Progress in Electrodeposition of Zinc and Zinc Nickel Alloys Using Ionic Liquids
Abstract
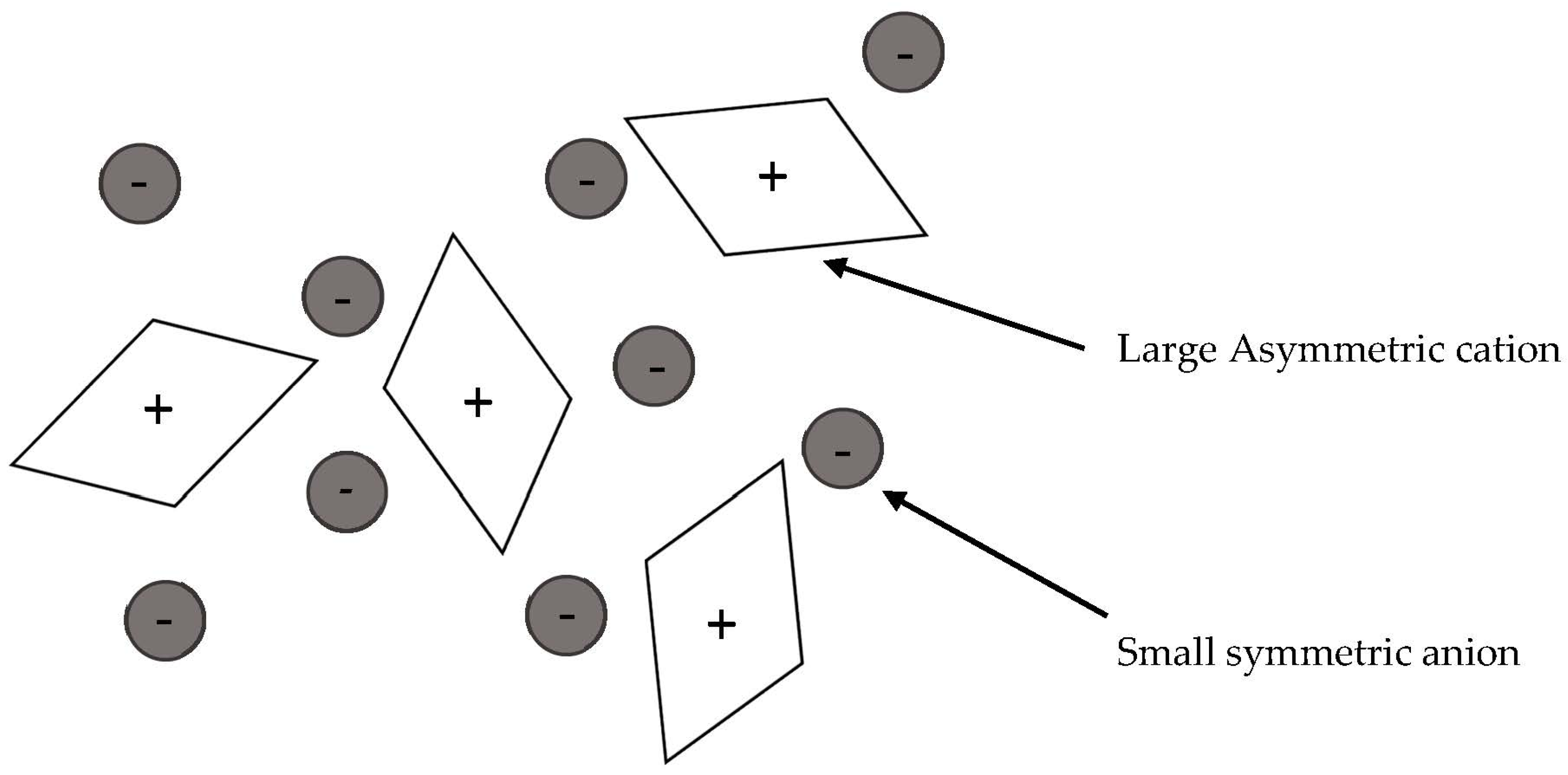
:1. Introduction
2. Zinc Deposition in Ionic Liquids
3. Zinc-Nickel Alloy Deposition in Ionic Liquids
4. Influence of Additives
4.1. Zinc
4.2. Zinc-Nickel
4.3. Ionic Liquids as Additives
5. Substrate Effect
6. Recent Developments
7. Industrial Scope
8. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Chemicals Agency (ECHA). Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/substances-restricted-under-reach/-/dislist/details/0b0236e1807e2518 (accessed on 1 July 2020).
- Winand, R. Electrodeposition of Zinc and Zinc Alloys. Mod. Electroplat. Fifth Ed. 2011, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira Fernandes, M.; dos Santos, J.R.M.; de Oliveira Velloso, V.M.; Voorwald, H.J.C. AISI 4140 Steel Fatigue Performance: Cd Replacement by Electroplated Zn-Ni Alloy Coating. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alesary, H.F.; Cihangir, S.; Ballantyne, A.D.; Harris, R.C.; Weston, D.P.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Influence of additives on the electrodeposition of zinc from a deep eutectic solvent. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 304, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lotfi, N.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Rahmani, H.; Darband, G.B. Zinc–Nickel Alloy Electrodeposition: Characterization, Properties, Multilayers and Composites. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2018, 54, 1102–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas-Esquivel, F.M.; Brisard, G.M.; Ortega-Borges, R.; Trejo, G.; Meas, Y. Zinc electrochemical deposition from ionic liquids and aqueous solutions onto indium tin oxide. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 2026–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczak-Radzimska, A.; Jesionowski, T. Zinc oxide-from synthesis to application: A review. Materials 2014, 7, 2833–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brooman, E.W. Ionic liquids for surface finishing processes. Plat. Surf. Finish. 2007, 7, 54–57. Available online: http://www.nmfrc.org/pdf/psf2007/070754.pdf (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Shamsuri, A.A. Ionic Liquids: Preparations and Limitations. Makara Sci. Ser. 2011, 14, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danilov, F.I.; Protsenko, V.S. Electrodeposition of composite coatings using electrolytes based on deep eutectic solvents: A mini-review. Vopr. Khimii Khimicheskoi Tekhnol. 2018, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Tomé, L.I.N.; Baião, V.; da Silva, W.; Brett, C.M.A. Deep eutectic solvents for the production and application of new materials. Appl. Mater. Today 2018, 10, 30–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, Y. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents. In Deep Eutectic Solvents; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 111–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endres, F.; Douglas, R.M.; Abbott, A. Electrodeposition from Ionic Liquids; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, A.P.; McKenzie, K.J. Application of ionic liquids to the electrodeposition of metals. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 4265–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernasconi, R.; Panzeri, G.; Accogli, A.; Liberale, F.; Nobili, L.; Magagnin, L. Electrodeposition from Deep Eutectic Solvents. In Progress and Developments in Ionic Liquids; Intechopen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Deng, Y.; Han, X.; Hu, W.; Zhong, C. Electrodeposition of metals and alloys from ionic liquids. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 654, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jiang, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, X.; Mu, T. The electrochemical stability of ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvents. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 59, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Frisch, G.; Ryder, K.S. Electroplating Using Ionic Liquids. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2013, 43, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Dalrymple, J.; Endres, F.; MacFarlane, D.R. Why Use Ionic Liquids for Electrodeposition? In Electrodeposition from Ionic Liquids; Endres, F., Abbott, A., MacFarlane, Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel ambient temperature ionic liquids for zinc and zinc alloy electrodeposition. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2001, 79, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Ryder, K.S. Electrolytic deposition of Zn coatings from ionic liquids based on choline chloride. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2009, 87, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Frisch, G.; Ryder, K.S.; Silva, A.F. Double layer effects on metal nucleation in deep eutectic solvents. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 21, 10224–10231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; McKenzie, K.J.; Ryder, K.S. Electrodeposition of zinc-tin alloys from deep eutectic solvents based on choline chloride. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2007, 599, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.M.; Salomé, S.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F. Zn–Sn electrodeposition from deep eutectic solvents containing EDTA, HEDTA, and Idranal VII. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2012, 42, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pölzler, M.; Whitehead, A.H.; Gollas, B. A Study of Zinc Electrodeposition from Zinc Chloride: Choline Chloride: Ethylene Glycol. ECS Trans. 2010, 25, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, A.H.; Pölzler, M.; Gollas, B. Zinc Electrodeposition from a Deep Eutectic System Containing Choline Chloride and Ethylene Glycol. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, D328–D334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Reddy, R.G. Electrochemical deposition of zinc from zinc oxide in 2:1 urea/choline chloride ionic liquid. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 147, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, L.; Whitehead, A.H.; Gollas, B. Mechanistic Studies of Zinc Electrodeposition from Deep Eutectic Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, D7–D13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiu, S.I.; Huang, J.F.; Sun, I.W.; Yuan, C.H.; Shiea, J. Lewis acidity dependency of the electrochemical window of zinc chloride-1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2002, 47, 4367–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieszporek, D.; Simka, W.; Matuszek, K.; Chrobok, A.; Maciej, A. Electrodeposition of zinc coatings from ionic liquid. Solid State Phenom. 2015, 227, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-S.; Yeh, H.-W.; Tang, Y.-H.; Kao, C.-L.; Chen, P.-Y. Voltammetric Study and Electrodeposition of Zinc in Hydrophobic Room-Temperature Ionic Liquid 1-Butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium Bis((trifluoromethyl)sulfonyl)imide ([BMP][TFSI]): A Comparison between Chloride and TFSI Salts of Zinc. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, D39–D47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sriraman, K.R.; Brahimi, S.; Szpunar, J.A.; Osborne, J.H.; Yue, S. Characterization of corrosion resistance of electrodeposited Zn-Ni Zn and Cd coatings. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 105, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriraman, K.R.; Strauss, H.W.; Brahimi, S.; Chromik, R.R.; Szpunar, J.A.; Osborne, J.H.; Yue, S. Tribological behavior of electrodeposited Zn, Zn-Ni, Cd and Cd-Ti coatings on low carbon steel substrates. Tribol. Int. 2012, 56, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Behera, P.; Sriraman, K.R.; Chromik, R.R. The effect of contact stress on the sliding wear behaviour of Zn-Ni electrodeposited coatings. Wear 2018, 400–401, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel Institute. Available online: https://www.nickelinstitute.org/media/1635/areviewofrecenttrendsinnickelelectroplatingtechnologyinnorthamericaandeurope_14024_pdf (accessed on 29 July 2020).
- Wilcox, G.D.; Gabe, D.R. Electrodeposited zinc alloy coatings. Corros. Sci. 1993, 35, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonntag, B.; Dingwerth, B.; Vogel, R.; Scheller, B. Cyanide formation in zinc-nickel electroplating. Galvanotechnik 2010, 101, 992–996. [Google Scholar]
- Gou, S.P.; Sun, I.W. Electrodeposition behavior of nickel and nickel-zinc alloys from the zinc chloride-1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride low temperature molten salt. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 2538–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Guo, X.W.; Chen, X.B.; Wang, S.H.; Wu, G.H.; Ding, W.J.; Birbilis, N. On the electrodeposition of nickel-zinc alloys from a eutectic-based ionic liquid. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 63, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Esary, H.; Ryder, K.S.; Abbott, A.P. Electrodeposition of Zn-Ni Alloy from Deep Eutectic Solvents. In Proceedings of the Electrochem Conference, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, 17–19 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Fashu, S.; Gu, C.D.; Wang, X.L.; Tu, J.P. Influence of electrodeposition conditions on the microstructure and corrosion resistance of Zn–Ni alloy coatings from a deep eutectic solvent. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 242, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, C.; Aremu, M.; Ushie, O. Electroplating in Novel Deep Eutectic Solvent Electrolytes. FUW Trends Sci. Technol. J. 2016, 1, 321–326. Available online: http://www.ftstjournal.com/uploads/docs/Articlethree.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Li, R.; Dong, Q.; Xia, J.; Luo, C.; Sheng, L.; Cheng, F.; Liang, J. Electrodeposition of composition controllable Zn–Ni coating from water modified deep eutectic solvent. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 366, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Lu, X.; Zhang, X. Electrodeposition in Ionic Liquids. ChemPhysChem 2016, 17, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steichen, M.; Brooks, N.R.; Van Meervelt, L.; Fransaer, J.; Binnemans, K. Homoleptic and heteroleptic N-alkylimidazole zinc(ii)-containing ionic liquids for high current density electrodeposition. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 12329–12341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rashmi, S.; Elias, L.; Hegde, A.C. Multilayered Zn-Ni alloy coatings for better corrosion protection of mild steel. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Esary, H. Influence of Additives on Electrodeposition of Metals from Deep Eutectic Solvents. Doctor of Philosophy Thesis, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, November 2017. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/2381/40869 (accessed on 23 July 2020).
- Koyama, K.; Iwagishi, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Shirai, H.; Kobayashi, H. Electrodeposition of zinc from l—ethyl—3—methylimidazolium bromide—zinc bromide molten salts with dihydric alcohols. Electrochemistry 2002, 70, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Barron, J.C.; Frisch, G.; Ryder, K.S.; Silva, A.F. The effect of additives on zinc electrodeposition from deep eutectic solvents. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 5272–5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.; Bakkar, A.; Ahmed, E.; Selim, A. Effect of additives and current mode on zinc electrodeposition from deep eutectic ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 191, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.M.; Fernandes, P.M.V.; Pereira, C.M.; Silva, A.F. Electrodeposition of Zinc from Choline Chloride-Ethylene Glycol Deep Eutectic Solvent: Effect of the Tartrate Ion. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, D501–D506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.M.; Pereira, C.M.; Araújo, J.P.; Silva, A.F. Zinc Electrodeposition from deep eutectic solvent containing organic additives. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 801, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpavanam, M. Critical review on alloy plating: A viable alternative to conventional plating. Bull. Electrochem. 2000, 16, 559–566. [Google Scholar]
- Fashu, S.; Gu, C.D.; Zhang, J.L.; Huang, M.L.; Wang, X.L.; Tu, J.P. Effect of EDTA and NH4Cl additives on electrodeposition of Zn-Ni films from choline chloride-based ionic liquid. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 2054–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.M.; Pereira, C.M.; Araújo, J.P.; Silva, A.F. Influence of amines on the Electrodeposition of Zn-Ni Alloy from a Eutectic-Type Ionic Liquid. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, D325–D330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.B.; Hua, Y.X.; Ren, Y.X.; Chen, L.Y. Influence of alkylpyridinium ionic liquids on copper electrodeposition from acidic sulfate electrolyte. J. Cent. South. Univ. 2013, 20, 2096–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahyarzadeh, M.H.; Roozbehani, B.; Ashrafi, A.; Shadizadeh, S.R.; Seddighian, A.; Kheradmand, E. A Novel Aspect of Two Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids in Electrodeposition of Amorphous/Nanocrystalline Ni-Mo. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, D473–D478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerens, K.; Matthijs, E.; Chmielarz, A.; Van der Bruggen, B. The use of ionic liquids based on choline chloride for metal deposition: A green alternative? J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 3245–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerens, K.; Matthijs, E.; Binnemans, K.; Van der Bruggen, B. Electrochemical decomposition of choline chloride based ionic liquid analogues. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1357–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbikain, G.; Perez, J.M.; López de Lacalle, L.N.; Andueza, A. Combination of friction drilling and form tapping processes on dissimilar materials for making nutless joints. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2016, 232, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petro, R.; Schlesingher, M.; Song, G.-L. Ionic liquid treatments for enhanced corrosion resistance of magnesium-based substrates. In Modern Plating, 5th ed.; Schlesingher, M., Paunovic, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 665–686. [Google Scholar]
- Bakkar, A.; Neubert, V. Electrodeposition onto magnesium in air and water stable ionic liquids: From corrosion to successful plating. Electrochem. Comm. 2007, 9, 2428–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.J.; Lin, P.C.; Chang, J.K.; Chen, J.M.; Lu, K.T. Electrochemistry of Zn(II)/Zn on Mg alloy from the N-butyl-N- methylpyrrolidinium dicyanamide ionic liquid. Electrochim. Acta 2011, 56, 6071–6077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starykevich, M.; Salak, A.N.; Ivanou, D.K.; Yasakau, K.A.; André, P.S.; Ferreira, R.A.S.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Effect of the Anodic Titania Layer Thickness on Electrodeposition of Zinc on Ti/TiO2 from Deep Eutectic Solvent. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, D88–D94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starykevich, M.; Salak, A.N.; Ivanou, D.K.; Lisenkov, A.D.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Electrochemical deposition of zinc from deep eutectic solvent on barrier alumina layers. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 170, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Q.; Zhao, L.; Jing, H.; Mao, A. Electrodeposition of zinc from low transition temperature mixture formed by choline chloride + lactic acid. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 14, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulletikurthi, G.; Shapouri Ghazvini, M.; Cui, T.; Borisenko, N.; Carstens, T.; Borodin, A.; Endres, F. Electrodeposition of zinc nanoplates from an ionic liquid composed of 1-butylpyrrolidine and ZnCl2: Electrochemical, in situ AFM and spectroscopic studies. Dalton. Trans. 2017, 46, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bernasconi, R.; Magagnin, L. Electrodeposition of nickel from DES on aluminium for corrosion protection. Surf. Eng. 2017, 33, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S.; Konig, U. Electrofinishing of metals using eutectic based ionic liquids. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2008, 86, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panzeri, G.; Accogli, A.; Gibertini, E.; Rinaldi, C.; Nobili, L.; Magagnin, L. Electrodeposition of high-purity nanostructured iron films from Fe(II) and Fe(III) non-aqueous solutions based on ethylene glycol. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 271, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panzeri, G.; Muller, D.; Accogli, A.; Gibertini, E.; Mauri, E.; Rossi, F.; Nobili, L.; Magagnin, L. Zinc electrodeposition from a chloride-free non-aqueous solution based on ethylene glycol and acetate salts. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 296, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Barrero, S.; Fernández-Larrinoa, J.; Azkona, I.; López De Lacalle, L.N.; Polvorosa, R. Enhanced Performance of Nanostructured Coatings for Drilling by Droplet Elimination. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2016, 31, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-M.; Gou, S.-P.; Sun, I.-W. Single-step large-scale and template-free electrochemical growth of Ni–Zn alloy filament arrays from a zinc chloride based ionic liquid. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 2686–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haerens, K.; Van Deuren, S.; Matthijs, E.; Van der Bruggen, B. Challenges for recycling ionic liquids by using pressure driven membrane processes. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 2182–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L. Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) and the metal finishing industry: Where are they now? Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2013, 91, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliszewski, D.; Stepniak, I.; Piekarski, H.; Lewandowski, A. Heat capacities of ionic liquids and their heats of solution in molecular liquids. Thermochim. Acta 2005, 433, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadormanesh, B.; Ghorbani, M.; Kordkolaei, N.L. Electrodeposition of nanocrystalline Zn/Ni multilayer coatings from single bath: Influences of deposition current densities and number of layers on characteristics of deposits. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 404, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, P.P.; Wang, J.; Durandet, Y. Deposition processes and properties of coatings on steel fasteners—A review. Friction 2019, 7, 389–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Type # | Name | Preparation Method |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | Halometallate | Mixing an organic chloride with a metal halide such as Cl− (ZnCl2) |
| Type II | Air and water stable | Generally composed of organic cations and discrete anions such as [BF4]− [PF6]− |
| Type III | Deep eutectic solvents | Simple eutectic mixtures of organic halides with hydrogen bond donors (HBDs) such as urea and ethylene glycol (EG) |
| Type IV | ILs with metal containing cations | Mixing an ionic liquid with cationic metal complex |
| Type V | Protic ILs | Mixing a bronsted acid to a bronsted base (formed through the transfer of proton) |
| System | Additive | Onset Reduction Potential (V vs. Ag wire) | Difference in Potential (mV vs. Ag wire) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChCl/urea (1:2 molar ratio) | Nil | −1.080 | − |
| Acetonitrile | −1.080 | 0 | |
| Ethylene diamine | −1.120 | −40 1 | |
| Ammonia | −1.020 | 60 | |
| ChCl/EG (1:2 molar ratio) | Nil | −1.080 | − |
| Acetonitrile | −1.080 | 0 | |
| Ethylene diamine | −1.034 | 46 | |
| Ammonia | −0.991 | 92 |
| System | Substrate | Temperature, °C | OCP (mV vs. Pt) | Ecorr (mV vs. Pt) | Icorr (µA cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChCl/ZnCl2 | Mg | 60 | −1253 | −1207 | 3.86 |
| ChCl/ZnCl2 | Mg | 25 | −1863 | −1857 | 3711.17 |
| ChCl.ZnCl2 | Low carbon steel | 25 | −664 | −651 | 109.42 |
| ChCl/urea | Mg | 60 | −1531 | −1446 | 0.48 |
| ChCl/EG | Mg | 60 | −1489 | −1347 | 12.72 |
| ChCl/Gl | Mg | 60 | −1594 | −1557 | 0.49 |
| ChCl/Mal | Mg | 60 | −1962 | −1940 | 31.58 |
| Ionic Liquid | Substrate | Zn/Zn-Ni | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEAP/ZnCl2 | ITO | Zn | [6] |
| ChCl/EG | Steel (AISI 304) | Zn | [25] |
| [BMIMCl]/ZnCl2 | Carbon steel sheet (S235JR) | Zn | [31] |
| ChCl/urea | Cu | Zn-Ni | [40] |
| ChCl/EG | Cu | Zn-Ni | [43] |
| ChCl/urea | Carbon steel | Zn-Ni | [44] |
| ChCl/urea | Steel | Zn | [51] |
| ChCl/ZnCl2 | Mg | Zn | [63] |
| ChCl/ZnCl2 | Mg-alloy (AZ91, WE43,QE22,MgGd5Sc1,MgY4Sc1) | Zn | [63] |
| ChCl/ZnCl2 | Low carbon steel | Zn | [63] |
| ChCl/urea | Mg | Zn | [63] |
| ChCl/EG | Mg | Zn | [63] |
| ChCl/Gl | Mg | Zn | [63] |
| ChCl/Mal | Mg | Zn | [63] |
| [BMP-DCA]/ZnCl2 | Mg | Zn | [64] |
| ChCl/EG | Ti/TiO2 | Zn | [65] |
| ChCl/EG | Alumina | Zn | [66] |
| ChCl/Lac | Low carbon steel | Zn | [67] |
| [BPyl]/ZnCl2 | Cu | Zn | [68] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maniam, K.K.; Paul, S. Progress in Electrodeposition of Zinc and Zinc Nickel Alloys Using Ionic Liquids. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5321. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155321
Maniam KK, Paul S. Progress in Electrodeposition of Zinc and Zinc Nickel Alloys Using Ionic Liquids. Applied Sciences. 2020; 10(15):5321. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155321
Chicago/Turabian StyleManiam, Kranthi Kumar, and Shiladitya Paul. 2020. "Progress in Electrodeposition of Zinc and Zinc Nickel Alloys Using Ionic Liquids" Applied Sciences 10, no. 15: 5321. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155321
APA StyleManiam, K. K., & Paul, S. (2020). Progress in Electrodeposition of Zinc and Zinc Nickel Alloys Using Ionic Liquids. Applied Sciences, 10(15), 5321. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10155321






