Electroacoustics, New Platz, NY, USA, 24 October 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begault, D.R.; Godfroy, M.; Miller, J.D.; Roginska, A.; Anderson, M.R.; Wenzel, E.M. Design and Verification of HeadZap, a Semi-automated HRIR Measurement System. In Proceedings of the 120th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Paris, France, 20–23 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. Fast Head-Related Transfer Function Measurement in Complex Environments. In Proceedings of the 20th International Congress on Acoustics, Sydney, Australia, 23–27 August 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, L.; Li, X. Dynamic Head-Related Transfer Function Measurement Using a Dual-Loudspeaker Array. In Proceedings of the 130th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, London, UK, 13–16 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Poppitz, J.; Blau, M.; Hansen, M. Entwicklung und Evaluation eines Systems zur Messung individueller HRTFs inprivater Wohn-Umgebung. In Proceedings of the Tagungsband Fortschritte der Akustik—DAGA, Aachen, Germany, 14–17 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Takane, S. Estimation of Individual HRIRs Based on SPCA from Impulse Responses Acquired in Ordinary Sound Fields. In Proceedings of the 139th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, New York, NY, USA, 29 October–1 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Denk, F.; Kollmeier, B.; Ewert, S.D. Removing Reflections in Semianechoic Impulse Responses by Frequency-Dependent Truncation. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2018, 66, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gupta, R.; Ranjan, R.; Gan, W.S. Non-Invasive Parametric HRTF Measurement for Human Subjects Using Binaural and Ambisonic Recording of Existing Sound Field. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Headphone Technology, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27–29 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, J.J.; Martinez-Sanchez, S.; Gutierrez-Parera, P. Array Processing for Echo Cancellation in the Measurement of Head-Related Transfer Functions; Euronoise: Crete, Greece, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Diepold, K.; Durkovic, M.; Sagstetter, F. HRTF Measurements with Recorded Reference Signal. In Proceedings of the 129th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–7 November 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Majdak, P.; Balazs, P.; Laback, B. Multiple Exponential Sweep Method for Fast Measurement of Head-Related Transfer Functions. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2007, 55, 623–637. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, P.; Masiero, B.; Vorländer, M. On the Optimization of the Multiple Exponential Sweep Method. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2013, 61, 113–124. [Google Scholar]
- Ajdler, T.; Sbaiz, L.; Vetterli, M. Dynamic measurement of room impulse responses using a moving microphone. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 122, 1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukudome, K.; Suetsugu, T.; Ueshin, T.; Idegami, R.; Takeya, K. The fast measurement of head related impulse responses for all azimuthal directions using the continuous measurement method with a servo-swiveled chair. Appl. Acoust. 2007, 68, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, J.G. Fast Measurement of Individual Head-Related Transfer Functions. Ph.D. Thesis, RWTH Aachen University, Aachen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzner, G. 3D-continuous-azimuth acquisition of head-related impulse responses using multi-channel adaptive filtering. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, New Paltz, NY, USA, 18–21 October 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, P.; Fu, Z.H. Fast and accurate high-density HRTF measurements using generalized frequency-domain adaptive filter. In Proceedings of the 21th International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Beijing, China, 13–17 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kanai, S.; Sugaya, M.; Adachi, S.; Matsui, K. Low-Complexity Simultaneous Estimation of Head-Related Transfer Functions by Prediction Error Method. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2016, 64, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; He, J.; Gan, W.S. Fast Continuous Acquisition of HRTF for Human Subjects with Unconstrained Random Head Movements in Azimuth and Elevation. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Headphone Technology, Aalborg, Denmark, 24–26 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Braun, R.; Li, S.; Peissig, J. A Measurement System for Fast Estimation of 2D Individual HRTFs with Arbitrary Head Movements. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Spatial Audio, Graz, Austria, 7–10 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Ranjan, R.; Gan, W.S.; Chaudhary, N.K.; Hai, N.D.; Gupta, R. Fast Continuous Measurement of HRTFs with Unconstrained Head Movements for 3D Audio. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2018, 66, 884–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heer, D.; de Mey, F.; Reijniers, J.; Demeyer, S.; Peremans, H. Evaluating Intermittent and Concurrent Feedback during an HRTF Measurement. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Headphone Technology, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27–29 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peksi, S.; Hai, N.D.; Ranjan, R.; Gupta, R.; He, J.; Gan, W.S. A Unity Based Platform for Individualized HRTF Research and Development: From On-the-Fly Fast Acquisition to Spatial Audio Renderer. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Headphone Technology, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27–29 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Reijniers, J.; Partoens, B.; Steckel, J.; Peremans, H. HRTF measurement by means of unsupervised head movements with respect to a single fixed speaker. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 92287–92300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagel, S.; Kabzinski, T.; Kühl, S.; Antweiler, C.; Jax, P. Acoustic Head-Tracking for Acquisition of Head-Related Transfer Functions with Unconstrained Subject Movement. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Audio for Virtual and Augmented Reality, Redmond, WA, USA, 20–22 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Arend, J.M.; Pörschmann, C. How wearing headgear affects measured head-related transfer functions. In Proceedings of the EAA Spatial Audio Signal Processing Symposium, Paris, France, 6–7 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.; Ranjan, R.; He, J.; Gan, W.-S. Investigation of Effect of VR/AR Headgear on Head Related Transfer Functions for Natural Listening. In Proceedings of the AES International Conference on Audio for Virtual and Augmented Reality, Redmond, WA, USA, 20–22 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann, F.; Lindau, A.; Weinzerl, S.; van de Par, S.; Müller-Trapet, M.; Opdam, R.; Vorländer, M. A High Resolution and Full-Spherical Head-Related Transfer Function Database for Different Head-Above-Torso Orientations. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2017, 65, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karjalainen, M.; Paatero, T. Frequency-dependent signal windowing. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on the Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, New Platz, NY, USA, 24 October 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E. Extending Quasi-Anechoic Measurements to Low Frequencies. In Proceedings of the 117th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28–31 October 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jot, J.M.; Larcher, V.; Warusfel, O. Digital Signal Processing Issues in the Context of Binaural and Transaural Stereophony. In Proceedings of the 98th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Paris, France, 25–28 February 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Theile, G. On the Standardization of the Frequency Response of High-Quality Studio Headphones. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1986, 34, 956–969. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim, A.V.; Schafer, R.W.; Buck, J.R. DiscRete-Time Signal Processing, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall and Prentice-Hall International (UK): Upper Saddler River, NJ, USA; London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Pike, C.W. Evaluating the Perceived Quality of Binaural Technology. Ph.D. Thesis, University of York, York, UK, 2019. Available online: http://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/24022/1/ChrisPike_PhDThesis.pdf (accessed on 13 July 2020).
- Møller, H.; Hammershøi, D.; Jensen, C.B.; Sørensen, M.F. Transfer Characteristics of Headphones Measured on Human Ears. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1995, 43, 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Schärer, Z.; Lindau, A. Evaluation of Equalization Methods for Binaural Signals. In Proceedings of the 126th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Munich, Germany, 7–10 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Masiero, B.; Fels, J. Perceptually Robust Headphone Equalization for Binaural Reproduction. In Proceedings of the 130th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, London, UK, 13–16 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Larcher, V.; Jot, J.M.; Vandernoot, G. Equalization Methods in Binaural Technology. In Proceedings of the 105th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, San Francisco, CA, USA, 26–29 September 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Algazi, V.R.; Duda, R.O.; Duralswami, R.; Gumerov, N.A.; Tang, Z. Approximating the head-related transfer function using simple geometric models of the head and torso. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2002, 112, 2053–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumerov, N.A.; O’Donovan, A.E.; Duraiswami, R.; Zotkin, D.N. Computation of the head-related transfer function via the fast multipole accelerated boundary element method and its spherical harmonic representation. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 127, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B. On the low frequency characteristics of head-related transfer function. Chin. J. Acoust. 2009, 28, 116–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, G.; Doyle, T. An HRTF Database for Virtual Loudspeaker Rendering. In Proceedings of the 139th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, New York, NY, USA, 29 October–1 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, A.; Colburn, H.S. Role of spectral detail in sound-source localization. Nature 1998, 396, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlrausch, A.; Breebaart, J. Perceptual (ir)relevance of HRTF magnitude and phase spectra. In Proceedings of the 110th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 12–25 May 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Riederer, K.A.J. Effect of Head Movements on Measured Head-Related Transfer Functions. In Proceedings of the 18th International Congress on Acoustics, Kyoto, Japan, 4–9 April 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wersényi, G.; Wilson, J. Evaluation of the Range of Head Movements in Measurements and Recordings with Human Subjects using Head-Tracking Sensors. Acta Technica Jaurinensis 2015, 8, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denk, F.; Heeren, J.; Ewert, S.D.; Kollmeier, B.; Ernst, S.M.A. Controlling the Head Position during individual HRTF Measurements and its Effecton Accuracy. In Proceedings of the Tagungsband Fortschritte der Akustik—DAGA, Kiel, Germany, 6–9 March 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Rothbucher, M.; Veprek, K.; Paukner, P.; Habigt, T.; Diepold, K. Comparison of head-related impulse response measurement approaches. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, EL223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajdler, T.; Faller, C.; Sbaiz, L.; Vetterli, M. Sound Field Analysis along a Circle and Its Applications to HRTF Interpolation. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2008, 56, 156–175. [Google Scholar]
- Wightman, F.; Kistler, D. Multidimensional scaling analysis of head-related transfer functions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics, New Paltz, NY, USA, 17–20 October 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemaire, V.; Clerot, F.; Busson, S.; Nicol, R.; Choqueuse, V. Individualized HRTFs from few measurements: A statistical learning approach. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Montreal, QC, Canada, 31 July–4 August 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Zhong, X.; He, N. Typical data and cluster analysis on head-related transfer functions from Chinese subjects. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 94, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulkki, V.; Karjalainen, M.; Huopaniemi, J. Analyzing Virtual Sound Source Attributes Using a Binaural Auditory Model. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 1999, 47, 203–217. [Google Scholar]
- Thiede, T.; Treurniet, W.C.; Bitto, R.; Schmidmer, C.; Sporer, T.; Beerends, J.G.; Colomes, C.; Keyhl, M.; Stoll, G.; Brandenburg, K.; et al. PEAQ—The ITU Standard for Objective Measurement of Perceived Audio Quality. J. Audio Eng. Soc. 2000, 48, 3–29. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, L.S.R.; Zacharov, N.; Katz, B.F.G. Perceptual attributes for the comparison of head-related transfer functions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2016, 140, 3623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, B.F.; Begault, D.R. Round robin comparison of HRTF measurement systems: Preliminary results. In Proceedings of the 19th International Congress on Acoustics, Madrid, Spain, 2–7 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Andreopoulou, A.; Begault, D.R.; Katz, B.F.G. Inter-Laboratory Round Robin HRTF Measurement Comparison. IEEE J. Select. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barumerli, R.; Geronazzo, M.; Avanzini, F. Round Robin Comparison of Inter-Laboratory HRTF Measurements—Assessment with an auditory model for elevation. In Proceedings of the 4th IEEE VR Workshop on Sonic Interactions for Virtual Environments, Reutlingen, Germany, 18 March 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreopoulou, A.; Roginska, A. Towards the Creation of a Standardized HRTF Repository. In Proceedings of the 131st Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, New York, NY, USA, 20–23 October 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wefers, F. OpenDAFF: A free, open-source software package for directional audio data. In Proceedings of the Tagungsband Fortschritte der Akustik—DAGA, Berlin, Germany, 15–18 March 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Majdak, P.; Iwaya, Y.; Carpentier, T.; Nicol, R.; Parmentier, M.; Roginska, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Wierstorf, H.; Ziegelwanger, H.; et al. Spatially Oriented Format for Acoustics: A Data Exchange Format Representing Head-Related Transfer Functions. In Proceedings of the 134th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Rome, Italy, 4–7 May 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guldenschuh, M.; Sontacchi, A.; Zotter, F.; Höldrich, R. HRTF modeling in due consideration variable torso reflections. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2008, 123, 3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, F.; Roden, R.; Lindau, A.; Weinzierl, S. Audibility and Interpolation of Head-Above-Torso Orientation in Binaural Technology. IEEE J. Select. Top. Signal Process. 2015, 9, 931–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkivirta, A.; Malinen, M.; Johansson, J.; Saari, V.; Karjalainen, A.; Vosough, P. Accuracy of photogrammetric extraction of the head and torso shape for personal acoustic HRTF modeling. In Proceedings of the 148th Convention of the Audio Engineering Society, Online Virtual Conference, Vienna, Austria, 2–5 June 2020. [Google Scholar]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Peissig, J. Measurement of Head-Related Transfer Functions: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10145014
Li S, Peissig J. Measurement of Head-Related Transfer Functions: A Review. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(14):5014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10145014
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Song, and Jürgen Peissig. 2020. "Measurement of Head-Related Transfer Functions: A Review" Applied Sciences 10, no. 14: 5014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10145014
APA StyleLi, S., & Peissig, J. (2020). Measurement of Head-Related Transfer Functions: A Review. Applied Sciences, 10(14), 5014. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10145014





